Spaceborne Detection Technology for Assessing Particle Radiation in Highly Elliptical Orbits
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Application Objective
2.1. Space Radiation Environment Disturbance Warnings
2.2. Particle Radiation Effect Assessment
2.3. Anti-Surface Charging Applications
3. Desired Performance Parameters
4. Payload Detection Technology
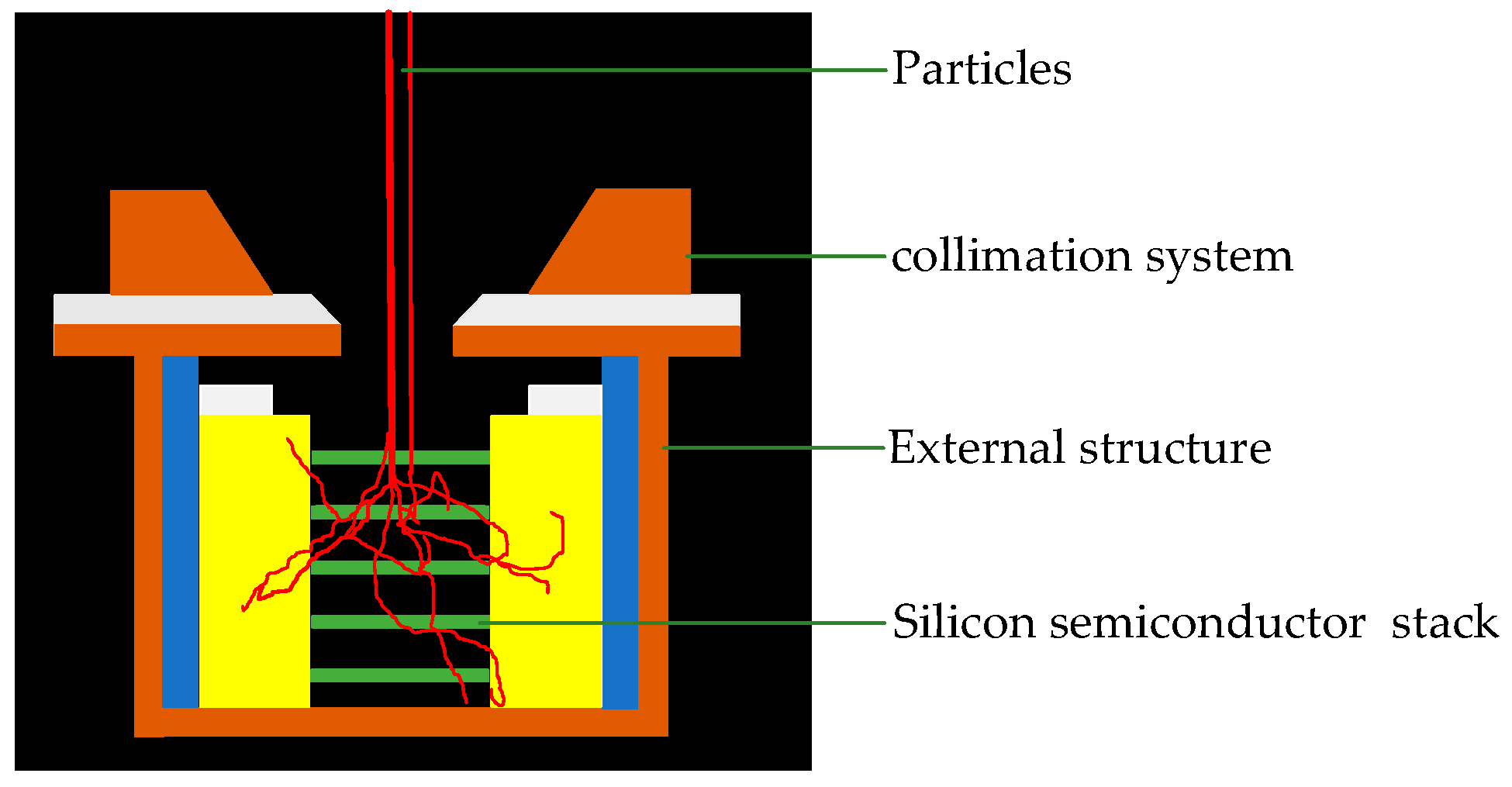
4.1. HEED Detection
4.1.1. Heed’s Collimation System
4.1.2. Heed’s Sensor System
4.1.3. Electronic System
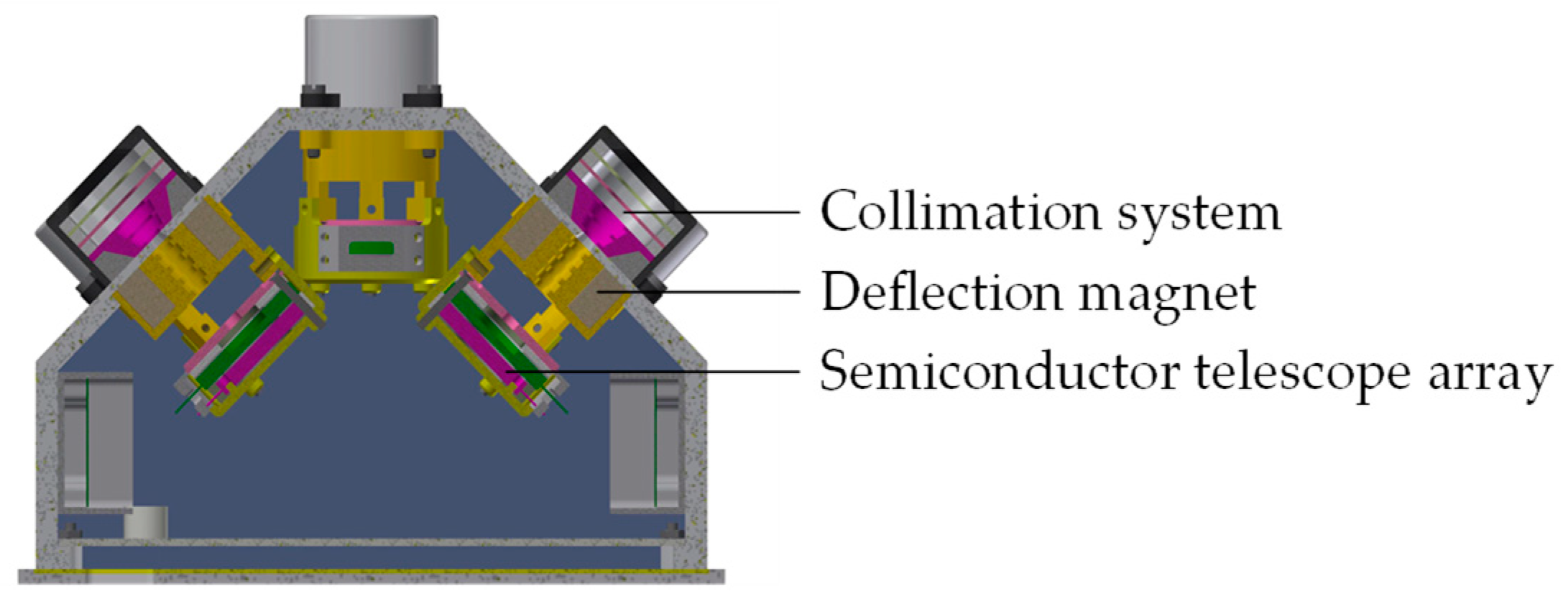
4.2. MEPD Detection
4.2.1. MEPD’s Sensor System
4.2.2. MEPD’s Collimation System
4.3. HEPDD Detection
4.4. Radiation Dose Detection
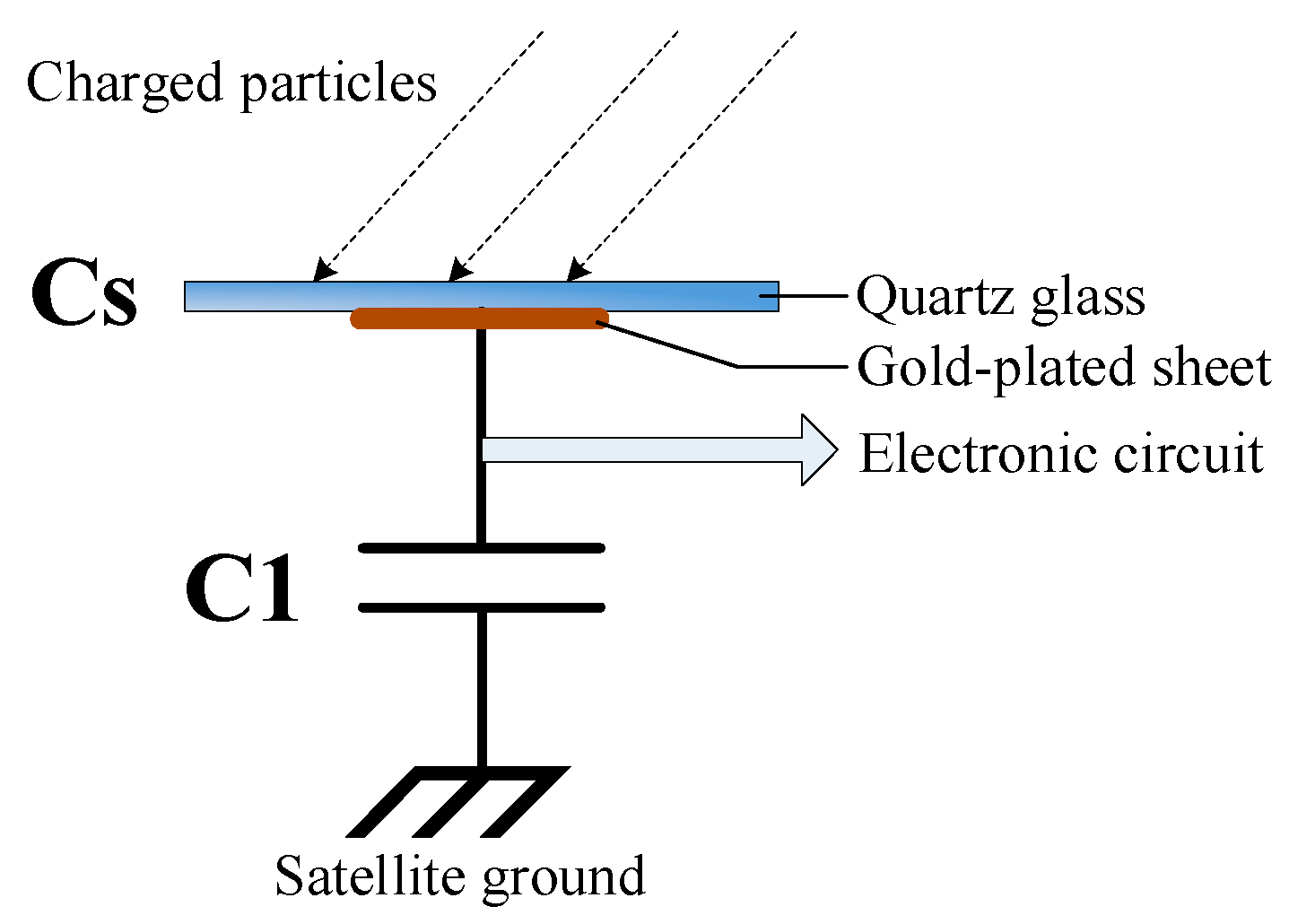
4.5. SPD Detection
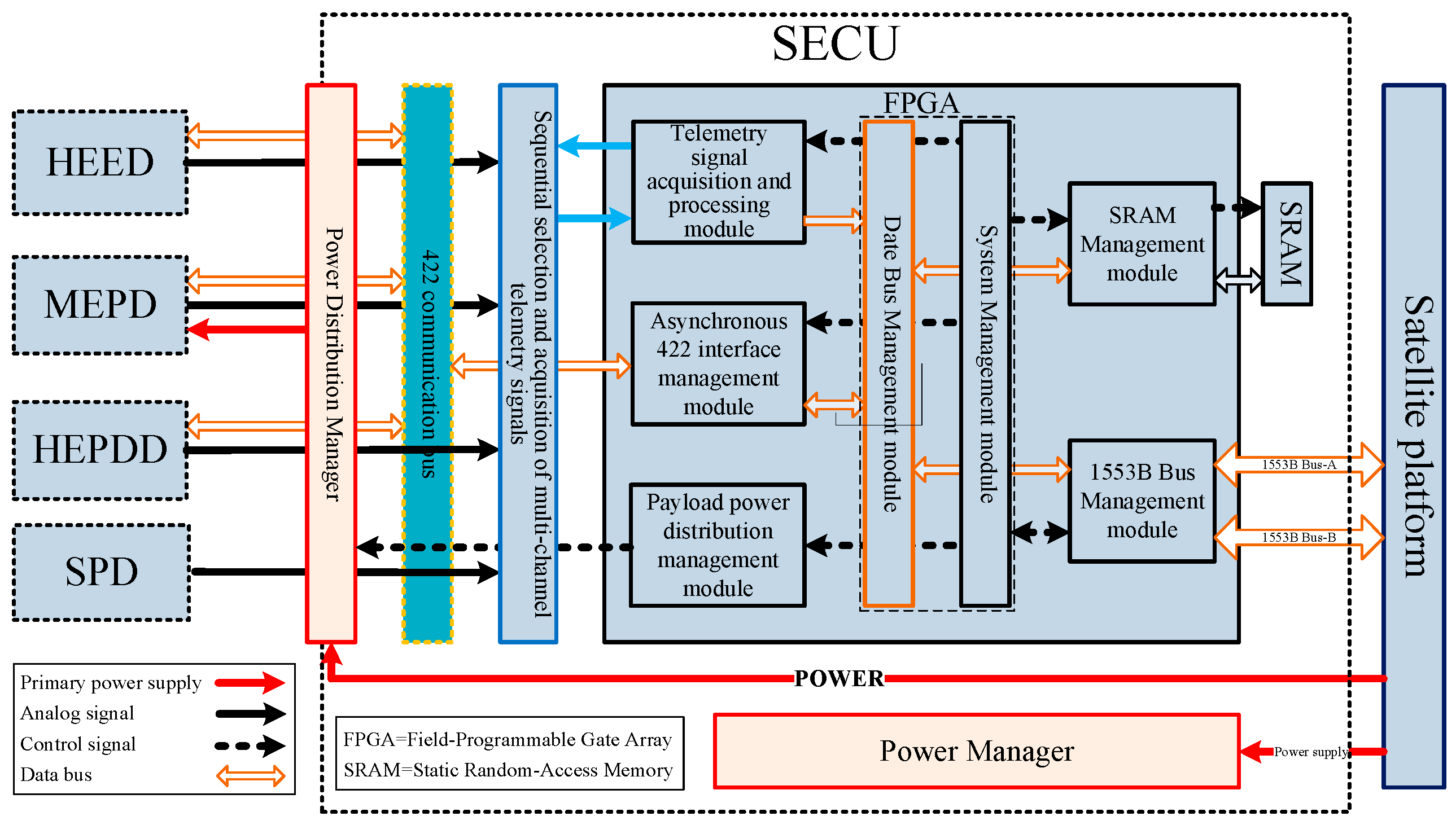
4.6. Data Management
5. Calibration Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, Y.; Tang, J.; Montenbruck, O. Chinese Navigation Satellite Systems. In Springer Handbook of Global Navigation Satellite Systems; Teunissen, P.J.G., Montenbruck, O., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 273–304. ISBN 978-3-319-42928-1. [Google Scholar]
- Bauer, W.; Braun, V.; Kitazawa, Y.; Telichev, I. Editorial: Space environment characterization. Front. Space Technol. 2023, 4, 1159825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.H.; Dou, H. Research on China’s Space Environment. Chin. J. Geophys. 1997, S1, 429–441. [Google Scholar]
- Asmar, S.W.; Armstrong, J.W.; Iess, L.; Tortora, P. Spacecraft Doppler tracking: Noise budget and accuracy achievable in precision radio science observations. Radio Sci. 2005, 40, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turyshev, S.G.; Toth, V.T. The Pioneer Anomaly. Living Rev. Relativ. 