An Object-Oriented Deep Multi-Sphere Support Vector Data Description Method for Impervious Surfaces Extraction Based on Multi-Sourced Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
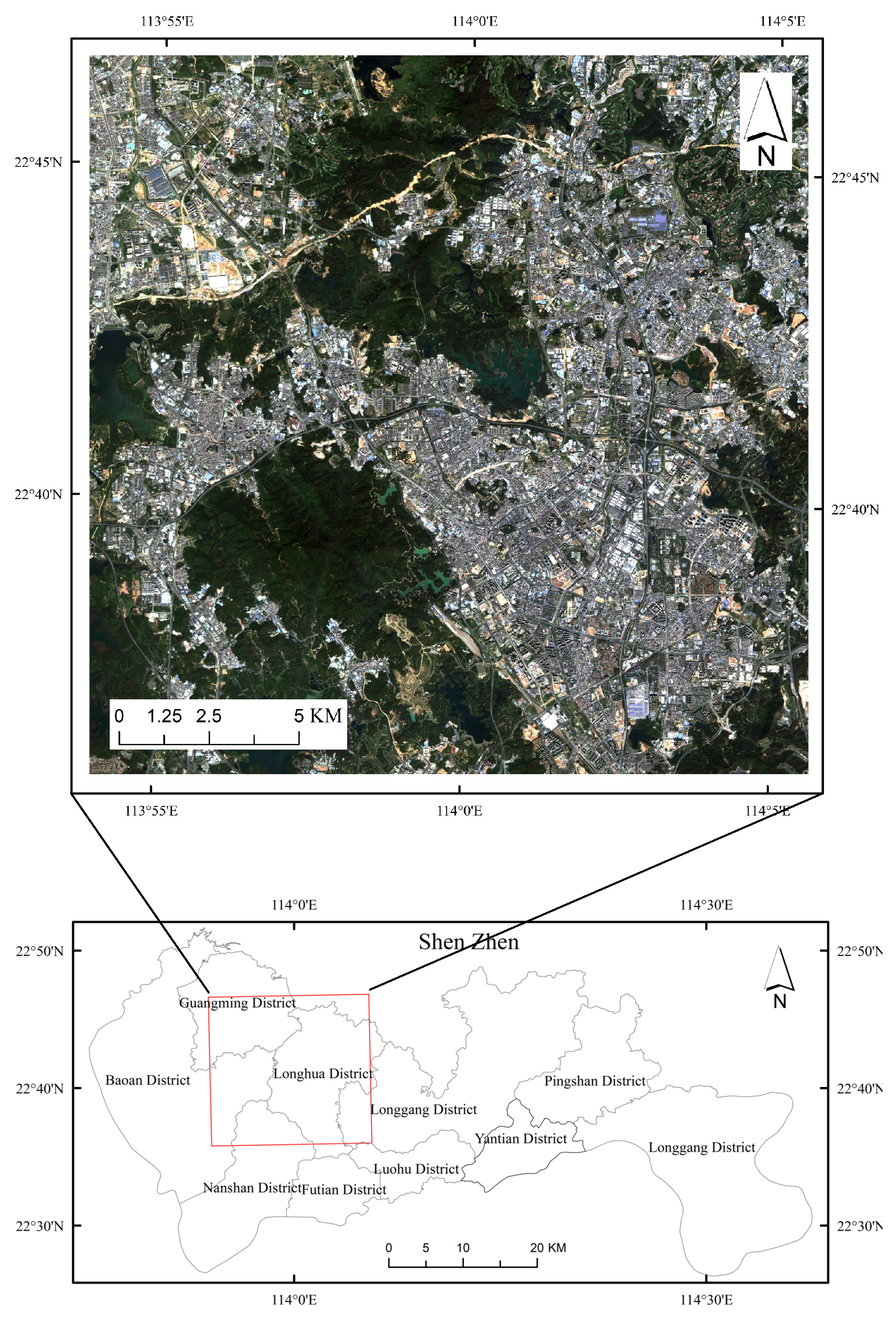
2.1. Study Area
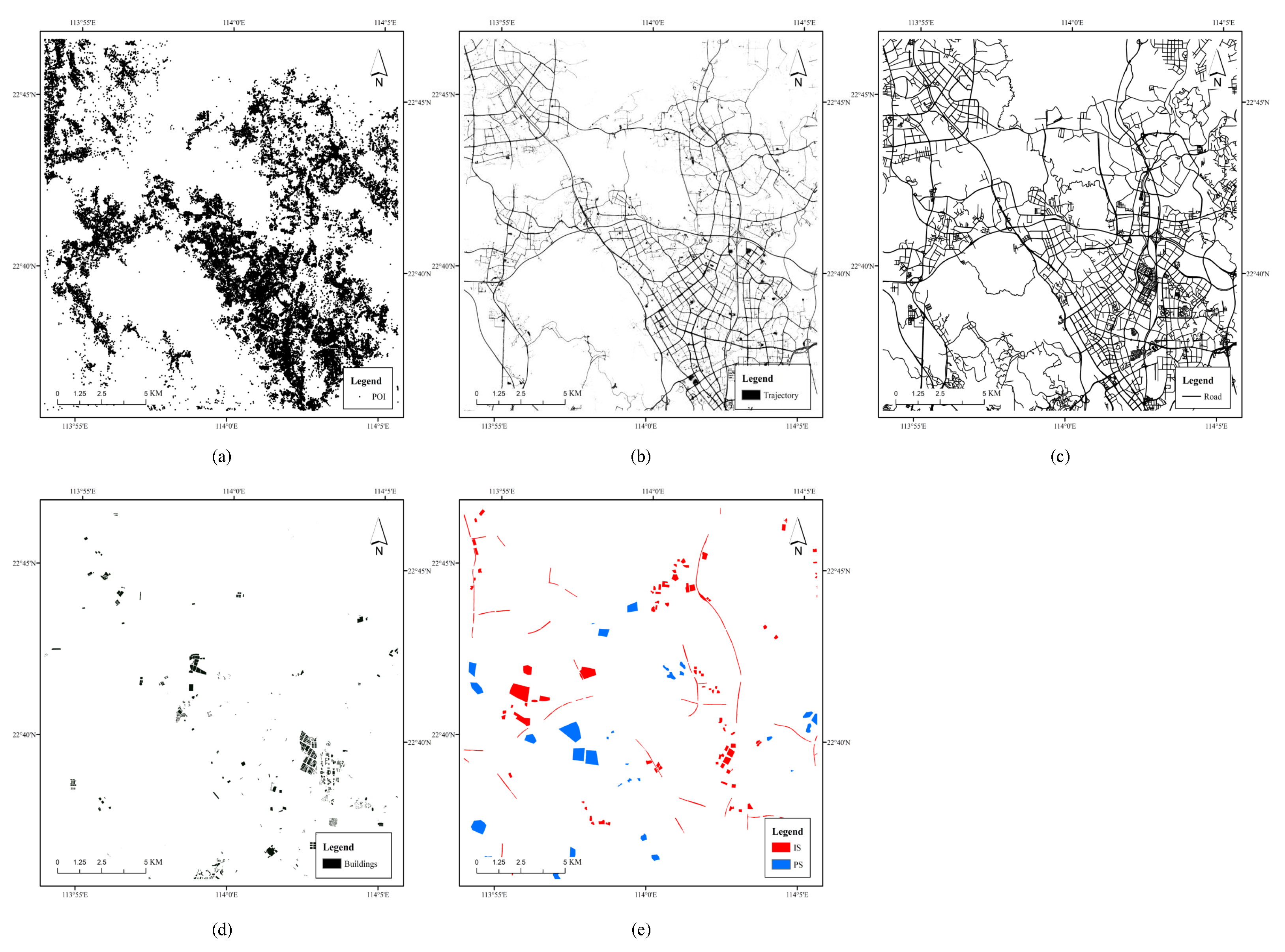
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Methods
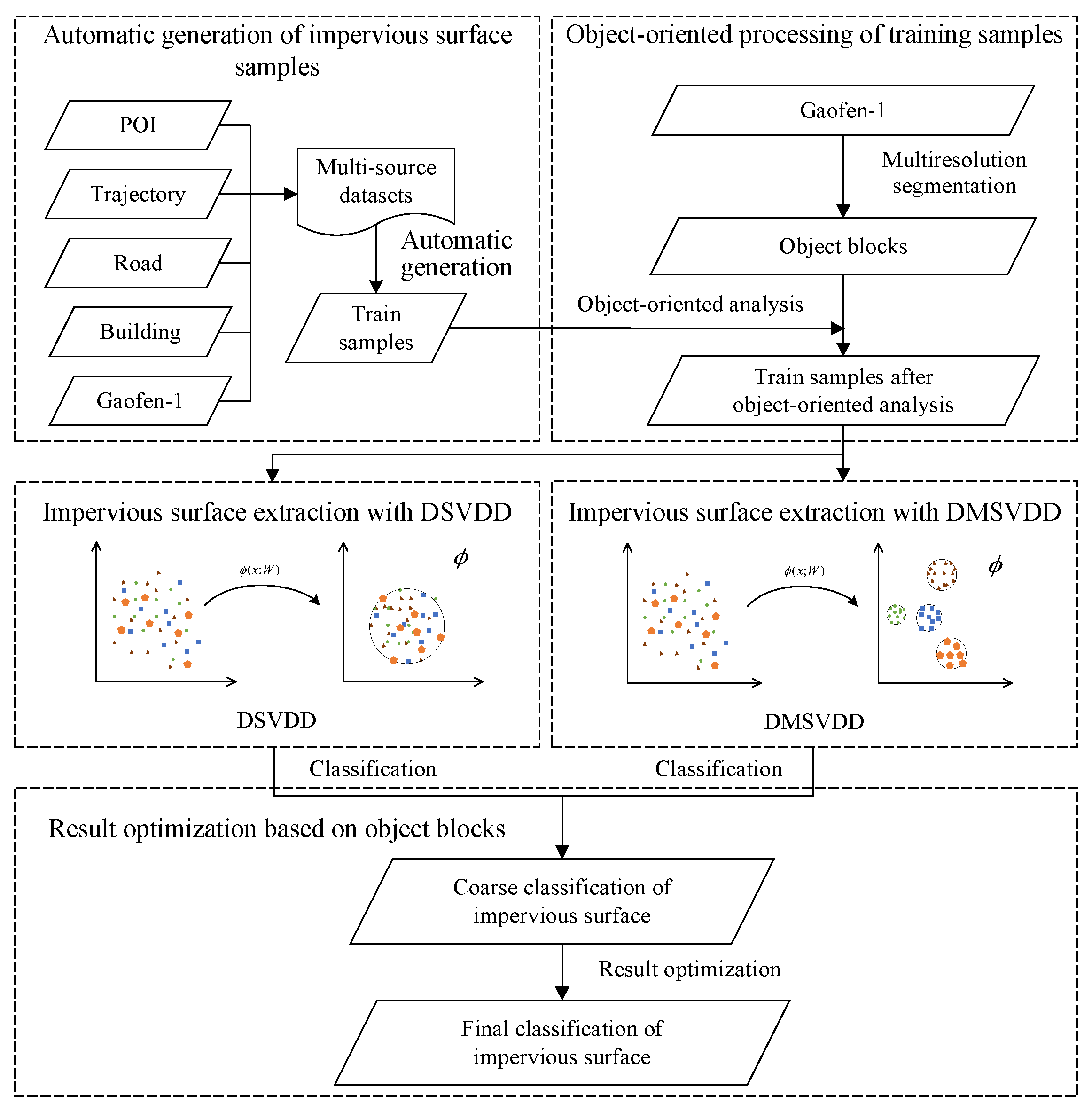
2.3.1. Framework
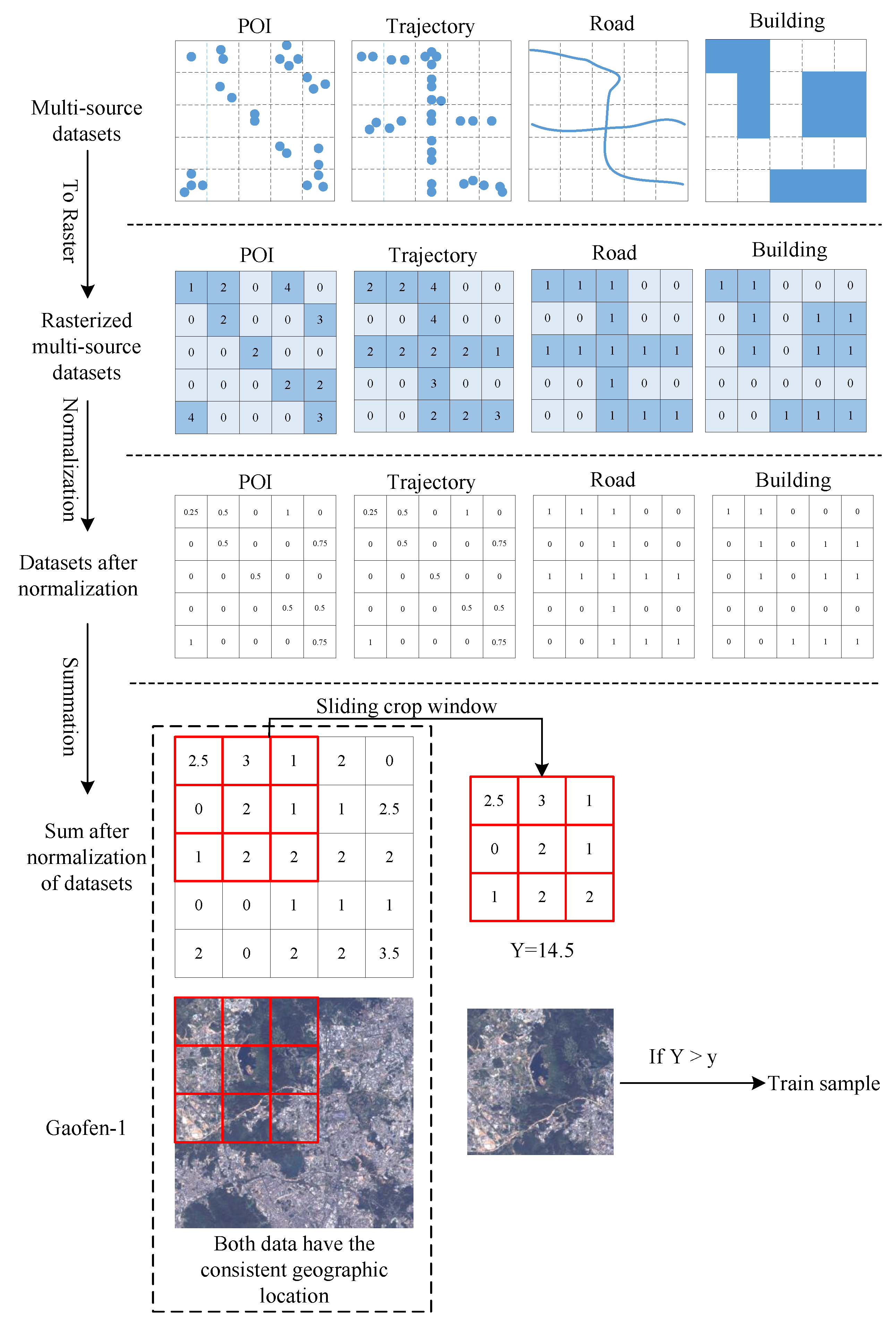
2.3.2. Automatic Generation of Impervious Surface Samples
2.3.3. Object-Oriented Processing of Training Samples
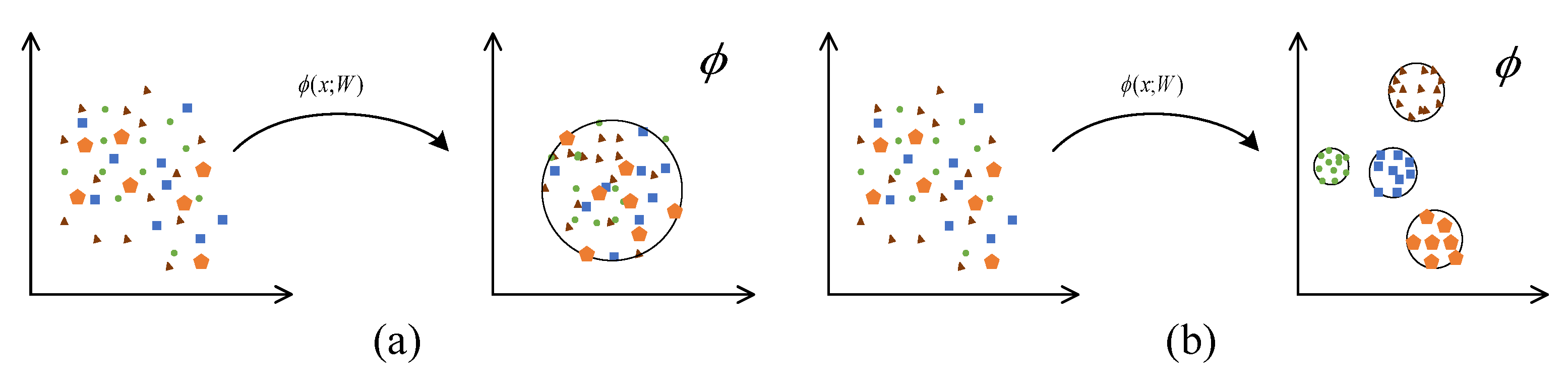
2.3.4. Impervious Surface Extraction Based on DSVDD
2.3.5. Impervious Surface Extraction Based on DMSVDD
2.3.6. Result Optimization Based on Object Blocks
2.3.7. Assessment of Results
3. Experimental Setup and Scenarios
3.1. Experimental Setup
3.2. Experimental Scenarios
4. Results and Analysis
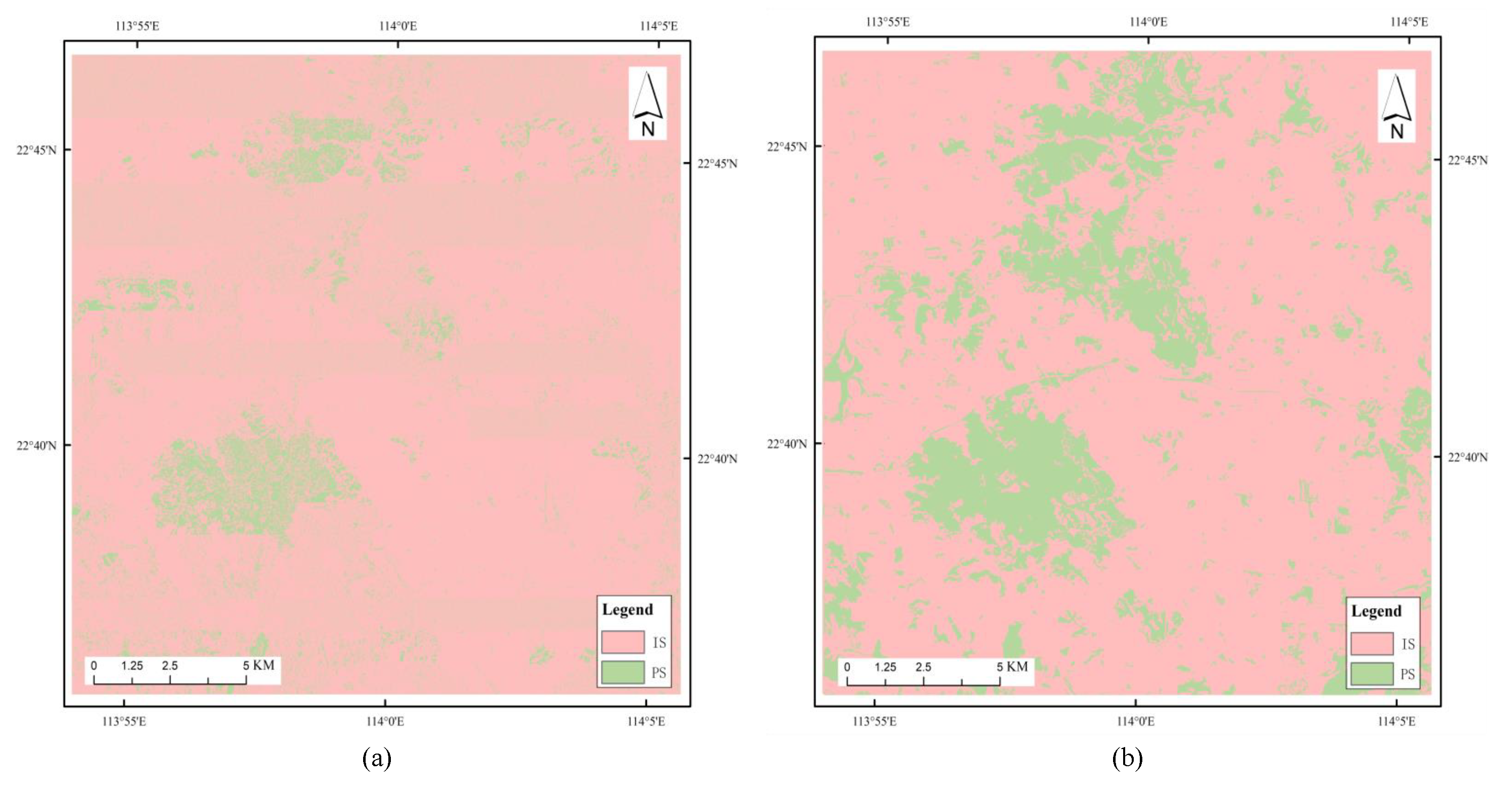
4.1. Experiment 1: Comparison between OODMSVDD and OODSVDD
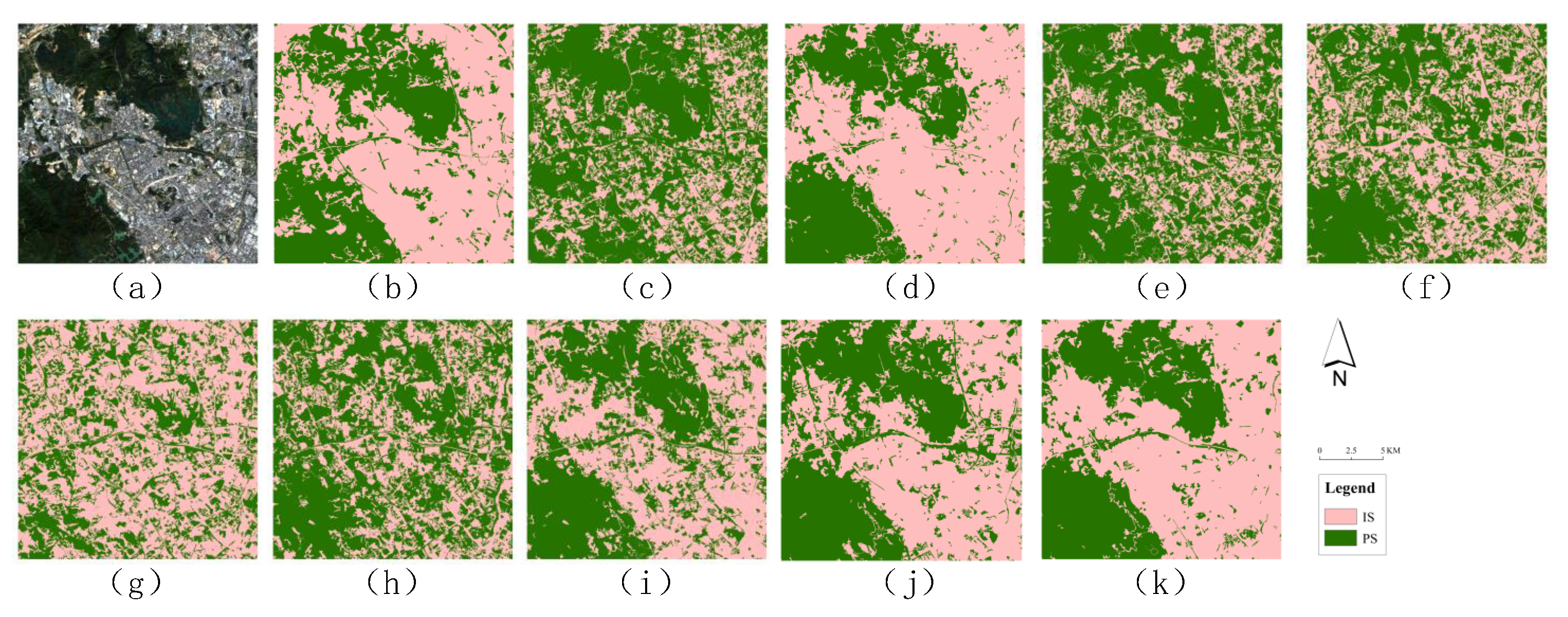
4.2. Experiment 2: Comparison between OODMSVDD and DSVDD/DMSVDD
4.3. Experiment 3: Evaluation of OODMSVDD Based on Different Data Sources
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Bank. Urban Development. Available online: https://www.worldbank.org/en/topic/urbandevelopment/overview (accessed on 25 December 2022).
