Condensed Combustion Products Characteristics of HTPB/AP/Al Propellants under Solid Rocket Motor Conditions
Abstract
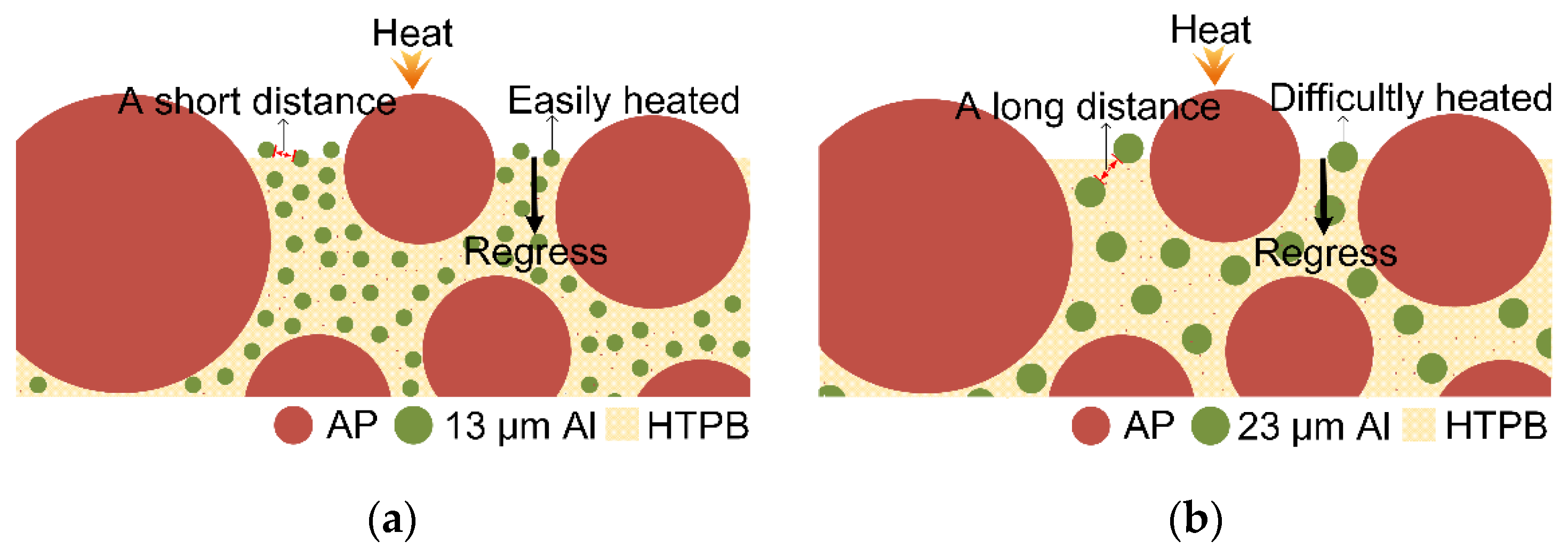
:1. Introduction
2. Constant Pressure Collection System
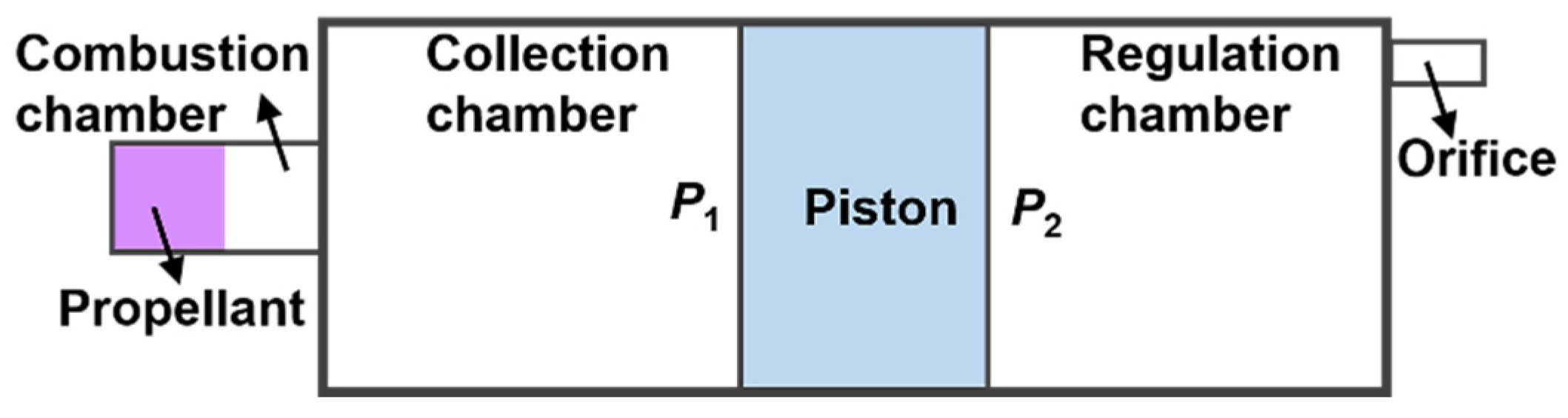
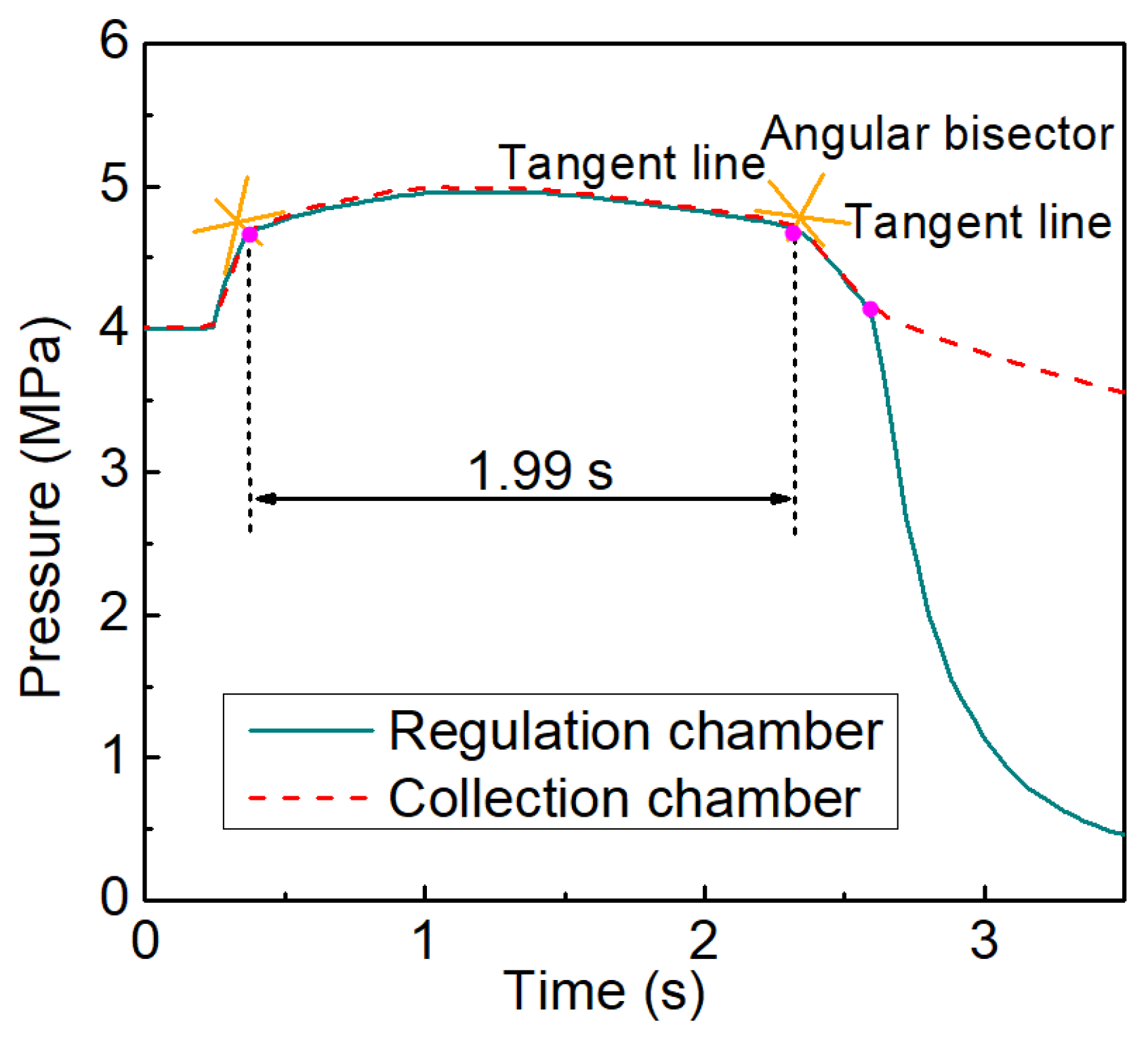
2.1. Principle of Pressure Maintenance
2.2. Experimental System
3. CCPs Collection and Analysis Experiments
3.1. Propellant Formulation
3.2. CCPs Collection
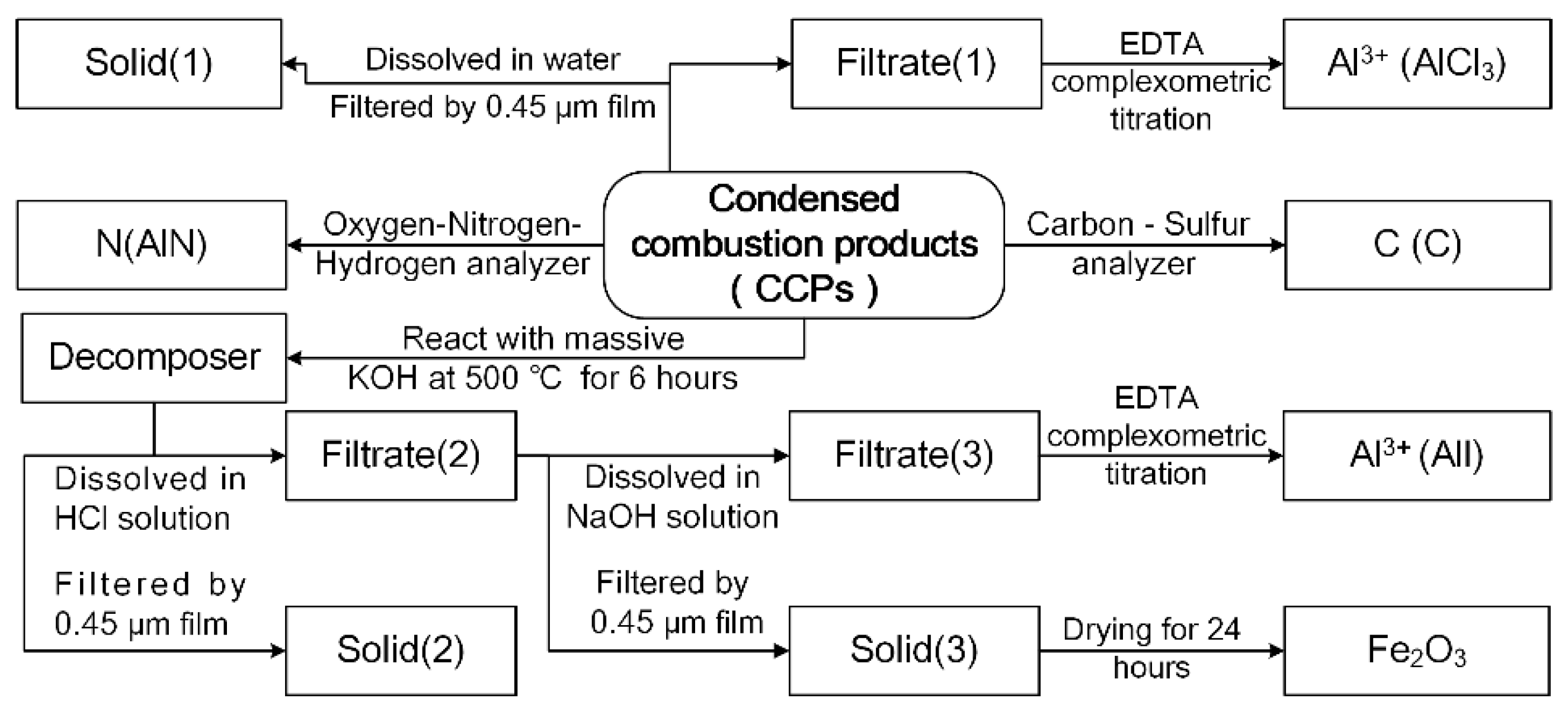
3.3. Characterization Method
4. Characterization of CCPs
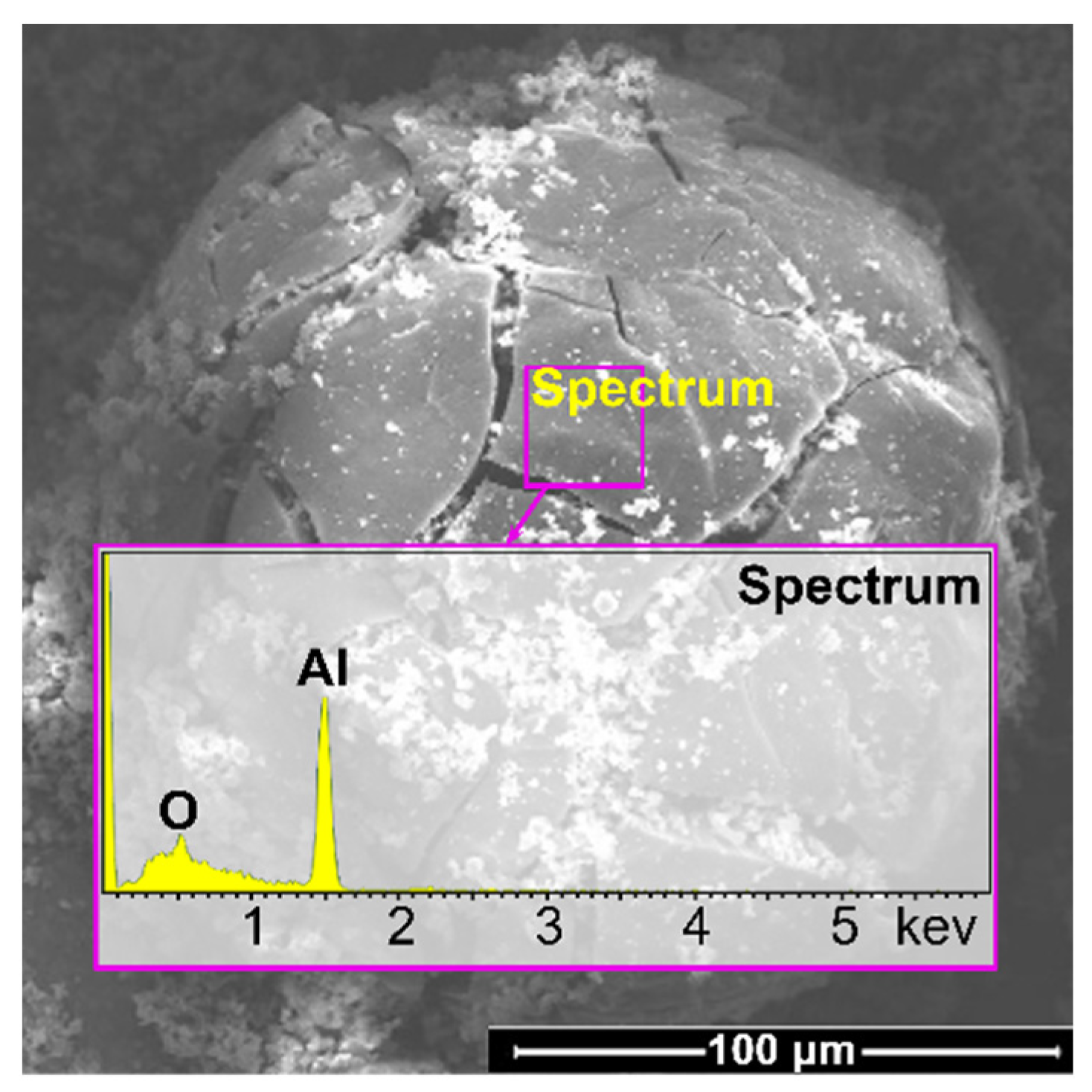
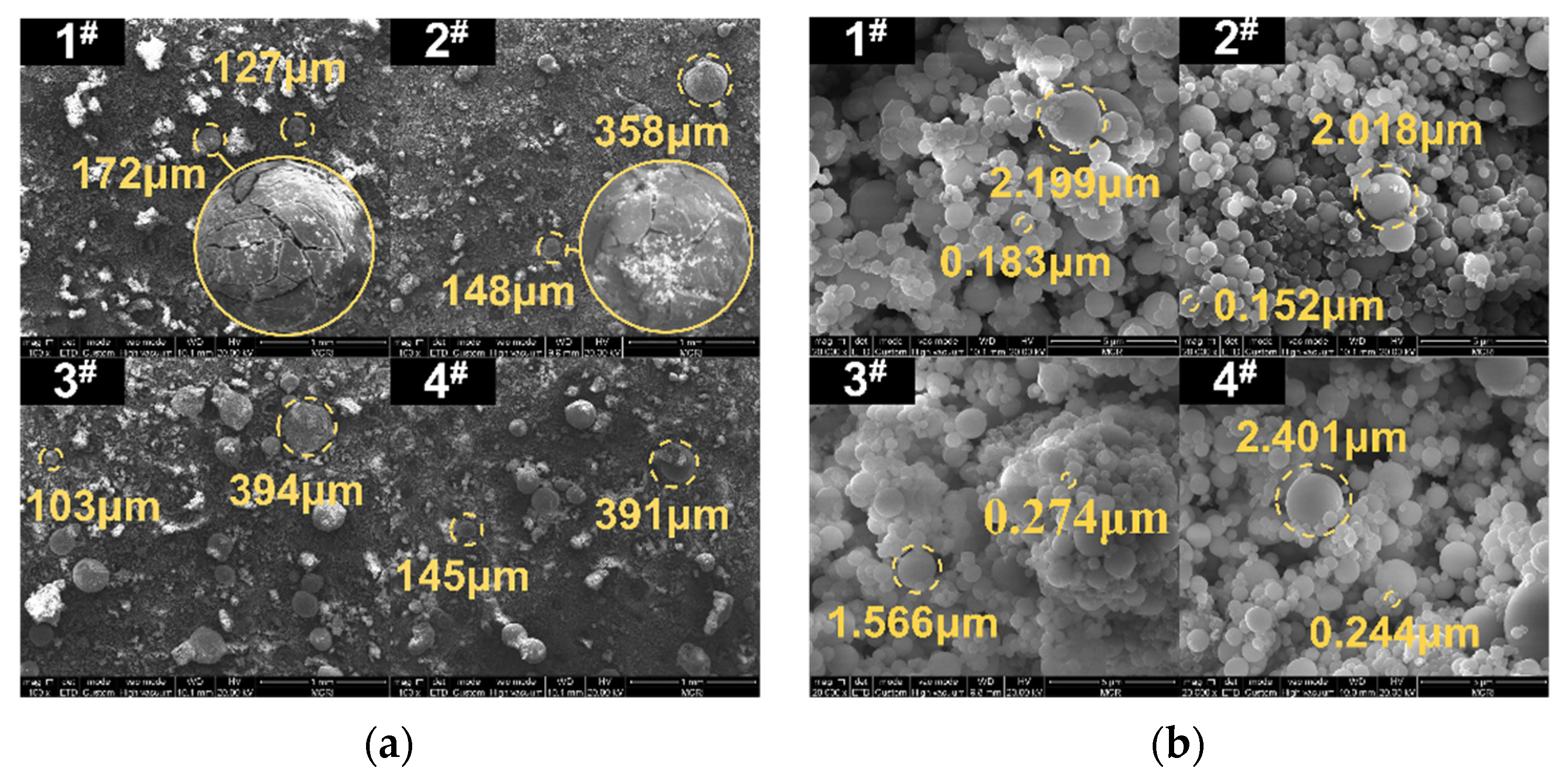
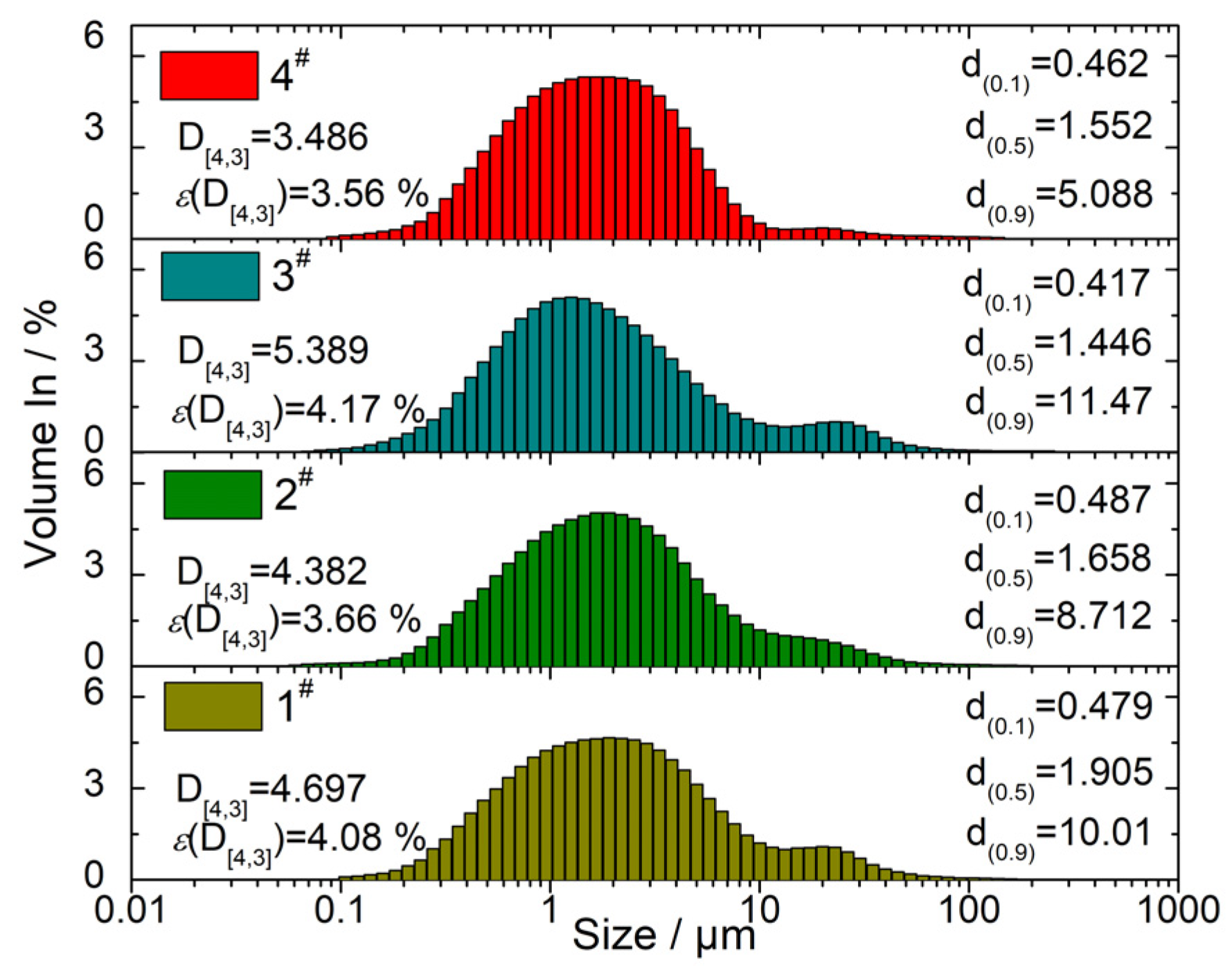
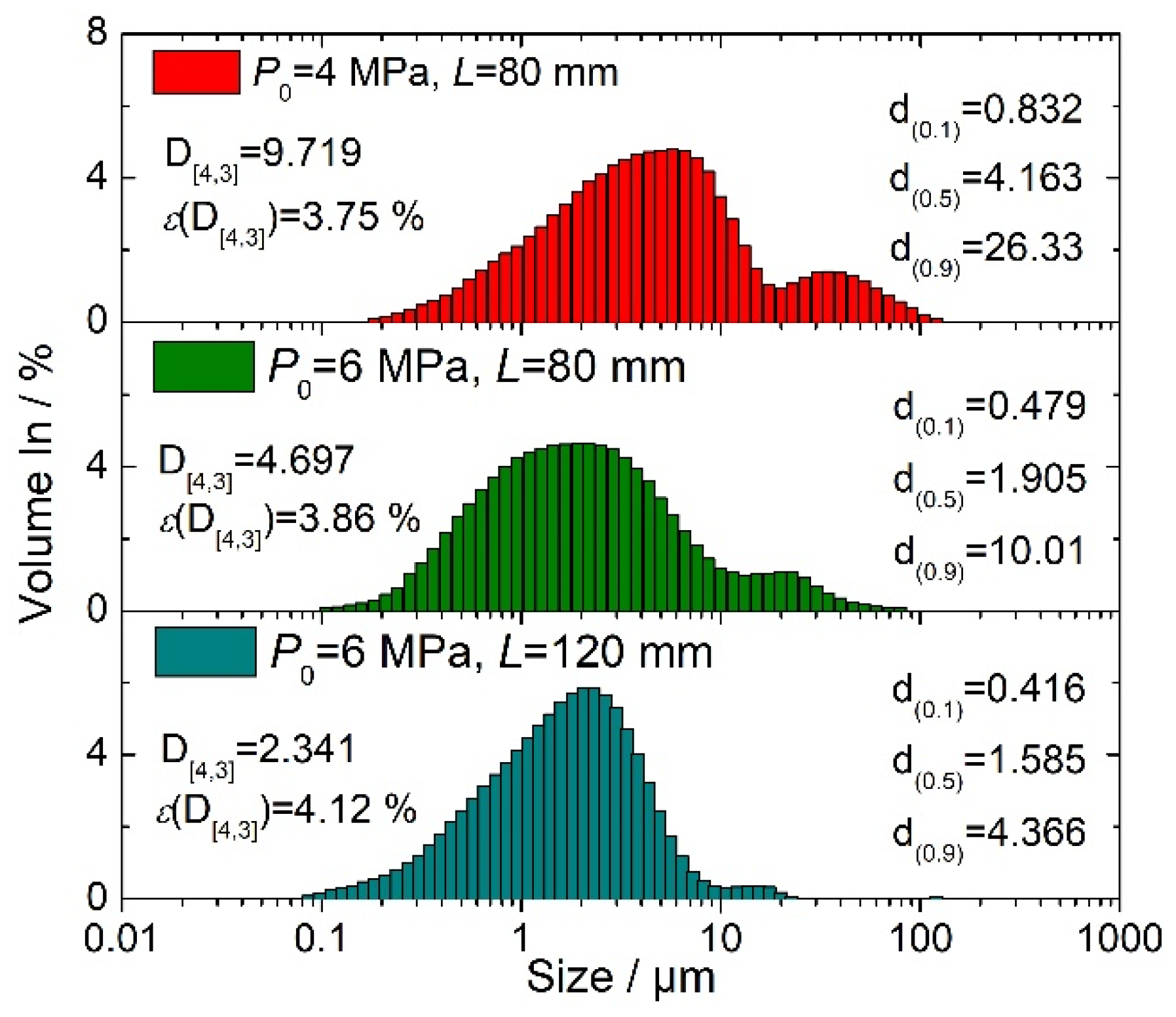
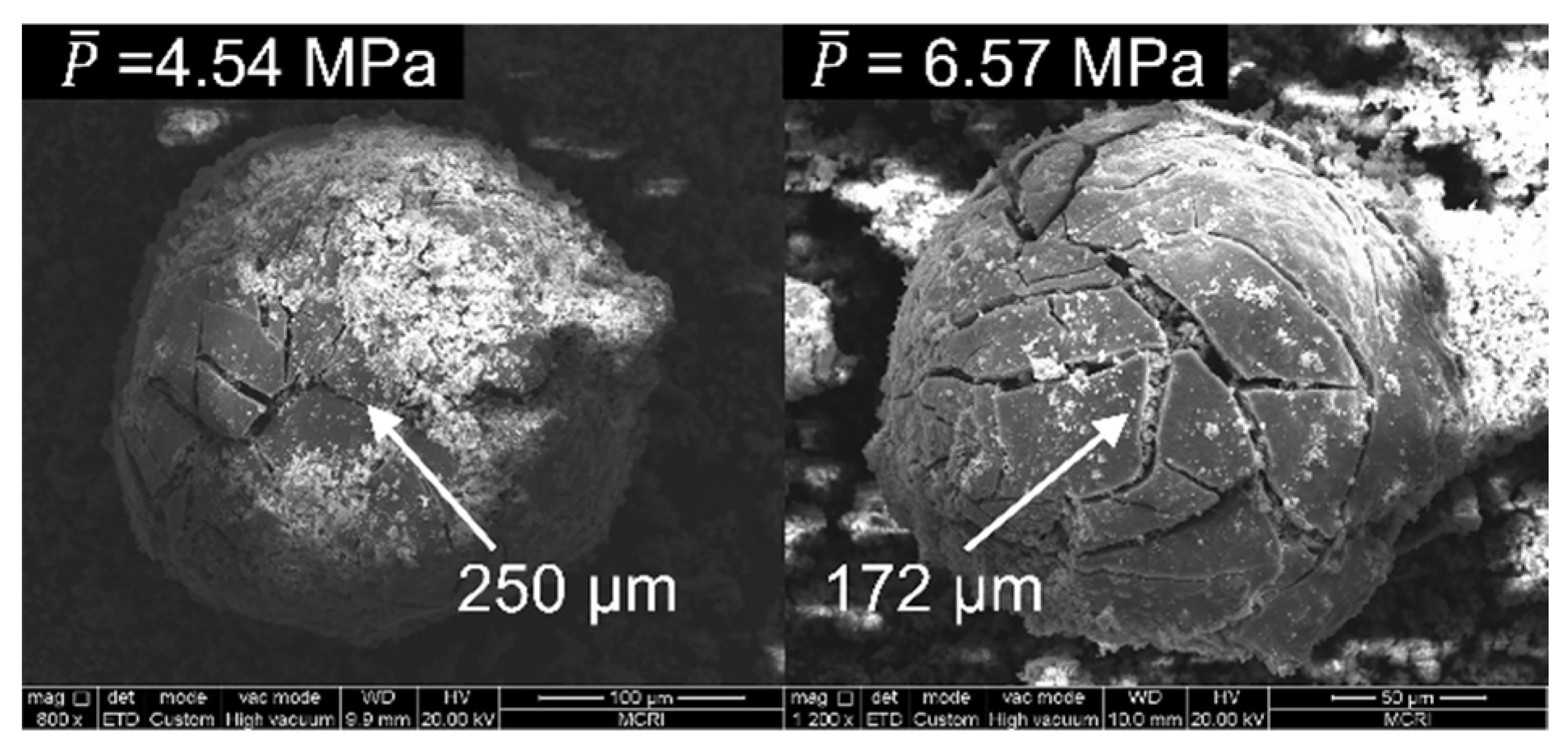
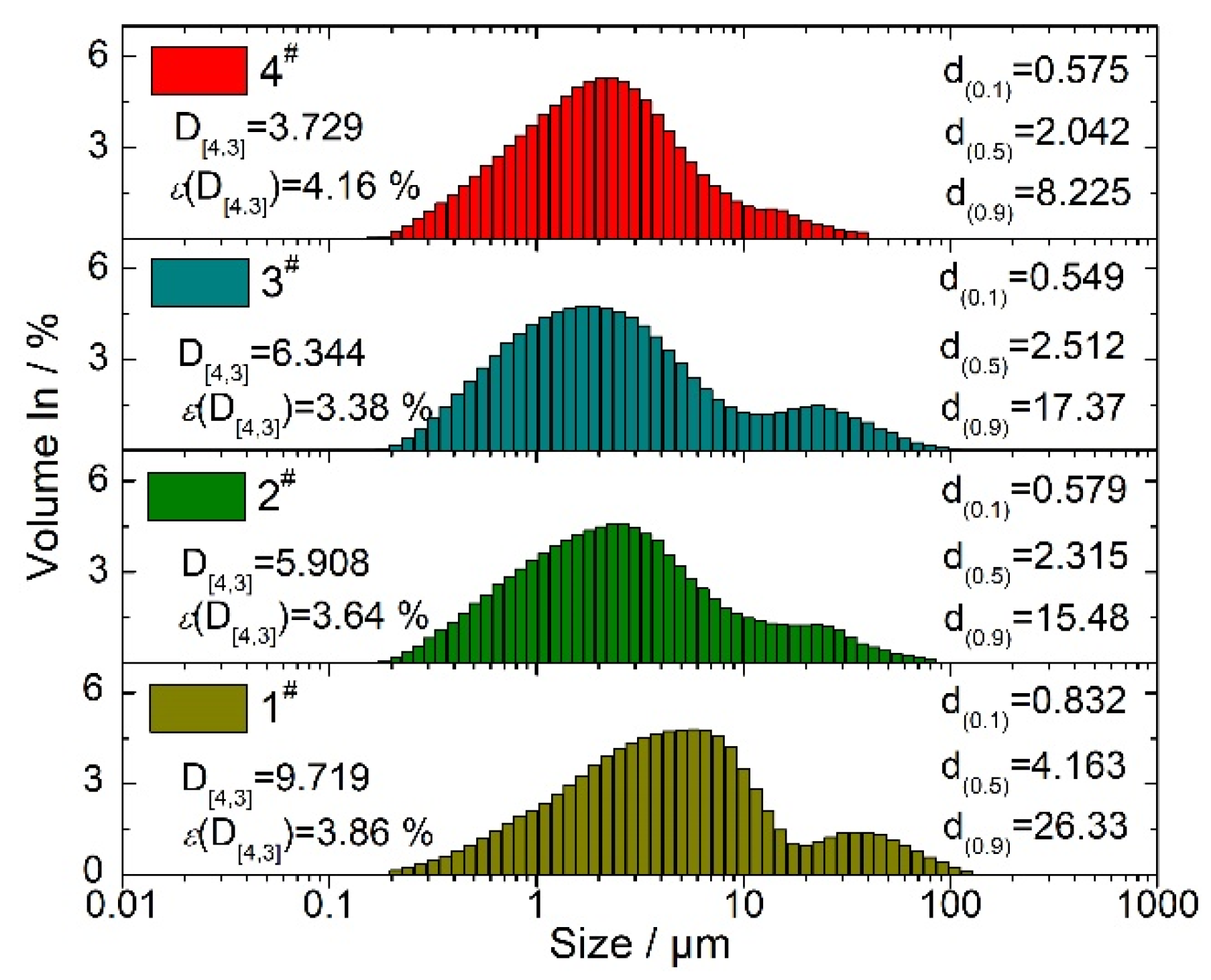
4.1. Morphology and Particle Size of CCPs
4.2. Chemical Composition of CCPs
4.3. Effect of Pressure
4.4. Effect of Formulation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| D[4,3] | the weighted average of the particle size to the surface area | [µm] |
| d(0.1) | the corresponding particle size when the sum of volume fraction is 10%. | [µm] |
| d(0.5) | the corresponding particle size when the sum of volume fraction is 50%. | [µm] |
| d(0.9) | the corresponding particle size when the sum of volume fraction is 90%. | [µm] |
| time-averaged pressure | [MPa] | |
| P | pressure | [MPa] |
| Pmax | the maximum pressure during combustion | [MPa] |
| Pmin | the minimum pressure during combustion | [MPa] |
| burning rate | [mm·s−1] | |
| tA | the start time of propellant combustion | [s] |
| tB | the end time of propellant combustion | [s] |
| Δt | burning time | [s] |
| ηAl | the combustion efficiency of aluminum | [%] |
| ε | relative error | [%] |
| Abbreviation | ||
