Abstract
The epidermal differentiation complex (EDC) is a cluster of genes that encode protein components of the outermost layers of the epidermis in mammals, reptiles and birds. The development of the stratified epidermis from a single-layered ectoderm involves an embryo-specific superficial cell layer, the periderm. An additional layer, the subperiderm, develops in crocodilians and over scutate scales of birds. Here, we review the expression of EDC genes during embryonic development. Several EDC genes are expressed predominantly or exclusively in embryo-specific cell layers, whereas others are confined to the epidermal layers that are maintained in postnatal skin. The S100 fused-type proteins scaffoldin and trichohyalin are expressed in the avian and mammalian periderm, respectively. Scaffoldin forms the so-called periderm granules, which are histological markers of the periderm in birds. Epidermal differentiation cysteine-rich protein (EDCRP) and epidermal differentiation protein containing DPCC motifs (EDDM) are expressed in the avian subperiderm where they are supposed to undergo cross-linking via disulfide bonds. Furthermore, a histidine-rich epidermal differentiation protein and feather-type corneous beta-proteins, also known as beta-keratins, are expressed in the subperiderm. The accumulating evidence for roles of EDC genes in the development of the epidermis has implications on the evolutionary diversification of the skin in amniotes.
Keywords:
epidermis; keratinocytes; cornification; periderm; subperiderm; loricrin; skin barrier; stratum corneum; chicken; evolution 1. Introduction: The Protective Functions of the Epidermis
The skin of amniotes prevents excessive loss of water in a dry environment and protects against mechanical, physical and biological threats. These functions are mediated by the epithelium of the skin, the epidermis, and in particular by the outermost layer of the epidermis, the cornified layer or stratum corneum. The epidermis is built by keratinocytes which undergo terminal differentiation, leading to their conversion into corneocytes, which are the cellular components of the stratum corneum. While the epidermis is continually renewed by cell proliferation, differentiation and cell death in adult organisms [1,2], the embryonic development of the epidermis involves special processes, such as the formation of a periderm, that are not active in the adult epidermis [3,4,5].
The molecular regulation of the epidermis is of great interest for evolutionary biology and medicine. Numerous specializations of skin development and regeneration have underlain the adaptation to diverse environments from dry deserts to the sea and the evolution of skin appendages, such as scales, hair, feathers and mammary glands, which are the characteristic features of major taxa of terrestrial vertebrates [6,7]. Dysregulations of epidermal homeostasis and stress responses cause highly prevalent skin diseases such as atopic dermatitis, which affects more than 10% of newborns [8]. Here, we review an important aspect of skin biology that has been uncovered by recent publications, namely the difference between the genetic regulation of the epidermis during development and during postnatal life.
2. Epidermal Differentiation in Mammals
The basic principles of the epidermal differentiation process have been identified in mammalian skin [9,10,11,12]. Keratinocytes proliferate in the basal layer, where also the stem cells reside, and subsequently move upwards into the suprabasal epidermal layers. Upon delamination, keratinocytes stop proliferation and undergo terminal differentiation, which depends on specific changes of gene expression, such as the upregulation of keratins K1 and K10, involucrin (IVL), small proline-rich proteins (SPRRs), transglutaminases and proteases [9,10]. Several differentiation-associated genes, such as loricrin and filaggrin, are expressed specifically in the granular layer of mammalian epidermis [13]. The final step of differentiation is the conversion of living keratinocytes into dead corneocytes that build the cornified layer (stratum corneum) on the skin surface [11,14,15]. This mode of cell death is called cornification or corneoptosis [16] and involves the breakdown of the nucleus and other cell organelles, while the cross-linking of proteins leads to the formation of the so-called cornified envelope underneath the cell membrane. The crosslinking of proteins requires the elevation of the intracytoplasmic concentration of calcium ions [17], which enables calcium-dependent transglutaminases TGM1, TGM3 and TGM5 to introduce Nɛ-(-glutamyl)lysine isopeptide bonds between proteins [11]. Ultimately, the cell membrane is replaced by inter-cellular lipids that fill the space between corneocytes and limit the diffusion of water through the stratum corneum. Cornified envelopes consist of cross-linked proteins, such as involucrin, loricrin, envoplakin, periplakin, SPRRs, filaggrin and keratins [11,13,15,18]. Desmosomes connect keratinocytes during differentiation and become modified by the interaction with corneodesmosin to form corneodesmosomes, which are the connections between corneocytes. Corneodesmosomes provide mechanically stable links between corneocytes and thereby establish the resilience of the stratum corneum. The proteolytic degradation of corneodesmosomes in the outermost layers of the stratum corneum, which is controlled by kallikreins and kallikrein inhibitors, leads to the desquamation of corneocytes [19].
The keratin cytoskeleton of keratinocytes undergoes major changes before and during keratinization. Filaggrin is considered a major regulator of this process because keratin filaments aggregate in its presence in vitro [20], and mutations of the filaggrin genes are associated with defects of the skin barrier. The precursor protein profilaggrin is synthesized in the granular layer where it is phosphorylated and located, at least when analyzed by histological procedures, in keratohyalin granules, which are the distinguishing characteristic of granular cells. Dephosphorylation, deimination and limited proteolysis control the maturation of filaggrin [21,22,23].
3. Epidermal Differentiation in Sauropsids
Sauropsids are the phenotypically diverse sister group of mammals, together forming the clade of amniotes. Extant sauropsids comprise Lepidosauria (Rhynchocephalia, represented by the tuatara, and Squamata, including geckos, lizards and snakes) and Archelosauria (turtles, crocodilians and birds). Numerous specialized cornified structures are present on the skin of sauropsids: for example, cornified scales of various shape in all reptiles, adhesive setae on the feet of geckos, scutes of the turtle shell, rhamphotheca of turtles and feathers of birds. Epidermal differentiation in squamates involves the regeneration and shedding of the outer layers of the epidermis, which is associated with a complex histological structure of the epidermis [24]. All these features of the sauropsidian epidermis are expected to depend on the molecular components of cornified structures and molecular mechanisms of regulation that are unique to sauropsids or subclades of sauropsids. Many of the proteins that build cornified epidermal cells of sauropsids have been identified by recent research, whereas the regulatory processes are largely unknown at present.
As the current knowledge on the skin of sauropsids has been reviewed extensively [7,25,26], we highlight only a few aspects here. Basic principles of epidermal differentiation, such as cell proliferation in the basal layer, changes in gene expression during movement through suprabasal layers and cell death with massive protein cross-linking (cornification), are equivalent to those in mammalian epidermis. Soft cornification, leading to a pliable skin surface like in mammals, occurs in the epidermis between feather follicles of birds, on regions of the neck and limbs of turtles, and in the hinge and inner segments of scales in all sauropsids. By contrast, hard cornification, leading to rigid scales, scutes, carapace, feathers etc., is very prominent in reptiles and birds. Of note, the morphogenesis of hard cornified skin appendages such as feathers, but also hair, requires complex regulation that goes beyond the control of epidermal differentiation discussed in the present review. Importantly, the existence of sauropsid-specific modes of epidermal differentiation mainly characterized at the histological level correlates with the existence of sauropsid-specific epidermal differentiation genes that have been identified and partially characterized [27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36].
4. Embryonic Development of the Epidermis in Amniotes
The epidermis is continuously renewed during postnatal life, but its initial stratification during embryonic development requires additional steps of epithelial differentiation [37]. In amniotes, the embryo is surrounded by the amniotic fluid, and the ectoderm gives rise to the embryonic epidermis. At first, the embryo is only covered by a monolayer of highly proliferative ectodermal cells. In the next step of skin development, the embryonic epidermis becomes bilayered with a transient protective layer called periderm covering the basal layer [38]. The limbs and tail are the first sites of periderm appearance, from which it extends to all other sites of the body surface in mice [39,40]. The periderm consists of flattened and tightly connected cells that are lost before birth [3,39,41,42]. While the periderm is often referred to as a single-layered epithelium, it is actually bilayered in rats [43] and mice [44] as well as reptiles [45]. In both single-layered and bi-layered periderm, the cells on the surface form microvilli.
After the formation of the periderm, epidermal stratification occurs through asymmetric cell division in the basal layer. The embryonic superbasal layers are not well characterized in early development but assume properties similar to the spinous layer and later by the granular layer as found in postnatal epidermis [5,46]. The developing epidermis is immature until the formation of tight junctions in the granular layer and the initiation of cornification. When the definitive cornified layer is formed, the periderm loses its function as a protective layer. Then, periderm cells undergo cornification, and the periderm detaches from the surface of the skin. These last steps of periderm cornification are coordinated with the maturation of the epidermis, as an impairment of epidermal cornification leads to the aberrant retention of the periderm in mutant mice [47].
