Effects of Stroke Amplitude and Wing Planform on the Aerodynamic Performance of Hovering Flapping Wings †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
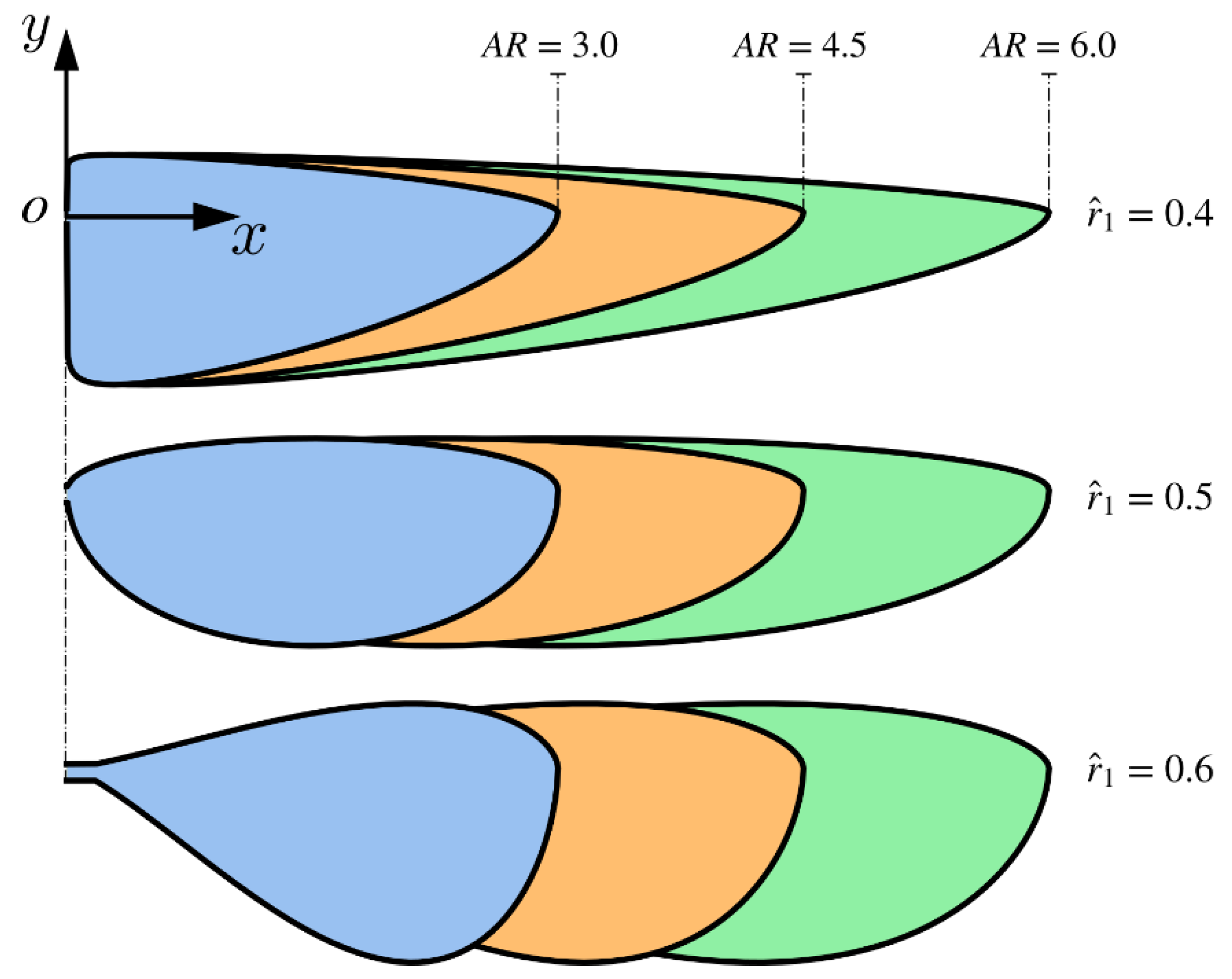
2.1. Wing Planform and Kinematics Definitions
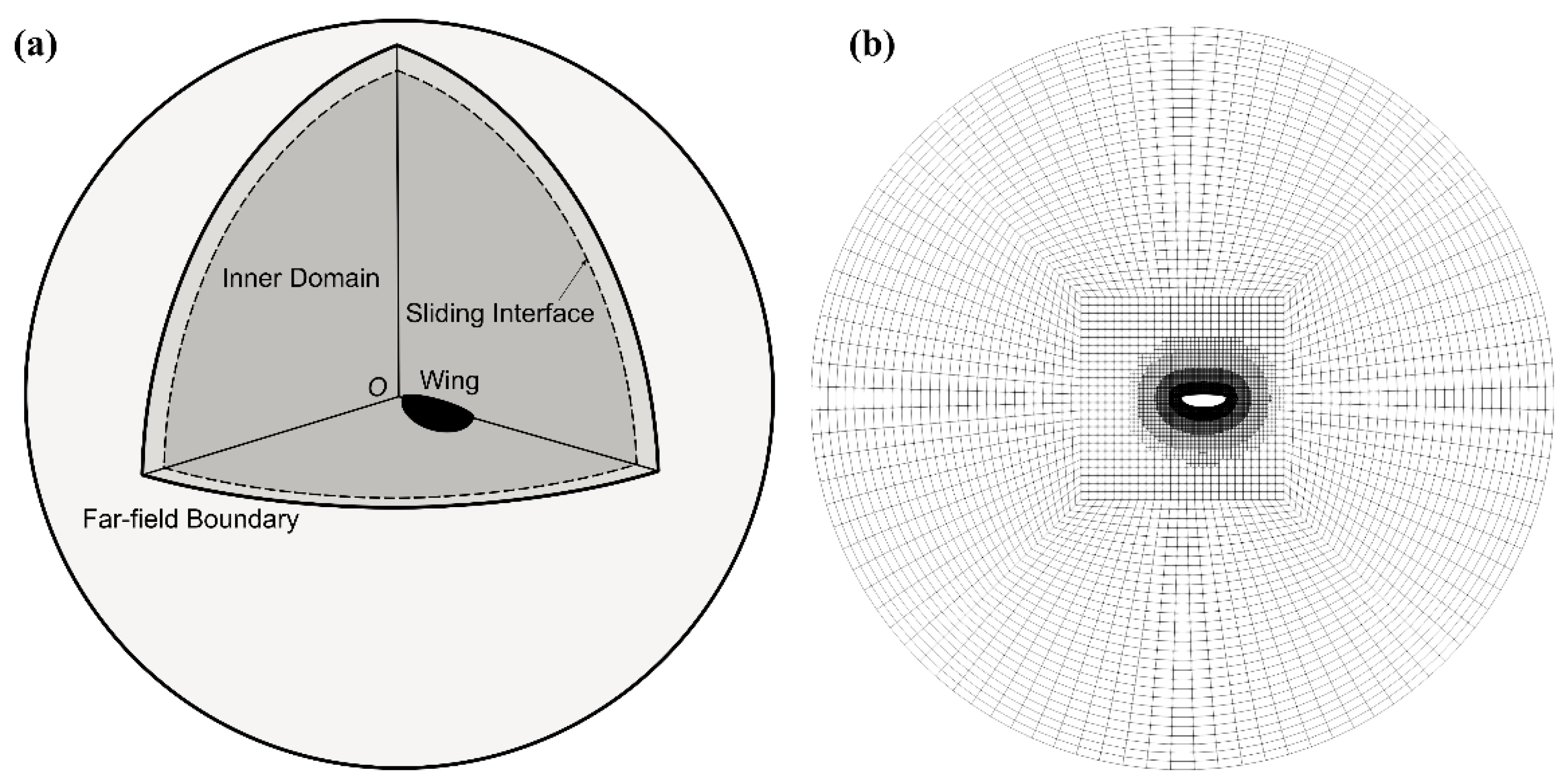
2.2. Numerical Simulation
3. Results and Discussion
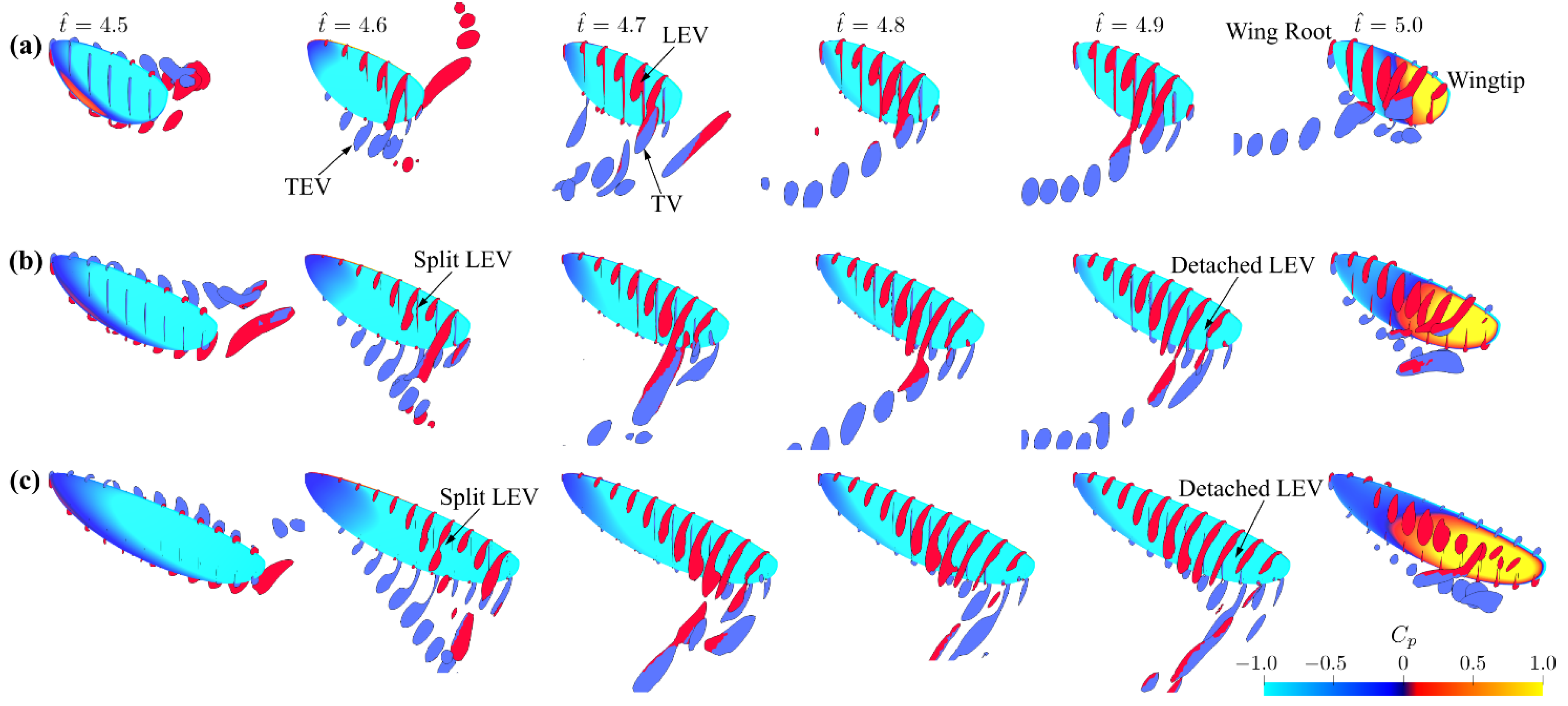
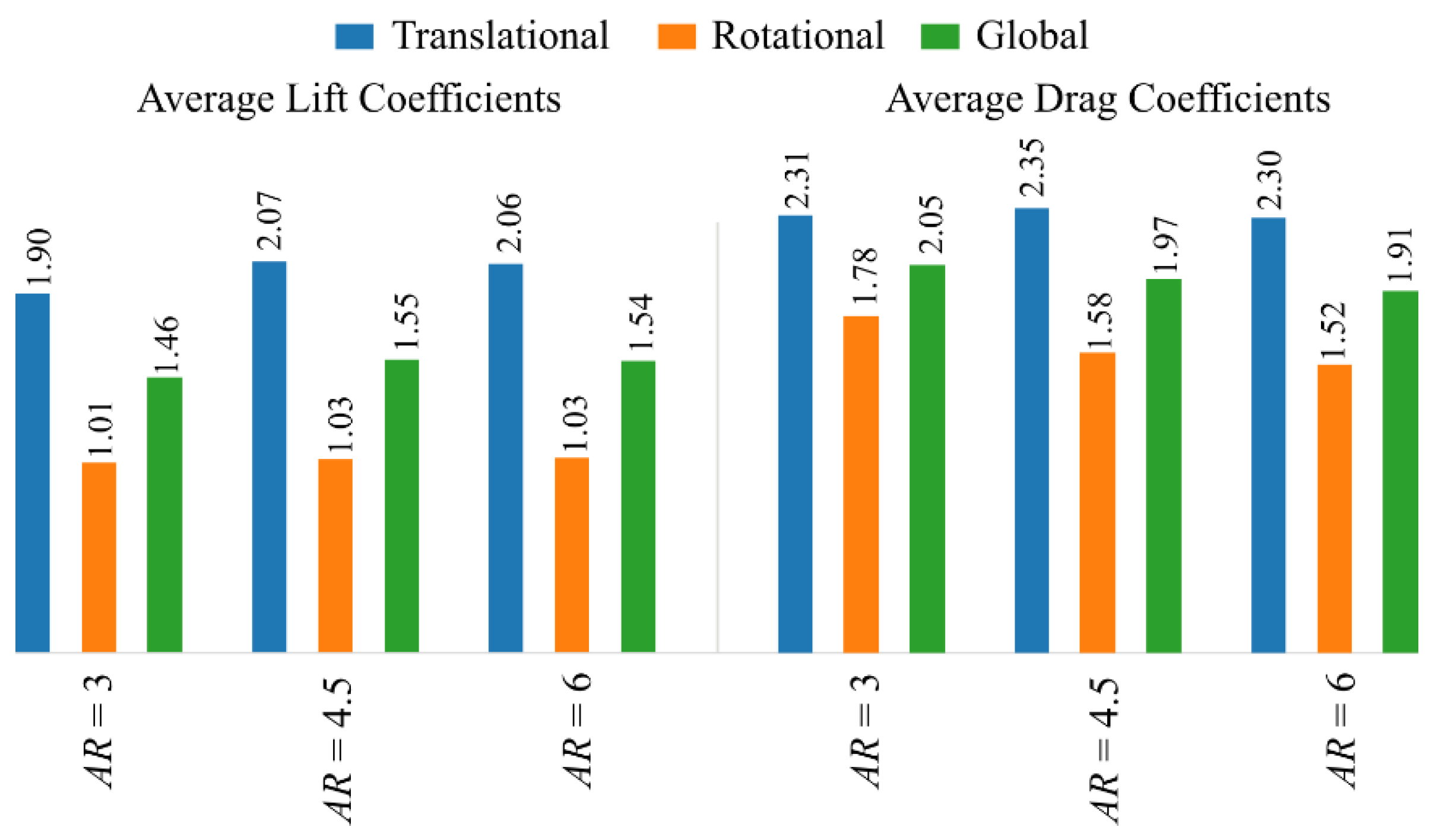
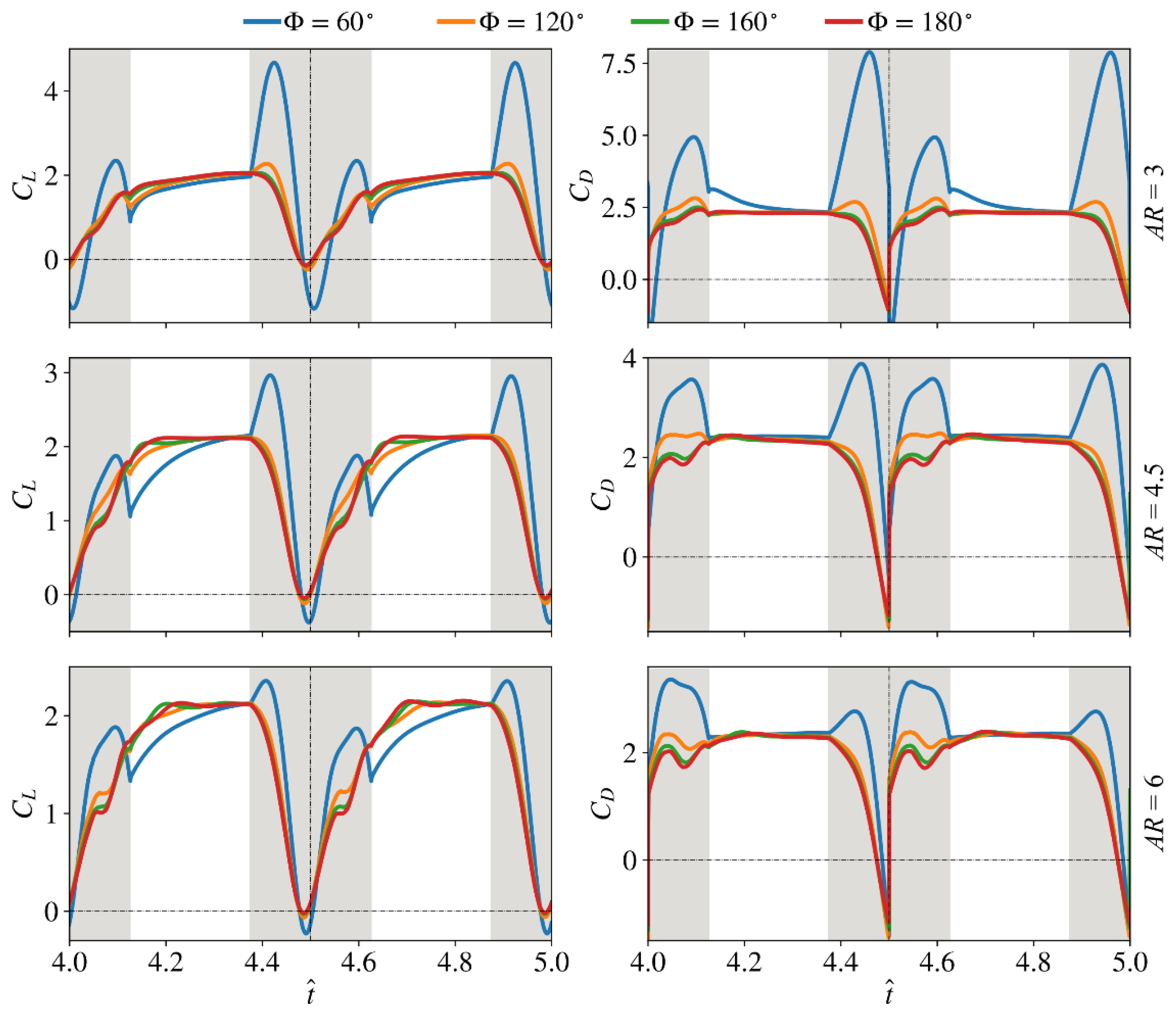
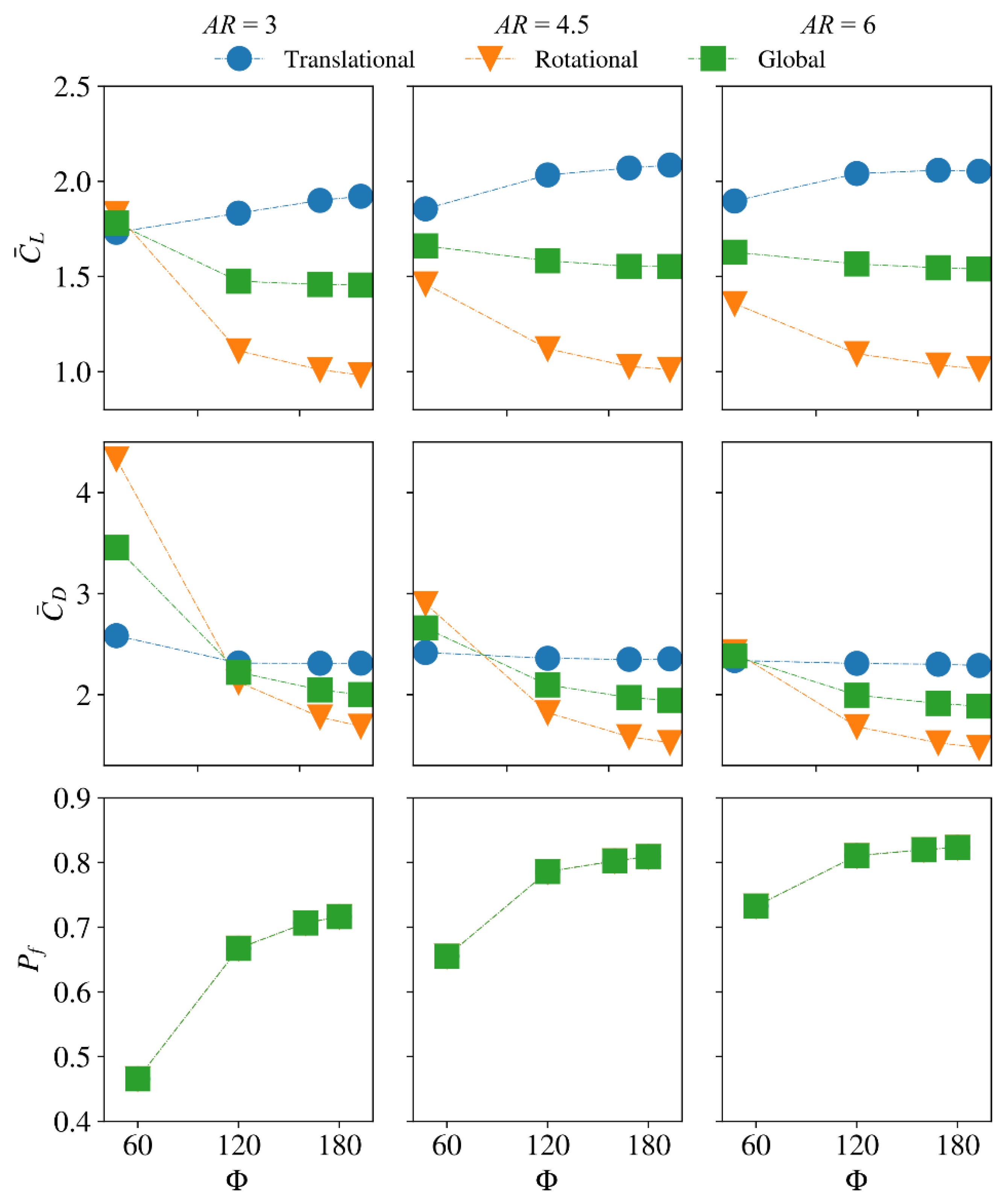
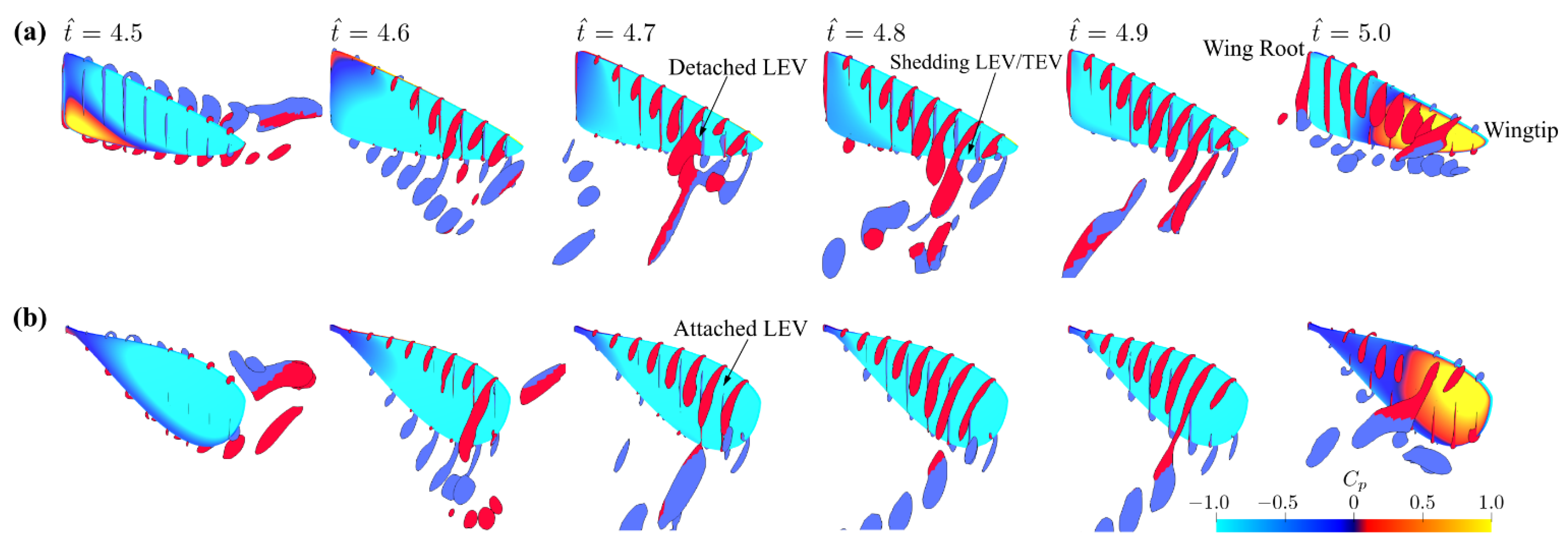
3.1. Effect of Aspect Ratio
3.2. Interaction Effect of Stroke Amplitude and Aspect Ratio
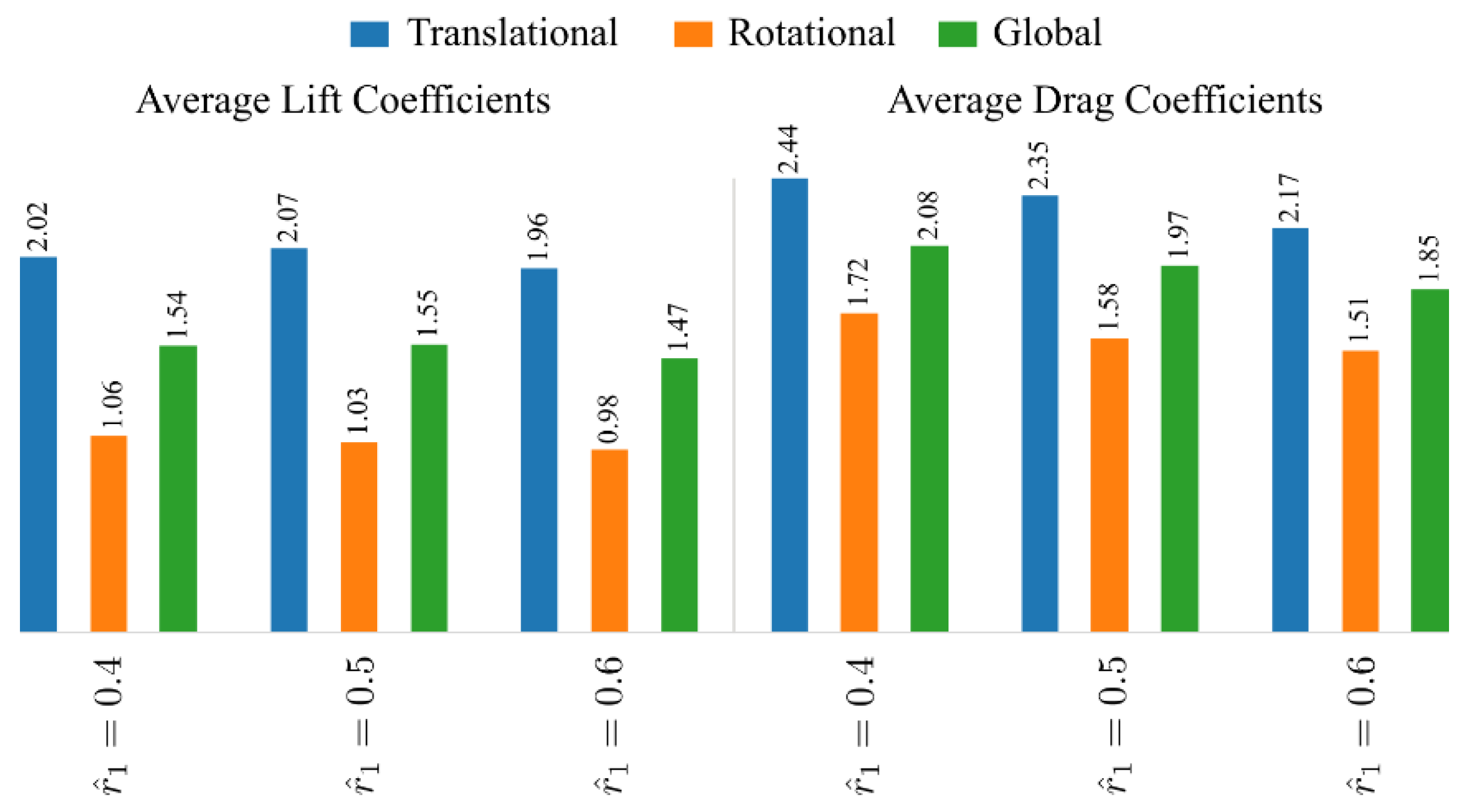
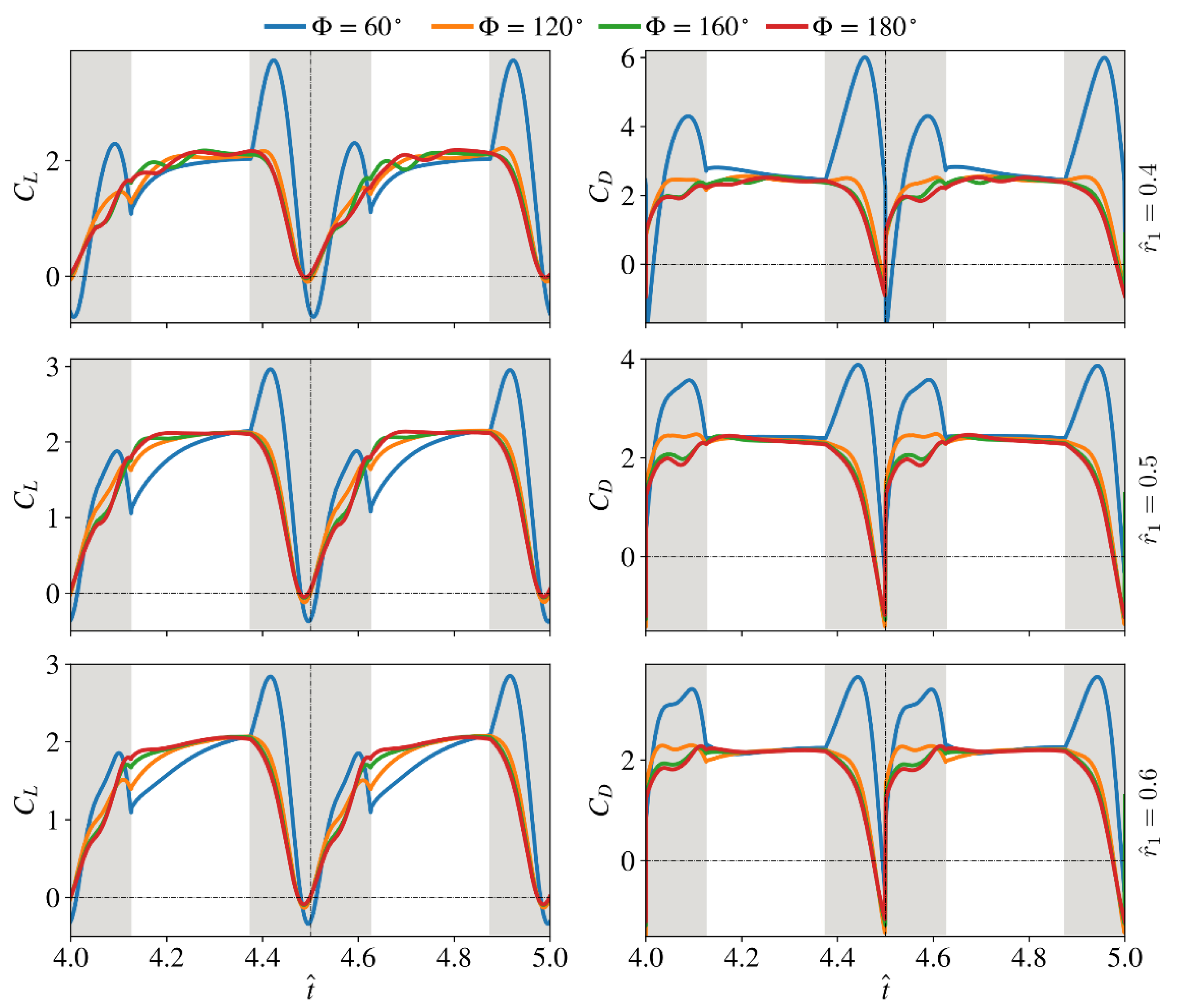
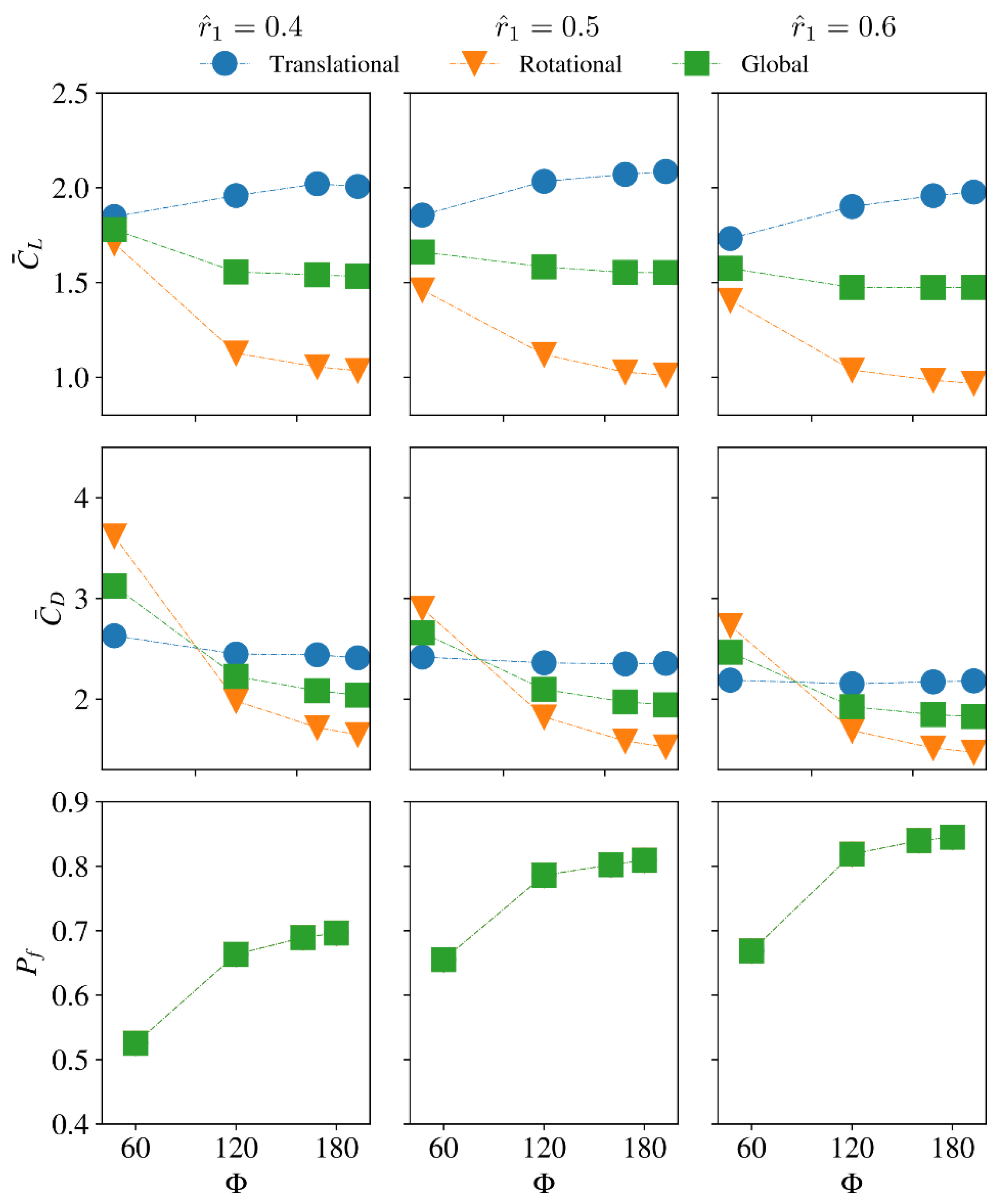
3.3. Effect of Radial Centroid Location
3.4. Interaction Effect of Stroke Amplitude and Radial Centroid Location
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, K.Y.; Chirarattananon, P.; Fuller, S.B.; Wood, R.J. Controlled Flight of a Biologically Inspired, Insect-Scale Robot. Science 2013, 340, 603–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lentink, D.; Jongerius, S.R.; Bradshaw, N.L. The Scalable Design of Flapping Micro-Air Vehicles Inspired by Insect Flight. In Flying Insects and Robots; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 185–205. ISBN 978-3-540-89392-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keennon, M.; Klingebiel, K.; Won, H. Development of the Nano Hummingbird: A Tailless Flapping Wing Micro Air Vehicle. In Proceedings of the 50th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting including the New Horizons Forum and Aerospace Exposition, Nashville, TN, USA, 9–12 January 2012; American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics: Reston, VA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabawy, M.R.A.; Marcinkeviciute, R. Scalability of Resonant Motor-Driven Flapping Wing Propulsion Systems. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2021, 8, 210452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Wang, L.; He, Y.; Tong, M.; Pan, Y.; Ji, B.; Guo, S. Aerodynamic Performance of a Flyable Flapping Wing Rotor with Passive Pitching Angle Variation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 69, 9176–9184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhao, J.; He, Y.; Guo, S.; Chen, S.; Ji, B. Aerodynamic Analysis of Insect-like Flapping Wings in Fan-Sweep and Parallel Motions with the Slit Effect. Biomim. Intell. Robot. 2022, 2, 100046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellington, C.P. The Aerodynamics of Hovering Insect Flight.3. Kinematics. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 1984, 305, 41–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxworthy, T. Experiments on the Weis-Fogh Mechanism of Lift Generation by Insects in Hovering Flight Part 1. Dynamics of the ‘Fling.’ J. Fluid Mech. 1979, 93, 47–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellington, C.P.; van den Berg, C.; Willmott, A.P.; Thomas, A.L.R. Leading-Edge Vortices in Insect Flight. Nature 1996, 384, 626–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, M.H.; Lehmann, F.O.; Sane, S.P. Wing Rotation and the Aerodynamic Basis of Insect Flight. Science 1999, 284, 1954–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabawy, M.R.A.; Crowther, W.J. The Role of the Leading Edge Vortex in Lift Augmentation of Steadily Revolving Wings: A Change in Perspective. J. R. Soc. Interface 2017, 14, 20170159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabawy, M.R.; Villamor, G.J.; Li, H. Aerodynamic