- Gong, P.; Li, X.; Zhang, W. 40-Year (1978–2017) Human Settlement Changes in China Reflected by Impervious Surfaces from Satellite Remote Sensing. Sci. Bull. 2019, 64, 756–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, C.L., Jr.; Gibbons, C.J. Impervious Surface Coverage: The Emergence of a Key Environmental Indicator. J. Am. Plan. Assoc. 1996, 62, 243–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derdouri, A.; Wang, R.; Murayama, Y.; Osaragi, T. Understanding the Links between LULC Changes and SUHI in Cities: Insights from Two-Decadal Studies (2001–2020). Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LI, H. Spatiotemporal Dynamics and Thermal Environment Effects of Urban Impervious Surfaces in Xuzhou. Master’s Thesis, China University of Mining and Technology, Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Y.; Ding, W.; Liu, C.; Li, K.; Cui, H.; Liu, B.; Chen, W. Influences of Impervious Surfaces on Ecological Risks and Controlling Strategies in Rapidly Urbanizing Regions. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 825, 153823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonneau, J.; Fletcher, T.D.; Costelloe, J.F.; Burns, M.J. Stormwater infiltration and the ‘urban karst’—A review. J. Hydrol. 2017, 552, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Pan, M.; Yang, R.; Song, Y.; Meng, C. Water environmental impacts of impervious surfaces and control measures in Dianchi Lake Basin, China. Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 2016, 10, 5407–5412. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, Z.; Pan, Y.; Cai, Y.; Shu, Y.; Wang, H. Remote Sensing Monitoring of Impervious Surface in Wuhan City Based on Landsat Imagery. Geospat. Inf. 2018, 16, 1–5+7. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, X.; Gao, X.; Shen, Z.; Li, R. Expansion of Urban Impervious Surfaces in Xining City Based on GEE and Landsat Time Series Data. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 147097–147111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Huang, M.; Du, W.; Chen, N.; Xiao, C. A Novel Impervious Surface Extraction Method Based on Automatically Generating Training Samples From Multisource Remote Sensing Products: A Case Study of Wuhan City, China. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 6766–6780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, M.; Kumar, D.; Shekhar, S. Assessing Machine Learning Based Supervised Classifiers For Built-Up Impervious Surface Area Extraction From Sentinel-2 Images. Urban For. Urban Green. 2020, 53, 126714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attarchi, S. Extracting Impervious Surfaces from Full Polarimetric SAR Images in Different Urban Areas. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2020, 41, 4642–4661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.; Fu, H.; Fu, P.; Yin, L. Mapping Urban Impervious Surface by Fusing Optical and SAR Data at the Decision Level. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Zhang, C.; Luo, W.; Yang, J.; Yang, M. Urban Impervious Surface Extraction Based on Multi-Features and Random Forest. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 226609–226623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Zhao, X.; Wu, M.; Wang, C. Extracting Urban Impervious Surface from WorldView-2 and Airborne LiDAR Data Using 3D Convolutional Neural Networks. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2019, 47, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi, A.M. Land Cover and Land Use Classification Performance of Machine Learning Algorithms in a Boreal Landscape Using Sentinel-2 Data. Gisci. Remote. Sens. 2020, 57, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, J.; Li, A.; Zuo, J.; Lei, G.; Zhang, Z.; Nan, X. Estimating 2009–2017 Impervious Surface Change in Gwadar, Pakistan Using the HJ-1A/B Constellation, GF-1/2 Data, and the Random Forest Algorithm. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Chen, S.; Qiao, K.; Cao, S. Integrating CART Algorithm and Multi-Source Remote Sensing Data to Estimate Sub-Pixel Impervious Surface Coverage: A Case Study from Beijing Municipality, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2017, 27, 614–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estima, J.; Painho, M. User Generated Spatial Content-Integrator: Conceptual Model to Integrate Data from Diverse Sources of User Generated Spatial Content. ISPRS Int. Geo-Inf. 2016, 5, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, T.; Fan, Y.; Zhi, S.; Tang, J. A Morphological Feature-Oriented Algorithm for Extracting Impervious Surface Areas Obscured by Vegetation in Collaboration with OSM Road Networks in Urban Areas. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Yang, J.; Wang, W.; Liu, Z. Mapping 10 m Global Impervious Surface Area (GISA-10m) Using Multi-Source Geospatial Data. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2022, 14, 3649–3672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ge, Y.; An, R.; Chen, Y. Super-Resolution Mapping of Impervious Surfaces from Remotely Sensed Imagery with Points-of-Interest. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Li, J.; Zhu, C.; Plaza, A. Urban Impervious Surface Estimation from Remote Sensing and Social Data. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2018, 84, 771–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Wu, C.; Wang, J. Improving Impervious Surface Estimation by Using Remote Sensed Imagery Combined With Open Street Map Points-of-Interest (POI) Data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 4265–4274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Shi, W.; He, Y.; Gamba, P.; Li, Z.; Samat, A.; Wu, L.; Li, J.; Wu, H. Integration of Satellite Images and Open Data for Impervious Surface Classification. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 1120–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Miao, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Li, Z.; Zang, A.; Samat, A.; Du, N.; Xu, Z.; Gamba, P. New Scheme for Impervious Surface Area Mapping From SAR Images With Auxiliary User-Generated Content. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 5954–5970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Fei, Y.; Wu, T.; Jin, R.; Xiao, T. A Novel Impervious Surface Extraction Method Integrating POI, Vehicle Trajectories, and Satellite Imagery. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 8804–8814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, A.; Chen, S. Study on One-Class Classifiers Based On Kernel Method. J. Nanjing Norm. Univ. Eng. Technol. Ed. 2008, 8, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, A.; Chen, B. Improved LP Algorithms of One-Class Classifier Based on Local Density Factor. J. Nanjing Univ. Aeronaut. Astronaut. 2006, 38, 727–731. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Mountrakis, G.; Quackenbush, L.J. Impervious surface extraction in imbalanced datasets: Integrating partial results and multi-temporal information in an iterative one-class classifier. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 43–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Feng, Y.; Kamigaito, H.; Takamura, H.; Okumura, M. One-class Text Classification with Multi-modal Deep Support Vector Data Description. J. Nat. Lang. Process. 2021, 28, 1053–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafoori, Z.; Leckie, C. Deep Multi-sphere Support Vector Data Description. In Proceedings of the 2020 SIAM International Conference on Data Mining, Cincinnati, OH, USA, 7–9 May 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Geography Department at Loughborough University. The World According to GaWC 2020. Available online: https://www.lboro.ac.uk/microsites/geography/gawc/world2020t.html (accessed on 15 October 2022).
- Transportation Bureau of Shenzhen Municipality. Shenzhen Municipal Government Data Open Platform. Available online: https://opendata.sz.gov.cn/ (accessed on 2 August 2019).
