Abstract
Background: Cerebrovascular accident, commonly known as stroke, Parkinson’s disease, and multiple sclerosis represent significant neurological conditions affecting millions globally. Stroke remains the third leading cause of death worldwide and significantly impacts patients’ hand functionality, making hand rehabilitation crucial for improving quality of life. Methods: A comprehensive literature review was conducted analyzing over 300 papers, and categorizing them based on mechanical design, mobility, and actuation systems. To evaluate each device, a database with 45 distinct criteria was developed to systematically assess their characteristics. Results: The analysis revealed three main categories of devices: rigid exoskeletons, soft exoskeletons, and hybrid devices. Electric actuation represents the most common source of power. The dorsal placement of the mechanism is predominant, followed by glove-based, lateral, and palmar configurations. A correlation between mass and functionality was observed during the analysis; an increase in the number of actuated fingers or in functionality automatically increases the mass of the device. The research shows significant technological evolution with considerable variation in design complexity, with 29.4% of devices using five or more actuators while 24.8% employ one or two actuators. Conclusions: While substantial progress has been made in recent years, several challenges persist, including missing information or incomplete data from source papers and a limited number of clinical studies to evaluate device effectiveness. Significant opportunities remain to improve device functionality, usability, and therapeutic effectiveness, as well as to implement advanced power systems for portable devices.
1. Introduction
Cerebrovascular accident, commonly known as stroke, is a global health challenge that affected 17 million individuals in 2021. Stroke is the third leading cause of mortality worldwide [1] and one of the main contributors to adult physical disability [2], impacting more than a person’s health [3]. While stroke remains significant, 1.12 million cases and 9.53 million survivors of which are reported annually in the EU [4], robotic rehabilitation serves a larger patient population, including patients who suffer from Parkinson’s disease, 8.5 million cases of which are reported globally [5,6], and patients with neuromuscular conditions like multiple sclerosis, 2.8 million cases of which are reported worldwide [7] as of 2020.
After a stroke, survivors often face various complications including movement problems, speech disorders, visual disturbances, personality alterations, cognitive dysfunction, and post-stroke depression, requiring comprehensive rehabilitation approaches [8,9]. The main motor impairments are represented by spasticity and weakness [10,11], with spasticity manifesting as muscle stiffness and increased resistance to passive movements [12], while weakness affects the motor function of the fingers [13].
The effectiveness of rehabilitation relies on neuroplasticity, the brain’s capacity to change, reorganize, and adapt, and to enhance its ability to handle new situations [14,15]. Two phases are involved in neuroplasticity: the transformation of the initial neural network [16,17] and subsequent neuronal connection reestablishment [18], enhanced by physical activity and neural stimulation [19,20]. The rehabilitation process involves three main techniques [21]: passive motion involving a therapist (or the healthy hand of the patient) to guide the motion that the affected hand cannot perform anymore, active motion that involves independent movement of the affected hand to the limits of spasticity, and active-assisted therapy that combines both techniques, involving independent motion of the affected hand to the limits of spasticity and beyond this limit with the help of a therapist or patient healthy hand. Active therapy is essential for muscular strengthening and the neuroplasticity process [22,23,24,25,26].
Motor impairments can vary from individual to individual, and muscle state, stroke phase, and severity [27] must be taken into consideration. Current technology can provide precise therapeutic guidance [28], but not considering individual patient differences can reduce the effectiveness of the rehabilitation process [29]. The current growing demand for rehabilitation therapy faces significant challenges such as an insufficient availability of trained therapists [30,31] and a reduced number of therapy sessions [32,33,34].The following tools are used to measure the progress of the rehabilitation process: the CAHAI (Chedoke Arm and Hand Activity Inventory) [35,36], BBT (Box and Block Test) [37,38,39], 9-HPT (9-Hole Peg Test) [40,41], and Ad-AHA (Adult Assisting Hand Assessment stroke) [42,43], complemented by patient-reported outcomes through the MHQ (Michigan Hand Outcomes Questionnaire) [44,45], JHFT (Jebsen–Taylor Hand Function Test), which simulates daily activities for unilateral hand function assessment [46,47], DHI (Dizziness Handicap Inventory) [48,49,50,51,52], and the ABILHAND questionnaire [53,54,55].
The need for new methods to deliver care to the affected patients is reflected in the growing rehabilitation robotics market, which reached approximately USD 500 million in North America in 2020 [56], with expected growth in Asia and Europe [57]. This combination of high neurological disorder prevalence, limited healthcare professional availability, and proven benefits of consistent rehabilitation necessitates the development of hand exoskeletons to supplement traditional therapy methods and address the growing gap between patient needs and available care.
This paper presents a systematic review of rehabilitation hand exoskeletons. Section 1 presents the global impact of neurological disorders, stressing the most important ones, such as stroke, Parkinson’s disease, or multiple sclerosis, and discusses rehabilitation needs, neuroplasticity importance, and growing market demand for rehabilitation robotics. Section 2 presents human hand biomechanics, joint types, and motions, and outlines systematic review methodology including database searches, inclusion criteria, and analysis frameworks for over 300 devices. Section 3 categorizes devices into orthoses, exoskeletons, and end-effector types, discusses design requirements including safety, comfort, force transmission, and affordability, and compares mechanical approaches and clinical considerations. Section 4 classifies exoskeletons by type (soft/rigid/hybrid), mobility, mechanism position, actuation, and transmission systems. Section 5 analyzes a database of 300+ devices, presenting trends in publication, geographic distribution, design approaches, and technical specifications, and includes statistical analysis of actuator types and device configurations. Section 6 summarizes findings showing that rigid exoskeletons dominate (50%), with soft (35%) and hybrid (15.5%) following. The section also notes electric actuation prevalence (55.8%) and identifies future research opportunities for improving functionality and therapeutic effectiveness.
2. Materials and Methods
The human hand is one of the most complex and highly versatile parts of the human body, with many degrees of freedom (DoF) that allow a wide range of movement. Various types of joints contribute to the overall dexterity of the human hand; however, the large number of DoF constitutes the main challenge in creating accurate models of the hand’s biomechanics [58].
2.1. Skeletal Model of the Human Hand
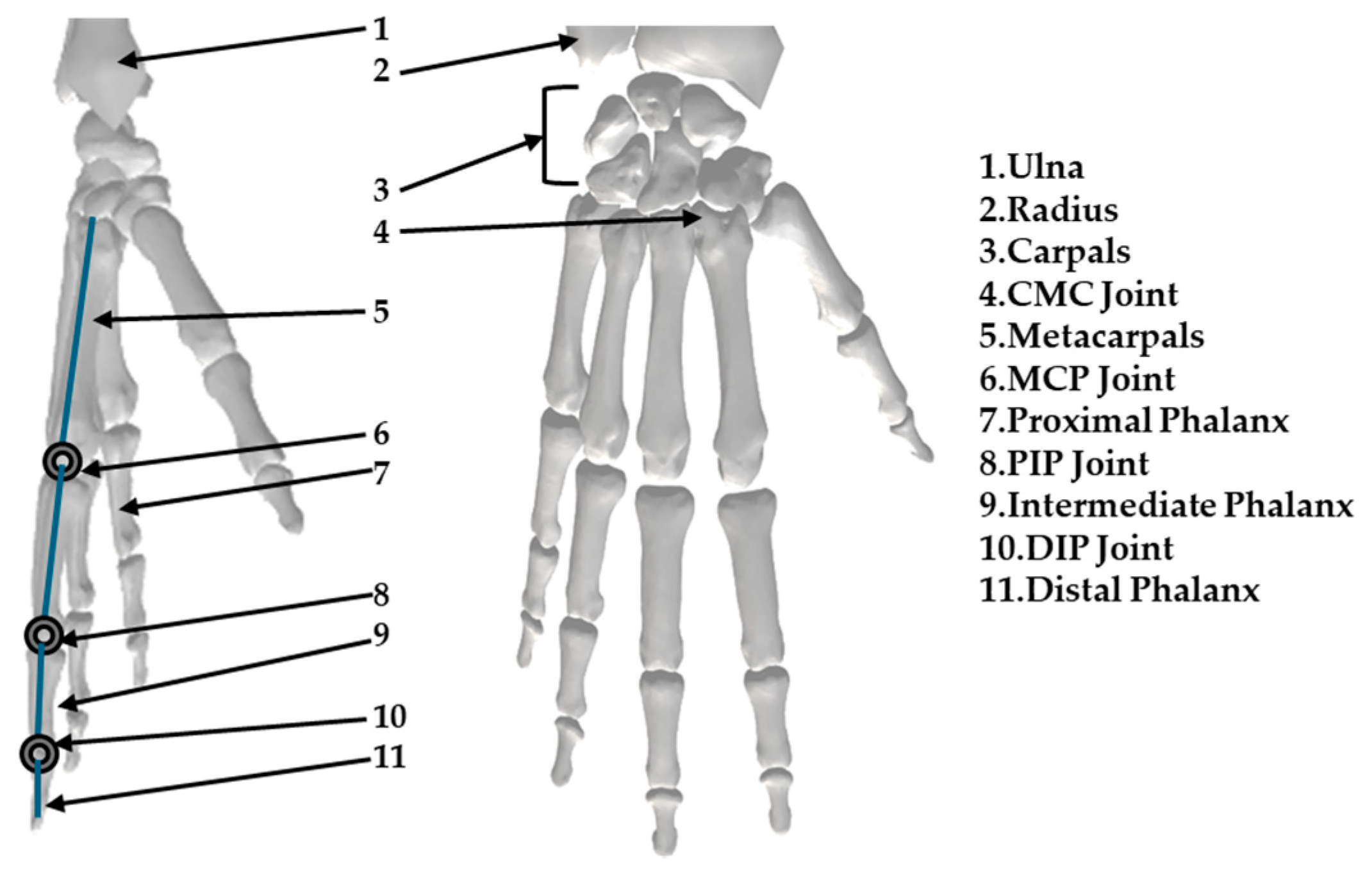
The skeletal model of the human hand is illustrated in Figure 1. The OpenSim [59] library’s hand skeleton model provides insight into the hand’s structure. The hand skeleton consists of the capitate bone near the wrist, metacarpals, and phalanges. Each digit contains one metacarpal segment. The four fingers consist of three segments: proximal, intermediate, and distal phalanges. In contrast, the thumb has only two phalanx segments: proximal and distal.
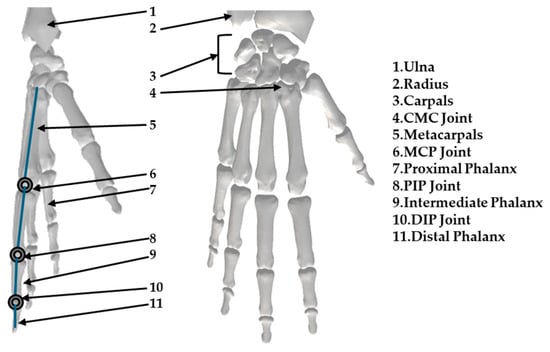
Figure 1.
Skeletal model of the human hand.
The names of the hand joints are based on the bones they connect. Each of the four fingers consists of one metacarpophalangeal joint (MCP), one distal interphalangeal joint (DIP), and one proximal interphalangeal joint (PIP). The thumb consists of a MCP and one DIP joint. Near the wrist, each digit connects through a carpometacarpal joint (CMC). The joint that connects the phalanges can be considered a 1 DoF hinge joint because each pair of phalanges can only perform bending and extending movements.
The MCP joint is more complex and can be considered a 2 DoF joint. It can be modeled as a ball-and-socket joint that allows for rotation along two different directions.
The CMC joints, positioned near the wrist, can be considered 2 DoF saddle joints.
2.2. Motions of the Human Hand
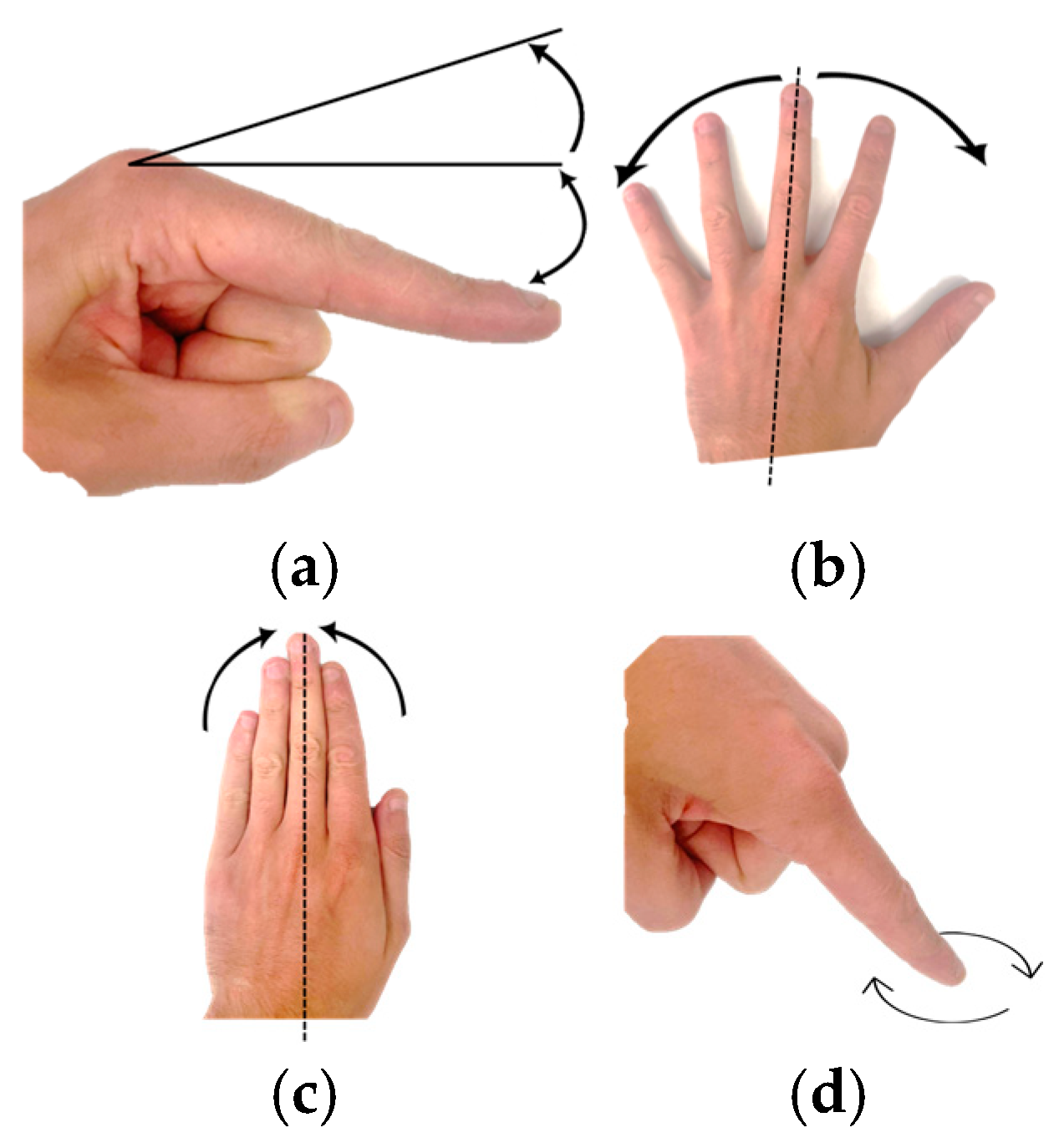
Precise terminology is mandatory in the study of human hand biomechanics to describe the various movements of the digits and joints. Flexion and extension motions refer to the decrease and increase of joint angles, respectively. Abduction and adduction describe the movements of fingers away from and towards the middle finger, except for the middle finger itself, which can perform only bilateral abduction [60,61].
Due to its unique anatomical structure, the thumb possesses a more complex range of motion. The abduction of the thumb can be defined as anterior movement perpendicular to the palm, while adduction returns it to the palmar plane.
Circumduction refers to the thumb’s movement in a conical pattern at the TMC joint. Pronation represents the movement of the thumb along its longitudinal axis inward toward the index finger. The outward rotation of the thumb is termed supination. The terminology described above provides an accurate description of finger movement. Finger motions, flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, and circumduction are illustrated in Figure 2.
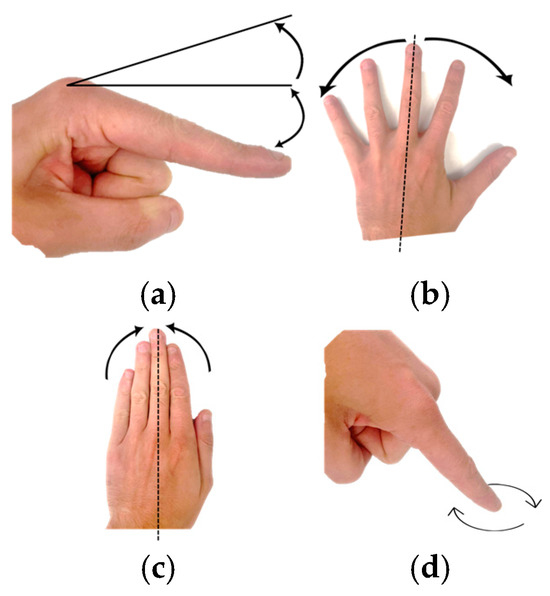
Figure 2.
Finger motions: (a) Hyperextension-extension-flexion, (b) Abduction, (c) Adduction, (d) Circumduction.
2.3. Predominant Human Hand Postures
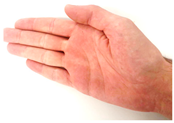
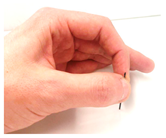
The main movements of the human hand are illustrated in Table 1 and are in-depth analyzed in reference [62].

Table 1.
Predominant human hand movements.
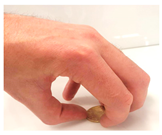
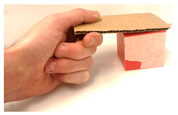
The most common grasp movements of the human hand are depicted in Table 2 and in-depth analyzed in reference [62].

Table 2.
Common human hand grasping gestures.
2.4. Data Extraction and Categorization
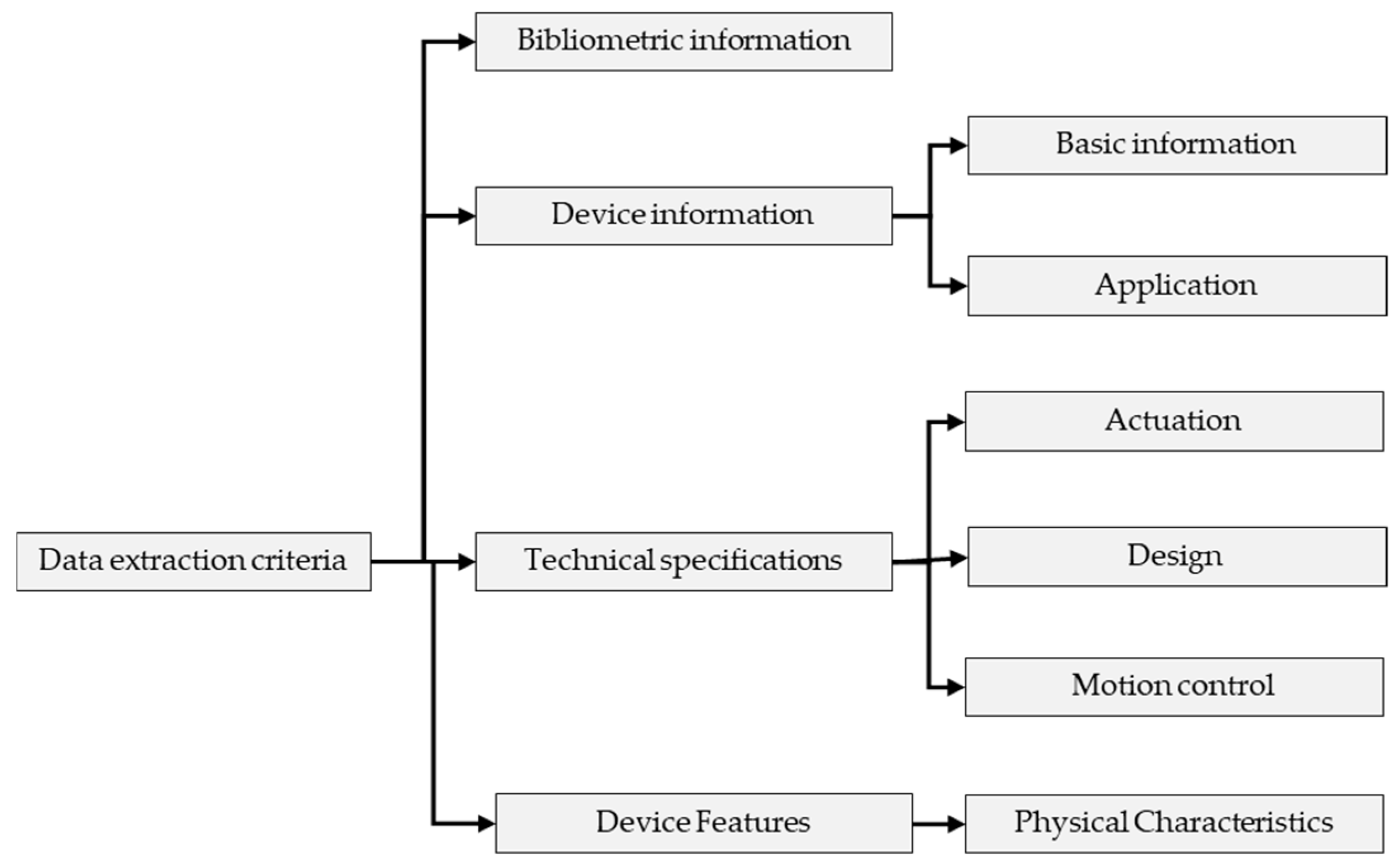
The protocol illustrated in Figure 3 was used to systematically identify and analyze relevant research articles focusing on hand exoskeleton devices for rehabilitation and assistance.
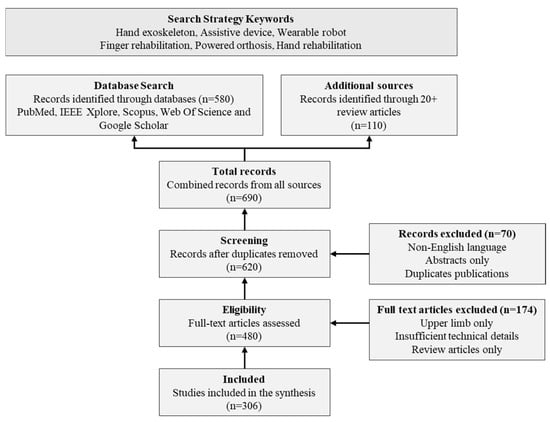
Figure 3.
Classification Framework.
From each included article, a wide range of data were extracted. This included bibliometric information such as authors, year of publication, country of origin, and publication type (journal article or conference paper). Technical details extracted included the device name (if applicable), type of exoskeleton (rigid, soft, or hybrid), actuation method and type, transmission mechanism, number of actuators, degrees of freedom (total and active), mechanism placement, finger motions assisted, independent vs. coupled finger assistance, number of fingers covered, and range of motion. Additional information on target application, portability, safety features, adaptability features, weight, and any clinical testing was also recorded.