The periderm of birds displays a special cytological feature: periderm granules [26]. These membrane-less granules of diameters between 100 nm and several micrometers are eosinophilic on histological sections. In samples prepared for ultrastructural studies, periderm granules appear to contain filaments 20–60 nm in diameter [48]. Recent studies on keratohyalin granules, which differ biochemically from periderm granules, but also appear in differentiated epithelial cells, have identified liquid–liquid phase separation as the main driver of granule formation. It is conceivable that a similar phenomenon occurs in the periderm and that the ribbon-like aggregations may be largely an artifact of tissue fixation. Peridermal granules in the transient embryonic layers disappear during the later stages of development once the cornified layer is formed [26,49,50].
While in all sauropsids two periderm layers (outer/primary and inner/secondary) are present [45,51], in birds and crocodilians, which together form the clade Archosauria, a unique peridermal derivative, termed the subperiderm, has been reported [52,53,54,55,56]. To avoid confusion, we have to point to inconsistent use of this term in the literature with some papers referring to the inner layer of periderm as subperiderm [57] and others referring to the outer layers of the epidermis proper as subperidermal layers. Here, we follow the definition of the subperiderm by Roger H. Sawyer [51]. The subperiderm is the innermost layer of embryo-specific epithelial cells and is located between the inner periderm and the outermost layer of the immature epidermis. Although, to the best of our knowledge, experimental evidence is not available, the cells of the subperiderm are derived from precursors in the periderm. In contrast to the flattened cells of the periderm, subperidermal cells are thick and appear mechanically robust in histological sections. At the ultrastructural level, they are distinguished from the inner periderm by the absence of periderm granules, and at the molecular level, they contain specific corneous beta-proteins, which are also known as beta-keratins similar or identical to proteins of feathers [51]. A subperiderm develops on top of scutate scales on the legs of birds and on other types of scales in alligators and crocodiles [56] (Figure 1).
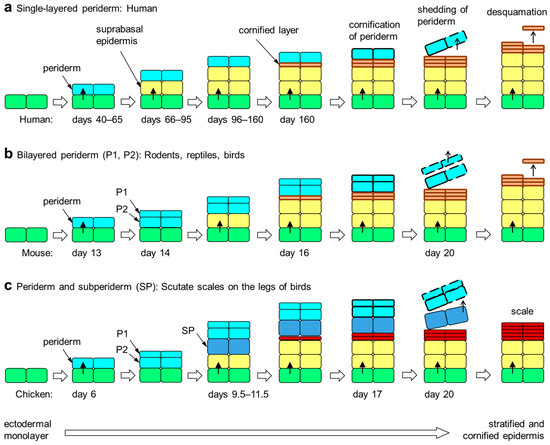
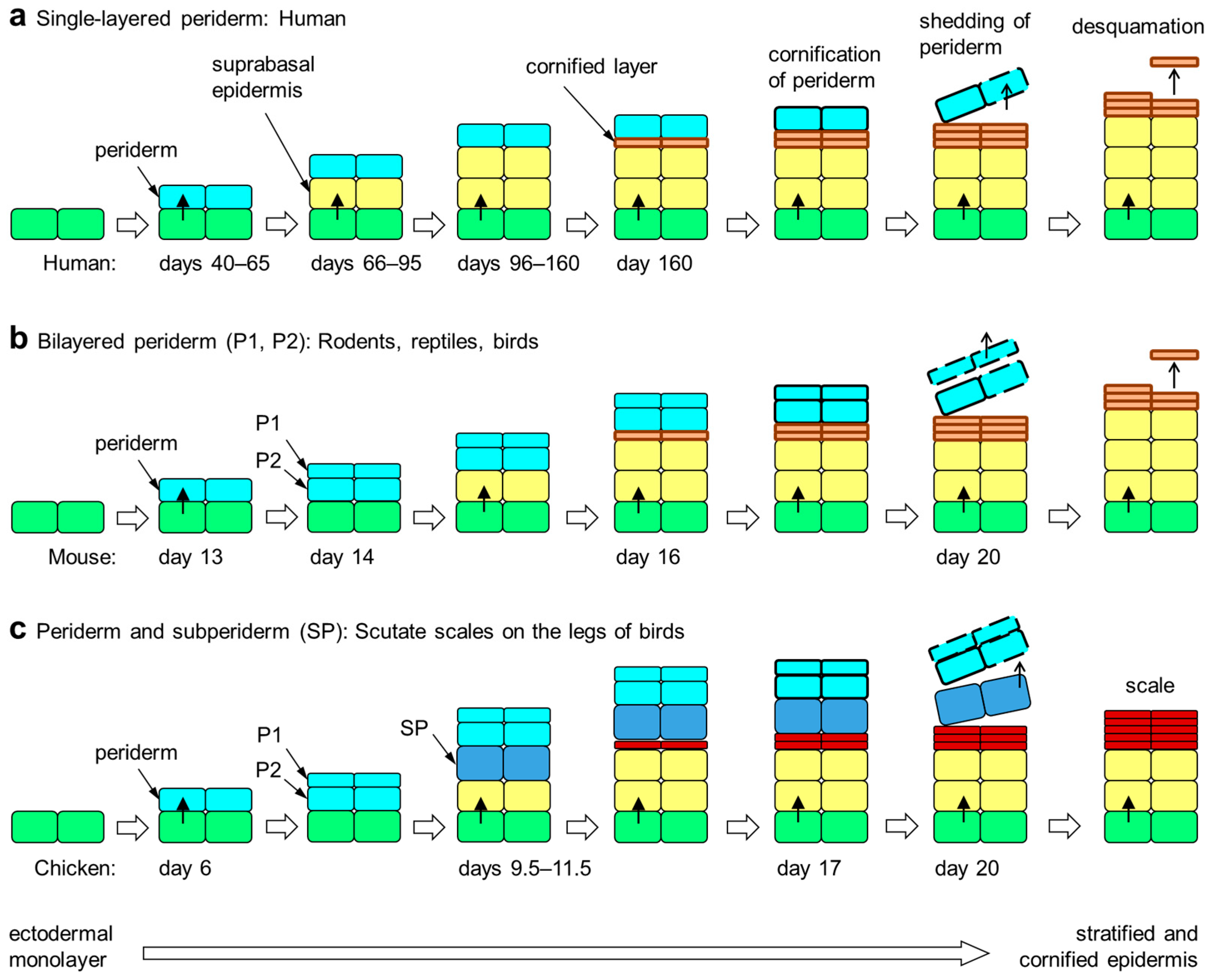
Figure 1.
Embryonic development of the epidermis in amniotes. The periderm is a transient layer of epithelial cells covering the epidermis during its initial stratification in the embryo. Upon formation of the cornified layer of the epidermis, peridermal cells also undergo cornification. Subsequently, the periderm is shed from the surface. The periderm is either single-layered (a), two-layered (b) or multi-layered (not shown). Developing scutate scales of birds are covered by a subperiderm in addition to the bilayered periderm (c) [51,58]. The timing (days of embryonic development) of epithelial stratification events in selected species [5,44,51,59] is shown in each panel. Colors indicate the differentiation states of epithelial cells: green, basal layer keratinocytes; yellow suprabasal keratinocytes; orange, cornified keratinocytes of the stratum corneum; red, cornified keratinocytes of cornified scales; light blue, periderm; dark blue, subperiderm.
Specific body sites of sauropsids are covered by multiple transient layers of epithelial cells during development. For instance, the cornified egg tooth, also known as caruncle, is surrounded by a multilayered periderm in birds [50,60] and turtles [61]. The carapace of turtles is covered by several embryonic epithelial layers, which are shed at hatching [45,62].
5. The Epidermal Differentiation Complex (EDC)
The EDC is a cluster of genes that are expressed during the terminal differentiation of keratinocytes [13,63]. First identified in humans on chromosome 1q21 [64,65] and later on chromosome 3q of the mouse, this locus is generally conserved in mammals [63,66] and sauropsids [31]. The EDC is delimited by S100A genes at both ends. One or two genes encoding peptidoglycan recognition proteins (PLGYRPs) are present close to the S100A9 gene in the EDC of amniotes [31]. The sauropsid-specific gene EDKM (epidermal differentiation protein containing a KKLIQQ motif) is located next to PLGYRP3 [31]. The remaining genes are classified into two types, single-coding exon EDC (SEDC) genes and S100 fused-type protein (SFTP) genes, which will be described in detail below (Figure 2).
The arrangement of genes in the EDC, as depicted schematically in Figure 2, is conserved in amniotes [31] and partially similar to a less complex gene cluster in amphibians [67]. The relative position of genes is important for the regulation of EDC gene expression, which depends on proximal promoters, distal enhancers and chromatin interaction networks [66,67,68,69,70,71]. The mechanisms of EDC gene regulation during keratinocyte differentiation and epidermal development and aging are proposed to be critical for the function of the EDC.
