Review of On-Orbit Assembly Technology with Space Robots
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Classification of On-Orbit Assembly
2.1. Target and Task Characteristics-Based Classification
2.2. Assembly Realization-Based Classification Method
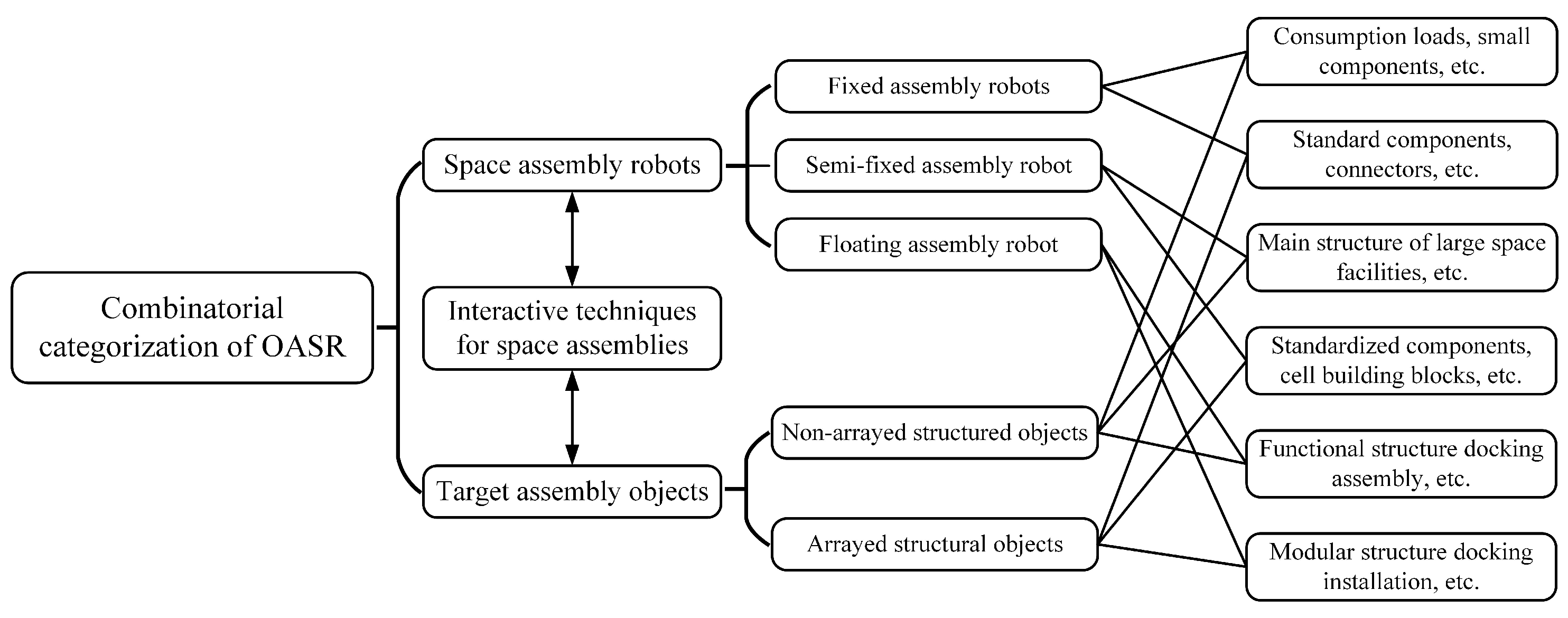
2.3. Combination-Based Classification Method
3. Overview of Space Robotic Arms
3.1. Status of North American Space Robotic Arm Research
3.2. Status of European Space Robotic Arm Research
3.3. Status of Japanese Space Robotic Arm Research
3.4. Status of Chinese Space Robotic Arm Research
3.5. Summary of Space Robotic Arm Parameters
4. Status of On-Orbit Assembly with Space Robots
4.1. Status of Research on Floating Space Assembly
4.1.1. Status of Floating Space Assembly in North America
4.1.2. Status of Floating Space Assembly in Europe
4.1.3. Status of Floating Space Assembly in Japan
4.2. Status of Research on Semi-Fixed Space Assembly
4.2.1. Status of Semi-Fixed Assembly in North America
4.2.2. Status of Semi-Fixed Assembly in Europe
4.2.3. Status of Semi-Fixed Assembly in China
4.3. Status of Research on Fixed Space Assembly
4.4. Summary of the Space Robot On-Orbit Assembly Project
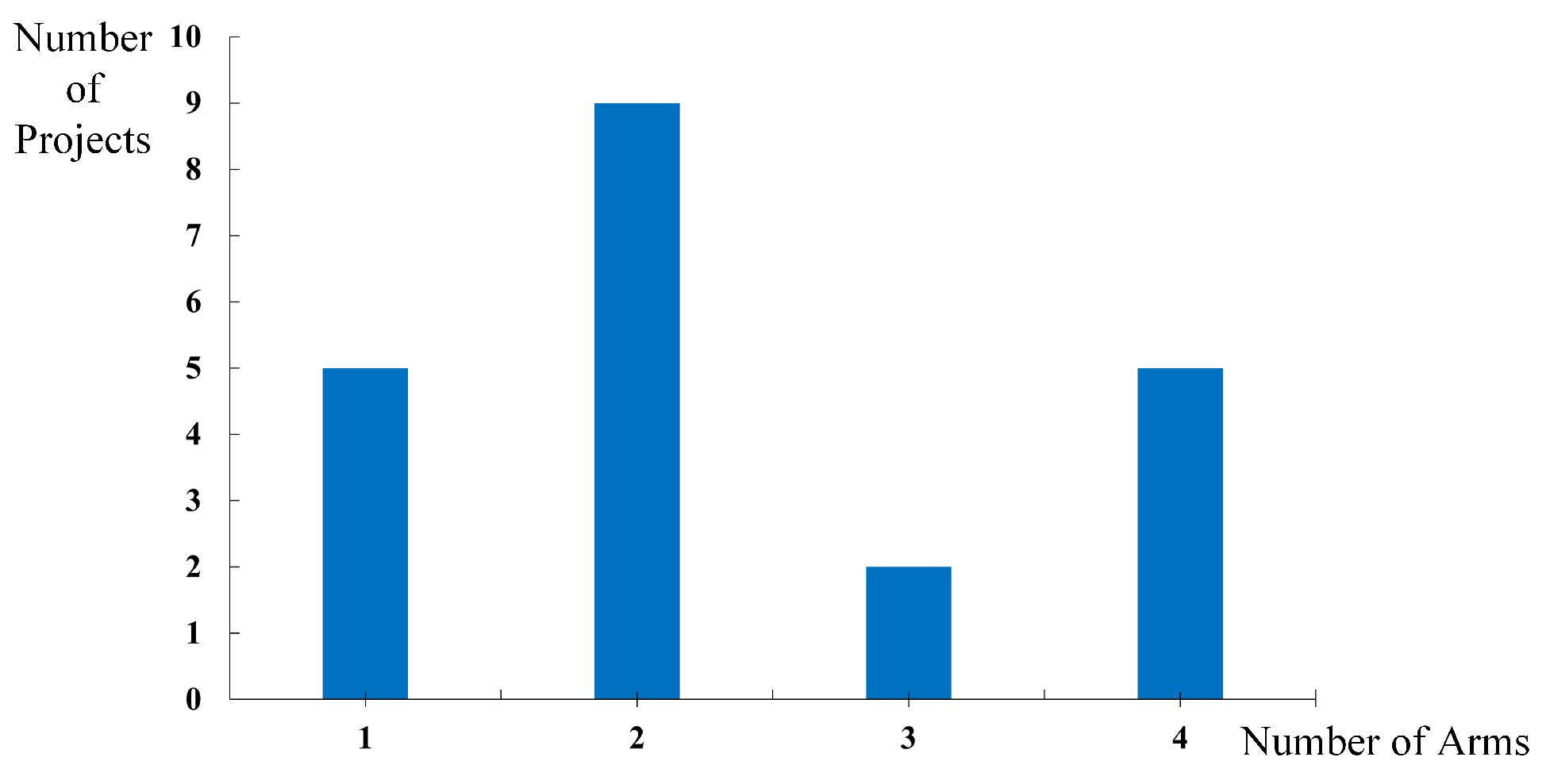
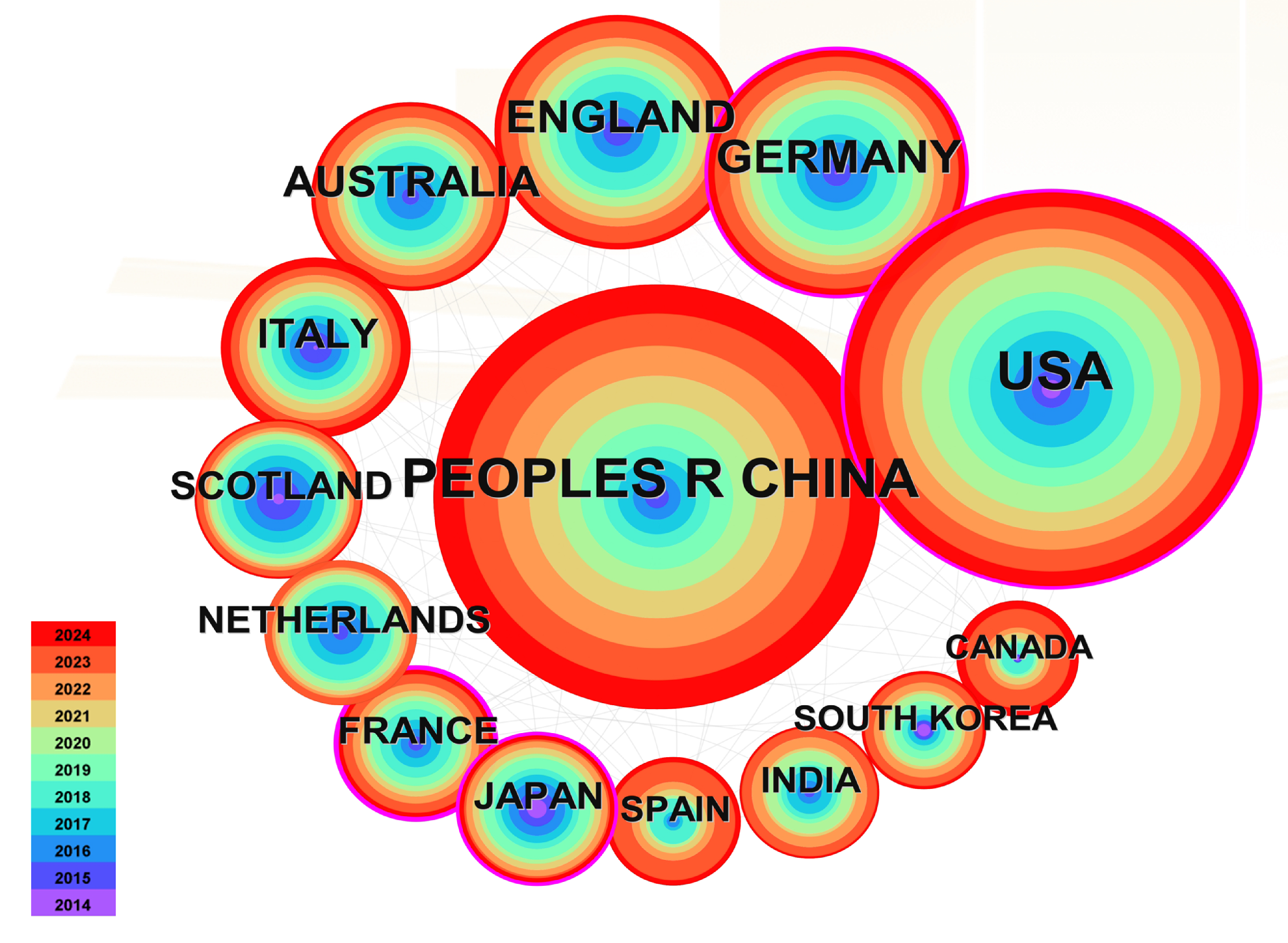
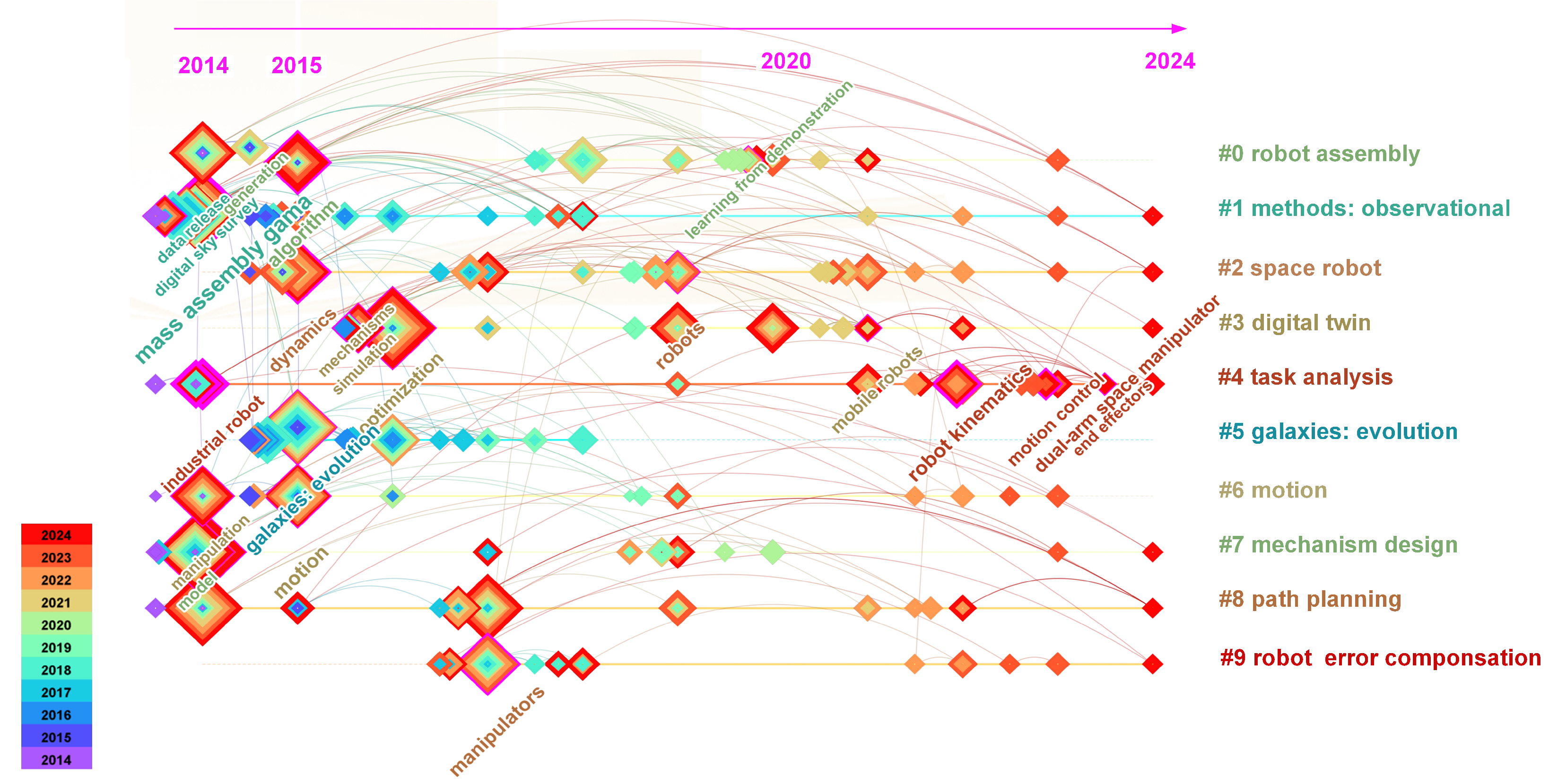
5. Literature Analysis of On-Orbit Assembly with Space Robots
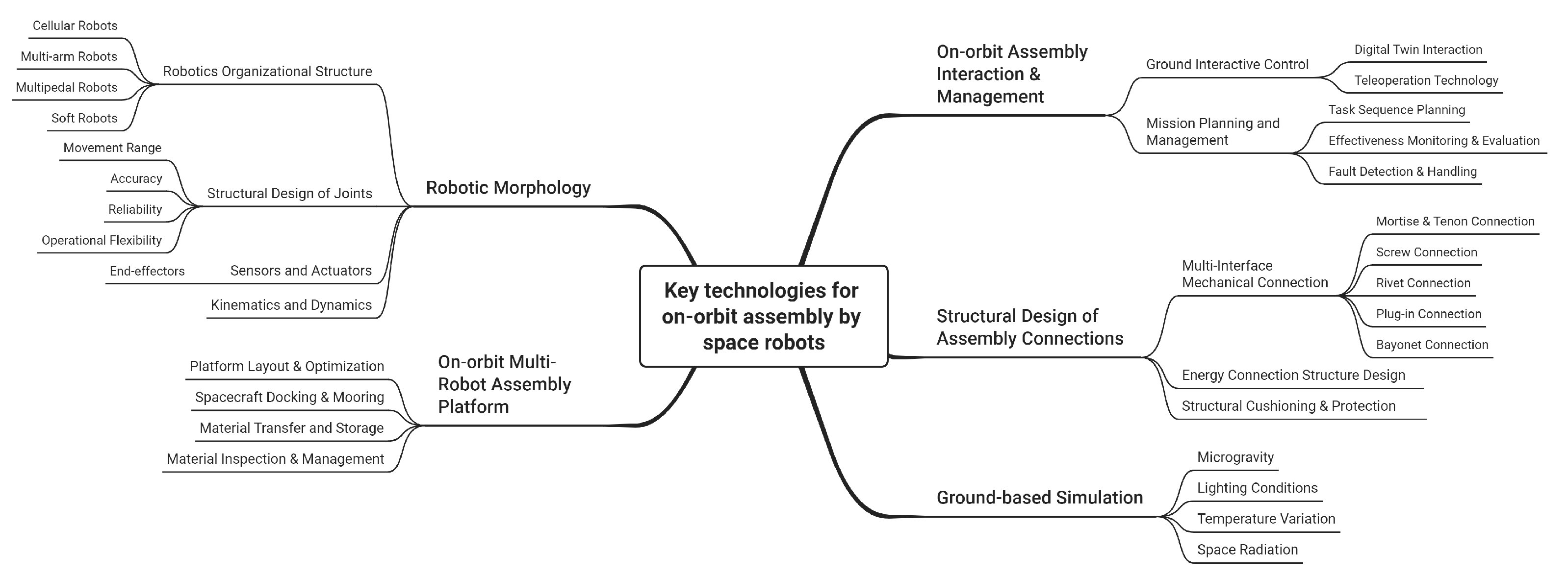
6. Key Technologies for On-Orbit Assembly with Space Robots
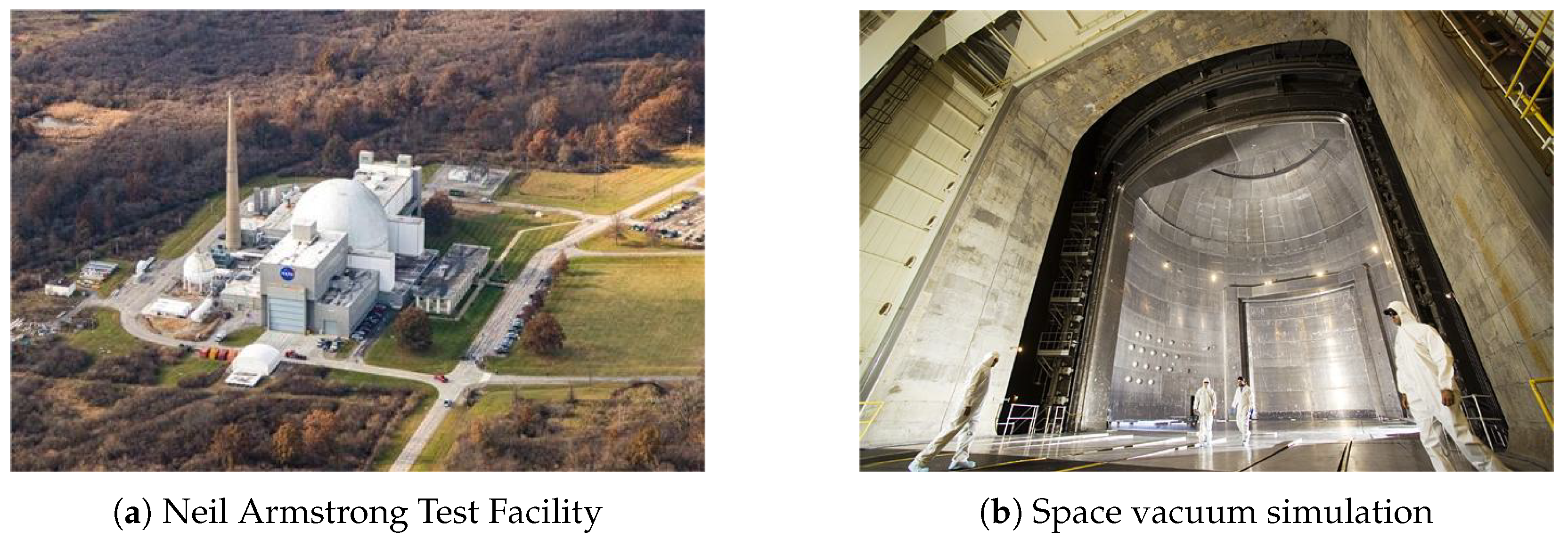
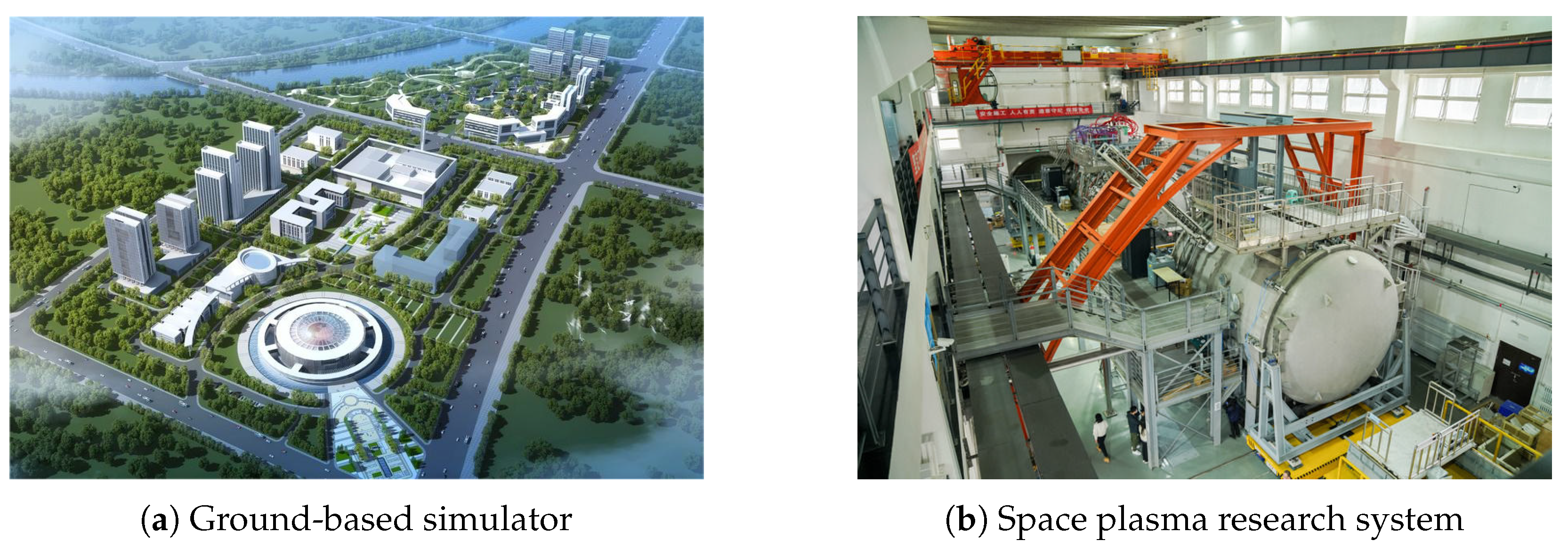
6.1. Ground-Based Simulation Technology
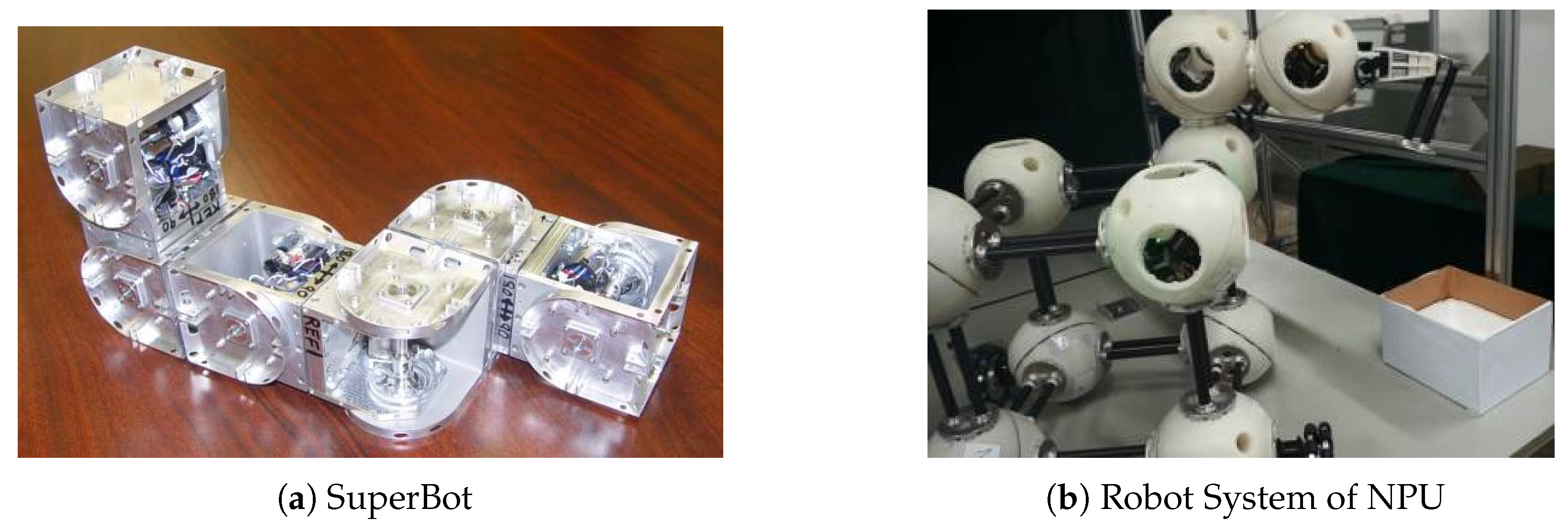
6.2. Space Robot Morphology Theory and Technology
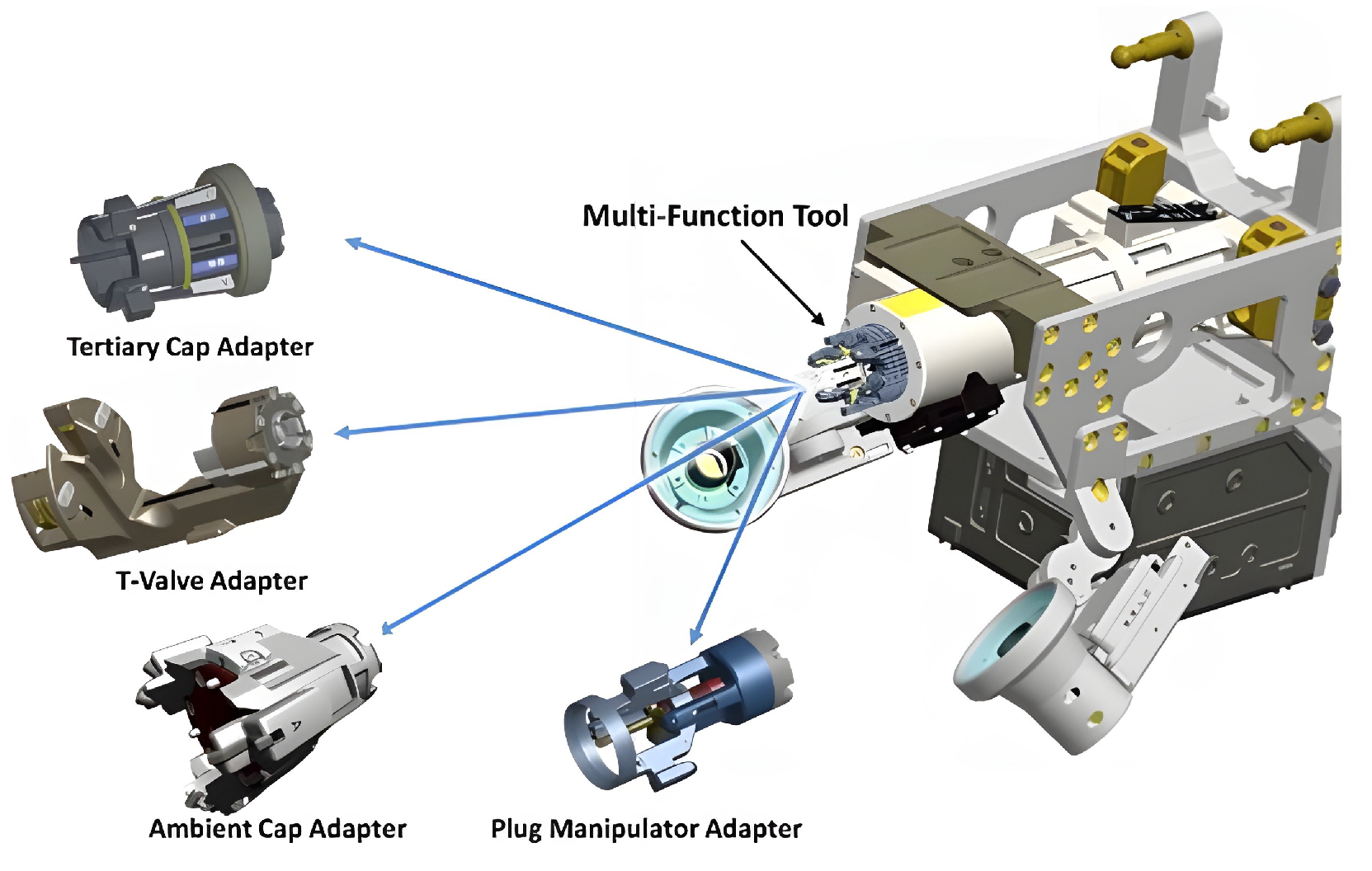
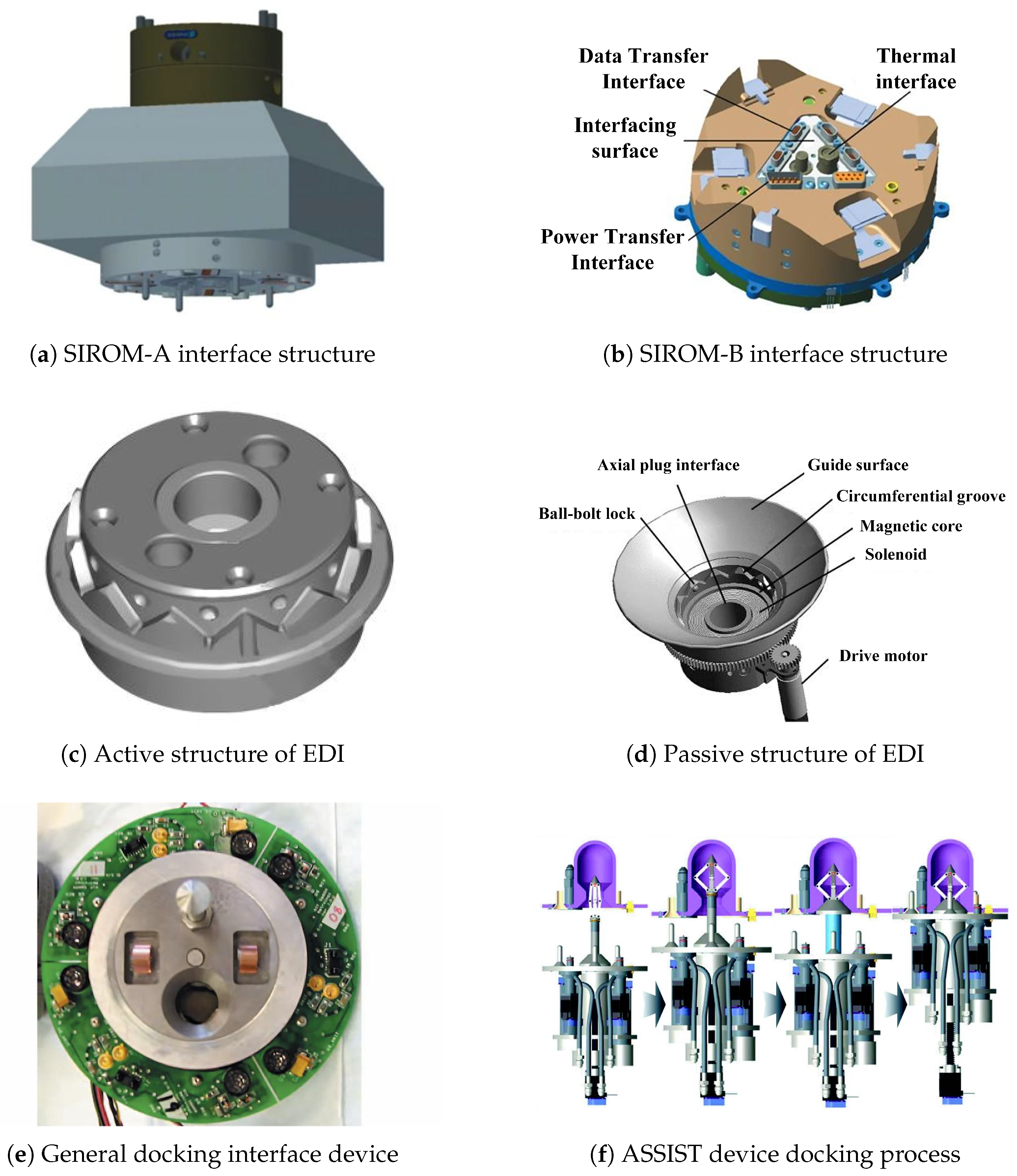
6.3. Assembly Connection Structure Design Technology
6.4. On-Orbit Assembly Interactive Management Technology
6.5. Multi-Robot On-Orbit Assembly Platform Technology
7. Development Trend of On-Orbit Assembly with Robots
7.1. Space In-Situ Assembly
7.2. Collaborative Multi-Robot Clusters
7.3. Evolution of Individual Intelligence
7.4. Smart Materials and Self-Assembly
7.5. On-Orbit Assembly of Micro- and Macro-Scales
7.6. Space-Based Supporting Platforms
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, W.J.; Cheng, D.Y.; Liu, X.G.; Wang, Y.B.; Shi, W.H.; Tang, Z.X.; Gao, F.; Zeng, F.M.; Chai, H.Y.; Luo, W.B.; et al. On-orbit service (OOS) of spacecraft: A review of engineering developments. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2019, 108, 32–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Abad, A.; Ma, O.; Pham, K.; Ulrich, S. A review of space robotics technologies for on-orbit servicing. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2014, 68, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, T.; Liu, H. Brief analysis of NASA robotic refueling task. Aerosp. China 2019, 4, 42–47. [Google Scholar]
- Gebhardt, C. Northrop Grumman makes history, Mission Extension Vehicle docks to target satellite. NASASpaceflight.com, 26 February 2020. [Google Scholar]
- HJ, W. Space fueling technology completes on-orbit verification of China. Dual Use Technol. Prod. 2016, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.; Jia, D.; Bai, M.; Feng, Y.; Li, X. Research and Development of the Tianzhou Cargo Spacecraft. Space Sci. Technol. 2023, 3, 0006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oegerle, W.; Purves, L.; Budinoff, J.; Moe, R.; Carnahan, T.; Evans, D.; Kim, C. Concept for a large scalable space telescope: In-space assembly. In Proceedings of the Space Telescopes and Instrumentation I: Optical, Infrared, and Millimeter, Orlando, FL, USA, 24–31 May 2006; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2006; Volume 6265, pp. 755–766. [Google Scholar]
- Datashvili, L.; Endler, S.; Wei, B.; Baier, H.; Langer, H.; Friemel, M.; Tsignadze, N.; Santiago-Prowald, J. Study of mechanical architectures of large deployable space antenna apertures: From design to tests. CEAS Space J. 2013, 5, 169–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
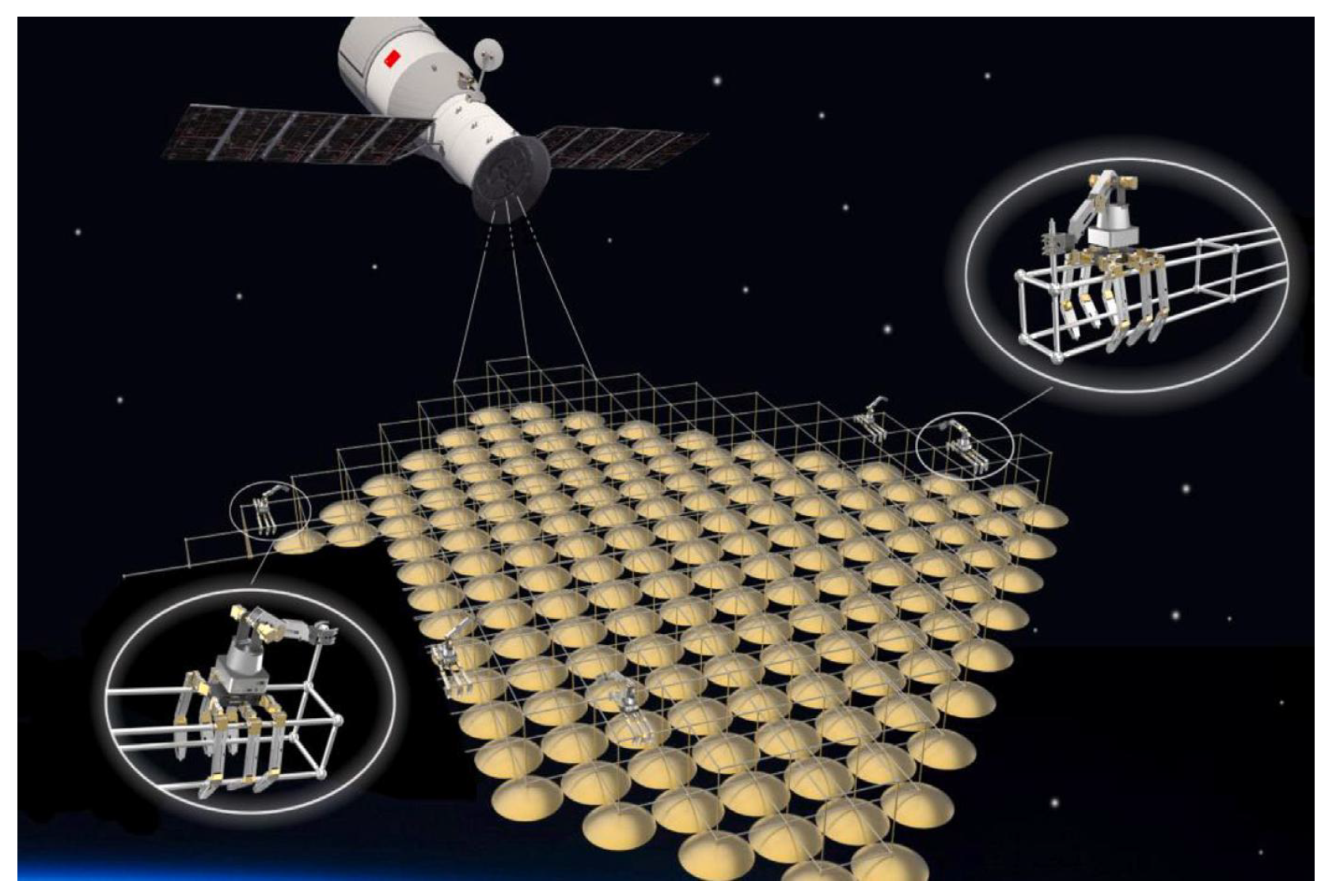
- Cheng, Z.; Hou, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, L.; Guo, J.; Song, C. In-orbit assembly mission for the space solar power station. Acta Astronaut. 2016, 129, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.P.; Mayberry, J.P.; Penn, J.P. On-Orbit Servicing: Inspection, Repair, Refuel, Upgrade, and Assembly of Satellites in Space; The Aerospace Corporation: Chantilly, VA, USA, 2019; 14p. [Google Scholar]
- Thronson, H.; Geffre, J.; Prusha, S.; Caroff, L.; Weisbin, C. The lunar L1 gateway concept: Supporting future major space science facilities. In New Concepts for Far-Infrared and Submillimeter Space Astronomy; NASA: Washington, DC, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Benaroya, H.; Bernold, L. Engineering of lunar bases. Acta Astronaut. 2008, 62, 277–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benaroya, H.; Bernold, L.; Chua, K.M. Engineering, design and construction of lunar bases. J. Aerosp. Eng. 2002, 15, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Luo, J.; Yuan, J.; Wang, J.; Liu, C. In-orbit assembly technology: Review. Acta Aeronaut. Astronaut. Sin. 2021, 42, 523913. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.; Wang, P.; Cui, N. Development of on-orbit assembly of large space structures. Missiles Space Veh. 2006, 3, 28–35. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, Z.; Liu, J.; Wu, C.; Tong, Y. Review of in-space assembly technologies. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2021, 34, 21–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NASA. On-Orbit Satellite Servicing Study; Project Report: NP-2010-08-162-GSFC; NASA Goddard Space Flight Center: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2010.