2.5. Literature Search and Selection
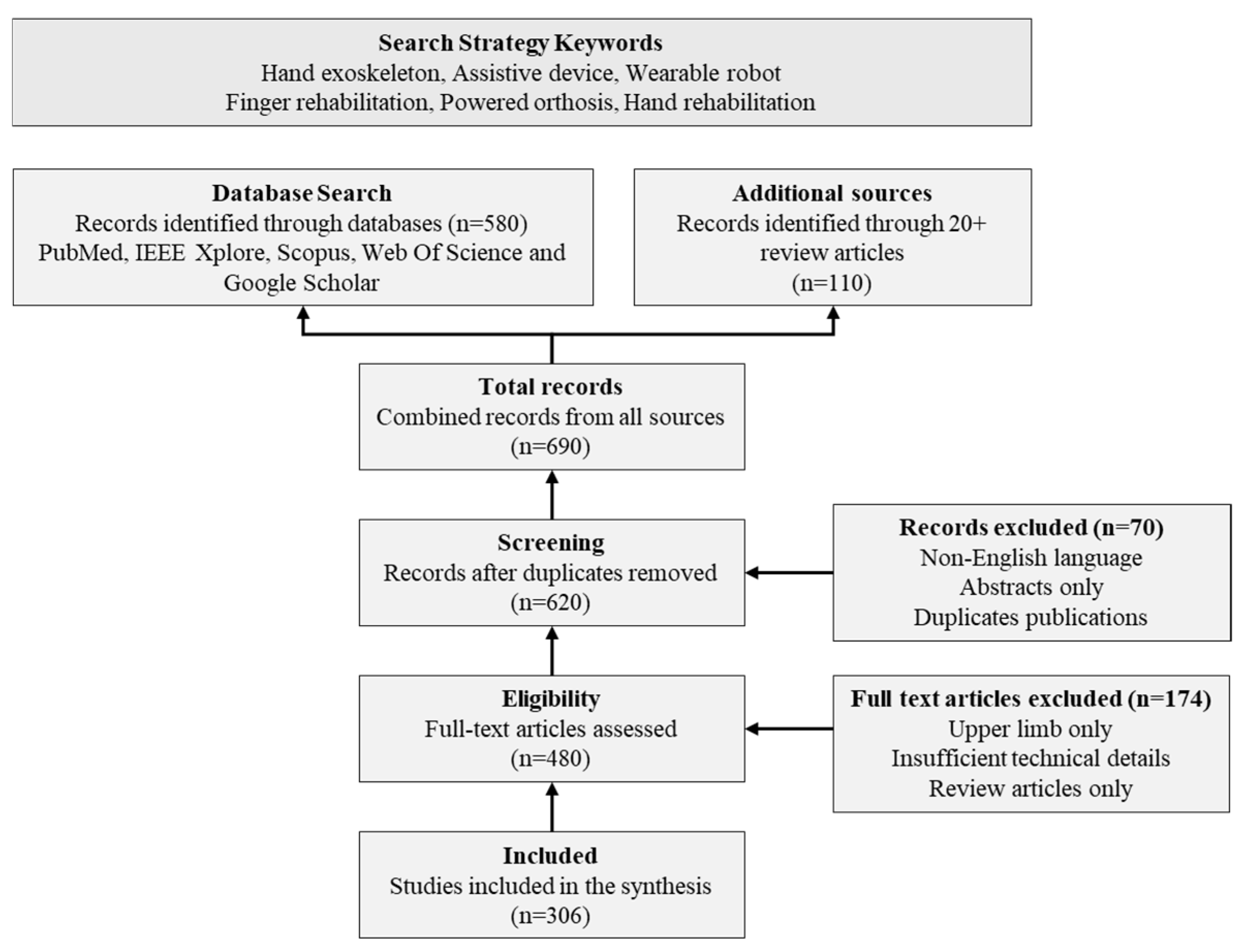
To identify relevant studies on hand robotic exoskeletons for rehabilitation and assistance, a comprehensive literature search was conducted. The search covered multiple databases including PubMed, IEEE Xplore, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar, using search terms such as “hand exoskeleton” and “hand rehabilitation robot”.
The extracted data was organized into a structured database for analysis as illustrated in Figure 4. Devices were categorized based on their design characteristics, actuation methods, and intended applications, facilitating comprehensive analysis.
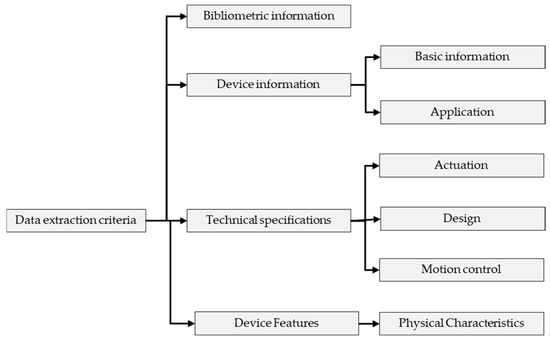
Figure 4.
Flow Diagram of Literature Search and Selection Process.
Initially, more articles were identified. After removing duplicates and screening titles and abstracts, articles were selected for full-text review. Following the application of inclusion and exclusion criteria, a final set of 306 articles was included in this review. Additionally, over 20 existing review articles in the field were examined to identify any potentially missing relevant studies.
The inclusion criteria for the review encompassed studies describing hand exoskeleton devices for rehabilitation or assistance, conference proceedings, and articles. Exclusion criteria included studies focused only on upper limb exoskeletons without specific hand components.
2.6. Data Analysis
The analysis of the extracted data involved quantitative approaches. The quantitative analysis utilized descriptive statistics to summarize trends in hand exoskeleton design and functionality. This included examining the distribution of exoskeleton types, distribution of different actuation methods, distribution of transmission mechanisms, average number of DoF, distribution of finger coverage, assisted motions, and weight distribution analysis. Trends in publication types and research output over time, as well as the geographical distribution of research, were also analyzed.
2.7. Limitations
Several limitations of this review were identified. The focus on English-language publications may have excluded relevant studies published in other languages. Despite efforts to be comprehensive, it is possible that some relevant studies were missed due to the specific search terms used or limitations of the databases searched.
3. Hand Rehabilitation Devices
Hand rehabilitation devices (HRDs) can be classified into three main categories: orthoses, exoskeletons, and end-effector devices. Orthoses, similar to traditional hand braces, provide fundamental support. Exoskeletons and end-effector devices go a step further by incorporating powered systems that enable passive exercises. These advanced devices offer crucial support and movement of the fingers through various actuation methods, adding an important dimension to rehabilitation therapy [21,22]. Robot-assisted therapy for upper extremity rehabilitation post-stroke emerged in the 1990s [63] the initial hand rehabilitation robots were designed to take over the physically demanding aspects of therapy from human therapists. The main objectives were to better reproduce the natural motion patterns of human joints and more effectively address the specific needs of rehabilitation. This approach developed better and more flexible robotic systems in hand rehabilitation, leading to the modern devices used today [64].
The field of rehabilitation robotics integrates multidisciplinary knowledge fields, such as anatomy, neuroscience, cognitive and learning sciences, and extensive clinical experience [65].
The development of hand rehabilitation robots requires more than mechanical and engineering considerations; the characteristics of stroke patients, current rehabilitation theories, and methods for assessing therapeutic progress should be taken into consideration [66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74].
Based on mechanical structure, hand rehabilitation devices can be classified into two main categories, exoskeleton devices and end-effector devices.
- Exoskeleton Devices
Exoskeletons are devices that wrap around the target body part, similar to orthoses in their ability to provide safety and support. However, exoskeletons are distinguished by their additional powered components. These extra elements enable exoskeletons to offer active, powered functions to the user. This combination of supportive structure and powered assistance makes exoskeletons particularly useful for rehabilitation, movement augmentation, or other specialized applications where active support is beneficial [21,75].
Finger exoskeletons enable precise actuation of specific joints while providing support, which is crucial for patients with advanced injuries. Their portability makes them valuable for elderly or remote patients, offering consistent rehabilitation or assistance outside clinical settings [75].
- End-Effector Devices
End-effector devices offer a distinct approach to hand rehabilitation compared to exoskeletons. These devices focus on controlling the endpoint or the distal interphalangeal joint of the finger, rather than encompassing and actuating the entire finger structure.
The primary advantages of end-effector devices are their high level of control and feedback precision. By concentrating on the fingertip or the most distal joint, these devices can achieve accurate movement and force application without the complexity of managing multiple joints simultaneously.
4. Exoskeleton Rehabilitation Devices
Exoskeletons are designed to match the shape and the movement of the user’s hand. Each degree of freedom in the exoskeletons’ design must be precisely aligned with the corresponding human joint. By mimicking human anatomy and joint movements so closely, exoskeletons can provide targeted support and assistance, making them a valuable tool in robotic rehabilitation [75].
Exoskeleton rehabilitation devices can be classified as follows.
4.1. Classification by Type
Exoskeleton hand rehabilitation devices can be divided into three main categories: rigid, soft, and hybrid, as illustrated in Figure 5.
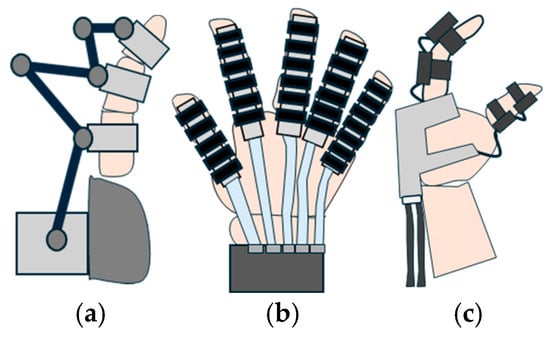
Figure 5.
Schematic representation of the three classes of robotic hand rehabilitation exoskeletons: (a) rigid, (b) soft, and (c) hybrid.
4.1.1. Soft Exoskeletons
In recent years, the development of soft robotics rehabilitation systems based on soft actuation has increased significantly [76].
Soft exoskeletons, sometimes referred to as soft gloves [77], offer unique advantages in rehabilitation. These soft exoskeletons can reduce the overall weight of hand rehabilitation systems and provide better self-alignment between the device and finger joints due to their soft actuation [78,79]. These exoskeletons are typically manufactured using fabric-, plastic-, or silicone-based materials. This flexibility allows the exoskeleton to be customized for each patient’s finger size, offering a more personalized rehabilitation experience [78].
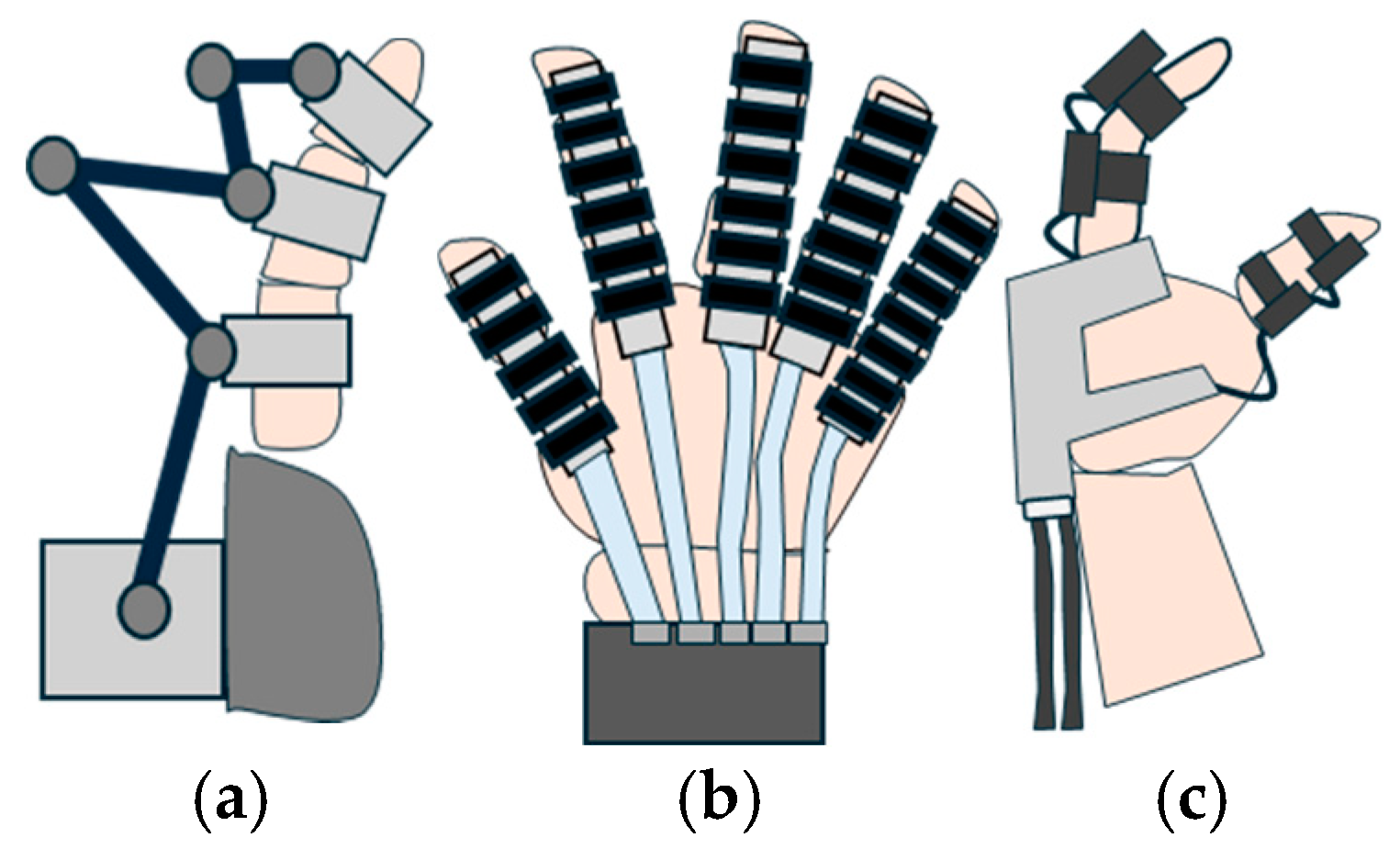
4.1.2. Rigid Exoskeletons
Rigid exoskeletons utilize rigid transmission mechanisms, which are systems of rigid links joined together [80]. This is one of the simple ways to translate the movements of the actuator to the intended human joint.
In systems that are fully actuated, both direct and indirect relationships can be established. Using this feature, any measurements taken from the actuator, such as encoder signals, torque, or current, can be used to determine the finger’s state. Simple and natural control of the hand is possible due to the direct connection between actuators and hand joints and, as a result, additional tracking systems are not required.
Control algorithms are simplified due to the natural matching of actuator and joint movements, and the overall reliability and precision of the exoskeleton are enhanced. Rigid exoskeletons enable more accurate position control and force transmission, which are crucial for both rehabilitation exercises and assistive applications [76].
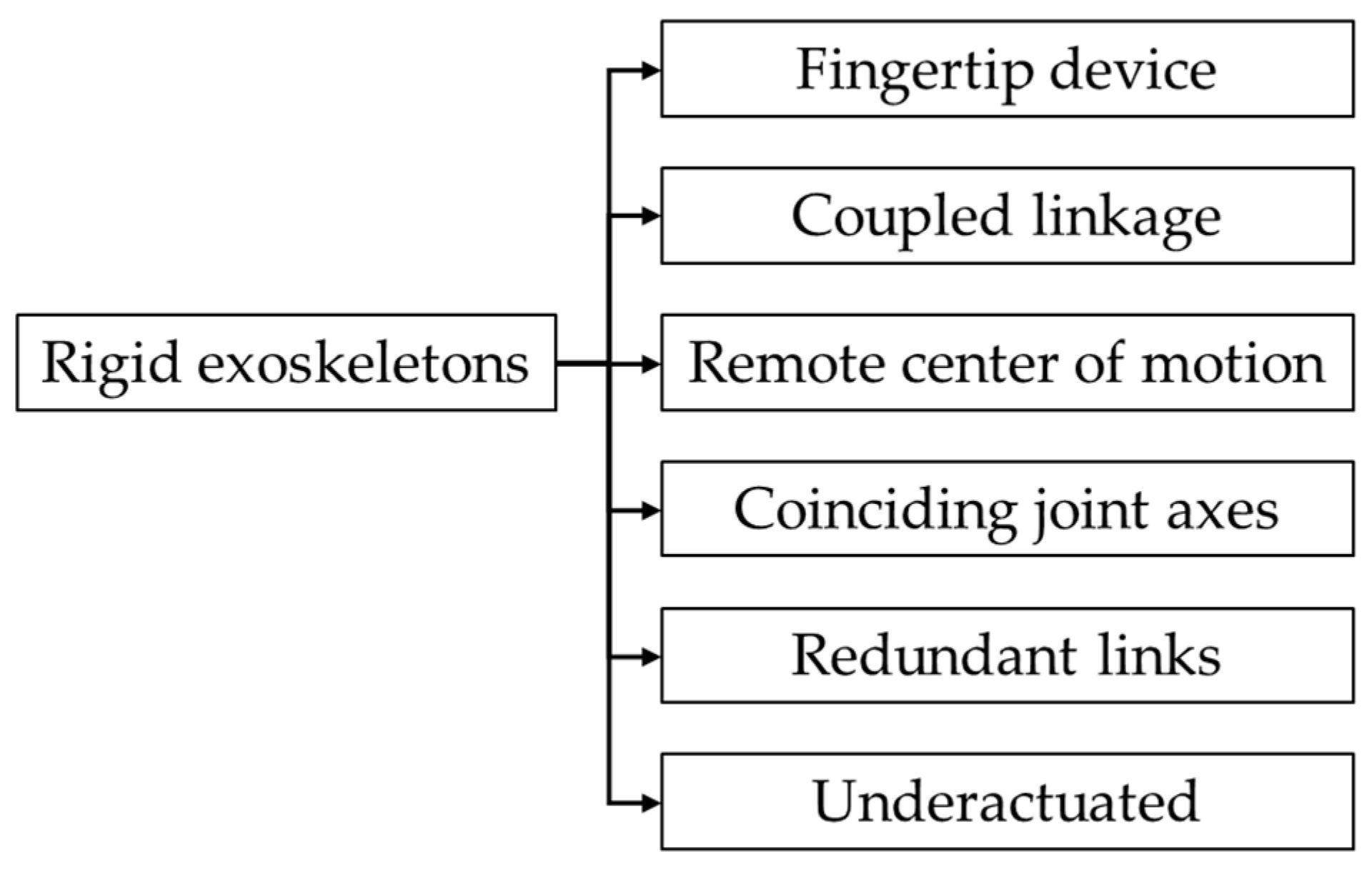
Based on the linkage type, the rigid hand exoskeletons can be classified as illustrated in Figure 6. Figure 7 illustrates a schematic representation of each linkage type.
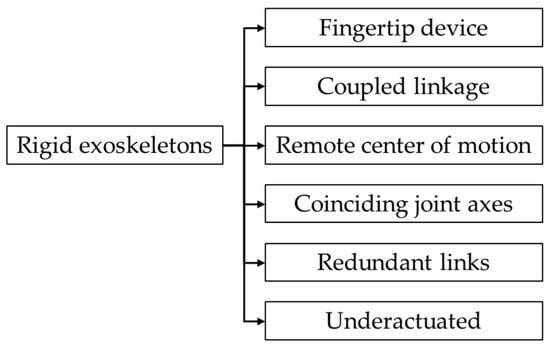
Figure 6.
Classification of rigid exoskeletons based on linkage type.
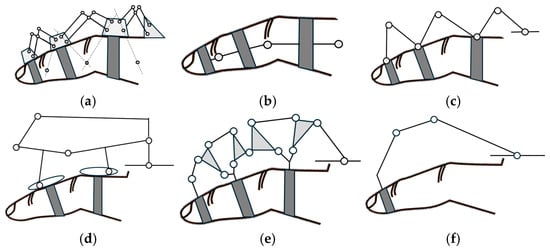
Figure 7.
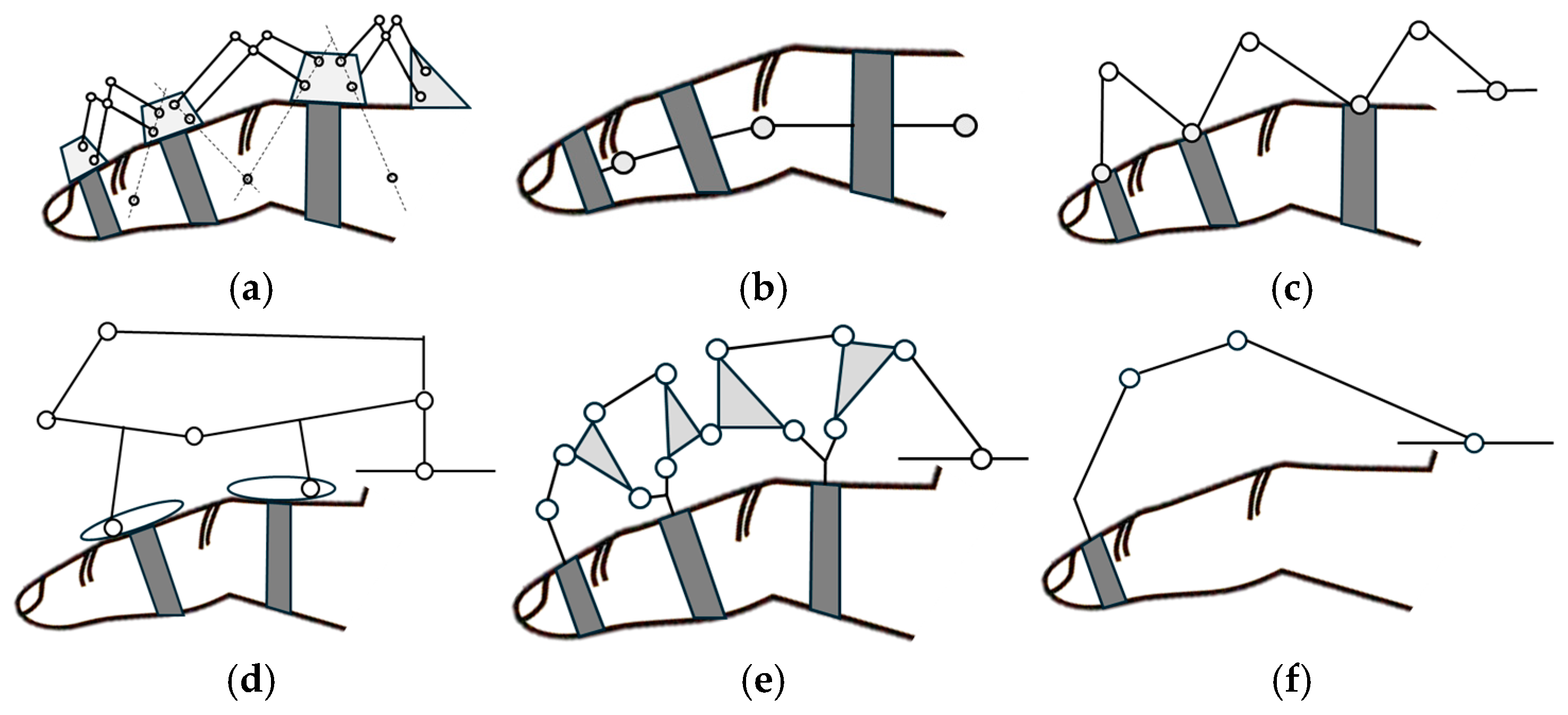
Schematic representation of the main types of linkages. (a) Remote center of motion, (b) coinciding joint axes, (c) redundant links, (d) underactuated device, (e) coupled linkage device, and (f) fingertip device.
Hand exoskeletons can be developed with mechanisms that create remote centers of motion for each link, aligning with the finger joints’ natural pivot points, as illustrated in Figure 7a. This type of mechanism has been explored with various potential designs discussed in reference [81]. Popular mechanisms include the parallelogram mechanism and circular prismatic joints [82].
Matched axis types of exoskeletons aim to align joints precisely with those of the human hand, as illustrated in Figure 7b. This method is one of the simplest ways to control hand movements predictably; however, the design presents challenges to implement in practice. The main reason is represented by the placement of the exoskeleton’s joints directly next to the finger joints. This type of placement is problematic for multiple fingers due to interference with natural hand movements when fingers need to come close together during grasping. Due to these practical limitations, the matched axes topology is generally not considered a viable option for exoskeletons designed to support multiple fingers simultaneously [82].
An alternative method for connecting the movement of a specific exoskeleton joint to a single hand joint is represented by a redundant linkage. This topology involves the attachment of the system to the digit at points before and after each actuated joint. However, additional linkages and joints should be incorporated between attachment points, as illustrated in Figure 7c. Well-defined relationships between the motions of the exoskeleton and the hand joints are established using this type of mechanism [82].
