Dynamic Analysis of a Large Deployable Space Truss Structure Considering Semi-Rigid Joints
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Problem Description
3. Model Establishment of Truss Structure
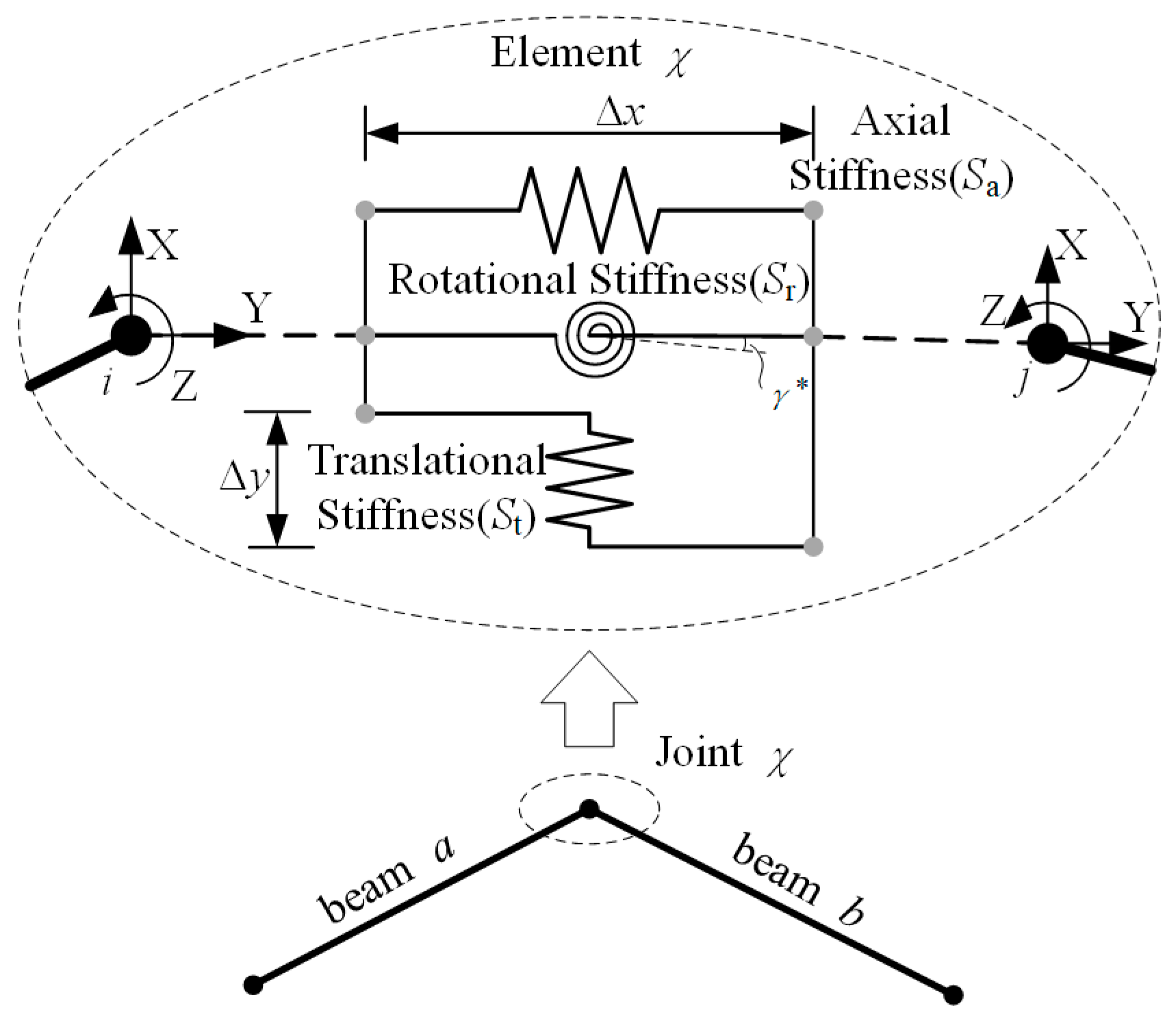
3.1. Connection Element of Semi-Rigid Joints
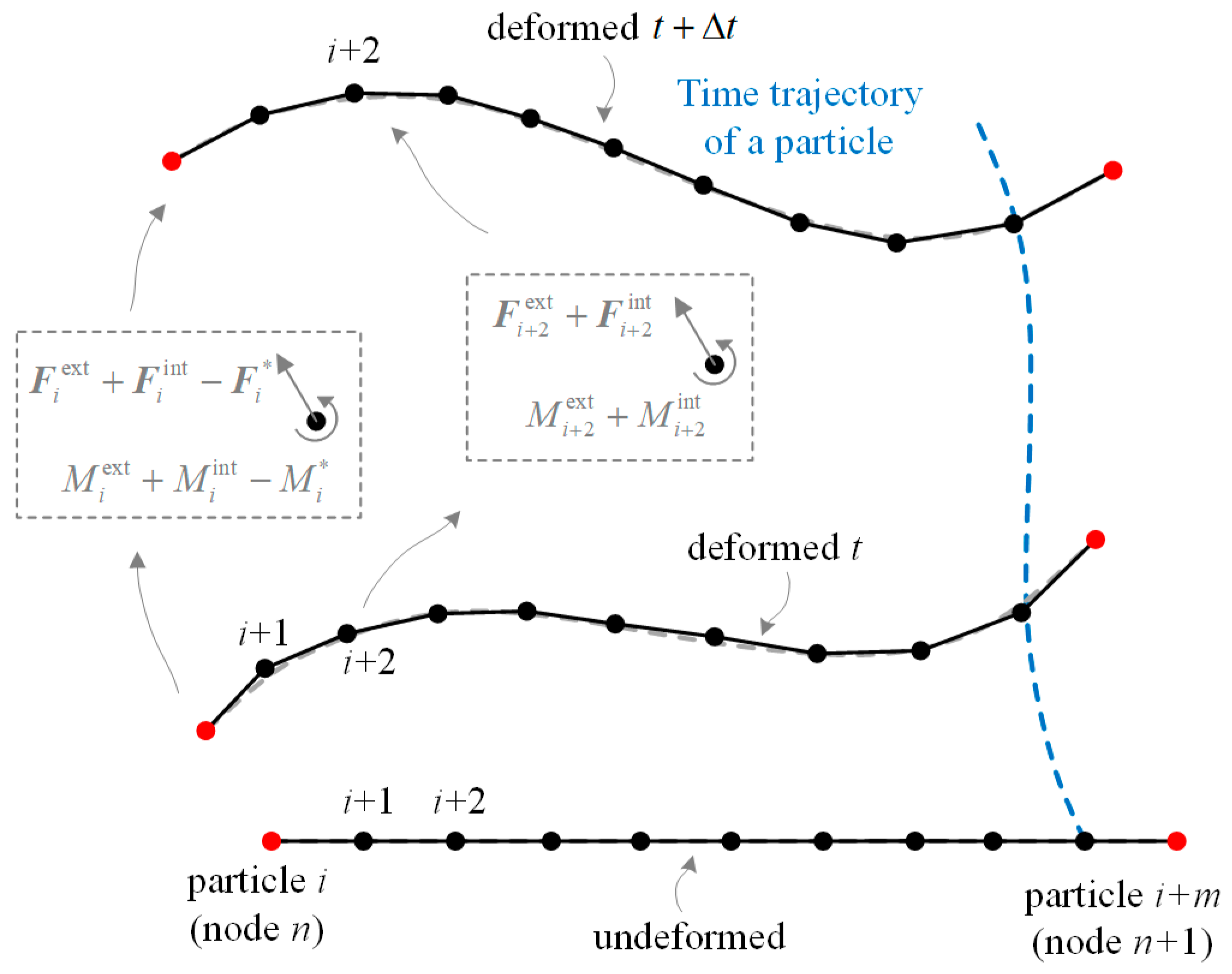
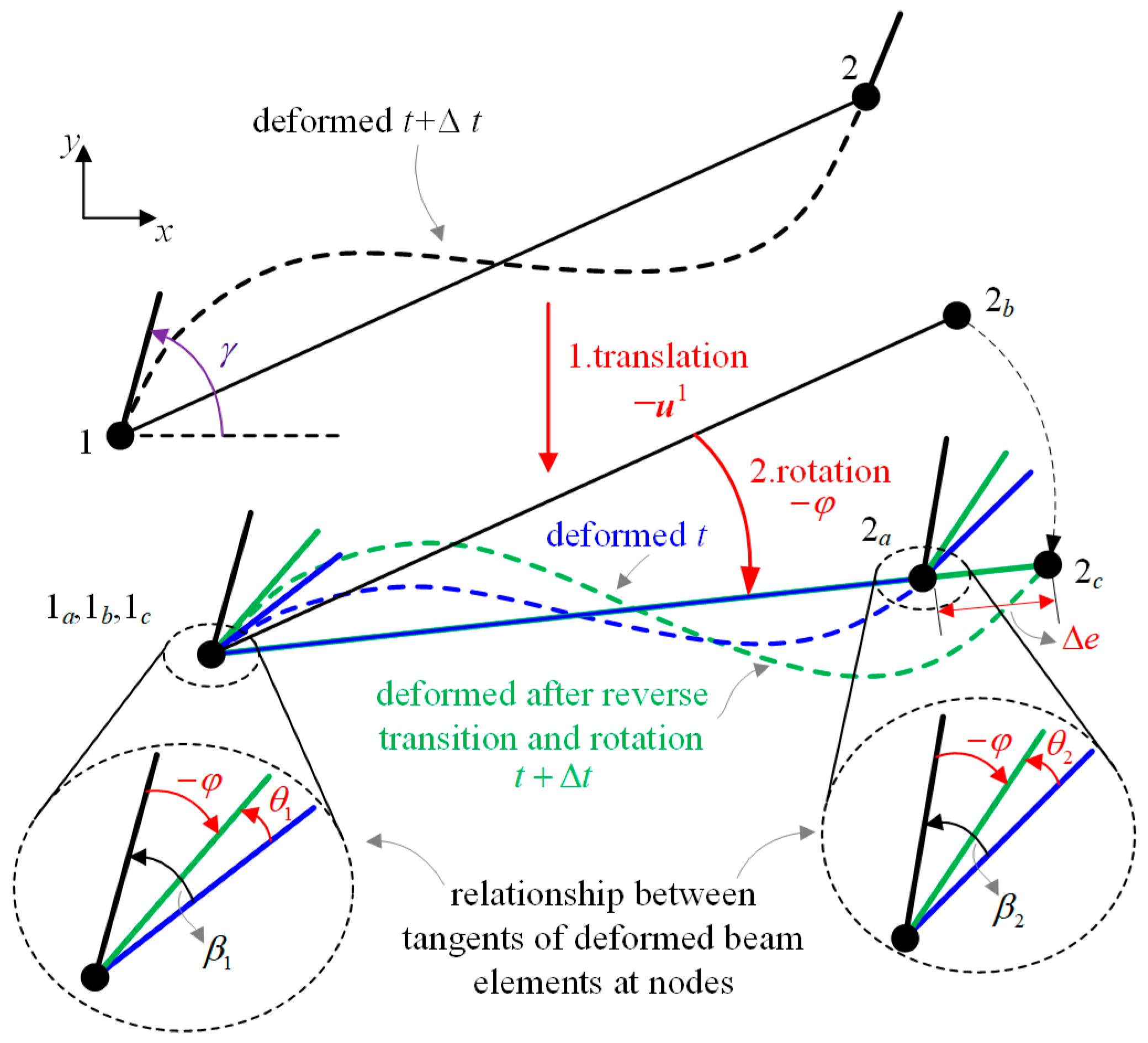
3.2. VFIFE Model for Beams
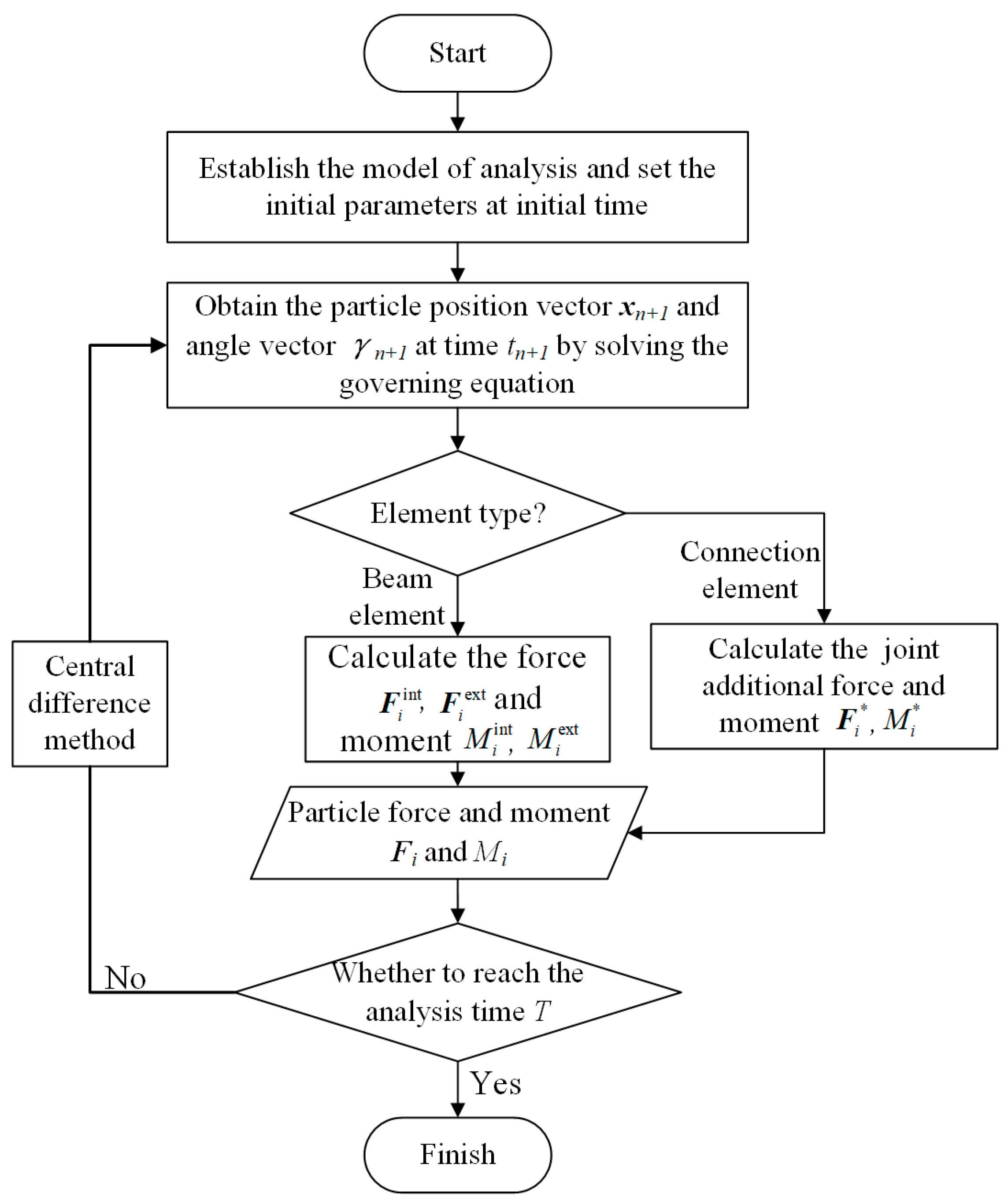
3.3. Solution Procedure
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Method Validation
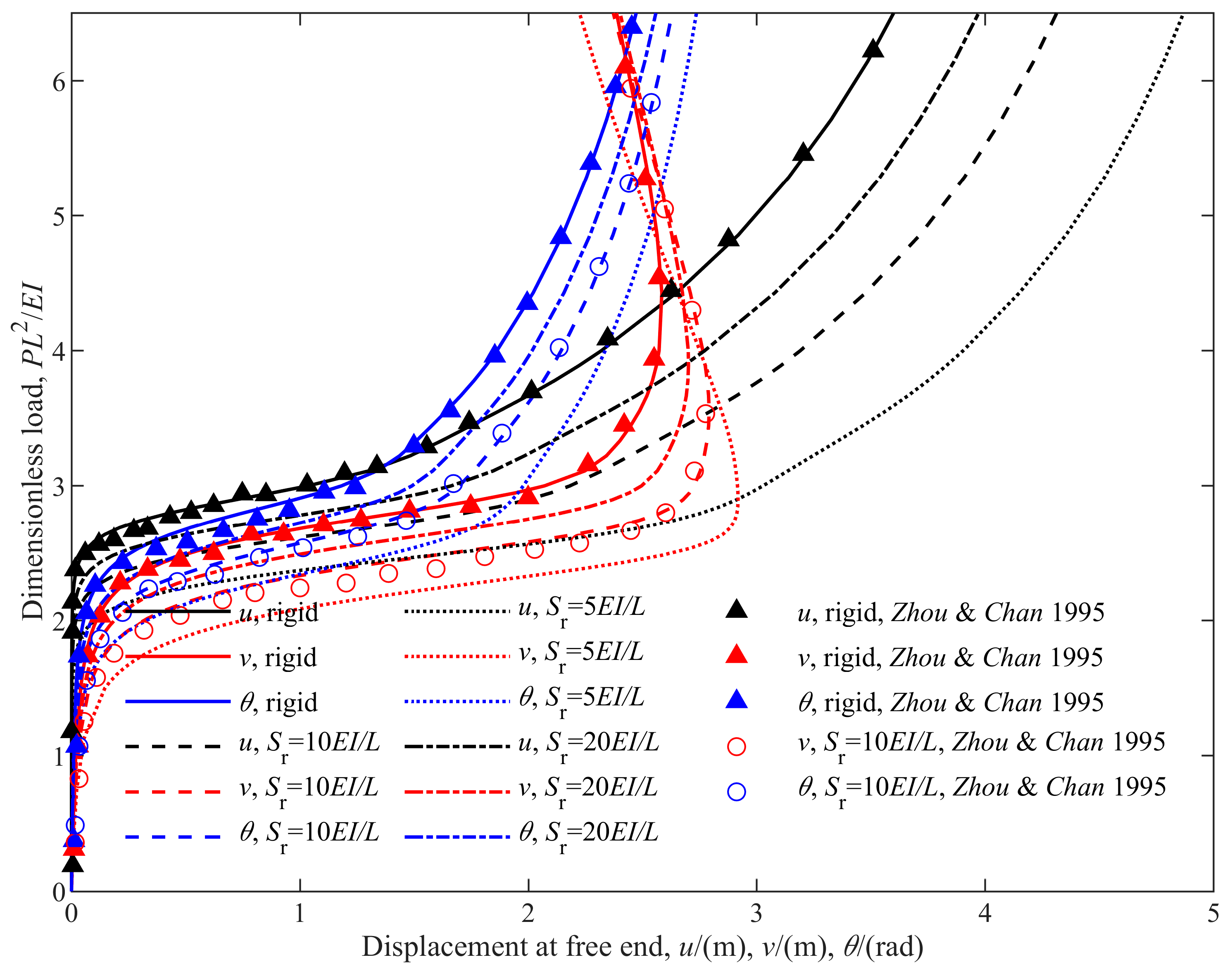
4.1.1. Geometrically Nonlinear Analysis of Column with Semi-Rigid Connection
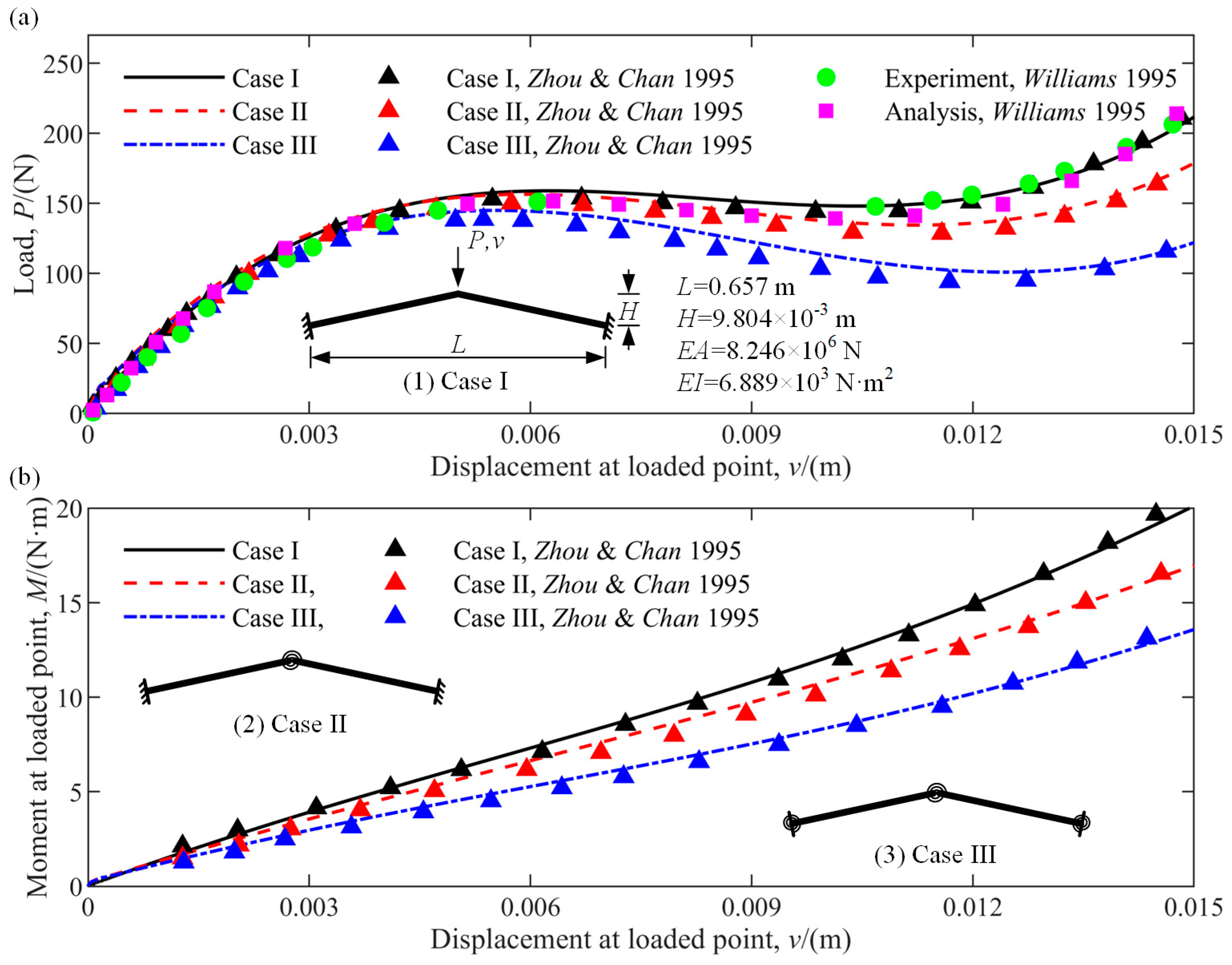
4.1.2. Snap-through Analysis of William’s Toggle Frame
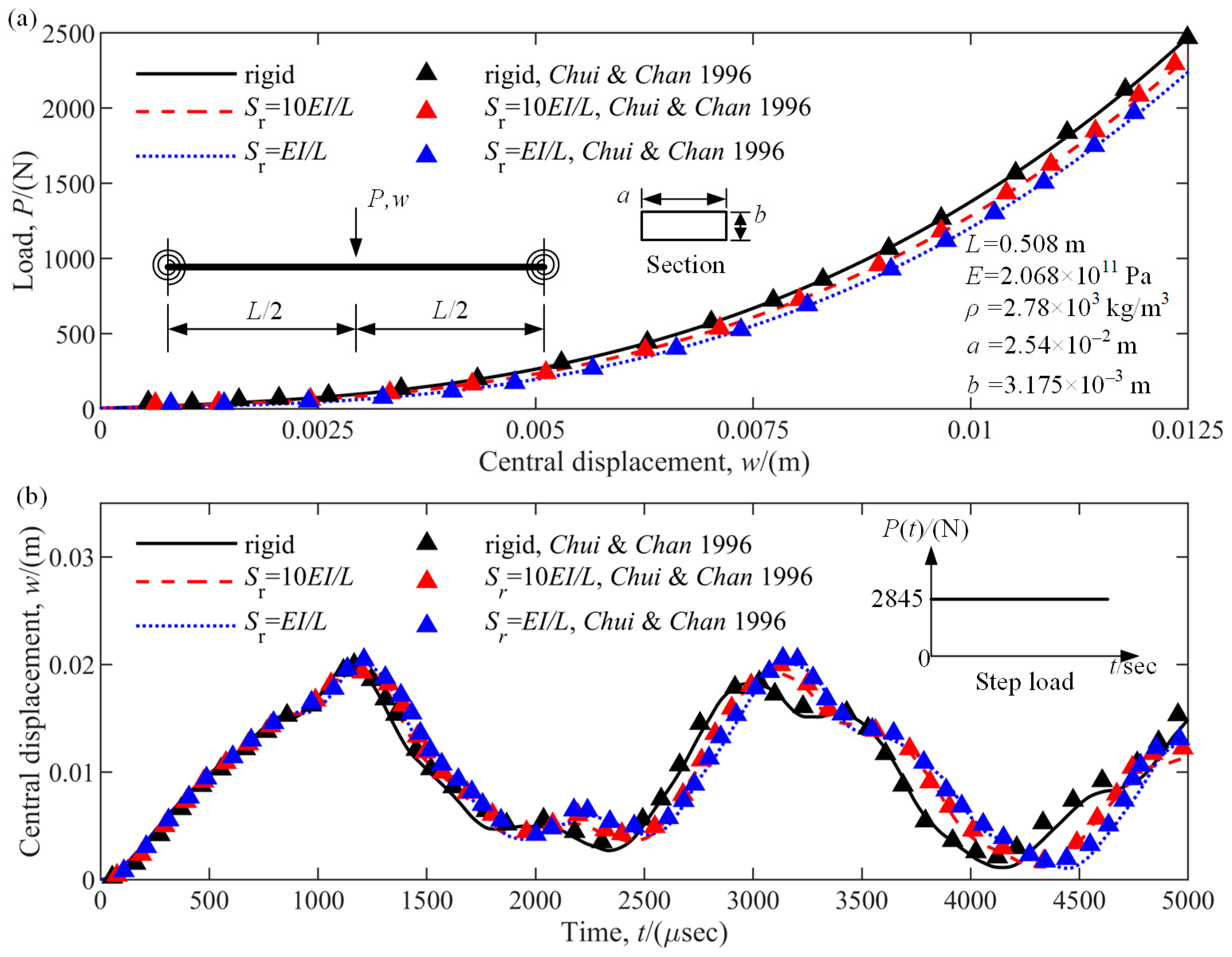
4.1.3. Static and Dynamic Response of a Clamped-Clamped Beam
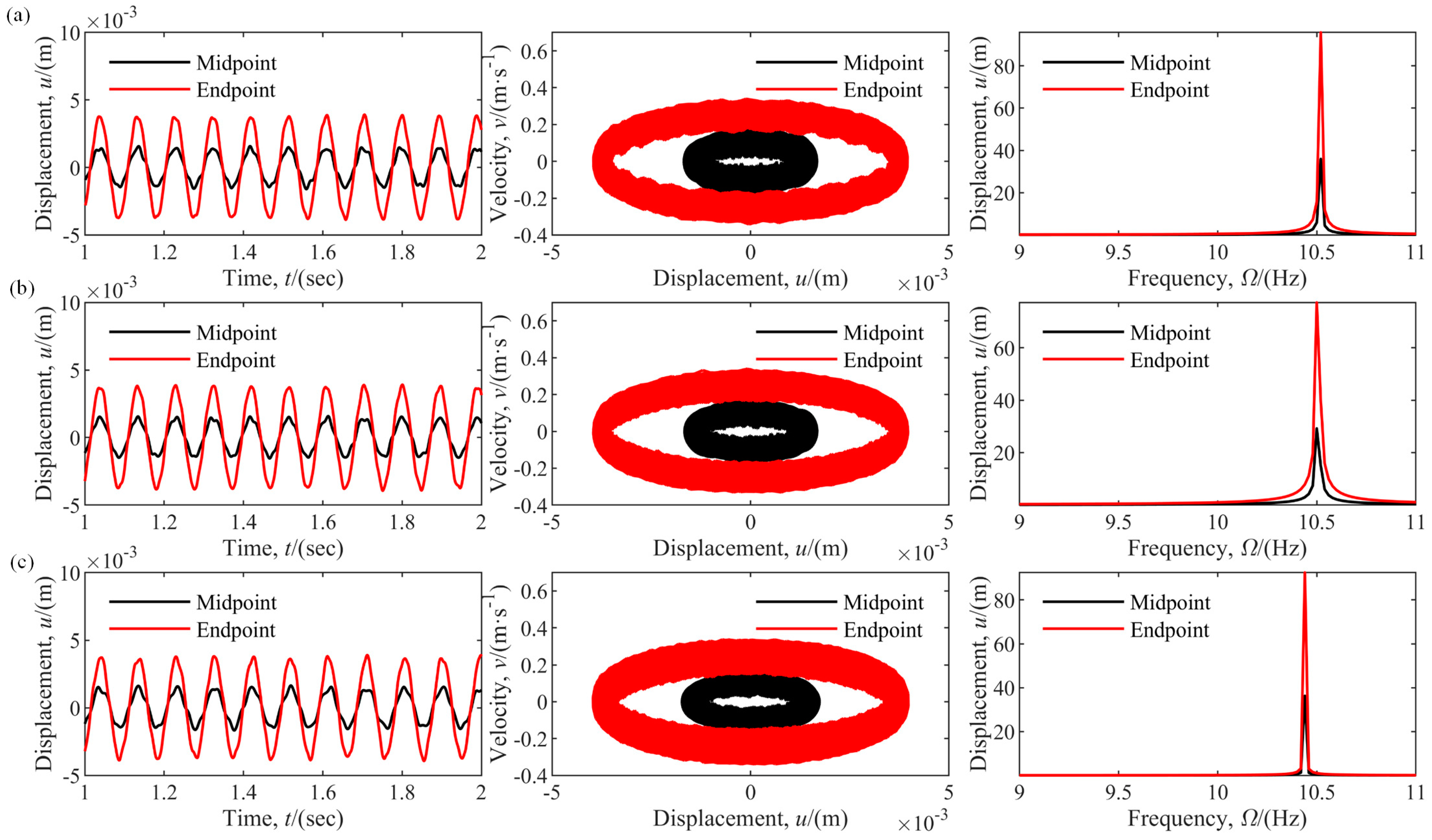
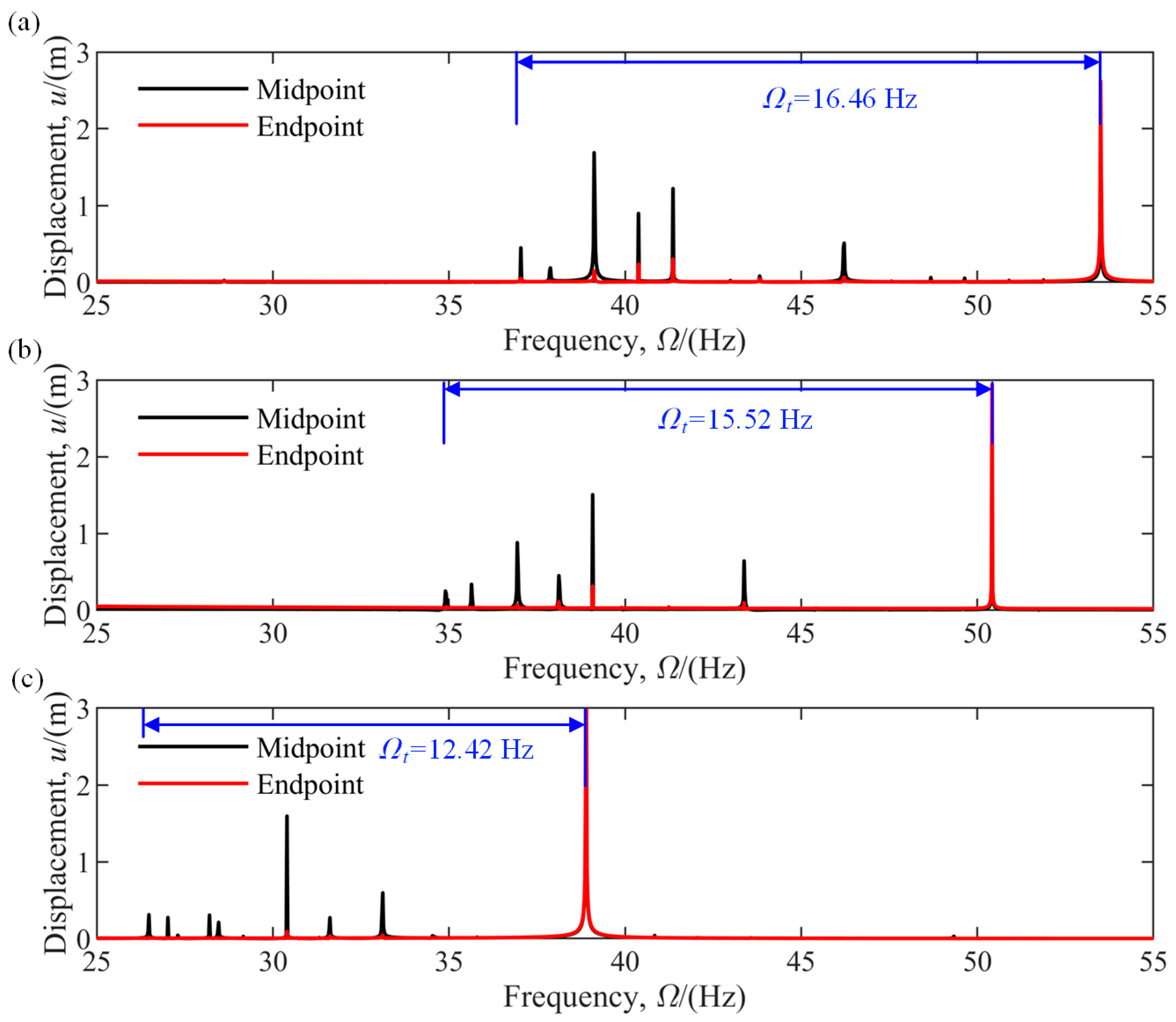
4.2. Influence of Semi-Rigid Joints on Dynamics of Deployable Structures
4.2.1. Effects of Linear Joint Stiffness
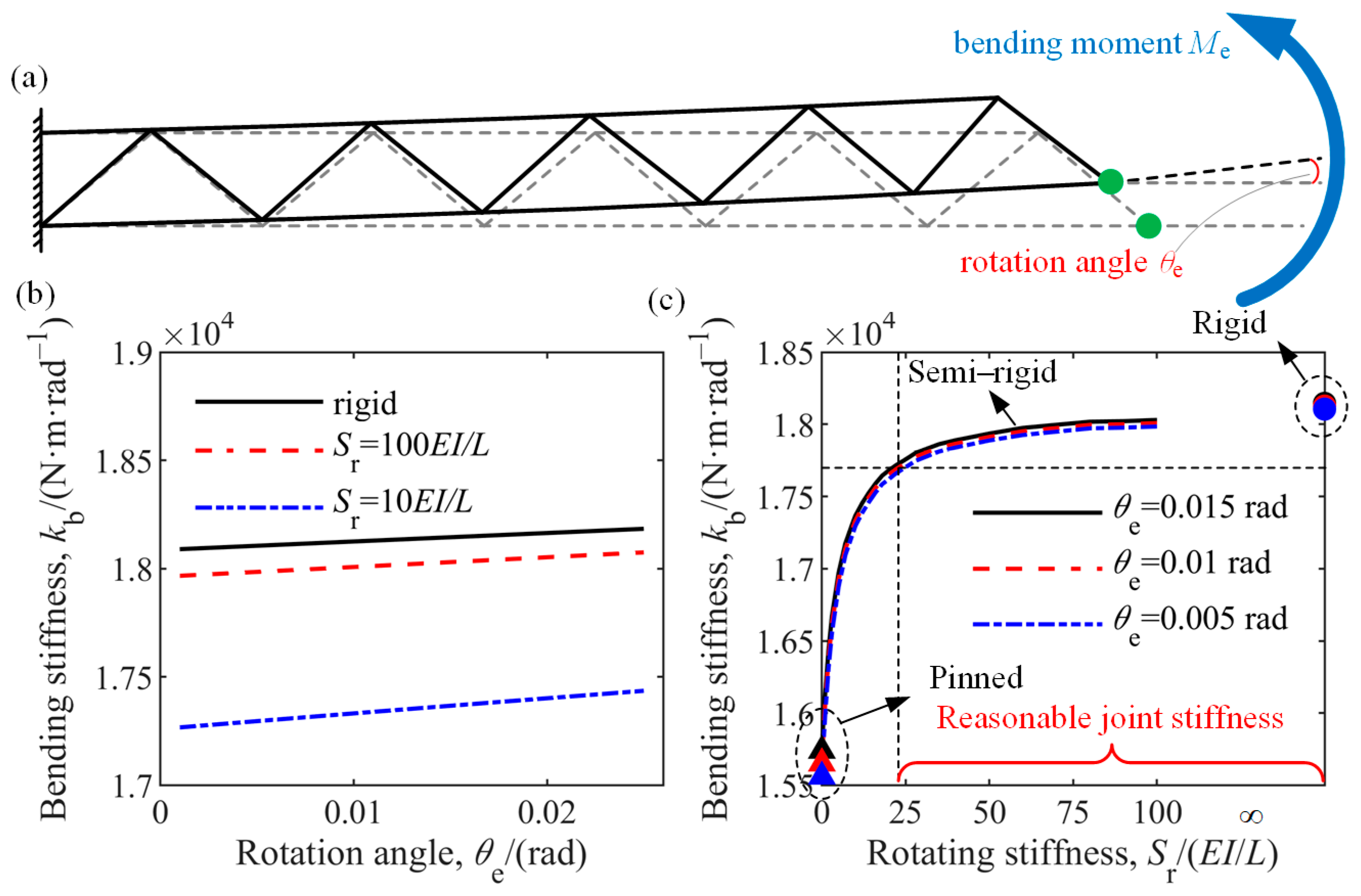
- Case 1: Effects on structural bending stiffness
- 2.
- Case 2: Effects on natural frequencies
- 3.
- Case 3: Effects on the dynamic response
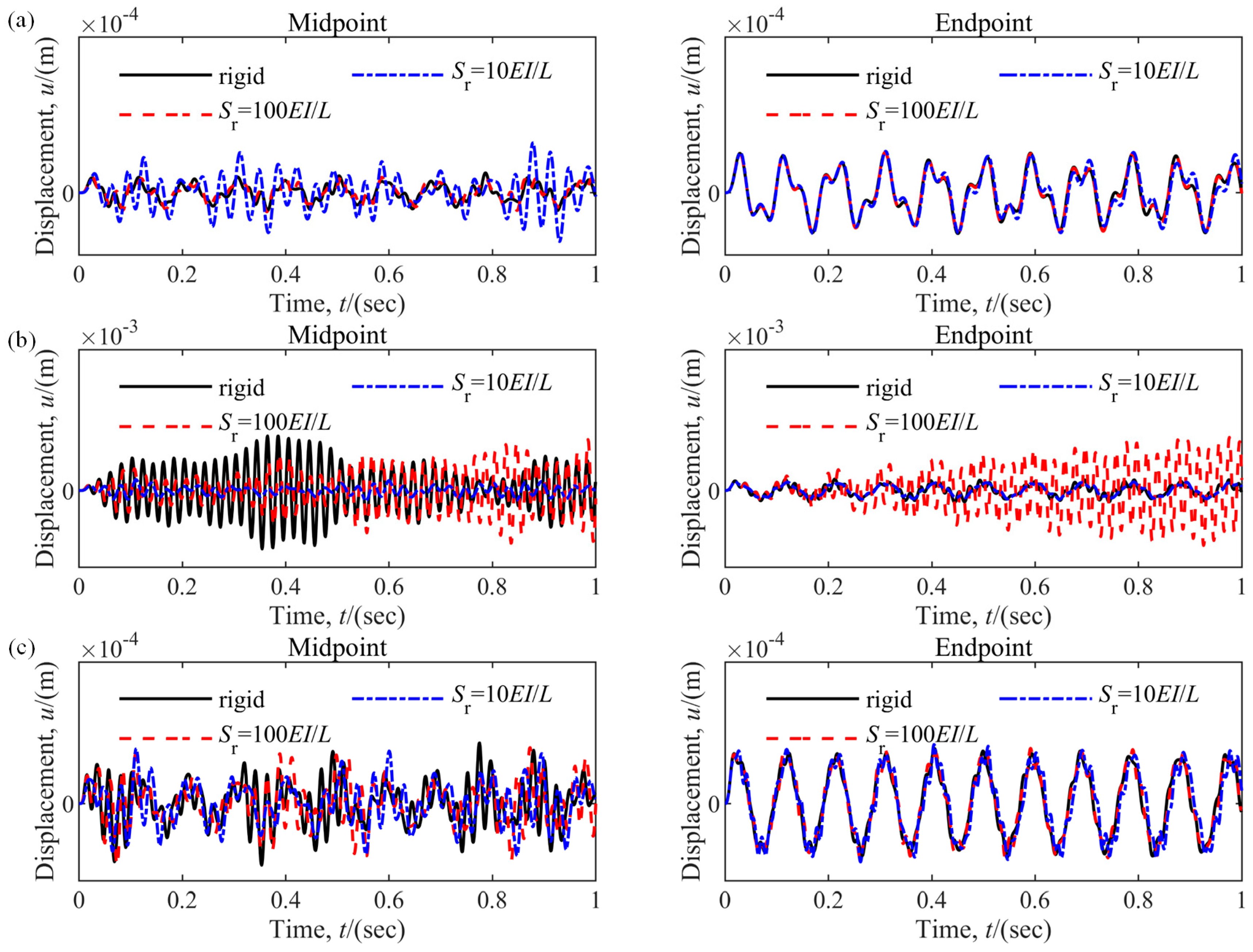
4.2.2. Effects of Nonlinear Joint Stiffness