- David, S. Skylab: America’s Space Station; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- China National Space Administration. Let’s Get to Know the Two Strong and Capable “Cuties” on the Space Station, Not the Lab Module. 2023. Available online: https://www.cnsa.gov.cn/n6758968/n6758973/c10388340/content.html (accessed on 13 October 2023).
- Jorgensen, G.; Elizabeth, B. SRMS History, Evolution and Lessons Learned. 2023. Available online: https://ntrs.nasa.gov/citations/20110015563 (accessed on 2 October 2023).
- Meng, G.; Han, L.; Zhang, C. Research progress and technical challenges of space robot. Acta Aeronaut. Astronaut. Sin. 2021, 42, 523963. [Google Scholar]
- Coleshill, E.; Oshinowo, L.; Rembala, R.; Bina, B.; Rey, D.; Sindelar, S. Dextre: Improving maintenance operations on the international space station. Acta Astronaut. 2009, 64, 869–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- eoPortal. ISS: MSS (Mobile Servicing System). 2023. Available online: https://www.eoportal.org/satellite-missions/iss-mss#iss-servicing-mss-mobile-servicing-system (accessed on 13 October 2023).
- Government of Canada. About Canadarm3. Available online: https://www.asc-csa.gc.ca/eng/canadarm3/about.asp (accessed on 13 October 2023).
- Government of Canada. Canadarm, Canadarm2, and Canadarm3—A Comparative Table. Available online: https://www.asc-csa.gc.ca/eng/iss/canadarm2/canadarm-canadarm2-canadarm3-comparative-table.asp (accessed on 13 October 2023).
- Tzvetkova, G.V. Robonaut 2: Mission, technologies, perspectives. J. Theor. Appl. Mech. 2014, 44, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruijssen, H.; Ellenbroek, M.; Henderson, M.; Petersen, H.; Verzijden, P.; Visser, M. The european robotic arm: A high-performance mechanism finally on its way to space. In Proceedings of the 42nd Aerospace Mechanism Symposium, Baltimore, MD, USA, 14–16 May 2014. [Google Scholar]
- ESA. European Robotic Arm. Available online: https://www.esa.int/Science_Exploration/Human_and_Robotic_Exploration/International_Space_Station/European_Robotic_Arm (accessed on 20 September 2023).
- ESA. Eurobot Makes a Splash. Available online: https://www.esa.int/Science_Exploration/Human_and_Robotic_Exploration/International_Space_Station/Eurobot_makes_a_splash (accessed on 23 September 2023).
- Hirzinger, G.; Brunner, B.; Dietrich, J.; Heindl, J. ROTEX-the first remotely controlled robot in space. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 1994 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, San Diego, CA, USA, 8–13 May 1994; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 1994; pp. 2604–2611. [Google Scholar]
- Albu-Schaffer, A.; Bertleff, W.; Rebele, B.; Schafer, B.; Landzettel, K.; Hirzinger, G. ROKVISS-robotics component verification on ISS current experimental results on parameter identification. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, ICRA 2006, Orlando, FL, USA, 15–19 May 2006; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2006; pp. 3879–3885. [Google Scholar]
- Institute of Robotics and Mechatronics. ROKVISS. Available online: https://www.dlr.de/en/rm/research/robotic-systems/arms/rokviss (accessed on 13 December 2024).
- Beyer, A.; Grunwald, G.; Heumos, M.; Schedl, M.; Bayer, R.; Bertleff, W.; Brunner, B.; Burger, R.; Butterfaß, J.; Gruber, R.; et al. Caesar: Space robotics technology for assembly, maintenance, and repair. In Proceedings of the 69th International Astronautical Congress (IAC), Bremen, Germany, 1–5 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, Z.; Liu, J. Review of Space Manipulator Control Technologies. Robot 2022, 44, 107–128. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, N.; Wakabayashi, Y. JEMRMS design features and topics from testing. In Proceedings of the 6th International Symposium on Artificial Intelligence, Robotics and Automation in Space (i-SAIRAS), Montreal, QC, Canada, 18–22 June 2001; Volume 214, p. 8. [Google Scholar]
- Matsueda, T.; Kuraoka, K.; Goma, K.; Sumi, T.; Okamura, R. JEMRMS system design and development status. In Proceedings of the NTC’91—National Telesystems Conference Proceedings, Atlanta, GA, USA, 26–27 March 1991; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 1991; pp. 391–395. [Google Scholar]
- GITAI. SpaceX Dragon Spacecraft Carrying the GITAI Robot Successfully Launches and Arrives at the ISS. Available online: https://gitai.tech/2021/08/31/successful-launch-of-spacex-rocket-with-gitai-robot-on-board-arrives-at-iss/ (accessed on 15 October 2023).
- GITAI. GITAI Completes Fully Successful Technology Demonstration Outside the ISS. Available online: https://gitai.tech/2024/03/19/gitai-completes-fully-successful-technology-demonstration-outside-the-iss/ (accessed on 18 October 2024).