Multiple finger joints can be controlled using a single actuator through an underactuated mechanism. The main feature of this design is represented by the ability to automatically adjust the forces that act on the different finger phalanges based on the interaction between the device and the user’s finger. The adaptive behavior of the device is possible due to the incorporation of passive elements in the mechanism design [72], as illustrated in Figure 7d.
Coupled exoskeleton devices coordinate the movement of different finger joints simultaneously and are designed to interact with the user’s finger at multiple contact points, as illustrated in Figure 7e. This type of design allows for more natural finger movement. Through mechanical adjustments of the ratios, these devices can accommodate different motion patterns and adapt to various users without complex control systems [72].
Another type of exoskeleton linkage is represented by the fingertip exoskeleton. Using this type of mechanism, the fingertip’s position in space is controlled, regardless of how the individual finger joints move. As illustrated in Figure 7f, this design allows precise fingertip manipulation while enabling natural movement of the finger joints [72]. This type of mechanism is simpler than multi-joint mechanisms. Figure 8 provides visual representations of various linkage types.
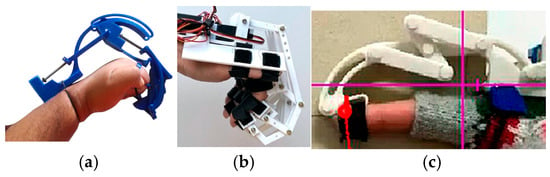
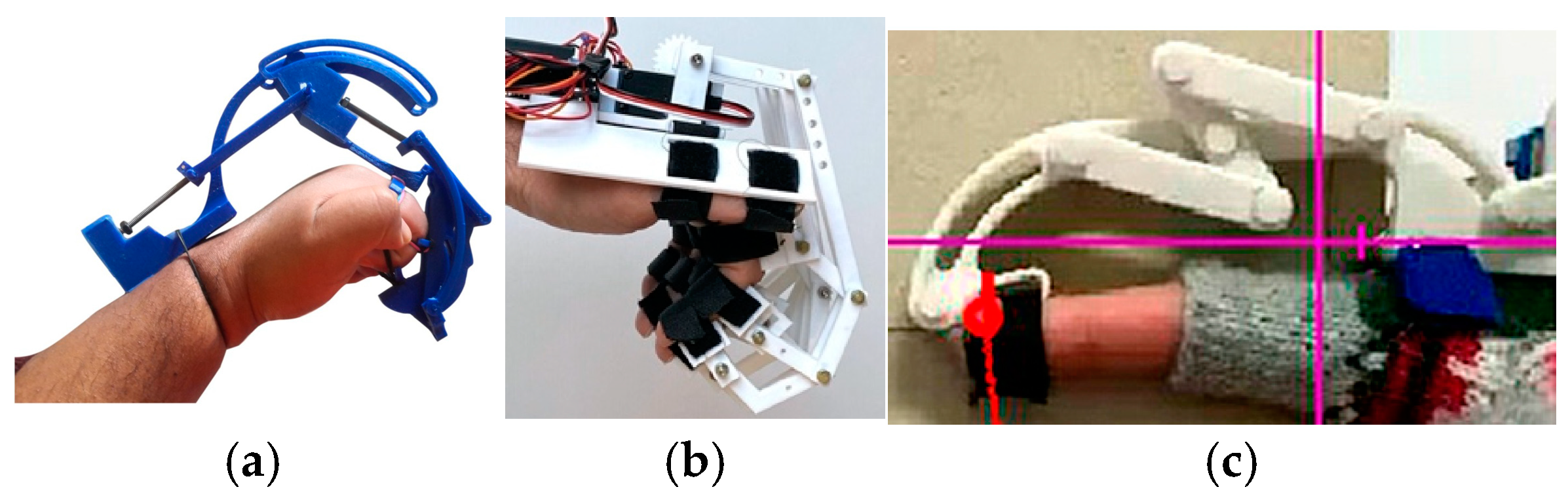
Figure 8.
Exoskeleton types: (a) Underactuated device [83], (b) coinciding joint axes [84], and (c) fingertip linkage device [85].
Prior investigations into redundant linkage exoskeletons include the works of [86,87,88,89,90,91]. Additional research exploring fingertip linkage devices has been conducted by several authors [92,93,94,95,96]. Investigations into underactuated devices have been studied in [97,98]. Understanding human hand proportions and exoskeleton connectivity has been explored in [99,100].
A considerable number of studies have investigated coupled devices utilizing a single actuator, for example, the work of [101,102,103,104,105,106]. Another strand of research has focused on coupled devices employing two actuators [107,108,109,110,111]. The research conducted by [81] introduced an exoskeleton design utilizing a remote center of motion (RCM) mechanism.
4.1.3. Hybrid Exoskeletons
Efficient power transmission, robust force control, and precise kinematics are advantageous characteristics provided by rigid exoskeletons. However, excessive mass, bulky design, and high stiffness are some of the main disadvantages of this type of rigid exoskeleton. To address the disadvantages, researchers developed innovative approaches such as the incorporation of elastic elements within the rigid mechanism to enhance compliance while preserving the advantages of structural rigidity. Hybrid exoskeletons integrate a rigid frame with deformable materials to achieve an optimal balance between mechanical performance and ergonomic consideration [76].
The integration of compliant materials in exoskeleton design significantly enhances device wearability and user comfort. These materials facilitate compatibility with the natural biomechanics of human fingers, improving force output capabilities [112]. Additive manufacturing technologies have facilitated the development of diverse exoskeleton architectures [113]. Some researchers have leveraged these capabilities to create single-unit designs [114,115,116] while others have explored modular structures [117,118]. An alternative strategy involves the incorporation of elastic spring elements [119]. This approach aims to mitigate the limitations typically associated with rigid structures while preserving their mechanical advantages. Another strategy employs fiber-reinforced soft bending actuators [120,121,122].
4.2. Classification by Hand Mobility
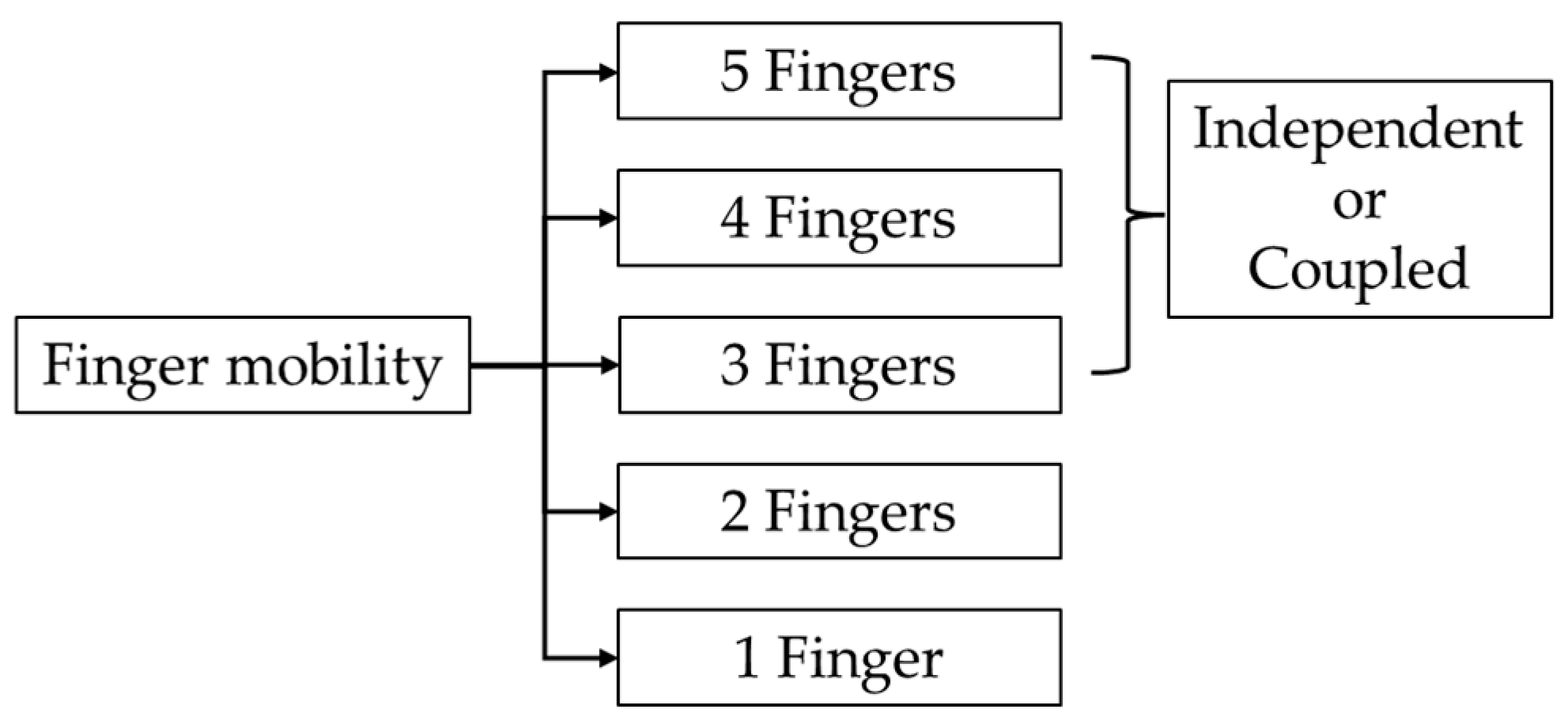
Exoskeletons can be classified according to hand mobility. Devices can be designed to assist and control different numbers of fingers on the human hand, which typically has five fingers. Figure 9 illustrates various configurations of finger assistance in exoskeleton designs.
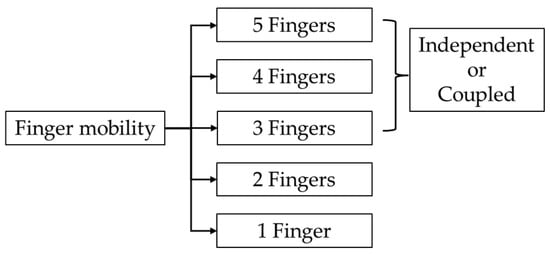
Figure 9.
Different configurations based on hand mobility.
Hand exoskeletons can be categorized by the number of actuated fingers. Single-finger designs [13,83,85,95,97,102,103,118,123,124,125,126,127,128,129,130,131,132,133,134,135,136,137,138,139,140,141,142,143,144,145,146,147,148,149,150,151,152,153,154,155], often focusing on the index finger [13,83,102,118,123,124,144,151,152], serve as initial investigations for multi-finger exoskeletons. Other single-finger exoskeletons target the thumb [142,150,156] or middle finger [133].
Two-finger exoskeletons [157,158,159,160,161,162,163,164,165,166,167,168,169,170], which independently control multiple finger configurations such as thumb–index [103,158,164,167] or index–middle [159,171], have been developed to support targeted hand movements for rehabilitation, such as precision grip tasks. However, most activities of daily living require assistance from at least three fingers [96,98,110,172,173,174,175,176,177,178,179,180,181,182,183,184]. Three-finger combinations typically focus on thumb–index–middle configurations [175,176,182,183,185,186].
While three-finger designs can support many tasks, configurations of four fingers [84,88,89,91,112,187,188,189,190,191,192,193,194,195,196,197,198,199,200,201,202,203,204] offer improved functionality. These include designs assisting all fingers except the thumb [84,106,205], configurations excluding the little finger [189,201,206], and systems actuating thumb–index–middle–ring combinations [89].
Most of the full hand (five fingers) exoskeletons employ independent actuation of all digits [15,93,117,119,120,146,207,208,209,210,211,212,213,214,215,216,217,218,219,220,221,222,223,224,225,226,227,228,229,230,231]. These systems enable individual control of each finger, offering maximum dexterity for both rehabilitation and assistive functions. While such designs typically require more complex control systems and a higher number of actuators, they provide the flexibility needed for precise manipulation tasks and personalized rehabilitation strategies.
Some devices implement coupled actuation designs [15,84,109,114,117,119,196,232,233,234,235,236,237,238,239,240,241,242,243,244,245,246], where certain fingers are mechanically linked to move together. Common coupling strategies include grouping four fingers together with independent control of the thumb [15,114,210,233,235,245,247], using ring–little finger coupling while maintaining independent control of the other digits [232,248,249], or coupling all fingers into a single actuation unit [237,238,250,251]. Some designs implement different coupling combinations for flexion and extension movements [242,243,244,252], offering a balance between functionality and complexity. These approaches offer advantages in terms of mechanical simplicity and a reduced number of actuators.
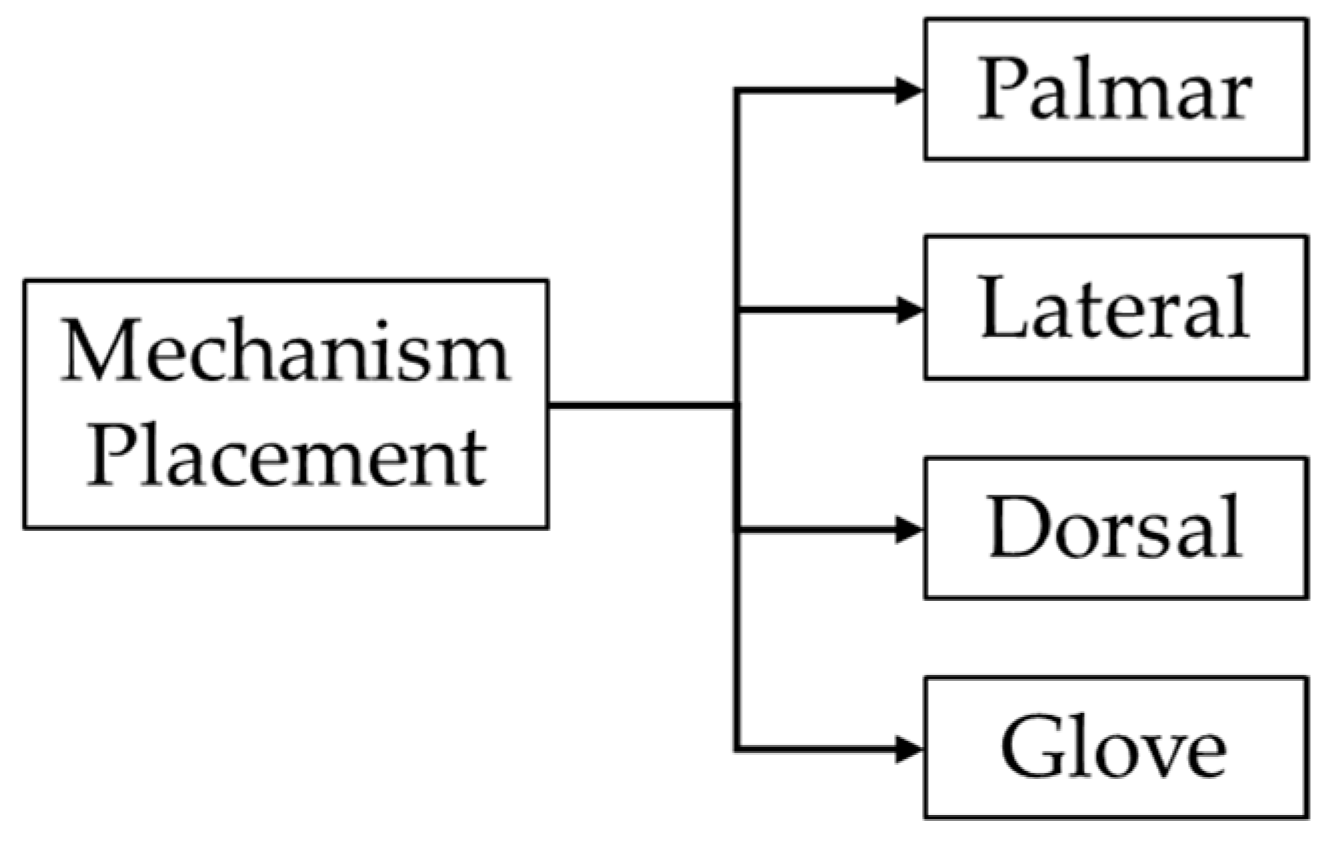
4.3. Classification by Mechanism Position
Robotic exoskeletons can be categorized based on the placement of the mechanism. This classification includes palmar, lateral, dorsal, and glove-type configurations, as illustrated in Figure 10. Each placement modality offers distinct biomechanical advantages and constraints, influencing the exoskeleton’s functionality [72].
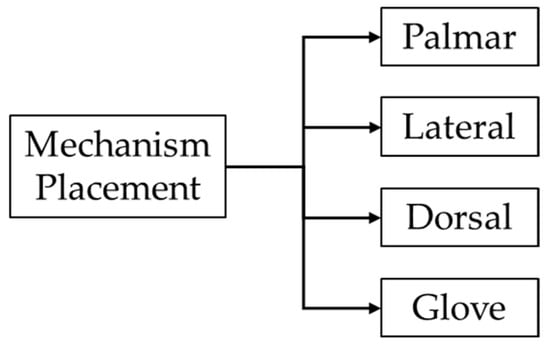
Figure 10.
Exoskeletons classification based on mechanism placement.
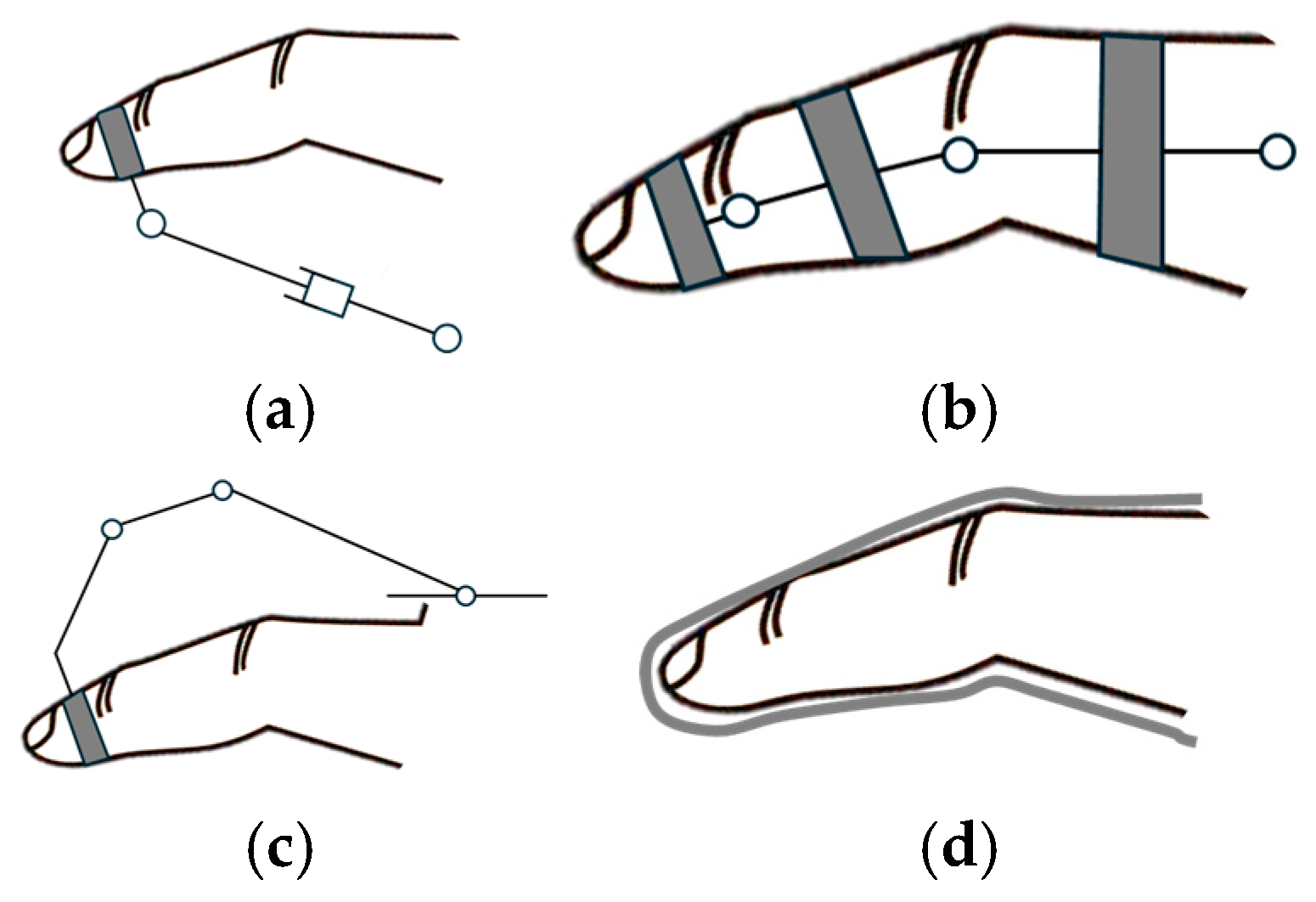
A schematic representation of each exoskeleton configuration is depicted in Figure 11, illustrating the palmar, lateral, dorsal, and glove-type designs.
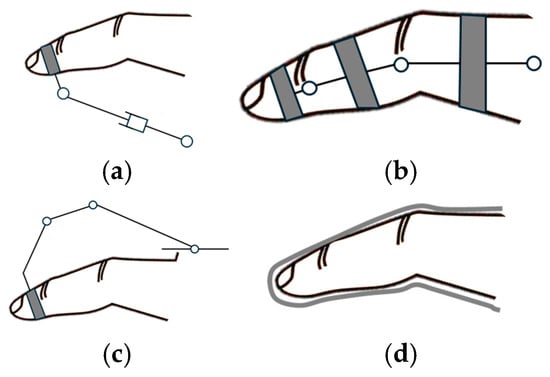
Figure 11.
Classification by mechanism placement: (a) palmar, (b) lateral, (c) dorsal, (d) glove.
4.3.1. Palmar
Palmar devices are characterized by the placement of mechanical or transmission components within the palmar region of the hand, as illustrated in Figure 11a. This type of mechanism placement has been studied in papers [190,253,254,255,256]. However, this configuration presents a limitation for assistive applications.
4.3.2. Lateral
Lateral devices are characterized by the positioning of mechanical or transmission components along the lateral aspects of finger phalanges, as depicted in Figure 11b, and were studied in [85,90,103,129,132,157,158,201,209,234,237,239,256,257,258]. An important advantage of lateral devices is the preservation of palmar surface availability for tactile interactions with the environment. However, lateral configurations present certain limitations; in multi-finger implementations, there is a potential for inter-digit collisions [72].
4.3.3. Dorsal
Dorsal devices are characterized by the placement of mechanical transmission above the finger phalanges, as illustrated in Figure 11c [59,83,84,85,87,88,89,90,91,92,93,94,95,96,98,101,102,105,106,107,108,109,110,111,112,113,114,117,120,123,124,125,126,127,128,130,131,134,135,136,137,139,140,141,142,143,144,145,146,147,148,149,150,151,153,154,156,158,160,161,162,163,164,166,169,173,181,182,183,185,188,195,196,197,198,199,200,201,202,203,204,205,206,207,210,211,212,213,214,217,219,220,221,222,224,225,226,227,230,233,235,236,238,240,242,244,245,247,250,251,259,260,261,262,263,264,265,266,267,268,269,270,271,272,273,274,275,276,277,278,279,280,281,282,283,284,285,286,287,288,289,290,291,292,293,294,295,296,297,298,299,300,301,302,303,304,305,306,307,308,309,310,311,312,313,314,315,316,317,318,319,320,321,322,323,324,325,326,327,328,329,330,331,332,333,334,335,336,337,338,339,340,341,342,343,344,345,346,347,348,349,350,351,352,353,354,355,356,357]. This configuration minimizes inter-digit collisions while preserving palmar surface availability.
4.3.4. Glove
Glove exoskeletons depicted in Figure 11d are characterized by their flexible, fabric-like construction that envelops the hand, with actuation components integrated into or attached to the glove material. This type of design offers several advantages. The soft, pliable nature of these devices allows for extended wear without causing discomfort or restricting natural hand movements. Soft gloves can conform to various hand sizes and shapes, making them suitable for a wider range of users without extensive customization. By using thin, flexible materials, soft gloves preserve much of the user’s natural tactile sensation, allowing for better interaction with objects during rehabilitation exercises.