| CCPs | condensed combustion products | |
| HTPB | hydroxyl-terminated polybutadiene | |
| AP | ammonium perchlorate | |
| Al | aluminum | |
| SEM | scanning electron microscope | |
| EDS | energy disperse spectroscopy | |
| XRD | x-ray diffraction | |
References
- Sippel, T.R.; Son, S.F.; Groven, L.J. Aluminum agglomeration reduction in a composite propellant using tailored Al/PTFE particles. Combust. Flame 2014, 161, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.K.; Perng, H.C.; Luh, S.P.; Liu, F. Aluminum agglomeration in ammonium perchlorate/cyclotrimethylene trinitramine/aluminum/hydroxy-terminated polybutadiene propellant combustion. J. Propuls. Power 1992, 8, 1177–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.F.; Liu, J.Z.; Zhou, Y.N.; Wang, J.R.; Xv, T.W. Aluminum agglomeration of AP/HTPB composite propellant. Acta Astronaut. 2019, 156, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlandi, O.; Plaud, M.; Godfroy, F.; Larrieu, S.; Cesco, N. Aluminium droplets combustion and SRM instabilities. Acta Astronaut. 2019, 158, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babuk, V.A.; Vassiliev, V.A.; Sviridov, V.V. Propellant formulation factors and metal agglomeration in combustion of aluminized solid rocket propellant. Combust. Sci. Technol. 2001, 163, 261–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.K. Experimental and model study of agglomeration of burning aluminized propellants. J. Propuls. Power 2005, 21, 797–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullen, J.C.; Brewster, M.Q. Reduced agglomeration of aluminum in wide-distribution composite propellants. J. Propuls. Power 2011, 27, 650–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babuk, V.A.; Vasil’Ev, V.A.; Potekhin, A.N. Experimental investigation