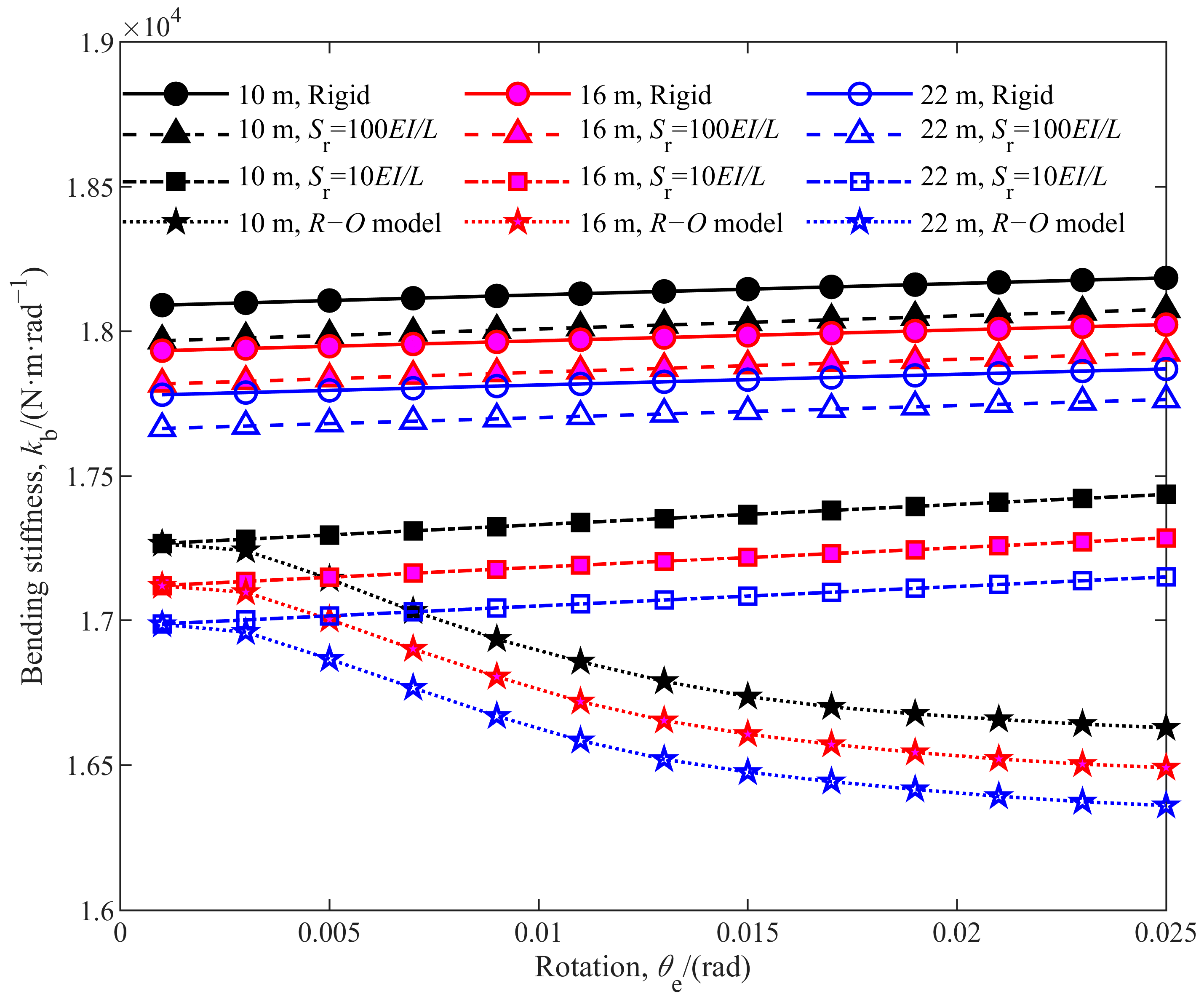
4.2.3. Effects of the Size of Deployable Structure
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thornton, E.A.; Paul, D.B. Thermal-structural analysis of large space structures-an assessment of recent advances. J. Spacecr. Rocket. 1985, 22, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Jiang, J.; Deng, H.; Lin, Z.; Wang, Z. Form-finding methods for deployable mesh reflector antennas. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2013, 26, 1276–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Guan, F.; Chen, J.; Zheng, Y. Structural design and static analysis of a double-ring deployable truss for mesh antennas. Acta Astronaut. 2012, 81, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Deng, Z.; Guo, H.; Liu, R. Equivalence and dynamic analysis for jointed trusses based on improved finite elements. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part K J. Multi-Body Dyn. 2014, 228, 47–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Cao, D.; Zhu, D. Equivalent dynamic model of the space antenna truss with initial stress. AIAA J. 2020, 58, 1851–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siriguleng, B.; Zhang, W.; Liu, T.; Liu, Y. Vibration modal experiments and modal interactions of a large space deployable antenna with carbon fiber material and ring-truss structure. Eng. Struct. 