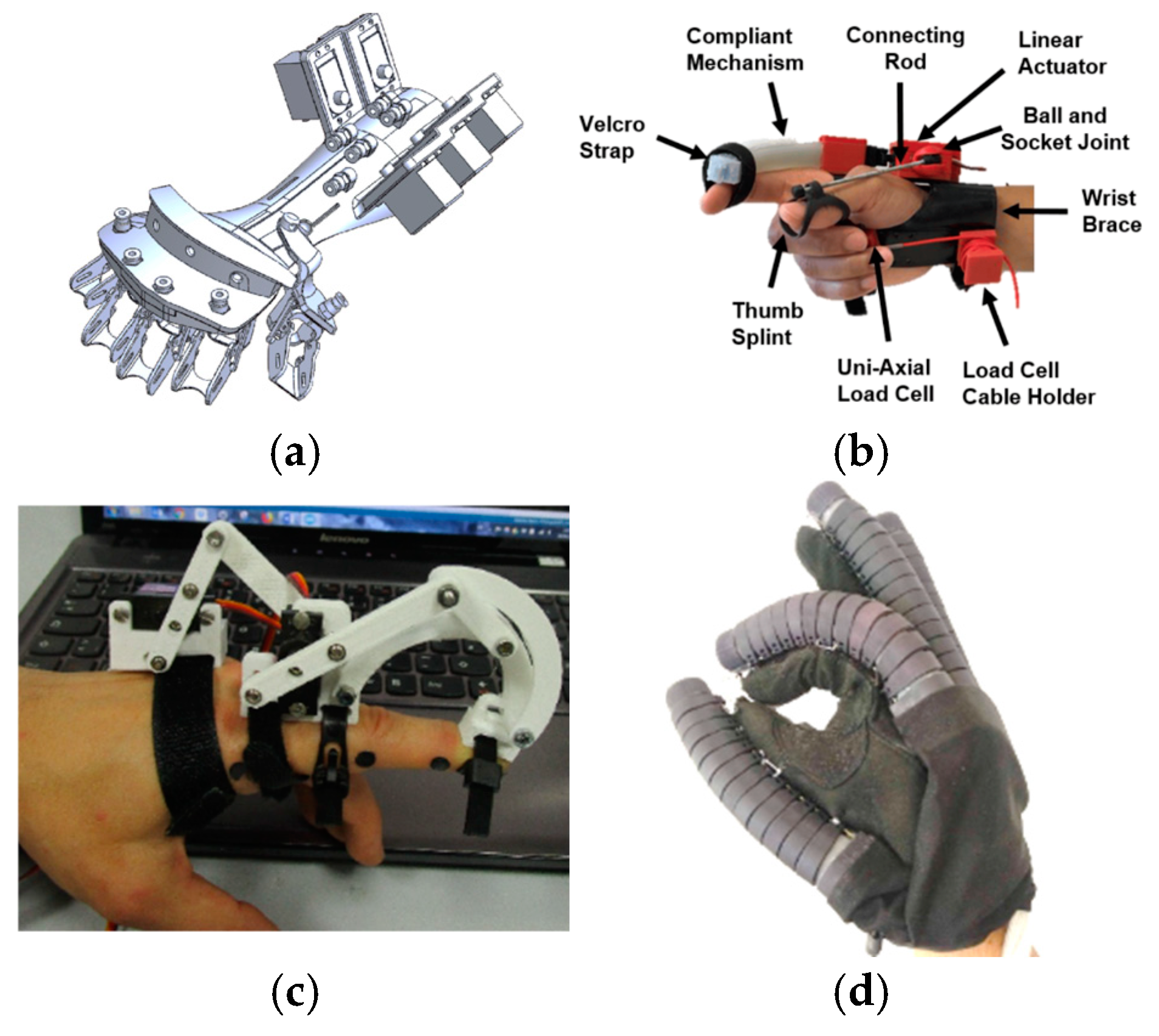
Soft glove exoskeletons have been the subject of extensive research and development in recent years, with significant contributions from various studies [121,133,173,174,175,176,180,184,186,189,191,192,193,222,228,229,240,243,248,249,262,358,359,360,361,362,363,364,365,366,367,368,369,370,371,372,373,374,375,376,377,378,379,380,381,382,383,384,385,386,387,388]. These investigations have explored diverse aspects of glove design, fabrication, and implementation, advancing the field of wearable rehabilitation technology. Figure 12 illustrates each type of mechanism placement with examples from the literature.
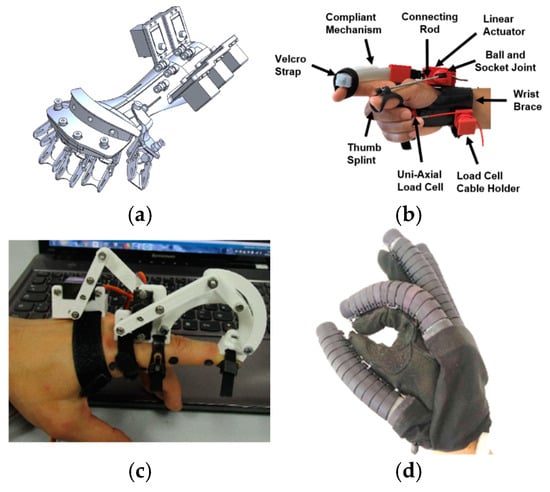
Figure 12.
Classification by mechanism placement: (a) Palmar [146], (b) lateral [132], (c) dorsal [144], (d) glove [358].
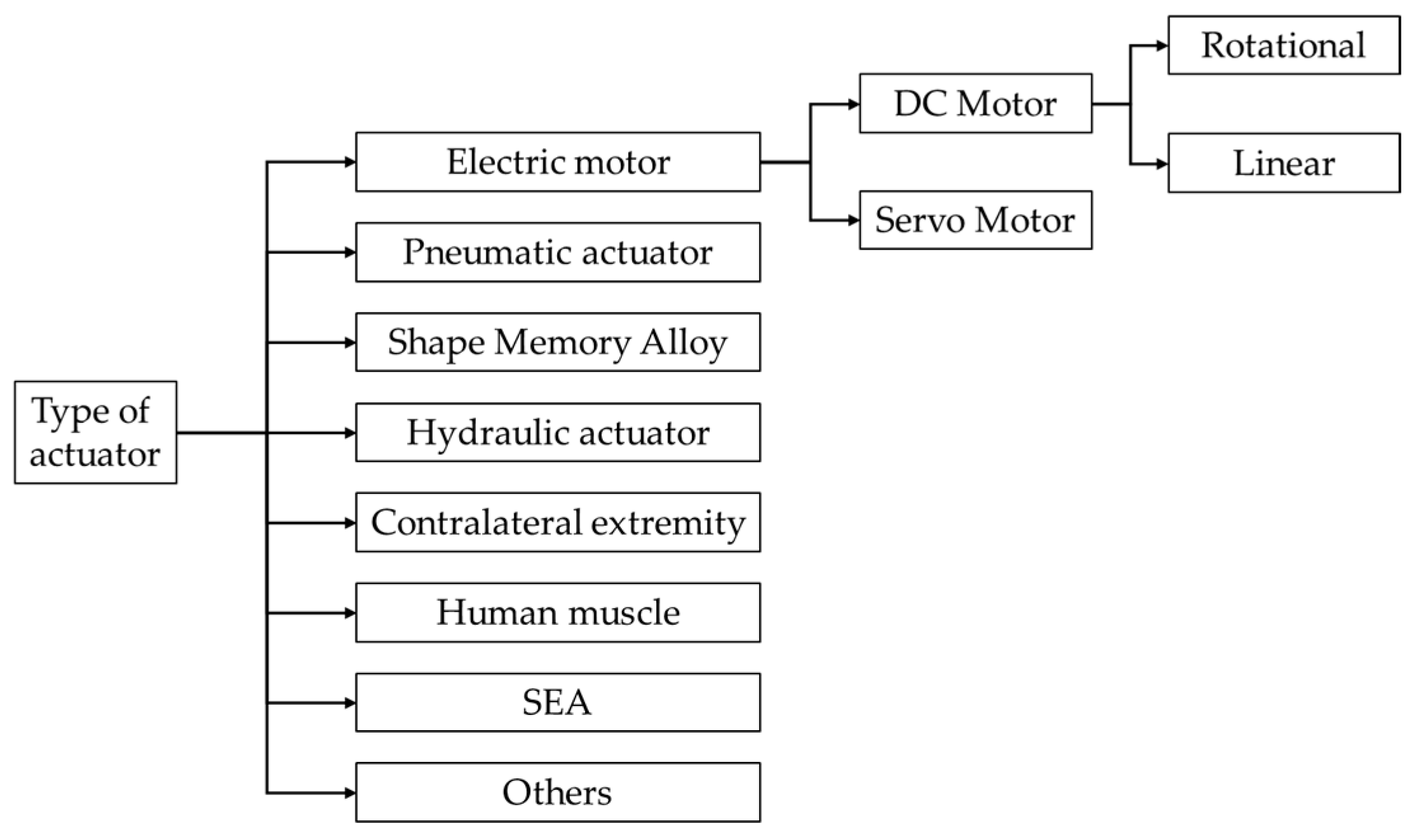
4.4. Classification by Actuator Type
Exoskeleton actuation modalities can be classified into electromechanical, pneumatic, shape memory alloy-based, hydraulic, contralateral extremity-driven, human muscle, series elastic actuators, and other approaches as depicted in Figure 13.
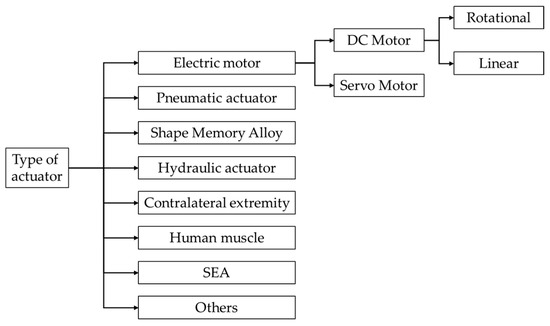
Figure 13.
Classification by actuator type.
4.4.1. Electric Motors
Exoskeletons that use rotary DC motors as their actuation method have been the subject of extensive research in recent years, and numerous studies have explored various aspects of implementing this type of motor in exoskeleton systems [13,15,83,87,90,92,93,94,95,96,97,101,103,106,108,110,121,122,123,125,126,128,129,130,133,135,136,137,138,139,140,141,142,143,154,157,158,160,161,162,164,167,170,173,175,184,185,186,189,192,194,195,202,204,208,211,227,228,231,234,237,239,240,244,247,248,250,251,255,256,261,262,263,264,273,279,306,308,311,321,324,338,340,361,365,366,370,376,384,387,389,390,391,392,393,394,395]. Linear motors are a good choice for controlling finger movements in exoskeleton hands. They can be easily placed on top of the hand and can open and close multiple fingers together [15,59,84,98,104,112,117,132,144,145,146,150,156,159,171,180,196,197,200,207,212,213,214,217,231,232,233,253,260,269,281,283,284,285,286,288,299,310,331,367,368,372,376,383,396,397]. Servomotors represent another type of electric actuator that is used in exoskeleton design. These types of motors offer precise position control and rapid response, making them suitable for accurate joint angle manipulation. Several researchers used servomotors in their exoskeleton prototypes, as documented in various publications [84,91,107,119,127,144,145,171,174,188,190,197,205,212,229,235,254,280,282,283,284,285,286,287,309,325,337,339,396,398].
4.4.2. Pneumatic Actuators
Pneumatic actuators [132,134,152,153,163,180,191,193,198,201,203,206,217,219,221,222,224,225,241,243,249,252,257,270,271,272,289,290,291,292,293,294,312,313,316,318,319,323,326,328,330,342,358,359,360,363,364,371,372,373,374,375,377,378,380,382,385,386,388,399,400,401,402] are widely used in hand rehabilitation robots due to their advantages in force generation, control, and weight-to-torque ratio [214,288]. They operate using air flow through various mechanisms such as pneumatic cylinders [102,109,187], air balloons [238], air bladders [241,359], flexible thermoplastic fabrics [249,360], or pneumatic artificial muscles [88,124,203,262,272,318,330,402]. Different categories of soft pneumatic actuators have been developed. Pneu-nets soft actuators (PNSAs) [198,221], made of elastomers, move finger joints directly. Optimized designs use semicircular chambers for better performance [217]. Fiber-reinforced actuators generate higher forces compared to PNSAs and allow for better designs [163,220,289,290,403]. Positive-negative pneumatic actuators allow active control of both flexion and extension [291,292]. Soft tissue-based pneumatic actuators use flexible, lightweight tissues and can achieve high forces [252,293]. McKibben-type pneumatic artificial muscles, made of a rubber inner tube with a braided shell, inflate and contract when pressurized [404]. Manufacturing processes for these actuators include casting in molds, direct 3D printing, and monolithic molding techniques [134].
The main advantages of pneumatic actuators include high, adjustable force and speed at a low cost, good weight-to-torque ratio [214], less maintenance [66,405,406,407], and the ability to stop under load without damage [69,405]. Some alternative approaches include EMG-controlled systems [226] and various mechanical design configurations [408], each offering distinct benefits for rehabilitation applications.
However, pneumatic actuators have several limitations. These include size constraints due to compressors and air storage chambers, noise, control difficulties due to time variability and nonlinearity, and slower response times in some cases [29,32].
Other studies on pneumatic actuation explored various designs for hand exoskeletons, for example, the work of [295,380]. These designs include soft actuators [198,218], fabric-based systems [216,249,252,293,312,400], and fiber-reinforced silicone actuators [380]. Specialized approaches like thin McKibben muscles [401] and bending-type pneumatic muscles [294] were also investigated. Research has focused on soft exoskeletons for rehabilitation and assistance [193,271,272,358,364,371,374,378] and incorporating various materials such as silicone rubber [134,152,153,163,191,193,206,217,219,220,224,225,290,291,292,313,316,319,328,342,358,360,363,364,371,373,375,377,380,385,390], flexible 3D-printed materials [270,333,374], and custom pneumatic actuators [270,271].
4.4.3. Shape Memory Alloys
SMAs have two key properties: shape memory effect and super elasticity [409,410]. The shape memory effect is the property of recovering the original shape upon heating to a critical temperature when it is deformed in the low-temperature phase [411]. SMAs work on the principle of phase transformation between two crystalline structures: martensite, the low-temperature phase, and austenite, the high-temperature phase [412]. After plastic deformation, SMA wire can return to its original shape when heated to a certain temperature. Additionally, under isothermal conditions, it can undergo great deformation, consume and absorb mechanical energy, and return to its original shape after removing the load, demonstrating a good damping effect [409,410].
Common materials used for SMAs include Ni–Ti and Cu–Al–Ni, among other combinations. The actuation is typically achieved by heating the SMA wire or rod by applying an electric current through it.
SMAs have been explored by several researchers [296,297,298,381,413,414,415] and have several advantages, including a high power-to-weight ratio [266]. This makes them suitable for a wide range of applications as both actuators and sensors.
SMA actuators also present several challenges. Their output motion is characterized by hysteresis, high nonlinearity, and saturation, making precise control difficult [416]. Additionally, SMA wires or rods produce significant heat during operation, thus safety considerations must be implemented when used in exoskeleton systems.
4.4.4. Hydraulic Actuators
Hydraulic actuators operate on a principle similar to pneumatic systems, but they use an incompressible liquid instead of air [277]. These actuators are known for their excellent performance characteristics [32]. Various hydraulic devices have been explored for power transfer in exoskeleton applications, including hydraulic cylinders [417], flexible inflatable materials [265], and certain types of artificial muscles [362]. However, hydraulic actuators have some limitations that affect their use in certain applications. The primary drawback is the requirement for a wider space to accommodate the liquid-transmitting pipes [32]. This spatial requirement makes hydraulic actuators less commonly used in hand rehabilitation robots [418].
4.4.5. Human MUSCLE
An innovative approach involves harnessing the power of the patient’s own muscles. This method, which can be broadly categorized as a form of actuation, utilizes functional electrical stimulation, FES, to activate impaired hand muscles [417]. This hybrid approach combines the benefits of electrical muscle stimulation with robotic assistance, potentially improving the effectiveness of hand rehabilitation. A notable example of this combined strategy is the FES and robotic glove system developed by Rong et al. [419].
4.4.6. Contralateral Extremity
In the field of hand rehabilitation, another approach involves utilizing the unaffected limb as a form of actuation for the impaired hand. This method, known as contralateral extremity actuation, is particularly relevant in rehabilitation systems that employ bilateral training strategies [419]. There are two primary ways in which the healthy extremity can drive the rehabilitation of the impaired hand. The first, which remains largely theoretical, involves direct force transfer from the unaffected hand to actuate devices on the impaired side. The second, and more researched approach, uses signals or data from the healthy hand to indirectly control rehabilitation devices on the affected side [420].
4.4.7. Series Elastic Actuators
Series elastic actuators (SEAs) represent an innovative approach to exoskeleton design, combining the power of electric motors with the compliance of spring elements. Unlike traditional actuators that prioritize joint stiffness, SEAs intentionally reduce it, opening new possibilities in rehabilitation robotics [165]. The incorporation of a spring element between the motor and the load in SEAs offers several advantages such as enhanced shock absorption and improved force control accuracy and stability. While SEAs seem to present an ideal solution for hand exoskeletons, they come with some disadvantages; the intentional reduction in joint stiffness limits the magnitude of the force that can be transferred to the exoskeleton and mechanical complexity. Some researchers have explored the potential of SEAs in hand rehabilitation devices [165,199].
4.4.8. Other Types of Actuators
Research into alternative actuator technologies continues, as engineers and researchers develop more efficient and effective solutions. Among the emerging solutions being explored are electroactive polymers and ultrasonic motors [421].
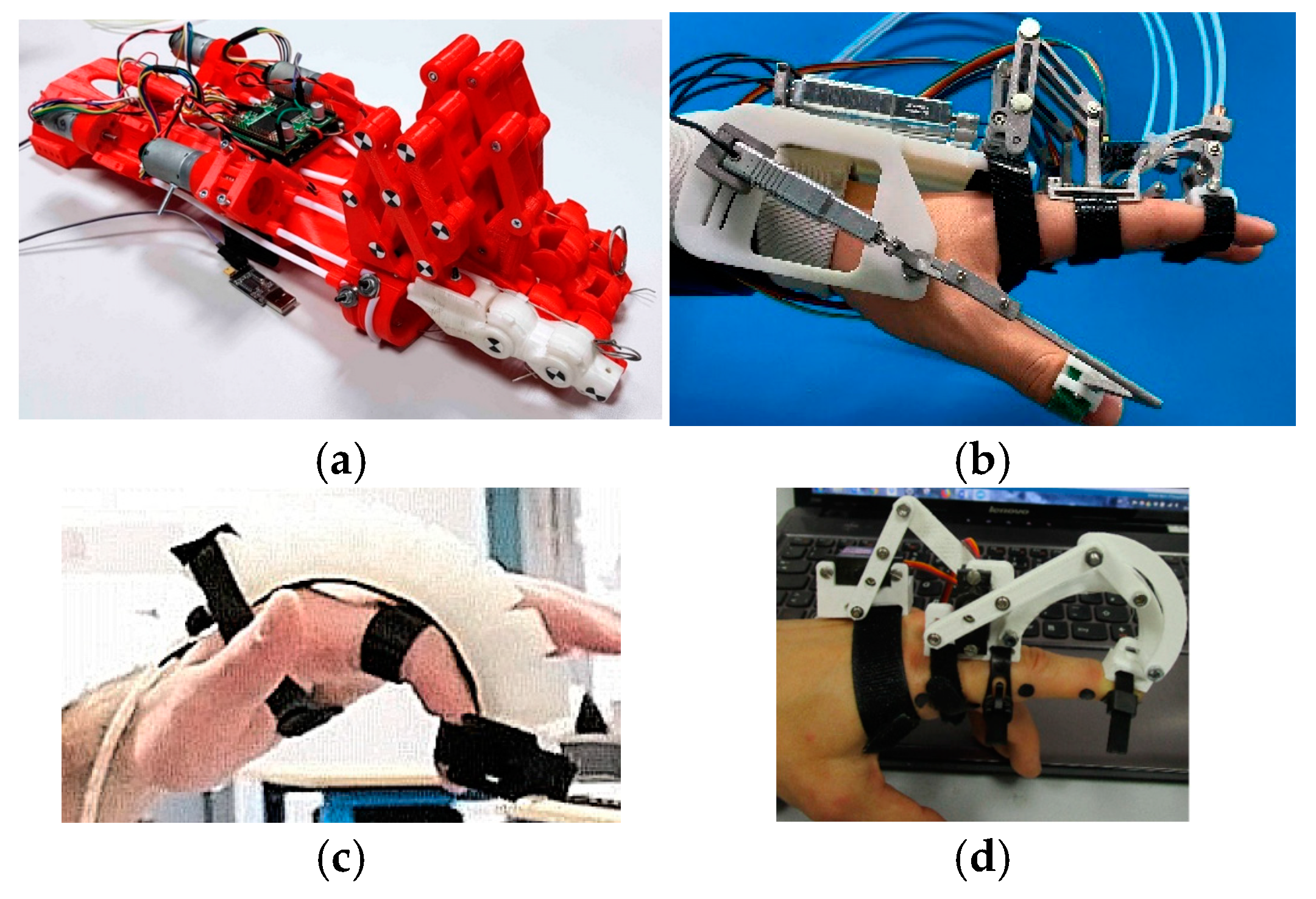
Figure 14 illustrates different types of hand exoskeletons using various actuation methods.
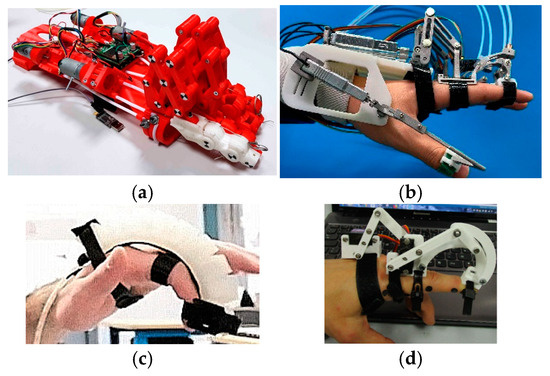
Figure 14.
Classification by type of actuator: (a) DC Motor [194], (b) linear actuator [354], (c) pneumatic [134], (d) servomotor [144].