of agglomeration during combustion of aluminized solid propellants in an acceleration field. Combust. Explos. Shock Waves 2009, 45, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Liu, Z.; Li, S.; Yu, W.; Cao, J.; Wang, N. Study on size distribution and flow characteristics of condensed products in solid rocket motor. Int. J. Aerosp. Eng. 2021, 5, 5481436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLuca, L.T.; Maggi, F.; Dossi, S.; Weiser, V.; Franzin, A.; Gettwert, V.; Heintz, T. High-energy metal fuels for rocket propulsion: Characterization and performance. Chin. J. Explos. Propellants 2013, 6, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glotov, O.G. Condensed combustion products of aluminized propellants. III. Effect of an inert gaseous combustion environment. Combust. Explos. Shock Waves 2002, 38, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Oide, S.; Kuwahara, T. Agglomeration characteristics of aluminum particles in AP/AN composite propellants. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 2013, 38, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuchi, A.B. Effect of aluminum particle size on agglomeration size and burning rate of composite propellant. J. Therm. Sci. Technol. 2022, 17, 321–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLuca, L.T.; Galfetti, L.; Maggi, F.; Colombo, G.; Bandera, A.; Cerri, S.; Donegà, P. Burning of metallized composite solid rocket propellants: Toward nanometric fuel size. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Symposium on Propulsion for Space Transportation, Heraklion, Greece, 5–8 May 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Bhadran, A.; Manathara, J.G.; Ramakrishna, P.A. Thrust Control of Lab-Scale Hybrid Rocket Motor with Wax-Aluminum Fuel and Air