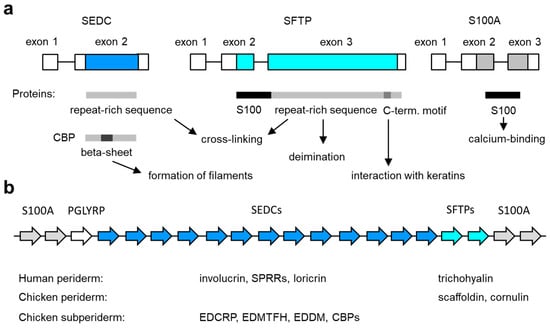
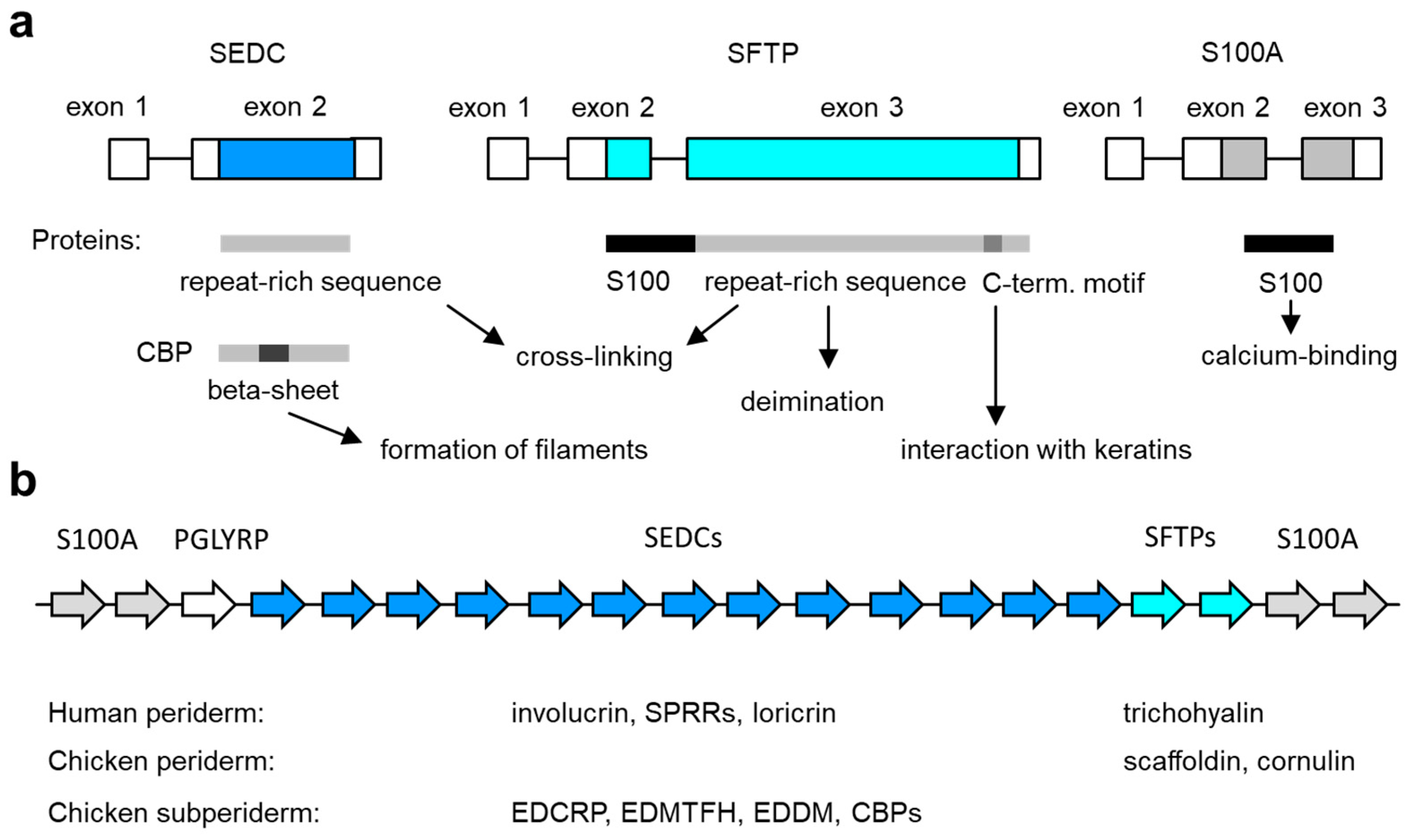
Figure 2.
Genes of the epidermal differentiation complex (EDC). (a) Exon–intron structure of the main types of EDC genes. The basic structure of the encoded proteins and their functions are schematically depicted below. C-term., carboxy-terminal; SEDC, single-coding exon EDC gene; SFTP, S100 fused-type protein. (b) Arrangement of genes in the EDC. The relative arrangement of EDC gene types (indicated by arrows of different color, labeled at the top) in amniotes is depicted schematically. The number of genes in the diagram does not represent a particular species. The EDC contains 39 SEDC and 7 SFTP genes in humans [72] and 100 SEDC and 2 SFTP genes in the chicken [35]. The expression profile of SEDC and SFTP genes in the embryonic periderm and subperiderm is indicated below the schematic. See the main text for information on individual genes.
Figure 2.
Genes of the epidermal differentiation complex (EDC). (a) Exon–intron structure of the main types of EDC genes. The basic structure of the encoded proteins and their functions are schematically depicted below. C-term., carboxy-terminal; SEDC, single-coding exon EDC gene; SFTP, S100 fused-type protein. (b) Arrangement of genes in the EDC. The relative arrangement of EDC gene types (indicated by arrows of different color, labeled at the top) in amniotes is depicted schematically. The number of genes in the diagram does not represent a particular species. The EDC contains 39 SEDC and 7 SFTP genes in humans [72] and 100 SEDC and 2 SFTP genes in the chicken [35]. The expression profile of SEDC and SFTP genes in the embryonic periderm and subperiderm is indicated below the schematic. See the main text for information on individual genes.
5.1. SEDCs
Single-coding exon EDC (SEDC, in some publications also referred to as simple EDC) genes have two exons of which the first contains only a non-coding sequence and the second codes for a protein. Exon 1 of most SEDC genes is preceded by a canonical TATA box [73], indicating that the expression of SEDCs is inducible and not required for constitutive cell functions [74]. The amino acid sequences of SEDC-encoded proteins are highly diverse, but there are several conserved features. Many SEDC proteins contain a conserved sequence motif close to their amino-terminus (consensus sequence QCKQPCxPP) and another imperfectly conserved motif close to their carboxy-terminus (consensus sequence QQxKQPXXWPxxxK-stop) [31,34]. Most SEDC proteins contain multiple tandem sequence repeats, and their amino acid composition is biased toward either glycine, proline or cysteine [31].
Although all SEDC genes are homologous, it is difficult to determine which SEDC genes of two species are orthologous, which means that they are more closely related to each other than to any other SEDC gene of the two species. There is good support for the orthology of loricrin in mammals and sauropsids [31], and possibly mammalian SPRRs and specific proline-rich proteins of sauropsids are also orthologs [36]. In contrast, a gene partially identified in the chicken and termed involucrin [30] is likely not closely related to mammalian involucrin [31]. Accordingly, new names had to be given to these sauropsid SEDC genes when a large number was identified by comparative analysis in the genomes of chicken and green anole lizard [31]. As detailed data on expression patterns and functions were not available at that time, the names refer to the location in the EDC, indicated by the letters ED for epidermal differentiation, and amino acid sequence features of the proteins encoded by these genes. Accordingly, EDPE stands for Epidermal Differentiation protein rich in Proline and glutamic acid (E) [31].
5.2. SFTPs
SFTPs have three exons, of which the second and third contain the protein-coding sequence [31]. Like in SEDC genes, the first exon of SFTPs is non-coding (Figure 2a) [31,63]. SFTPs have an amino-terminal S100 domain containing two Ca2+-binding EF-hand motifs. The S100 domain is followed by a segment of low-sequence complexity of 200–4000 residues, which is likely to result in an intrinsically disordered structure [75]. Both the length and amino acid sequence of this segment varies greatly between different SFTPs, but, in majority of SFTPs reported so far, this segment contains sequence repeats, and its amino acid composition is biased toward arginine and glutamic acid (e.g., in scaffoldin and trichohyalin, see below) or glycine and serine (e.g., filaggrin). Glutamine residues, potentially serving as sites of transglutamination, are frequent in all SFTPs [63]. A short sequence motif with the core sequence SPLY(E/D)Y is present close to the carboxy-terminal of most SFTPs. This motif has been proposed to mediate the binding of SFTPs to keratins [76,77,78].