- Hu, C.; Gao, S.; Xiong, M.; Tang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liang, C.; Dong, N. Key technologies of the China space station core module manipulator. Sci. Sin. 2022, 52, 1299–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Liu, D.; Jiang, Z. Space manipulator technology:Review and prospect. Acta Aeronaut. Astronaut. Sin. 2021, 42, 33–46. [Google Scholar]
- Amazing Chinese Manufacturing. What’s It Like to Catch a Doll in Space? You’ll Have to Ask It. Available online: https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/40430622 (accessed on 28 September 2023).
- Liu, H.; Li, Z.; Liu, Y.; Jin, M.; Fenglei, N.; Liu, Y.; Xia, J.; Zhang, Y. Key technologies of TianGong-2 robotic hand and its on-orbit experiments. Sci. Sin. 2018, 48, 1313–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhao, P.; Chen, K.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X. 1U-Sized Deployable Space Manipulator for Future On-Orbit Servicing, Assembly, and Manufacturing. Space Sci. Technol. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, S.; Mast, T.; Miyata, G. A proposed autonomously assembled space telescope (AAST). In Proceedings of the AIAA Space 2003 Conference & Exposition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 23–25 September 2003; p. 6369. [Google Scholar]
- Basu, S. Conceptual design of an autonomously assembled space telescope (AAST). In Proceedings of the UV/Optical/IR Space Telescopes: Innovative Technologies and Concepts, San Diego, CA, USA, 3–8 August 2003; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2004; Volume 5166, pp. 98–112. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, B. United States test of the small-satellite XSS-10 system. Aerosp. China 2006, 36–38+43. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=04fY48Ac_vwgizUDh78VUAhVgdkKatD4nAmCVmiWobZ_GoqjRHPofwqZH8QrC2_z3HAf0luobxQ1aV5Y8ZPXRTJoZWvBcREpVIrznXXH34fq3kLvclQj9qwLoQHZisrxx3r4LplhYjythtanv_ByvHDV3vFVGthYALmoQb8vGOi9aRuZkBaq9w==&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 23 April 2025).
- Davis, T.M.; Melanson, D. Xss-10 micro-satellite flight demonstration. In Proceedings of the Georgia Institute of Technology Space Systems Engineering Conference, Cork, Ireland, 7–9 September 2005; Volume 3. Paper no. GT-SSEC.D.3. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, B. United States test of the small-satellite XSS-11 system. Aerosp. China 2006, 22–25. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=04fY48Ac_vyzH-YAnz7_X2XZMWOoh7jy9eDaxkE8tWEcaBDsITCM6OOANqQ9PEGihquZLU7SNCvnGTnOvau9V-EKJRjaMqWXOx43hGVuWhaOwGHY5TMRVX8YcfDLWOzMSJh5AHOUG1B_1mv1IZKyMdJMWptlZLiByCa0jIBdZVuFNyC_4oIFBA==&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 23 April 2025).
- Malaviarachchi, P.; Reedman, T.; Allen, A.; Sinclair, D. A Small Satellite Concept for On-Orbit Servicing of Spacecraft. 2003. Available online: https://digitalcommons.usu.edu/smallsat/2003/All2003/29/ (accessed on 28 September 2023).
- Bosse, A.B.; Barnds, W.J.; Brown, M.A.; Creamer, N.G.; Feerst, A.; Henshaw, C.G.; Hope, A.S.; Kelm, B.E.; Klein, P.A.; Pipitone, F.; et al. SUMO: Spacecraft for the universal modification of orbits. In Proceedings of the Spacecraft Platforms and Infrastructure, Orlando, FL, USA, 12–16 April 2004; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2004; Volume 5419, pp. 36–46. [Google Scholar]
- Friend, R.B. Orbital express program summary and mission overview. In Proceedings of the Sensors and Systems for Space Applications II, Orlando, FL, USA, 16–20 March 2008; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2008; Volume 6958, pp. 11–21. [Google Scholar]
- Henshaw, C.G. The darpa phoenix spacecraft servicing program: Overview and plans for risk reduction. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Artificial Intelligence, Robotics and Automation in Space (i-SAIRAS), Montreal, QC, Canada, 17–19 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, P. Development Analysis of Foreign On-orbit Assembly Technologies. Space Int. 2016, 61–64. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=04fY48Ac_vxrhlp2DLgSVuPPNbWw23VGxd704ELtqshW_VsrdqWLc7fFcsHTgEHpY2nzesG0urnAReV4C2dy4f3r_MQjBW5H-oaYhiu9UWeRUECoSpvf4M67QA0g3wq7EkbwmzU1l_S14O6dbY8Mz5lMhREYqW1S_z7uGiQpolL6d1eRYO1pBA==&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 23 April 2025).
- Benedict, B.L. Rationale for need of in-orbit servicing capabilities for GEO spacecraft. In Proceedings of the AIAA SPACE 2013 Conference and Exposition, San Diego, CA, USA, 10–12 September 2013; p. 5444. [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg, L.D.; Budinoff, J.; MacEwen, H.; Matthews, G.; Postman, M. Modular assembled space telescope. Opt. Eng. 2013, 52, 091802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacEwen, H.A. In-space infrastructures and the modular assembled space telescope (MAST). In Proceedings of the UV/Optical/IR Space Telescopes and Instruments: Innovative Technologies and Concepts VI, San Diego, CA, USA, 25–29 August 2013; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2013; Volume 8860, pp. 49–60. [Google Scholar]
- Henry, C. DARPA Seeking Private Partners for In-Orbit Servicing Program. 2016. Available online: https://www.satellitetoday.com/government-military/2016/03/28/darpa-seeking-private-partners-for-in-orbit-servicing-program/ (accessed on 1 December 2023).