2010, 13, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, A.F.; Madrid, G.A.; Pease, G.E. Effects of Major Errors Sources on Planetary Spacecraft Navigation Accuracies. J. Spacecr. Rocket. 2012, 9, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hang, B.; Chen, Q.; Cui, X.T. Overview of Satellite Systems and Earth Orbit. Sci. Technol. Innov. Her. 2014, 11, 18–19. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, X.B.; Lu, T.S. Analyses of Environmental Effects of Typical Orbits and Their Influence on In-orbit Satellites. Aerosp. Shanghai (Chin. Engl.) 2021, 38, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagatsuma, T.; Nakamizo, A.; Kubota, Y.; Nakamura, M.; Koga, K.; Miyoshi, Y.; Matsumoto, H. Development of space environment customized risk estimation for satellites (SECURES). Earth Planets Space 2021, 73, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, Q.G.; Yuan, C.J.; Wang, Y.F.; Su, Z.P. Dynamic variation and the fast acceleration of particles in Earth’s radiation belt. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2013, 56, 1118–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.J.; Hua, G.X.; Liu, S.F. Review of research on radiation resistance of aerospace electronics. J. Astronaut. 2007, 28, 1071–1080. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, Y.X.; Yang, S.S.; Ba, D.S.; An, H.; Liu, Q.; Shi, H.; Cao, Z. Analyze of spacecraft system failures and anomalies attributed to the natural space radiation environment. Vac. Cryog. 2012, 18, 63–70. [Google Scholar]
- Jiyeon, C.; Yong-Sik, Y.; Kyung-Joo, M. Study on Space radiation effect technology of space structural materials. Curr. Ind. Technol. Trends Aerosp. 2016, 14, 99–105. [Google Scholar]
- Abd El Hameed Afaf, M. Radiation effects on composite materials used in space systems: A review. NRIAG J. Astron. Geophys. 2022, 11, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, A. Spacecraft Charging: Environment-Induced Anomalies. J. Spacecr. Rocket. 1976, 13, 129–136. [Google Scholar]