6. Expression and Function of EDC Genes in Epidermal Development
6.1. EDC Genes Expressed in the Embryonic Precursor of the Postnatal Epidermis
While the periderm and subperiderm are specifically embryonic layers of the epidermis, the basal, spinous, granular and cornified layers of stratified epidermis are present in the late embryonic skin and in postnatal skin. Accordingly, the expression of genes in the periderm and subperiderm differs significantly from gene expression in the postnatal epidermis, but gene expression in the inner layers of developing epidermis resembles that of mature epidermis. For example, the prototypical skin barrier gene Filaggrin is expressed during epidermal development, and the corresponding protein is processed in a similar manner as in the epidermis of the adult organism [79]. Likewise, loricrin is expressed in the granular layer of embryonic epidermis [59,80], and the upregulation of SPRR and LCE genes, reminiscent of stress responses of adult skin, can be increased prenatally by the deletion of the Loricrin gene [80,81,82]. The expression of several EDC genes of chickens and turtles was detected in developing skin [31,33], but only a few of them have been localized by mRNA in situ hybridization or immunohistochemistry within embryonic tissues of sauropsids. Comprehensive maps of EDC gene expression during embryonic and postnatal epidermal stratification are established by tissue transcriptomics, single-cell transcriptomics and spatial transcriptomic studies of skin development in phylogenetically diverse amniotes [83,84,85,86].
6.2. EDC Genes Expressed in the Embryonic Periderm or Subperiderm
Several genes of the EDC of different species of amniotes have been reported to be expressed in the embryonic periderm or subperiderm (Table 1). Here, we first discuss the evidence for the peridermal or subperidermal expression of SEDC-type genes and later discuss the expression of SFTP genes in the transient layers of the embryonic epidermis.

Table 1.
EDC genes expressed in embryo-specific epithelial skin layers.
6.2.1. Loricrin
Loricrin is encoded by an SEDC gene. The official gene symbol is now LORICRIN, whereas LOR was used previously in GenBank and in most publications until recently. In both mouse and human, loricrin is the main component of the cornified cell envelope [95,96]. Loricrin is highly enriched in glycine residues [20,97]. Its glutamine and lysine residues are target sites for cross-linking to SPRRs, other loricrin proteins and keratins filaments [20,98]. An ortholog of loricrin has been localized in the epidermis of the green anole lizard [31,99]. By immunolabeling with a carboxy-terminal specific antibody, it was detected in both the maturing “soft” alpha layer (lacunar cells) of scale epidermis and corneocytes of wound epidermis in the regenerating tail but not in the “hard” beta layer [99]. The lizard has two loricrin genes, and even three loricrin genes were identified in the chicken with each of them being expressed in both adult and embryonic skin [31]. By RT-PCR, loricrin mRNA was also detected in the skin of a turtle during embryonic development [33]. Loricrin was localized by fluorescent immunolabeling in the periderm of developing human skin [59]. At the ultrastructural level, immunogold electron microscopy detected loricrin in the cornified envelope of periderm cells [59].
6.2.2. SPRRs
Small proline rich proteins (SPRRs) have a size of less than 20 kDa. They contain numerous proline-rich repeats and several glutamine and lysine residues which are sites of cross-linking to other proteins through the activity of transglutaminases [11,100]. The transcription of SPRR genes is upregulated in epidermal keratinocytes during wound healing [101]. Apart from their structural function in the cornified envelope, SPRRs have anti-oxidative properties [102]. SPRR2 and SPRR3 proteins were detected by immunofluorescence labeling during skin embryogenesis in humans. SPRR staining was observed in the periderm of the two-layered embryonic epidermis and in the embryonic spinous, granular and cornified epidermal layers at a later stage [59]. Many different classes of proline-rich proteins have been identified in all sauropsids, but no definitive orthology has been established [31,33,34,35,36]. EDC genes encoding SPRR-like proteins were reported to be expressed during the embyronic development in chickens and turtles [31,33].
6.2.3. EDMTFH
EDMTFH is an SEDC gene located between the loricrin and CBP genes of the chicken genome. Its name stands for “Epidermal Differentiation Protein starting with an MTF motif and rich in Histidine” and indicates some of the few protein features that could be deduced from the amino acid sequence at the time of identification [31]. EDMTFH of the chicken has 99 amino acid residues of which 40% have aromatic side groups (F, W, Y, H). There are five EDMTF proteins in chicken, but only EDMTFH has a high content of histidine residues (>15%). A partial sequence of the protein was originally published as histidine-rich protein, HRP-B [103], leading to confusion with the mammalian SFTP, filaggrin, which is also rich in histidine residues [88]. EDMTFH belongs to a subcluster of gene EDC genes, initially named epidermal differentiation proteins starting with the MTF motif (EDMTFs) [31] and later renamed EDAAs (epidermal differentiation proteins rich in aromatic amino acids) [33,104]. EDMTF/EDAA genes underwent expansion by gene duplications in alligators [35], and genes of this family have been translocated to a non-EDC locus in turtles [33], whereas EDMTF/EDAA genes are not found in lepidosaurs (lizards, snakes and tuatara).
The EDMTFH protein was localized through both immunohistochemistry and immunogold labeling in the subperiderm of scutate scales and feather barb and barbules (E16–E19) of chickens [88]. It is expressed neither in the periderm nor in the normal epidermis. Electron microscopy indicated that EDMTFH partially co-localized with feather CBP bundles in barbule cells during the embryonic feather formation [88]. The results of the EDMTFH immunolocalization study supported the previously proposed evolutionary–developmental link between subperiderm and feather barb and barbules [51].
6.2.4. EDCRP
Epidermal differentiation cysteine-rich protein (EDCRP) has an unusually high content of cysteine residues (36%) and is therefore considered a candidate for disulfide cross-linking [73]. It contains sequence repeats with the consensus sequence CCDPCQ(K/Q)(S/P)V. The sequence of avian EDCRP is similar to the sequences of cysteine-rich keratin-associated proteins (KRTAPs) of mammals, although these proteins are not phylogentically related [73]. Chicken EDCRP contains 385 amino acid residues among which paired cysteine residues (CC) are periodically found [73].
EDCRP was detected by RT-PCR in chicken embryonic skin, feathers and scales as well as adult feathers [31]. The expression in feathers was confirmed by a mass spectrometry-based proteomic analysis of chicken feathers [31]. In a later study, the expression of EDCRP was determined by mRNA in situ hybridization during embryonic development. EDCRP mRNA was detected in feather barbs and barbules of day E18 of embryonic development [73] and, importantly, in the subperiderm over the embryonic scutate scales [73]. The subperidermal keratinocytes were the only cells outside of feather follicles that were positive for EDCRP. Because of the above-mentioned sequence similarity with mammalian KRTAPs, it is conceivable that EDCRP is covalently linked by disulfide bonds to cysteine-rich keratins or other proteins to increase the mechanical resistance of cells [73]. The specific role of EDCRP in the subperiderm and the properties of the subperiderm require further investigations.
6.2.5. EDDM
Epidermal Differentiation protein containing DPCC Motifs (EDDM) has even more cysteine residues than EDCRP and all other chicken EDC proteins [89]. The expression pattern of EDDM during skin development in chicken was studied using RT-qPCR and immunohistochemical analysis [89]. Immunolabeling with an EDDM antibody detected the protein in feathers [89] where EDDM was also detected by proteomics [31]. Furthermore, EDDM was detected by immunostaining in the subperiderm of embryonic scutate scales [89].
EDDM is conserved in birds, and orthologs of EDDM exist in crocodilians [35,89]. Of note, an ortholog of the other major avian cysteine-rich EDC protein, EDCRP, is also present in crocodilians [38]. The characteristic internal sequence repeats are conserved in the EDDM ortholog [89] but not in the EDCRP ortholog of alligators and crocodiles. As crocodilians develop a subperiderm, it will be very interesting to determine whether the subperidermal expression of EDCRP and EDDM is conserved in crocodilians.
6.2.6. Corneous Beta Proteins (CBPs), Previously Referred to as Beta-Keratins
CBPs, formerly called beta-keratins, are characteristic and quantitatively dominant proteins of the epidermis in sauropsids. The name CBP indicates the expression in corneous skin structures and the ability to form a beta sheet (beta-pleated sheet). The latter trait depends on a conserved core domain of 34 amino acid residues [105,106]. Through face-to-face interactions between beta sheets, CBPs form dimers, and dimers subsequently form fibers. The terminal domains of CBPs are predicted to interact with other proteins [105,106]. The original name, beta-keratins, was meant to indicate the presence in the skin but is now considered misleading. CBPs are not related to keratins, which are members of the intermediate filament protein family [31,107].
The genes that encode CBPs have evolved as a subtype of SEDC genes [31] which are typically arranged in a clustered manner within the EDC of birds [92,108,109], crocodilians [93], turtles [33,110], lizards [32], geckos [36,111] and the tuatara [36]. The number of CBP genes ranges from 22 in crocodiles to more than 140 in chickens [106]. Based on the major expression sites and sequence similarities, CBPs have been classified into claw, scale, feather, feather-like and keratinocyte subfamilies [28,29,92,112]. In birds and turtles, the CBP genes underwent an expansion of copy numbers and gene translocations to loci outside of the EDC [33,108,109,110]. Feather CBP genes can be found on at least seven different loci of the chicken genome [108].