as Oxidizer. Aerospace 2022, 9, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paravan, C. Nano-Sized and Mechanically Activated Composites: Perspectives for Enhanced Mass Burning Rate in Aluminized Solid Fuels for Hybrid Rocket Propulsion. Aerospace 2019, 6, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sippel, T.R.; Son, S.F.; Groven, L.J.; Zhang, S.; Dreizin, E. Exploring mechanisms for agglomerate reduction in composite solid propellants with polyethylene inclusion modified aluminum. Combust. Flame 2015, 162, 846–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lade, R.; Wasewar, K.; Sangtyani, R.; Kumar, A.; Shende, D.; Peshwe, D. Influence of the addition of aluminium nanoparticles on thermo-rheological properties of hydroxyl-terminated polybutadiene-based composite propellant and empirical modelling. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2019, 138, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ao, W.; Liu, H.; Liu, P. Aluminum Agglomeration on Burning Surface of NEPE Propellants at 3–5 MPa. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 2017, 42, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejasvi, K.; Venkateshwara, R.V.; PydiSetty, Y.; Jayaraman, K. Studies on Aluminum Agglomeration and Combustion in Catalyzed Composite Propellants. Combust. Explos. Shock Waves 2021, 57, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaraman, K.; Chakravarthy, S.R.; Sarathi, R. Quench collection of nano-aluminium agglomerates from combustion of sandwiches and propellants. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2011, 33, 1941–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhao, F.