Modelling of Insect Wings Using Joukowski Transformation. In Proceedings of the AIAA AVIATION 2021 FORUM, Virtual Event, 2–6 August 2021; American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics: Reston, VA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bomphrey, R.J.; Nakata, T.; Phillips, N.; Walker, S.M. Smart Wing Rotation and Trailing-Edge Vortices Enable High Frequency Mosquito Flight. Nature 2017, 544, 92–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Nabawy, M.R. Wake Effects on Force Production of a Translating-Pitching Flat Plate. In Proceedings of the AIAA AVIATION 2021 FORUM, Virtual Event, 2–6 August 2021; American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics: Reston, VA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabawy, M.R.A.; Crowther, W.J. Optimum Hovering Wing Planform. J. Theor. Biol. 2016, 406, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usherwood, J.R.; Ellington, C.P. The Aerodynamics of Revolving Wings-II. Propeller Force Coefficients from Mayfly to Quail. J. Exp. Biol. 2002, 205, 1565–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruyt, J.W.; Van Heijst, G.J.F.; Altshuler, D.L.; Lentink, D. Power Reduction and the Radial Limit of Stall Delay in Revolving Wings of Different Aspect Ratio. J. R. Soc. Interface 2015, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broadley, P.; Nabawy, M.R.; Quinn, M.K.; Crowther, W.J. Wing Planform Effects on the Aerodynamic Performance of Insect-like Revolving Wings. In Proceedings of the AIAA AVIATION 2020 FORUM, Virtual Event, 15–19 June 2020; American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics: Reston, VA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broadley, P.; Nabawy, M.R. Effects of