- Duke, H. On-Orbit Servicing; Center for Strategic and International Studies: Washington, DC, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
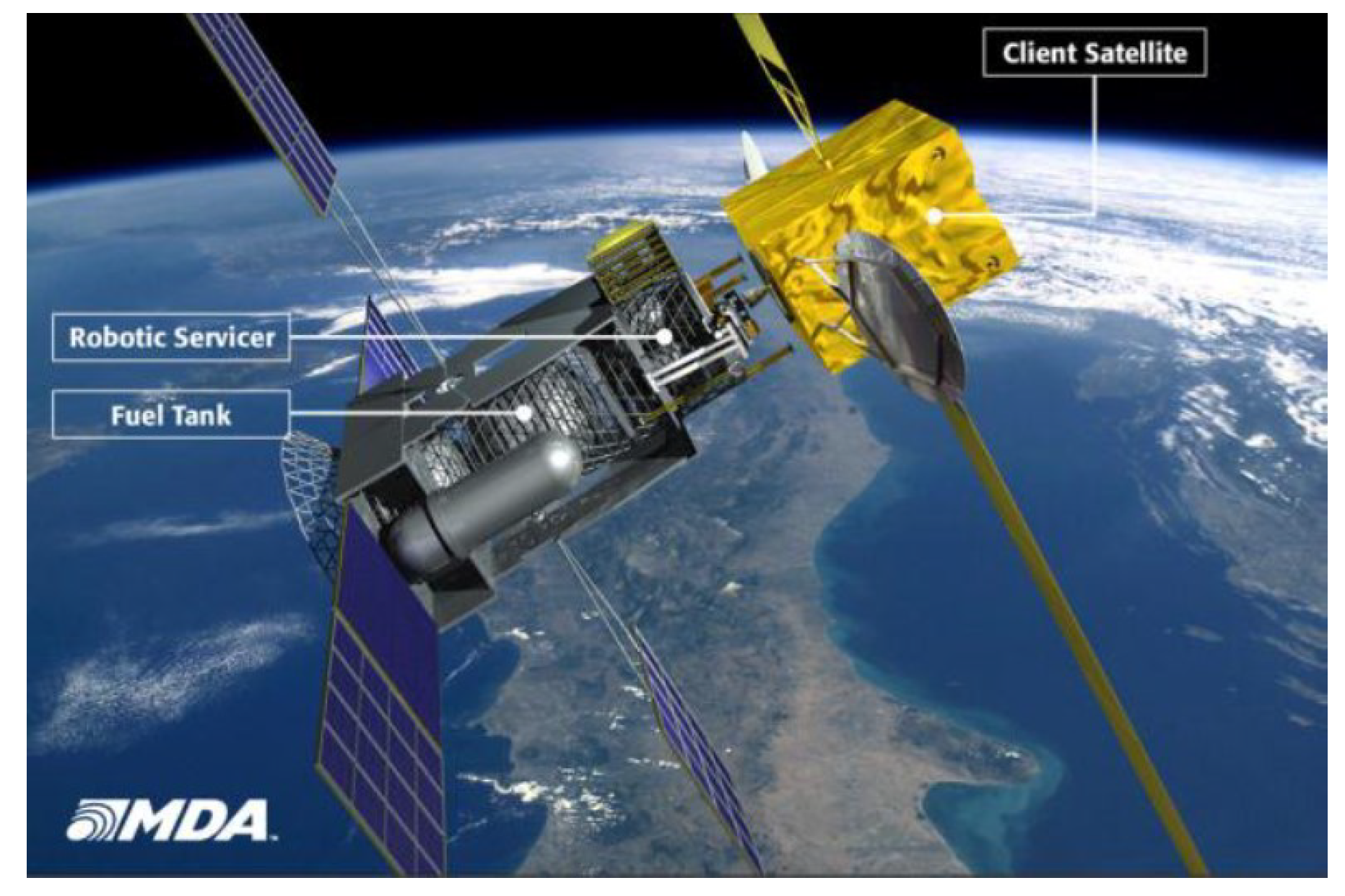
- Reed, B.B.; Smith, R.C.; Naasz, B.J.; Pellegrino, J.F.; Bacon, C.E. The restore-L servicing mission. In Proceedings of the AIAA SPACE 2016, Long Beach, CA, USA, 13–16 September 2016; p. 5478. [Google Scholar]
- NASA. On-Orbit Servicing, Assembly, and Manufacturing 1 (OSAM-1). 2023. Available online: https://www.nasa.gov/mission/on-orbit-servicing-assembly-and-manufacturing-1/ (accessed on 28 November 2023).
- Coll, G.T.; Webster, G.; Pankiewicz, O.; Schlee, K.; Aranyos, T.; Nufer, B.; Fothergill, J.; Tamasy, G.; Kandula, M.; Felt, A.; et al. Satellite servicing projects division restore-L propellant transfer subsystem progress 2020. In Proceedings of the AIAA Propulsion and Energy 2020 Forum, Virtual Event, 24–28 August 2020; p. 3795. [Google Scholar]
- NASA. NASA’s Dragonfly Project Demonstrates Robotic Satellite Assembly Critical to Future Space Infrastructure Development. 2017. Available online: https://www.nasa.gov/technology/nasas-dragonfly-project-demonstrates-robotic-satellite-assembly-critical-to-future-space-infrastructure-development/ (accessed on 28 November 2023).
- Arney, D.; Mulvaney, J.; Williams, C.; Stockdale, C.; Gelin, N.; le Gouellec, P. In-space Servicing, Assembly, and Manufacturing (ISAM) State of Play-2023 Edition. In Proceedings of the Consortium for Space Mobility and ISAM Capabilities (COSMIC) Kickoff, College Park, MD, USA, 7–8 November 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Dorsey, J.; Watson, J. Space assembly of large structural system architectures (SALSSA). In Proceedings of the AIAA SPACE 2016, Long Beach, CA, USA, 13–16 September 2016; p. 5481. [Google Scholar]
- NASA. NASA Puts In-Space Assembly Robots to the Test. 2018. Available online: https://www.nasa.gov/news-release/nasa-puts-in-space-assembly-robots-to-the-test/ (accessed on 28 November 2023).
- NASA. Orbital ATK Supports Ground Testing on CIRAS at NASA’s Langley Research Center. 2017. Available online: https://www.nasa.gov/missions/tech-demonstration/orbital-atk-supports-ground-testing-on-ciras-at-nasas-langley-research-center/ (accessed on 28 November 2023).
- Patane, S.; Joyce, E.R.; Snyder, M.P.; Shestople, P. Archinaut: In-space manufacturing and assembly for next-generation space habitats. In Proceedings of theAIAA SPACE and Astronautics Forum and Exposition, Orlando, FL, USA, 12–14 September 2017; p. 5227. [Google Scholar]
- NASA. On-Orbit Servicing, Assembly, and Manufacturing 2 (OSAM-2). 2023. Available online: https://www.nasa.gov/mission/on-orbit-servicing-assembly-and-manufacturing-2-osam-2/ (accessed on 28 November 2023).
- Bualat, M.G.; Smith, T.; Smith, E.E.; Fong, T.; Wheeler, D. Astrobee: A new tool for ISS operations. In Proceedings of the 2018 SpaceOps Conference, Marseille, France, 28 May–1 June 2018; p. 2517. [Google Scholar]
- NASA. NASA’s Honey Astrobee Robot Returns to Space. 2023. Available online: https://www.nasa.gov/missions/station/iss-research/honey-astrobee-returns-space/ (accessed on 16 October 2023).
- Kwok-Choon, S.T.; Romano, M.; Hudson, J. Orbital hopping maneuvers with Astrobee on-board the International Space Station. Acta Astronaut. 2023, 207, 62–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NASA. NASA Seeks Input for Astrobee Free-Flying Space Robots. Available online: https://www.nasa.gov/technology/robotics/nasa-seeks-input-for-astrobee-free-flying-space-robots/ (accessed on 16 December 2024).
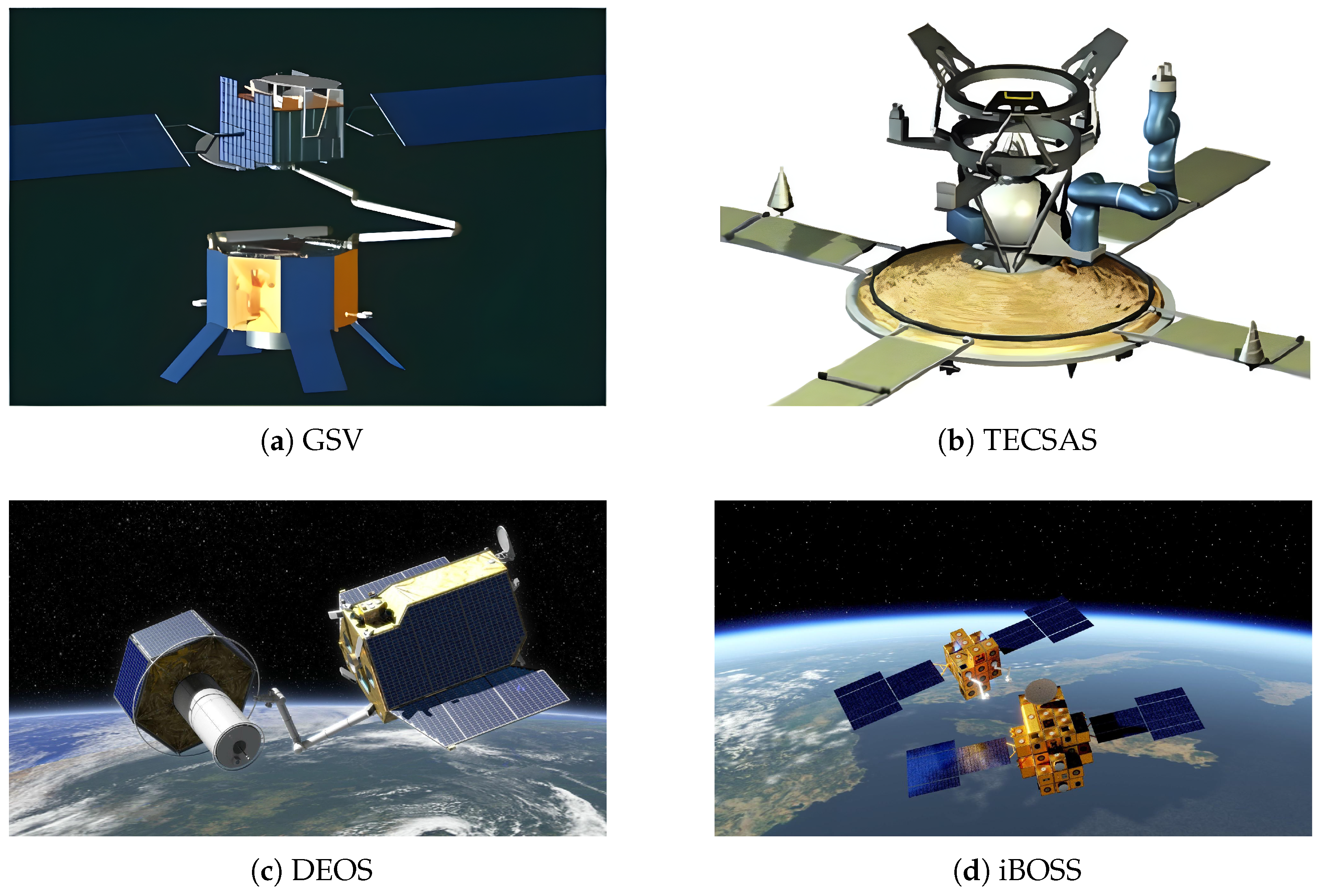
- ESA. The Geostationary Servicing Vehicle (GSV). 2011. Available online: https://www.esa.int/Enabling_Support/Space_Engineering_Technology/Automation_and_Robotics/The_Geostationary_Servicing_Vehicle_GSV (accessed on 23 October 2023).
- Yasui, Y.; Yasaka, T. Geostationary Service Vehicle (GSV) and Its Potentiality in Space Business. J. Space Technol. Sci. 1990, 6, 1_32–1_39. [Google Scholar]
- ESA. Geostationary Servicing Robotics. 2011. Available online: https://www.esa.int/Enabling_Support/Space_Engineering_Technology/Automation_and_Robotics/Geostationary_servicing_robotics (accessed on 23 October 2023).
- Martin, E.; Dupuis, E.; Piedboeuf, J.C.; Doyon, M. The TECSAS mission from a Canadian perspective. In Proceedings of the 8th International Symposium on Artificial Intelligence and Robotics and Automation in Space (i-SAIRAS), Munich, Germany, 5–8 September 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Landzettel, K.; Brunner, B.; Lampariello, R.; Preusche, C.; Reintsema, D.; Hirzinger, G.; Center, D.G.A. System prerequisites and operational modes for on orbit servicing. In Proceedings of the ISTS International Symposium on Space Technology and Science, Miyazaki, Japan, 30 May–6 June 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Wolf, T.; Reintsema, D.; Sommer, B.; Rank, P.; Sommer, J. Mission deos proofing the capabilities of german’s space robotic technologies. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Artificial Intelligence, Robotics and Automation in Space (i-SAIRAS), Turin, Italy, 4–7 September 2012. [Google Scholar]
- DLR. COUNTDOWN 15 (Hohe Auflösung). 2011. Available online: https://www.dlr.de/en/media/publications/magazines/15-countdown-hi-res (accessed on 11 November 2023).
- Reintsema, D.; Sommer, B.; Wolf, T.; Theater, J.; Radthke, A.; Naumann, W.; Rank, P.; Sommer, J. DEOS-the in-flight technology demonstration of german’s robotics approach to dispose malfunctioned satellites. In Proceedings of the ESA 11th Symposium on Advanced Space Technologies in Robotics and Automation, Noordwijk, The Netherlands, 12–14 April 2011; p. 10. [Google Scholar]
- Oberländer, J.; Uhl, K.; Pfotzer, L.; Göller, M.; Rönnau, A.; Dillmann, R. Management and manipulation of modular and reconfigurable satellites. In Proceedings of the ROBOTIK 2012: 7th German Conference on Robotics, Munich, Germany, 21–22 May 2012; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Kortman, M.; Ruhl, S.; Weise, J.; Kreisel, J.; Schervan, T.; Schmidt, H.; Dafnis, A. Building block based iBoss approach: Fully modular systems with standard interface to enhance future satellites. In Proceedings of the 66th International Astronautical Congress, Jerusalem, Israel, 12–16 October 2015; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Institut für Strukturmechanik und Leichtbau (SLA). iBOSS-2 (Intelligent Building Blocks for On-Orbit Satellite Servicing). 2015. Available online: https://www.sla.rwth-aachen.de/cms/Institut-fuer-Strukturmechanik-und-Leichtbau/Forschung/Projekte/~gtfd/iBOSS2/ (accessed on 13 November 2023).
- Institut für Strukturmechanik und Leichtbau (SLA). iBOSS-3 (Intelligent Building Blocks for On-Orbit Satellite Servicing). 2023. Available online: https://www.sla.rwth-aachen.de/cms/Institut-fuer-Strukturmechanik-und-Leichtbau/Forschung/Projekte/Abgeschlossene-Projekte/~lhor/iBOSS-3/ (accessed on 13 November 2023).
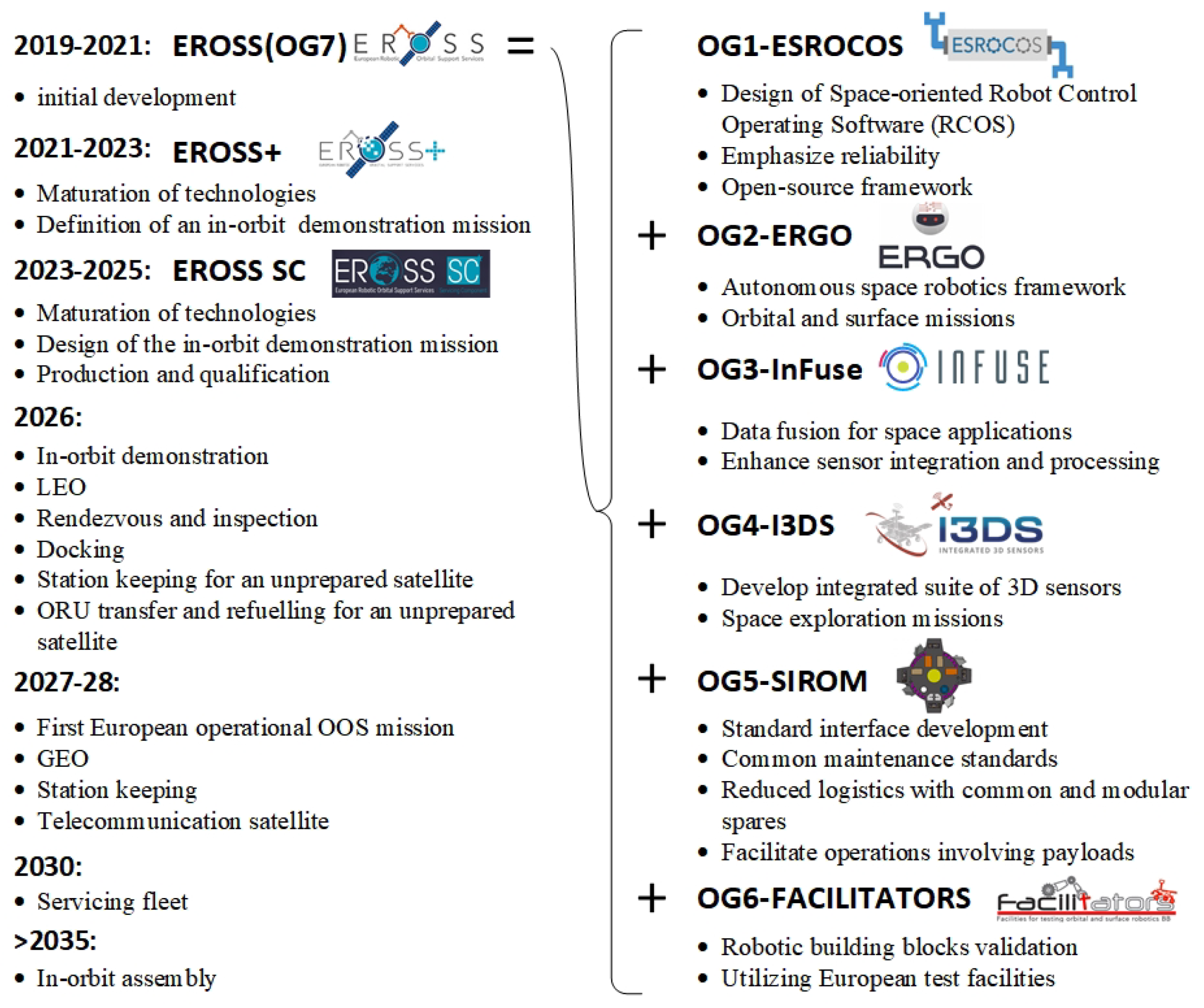
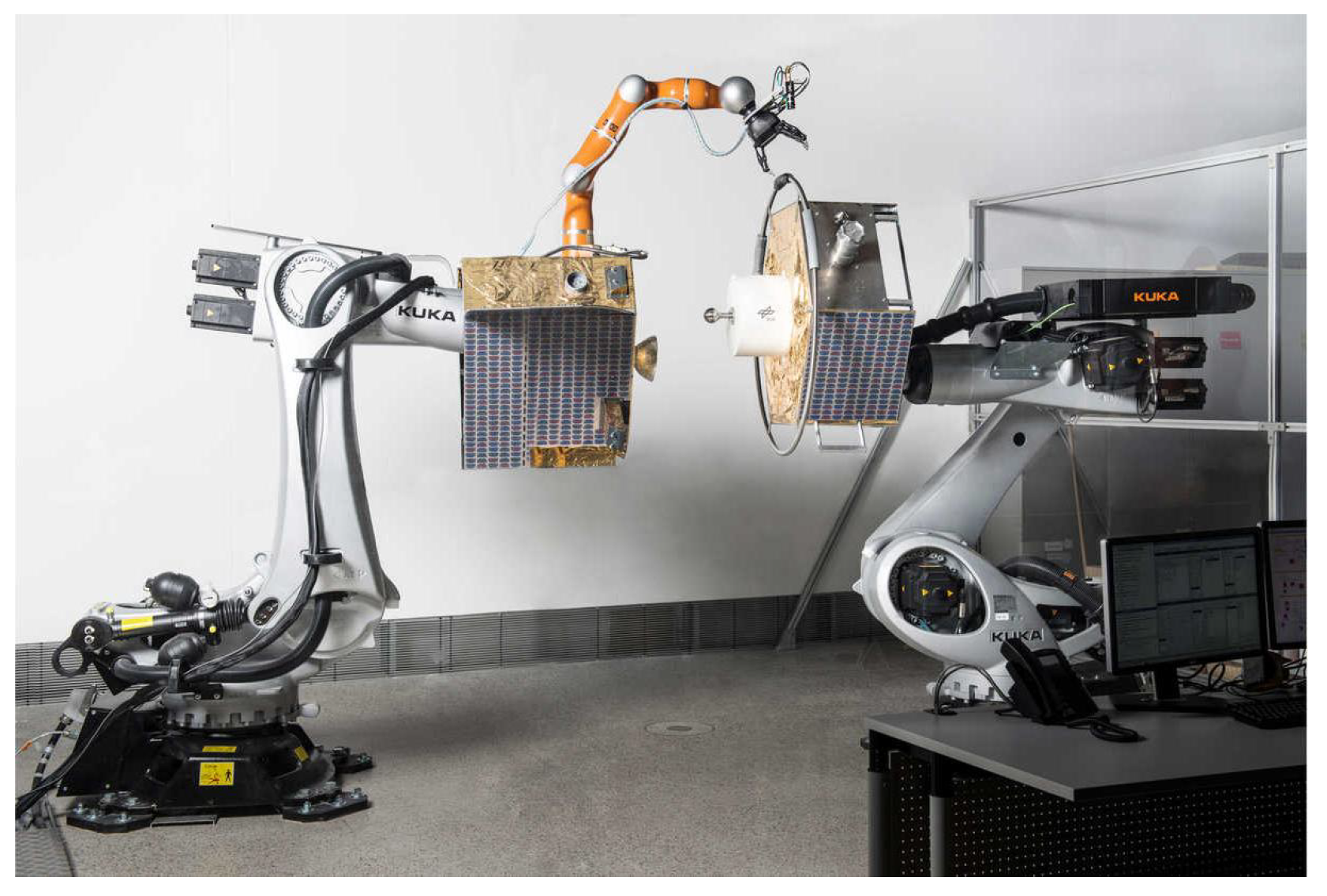
- Roa, M.A.; Beyer, A.; Rodríguez, I.; Stelzer, M.; de Stefano, M.; Lutze, J.P.; Mishra, H.; Elhardt, F.; Grunwald, G.; Dubanchet, V.; et al. EROSS: In-Orbit Demonstration of European Robotic Orbital Support Services. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, MT, USA, 2–9 March 2024; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2024; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- PIAP Space Sp. z o.o. SRC Operational Grants. Available online: https://eross-h2020.eu/src-operational-grants (accessed on 13 November 2024).