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Pei, Q.; Xu, H.; Hao, H.; Yang, Y.; Li, H. Evaluation of graphene-ferrocene nanocomposite as multifunctional combustion catalyst in AP-HTPB propellant. Fuel 2021, 302, 121229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeenu, R.; Pinumalla, K.; Deepak, D. Size Distribution of Particles in Combustion Products of Aluminized Composite Propellant. J. Propuls. Power 2010, 26, 715–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, B.-N.; Wang, Z.-X.; Xu, G.; Ao, W.; Liu, P.-J. Three-dimensional spatial distributions of agglomerated particles on and near the burning surface of aluminized solid propellant using morphological digital in-line holography. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2020, 106, 106066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, W.; Liu, X.; Rezaiguia, H.; Liu, H.; Wang, Z.; Liu, P.J. Aluminum agglomeration involving the second mergence of agglomerates on the solid propellants burning surface: Experiments and modeling. Acta Astronaut. 2017, 136, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babuk, V.A.; Vasilyev, V.A.; Malakhov, M.S. Condensed Combustion Products at the Burning Surface of Aluminized Solid Propellant. J. Propuls. Power 1999, 15, 783–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, K.V.; Roy, A.; Mulla, I.; Balbudhe, K.; Jayaraman, K.; Chakravarthy, S.R. Experimental data and model predictions of aluminium agglomeration in ammonium perchlorate-based composite propellants including plateau-burning formulations. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2013, 34, 2139–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glotov, O.G. Condensed combustion products of aluminized propellants. IV. Effect of the nature of nitramines on aluminum agglomeration and combustion efficiency. Combust. Explos. Shock Waves 2006, 42, 