Wing Planform Shape on Low Reynolds Number Revolving Wings. In Proceedings of the AIAA AVIATION 2021 FORUM, Virtual Event, 2–6 August 2021; American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics: Reston, VA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harbig, R.R.; Sheridan, J.; Thompson, M.C. Reynolds Number and Aspect Ratio Effects on the Leading-Edge Vortex for Rotating Insect Wing Planforms. J. Fluid Mech. 2013, 717, 166–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, N.; Knowles, K.; Bomphrey, R.J. The Effect of Aspect Ratio on the Leading-Edge Vortex over an Insect-like Flapping Wing. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2015, 10, 056020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, N.; Knowles, K.; Bomphrey, R.J. Petiolate Wings: Effects on the Leading-Edge Vortex in Flapping Flight. Interface Focus 2017, 7, 20160084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.S.; Chang, J.W.; Cho, H.K. Vortices Behavior Depending on the Aspect Ratio of an Insect-like Flapping Wing in Hover. Exp. Fluids 2015, 56, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.; Sun, M. Effects of Corrugation and Wing Planform on the Aerodynamic Force Production of Sweeping Model Insect Wings. Acta Mech. Sin. Xuebao 2005, 21, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, A.; Tian, F.-B.; Young, J.; Lai, J.C.S. Effects of Wing Shape, Aspect Ratio and Deviation Angle on Aerodynamic Performance of Flapping Wings in Hover. Phys. Fluids 2016, 28, 111901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, S.S.; Zhao, J.; Sheridan, J.; Hourigan, K.; Thompson, M.C. Aspect Ratio Studies on Insect Wings. Phys. Fluids 2019, 31, 121301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sane, S.P.; Dickinson, M.H. The Control