2020, 207, 109932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Xi, A.; Siriguleng, B.; Liu, G. An equivalent cylindrical shell model of vibration analysis based on simplified repeating unit cell for ring truss structure. J. Sound Vib. 2019, 459, 114847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Zhang, J.; Liu, R.; Deng, Z. Effects of joint on dynamics of space deployable structure. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2013, 26, 861–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, D.D. Modal analysis of jointed structures. J. Sound Vib. 2012, 331, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, D.R.; Ismael, M.A. Effect of Semi-rigid Connection on Post-buckling Behavior of Braced-Steel Frames. In Proceedings of AICCE’19: Transforming the Nation for a Sustainable Tomorrow 4; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 547–556. [Google Scholar]
- van Keulen, D.C.; Nethercot, D.A.; Snijder, H.H.; Bakker, M. Frame analysis incorporating semi-rigid joint action: Applicability of the half initial secant stiffness approach. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2003, 59, 1083–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Bermani, F.G.A.; Kitipornchai, S. Elastoplastic nonlinear analysis of flexibly jointed space frames. J. Struct. Eng. 1992, 118, 108–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tin-Loi, F.; Misa, J.S. Large displacement elastoplastic analysis of semi-rigid steel frames. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 1996, 39, 741–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.; Atluri, S.N. Static and dynamic analysis of space frames with nonlinear flexible connections. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 1989, 28, 2635–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawashima, S.; Fujimoto, T. Vibration analysis of frames with semi-rigid connections. Comput. Struct. 1984, 19, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, S.L. Vibration and modal analysis of steel frames with semi-rigid connections. Eng. Struct. 1994, 16, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chui PP, T.; Chan, S.L. Transient response of moment-resistant steel frames with flexible and hysteretic joints. J. Constr. Steel Res. 1996, 39, 221–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Živković, S.; Stojković, N.; Spasojević-Šurdilović, M. Global analysis of steel constructions with semi-rigid connections. Teh. Vjesn. 2020, 27, 951–960. [Google Scholar]