- PIAP Space Sp. z o.o. Application Context and Needs. Available online: https://eross-h2020.eu/eross/about-us/strategic-research-cluster (accessed on 13 November 2024).
- EROSS SC. Our Mission and Values. Available online: https://eross-sc.eu/about/what-is-eross-sc/ (accessed on 13 November 2024).
- Artigas, J.; De Stefano, M.; Rackl, W.; Lampariello, R.; Brunner, B.; Bertleff, W.; Burger, R.; Porges, O.; Giordano, A.; Borst, C.; et al. The OOS-SIM: An on-ground simulation facility for on-orbit servicing robotic operations. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Seattle, WA, USA, 26–30 May 2015; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 2854–2860. [Google Scholar]
- Giordano, A.M.; Ott, C.; Albu-Schäffer, A. Coordinated control of spacecraft’s attitude and end-effector for space robots. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2019, 4, 2108–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DLR Institute of Robotics and Mechatronics. EROSS+. Available online: https://www.dlr.de/en/rm/research/projects/completed-projects/eross (accessed on 15 December 2024).
- DLR Institute of Robotics and Mechatronics. EROSS IOD. Available online: https://www.dlr.de/en/rm/research/projects/eross-iod (accessed on 15 December 2024).
- eoPortal. ETS-VII (Engineering Test Satellite VII). Available online: https://www.eoportal.org/satellite-missions/ets-vii#spacecraft (accessed on 23 September 2023).
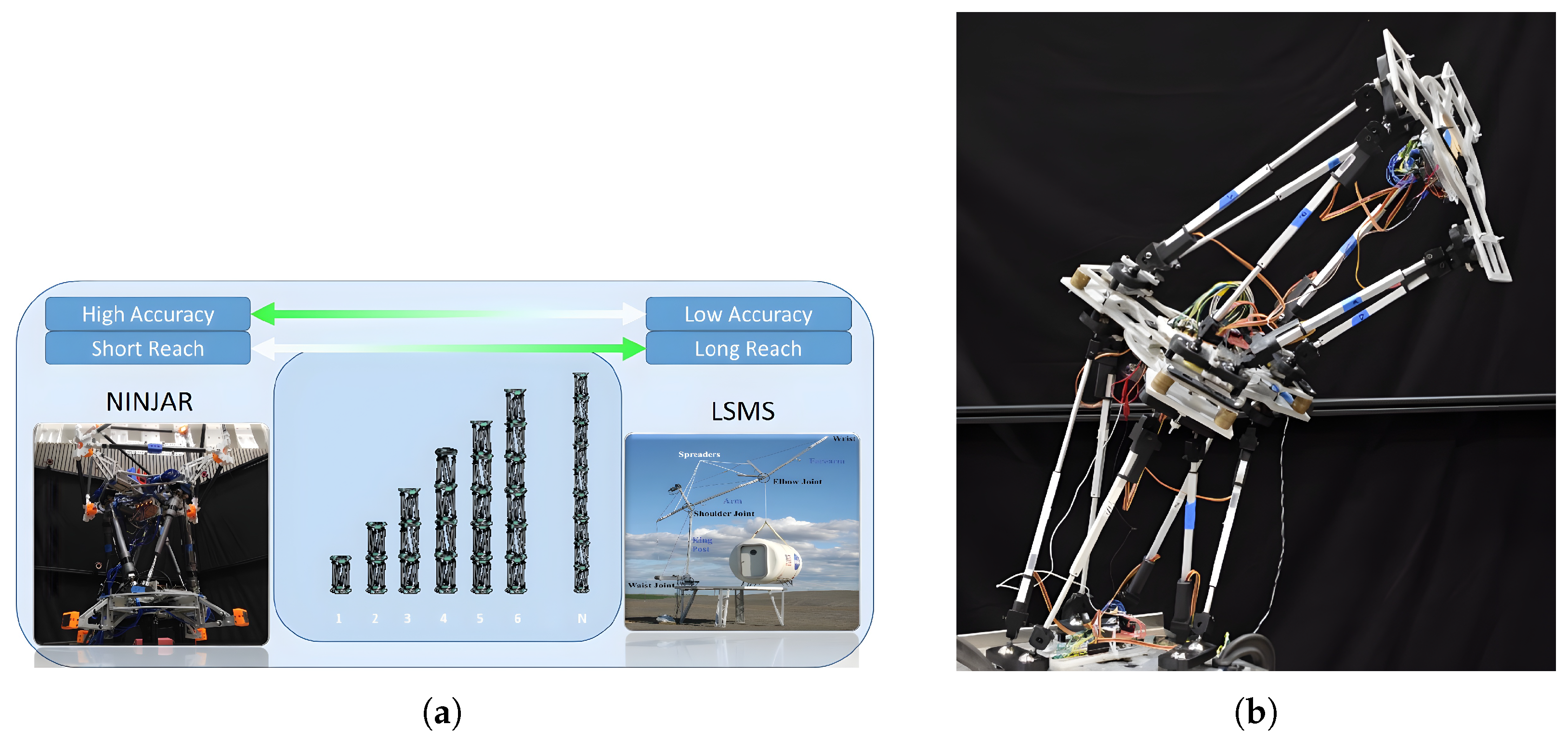
- Skaff, S.; Staritz, P.; Whittaker, W. Skyworker: Robotics for space assembly, inspection and maintenance. In Proceedings of the Space Studies Institute Conference, Canaveral, FL, USA, 1–3 May 2001; pp. 4180–4185. [Google Scholar]
- Staritz, P.J.; Skaff, S.; Urmson, C.; Whittaker, W. Skyworker: A robot for assembly, inspection and maintenance of large scale orbital facilities. In Proceedings of the 2001 ICRA: IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (Cat. No. 01CH37164), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 21–26 May 2001; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2001; Volume 4, pp. 4180–4185. [Google Scholar]
- Hoyt, R.P.; Cushing, J.; Jimmerson, G.; Slostad, J.; Dyer, R.; Alvarado, S. SpiderFab: Process for On-Orbit Construction of Kilometer-Scale Apertures; Technical Report; NASA: Washington, DC, USA, 2018.
- NASA. SpiderFab: Architecture for On-Orbit Construction of Kilometer-Scale Apertures. 2013. Available online: https://www.nasa.gov/general/spiderfab-architecture-for-on-orbit-construction-of-kilometer-scale-apertures/#.VFOnmt7j4yB (accessed on 16 November 2023).
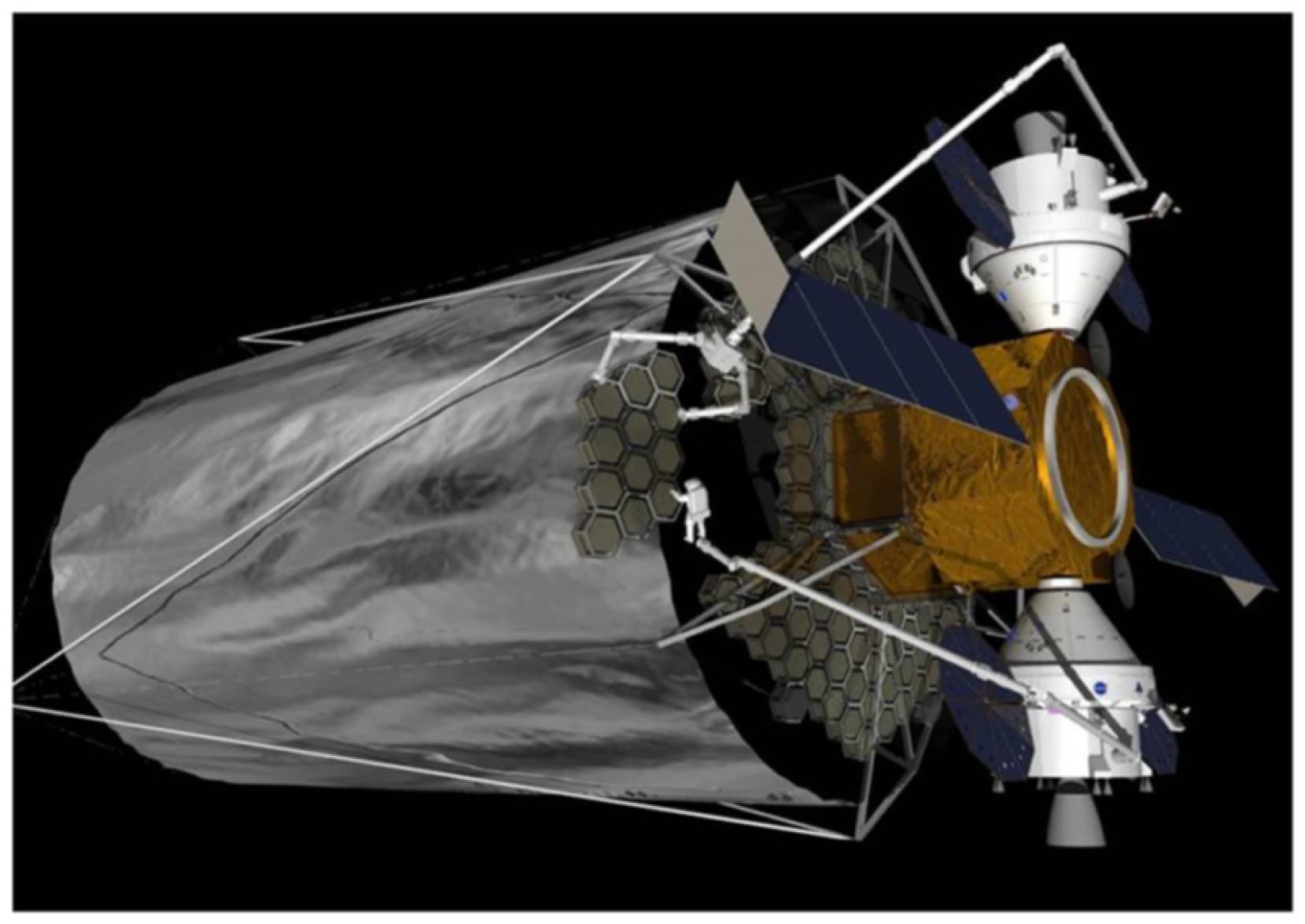
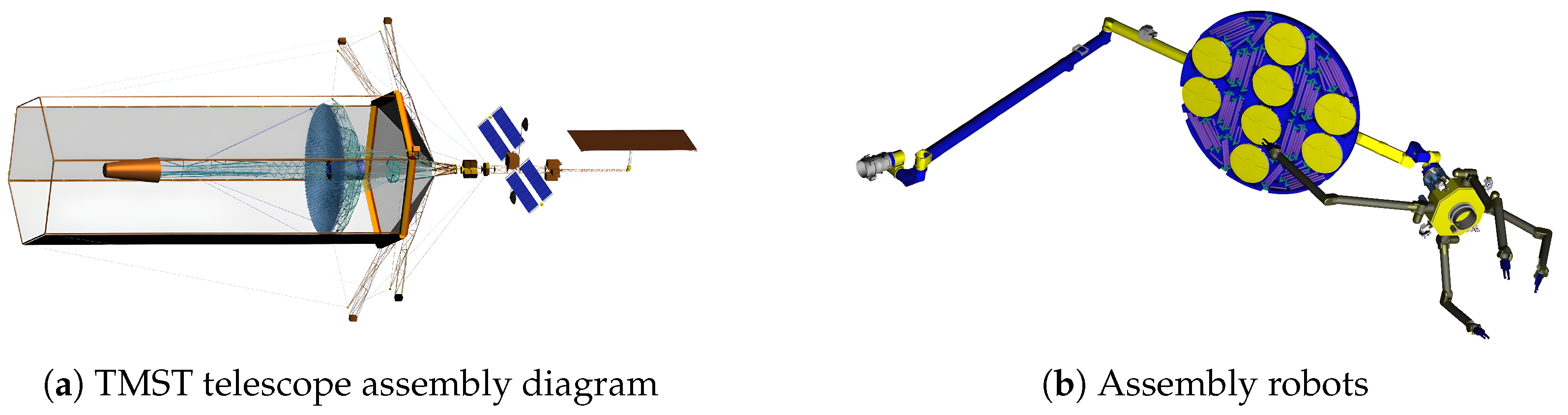
- Lee, N.; Backes, P.; Burdick, J.; Pellegrino, S.; Fuller, C.; Hogstrom, K.; Kennedy, B.; Kim, J.; Mukherjee, R.; Seubert, C.; et al. Architecture for in-space robotic assembly of a modular space telescope. J. Astron. Telesc. Instrum. Syst. 2016, 2, 041207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogstrom, K.; Backes, P.; Burdick, J.; Kennedy, B.; Kim, J.; Lee, N.; Malakhova, G.; Mukherjee, R.; Pellegrino, S.; Wu, Y.H. A robotically-assembled 100-meter space telescope. In Proceedings of the 65th International Astronautical Congress (IAC-2014), Toronto, ON, Canada, 29 September–3 October 2014; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, J.R.; Neilan, J.H.; Mahlin, M.; White, L.M. Assemblers: A modular, reconfigurable manipulator for autonomous in-space assembly. In In Proceedings of the ASCEND 2020, Virtual Event, 16–18 November 2020; p. 4132.
- Trinh, G.; Formoso, O.; Gregg, C.; Taylor, E.; Cheung, K.; Catanoso, D.; Olatunde, T. Hardware Autonomy for Space Infrastructure. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, MT, USA, 4–11 March 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Figliozzi, G. Robot Team Builds High-Performance Digital Structure for NASA. Available online: https://www.nasa.gov/general/robot-team-builds-high-performance-digital-structure-for-nasa/ (accessed on 23 December 2024).