of Flight Force by a Flapping Wing: Lift and Drag Production. J. Exp. Biol. 2001, 204, 2607–2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, N.; Knowles, K. Reynolds Number and Stroke Amplitude Effects on the Leading-Edge Vortex on an Insect-like Flapping Wing. In Proceedings of the International Powered Lift Conference, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 5–7 October 2010; pp. 365–374. [Google Scholar]
- Altshuler, D.L.; Dickson, W.B.; Vance, J.T.; Roberts, S.P.; Dickinson, M.H.; Altshuler, D.L.; Dickinson, M.H. Short-Amplitude High-Frequency Wing Strokes Determine the Aerodynamics of Honeybee Flight. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 18213–18218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lentink, D.; Dickinson, M.H. Rotational Accelerations Stabilize Leading Edge Vortices on Revolving Fly Wings. J. Exp. Biol. 2009, 212, 2705–2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellington, C.P. The Aerodynamics of Hovering Insect Flight.2. Morphological Parameters. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 1984, 305, 17–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broadley, P.; Nabawy, M.R.A.; Quinn, M.K.; Crowther, W.J. Dynamic Experimental Rigs for Investigation of Insect Wing Aerodynamics. J. R. Soc. Interface 2022, 19, 20210909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Huang, Q.; Deng, X.; Sane, S.P. Aerodynamic Effects of Flexibility in Flapping Wings. J. R. Soc. Interface 2010, 7, 485–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, G.; Sun, M. Effects of Wing Deformation on Aerodynamic Forces in Hovering Hoverflies. J. Exp. Biol. 2010, 213, 2273–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toomey, J.; Eldredge, J.D. Numerical and Experimental Study of the