- Blandford, G.E. Progressive failure analysis of inelastic space truss structures. Comput. Struct. 1996, 58, 981–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tada, M.; Suito, A. Static and dynamic post-buckling behavior of truss structures. Eng. Struct. 1998, 20, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, E.C.; Shih, C.; Wang, Y.K. Fundamentals of a vector form intrinsic finite element: Part I. Basic procedure and a plane frame element. J. Mech. 2004, 20, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, E.C.; Shih, C.; Wang, Y.K. Fundamentals of a vector form intrinsic finite element: Part II. Plane solid elements. J. Mech. 2004, 20, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, C.; Wang, Y.K.; Ting, E.C. Fundamentals of a vector form intrinsic finite element: Part III. Convected material frame and examples. J. Mech. 2004, 20, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.Y.; Tsai, W.C.; Lee, J.J. Dynamic elastic–plastic and large deflection analyses of frame structures using motion analysis of structures. Thin-Walled Struct. 2009, 47, 1177–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Guo, X.; Guo, H. Vector form intrinsic finite element method for nonlinear analysis of three-dimensional marine risers. Ocean Eng. 2018, 161, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lien, K.H.; Chiou, Y.J.; Wang, R.Z.; Hsiao, P.A. Vector form intrinsic finite element analysis of nonlinear behavior of steel structures exposed to fire. Eng. Struct. 2010, 32, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.F.; He, K.; Zhang, H.M.; Ting, E.C.; Wang, C.Y.; Chen, S.K.; Wang, R.Z. Entire-process simulation of earthquake-induced collapse of a mockup cable-stayed bridge by vector form intrinsic finite element (VFIFE) method. Adv. Struct. Eng. 2014, 17, 347–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.Z.; Tsai, K.C.; Lin, B.Z. Extremely large displacement dynamic analysis of elastic–plastic plane frames. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2011, 40, 1515–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Türker, T.; Kartal, M.E.; Bayraktar, A.; Muvafik, M. Assessment of semi-rigid connections in steel structures by modal testing. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2009, 65, 1538–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.H.; Chan, S.L. Self-equilibrating element for second-order analysis of semi-rigid jointed frames. J. Eng. Mech. 1995, 121, 896–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, F.W. An approach to the nonlinear behaviour