- Brautigam, D. CRRES in review: Space weather and its effects on technology. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2002, 64, 1709–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Baker, N.D.; Califf, S.; Li, X.; Jaynes, A.N.; Leonard, T.; Kanekal, S.G.; Blake, J.B.; Fennell, J.F.; Claudepierre, S.G.; et al. Van Allen Probes Measurements of Energetic Particle Deep Penetration Into the Low L Region (L < 4) During the Storm on 8 April 2016. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2017, 122, 12–140. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.S.; Zhang, X.; Dong, Y.H.; Zhang, X.G.; Sun, Y.Q.; Zong, W.G.; Chen, A.Q.; Zhang, L.G.; Zhang, X.X. Design and performance of the Space Environment In-Situ Suite on the FY-4B Satellite. Adv. Space Res. 2025; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.W.; Huang, C.; Yu, C.; Zhang, X.G.; Wang, C.Q.; Zhang, X.X.; Cao, G.W.; Sun, Y.Q. Inspection and application of energetic particles data of FY-3C/SEM satellite. J. Remoting Sens. 2018, 22, 76–86. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, G.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Yuan, B.; Hou, D.; Wang, C.; Quan, Z.; Yang, Z.; Sun, Y. Using Energy Particle Detection Technology on the Tiangong’s Space Station’s Wentian Laboratory Cabin Module. Aerospace 2023, 10, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Shen, G.; Zhang, H.; Hou, D.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Quan, Z.; Liao, J.; Ji, W.; Sun, Y. Design and Development of Energy Particle Detector on China’s Chang’e-7. Aerospace 2024, 11, 893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.H. Space Particle Radiation Detection Technology; Beijing Science Press: Beijing, China, 1986; pp. 77–78. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, D.H.; Zhang, S.Y.; Zhang, X.X.; Zong, W.G. Design and research of collimator for space high-energy electron detector. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. 2020, 40, 965–970. [Google Scholar]
- Apostolakis, J.; Asai, M.; Bogdanov, A.G.; Burkhardt, H.; Cosmo, G.; Elles, S.; Folger, G.; Grichine, V.M.; Gumplinger, P.; Heikkinen, A.; et al. Geometry and physics of the Geant4 toolkit for high and medium energy application. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2009, 78, 859–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.Y.; Zhang, X.G.; Wang, C.Q.; Shen, G.H.; Jing, T.; Zhang, B.Q.; Sun, Y.Q.; Zhu, G.W.; Liang, J.B.; Zhang, X.X. Calculation of geometric factors of space high-energy proton detector of FY-3 satellite. Sci. Sin. 2014, 44, 2479–2486. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, G.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Huang, C.; Li, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Sun, Y. Development and Calibration of a Three-Directional High-Energy Particle Detector for FY-3E Satellite. Aerospace 2023, 10, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Zhu, W.B.; Li, Y.J.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.N. Low noise sensitive preamplifier A250 for CZT detector readout. Nucl. Electron. Detect. Technol. 2007, 6, 1103–1105. [Google Scholar]
- Miyoshi, Y.; Kataoka, R. Flux enhancement of the outer radiation belt electrons after the arrival of stream interaction regions. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2008, 113, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marubashi, K. The Space Weather Forecast Program. Space Sci. Rev. 1989, 51, 197–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Zong, Q.G.; Chen, H.F.; Zou, J.Q.; Chen, J.; Shi, W.H.; Yu, X.Q.; Zhong, W.Y.; Wang, Y.F.; Ye, Y.G.; et al. An imaging spectrometer for energetic electrons based on pin-hole imaging technique and its space observations. Spacecr. Environ. Eng. 2018, 35, 307–314. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Huang, C.; Li, J.; Zong, W.; Shen, G.; Zhang, S.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, P. Design and Development of Medium Energy Proton Detector Onboard FY-3E Satellite. Aerospace 2023, 10, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.Y.; Wang, S.J. Design and research of deflection magnet in spaceborne particle detector. Chin. J. Geophys. 2007, 50, 684–690. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.C.; Wang, S.J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, W. Observation and Research of Space Particle Radiation Dose on Sun-synchronous Orbit. J. Astronaut. 2008, 1, 357–361. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, B.Q.; Zhang, X.X.; Shen, G.H.; Jing, T.; Zhang, S.Y.; Zhang, X.G.; Huang, C.; Zong, W.G.; Zhang, X.; et al. Radiation Dose Detection on FY-4B Satellite. Aerospace 2023, 10, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ecoffet, R. Overview of In-Orbit Radiation Induced Spacecraft Anomalies. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2013, 60, 1791–1815. [Google Scholar]
- Shastry, S.V.K.; Mishra, B.N.; Pramod, V.B.; Renuka, R. Surface charge monitor payload of GSAT-2 spacecraft. In Proceedings of the INCEMIC-2003: 8th International Conference on Electromagnetic Interference and Compatibility, Chennai, India, 18–19 December 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, G.; Zhang, S.; Quan, L.; Tian, C.; Zhang, H.; Chang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Sun, Y.; Yang, Z.; et al. High-energy proton detector based on semiconductor telescope. Open Astron. 