Fluid Dynamics of a Flapping Wing with Low Order Flexibility. Phys. Fluids 2008, 20, 073603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldredge, J.D.; Toomey, J.; Medina, A. On the Roles of Chord-Wise Flexibility in a Flapping Wing with Hovering Kinematics. J. Fluid Mech. 2010, 659, 94–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, B.; Luo, H. Effect of Wing Inertia on Hovering Performance of Flexible Flapping Wings. Phys. Fluids 2010, 22, 111902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.; Shyy, W. Scaling Law and Enhancement of Lift Generation of an Insect-Size Hovering Flexible Wing. J. R. Soc. Interface 2013, 10, 20130361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakata, T.; Liu, H. Aerodynamic Performance of a Hovering Hawkmoth with Flexible Wings: A Computational Approach. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2012, 279, 722–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahzad, A.; Tian, F.-B.; Young, J.; Lai, J.C.S. Effects of Flexibility on the Hovering Performance of Flapping Wings with Different Shapes and Aspect Ratios. J. Fluids Struct. 2018, 81, 69–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Luo, H.; Doyle, J.F. Dynamic Pitching of an Elastic Rectangular Wing in Hovering Motion. J. Fluid Mech. 2012, 693, 473–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Tian, F.-B. Numerical Study of Sound Generation by Three-Dimensional Flexible Flapping Wings during Hovering Flight. J. Fluids Struct. 2020, 99, 103165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridhar, M.; Kang, C. Aerodynamic Performance of Two-Dimensional, Chordwise Flexible Flapping Wings at Fruit Fly Scale in Hover Flight. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2015, 10, 036007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.