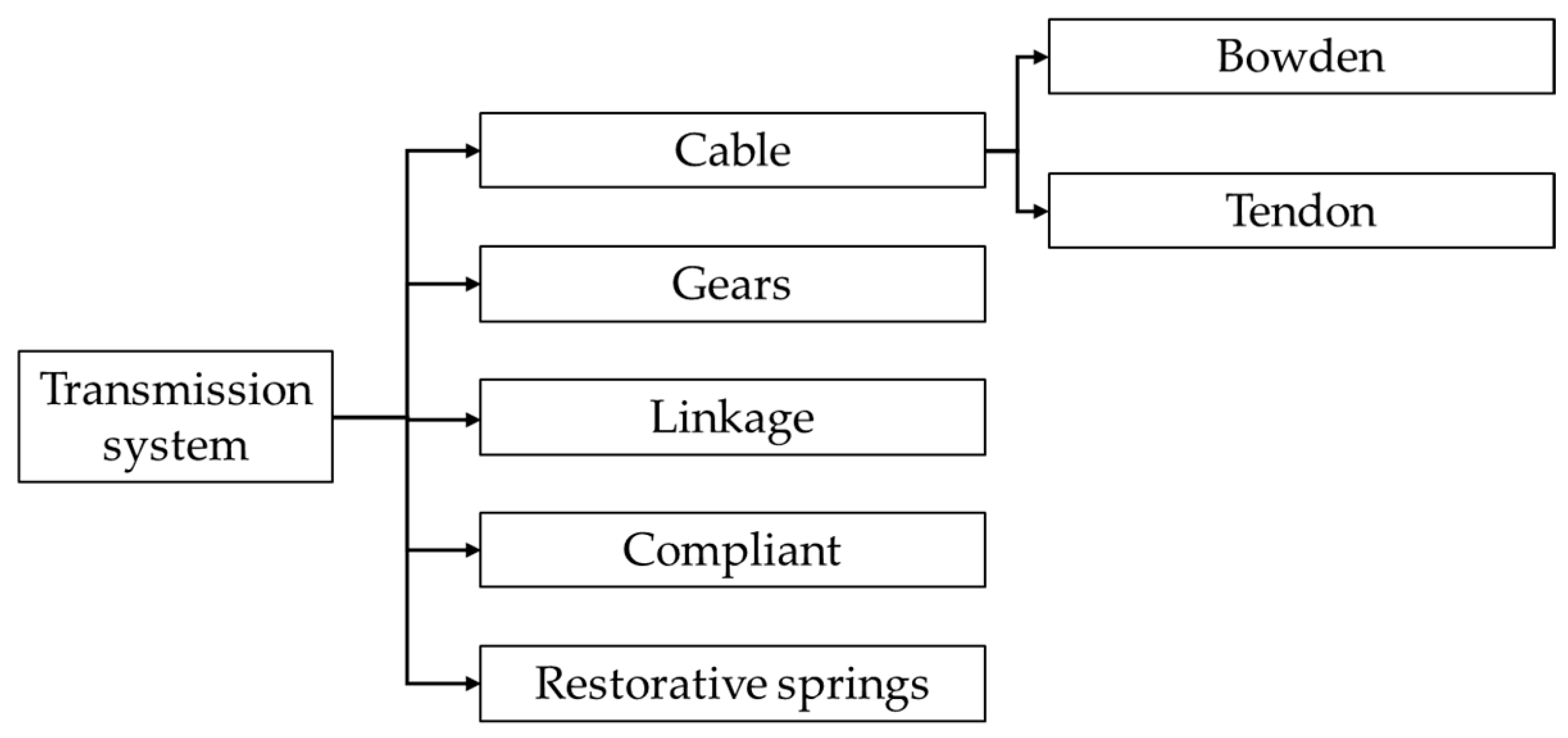
4.5. Classification by Transmission Type
An alternative classification method is based on power transmission mechanisms. This approach categorizes systems into several types: geared systems, linkage mechanisms, cable-driven systems, compliant structures, and restorative springs. Figure 15 illustrates these various transmission types.
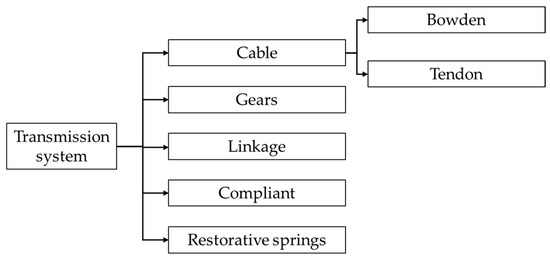
Figure 15.
Classification by transmission system.
4.5.1. Linkage
Linkage-based devices are a popular choice in hand rehabilitation robotics. These devices use mechanical links to form finger components and can be categorized based on their control mechanisms and structural designs.
Linkage-based actuation offers several advantages. It can be implemented with various control methods. By combining actuators with rigid exoskeletons, these devices can secure the range of motion and prevent out-of-plane flexion or extension [422,423].
This type of device also presents challenges. Motors and translational linkages can add weight to the system, even for simple motions, and compact designs require more expensive actuators [424,425,426]. The addition of linkages complicates the exoskeleton’s kinematics, with each link’s mass, inertia, and center of gravity changing for different hand sizes. Simplified designs with fewer actuators limit mobility and task adjustability.
Several studies have expanded our understanding of linkage-based devices [59,83,84,85,87,90,91,94,95,96,97,98,110,137,139,140,144,146,147,149,150,151,156,159,160,162,166,170,171,200,207,211,212,214,233,236,245,247,250,260,269,273,280,281,282,286,287,288,297,299,300,301,305,306,309,310,321,322,332,376,392,396,399].
4.5.2. Gears
Gear-motor actuation, while often considered a direct approach, can be expensive and challenging to implement. With a human hand, several gears and gear trains would be used to provide actuation. Designs that use gear-motor actuation face similar weight issues experienced by linkage-based actuation.
There is a fine line between direct drive and gear assembly. Some devices [279,311] are classified as geared systems because the motor is connected through a gear train to the structure. The idea behind a direct drive or geared system is for the actuators to be as close to the structure as possible, typically mounted on the dorsal side of the hand. This type of transmission enables the devices to be portable and less complex, simultaneously minimizing the power or transmission losses, but increasing the weight on the hand.
4.5.3. Cable
Cable-driven exoskeletons [13,15,88,93,120,124,127,130,131,133,138,154,158,161,164,167,168,173,174,175,176,178,179,180,181,182,184,185,186,189,190,195,197,204,205,208,209,213,222,223,230,234,235,237,240,242,244,248,251,254,255,256,277,284,285,296,298,317,325,327,329,334,335,337,338,339,340,365,367,368,369,370,372,381,383,384,386,387,390,393,394,395,397,427,428,429] are a popular choice for hand rehabilitation, using servo or rotary motors. These systems utilize cables to achieve low-weight solutions. The main advantage of cable-driven systems is their ability to shift the weight of actuation components away from the hand, resulting in lighter devices. Cable mechanisms can be categorized into two types: Bowden cable-driven devices and tendon-driven devices [256]. Bowden cable transmission involves routing cables or rigid rods through low-friction tubes to connect the actuating unit with the hand exoskeleton. This allows for remote placement of the actuating unit, making it suitable for stationary rehabilitation or wheelchair-mounted systems [160,251,256,275,393,430,431]. Another advantage of cable-driven systems is their use of soft exoskeletons, which provide an adaptable design that can adjust to various hand shapes and sizes [432]. This flexibility is particularly beneficial given the diverse dimensions of patients’ hands.
Cable-driven systems present several challenges; one major disadvantage is the loss of power and control issues; the actuation experiences transmission losses as the device performs exercises, mainly due to friction.
The main difference between tendon and Bowden cable systems is that tendon cables mimic the hand anatomy structure by flexing and extending the fingers with a cable routed in a glove, whereas Bowden cables use a rigid structure to transfer the cable forces to the fingers, as mentioned previously. Tendon cables are usually connected to the distal part of the finger and flex or extend the finger by applying tension to the cable. This type of transmission is normally unidirectional, meaning only one cable can execute a single task such as flexion or extension. A second cable is required to have a bidirectional actuation, which means another actuator is generally required. These types of developed hand exoskeletons are usually underactuated systems where a single actuator can flex or extend multiple fingers such as in [56,57,58] using a single cable routed in a loop across or between the fingers.
Tendon cables can suffer from cable breakage, and the routing paths are sometimes complex and can cause power losses due to friction, but they can apply the required forces to the digit itself instead of the joints.
Tendon actuation has been explored and implemented in other numerous studies, as evidenced by the research presented in [34,35,133,173,175,176,177,179,182,183,186,189,190,208,222,234,240,242,248,296,298,325,327,365,366,367,370,383,386,390,397,428,433,434,435]. Despite these challenges, cables remain an attractive option for hand rehabilitation robots due to their similarity to hand muscles [158,376].
Bowden cable mechanisms have been studied in the following studies [154,159,164,181,202,223,227,254,308,329,335,337,394,395]. Bowden cables offer more flexibility due to their cable conduit but suffer from variable and high friction forces caused by curves [125].
Pulley cables require continuous tension to maintain traction, limiting their use [128,436]. Examples of devices using pulley cables include the work of [88,235,251,393].
4.5.4. Restorative Springs
Springs, despite being passive components, are commonly integrated into hand exoskeletons that primarily use unidirectional actuation. They are often paired with either tendons or pneumatic cylinders, which typically control only flexion or extension. The springs serve to passively facilitate the opposite motion, complementing the active actuator. Numerous studies have explored and implemented spring-based actuation mechanisms in hand exoskeletons [83,197,232,274,276,284].
4.5.5. Compliant Transmission
Artificial muscles and flexible jointless structures represent innovative approaches in the field of soft robotics, offering compliant and adaptable solutions for finger flexion and extension [437].
Artificial muscles, typically driven by pneumatic or hydraulic systems, consist of a flexible material encased in a braided sheath. When fluid is injected, the muscle contracts, and when pressure is released, it extends [201,203,257,265,272,318,319,330,402]. These systems provide a high degree of flexibility [438]. However, they can face challenges such as ballooning, where excessive pressure causes the flexible material to expand beyond its functional range. Researchers have addressed this issue through careful selection of braiding materials and design optimizations [201,265].
Flexible jointless structures represent an evolution of the artificial muscle concept. These devices, often made from silicone rubber, are molded in specific configurations to achieve bending motions without the need for a braided sheath [302,360]. These structures offer the advantages of simplicity and potentially lower manufacturing costs, as they can be custom-designed for individual users using relatively inexpensive materials.
Further research on flexible jointless structures has been extensively conducted, as evidenced by numerous studies, for example [72,134,153,163,191,193,198,206,217,219,220,221,225,270,290,292,313,316,328,342,358,360,362,363,364,371,373,374,375,377,380,385]. These investigations have significantly contributed to the advancement of this technology, exploring various design configurations, materials, and applications in the field of soft robotics for rehabilitation.
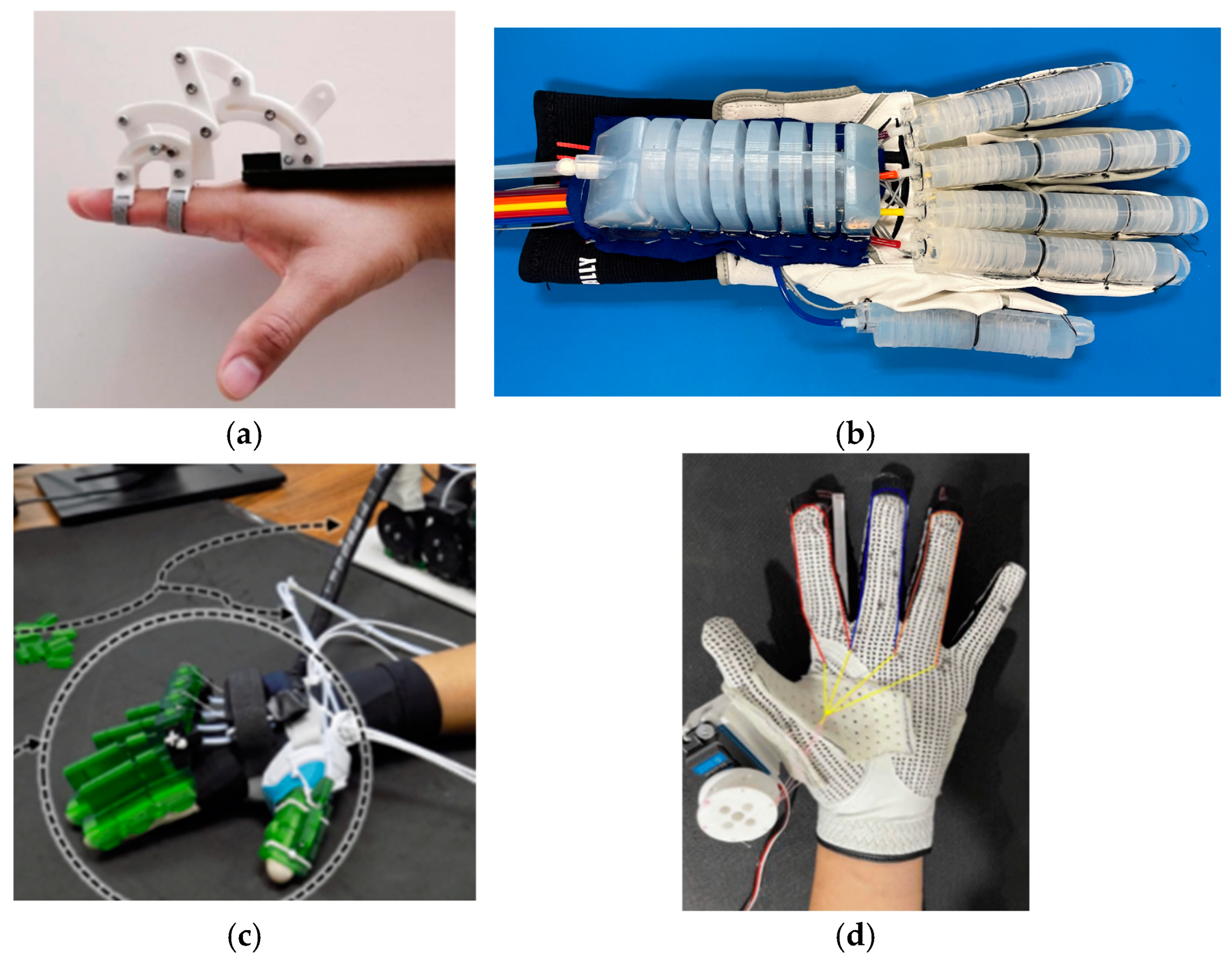
Figure 16 illustrates different types of hand exoskeletons using various transmission systems.
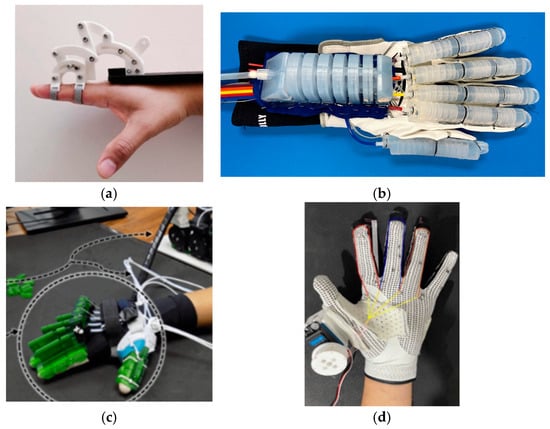
Figure 16.
Classification by type of transmission: (a) Linkage [144], (b) silicone-rubber [364], (c) cable [285], (d) tendon [178].
Hand exoskeletons use a wide variety of transmission combinations to achieve optimal performance and functionality. Researchers often combine multiple transmission elements to leverage the strengths of each and address the complex requirements of hand rehabilitation and assistance.
Hand exoskeletons utilize various transmission combinations like cable and steel wire systems [119]. Some designs incorporate cable and spring mechanisms [127] while others explore linkage and spring combinations [281].
The linkage and cable combination appears to be particularly popular among researchers [91,102,103,106,109,118,123,125,130,135,136,141,142,143,148,157,159,160,169,194,196,202,227,231,259,261,278,303,391].
5. Results and Discussion
A comprehensive database was developed to catalog and analyze hand rehabilitation devices reported in the literature. The database contains over 300 devices, each of them characterized by 45 criteria. The criteria were defined in such a way to cover the technical specifications of each device.
5.1. Database Parameters Organization
To facilitate the analysis of the papers, the database was structured into six primary categories. The bibliometric information category contains fundamental publication data including author details, publication year, and article identification.
The database core structure is represented by technical specifications that include information about actuation systems, transmission mechanisms, motion characteristics such as DoF, and range of motion.
Another significant category is represented by control and sensing criteria that include the implementation of different sensors, control methods, intention detection methodologies, feedback, and the interface between the device and the patient.
Each device was documented with its practical features, covering portability, safety, weight, and how well it could adapt to different uses.
Regarding the validation of each device, implementation details were recorded such as test status and commercial availability. The information can be used to evaluate the transition from research prototype to practical application.
5.2. Database Population Process
Each device was analyzed across all six primary categories, with careful attention to maintaining uniform terminology. Missing information was explicitly noted to maintain database integrity and facilitate future updates.
The information organization enables easy access to specific device characteristics, while the structure supports detailed examination of individual devices.
5.3. Limitations and Constraints
During the development of the database, several limitations were identified such as incomplete reporting in original sources, variations in measurements, and incomplete information regarding all criteria that were used.
5.4. Discussions
The systematic data visualization conducted in this study covers design characteristics, technological implementations, and performance metrics across different hand exoskeleton configurations. The following graphs explore these findings in detail.
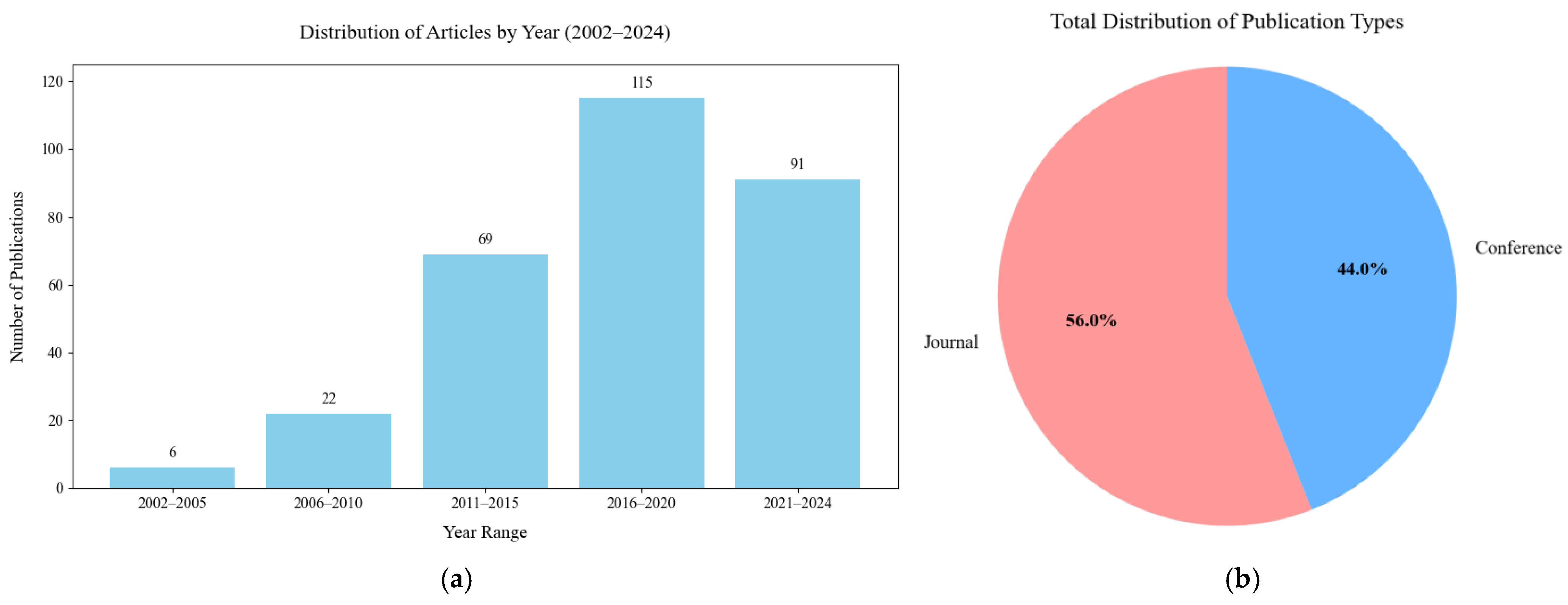
Figure 17a illustrates the temporal distribution of publications related to hand exoskeleton rehabilitation devices from 2002 to 2024, grouped in 5-year intervals. An important peak research output was observed in the 2016–2020 interval. This trend suggests a growing interest and investment in the field.
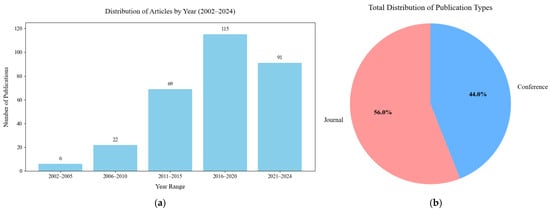
Figure 17.
Distribution of publication types (a) temporal distribution of publications related to hand exoskeleton rehabilitation devices, (b) distribution of publication types.
Figure 17b provides a concise overview of overall distribution of publication types across all years. Journal articles account for 56% of total publications while conference papers account for 44% of total publications.
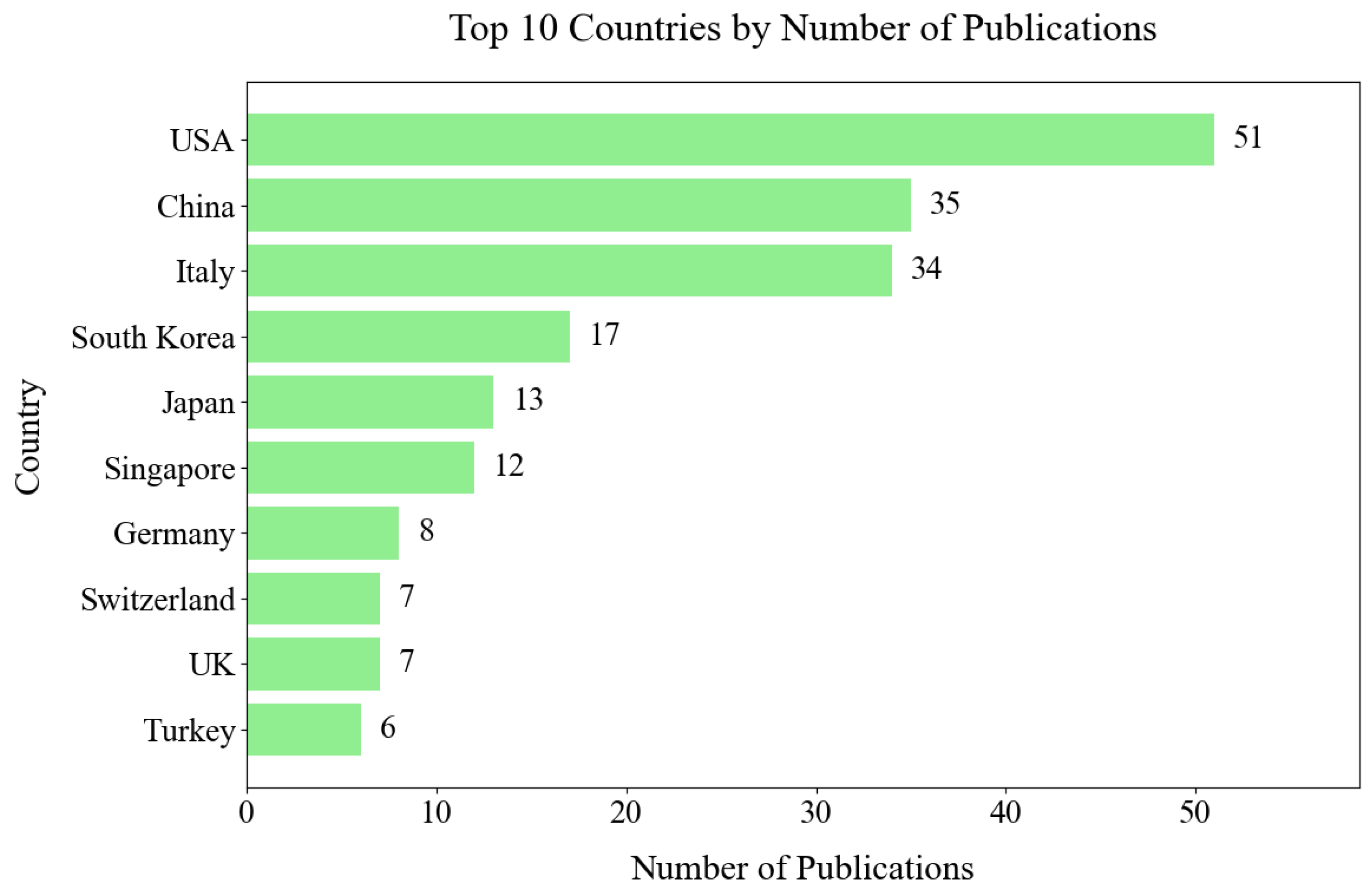
Figure 18 illustrates the top ten countries that contribute to hand exoskeleton device research based on their publication output. The United States leads, followed by China and Italy.