CBPs are expressed during chicken skin development, as demonstrated by both in situ hybridization [113,114,115] and immunolabeling [91,116,117]. Using an antibody raised against a scale CBP, CBPs were detected in the embryonic epidermal layers over developing scutate and reticulate scales as well as apteric skin of embryonic day 17, whereas only scutate scales were immunopositive for these CBPs in mature skin [91], which indicated a temporal and region-specific control of CBP expression during development. An antibody against feather CBPs revealed specific expression in the subperiderm over scutate scales, suggesting a homologous protein composition of feathers and subperiderm [58,117]. Subsequently, feather CBP homologs were also detected by immunostaining in the subperiderm of alligators. Together, these findings led to the hypothesis that the subperiderm originated in a common archosaurian ancestor and feathers coopted subperidermal proteins to the development of feathers [51,94].
Transcriptomic analyses showed that CBPs are differentially expressed in different types of embryonic chicken tissues, such as scales and feathers [110]. The expression sites were determined by mRNA in situ hybridization of chicken embryos [90]. CBPs named Chr25-FK12 and Chr27-FK12 and possibly Chr25-Claw9 were expressed in the subperiderm. However, the interpretation of CBP expression data is currently complicated because the nomenclature of CBPs and the nomenclature of embryonic skin layers is not consistently used by all research groups.
The embryonic skin development of crocodilians was investigated in several detailed histological and cytological studies. An antibody against chicken scale CBP (β1) was used to study epidermal development in alligators [49,51,94]. CBP expression was detected in the subperiderm of early stages of development (stages 24 and 25). The immunopositivity was maintained only in the definitive beta layer of stage 28 epidermis of hard outer (dorsal) scales but not in the ventral and hinge regions of scales [49,94]. By applying CBP gene-specific RT-PCRs, the expression of nine individual CBPs was detected in claws, the caruncle and scales at developmental stages 21, 23, 25 and 27, revealing a variation in CBP expression levels between stages and tissue types [93].
In lepidosaurs, CBPs were reported to be expressed during the development of the adhesive setae of geckos [118] and during skin development of the green anole lizard [32]. However, the expression of CBPs and other epidermal differentiation-associated proteins in the embryonic skin of all sauropsids except birds is largely unexplored. Further studies are necessary to integrate gene expression during development with hypotheses on the evolution of genes and skin in reptiles [33,51,58,90,92,93,108,110].
6.2.7. Scaffoldin and Trichohyalin
Members of the SFTP family are expressed both during the initial formation of the stratum corneum and during the embryo-specific differentiation of the periderm. Filaggrin, filaggrin 2, hornerin and repetin are expressed in the developing epidermis of mouse embryos [79,119,120]. Trichohyalin and cornulin, which are evolutionarily more ancient than the aforementioned SFTPs, are not only expressed in immature epidermis and epidermal appendages but also in the periderm.
Trichohyalin, encoded by the gene TCHH, is mainly known as a protein of filiform papillae, the inner root sheath of the hair follicle and the medulla of hair shafts, where it forms intracellular granules, which are known as trichohyalin granules [13,121,122]. Trichohyalin interacts with keratin filaments via a short carboxy-terminal sequence motif that is conserved in many other SFTPs [76]. Scaffoldin (SCFN) is a homolog of mammalian trichohyalin in sauropsids [77]. It was named differently from trichohyalin because molecular phylogenetics based on S100 domain sequences of SFTPs did not unambiguously support orthology between trichohyalin and scaffoldin. However, the similarity between the two proteins is most striking in the segment following the S100 domain. Like trichohyalin, scaffoldin is extremely rich in the amino acid residues arginine (17% in alligator, 18% in chicken) and glutamic acid (17% in alligator, 19% in chicken) [77]. Also, the extreme length of scaffoldin of around 3200 amino acid (aa) residues in the chicken and 2678 aa in the alligator is similar to the length of human trichohyalin (1943 aa) [77].
SCFN is prominently expressed in the periderm of embryonic chicken skin [77]. It was specifically localized by mRNA in situ hybridization in the periderm but also in the subunguis of the claw [77]. At the protein level, SCFN was detected in the periderm of the skin leg (E18), where it localized to the periderm granules. The highest abundance of scaffoldin was observed in the multilayered periderm surrounding the egg tooth on the beak (E10) [60,77]. Further evidence for the expression of SCFN protein was obtained by immunoblotting, which revealed a band at the predicted size of 385 kDa in the embryonic beak, toe, skin, and tongue and an additional band reminiscent of the trichohyalin band that is linked to the deimination of arginine residues [77,123]. Immunogold electron microscopy indicated that scaffoldin forms the filamentous structures of periderm granules [50]. Periderm granules are not formed in the mammalian periderm, although some papers discussed the appearance of similar structures. However, trichohyalin was detected by immunohistochemical staining in the human periderm [87]. Recently, the expression of trichohyalin in the periderm was confirmed by single-cell transcriptomics of embryonic mouse skin [83]. These data suggest an evolutionarily conserved function of scaffoldin and trichohyalin in the periderm.
6.2.8. Cornulin
Cornulin is an evolutionarily ancient SFTP that is expressed in the granular layer of the epidermis, the inner root sheath of hair follicles and the epithelium of the esophagus [124]. Like scaffoldin, cornulin is expressed in the periderm of embryonic chicken skin [58,77]. Immunolabeling of cornulin in embryonic mouse skin did not show expression in the periderm, but in the granular layer [77]. Of note, orthologs of cornulin exist in sauropsids and mammals, but cornulin is not conserved in green anole lizards, songbirds and whales [77,125,126]. These reported expression patterns suggest a partial redundancy of scaffoldin and cornulin in some but not all species of amniotes.
7. Conclusions
The accumulating evidence for the expression of EDC genes in embryo-specific layers of the epidermis, that is, the periderm and subperiderm, indicates functions of the EDC in controlling the development of the epidermis prior to its functions in the skin barrier and in the cornification of skin appendages of amniotes. This raises important questions regarding the molecular interactions of EDC proteins during development and the potential involvement in developmental defects due to aberrant or incomplete differentiation of the periderm [40]. Furthermore, the evolution of the EDC was linked not only to the adaptation to life in a dry environment [31] but also to new steps in the skin development of amniotes.
To better understand the functions of EDC proteins in skin development, detailed studies of gene expression, gene ablation or overexpression studies in phylogenetically diverse animal models and tests of protein interactions under defined conditions in vitro will be required. Together with detailed histological investigations, the identification of molecular markers of cell differentiation stages will help to close several important gaps in knowledge.
In conclusion, the recent progress in comparative genomics and gene expression studies have identified new roles of the EDC in skin development. Future studies will investigate the contribution of these roles of EDC genes in the phenotypic diversification of the skin during the evolution of mammals, reptiles and birds.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.B.H. and L.E.; writing—original draft preparation, K.B.H. and L.E.; writing—review and editing, K.B.H. and L.E. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Austrian Science Fund (FWF): P32777.