436–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambamurthi, J.K.; Price, E.W.; Sigman, R.K. Aluminum Agglomeration in Solid-Propellant Combustion. AIAA J. 1984, 22, 1132–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaraman, K.; Anand, K.V.; Chakravarthy, S.R.; Sarathi, R. Effect of nano-aluminium in plateau-burning and catalyzed composite solid propellant combustion. Combust. Flame 2009, 156, 1662–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaraman, K.; Chakravarthy, S.R.; Sarathi, R. Accumulation of nano-aluminium during combustion of composite solid propellant mixtures. Combust. Explos. Shock Waves 2010, 46, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejasvi, K.; Venkateshwara Rao, V.; Pydi Setty, Y.; Jayaraman, K. Ultra-Fine Aluminium Characterization and its Agglomeration Features in Solid Propellant Combustion for Various Quenched Distance and Pressure. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 2020, 45, 714–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babuk, V.A.; Dolotkazin, I.N.; Glebov, A.A. Burning Mechanism of Aluminized Solid Rocket Propellants Based on Energetic Binders. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 2005, 30, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Liu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cen, K. Thermal decomposition and combustion characteristics of Al/AP/HTPB propellant. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2021, 143, 3935–3944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.K.; Hsieh, C.F. Analysis of agglomerate size from burning aluminized AP/RDX/HTPB propellants in quench bomb. J. Propuls. Power 1996, 12, 995–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarou-Kanian, V.; Rifflet, J.C.; Millot, F.; Matzen, G.; Gökalp, I. Influence