2023, 32, 20220197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.Q.; Shen, G.H.; Huang, C.; Sun, Y.; Chang, Y.; Lü, J.T.; Zhang, P.F.; Wang, C.Q.; Chang, Z.; Zhang, X.G. Total Ionizing Dose Measured with the Radiation Dosimeter Onboard the FY-3E Satellite. JGR Space Phys. 2024, 130, e2024JA033016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, M.T.; Zhang, S.Y.; Hou, D.H.; Shen, G.H.; Zhang, H.X.; Su, B.; Bai, C.P.; Sun, Y.; Zhou, P.; Ji, W.T. Calibration of the Medium Energy Proton Detector of FY-3E. Chin. J. Space Sci. 2023, 43, 558–566. [Google Scholar]
- Borghello, G.; Faccio, F.; Termo, G.; Michelis, S.; Costanzo, S.; Koch, H.D.; Fleetwood, D.M. Effects of Bias and Temperature on the Dose-Rate Sensitivity of 65-nm CMOS Transistors. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2021, 68, 573–580. [Google Scholar]
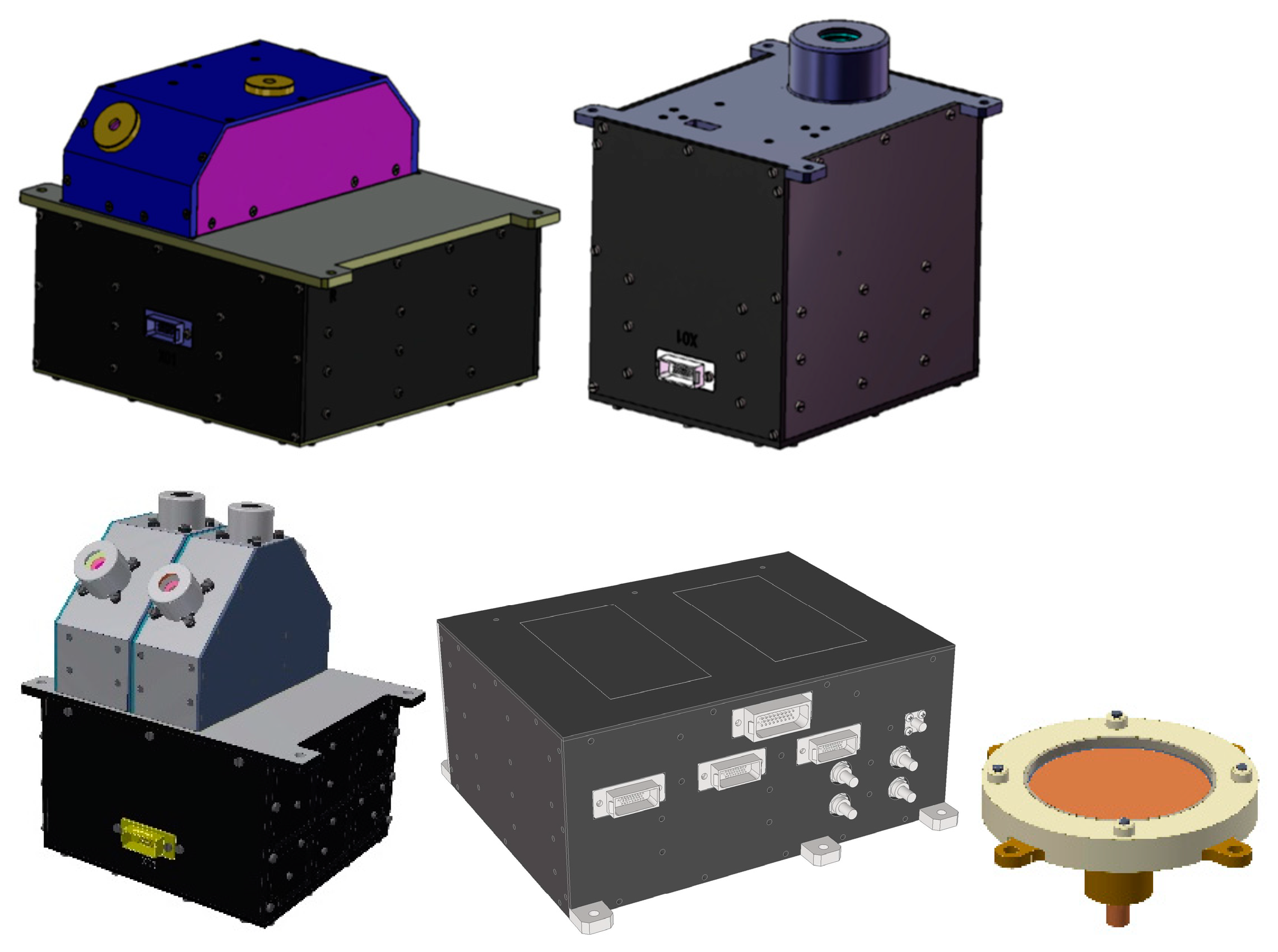




| Item | Energy Range | Energy Resolution | Detection Direction |
|---|---|---|---|
| High-energy proton | 2.5 MeV~300 MeV, 8 energy channels (2.5 MeV~5 MeV~10 MeV~15 MeV~25 MeV~40 MeV~80 MeV~165 MeV~300 MeV) | <15% | −Z |
| High-energy electron | 0.2 MeV–2.0 MeV, 9 energy channels (0.2 MeV~0.3 MeV~0.4 MeV~0.5 MeV~0.6 MeV~0.8 MeV~1.0 MeV~1.3 MeV~1.7 MeV~2.0 MeV) | <15% | X, Y, −Z |
| Medium-energy proton | 0.03 MeV–2.5 MeV, 7 energy channels (0.03 MeV~0.055 MeV~0.102 MeV~0.188 MeV~0.33 MeV~0.65 MeV~1.0 MeV~2.5 MeV) | <15% | X, Y, −Z |
| Medium-energy electron | 30 keV~410 keV, 5 energy channels (30 keV~50 keV~85 keV~144 keV~243 keV~410 keV) | <20% | X, Y, −Z |
| Item | Measuring Range | Sensitivity | Detection Direction |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total radiation dose | 0~3 × 106 rad (Si) | <10 rad (Si) | −Z |