-K.; Aono, H.; Cesnik, C.E.S.; Shyy, W. Effects of Flexibility on the Aerodynamic Performance of Flapping Wings. J. Fluid Mech. 2011, 689, 32–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Tang, J. Unsteady Aerodynamic Force Generation by a Model Fruit Fly Wing in Flapping Motion. J. Exp. Biol. 2002, 205, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabawy, M.R.A.; Crowther, W.J. Aero-Optimum Hovering Kinematics. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2015, 10, 044002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Nabawy, M.R. The Combined Effect of Wing Planform and Stroke Kinematics on Aerodynamics of Flapping Insect Wings. In Proceedings of the AIAA SCITECH 2022 Forum, San Diego, CA, USA & Virtual Event, 3–7 January 2022; American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics: Reston, VA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patankar, S.V.; Spalding, D.B. A Calculation Procedure for Heat, Mass and Momentum Transfer in Three-Dimensional Parabolic Flows. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 1972, 15, 1787–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issa, R.I. Solution of the Implicitly Discretised Fluid Flow Equations by Operator-Splitting. J. Comput. Phys. 1986, 62, 40–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Nabawy, M.R.A. Wing Planform Effect on the Aerodynamics of Insect Wings. Insects 2022, 13, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunt, J.C.R.; Wray, A.A.; Moin, P. Eddies, Streams, and Convergence Zones in Turbulent Flows. Center for Turbulence Research, Proceedings of the Summer Program 1988. Document ID: 19890015184. pp. 193–208. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/234550074_Eddies_streams_and_convergence_zones_in_turbulent_flows (accessed on 2 July 2022).