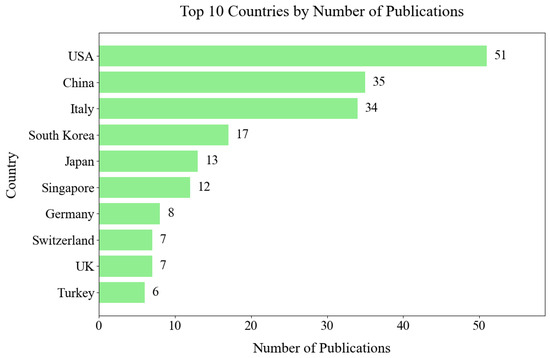
Figure 18.
Country contribution based on publication output.
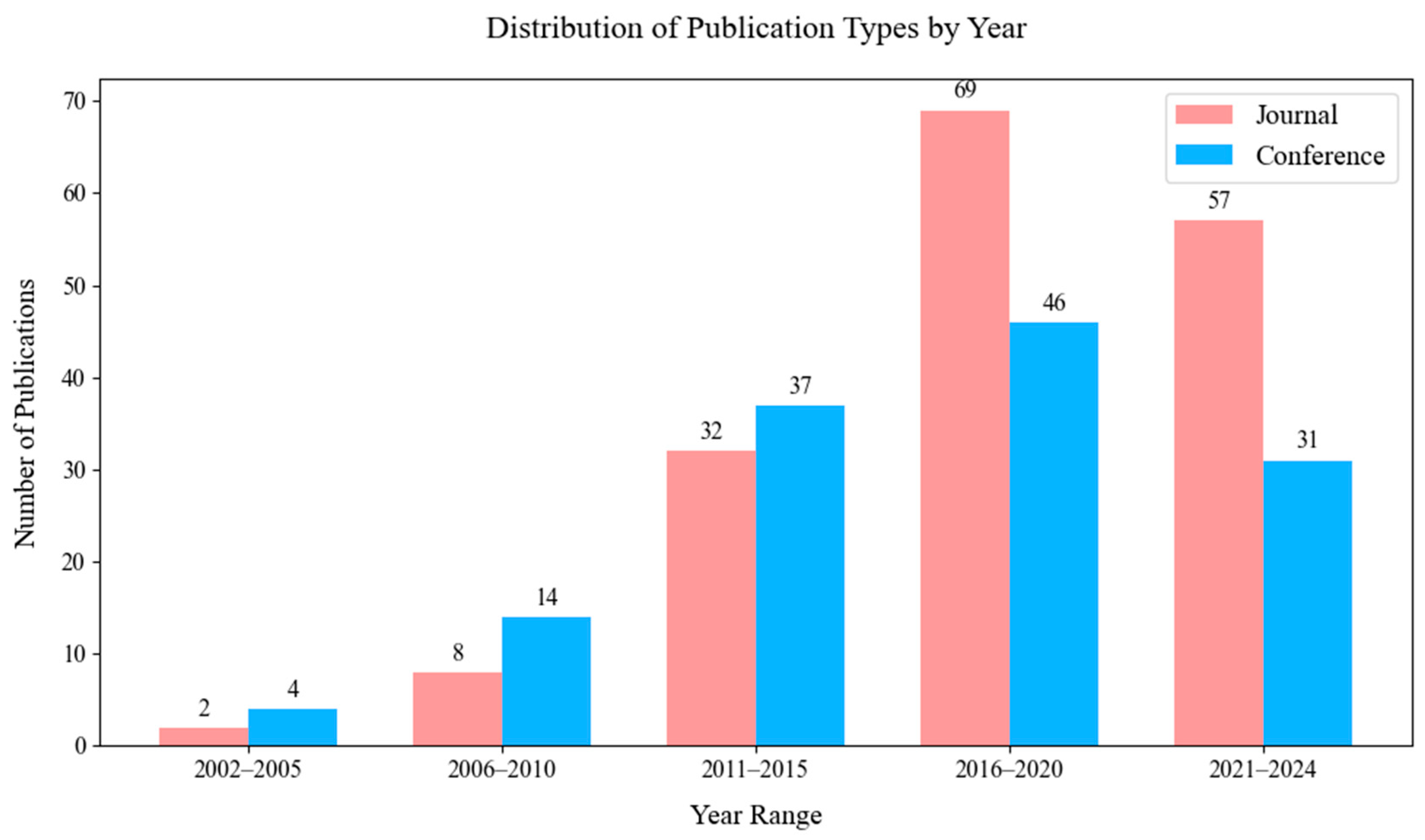
Figure 19 illustrates the evolution of publication types across time. In the early years of the study period, conference papers were more prevalent, but a shift towards journals can be observed in recent years.
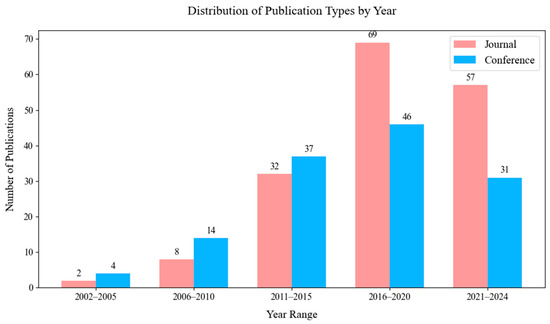
Figure 19.
Overall distribution of publication types across all years.
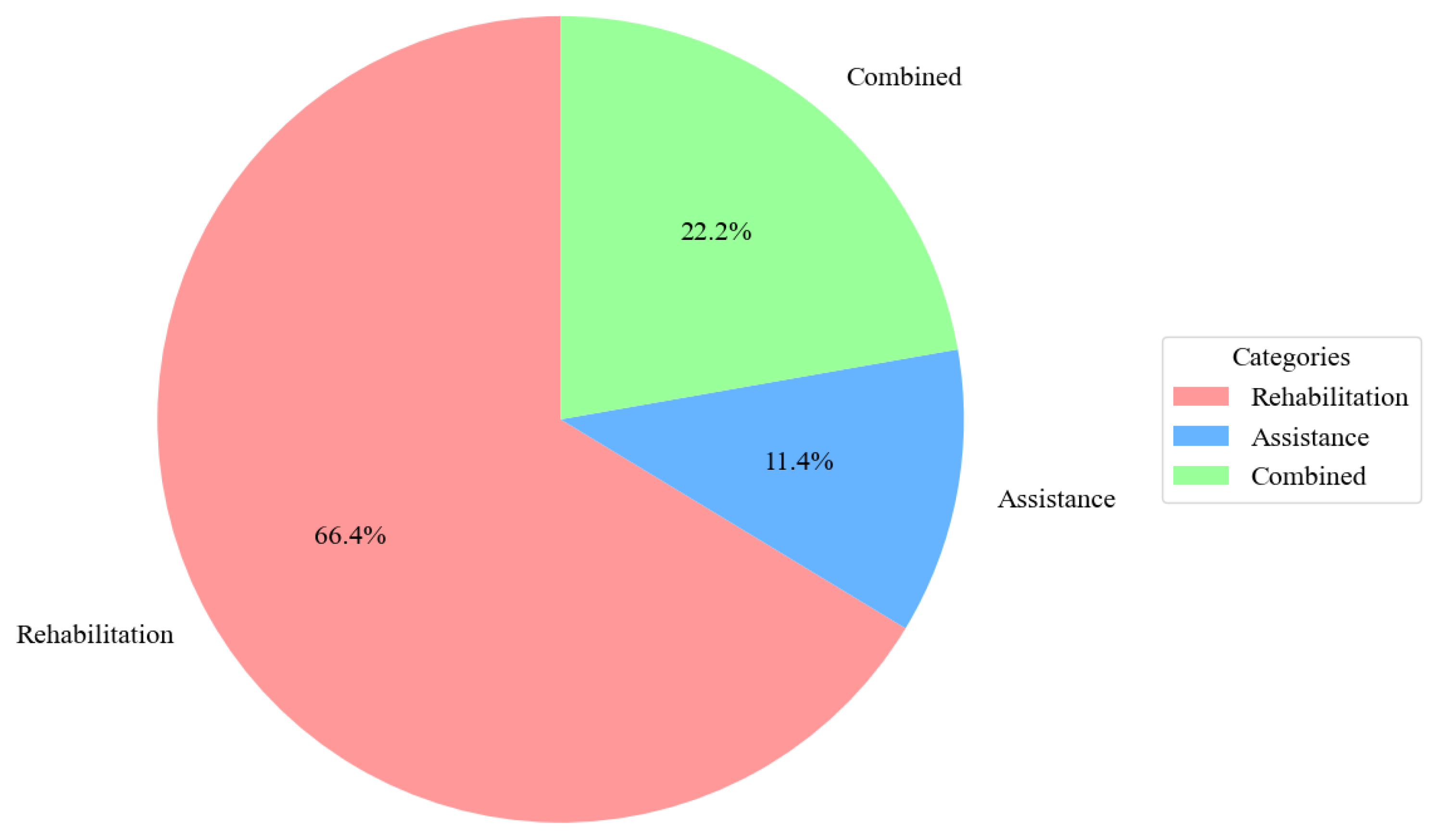
The distribution of hand exoskeleton applications across categories is illustrated in Figure 20. Rehabilitation made up 66% of the total, followed by devices used for both rehab and assistance.
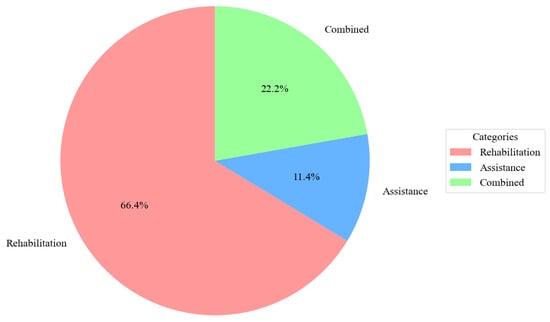
Figure 20.
The distribution of hand exoskeleton applications across categories.
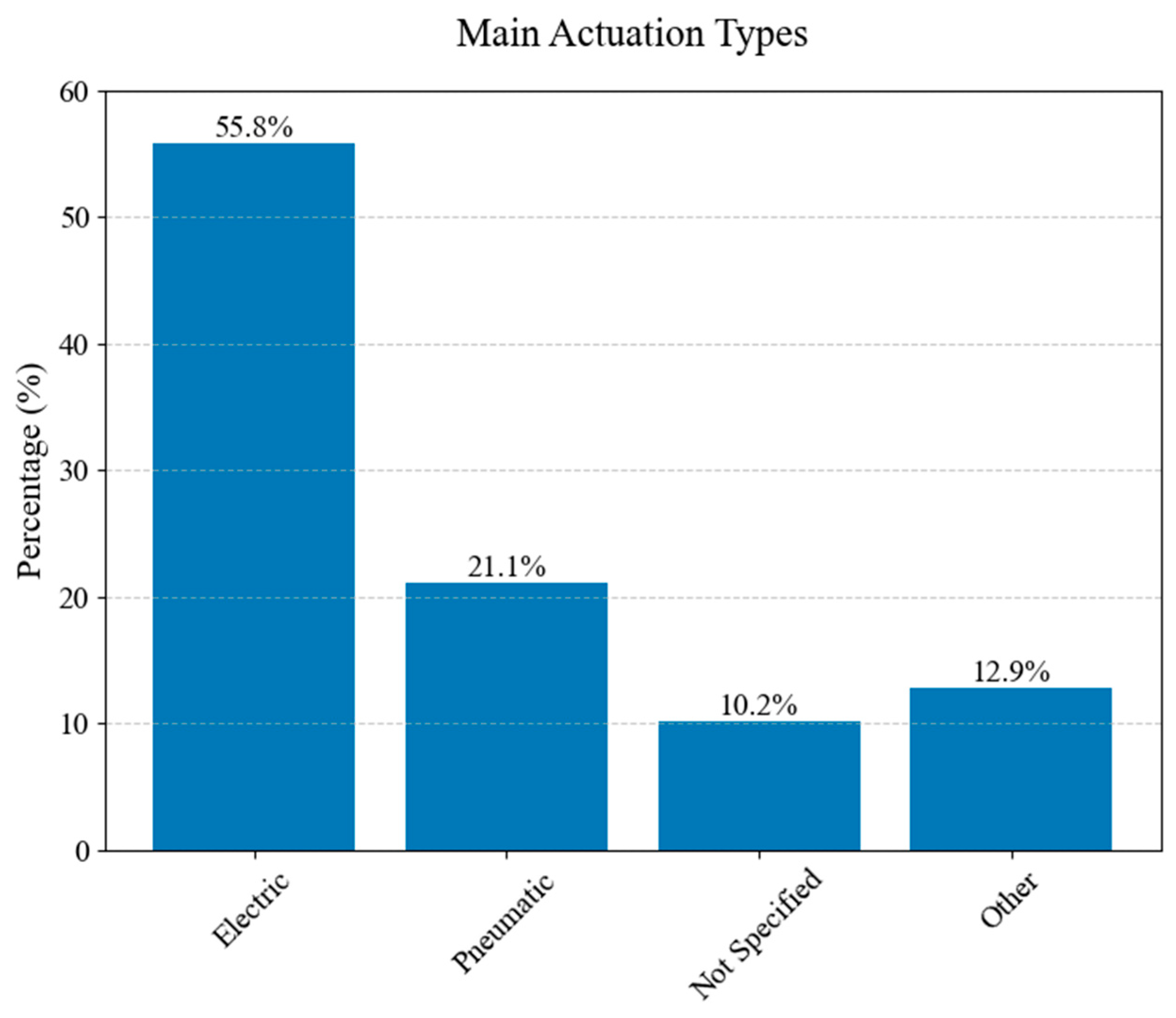
The distribution of primary actuation types used in hand exoskeletons is illustrated in Figure 21. The chart categorizes actuation mechanisms into four main groups: electric, pneumatic, other, and not specified.
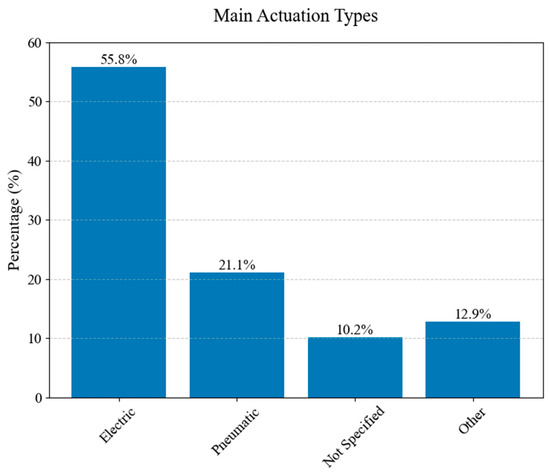
Figure 21.
The distribution of actuation types.
Electric actuation represents 55.8% of the studied exoskeletons, followed by pneumatic actuation and other types of actuation. A notable “other” category stands for 12.9% of the total studied exoskeletons.
Electric actuation represents 55.8% of the studied exoskeletons, followed by pneumatic actuation and other types of actuation.
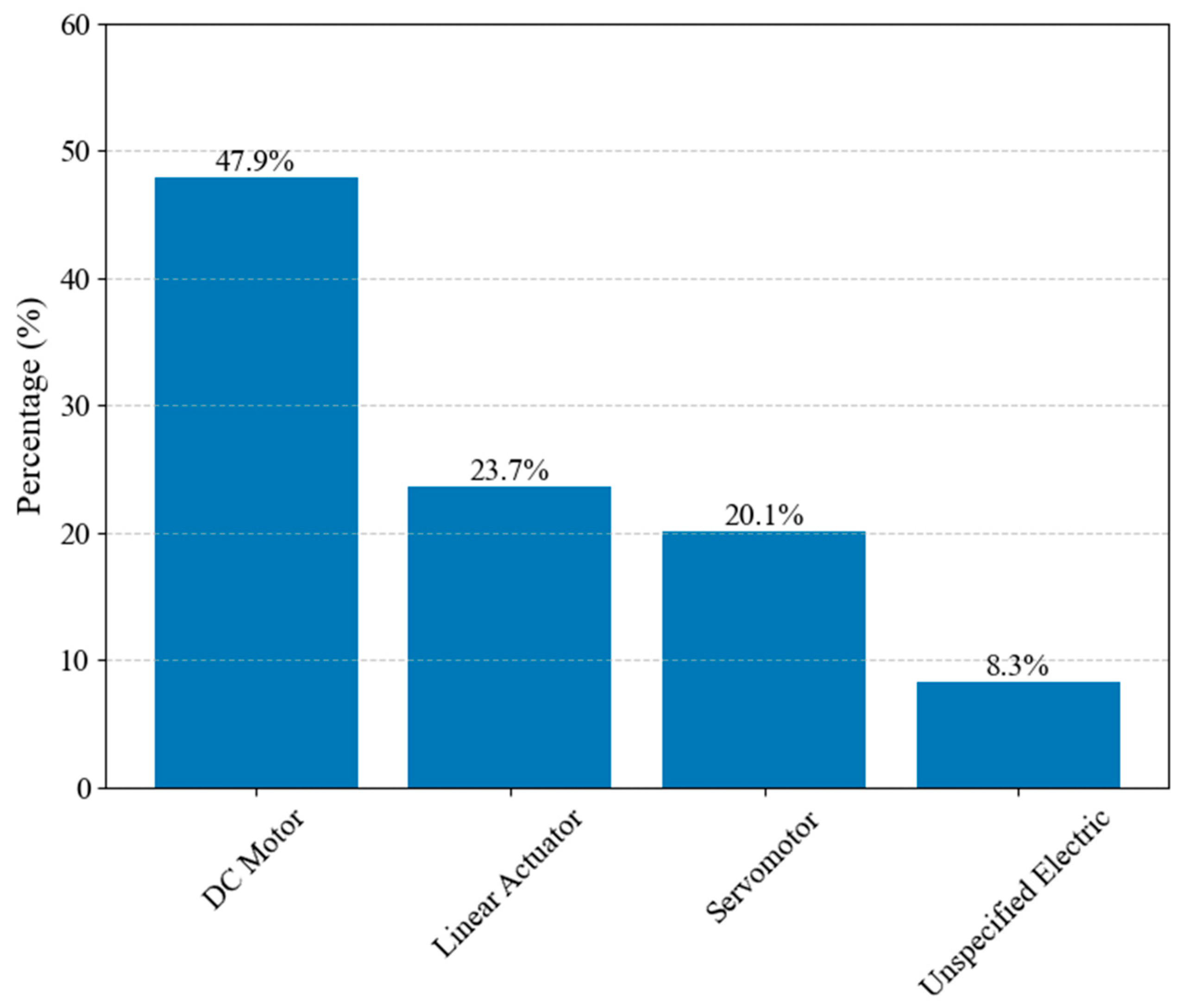
Figure 22 breaks down the types of electric motors found in hand exoskeletons. DC motors are the predominant choice, followed by linear actuators and servomotors. Unspecified electric motors account for 8.3% of the actuators used.
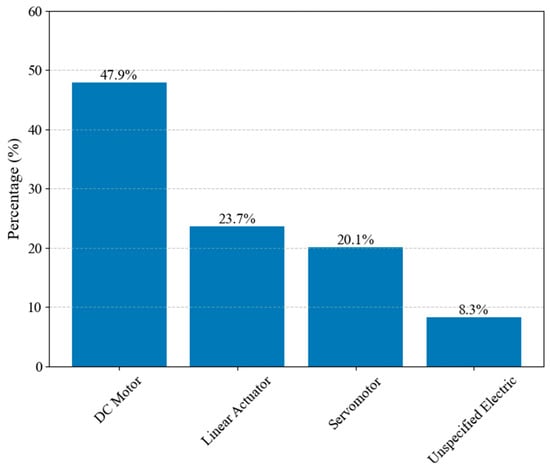
Figure 22.
The distribution of electric actuator types.
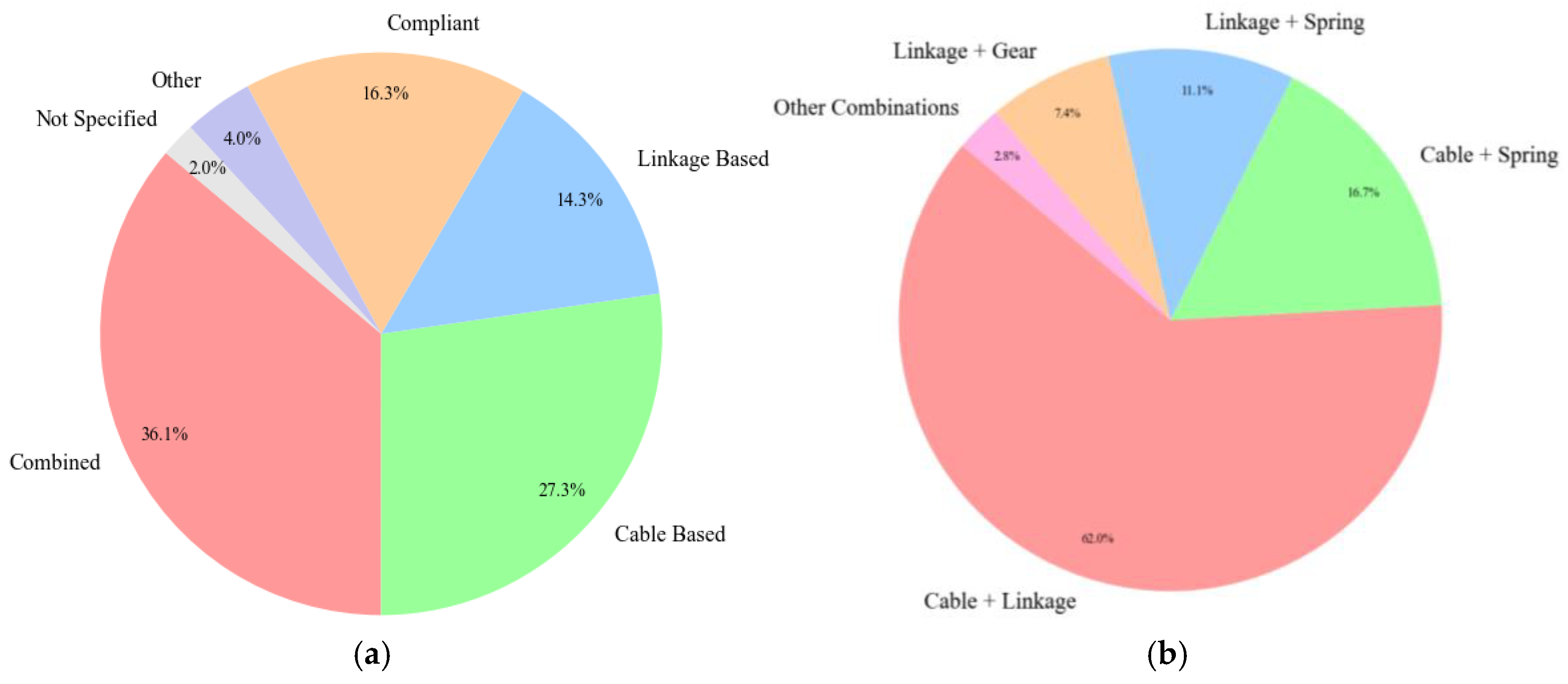
Figure 23a illustrates the distribution of the main transmissions in hand exoskeleton designs. Combined mechanisms stand in the first place, followed by cable-based solutions, compliant, and linkage-based solutions. Figure 23b describes the combined transmission systems. Cable–linkage combinations are the most frequently used solution, followed by cable–spring, linkage–spring, and gear–linkage configurations.
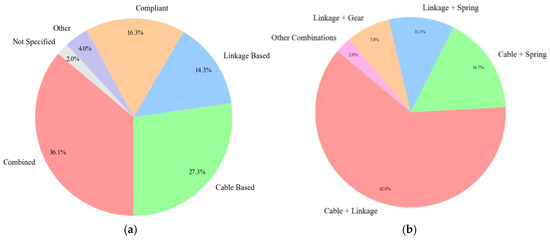
Figure 23.
Transmission types (a) distribution of main transmission, (b) combined transmission systems.