- Wu, H.; Lin, A.; Clarke, K.C.; Shi, W.; Cardenas-Tristan, A.; Tu, Z. A Comprehensive Quality Assessment Framework for Linear Features from Volunteered Geographic Information. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2021, 35, 1826–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, J.; Seto, T.; Nishimura, Y.; Iwasaki, N. VGI Contributors’ Awareness of Geographic Information Quality and Its Effect on Data Quality: A Case Study from Japan. Int. J. Cartogr. 2019, 5, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Zhu, A.X. The Representativeness and Spatial Bias of Volunteered Geographic Information: A Review. Ann. GIS 2018, 24, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.D.; Chen, D. Segmentation for Object-Based Image Analysis (OBIA): A review of algorithms and challenges from remote sensing perspective. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 150, 115–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruff, L.; Görnitz, N.; Deecke, L.; Siddiqui, S.A.; Vandermeulen, R.A.; Binder, A.; Müller, E.; Kloft, M. Deep One-Class Classification. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Stockholm, Sweden, 10–15 July 2018. [Google Scholar]


| Data | Time | Source |
|---|---|---|
| POIs | 31/12/2018 | Amap |
| Vehicle trajectory GPS data | 8/10/2018–14/10/2018 | Shenzhen Municipal Government Data Open Platform |
| Roads data | 31/12/2018 | OpenStreetMap (OSM) |
| Buildings data | 31/12/2018 | OpenStreetMap (OSM) |
| Threshold | OODMSVDD | OODSVDD | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recall | Precision | OA | F1-Score | AUC | Recall | Precision | OA | F1-Score | AUC | |
| 10 | 93.13 | 81.63 | 85.75 | 86.82 | 91.19 | 94.60 | 79.73 | 85.19 | 86.45 | 90.85 |
| 20 | 90.90 | 82.75 | 85.68 | 86.36 | 92.15 | 92.28 | 81.10 | 84.93 | 86.07 | 91.99 |
| 30 | 91.42 | 84.68 | 87.43 | 87.91 | 92.40 | 92.66 | 81.81 | 85.90 | 86.84 | 91.53 |
| 40 | 89.53 | 81.34 | 84.21 | 85.04 | 90.07 | 94.00 | 78.32 | 83.73 | 85.29 | 89.25 |
| 50 | 93.42 | 79.37 | 84.16 | 85.58 | 90.40 | 92.70 | 80.14 | 84.78 | 85.93 | 90.81 |
| Method | Metrics | Threshold | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | ||
| DSVDD | Recall | 89.83 | 91.03 | 89.68 | 89.86 | 93.42 |
| Precision | 81.52 | 84.22 | 84.36 | 83.91 | 82.53 | |
| OA | 84.61 | 86.95 | 86.33 | 86.00 | 86.66 | |
| F1-Score | 85.39 | 87.45 | 86.80 | 86.59 | 87.57 | |
| AUC | 90.95 | 92.90 | 92.39 | 91.79 | 91.92 | |
| DMSVDD | Recall | 88.67 | 92.35 | 88.11 | 91.00 | 89.10 |
| Precision | 84.22 | 82.80 | 86.56 | 79.60 | 83.91 | |
| OA | 85.76 | 86.54 | 86.96 | 83.68 | 85.94 | |
| F1-Score | 86.16 | 87.30 | 87.14 | 84.83 | 86.33 | |
| AUC | 91.66 | 92.35 | 93.84 | 89.58 | 91.92 | |
| OODMSVDD | Recall | 93.13 | 90.90 | 91.42 | 89.53 | 93.42 |
| Precision | 81.63 | 82.75 | 84.68 | 81.34 | 79.37 | |
| OA | 85.75 | 85.68 | 87.43 | 84.21 | 84.16 | |
| F1-Score | 86.82 | 86.36 | 87.91 | 85.04 | 85.58 | |
| AUC | 91.19 | 92.15 | 92.40 | 90.07 | 90.40 | |
| Data | Recall | Precision | OA | F1-Score | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| POI | 85.31 | 87.44 | 86.52 | 86.34 | 93.18 |