- Cheng, X.; Sun, M. Wing-Kinematics Measurement and Aerodynamics in a Small Insect in Hovering Flight. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dillon, M.E.; Dudley, R. Surpassing Mt. Everest: Extreme Flight Performance of Alpine Bumble-Bees. Biol. Lett. 2014, 10, 20130922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellington, C.P. The Aerodynamics of Hovering Insect Flight.4. Aerodynamic Mechanisms. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 1984, 305, 79–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, S.S.; Zhao, J.; Sheridan, J.; Hourigan, K.; Thompson, M.C. Evolutionary Shape Optimisation Enhances the Lift Coefficient of Rotating Wing Geometries. J. Fluid Mech. 2019, 868, 369–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.; Nabawy, M.R.A. Effects of Stroke Amplitude and Wing Planform on the Aerodynamic Performance of Hovering Flapping Wings. Aerospace 2022, 9, 479. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace9090479
Li H, Nabawy MRA. Effects of Stroke Amplitude and Wing Planform on the Aerodynamic Performance of Hovering Flapping Wings. Aerospace. 2022; 9(9):479. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace9090479
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Hao, and Mostafa R. A. Nabawy. 2022. "Effects of Stroke Amplitude and Wing Planform on the Aerodynamic Performance of Hovering Flapping Wings" Aerospace 9, no. 9: 479. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace9090479
APA StyleLi, H., & Nabawy, M. R. A. (2022). Effects of Stroke Amplitude and Wing Planform on the Aerodynamic Performance of Hovering Flapping Wings. Aerospace, 9(9), 479. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace9090479