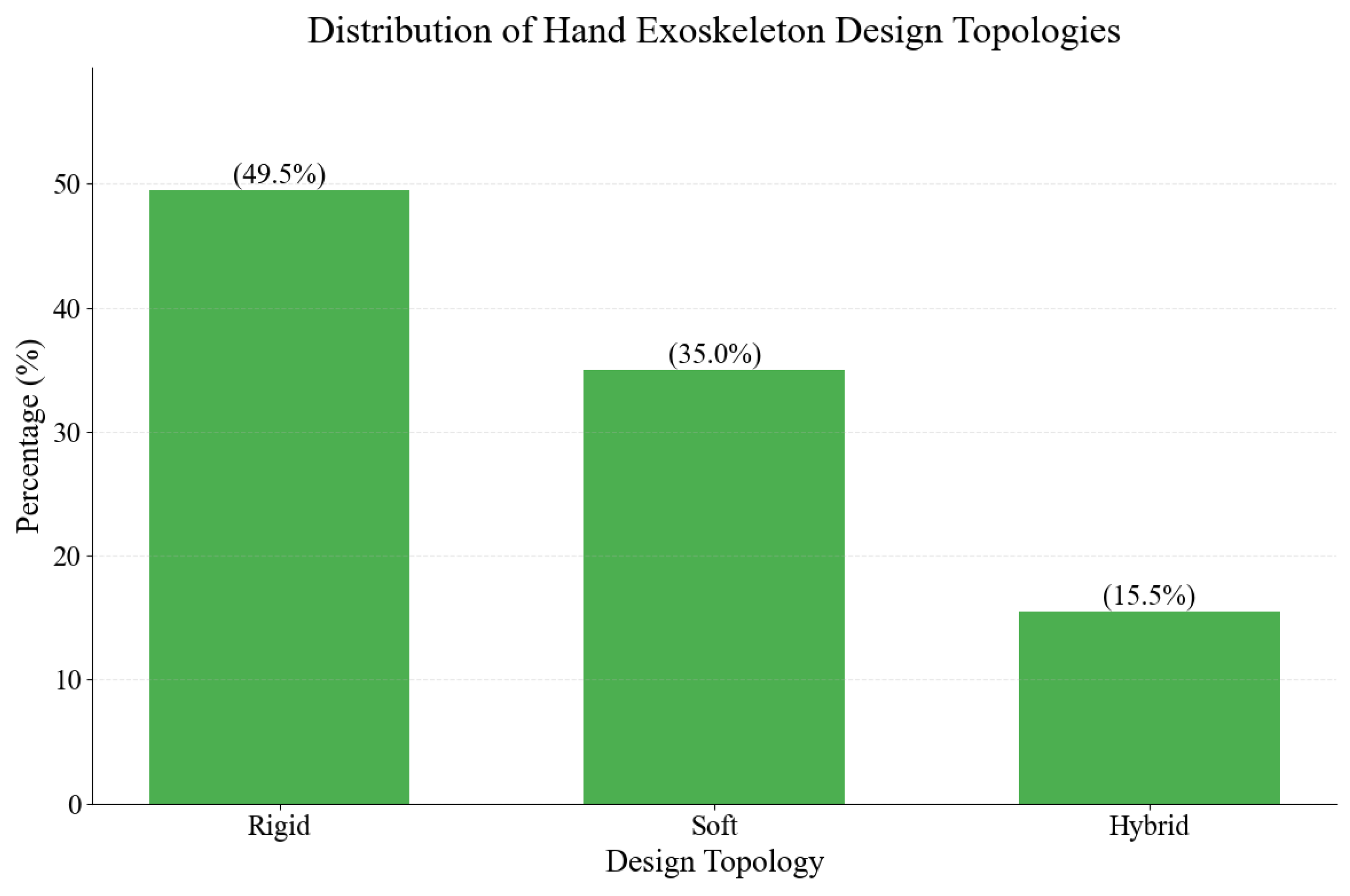
Figure 24 breaks down the different types of hand exoskeleton designs. The study categorized exoskeletons into three main categories: rigid, soft, and hybrid. The distribution reveals that rigid designs dominate the field, accounting for approximately 50% of analyzed exoskeletons; soft designs represent a significant proportion of the dataset, comprising 35.0% of the total studied hand exoskeletons. This presence reflects the growing interest in soft robotics. Hybrid designs combine elements of both rigid and soft structures and constitute 15.5% of the studied exoskeletons.
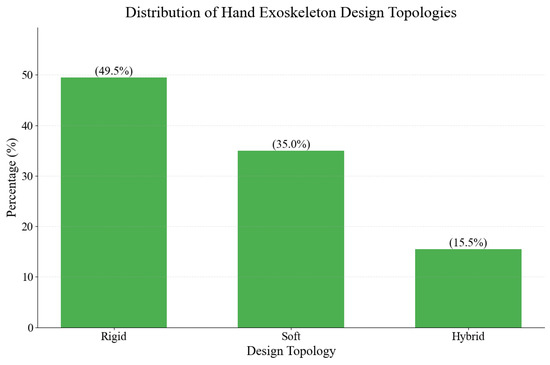
Figure 24.
Distribution of the design topologies.
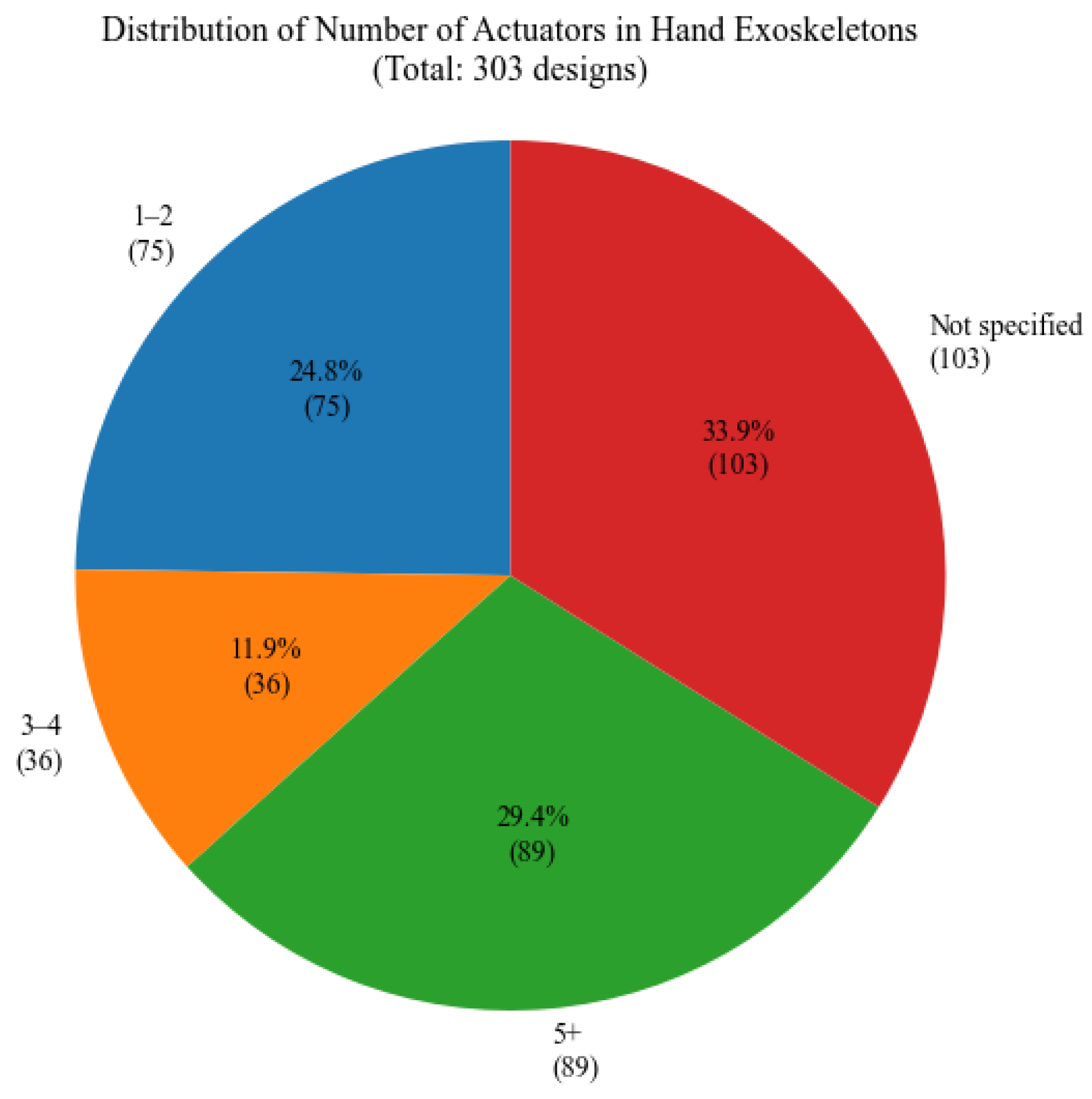
Figure 25 illustrates the distribution of the number of actuators used. The chart reveals a various range of actuator configurations; 29.4% utilize five or more actuators, while 24.8% use only one to two actuators, indicating the prevalence of underactuated, coupled mechanisms or hand exoskeletons that are used for a limited number of fingers. A substantial percentage of 33.9% of the studied papers did not specify the number of actuators that were used.
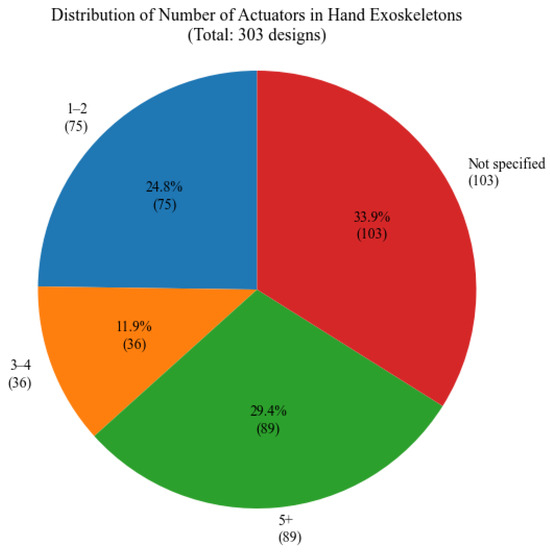
Figure 25.
Distribution of actuators number.
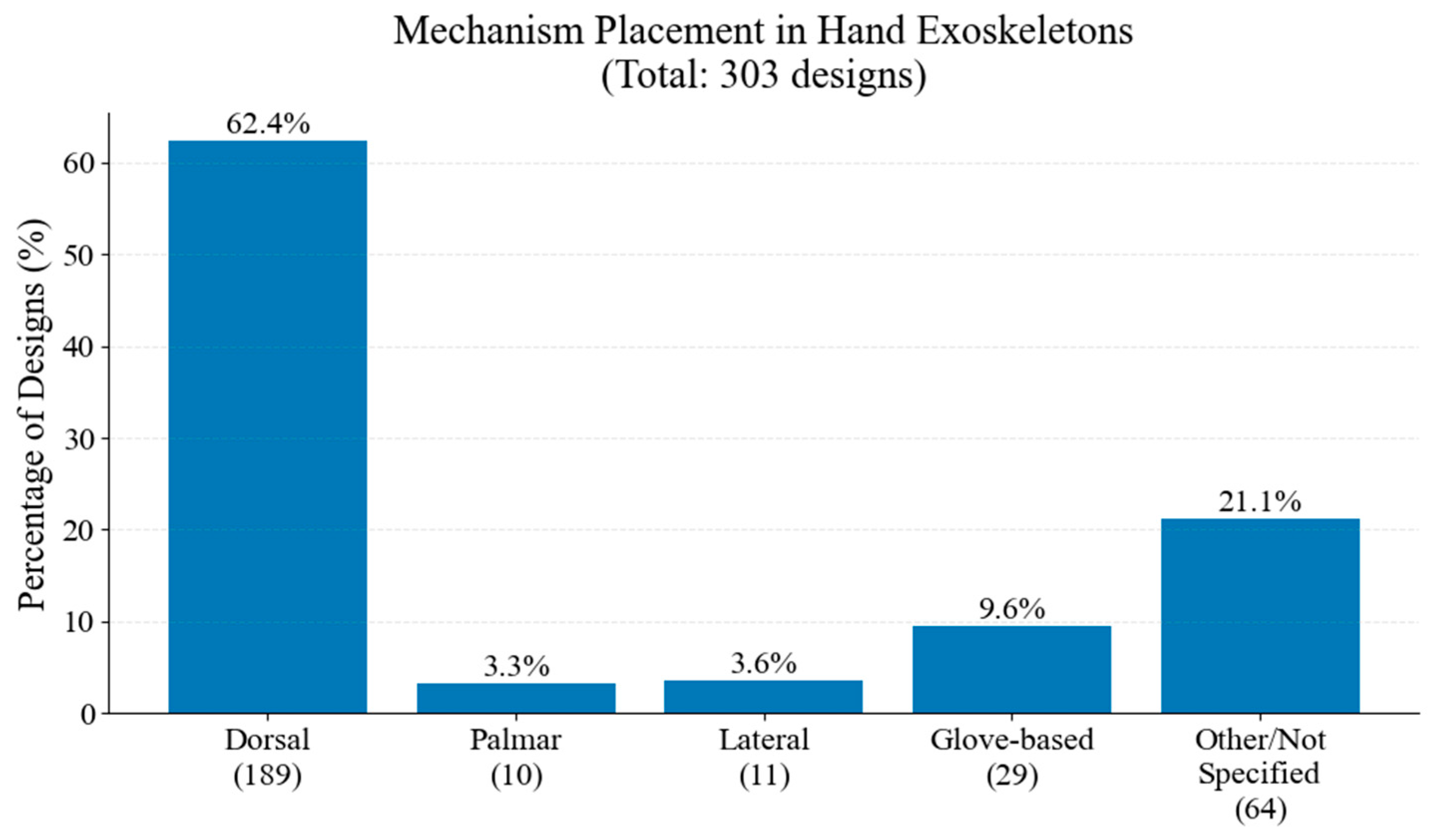
In Figure 26, the distribution of mechanism placements is illustrated. Dorsal placement constitutes the majority of the studied hand exoskeletons, followed by glove-based, lateral, and palmar configurations.
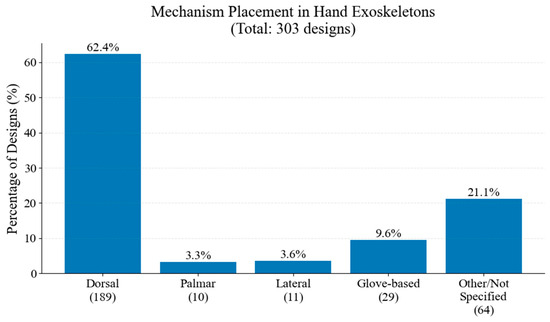
Figure 26.
Distribution of mechanism placement.
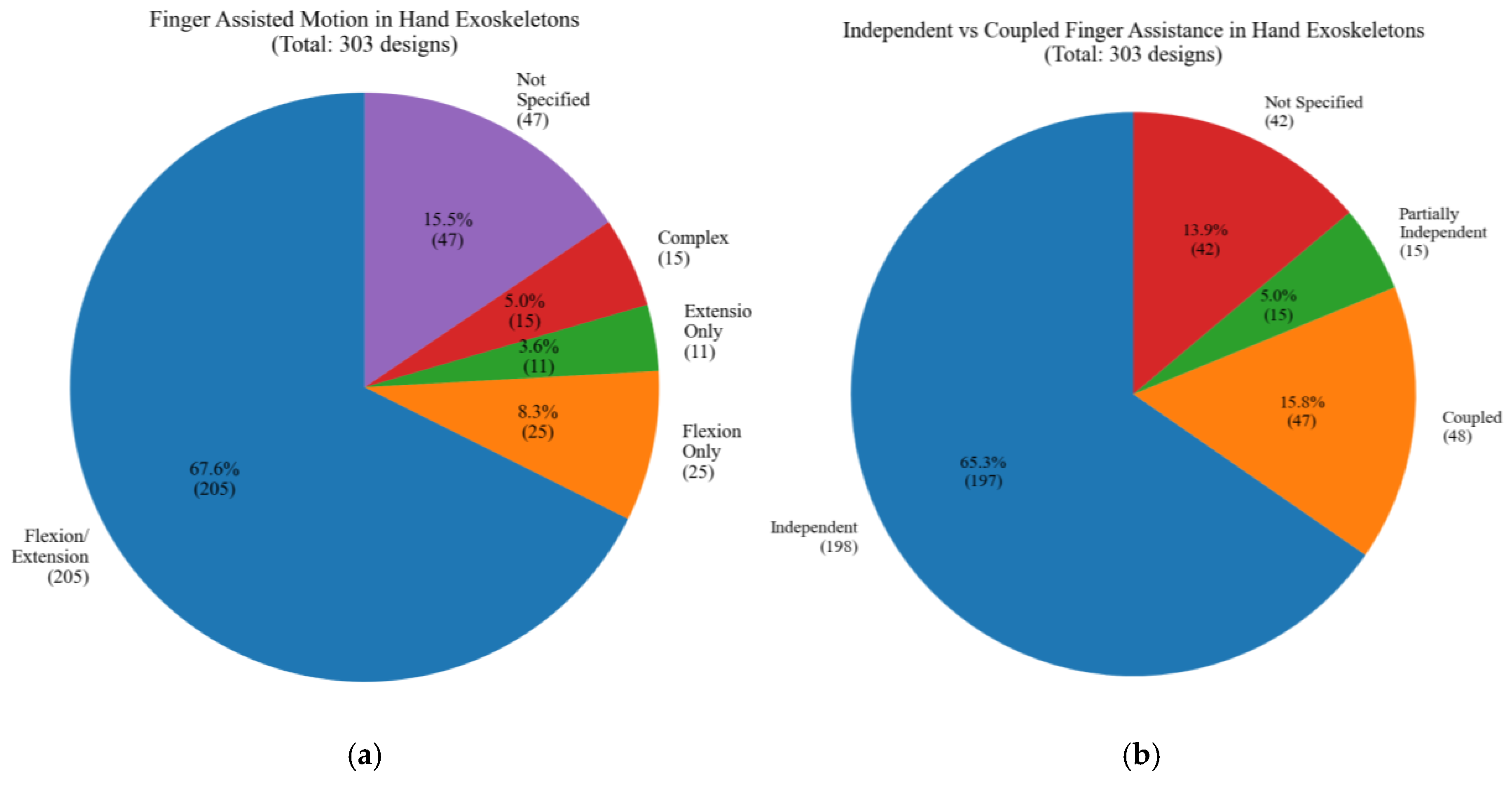
Figure 27a presents the types of finger motions assisted by the studied hand exoskeleton designs. Most designs focus on both flexion and extension, aiming to provide a full range of motion. Figure 27b illustrates the distribution of independent vs. coupled finger assistance in studied hand exoskeleton designs. A significant majority implement independent finger actuation, allowing for more precise and versatile hand movements. Coupled designs and partially independent designs represent alternative approaches.
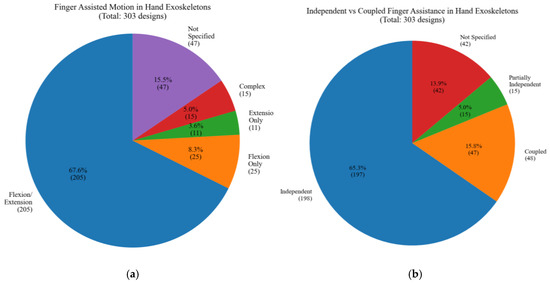
Figure 27.
Type of motions: (a) Finger assisted motion, (b) independent or coupled.
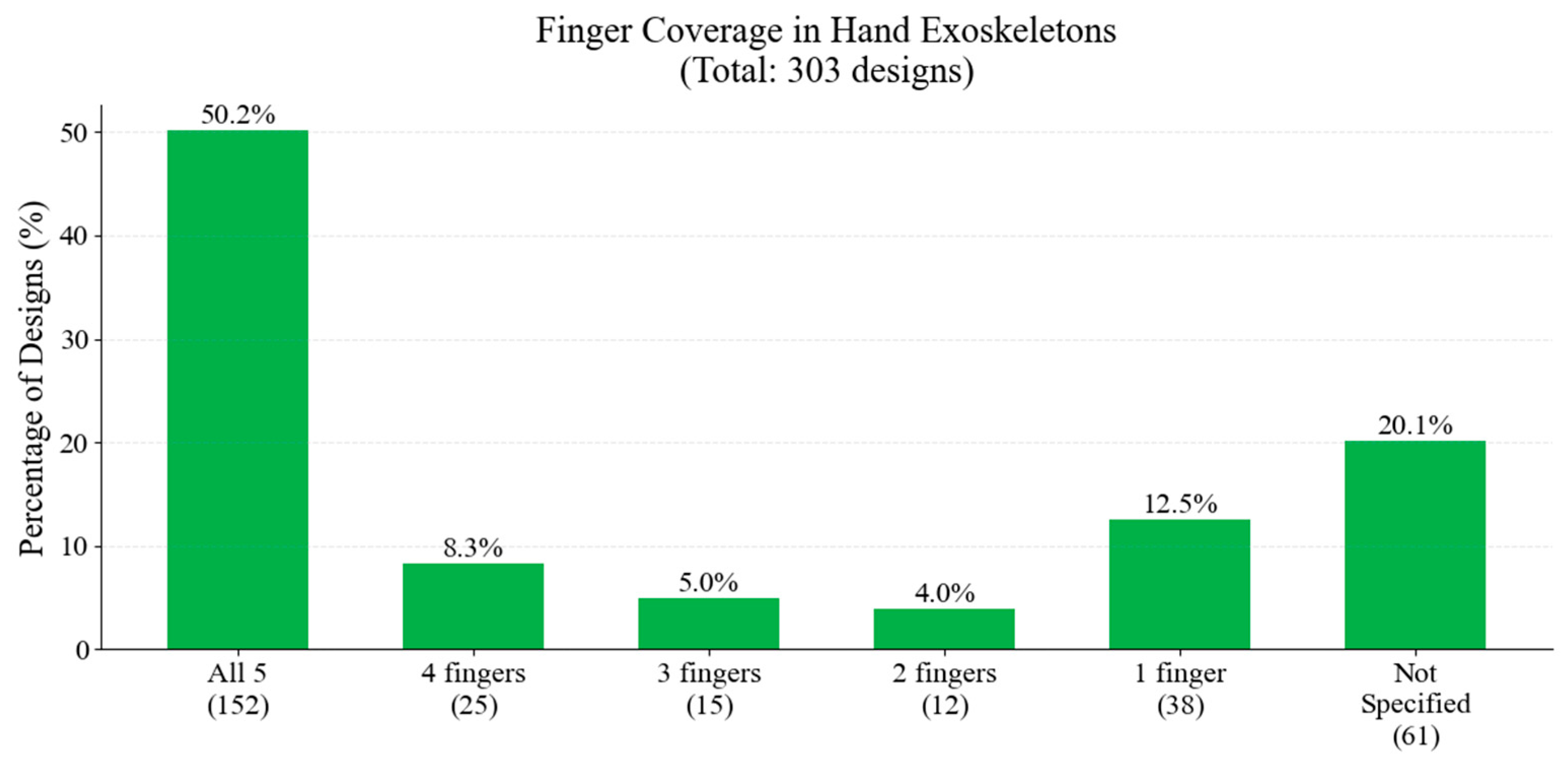
Figure 28 illustrates the distribution of finger coverage across the studied hand exoskeletons. The majority of designs aim to assist all five fingers. There is a notable diversity in approaches, with 12.5% of designs focusing on single-finger assistance.
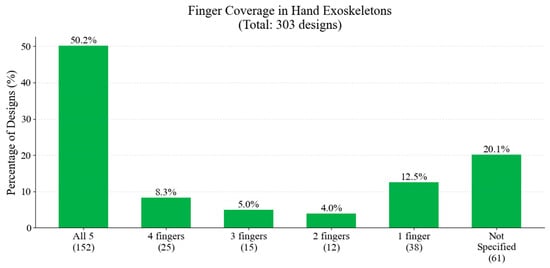
Figure 28.