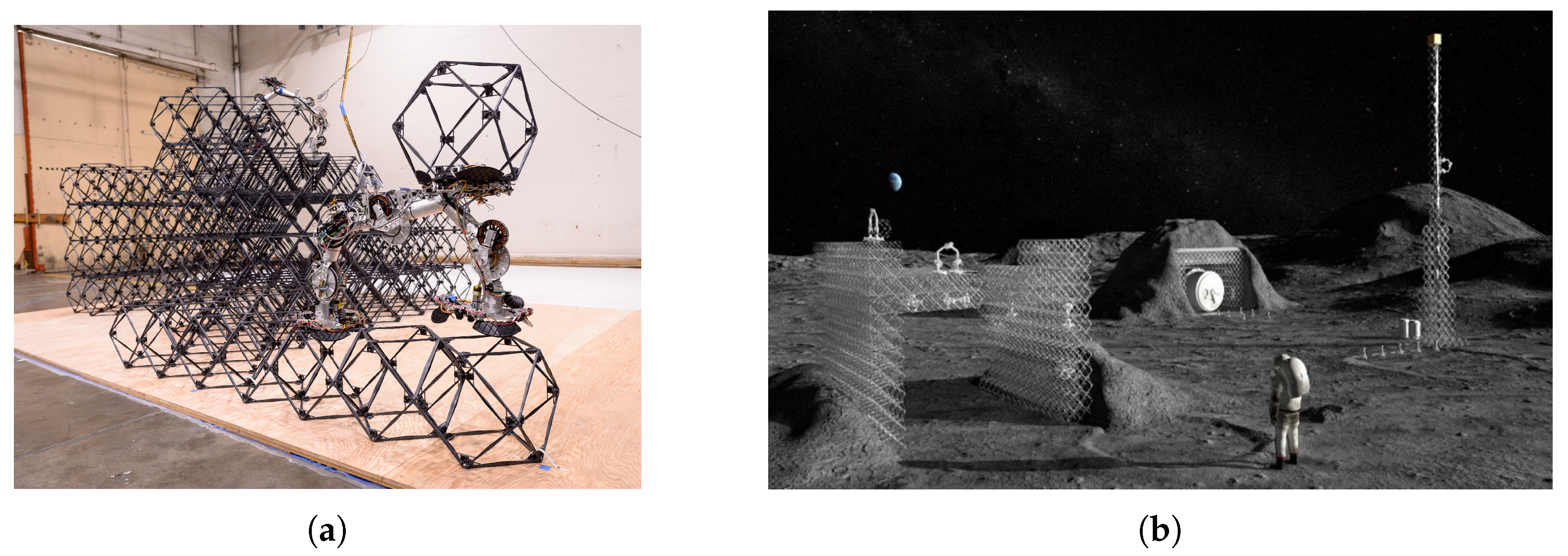
- Gregg, C.E.; Catanoso, D.; Formoso, O.I.B.; Kostitsyna, I.; Ochalek, M.E.; Olatunde, T.J.; Park, I.W.; Sebastianelli, F.M.; Taylor, E.M.; Trinh, G.T.; et al. Ultralight, strong, and self-reprogrammable mechanical metamaterials. Sci. Robot. 2024, 9, eadi2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregg, C.; Cheung, K. Automated Reconfigurable Mission Adaptive Digital Assembly Systems (ARMADAS): Robotically Assembled Sustainable Lunar Infrastructure. In Proceedings of the Lunar Surface Innovation Consortium Spring Meeting (LSIC 2023), Laurel, MD, USA, 24–25 April 2023. [Google Scholar]
- FRAZER-NASH. Frazer-Nash Report for UK Government Shows Feasibility of Space Solar Power. 2021. Available online: https://www.fnc.co.uk/discover-frazer-nash/news/frazer-nash-report-for-uk-government-shows-feasibility-of-space-solar-power/ (accessed on 28 November 2023).
- CIOMP: New Progress in the Development of XunTian Space Telescope. Available online: https://www.cas.cn/spx/202207/t20220728_4843238.shtml (accessed on 23 December 2024).
- Hou, X.; Zhu, M.; Sun, L.; Ding, T.; Huang, Z.; Shi, Y.; Su, Y.; Li, L.; Chen, T.; Lee, C. Scalable self-attaching/assembling robotic cluster (S2A2RC) system enabled by triboelectric sensors for in-orbit spacecraft application. Nano Energy 2022, 93, 106894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Hou, X.; Na, Z.; Zhou, J.; Yu, N.; Liu, S.; Xin, L.; Gao, G.; Liu, Y. Bio-inspired attachment mechanism of dynastes Hercules: Vertical climbing for on-orbit assembly legged robots. J. Bionic Eng. 2024, 21, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
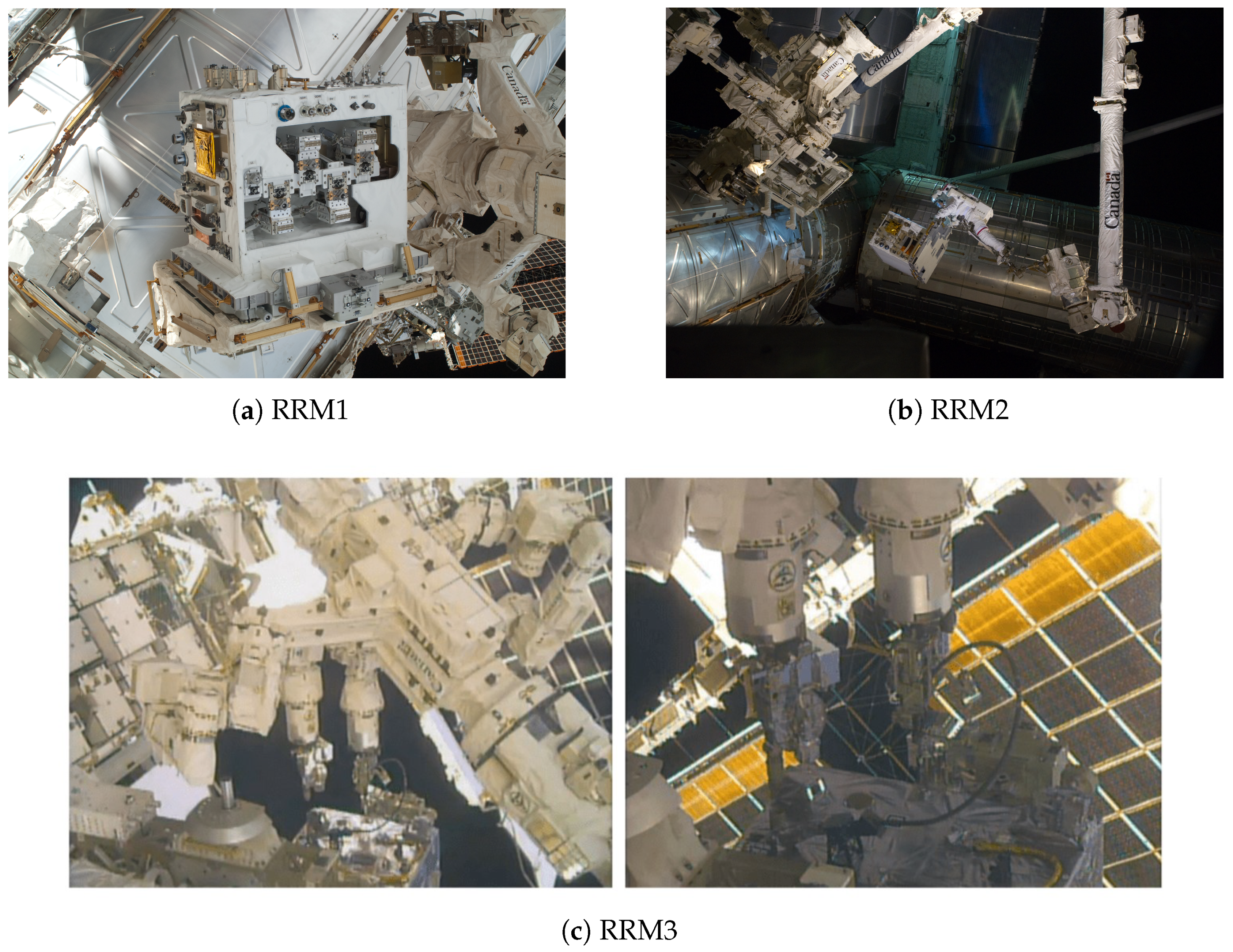
- NASA. Robotic Refueling Mission. 2023. Available online: https://www.nasa.gov/nexis/rrm-1-2/ (accessed on 27 October 2023).
- Breon, S.; Boyle, R.; Francom, M.; DeLee, C.; Francis, J.; Mustafi, S.; Barfknecht, P.; McGuire, J.; Krenn, A.; Zimmerli, G.; et al. Robotic Refueling Mission-3—An overview. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 755, 012002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
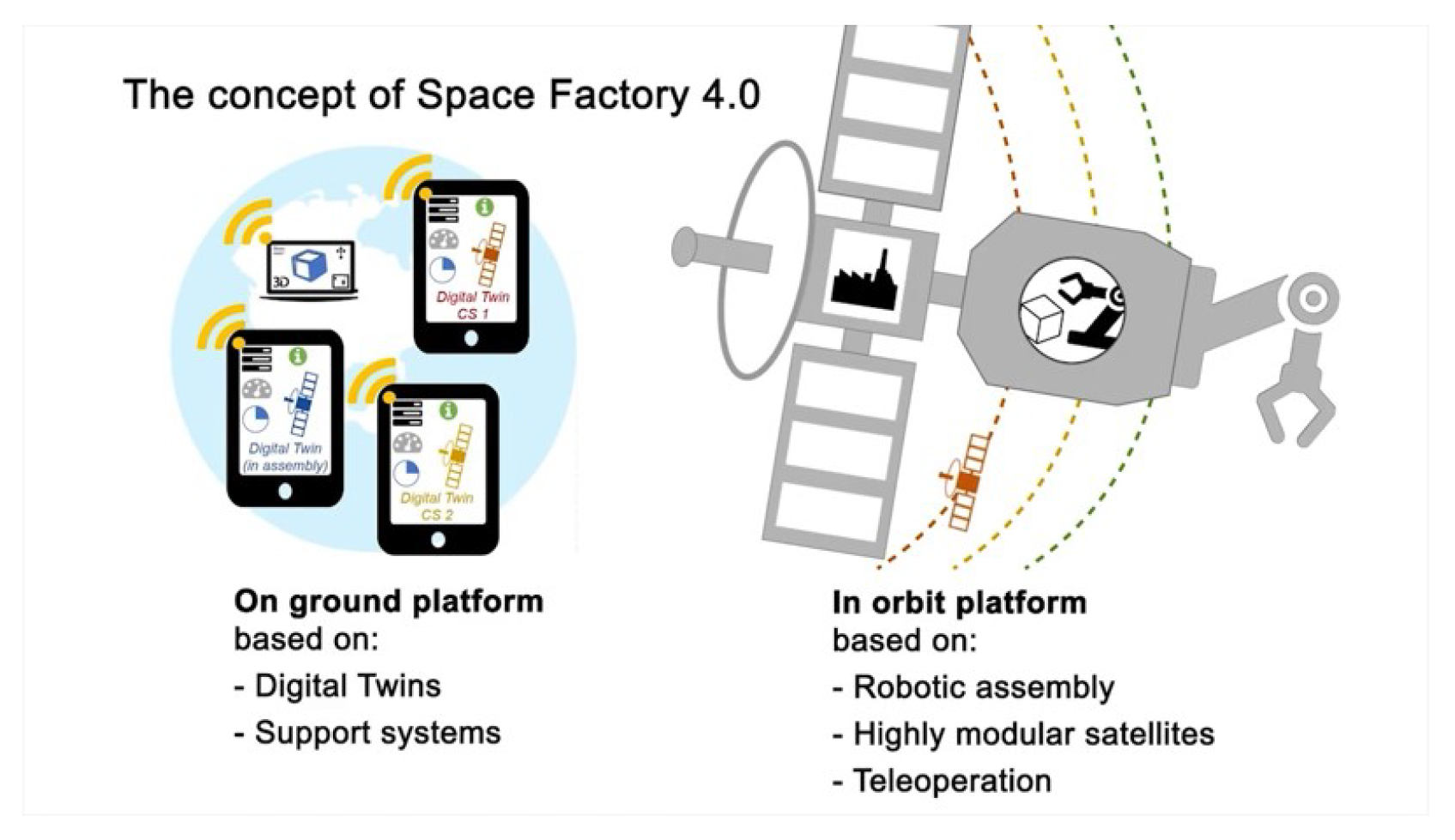
- Weber Martins, T.; Pereira, A.; Hulin, T.; Ruf, O.; Kugler, S.; Giordano, A.; Balachandrand, R.; Benedikt, F.; Lewis, J.; Anderl, R.; et al. Space Factory 4.0-New processes for the robotic assembly of modular satellites on an in-orbit platform based on “Industrie 4.0” approach. In Proceedings of the International Astronautical Congress, IAC, Bremen, Germany, 1–5 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- AIRBUS. Airbus Pioneers First Satellite Factory in Space. 2021. Available online: https://www.airbus.com/en/newsroom/press-releases/2021-03-airbus-pioneers-first-satellite-factory-in-space (accessed on 28 October 2023).
- AIRBUS. In Space Manufacturing and Assembly. 2022. Available online: https://www.airbus.com/en/newsroom/news/2022-05-in-space-manufacturing-and-assembly (accessed on 28 October 2023).
- NASA. Neil Armstrong Test Facility. 2023. Available online: https://www.nasa.gov/neil-armstrong-test-facility/ (accessed on 26 December 2023).
- Fernandez, R.; Allred, J.; Meigs, R.; Greenwalt, C.; Hritz, J.; Otterson, M. Managing Spacecraft Risk with Space Environments Testing via Process Safety Management at the NASA Neil A. Armstrong Test Facility. In Proceedings of the 11th IAASS (International Association for the Advancement of Space Safety) Conference, Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 19–21 October 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Center, G.R. Zero Gravity Research Facility. 2022. Available online: https://www1.grc.nasa.gov/facilities/zero-g/ (accessed on 26 December 2023).
- NASA. What Is Microgravity? 2009. Available online: https://www.nasa.gov/centers-and-facilities/glenn/what-is-microgravity/ (accessed on 26 December 2023).
- Zhao, Y. Harbin Institute of Technology (HIT) is bringing the space station to Earth. Heilongjiang Daily, 15 April 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Harbin Qingtian Intelligent Technology Co., Ltd. PRODUCT. 2024. Available online: http://www.qingtianitech.com/ (accessed on 11 January 2024).
- China Aerospace Science and Industry Corporation Limited. China’s largest vacuum solar simulator successfully developed. Hoisting Conveying Mach. 2016, 33. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=04fY48Ac_vyXQdcfCDhC3mpUzWUBTqIXh3tvTgBG81-OZ3qNGri9-EtZ4SNwlBGpgyeQOhPnD8Rhu9dImhY-MPbMHKpDMEXu-31sjwqsqSh64OwQKFsPnLzn343-d6aqIezypL4nZPhq3l2y_RztMCqVhD16YHlPvLZlfvn3O20dgcsN-xv1vw==&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 23 April 2025).