| Building | 91.20 | 78.73 | 83.03 | 84.38 | 88.69 |
| Trajectory GPS | 90.07 | 81.40 | 84.63 | 85.42 | 89.76 |
| Road | 92.86 | 77.16 | 82.49 | 84.22 | 87.40 |
| OSM | 88.76 | 83.90 | 85.39 | 85.93 | 91.46 |
| OSM+Trajectory GPS | 91.78 | 79.27 | 83.62 | 84.99 | 89.06 |
| OSM+POI | 89.69 | 85.71 | 87.23 | 87.53 | 93.08 |
| POI+Trajectory GPS | 91.70 | 83.48 | 86.74 | 87.38 | 93.14 |
| All of the above | 91.42 | 84.68 | 87.43 | 87.91 | 92.40 |
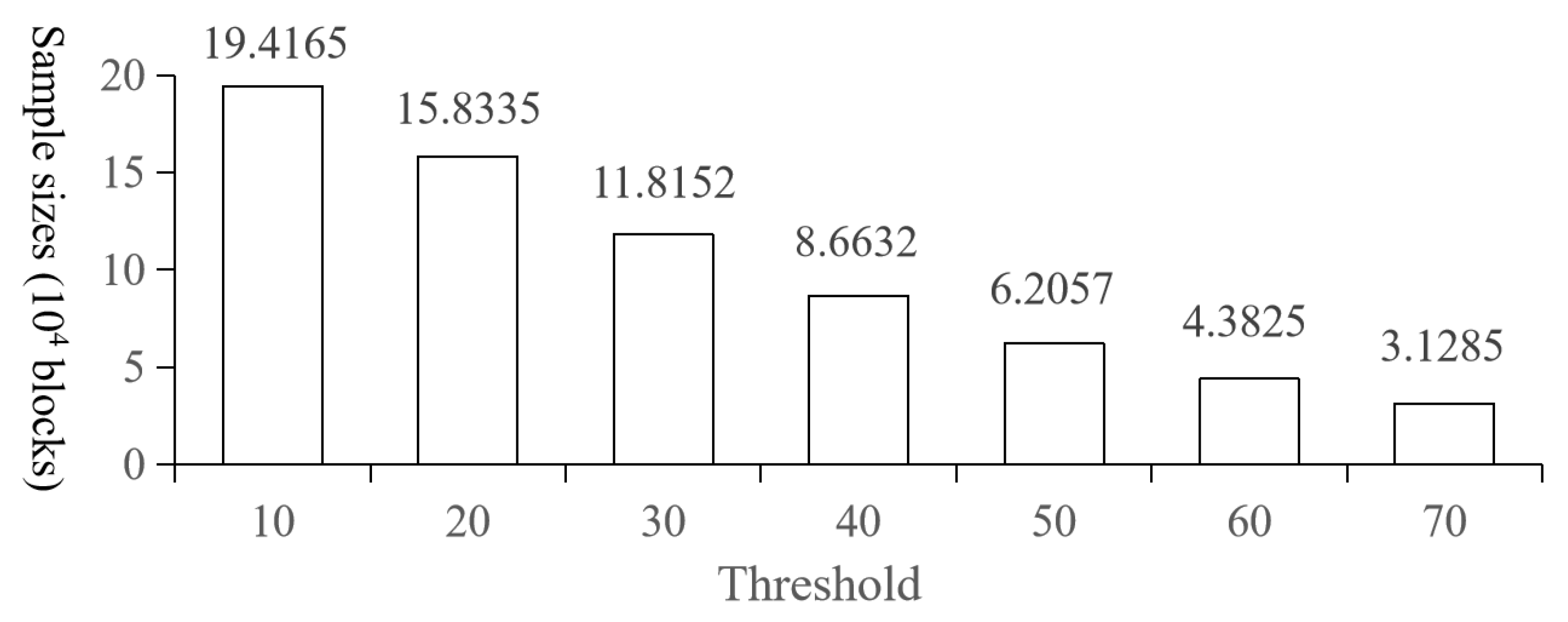
| Threshold | Metrics | Sample Size ( blocks) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | ||
| 10 | Recall | 90.44 | 93.26 | 93.13 | 91.12 |
| Precision | 68.40 | 78.91 | 81.63 | 77.23 | |
| OA | 74.10 | 83.95 | 85.75 | 81.05 | |
| F1-Score | 77.78 | 85.38 | 86.82 | 82.85 | |
| AUC | 77.32 | 89.64 | 91.19 | 87.69 | |
| 20 | Recall | 92.05 | 94.65 | 90.90 | 90.93 |
| Precision | 72.08 | 80.68 | 82.75 | 81.09 | |
| OA | 77.94 | 85.78 | 85.68 | 84.63 | |
| F1-Score | 80.75 | 87.01 | 86.36 | 85.60 | |
| AUC | 85.16 | 91.80 | 92.15 | 91.77 | |
| 30 | Recall | 92.72 | 91.92 | 91.42 | 91.50 |
| Precision | 71.70 | 83.12 | 84.68 | 81.74 | |
| OA | 78.00 | 86.58 | 87.43 | 85.31 | |
| F1-Score | 80.84 | 87.25 | 87.91 | 86.23 | |
| AUC | 85.93 | 91.81 | 92.40 | 91.27 | |
| 40 | Recall | 91.81 | 91.31 | 89.53 | 91.33 |
| Precision | 68.90 | 82.22 | 81.34 | 80.79 | |
| OA | 75.00 | 85.71 | 84.21 | 84.46 | |
| F1-Score | 78.66 | 86.49 | 85.04 | 85.57 | |
| AUC | 80.68 | 91.44 | 90.07 | 90.20 | |
| 50 | Recall | 90.71 | 89.40 | 93.42 | 89.44 |
| Precision | 67.73 | 80.78 | 79.37 | 81.06 | |
| OA | 73.71 | 83.00 | 84.16 | 84.13 | |
| F1-Score | 77.54 | 84.14 | 85.58 | 84.93 | |
| AUC | 79.65 | 91.61 | 90.40 | 89.73 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wan, Y.; Fei, Y.; Jin, R.; Wu, T.; He, X. An Object-Oriented Deep Multi-Sphere Support Vector Data Description Method for Impervious Surfaces Extraction Based on Multi-Sourced Data. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2023, 12, 219. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi12060219
Wan Y, Fei Y, Jin R, Wu T, He X. An Object-Oriented Deep Multi-Sphere Support Vector Data Description Method for Impervious Surfaces Extraction Based on Multi-Sourced Data. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information. 2023; 12(6):219. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi12060219
Chicago/Turabian StyleWan, Yiliang, Yuwen Fei, Rui Jin, Tao Wu, and Xinguang He. 2023. "An Object-Oriented Deep Multi-Sphere Support Vector Data Description Method for Impervious Surfaces Extraction Based on Multi-Sourced Data" ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information 12, no. 6: 219. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi12060219
APA StyleWan, Y., Fei, Y., Jin, R., Wu, T., & He, X. (2023). An Object-Oriented Deep Multi-Sphere Support Vector Data Description Method for Impervious Surfaces Extraction Based on Multi-Sourced Data. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 12(6), 219. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi12060219