of the members of a rigid jointed plane framework with finite deflections. Q. J. Mech. Appl. Math. 1964, 17, 451–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramberg, W.; Osgood, W.R. Description of Stress-Strain Curves by Three Parameters; Technical Note; National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics: Washington, DC, USA, 1943. [Google Scholar]

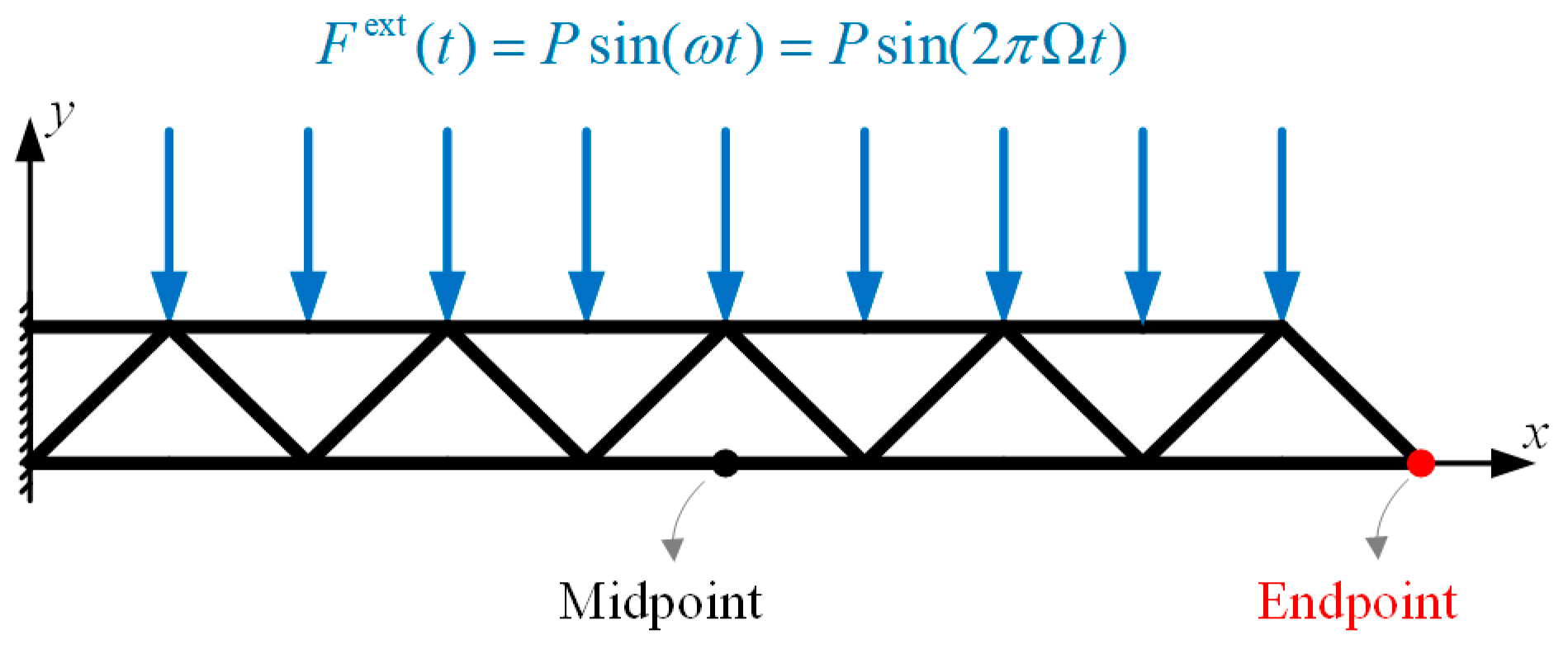
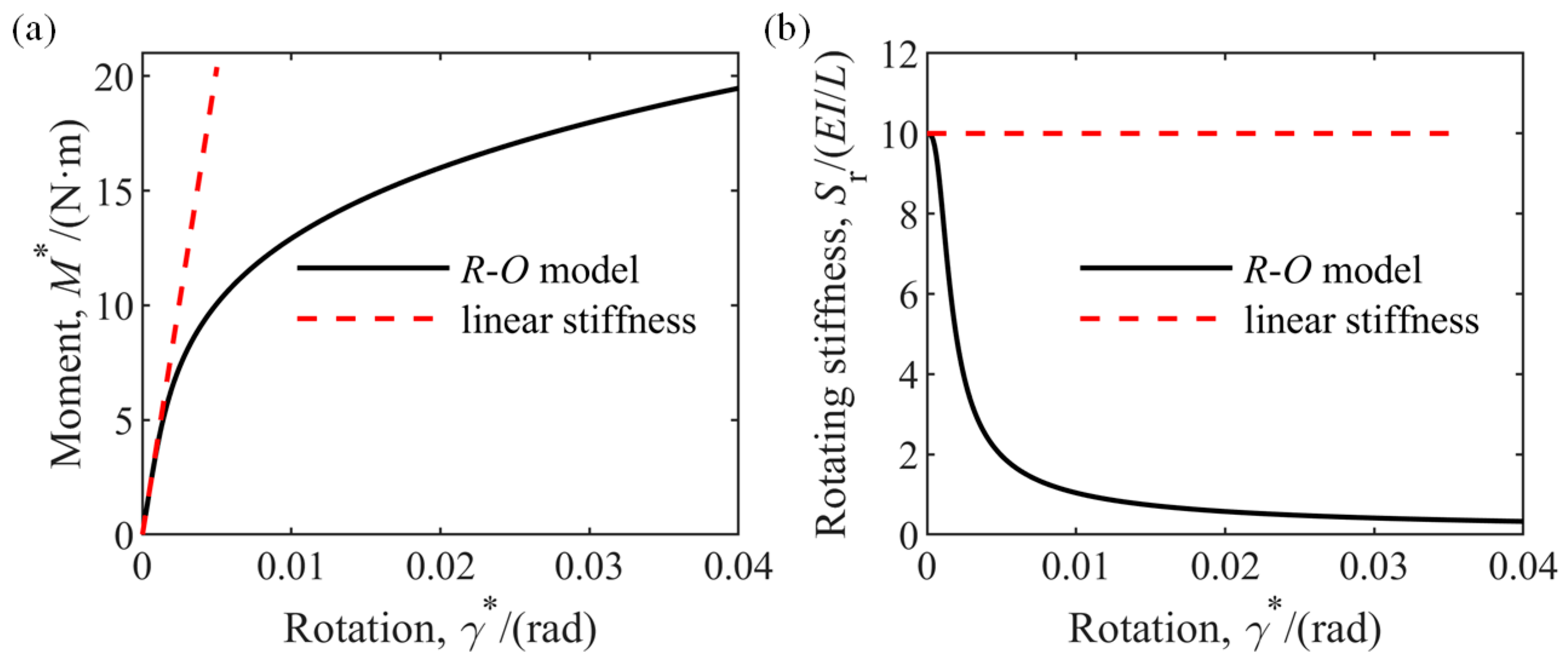
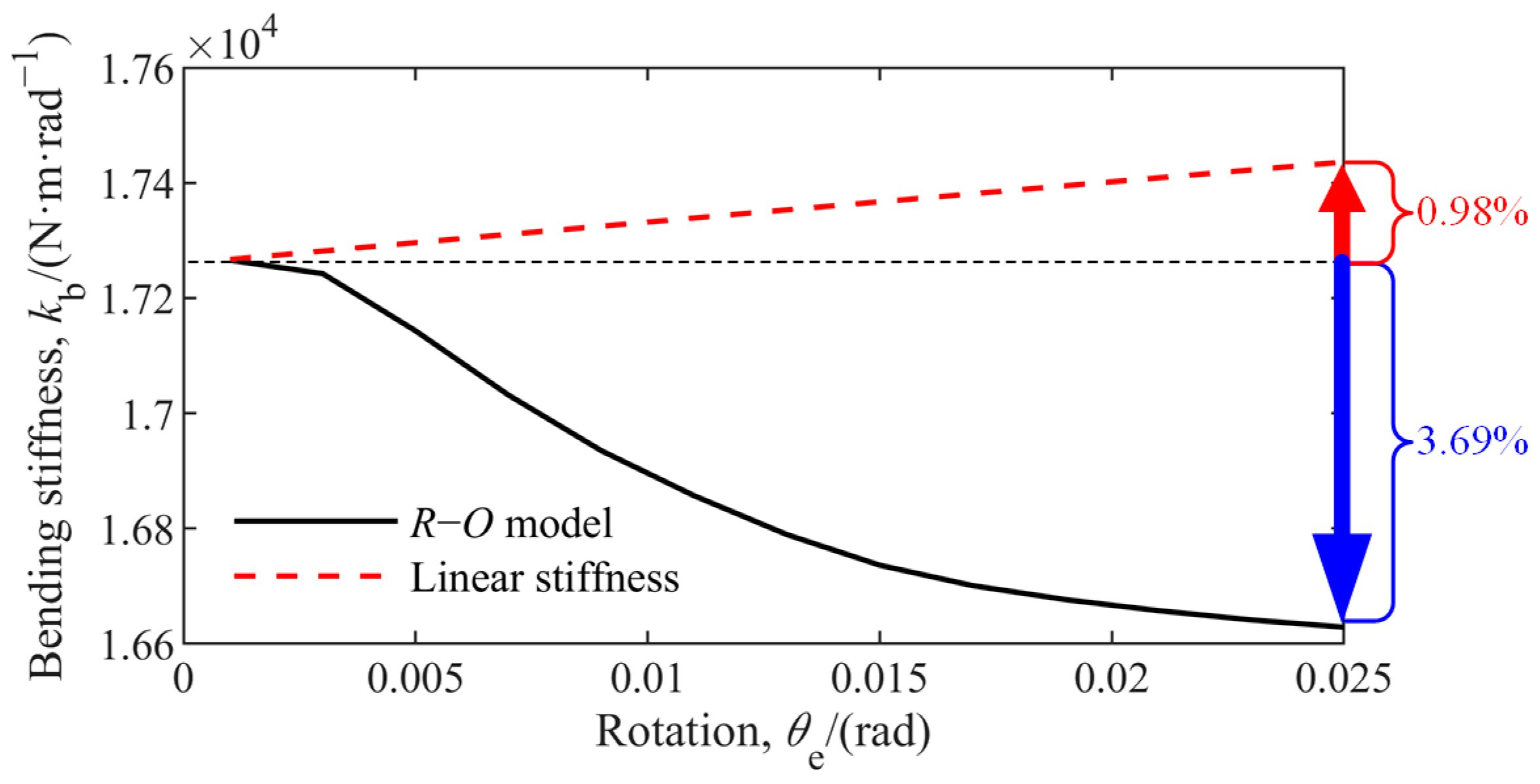
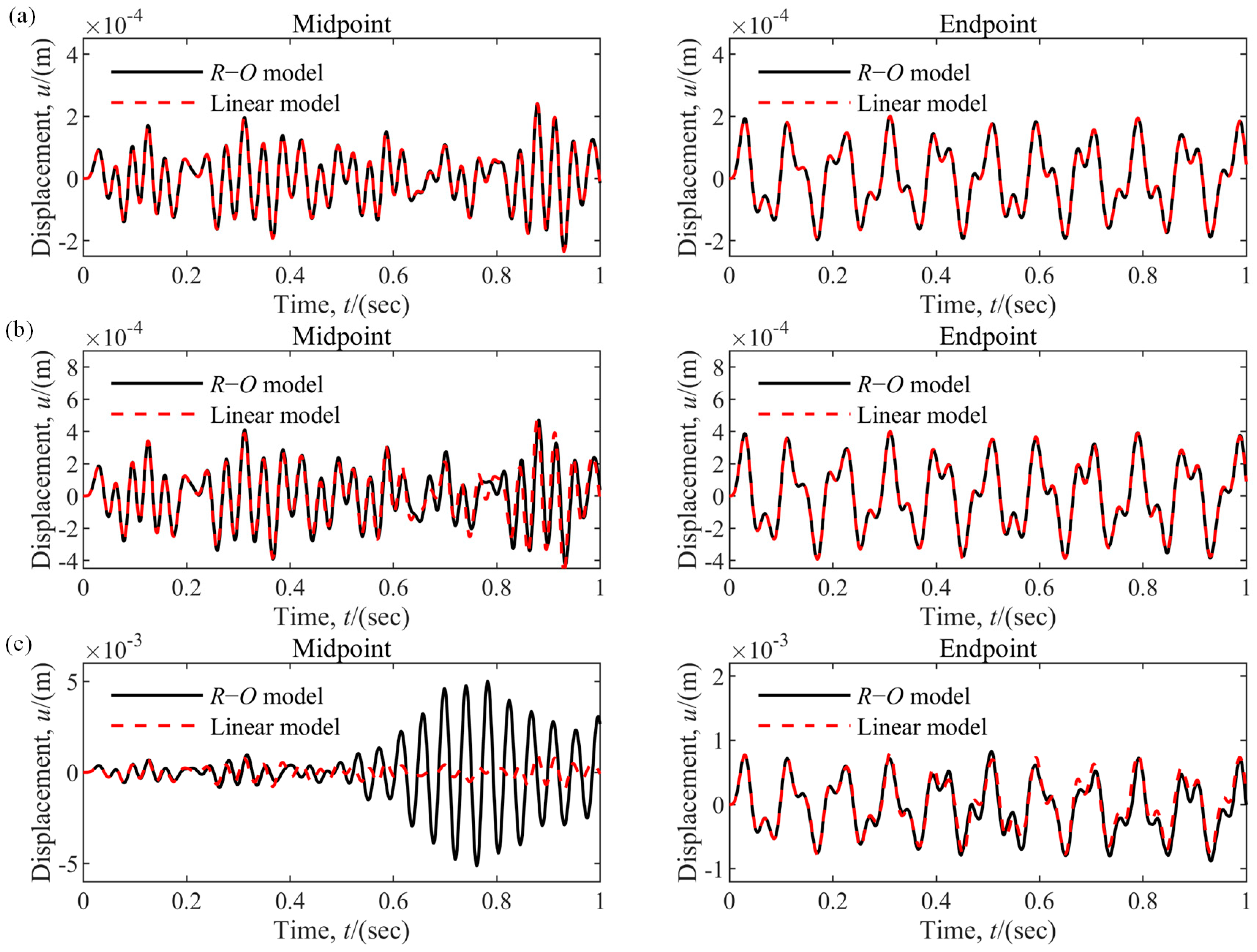
| Component | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Transverse beam | Length L1 (m) | 1 |
| Outer diameter d1 (m) | 0.04 | |
| Thickness δ1 (m) | 0.003 | |
| Young’s modulus E1 (Pa) | 6.8 × 1010 | |
| Poisson ratio μ1 | 0.3 | |
| Density ρ1 (kg/m3) | 2500 | |
| Diagonal beam | Length L2 (m) | 1.414 |
| Outer diameter d2 (m) | 0.04 | |
| Thickness δ2 (m) | 0.003 | |
| Young’s modulus E2 (Pa) | 6.8 × 1010 | |
| Poisson ratio μ2 | 0.3 | |
| Density ρ2 (kg/m3) | 2500 | |
| Semi-rigid joints | Equivalent mass m1 (kg) | 0.1392 |
| Rigid joints | Equivalent mass m2 (kg) | 0.1927 |
| Length (m) | Rigid | Sr = 100 EI/L | Sr = 10 EI/L | Ramberg–Osgood Model | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Result | Result | Diff (%) | Result | Diff (%) | Result | Diff (%) | |