of nitrogen in aluminum droplet combustion. Proc. Combust Inst. 2005, 30, 2063–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, W.; Liu, P.J.; Yang, W. Agglomerates, smoke oxide particles, and carbon inclusions in condensed combustion products of an aluminized GAP-based propellant. Acta Astronaut. 2016, 129, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggi, F.; DeLuca, L.T.; Bandera, A. Pocket Model for Aluminum Agglomeration Based on Propellant Microstructure. AIAA J. 2015, 53, 3395–3403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Propellant No. | HTPB (wt%) | Catocene (wt%) | AP (wt%) | Al (wt%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 200–300 µm | 105–150 µm | 1 µm | 23 µm | 13 µm | |||
| 1# | 13 | 2 | 45 | 25 | 0 | 15 | 0 |
| 2# | 13 | 2 | 40 | 25 | 5 | 15 | 0 |
| 3# | 13 | 2 | 40 | 25 | 5 | 0 | 15 |
| 4# | 15 | 0 | 40 | 25 | 5 | 0 | 15 |
| Propellant No. | P0 a (MPa) | Lb (mm) | Δt (s) | (MPa) | ΔP (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1# | 4 | 80 | 0.21 | 4.54 | 0.15 |
| 1# | 6 | 80 | 0.18 | 6.57 | 0.23 |
| 1# | 6 | 120 | 0.23 | 6.66 | 0.21 |
| 2# | 4 | 80 | 0.22 | 4.83 | 0.18 |
| 2# | 6 | 80 | 0.24 | 7.03 | 0.23 |
| 3# | 4 | 80 | 0.24 | 5.04 | 0.22 |
| 3# | 6 | 80 | 0.16 | 6.90 | 0.24 |
| 4# | 4 | 80 | 0.15 | 5.03 | 0.24 |
| 4# | 6 | 80 | 0.23 | 6.99 | 0.16 |
| Propellant No. | Weight Ratio (%) | Atom Ratio (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al K | O K | Al K | O K | |
| 1# | 56.93 | 43.07 | 43.92 | 56.08 |
| 2# | 53.09 | 46.91 | 40.14 | 59.86 |
| 3# | 52.16 | 47.84 | 39.25 | 60.75 |
| 4# | 50.84 | 49.16 | 37.99 | 62.01 |
| Propellant No | Mass Fraction (%) | ηAl (%) | ε (ηAl) (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | AlN | Fe2O3 | Al | Al2O3 | AlCl3 | |||