| Item | Measuring Range | Sensitivity | Detection Direction |
|---|---|---|---|
| Surface potential | +1 kV~−10 kV | <100 V | −Z |
| Parameter | Method | Expected Results | Achieved Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| High-energy proton | Heavy Ion Accelerator of China Atomic Energy Institute (Protons < 40 MeV); Huairou electron accelerator (20–1600 keV) at CAS; standard radioactive source 207Bi; other energies are analyzed using the combination of equivalent signal generator calibration and simulation analysis | Energy range: 2.5 MeV~300 MeV; Energy resolution: <15% | Energy range: 2.497 MeV–296 MeV; Energy resolution: 5.12%@80 MeV; Flux error: 8.75% |
| High-energy electron | Energy range: 0.2 MeV–2.0 MeV; Energy resolution: <15% | Energy range: 195.8 keV~2.003 MeV (Direction X), 196 keV~2.004 MeV (Direction Y), 202 keV~1.996 MeV (Direction −Z); Energy resolution: 10.44%@800 keV (Direction X), 10.22%@800 keV (Direction Y), 10.57%@800 keV (Direction −Z); Flux error: 8.75% | |
| Medium-energy proton | Energy range: 0.03 MeV–2.5 MeV; Energy resolution: <15% | Energy range: 30.9 keV~2.503 MeV (Direction X), 30.9 keV~2.505 MeV (Direction Y), 31.0 keV~2.497 MeV (Direction −Z); Energy resolution: 7.52%@72 keV (Direction X), 7.19%@72 keV (Direction Y), 8.82%@72 keV (Direction −Z); Flux error: 8.58% | |
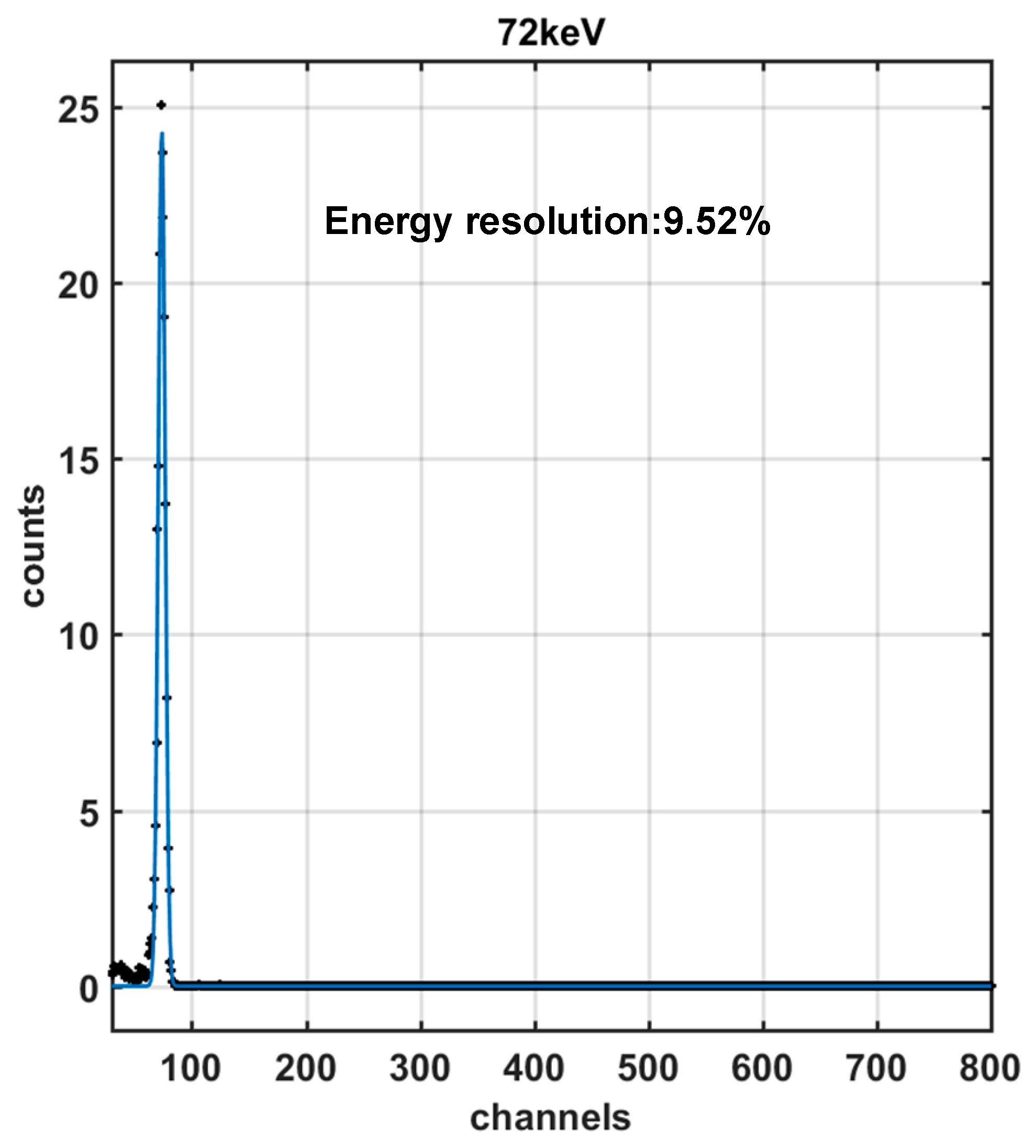
| Medium-energy electron | Energy range: 30 keV~410 keV; Energy resolution: <15% | Energy range: 29.1 keV~410.7 keV (Direction X), 29.1 keV~414.9 keV (Direction Y), 29.5 keV~409.0 keV (Direction −Z; Energy resolution: 9.52%@72 keV (Direction X), 9.65%@72 keV (Direction Y), 9.59%@72 keV (Direction −Z); Flux error: 8.58% | |
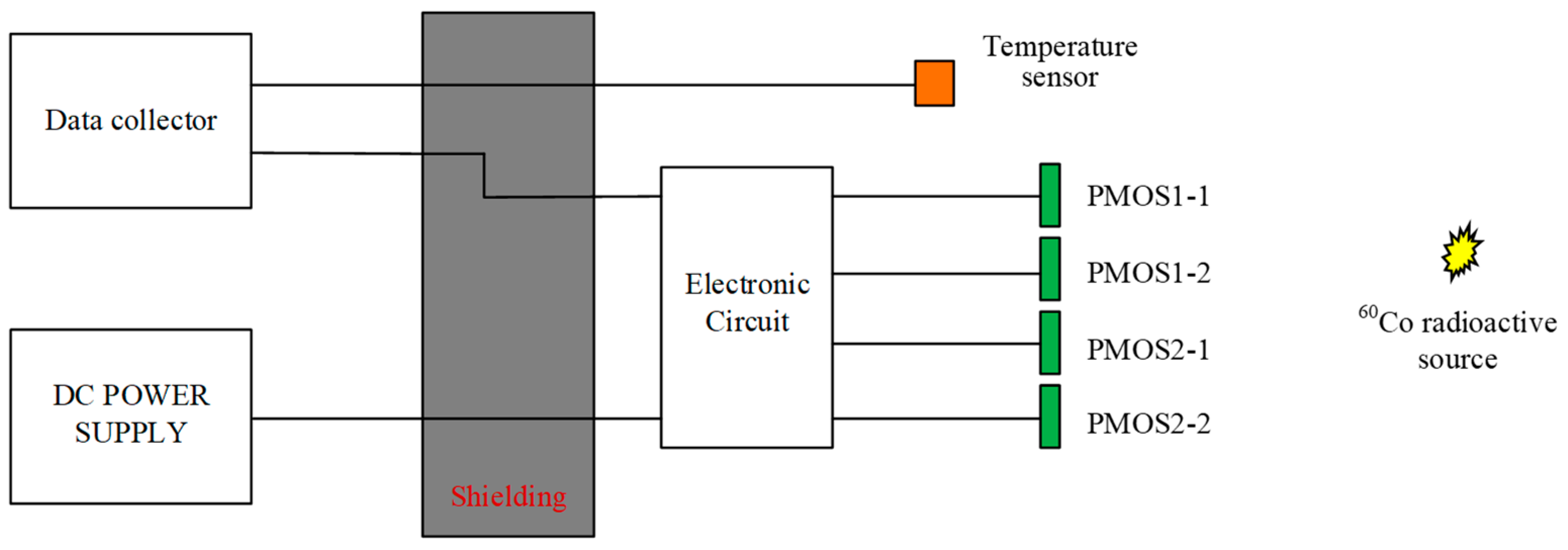
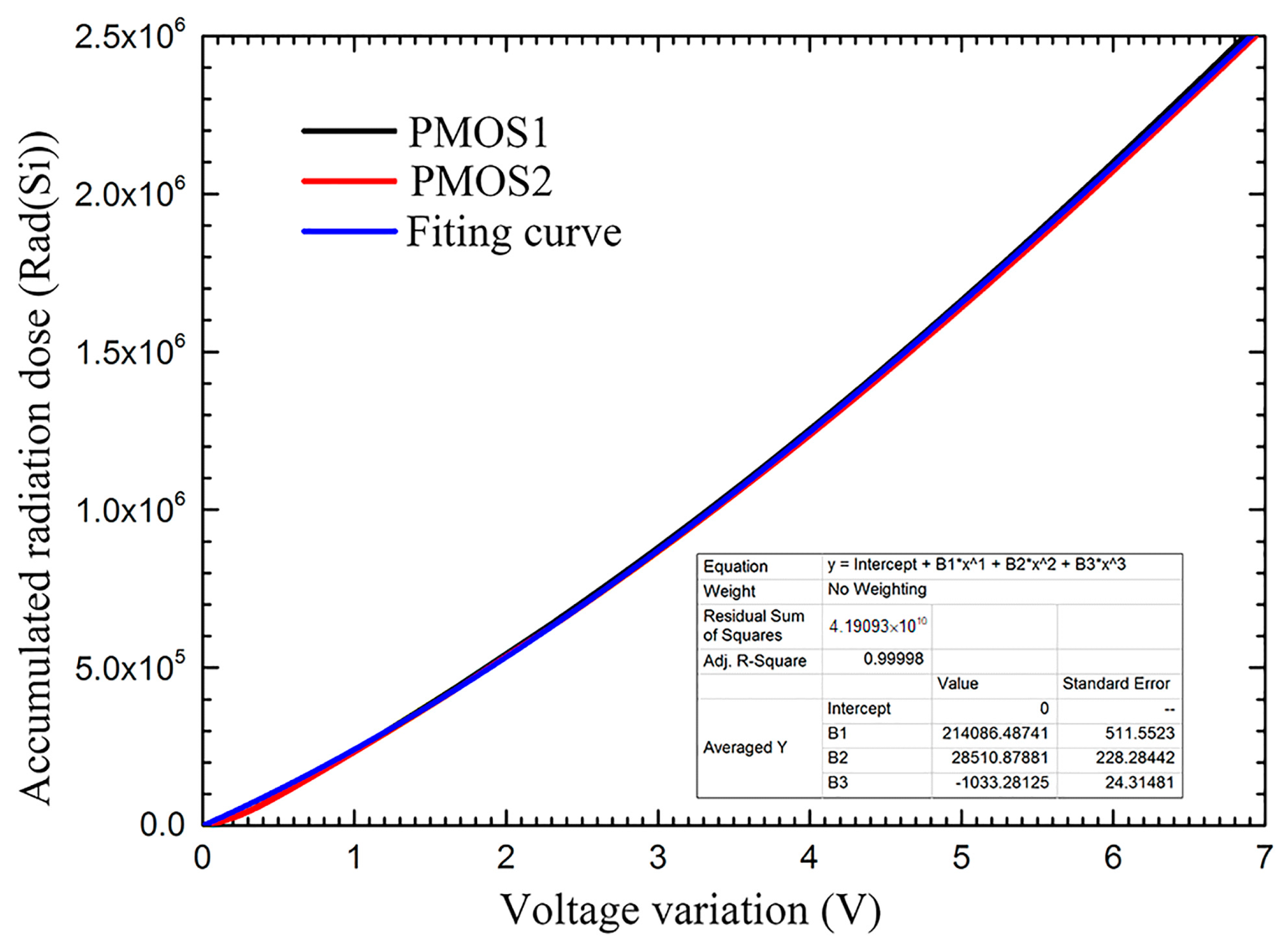