| 10 | 18,184.1 | 18,075.2 | −0.599 | 17,436.1 | −4.113 | 16,628.7 | −8.554 |
| 16 | 18,022.8 | 17,924.9 | −0.543 | 17,285.9 | −4.089 | 16,490.8 | −8.500 |
| 22 | 17,869.6 | 17,763.8 | −0.592 | 17,149.7 | −4.029 | 16,360.2 | −8.447 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yao, H.; Huang, Y.; Ma, W.; Liang, L.; Zhao, Y. Dynamic Analysis of a Large Deployable Space Truss Structure Considering Semi-Rigid Joints. Aerospace 2023, 10, 821. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace10090821
Yao H, Huang Y, Ma W, Liang L, Zhao Y. Dynamic Analysis of a Large Deployable Space Truss Structure Considering Semi-Rigid Joints. Aerospace. 2023; 10(9):821. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace10090821
Chicago/Turabian StyleYao, Huaibo, Yixin Huang, Wenlai Ma, Lei Liang, and Yang Zhao. 2023. "Dynamic Analysis of a Large Deployable Space Truss Structure Considering Semi-Rigid Joints" Aerospace 10, no. 9: 821. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace10090821
APA StyleYao, H., Huang, Y., Ma, W., Liang, L., & Zhao, Y. (2023). Dynamic Analysis of a Large Deployable Space Truss Structure Considering Semi-Rigid Joints. Aerospace, 10(9), 821. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace10090821