| 1# | 0.94 | 0.79 | 6.41 | 2.15 | 80.63 | 9.08 | 95.27 | 3.62 |
| 2# | 1.49 | 3.86 | 5.47 | 2.43 | 84.18 | 2.57 | 95.10 | 4.23 |
| 3# | 1.52 | 3.83 | 6.70 | 1.06 | 86.86 | 0.03 | 97.86 | 3.27 |
| 4# | 0.72 | 2.05 | 3.84 | 0.64 | 86.43 | 6.32 | 98.65 | 4.36 |
| P0 (MPa) | (MPa) | L (mm) | (mm·s−1) | ηAl (%) | ε(ηAl) (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 4.54 | 80 | 11.79 | 93.54 | 3.48 |
| 6 | 6.57 | 80 | 15.06 | 95.27 | 4.16 |
| 6 | 6.66 | 120 | 14.88 | 99.01 | 3.87 |
| Propellant No. | (mm·s−1) | ηAl (%) | ε (ηAl) (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1# | 11.79 | 93.54 | 4.02 |
| 2# | 12.56 | 93.93 | 3.25 |
| 3# | 13.66 | 97.00 | 3.56 |
| 4# | 8.39 | 97.49 | 4.27 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.-L.; Hu, S.-Q.; Liu, L.-L.; Zhang, Y. Condensed Combustion Products Characteristics of HTPB/AP/Al Propellants under Solid Rocket Motor Conditions. Aerospace 2022, 9, 677. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace9110677
Liu X-L, Hu S-Q, Liu L-L, Zhang Y. Condensed Combustion Products Characteristics of HTPB/AP/Al Propellants under Solid Rocket Motor Conditions. Aerospace. 2022; 9(11):677. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace9110677
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xue-Li, Song-Qi Hu, Lin-Lin Liu, and Yan Zhang. 2022. "Condensed Combustion Products Characteristics of HTPB/AP/Al Propellants under Solid Rocket Motor Conditions" Aerospace 9, no. 11: 677. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace9110677
APA StyleLiu, X.-L., Hu, S.-Q., Liu, L.-L., & Zhang, Y. (2022). Condensed Combustion Products Characteristics of HTPB/AP/Al Propellants under Solid Rocket Motor Conditions. Aerospace, 9(11), 677. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace9110677