- Zhao, H.; Zhao, Y.; Tian, H.; An, D.x. Key Techniques and Applications of Space Cellular Robotic System. J. Astronaut. 2018, 39, 1071. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, C. Research on Cell Robot Reconstruction Motion Planning and Trajectory Optimization. Master’s Thesis, Harbin University of Science and Technology, Harbin, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, W.M.; Salemi, B.; Moll, M. Modular, multifunctional and reconfigurable superbot for space applications. In Proceedings of the Space 2006, San Jose, CA, USA, 19–21 September 2006; p. 7405. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.; Yue, X.; Guo, M. Design and Dynamic Simulation Verification of an On-Orbit Operation-Based Modular Space Robot. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 12949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Li, Z.; Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Yuan, H. A Novel Space Robot with Triple Cable-Driven Continuum Arms for Space Grasping. Micromachines 2023, 14, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, M.; Wang, X. Soft Robots for Space Applications: Actuation, Modeling and Sensing. J. Astronaut. 2023, 44, 644. [Google Scholar]
- Gregory, T.; Newman, M. Thermal design considerations of the Robotic Refueling Mission (RRM). In Proceedings of the 41st International Conference on Environmental Systems, Portland, OR, USA, 17–21 July 2011; p. 5072. [Google Scholar]
- Teeple, C.B.; Koutros, T.N.; Graule, M.A.; Wood, R.J. Multi-segment soft robotic fingers enable robust precision grasping. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2020, 39, 1647–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.; Kong, N.; Ren, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, W.; Ma, S. Review of Docking Interface Technology for Orbital Replacement Units. China Mech. Eng. 2020, 31, 1917–1930. [Google Scholar]
- Dorsey, J.; Doggett, W.; Hafley, R.; Komendera, E.; Correll, N.; King, B. An efficient and versatile means for assembling and manufacturing systems in space. In Proceedings of the AIAA SPACE 2012 Conference & Exposition, Pasadena, CA, USA, 11–13 September 2012; p. 5115. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Li, S.; Wang, C.; Chen, M.; Wang, J. Dual-arm Robot Based Compliant Assembly of Space Truss Struts and Spherical Joints. Manned Spacefl. 2020, 26, 741–750. [Google Scholar]
- Leutert, F.; Bohlig, D.; Kempf, F.; Schilling, K.; Mühlbauer, M.; Ayan, B.; Hulin, T.; Stulp, F.; Albu-Schäffer, A.; Kutscher, V.; et al. AI-enabled Cyber–Physical In-Orbit Factory-AI approaches based on digital twin technology for robotic small satellite production. Acta Astronaut. 2024, 217, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Wang, P.; Cheng, X.; Yu, M. Prospect of Interactive Sensing Teleoperation on Orbit Service. Aerosp. Control 2022, 40, 3–10. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.; Zhao, Z.; Yin, H.; Sun, Y.; Shi, L.; Wang, Y. Development and Application of Space Target Situation Awareness and Multi-source Data Fusion. Vac. Cryog. 2023, 29, 543–554. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, M.; Liu, C. Sequence Planning Method for Robotic On-orbit Assemly of Space Truss Structure. J. Astronaut. 2021, 42, 437. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Gao, X.; Zhao, Z.; Huang, Z.; Fu, Y.; Fei, J. Review on Intelligent Planning and Control Technology of Space Manipulator. J. Nanjing Univ. Aeronaut. Astronaut. Hangkong Hangtian Daxue Xuebao 2022, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, G.; Zheng, J.; Wu, Y.; Hou, Z.; Yang, W.; Yuan, H.; Niu, Q. Survey and Expectation of Multi-robot Optimization Layout and Task Allocation. Mach. Tool Hydraul. 2022, 49, 161–167. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Yang, J. Spacecraft Docking and Capture Technology: Review. J. Mech. Eng. 2021, 57, 215–231. [Google Scholar]
- Bar, N.F.; Karakose, M. Collaborative approach for swarm robot systems based on distributed DRL. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2024, 53, 101701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorigo, M.; Theraulaz, G.; Trianni, V. Swarm robotics: Past, present, and future [point of view]. Proc. IEEE 2021, 109, 1152–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Tao, Y.; Lei, X.; Peng, X. Self-organized swarm robot for multi-target trapping based on self-regulated density interaction. Inf. Sci. 2024, 661, 120119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmermann, D.; Plasberg, C.; Graaf, F.; Rönnau, A.; Dillmann, R. AI-Based Assembly Sequence Planning in a Robotic On-Orbit Assembly Application. In Proceedings of the 2024 10th International Conference on Automation, Robotics and Applications (ICARA), Athens, Greece, 22–24 February 2024; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2024; pp. 69–74. [Google Scholar]
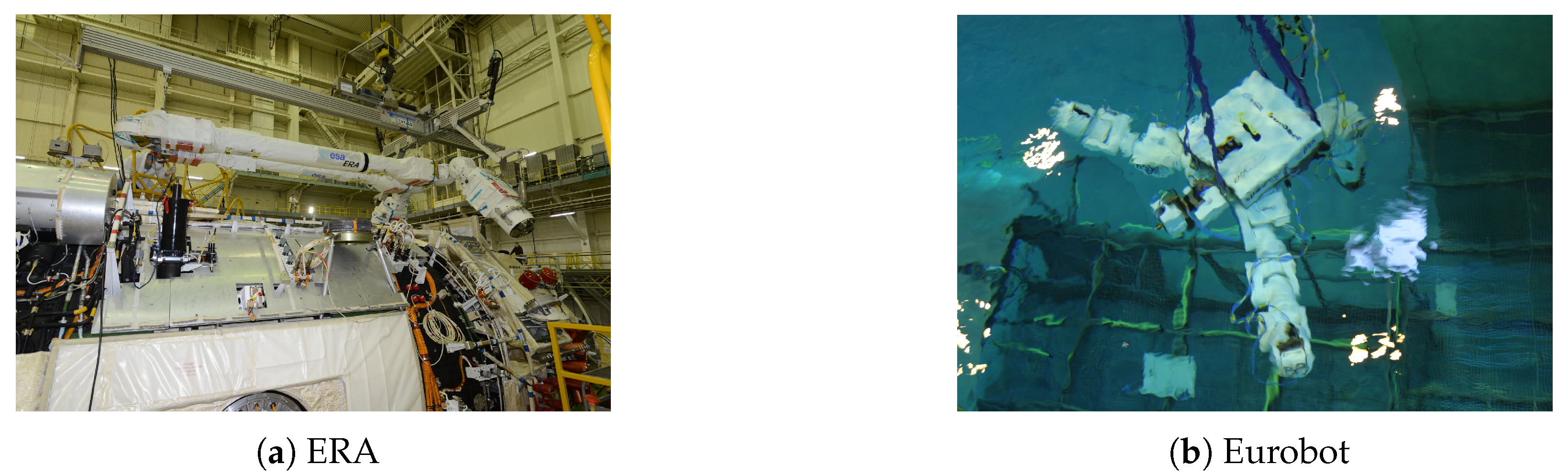
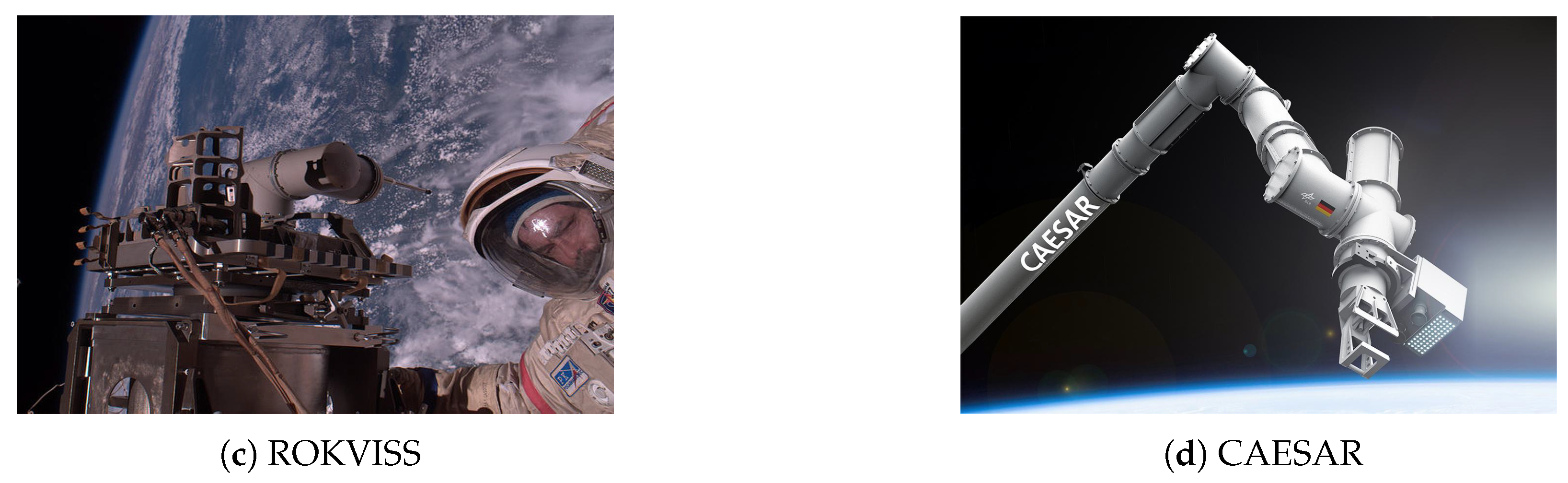
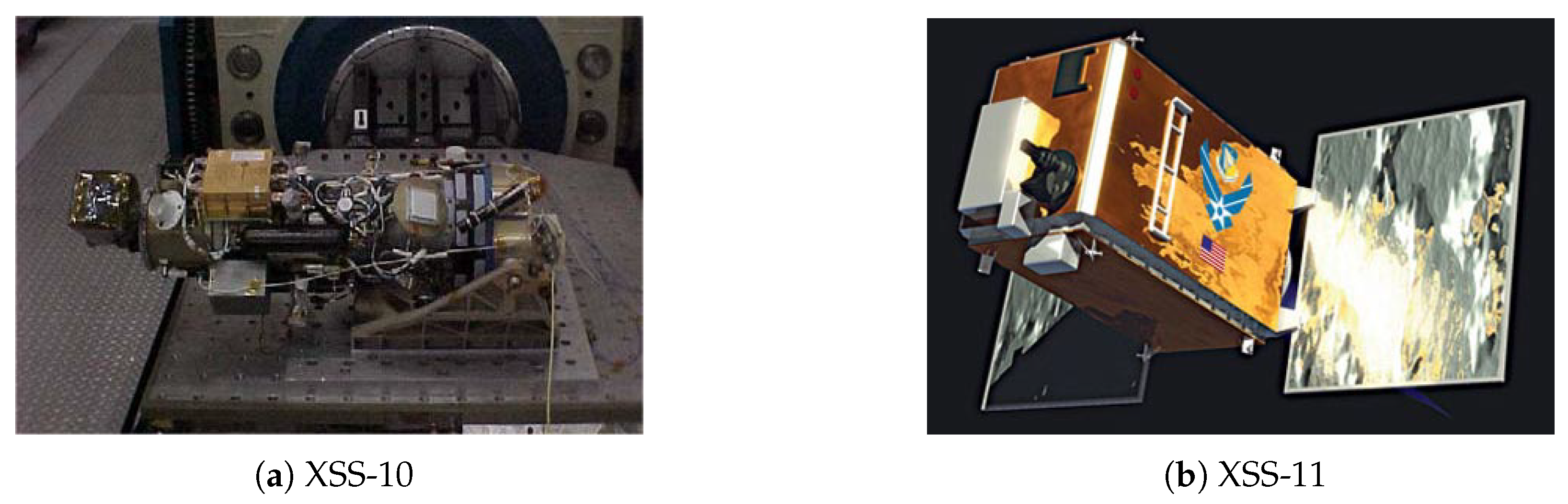
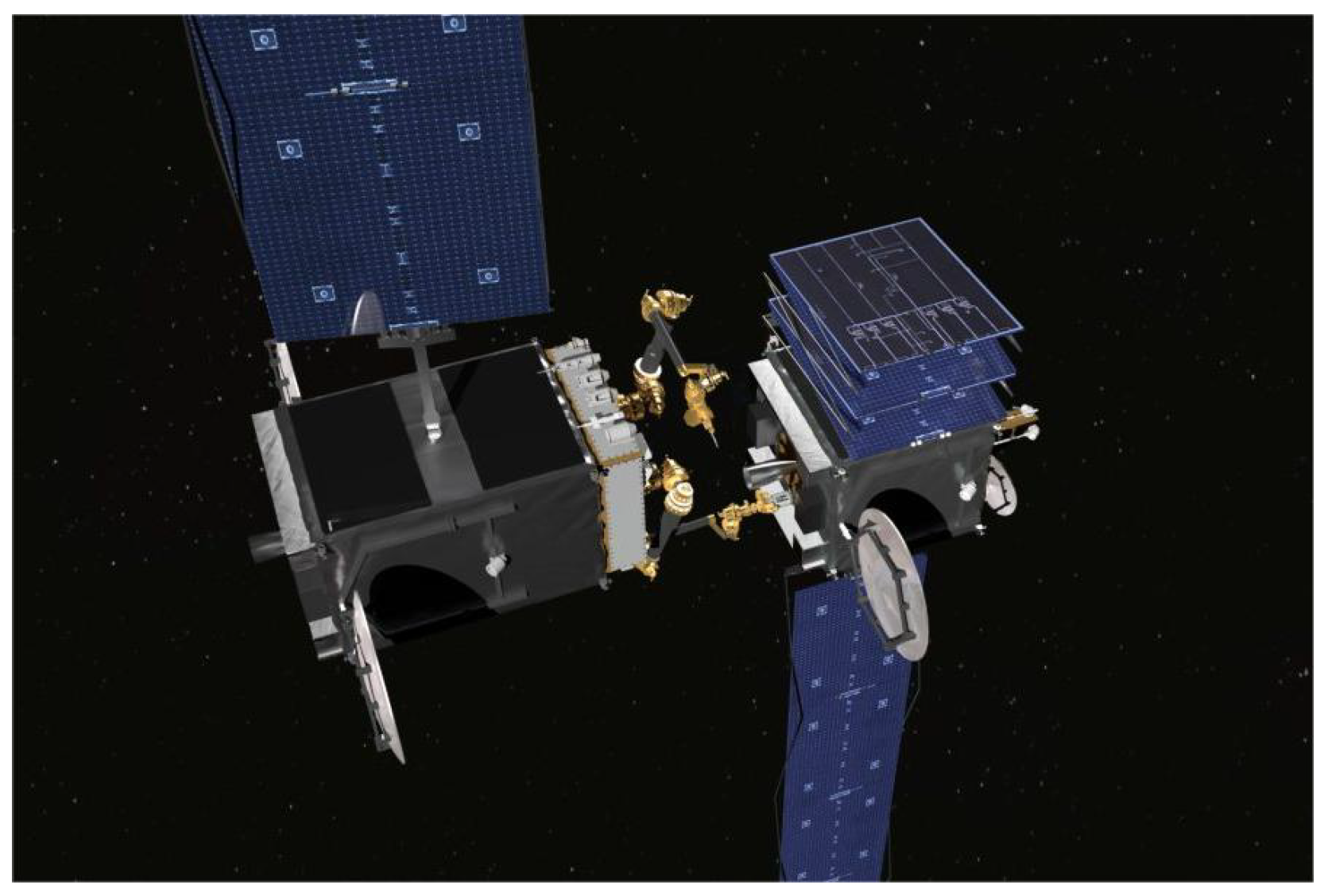
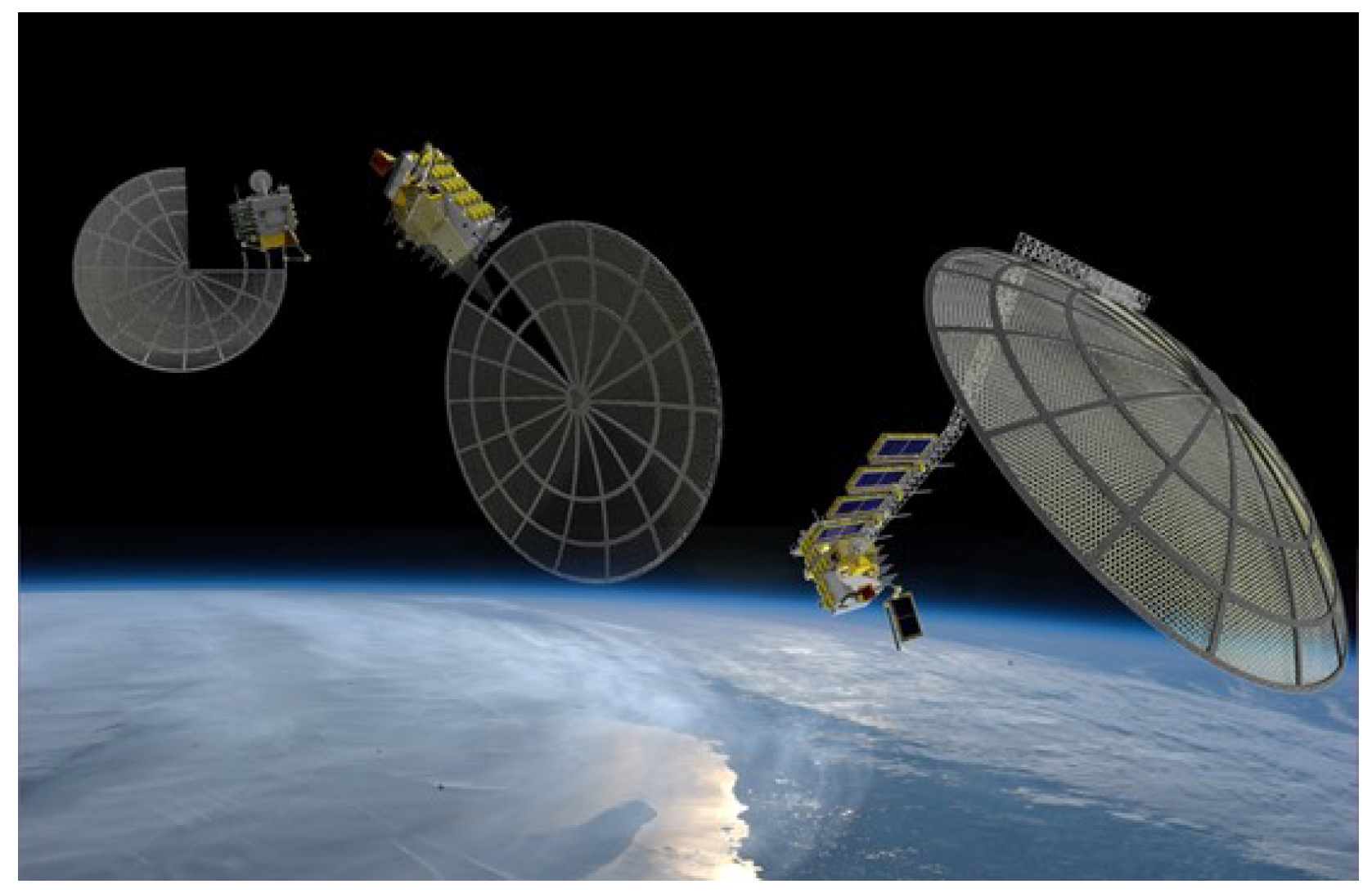


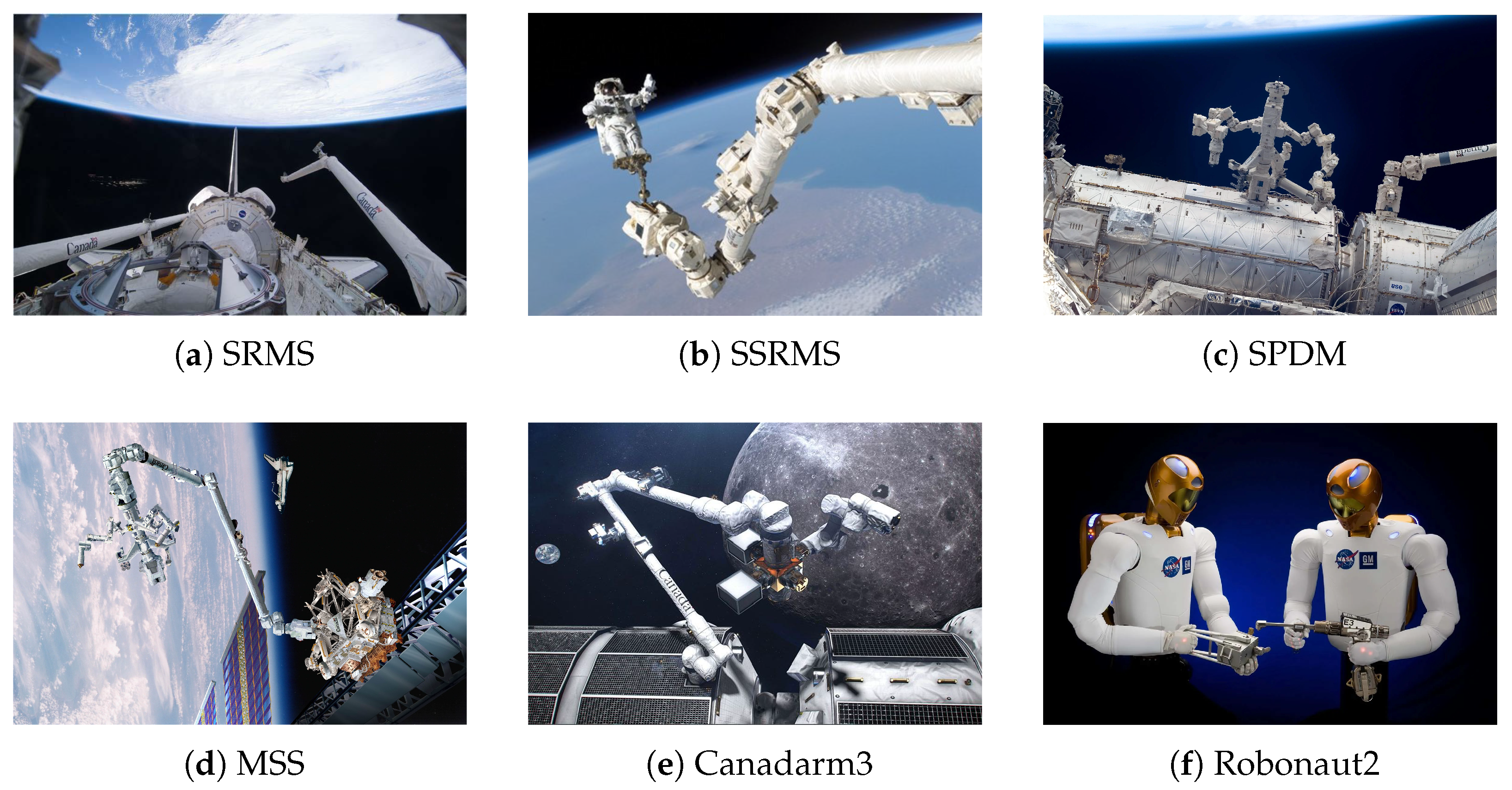


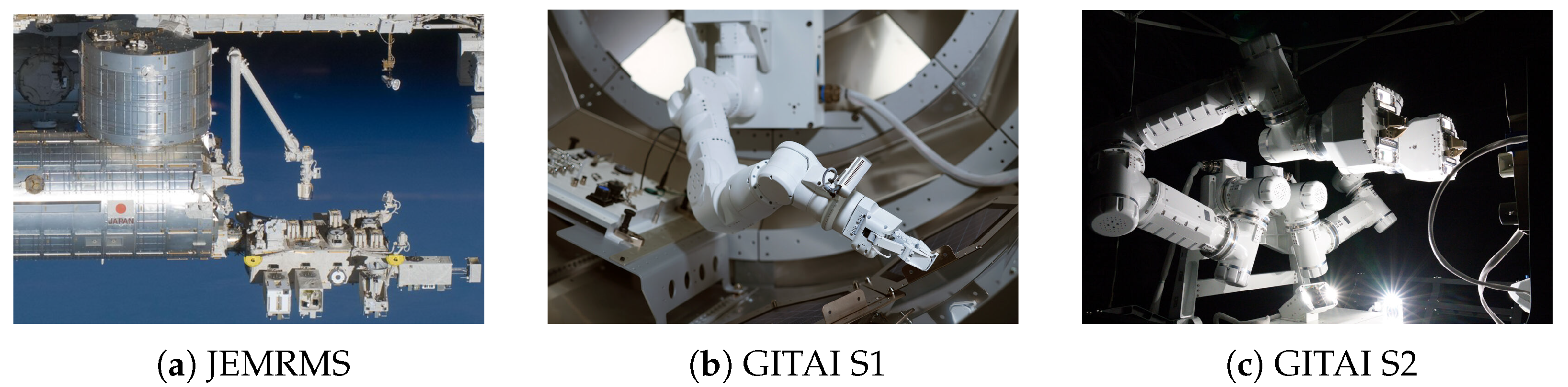





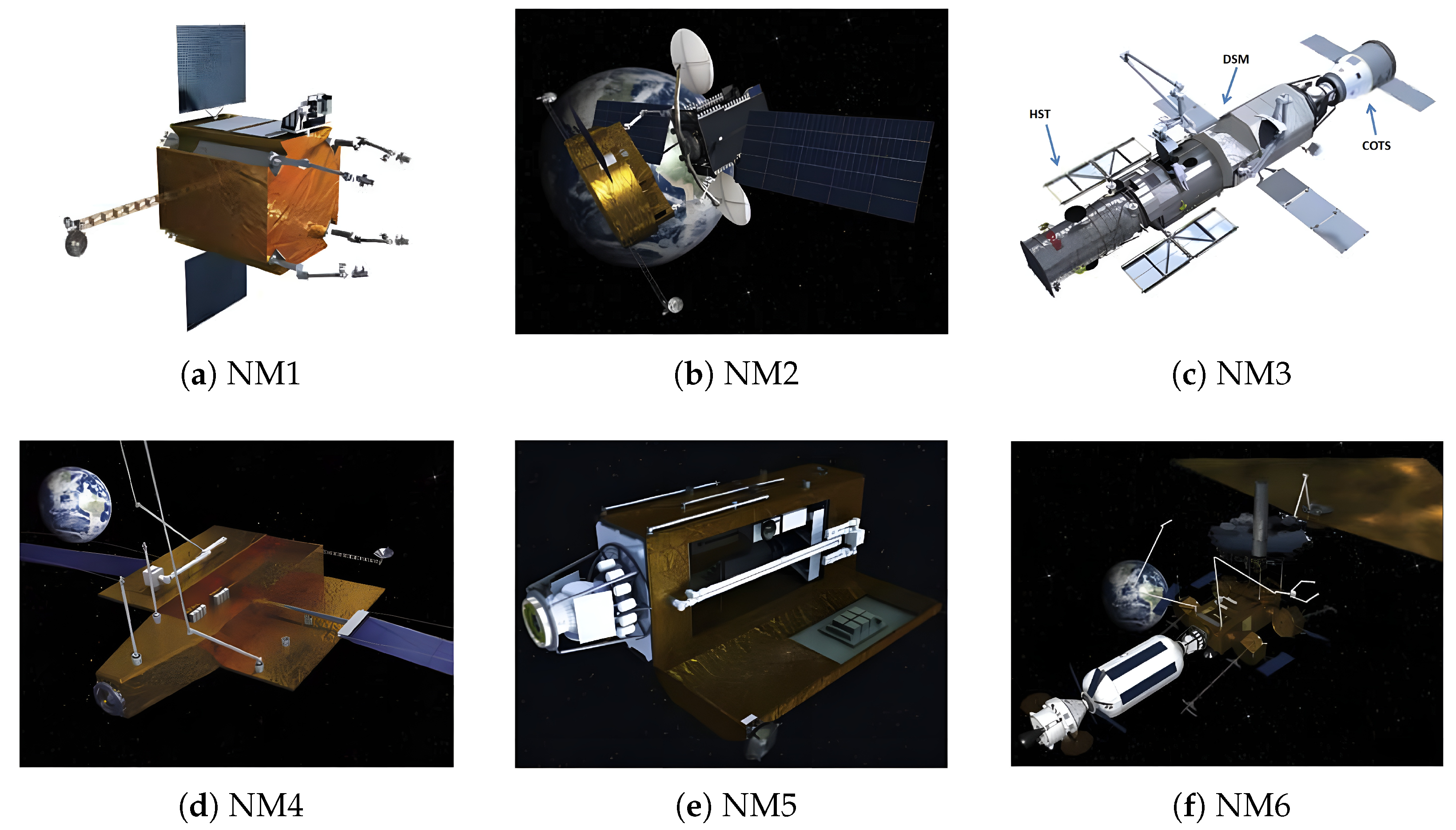


















| No. | Name | Country | Year | Dof | Length/m | Maximum Load/kg | Accuracy | Current State |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | SRMS | Canada | 1981 | 6 | 15.2 | 26,600 | 50.8 mm, 0.1° | On orbit |
| 2 | SSRMS | Canada | 2001 | 7 | 17.6 | 116,000 | 45 mm, 0.71° | On orbit |
| 3 | SPDM | Canada | 2007 | 7 + 1 + 7 | 3.5 | 600 | 6 mm | On orbit |
| 4 | Canadarm3 | Canada | 2012 | 7 | 8.5 | —— | —— | Research |
| 5 | Robonaut2 | America | 2011 | —— | 0.8 | 9 | —— | Returned |
| 6 | ROKVISS | German | 2005 | 2 | 0.5 | —— | —— | Ended |