Acknowledgments
We thank Bettina Ebner, Veronika Mlitz, Florian Ehrlich, Julia Lachner, Erwin Tschachler and Lorenzo Alibardi for helpful discussions about epidermal differentiaton in terrestrial vertebrates.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Peskoller, M.; Bhosale, A.; Göbel, K.; Löhr, J.; Miceli, S.; Perot, S.; Persa, O.; Rübsam, M.; Shah, J.; Zhang, H.; et al. How to build and regenerate a functional skin barrier: The adhesive and cell shaping travels of a keratinocyte. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2022, 142, 1020–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckhart, L.; Zeeuwen, P.L.J.M. The skin barrier: Epidermis vs. environment. Exp. Dermatol. 2018, 27, 805–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardman, M.J.; Sisi, P.; Banbury, D.N.; Byrne, C. Patterned acquisition of skin barrier function during development. Development 1998, 125, 1541–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Echten-Deckert, G.; Saathoff, M.; Kirfel, G.; Herzog, V. Specific distribution of barrier-relevant ceramides in the emerging epidermis and the periderm/subperiderm during chicken embryogenesis. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2007, 86, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammond, N.L.; Dixon, J.; Dixon, M.J. Periderm: Life-cycle and function during orofacial and epidermal development. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 91, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhouailly, D. Evo devo of the vertebrates integument. J. Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akat, E.; Yenmiş, M.; Pombal, M.A.; Molist, P.; Megías, M.; Arman, S.; Veselỳ, M.; Anderson, R.; Ayaz, D. Comparison of vertebrate skin structure at class level: A review. Anat. Rec. 2022, 305, 3543–3608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irvine, A.D.; McLean, W.H.; Leung, D.Y. Filaggrin mutations associated with skin and allergic diseases. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 1315–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, E.; Green, H. Changes in keratin gene expression during terminal differentiation of the keratinocyte. Cell 1980, 19, 1033–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koster, M.I.; Roop, D.R. Mechanisms regulating epithelial stratification. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2007, 23, 93–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candi, E.; Schmidt, R.; Melino, G. The cornified envelope: A model of cell death in the skin. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 6, 328–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokouchi, M.; Kubo, A. Maintenance of tight junction barrier integrity in cell turnover and skin diseases. Exp. Dermatol. 2018, 27, 876–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kypriotou, M.; Huber, M.; Hohl, D. The human epidermal differentiation complex: Cornified envelope precursors, S100 proteins and the ‘fused genes’ family. Exp. Dermatol. 2012, 21, 643–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemes, Z.; Steinert, P.M. Bricks and mortar of the epidermal barrier. Exp. Mol. Med. 1999, 31, 5–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckhart, L.; Lippens, S.; Tschachler, E.; Declercq, W. Cell death by cornification. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1833, 3471–3480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsui, T. Epidermal barrier development via corneoptosis: A unique form of cell death in sratum granulosum cells. J. Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murata, T.; Honda, T.; Egawa, G.; Yamamoto, Y.; Ichijo, R.; Toyoshima, F.; Dainichi, T.; Kabashima, K. Transient elevation of cytoplasmic calcium ion concentration at a single cell level precedes morphological changes of epidermal keratinocytes during cornification. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinin, A.E.; Kajava, A.V.; Steinert, P.M. Epithelial barrier function: Assembly and structural features of the cornified cell envelope. Bioessays 2002, 24, 789–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgoño, C.A.; Michael, I.P.; Komatsu, N.; Jayakumar, A.; Kapadia, R.; Clayman, G.L.; Sotiropoulou, G.; Diamandis, E.P. A potential role for multiple tissue kallikrein serine proteases in epidermal desquamation. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 3640–3652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinert, P.M.; Mack, J.W.; Korge, B.P.; Gan, S.Q.; Haynes, S.R.; Steven, A.C. Glycine loops in proteins: Their occurrence in certain intermediate filament chains, loricrins and single-stranded RNA binding proteins. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 1991, 13, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resing, K.A.; Johnson, R.S.; Walsh, K.A. Characterization of protease processing sites during conversion of rat profilaggrin to filaggrin. Biochemistry 1993, 32, 10036–10045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Resing, K.A.; Dale, B.A.; Walsh, K.A. Multiple copies of phosphorylated filaggrin in epidermal profilaggrin demonstrated by analysis of tryptic peptides. Biochemistry 1985, 24, 4167–4175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandilands, A.; Sutherland, C.; Irvine, A.D.; McLean, W.H. Filaggrin in the frontline: Role in skin barrier function and disease. J. Cell Sci. 2009, 122, 1285–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landmann, L. The skin of Reptiles: Epidermis and dermis. In Biology of the Integument, Volume 2 Vertebrates; Bereiter-Hahn, J., Matoltsy, A.G., Sylvia-Richards, K., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1986; pp. 150–187. [Google Scholar]
- Alibardi, L. The process of cornification evolved from the initial keratinization in the epidermis and epidermal derivatives of verte-brates: A new synthesis and the case of sauropsids. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2016, 327, 263–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alibardi, L. General aspects on skin development in vertebrates with emphasis on sauropsids epidermis. Dev. Biol. 2023, 501, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, D.J. Unique and repetitive sequences in multiple genes for feather keratin. Nature 1975, 254, 573–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Presland, R.B.; Gregg, K.; Molloy, P.L.; Morris, C.P.; Crocker, L.A.; Rogers, G.E. Avian keratin genes. I. A molecular analysis of the structure and expression of a group of feather keratin genes. J. Mol. Biol. 1989, 209, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Presland, R.B.; Whitbread, L.A.; Rogers, G.E. Avian keratin genes. II. Chromosomal arrangement and close linkage of three gene families. J. Mol. Biol. 1989, 209, 561–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhoutteghem, A.; Djian, P.; Green, H. Ancient origin of the gene encoding involucrin, a precursor of the cross-linked envelope of epidermis and related epithelia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 15481–15486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strasser, B.; Mlitz, V.; Hermann, M.; Rice, R.H.; Eigenheer, R.A.; Alibardi, L.; Tschachler, E.; Eckhart, L. Evolutionary origin and diversification of epidermal barrier proteins in amniotes. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2014, 31, 3194–3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalla Valle, L.; Nardi, A.; Bonazza, G.; Zucal, C.; Emera, D.; Alibardi, L. Forty keratin-associated beta-proteins (beta-keratins) form the hard layers of scales, claws, and adhesive pads in the green anole lizard, Anolis carolinensis. J. Exp. Zool. B Mol. Dev. Evol. 2010, 314, 11–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holthaus, K.B.; Strasser, B.; Sipos, W.; Schmidt, H.A.; Mlitz, V.; Sukseree, S.; Weissenbacher, A.; Tschachler, E.; Alibardi, L.; Eckhart, L. Comparative genomics identifies epidermal proteins associated with the evolution of the turtle shell. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 726–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holthaus, K.B.; Mlitz, V.; Strasser, B.; Tschachler, E.; Alibardi, L.; Eckhart, L. Identification and comparative analysis of the epidermal differentiation complex in snakes. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holthaus, K.B.; Strasser, B.; Lachner, J.; Sukseree, S.; Sipos, W.; Weissenbacher, A.; Tschachler, E.; Alibardi, L.; Eckhart, L. Comparative analysis of epidermal differentiation genes of crocodilians suggests new models for the evolutionary origin of avian feathers. Genome Biol. Evol. 2018, 10, 694–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holthaus, K.B.; Alibardi, L.; Tschachler, E.; Eckhart, L. Identification of epidermal differentiation genes of the tuatara provides insights into the early evolution of lepidosaurian skin. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrne, C.; Tainsky, M.; Fuchs, E. Programming gene expression in developing epidermis. Development 1994, 120, 2369–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, H.; Yasuda, M. An electron microscopic study of periderm cell development in mouse limb buds. Anat. Embryol. 1979, 157, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M’Boneko, V.; Merker, H.J. Development and morphology of the periderm of mouse embryos (days 9–12 of gestation). Acta Anat. 1988, 133, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, R.J.; Hammond, N.L.; Coulombe, P.A.; Saloranta, C.; Nousiainen, H.O.; Salonen, R.; Berry, A.; Hanley, N.; Headon, D.; Karikoski, R.; et al. Periderm prevents pathological epithelial adhesions during embryogenesis. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 3891–3900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holbrook, K.A.; Odland, G.F. The fine structure of developing human epidermis: Light, scanning, and transmission electron microscopy of the periderm. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1975, 65, 16–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, J. The histogenesis of the epidermis in the rat and mouse. J. Anat. 1947, 81, 174–197. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stern, I.B.; Dayton, L.; Duecy, J. The uptake of tritiated thymidine by the dorsal epidermis of the fetal and newborn rat. Anat. Rec. 1971, 170, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panteleyev, A.A. Dual nature of mouse periderm structure, function and fate. Exp. Dermatol. 2022, 31, 1102–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alibardi, L. Transition from embryonic to adult epidermis in reptiles occurs by the production of corneous beta-proteins. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2014, 58, 829–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lechler, T.; Fuchs, E. Asymmetric cell divisions promote stratification and differentiation of mammalian skin. Nature 2005, 437, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jennemann, R.; Rabionet, M.; Gorgas, K.; Epstein, S.; Dalpke, A.; Rothermel, U.; Bayerle, A.; van der Hoeven, F.; Imgrund, S.; Kirsch, J.; et al. Loss of ceramide synthase 3 causes lethal skin barrier disruption. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2012, 21, 586–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, T.; Mori, T. Peridermal granules of the chick embryo: Histochemical, ultrastructural and immuno-electron microscopical study. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 1987, 151, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alibardi, L.; Thompson, M.B. Keratinization and ultrastructure of the epidermis of late embryonic stages in the alligator (Alligator mississippiensis). J. Anat. 2002, 201, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alibardi, L.; Mlitz, V.; Eckhart, L. Immunolocalization of scaffoldin, a trichohyalin-like protein, in the epidermis of the chicken embryo. Anat. Rec. 2015, 298, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawyer, R.H.; Rogers, L.; Washington, L.; Glenn, T.C.; Knapp, L.W. Evolutionary origin of the feather epidermis. Dev. Dyn. 2005, 232, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawyer, R.H. Avian scale development: I. Histogenesis and morphogenesis of the epidermis and dermis during formation of the scale ridge. J. Exp. Zool. 1972, 181, 365–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawyer, R.H. Avian scale development: II. A study of cell proliferation. J. Exp. Zool. 1972, 181, 385–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawyer, R.H.; Abbott, U.K.; Fry, G.N. Avian scale development. III. Ultrastructure of the keratinizing cells of the outer and inner epidermal surfaces of the scale ridge. J. Exp. Zool. 1974, 190, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawyer, R.H.; Abbott, U.K.; Fry, G.N. Avian scale development. IV. Ultrastructure of the anterior shank skin of the scaleless mutant. J. Exp. Zool. 1974, 190, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alibardi, L.; Thompson, M.B. Fine structure of the developing epidermis in the embryo of the American alligator (Alligator mississippiensis, Crocodilia, Reptilia). J. Anat. 2001, 198, 265–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saathoff, M.; Blum, B.; Quast, T.; Kirfel, G.; Herzog, V. Simultaneous cell death and desquamation of the embryonic diffusion barrier during epidermal development. Exp. Cell Res. 2004, 299, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawyer, R.H.; Knapp, L.W. Avian skin development and the evolutionary origin of feathers. J. Exp. Zool. B Mol. Dev. Evol. 2003, 298, 57–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akiyama, M.; Smith, L.T.; Yoneda, K.; Holbrook, K.A.; Hohl, D.; Shimizu, H. Periderm cells form cornified cell envelope in their regression process during human epidermal development. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1999, 112, 903–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlitz, V.; Hermann, M.; Buchberger, M.; Tschachler, E.; Eckhart, L. The trichohyalin-like protein scaffoldin is expressed in the multilayered periderm during development of avian beak and egg tooth. Genes 2021, 12, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alibardi, L. Development, structure, and protein composition of the corneous beak in turtles. Anat. Rec. 2021, 304, 2703–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alibardi, L.; Thompson, M.B. Epidermal differentiation during carapace and plastron formation in the embryonic turtle Emydura macquarii. J. Anat. 1999, 194, 531–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henry, J.; Toulza, E.; Hsu, C.Y.; Pellerin, L.; Balica, S.; Mazereeuw-Hautier, J.; Paul, C.; Serre, G.; Jonca, N.; Simon, M. Update on the epidermal differentiation complex. Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed.) 2012, 17, 1517–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volz, A.; Korge, B.P.; Compton, J.G.; Ziegler, A.; Steinert, P.M.; Mischke, D. Physical mapping of a functional cluster of epidermal differentiation genes on chromosome 1q21. Genomics 1993, 18, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mischke, D.; Korge, B.P.; Marenholz, I.; Volz, A.; Ziegler, A. Genes encoding structural proteins of epidermal cornification and S100 calcium-binding proteins form a gene complex (“epidermal differentiation complex”) on human chromosome 1q21. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1996, 106, 989–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Guzman Strong, C.; Conlan, S.; Deming, C.B.; Cheng, J.; Sears, K.E.; Segre, J.A. A milieu of regulatory elements in the epidermal differentiation complex syntenic block: Implications for atopic dermatitis and psoriasis. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2010, 19, 1453–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachslehner, A.P.; Eckhart, L. Evolutionary diversification of epidermal barrier genes in amphibians. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 13634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.I.; Steinert, P.M.; Markova, N.G. Activator protein 1 activity is involved in the regulation of the cell type-specific expression from the proximal promoter of the human profilaggrin gene. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 24105–24114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poterlowicz, K.; Yarker, J.L.; Malashchuk, I.; Lajoie, B.R.; Mardaryev, A.N.; Gdula, M.R.; Sharov, A.A.; Kohwi-Shigematsu, T.; Botchkarev, V.A.; Fessing, M.Y. 5C analysis of the Epidermal Differentiation Complex locus reveals distinct chromatin interaction networks between gene-rich and gene-poor TADs in skin epithelial cells. PLoS Genet. 2017, 13, e1006966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.C.; Wu, P.; Lin, G.W.; Chen, C.K.; Yeh, C.Y.; Tsai, S.; Yan, J.; Jiang, T.X.; Lai, Y.C.; Huang, D.; et al. Folding keratin gene clusters during skin regional specification. Dev. Cell 2020, 53, 561–576.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, S.; Jiang, K.; Hope, E.; Cross, M.; Overmiller, A.; Naz, F.; Worrell, S.; Bajpai, D.; Hasneen, K.; Brooks, S.R.; et al. Chromatin landscape governing murine epidermal differentiation. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2023, 143, 1220–1232.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holthaus, K.B.; Lachner, J.; Ebner, B.; Tschachler, E.; Eckhart, L. Gene duplications and gene loss in the epidermal differentiation complex during the evolutionary land-to-water transition of cetaceans. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 12334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strasser, B.; Mlitz, V.; Hermann, M.; Tschachler, E.; Eckhart, L. Convergent evolution of cysteine-rich proteins in feathers and hair. BMC Evol. Biol. 2015, 15, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Maury, L.; Marguerat, S.; Bähler, J. Tuning gene expression to changing environments: From rapid responses to evolutionary adaptation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2008, 9, 583–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avecilla, A.R.C.; Quiroz, F.G. Cracking the skin barrier: Liquid-liquid phase separation shines under the skin. JID Innov. 2021, 1, 100036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takase, T.; Hirai, Y. Identification of the C-terminal tail domain of AHF/trichohyalin as the critical site for modulation of the keratin filamentous meshwork in the keratinocyte. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2012, 65, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mlitz, V.; Strasser, B.; Jaeger, K.; Hermann, M.; Ghannadan, M.; Buchberger, M.; Alibardi, L.; Tschachler, E.; Eckhart, L. Trichohyalin-like proteins have evolutionarily conserved roles in the morphogenesis of skin appendages. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 2685–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlitz, V.; Hussain, T.; Tschachler, E.; Eckhart, L. Filaggrin has evolved from an “S100 fused-type protein” (SFTP) gene present in a common ancestor of amphibians and mammals. Exp. Dermatol. 2017, 26, 955–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, H.; Rossiter, H.; Ghannadan, M.; Jaeger, K.; Barresi, C.; Declercq, W.; Tschachler, E.; Eckhart, L. Caspase-14 but not caspase-3 is processed during the development of fetal mouse epidermis. Differentiation 2005, 73, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, P.J.; de Viragh, P.A.; Scharer, E.; Bundman, D.; Longley, M.A.; Bickenbach, J.; Kawachi, Y.; Suga, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Huber, M.; et al. Lessons from loricrin-deficient mice: Compensatory mechanisms maintaining skin barrier function in the absence of a major cornified envelope protein. J. Cell Biol. 2000, 151, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huebner, A.J.; Dai, D.; Morasso, M.; Schmidt, E.E.; Schäfer, M.; Werner, S.; Roop, D.R. Amniotic fluid activates the nrf2/keap1 pathway to repair an epidermal barrier defect in utero. Dev. Cell 2012, 23, 1238–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishitsuka, Y.; Huebner, A.J.; Rice, R.H.; Koch, P.J.; Speransky, V.V.; Steven, A.C.; Roop, D.R. Lce1 family members are Nrf2-target genes that are induced to compensate for the loss of loricrin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2016, 136, 1656–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, T.; Annusver, K.; Czarnewski, P.; Dalessandri, T.; Kalk, C.; Levra Levron, C.; Campamà Sanz, N.; Kastriti, M.E.; Mikkola, M.L.; Rendl, M.; et al. Molecular and spatial landmarks of early mouse skin development. Dev. Cell 2023, 58, 2140–2162.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.; Jin, S.; Chen, J.; Li, Z.; Lin, Z.; Tang, L.; Nie, Q.; Andersen, B. Murine interfollicular epidermal differentiation is gradualistic with GRHL3 controlling progression from stem to transition cell states. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachner, J.; Ehrlich, F.; Wielscher, M.; Farlik, M.; Hermann, M.; Tschachler, E.; Eckhart, L. Single-cell transcriptomics defines keratinocyte differentiation in avian scutate scales. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Li, C.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, W.; Hu, C.; Qu, Y.; Li, H.; Yan, J.; Zhou, K.; Li, P. Expression analysis of alpha keratins and corneous beta-protein genes during embryonic development of Gekko japonicus. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2023, 47, 101116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.C.; Lee, J.B.; Kook, J.P.; Seo, J.J.; Nam, K.I.; Park, S.S.; Kim, Y.P. Expression of differentiation markers during fetal skin development in humans: Immunohistochemical studies on the precursor proteins forming the cornified cell envelope. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1999, 112, 882–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alibardi, L.; Holthaus, K.B.; Sukseree, S.; Hermann, M.; Tschachler, E.; Eckhart, L. Immunolocalization of a histidine-rich epidermal differentiation protein in the chicken supports the hypothesis of an evolutionary developmental link between the embryonic subperiderm and feather barbs and barbules. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachner, J.; Ehrlich, F.; Mlitz, V.; Hermann, M.; Alibardi, L.; Tschachler, E.; Eckhart, L. Immunolocalization and phylogenetic profiling of the feather protein with the highest cysteine content. Protoplasma 2019, 256, 1257–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Ng, C.S.; Yan, J.; Lai, Y.C.; Chen, C.K.; Lai, Y.T.; Wu, S.M.; Chen, J.J.; Luo, W.; Widelitz, R.B.; et al. Topographical mapping of α- and β-keratins on developing chicken skin integuments: Functional interaction and evolutionary perspectives. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E6770–E6779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapp, L.W.; Shames, R.B.; Barnes, G.L.; Sawyer, R.H. Region-specific patterns of beta keratin expression during avian skin development. Dev. Dyn. 1993, 196, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwold, M.J.; Sawyer, R.H. Genomic organization and molecular phylogenies of the beta (beta) keratin multigene family in the chicken (Gallus gallus) and zebra finch (Taeniopygia guttata): Implications for feather evolution. BMC Evol. Biol. 2010, 10, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenwold, M.J.; Sawyer, R.H. Molecular evolution and expression of archosaurian β-keratins: Diversification and expansion of archosaurian β-keratins and the origin of feather β-keratins. J. Exp. Zool. B Mol. Dev. Evol. 2013, 320, 393–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alibardi, L.; Knapp, L.W.; Sawyer, R.H. Beta-keratin localization in developing alligator scales and feathers in relation to the development and evolution of feathers. J. Submicrosc. Cytol. Pathol. 2006, 38, 175–192. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mehrel, T.; Hohl, D.; Rothnagel, J.A.; Longley, M.A.; Bundman, D.; Cheng, C.; Lichti, U.; Bisher, M.E.; Steven, A.C.; Steinert, P.M.; et al. Identification of a major keratinocyte cell envelope protein, loricrin. Cell 1990, 61, 1103–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steven, A.C.; Steinert, P.M. Protein composition of cornified cell envelopes of epidermal keratinocytes. J. Cell Sci. 1994, 107, 693–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohl, D.; Mehrel, T.; Lichti, U.; Turner, M.L.; Roop, D.R.; Steinert, P.M. Characterization of human loricrin. Structure and function of a new class of epidermal cell envelope proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 6626–6636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candi, E.; Tarcsa, E.; Digiovanna, J.J.; Compton, J.G.; Elias, P.M.; Marekov, L.N.; Steinert, P.M. A highly conserved lysine residue on the head domain of type II keratins is essential for the attachment of keratin intermediate filaments to the cornified cell envelope through isopeptide crosslinking by transglutaminases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 2067–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alibardi, L.; Strasser, B.; Eckhart, L. Immunolocalization of loricrin in the maturing α-layer of normal and regenerating epidermis of the lizard Anolis carolinensis. J. Exp. Zool. B Mol. Dev. Evol. 2015, 324, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinert, P.M.; Candi, E.; Tarcsa, E.; Marekov, L.N.; Sette, M.; Paci, M.; Ciani, B.; Guerrieri, P.; Melino, G. Transglutaminase crosslinking and structural studies of the human small proline rich 3 protein. Cell Death Differ. 1999, 6, 916–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Koning, H.D.; van den Bogaard, E.H.; Bergboer, J.G.; Kamsteeg, M.; van Vlijmen-Willems, I.M.; Hitomi, K.; Henry, J.; Simon, M.; Takashita, N.; Ishida-Yamamoto, A.; et al. Expression profile of cornified envelope structural proteins and keratinocyte differentiation-regulating proteins during skin barrier repair. Br. J. Dermatol. 2012, 166, 1245–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeij, W.P.; Alia, A.; Backendorf, C. ROS quenching potential of the epidermal cornified cell envelope. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2011, 131, 1435–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, G.L.; Sawyer, R.H. Histidine-rich protein B of embryonic feathers is present in the transient embryonic layers of scutate scales. J. Exp. Zool. 1995, 271, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.; Greenwold, M.J. Evolution of an epidermal differentiation complex (EDC) gene family in birds. Genes 2021, 12, 767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraser, R.D.; Parry, D.A. Filamentous structure of hard β-keratins in the epidermal appendages of birds and reptiles. Subcell. Biochem. 2017, 82, 231–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holthaus, K.B.; Eckhart, L.; Dalla Valle, L.; Alibardi, L. Review: Evolution and diversification of corneous beta-proteins, the characteristic epidermal proteins of reptiles and birds. J. Exp. Zool. B Mol. Dev. Evol. 2018, 330, 438–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrlich, F.; Lachner, J.; Hermann, M.; Tschachler, E.; Eckhart, L. Convergent evolution of cysteine-rich keratins in hard skin appendages of terrestrial vertebrates. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 982–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, C.S.; Wu, P.; Fan, W.L.; Yan, J.; Chen, C.K.; Lai, Y.T.; Wu, S.M.; Mao, C.T.; Chen, J.J.; Lu, M.Y.; et al. Genomic organization, transcriptomic analysis, and functional characterization of avian α- and β-keratins in diverse feather forms. Genome Biol. Evol. 2014, 6, 2258–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwold, M.J.; Bao, W.; Jarvis, E.D.; Hu, H.; Li, C.; Gilbert, M.T.; Zhang, G.; Sawyer, R.H. Dynamic evolution of the alpha (α) and beta (β) keratins has accompanied integument diversification and the adaptation of birds into novel lifestyles. BMC Evol. Biol. 2014, 14, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.I.; Kong, L.; Ponting, C.P.; Haerty, W. Rapid evolution of Beta-keratin genes contribute to phenotypic differences that distinguish turtles and birds from other reptiles. Genome Biol. Evol. 2013, 5, 923–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, Y.; Luo, L.; Yang, J.; Yang, L.; Liu, M.; Li, Y.; Qian, T.; Zheng, Y.; et al. Gekko japonicus genome reveals evolution of adhesive toe pads and tail regeneration. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 10033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitbread, L.A.; Gregg, K.; Rogers, G.E. The structure and expression of a gene encoding chick claw keratin. Gene 1991, 101, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shames, R.B.; Sawyer, R.H. Expression of beta keratin genes during skin development in normal and sc/sc chick embryos. Dev. Biol. 1986, 116, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shames, R.B.; Knapp, L.W.; Carver, W.E.; Sawyer, R.H. Identification, expression, and localization of beta keratin gene products during development of avian scutate scales. Differentiation 1988, 38, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shames, R.B.; Knapp, L.W.; Carver, W.E.; Sawyer, R.H. Region-specific expression of scutate scale type beta keratins in the developing chick beak. J. Exp. Zool. 1991, 260, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawyer, R.H.; Glenn, T.; French, B.; Mays, B.; Shames, R.B.; Barnes, G.L.; Ishikawa, Y. The expression of beta keratins in the epidermal appendages of reptiles and birds. Am. Zool. 2000, 40, 530–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawyer, R.H.; Salvatore, B.A.; Potylicki, T.T.; French, J.O.; Glenn, T.C.; Knapp, L.W. Origin of feathers: Feather beta (beta) keratins are expressed in discrete epidermal cell populations of embryonic scutate scales. J. Exp. Zool. B Mol. Dev. Evol. 2003, 295, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Chen, M.; Cai, F.; Li, P.; Yan, J.; Zhou, K. Expression of specific corneous beta proteins in the developing digits of the Japanese gecko (Gekko japonicus) reveals their role in the growth of adhesive setae. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2020, 240, 110370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kur-Piotrowska, A.; Kopcewicz, M.; Kozak, L.P.; Sachadyn, P.; Grabowska, A.; Gawronska-Kozak, B. Neotenic phenomenon in gene expression in the skin of Foxn1-deficient (nude) mice—A projection for regenerative skin wound healing. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makino, T.; Takaishi, M.; Morohashi, M.; Huh, N.H. Hornerin, a novel profilaggrin-like protein and differentiation-specific marker isolated from mouse skin. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 47445–47452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, E.H.; Payne, R.E., Jr.; O’Keefe, E.J. Trichohyalin: Presence in the granular layer and stratum corneum of normal human epidermis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1991, 96, 666–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tarcsa, E.; Marekov, L.N.; Andreoli, J.; Idler, W.W.; Candi, E.; Chung, S.I.; Steinert, P.M. The fate of trichohyalin. Sequential post-translational modifications by peptidyl-arginine deiminase and transglutaminases. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 27893–27901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Méchin, M.C.; Enji, M.; Nachat, R.; Chavanas, S.; Charveron, M.; Ishida-Yamamoto, A.; Serre, G.; Takahara, H.; Simon, M. The peptidylarginine deiminases expressed in human epidermis differ in their substrate specificities and subcellular locations. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2005, 62, 1984–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contzler, R.; Favre, B.; Huber, M.; Hohl, D. Cornulin, a new member of the “fused gene” family, is expressed during epidermal differentiation. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2005, 124, 990–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strasser, B.; Mlitz, V.; Fischer, H.; Tschachler, E.; Eckhart, L. Comparative genomics reveals conservation of filaggrin and loss of caspase-14 in dolphins. Exp. Dermatol. 2015, 24, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Stiller, J.; Deng, Y.; Armstrong, J.; Fang, Q.; Reeve, A.H.; Xie, D.; Chen, G.; Guo, C.; Faircloth, B.C.; et al. Dense sampling of bird diversity increases power of comparative genomics. Nature 2020, 587, 252–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).