| Total radiation dose | Standard radioactive source 60Coγ at Xinjiang Technical Institute of Physics & Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences | Measuring range: 0~3.0 × 106 rad (Si); Sensitivity: <10 rad (Si) | Measuring range: 0~3.38 × 106 rad (Si); Sensitivity: <3 rad (Si) |
| Surface potential | Static high-voltage source (+30 kV~−30 kV) | Measuring range: +1 kV~−10 kV; Sensitivity: <100 V | Measuring range: 1.414 kV~−11.571 kV; Sensitivity: <50 V |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, G.; Quan, L.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, H.; Hou, D.; Wang, C.; Sun, Y.; Yuan, B.; Tuo, C.; Quan, Z.; et al. Spaceborne Detection Technology for Assessing Particle Radiation in Highly Elliptical Orbits. Aerospace 2025, 12, 303. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace12040303
Shen G, Quan L, Zhang S, Zhang H, Hou D, Wang C, Sun Y, Yuan B, Tuo C, Quan Z, et al. Spaceborne Detection Technology for Assessing Particle Radiation in Highly Elliptical Orbits. Aerospace. 2025; 12(4):303. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace12040303
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Guohong, Lin Quan, Shenyi Zhang, Huanxin Zhang, Donghui Hou, Chunqin Wang, Ying Sun, Bin Yuan, Changsheng Tuo, Zida Quan, and et al. 2025. "Spaceborne Detection Technology for Assessing Particle Radiation in Highly Elliptical Orbits" Aerospace 12, no. 4: 303. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace12040303
APA StyleShen, G., Quan, L., Zhang, S., Zhang, H., Hou, D., Wang, C., Sun, Y., Yuan, B., Tuo, C., Quan, Z., Chang, Z., Zhang, X., & Sun, Y. (2025). Spaceborne Detection Technology for Assessing Particle Radiation in Highly Elliptical Orbits. Aerospace, 12(4), 303. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace12040303