| 7 | CAESAR | German | 2018 | 7 | 3.1 | —— | —— | Research |
| 8 | ERA | EU | 2021 | 7 | 11.3 | 8000 | 5 mm, 1° | On orbit |
| 9 | Eurobot | EU | 2003 | 3 × 7 | —— | —— | —— | Research |
| 10 | Skybot F-850 | Russia | 2019 | —— | —— | —— | —— | On orbit |
| 11 | ETS-VII | Japan | 1997 | 6 | 2 | —— | —— | Ended |
| 12 | JEMRMS | Japan | 2009 | MA: 6 | MA: 10 | MA: 7000 | MA: 50 mm, 1° | On orbit |
| SFA: 6 | SFA: 2 | SFA: 300 | SFA: 10 mm, 1° | |||||
| 13 | GITAI S1 | Japan | 2021 | 8 | 1 | —— | —— | On orbit |
| 13 | GITAI S2 | Japan | 2023 | 7 | 1.5 | —— | —— | On orbit |
| 14 | CSSRMS | China | 2021 | CMM: 7 | CMM: 10.2 | CMM: 25,000 | CMM: 45 mm, 1° | On orbit |
| EMM: 7 | EMM: 5 | EMM: 3000 | EMM: 10 mm, 1° | |||||
| 15 | Test-7 | China | 2013 | 6 | —— | —— | —— | On orbit |
| 16 | Oceanus-1 | China | 2016 | 6 | —— | —— | —— | On orbit |
| 17 | TianGong-2 | China | 2016 | 6 | —— | —— | —— | On orbit |
| 18 | Cubot | China | 2023 | 7 | 0.3035 | —— | —— | Research |
| Case | Full Project Name | Orbit | Task/Service | Task Execution | Customer Design | Attitude |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NM1 | GEO Supersync | GEO | orbit modification | robots | legacy | spinning |
| NM2 | GEO Refueling | GEO | refueling | robots | legacy | 3-axis stabilized |
| NM3 | LEO Refurbishing | LEO | upgrade | humans (COTS) + robots | designed for upgrade | 3-axis stabilized |
| NM4 | Earth-Moon L1 (EML1) | EML1 | assembly | robots | designed for assembly | 3-axis stabilized |
| Robotic Assembly | ||||||
| NM5 | Highly Elliptical Orbit | HEO | upgrade | humans (Orion) + robots | designed for upgrade | 3-axis stabilized |
| (HEO) Refurbishing | ||||||
| NM6 | Sun-Earth L2 (SEL2) | SEL2 | assembly | human (Orion + habitat) | designed for assembly | 3-axis stabilized |
| Human/Robotic Assembly | + robots |
| No. | Forms | Region | Year | Agency | Project Name | On-Orbit Goals | Number of Robotic Arms |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Floating | North America | 1999 | Boeing | NNGST | Space telescope | Concept |
| 2 | 2003 | Boeing | AAST | Space telescope | Concept | ||
| 3 | 2003 | AFRL, SMC, NRL | XSS | Inspection, docking, servicing | XSS-12: Concept | ||
| 4 | 2003 | Canada MD Robotics | Smallsat servicer | Maintenance, refueling | 1 | ||
| 5 | 2005 | NCST | SUMO | Satellites, debris | 3 | ||
| 6 | 2006 | GSFC | TMST | Space telescope | 4 | ||
| 7 | 2007 | DARPA, Boeing | Orbital Express | Satellite capture, parts replacement | 1 | ||
| 8 | 2010 | GSFC | NM | NM1: Non-cooperative satellite capture, re-orbiting; | NM1: 4; | ||
| NM2: Fuel filling; | NM2: 2; | ||||||
| NM3: On-orbit services; | NM3: 2; | ||||||
| NM4: Space telescope construction; | NM4: 2; | ||||||
| NM5: 2 Arms Capture and Berthing + 2 Arms Operation; | NM5: 4; | ||||||
| NM6: Space telescope construction | NM6: 4; | ||||||
| 9 | 2011 | MDA | SIS | Refueling | 1 | ||
| 10 | 2011 | DARPA | Phoenix | Dis/Assembly, maintenance, Fuel filling | 4 | ||
| 11 | 2013 | GSFC | MAST | Space telescope | Concept | ||
| 12 | 2014 | DARPA | RSGS | Satellite maintenance and repairs | 2 | ||
| 13 | 2014 | NASA | OSAM-1 | Assembly, service | 3 | ||
| 14 | 2015 | NASA | Dragonfly | Assembly | 1 | ||
| 15 | 2015 | NASA | SALSSA | Assembly, repair, reconfiguration | Concept | ||
| 16 | 2016 | JPL | RAMST | Space telescope | 6 | ||
| 17 | 2016 | NASA | CIRAS | Trusses, reflectors, satellites | 2 | ||
| 18 | 2016 | NASA | OSAM-2 | Solar array assembly | 1 | ||
| 19 | 2019 | NASA | Astrobee | Services within ISS | 1 | ||
| 20 | 2019 | TAS, GMV, DLR | EROSS series | Orbital support services | 1 | ||
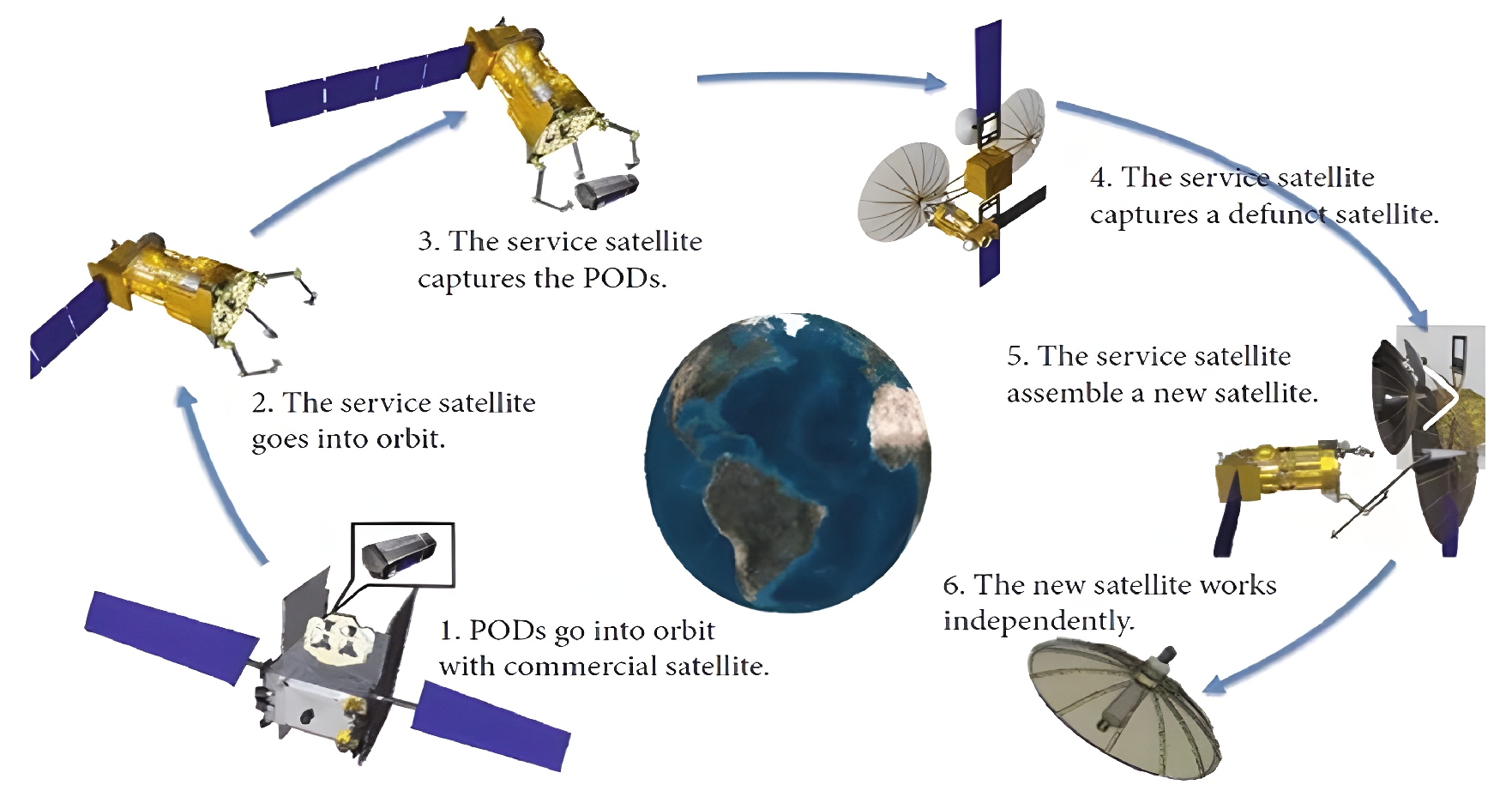
| 21 | Europe | 1996 | ESA | GSV | Satellite capture, re-orbiting | 1 | |
| 22 | 2004 | DLR, EADS, Babakin | TECSAS | Satellite maintenance and repairs | 1 | ||
| 23 | 2011 | DLR | DEOS | On-orbit services | 1 | ||
| 24 | 2010 | DLR | iBOSS | Modular spacecraft | 2 | ||
| 25 | Japan | 1997 | JAXA | ETS-VII | On-orbit services | 1 | |
| 26 | Semi-fixed | North America | 1999 | NASA, CMU | Skyworker | Assembly and maintenance of large space structures | Concept |
| 27 | 2012 | NASA | SpiderFab | Additive manufacturing and assembly of large space structures | 4 | ||
| 28 | 2019 | NASA, LaRC | Assemblers | Planetary surface infrastructure construction | Reconfigurable | ||
| 29 | 2017 | NASA | ARMADAS | Construction of large space structures | 1 (Multi-robots possible) | ||
| 30 | Europe | 2020 | Frazer-Nash | Space-Based Solar Power | Space solar power station | Concept | |
| 31 | China | 2014 | CIOMP | Ex-Large Aperture Space Telescope | Space telescope | 4 | |
| 32 | China | 2022 | HIT | S2A2RC | ultra-large-scale space truss | 7 (Multi-robots possible) | |
| 33 | Fixed | North America | 2011 | NASA | RRM | Fuel filling | 2 |
| 34 | Europe | 2017 | DLR, BMWi | Space Factory 4.0 | On-orbit manufacturing | Concept | |
| 35 | 2020 | AIRBUS | PERIOD | Space in-cabin assembly | 1 (Multi-robots possible) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Wang, P.; Duan, J.; Tian, W. Review of On-Orbit Assembly Technology with Space Robots. Aerospace 2025, 12, 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace12050375
Wang Z, Wang P, Duan J, Tian W. Review of On-Orbit Assembly Technology with Space Robots. Aerospace. 2025; 12(5):375. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace12050375
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zhengwei, Pengfei Wang, Jinjun Duan, and Wei Tian. 2025. "Review of On-Orbit Assembly Technology with Space Robots" Aerospace 12, no. 5: 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace12050375
APA StyleWang, Z., Wang, P., Duan, J., & Tian, W. (2025). Review of On-Orbit Assembly Technology with Space Robots. Aerospace, 12(5), 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace12050375


_Zhu.png)