Distribution of finger coverage.
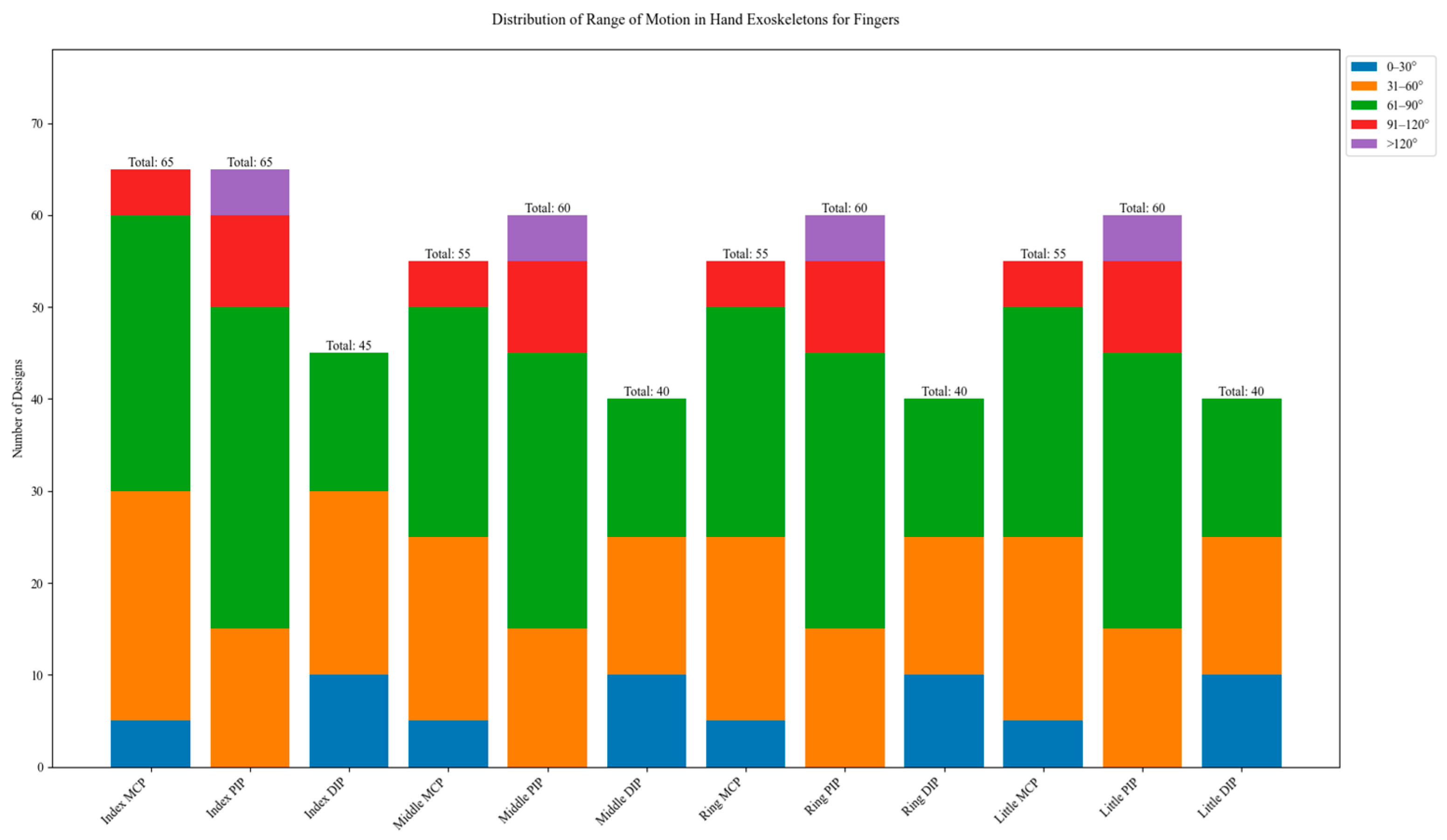
In Figure 29, the distribution of range of motion (ROM) is illustrated. The graph shows data for the metacarpophalangeal (MCP), proximal interphalangeal (PIP), and distal interphalangeal (DIP) joints of each finger. Across all fingers, MCP joints show a preference for ROMs in the 31–90° range, with the highest concentration in the 61–90° category. This aligns with the natural ROM of MCP joints in functional tasks. PIP joints demonstrate the widest range of motion, with significant representations in the 61–90° and 91–120° ranges. DIP joints consistently show smaller ROMs compared to MCP and PIP joints, with most designs in the range of 0–60°.
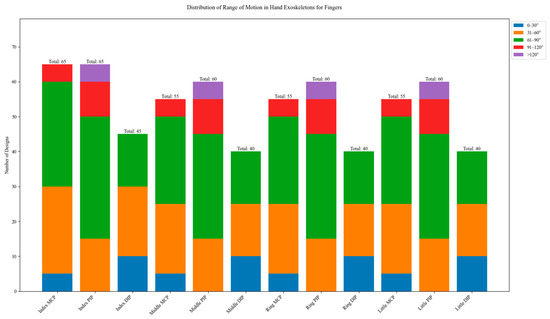
Figure 29.
Range of motion (ROM) for finger joints.
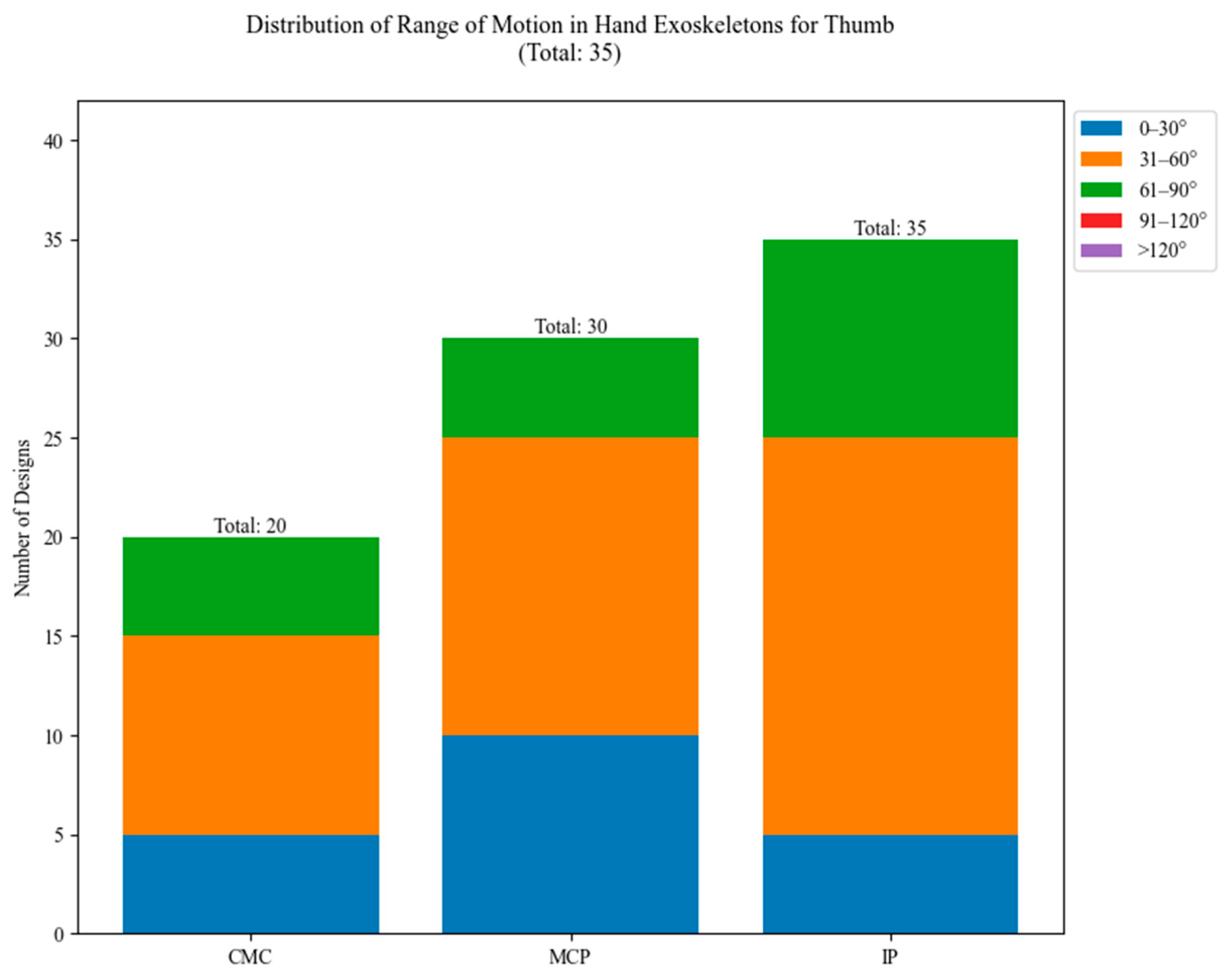
In Figure 30, the ROM distribution for the thumb joints of the studied exoskeletons is illustrated. The CMC joint, responsible for thumb opposition, shows a preference for smaller ROMs, primarily in the 0–60° range. The thumb MCP joint displays a slightly wider range, with most designs falling in the 31–60° category. The PIP joint shows the widest distribution among thumb joints, with a significant number of designs in the 31–60° and 61–90° ranges.
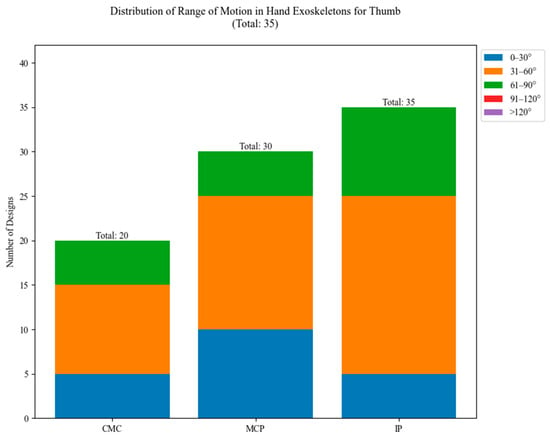
Figure 30.
Range of motion (ROM) for thumb joints.
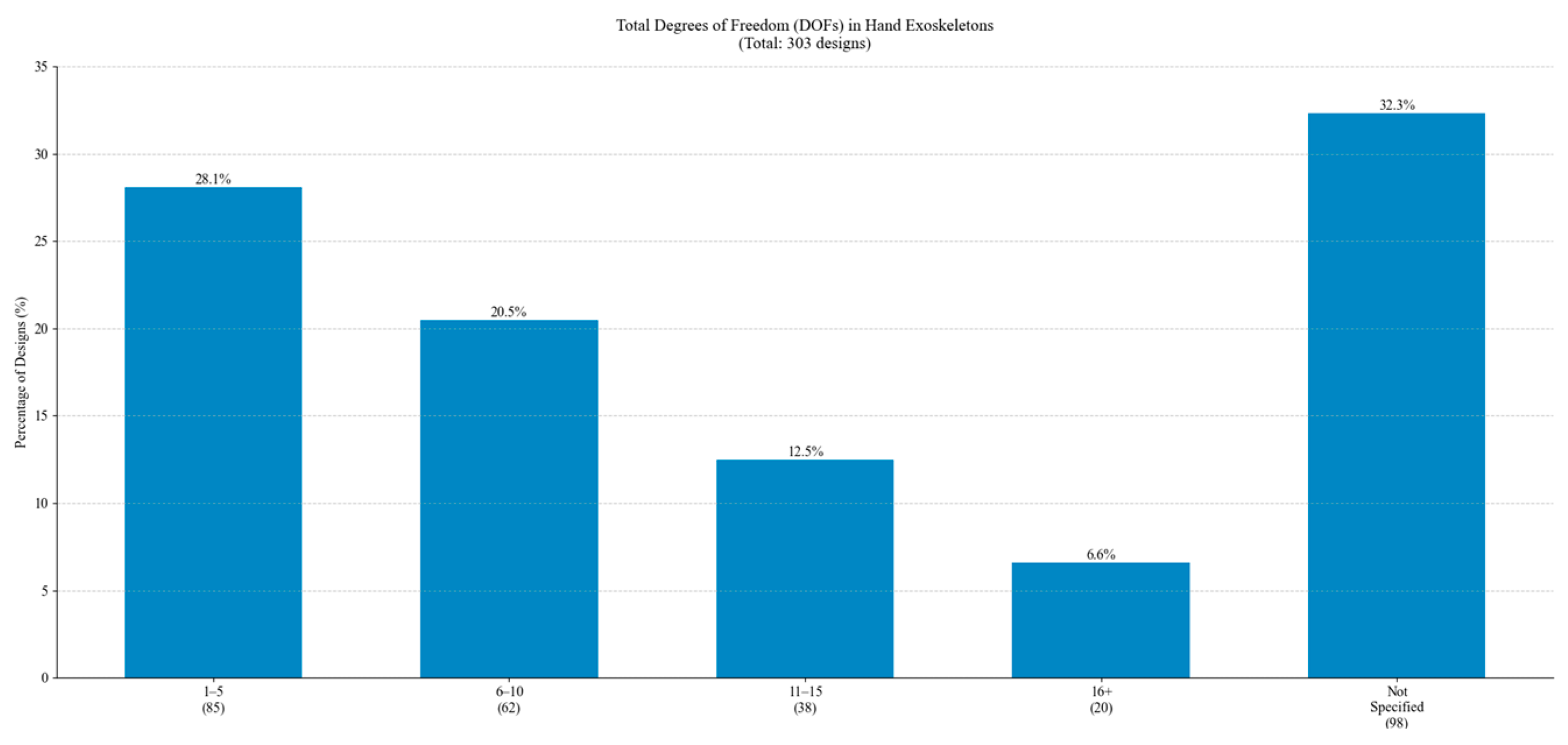
The total DoF distribution is illustrated in Figure 31. Most designs feature 1–5 DoF, followed by 6–10 DoF, corresponding to designs targeting multiple fingers and more complex movements. The presence of designs with 11–15 DoF and 16+ DoF indicates the development of complex systems.
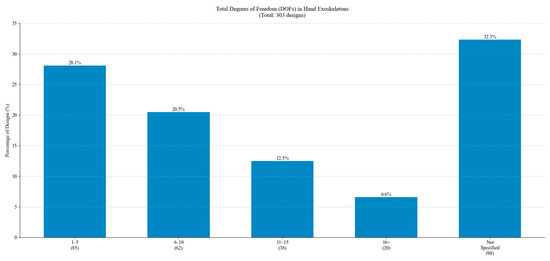
Figure 31.
Distribution of Total DoF.
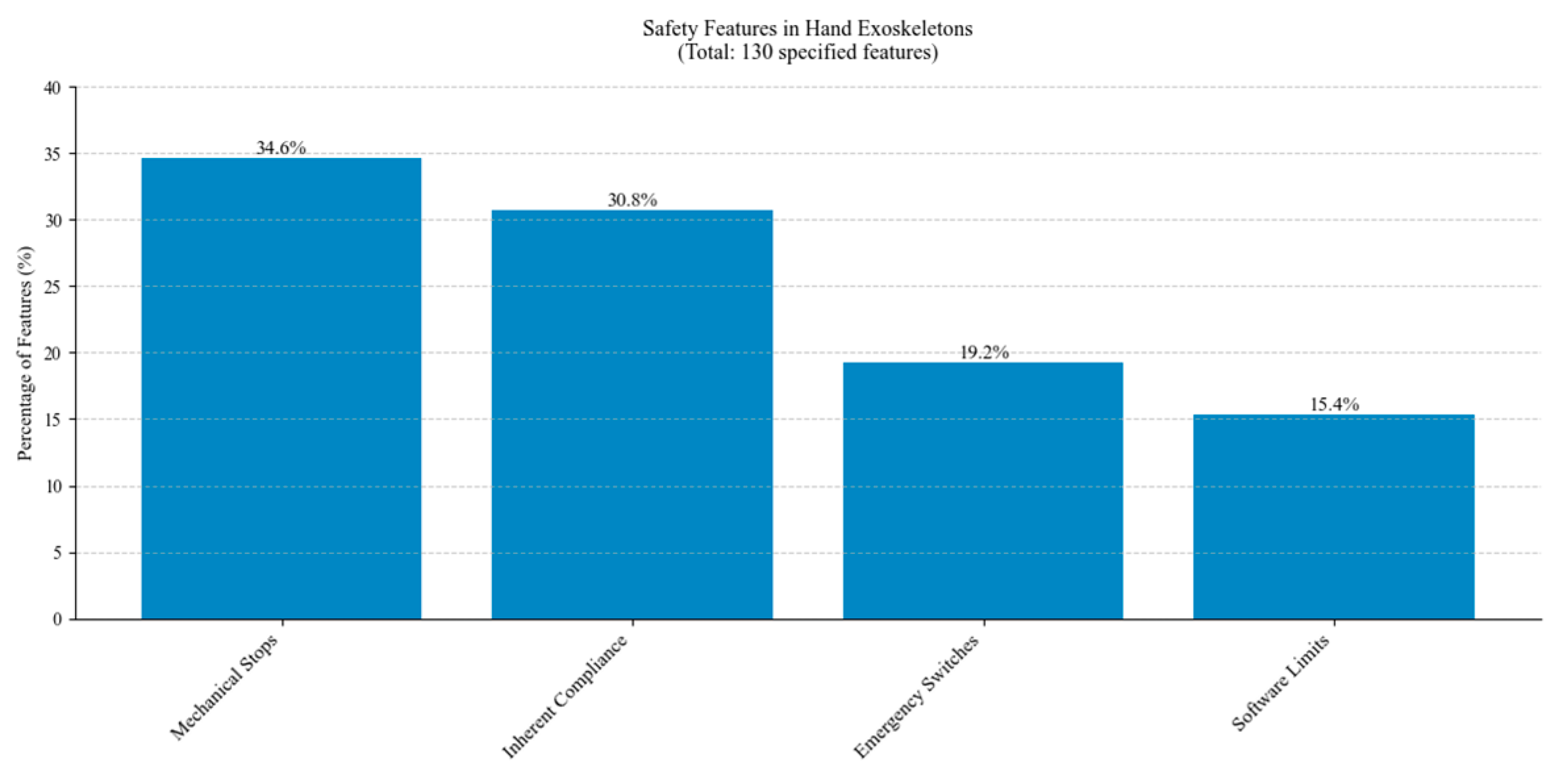
Figure 32 presents the distribution of safety features implemented in hand exoskeleton designs. Mechanical stops are the most common safety feature, closely followed by inherent compliance. Emergency stops and software limits are frequently used.
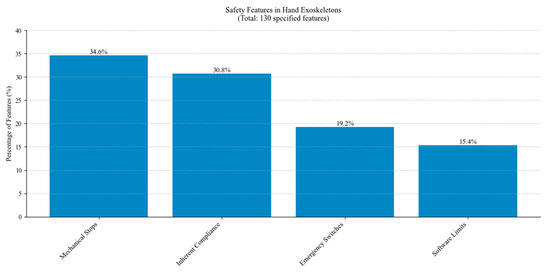
Figure 32.
Distribution of safety features across studied hand exoskeletons.
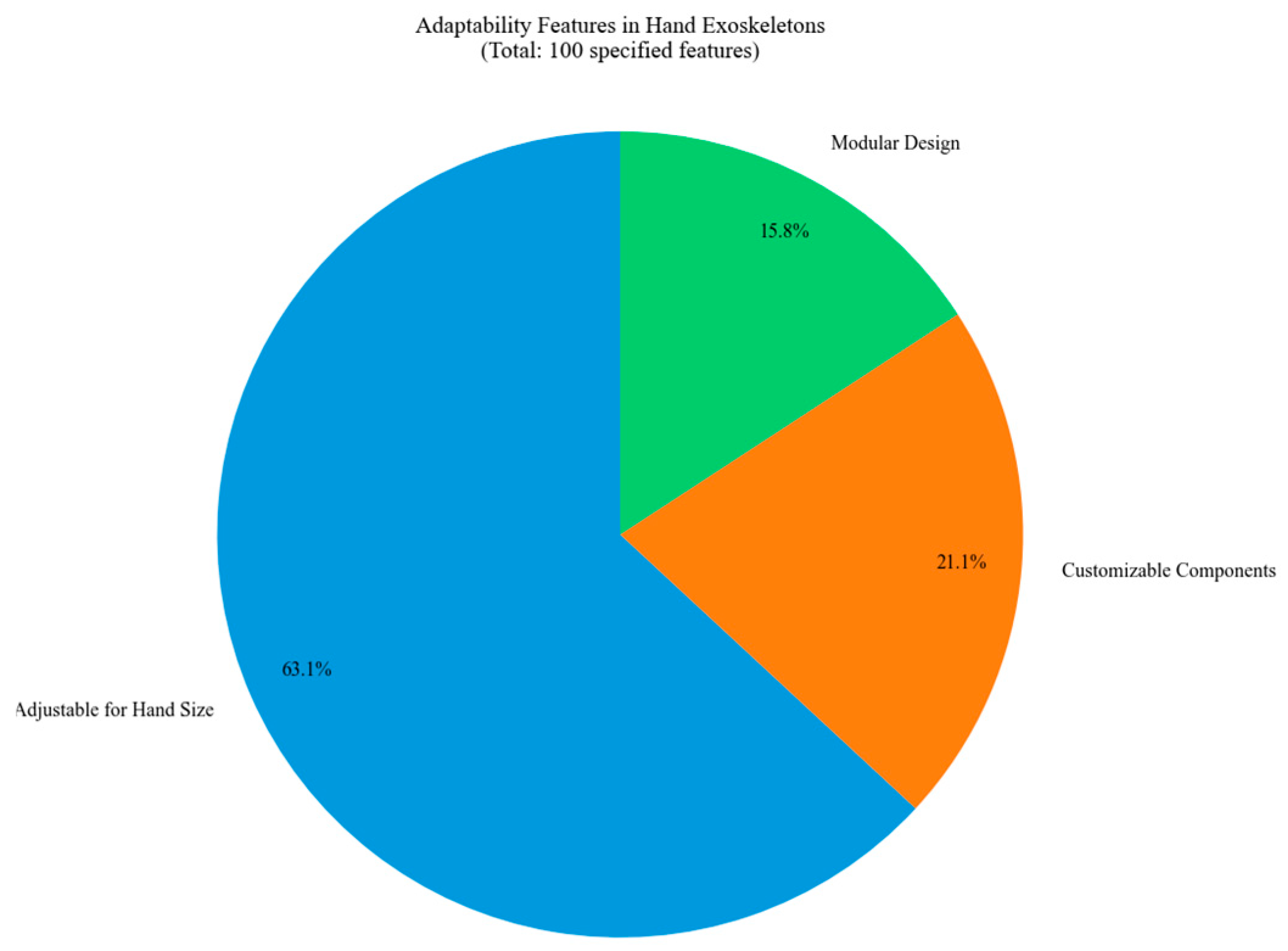
The distribution of adaptability features in hand exoskeleton designs is illustrated in Figure 33. Most of the designs are adjustable for different sizes of hands. Customizable components and modular designs contribute to the adaptability criterion.
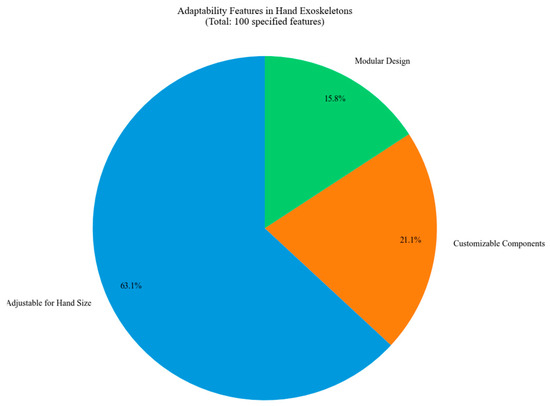
Figure 33.
Distribution of adaptability features across studied hand exoskeletons.
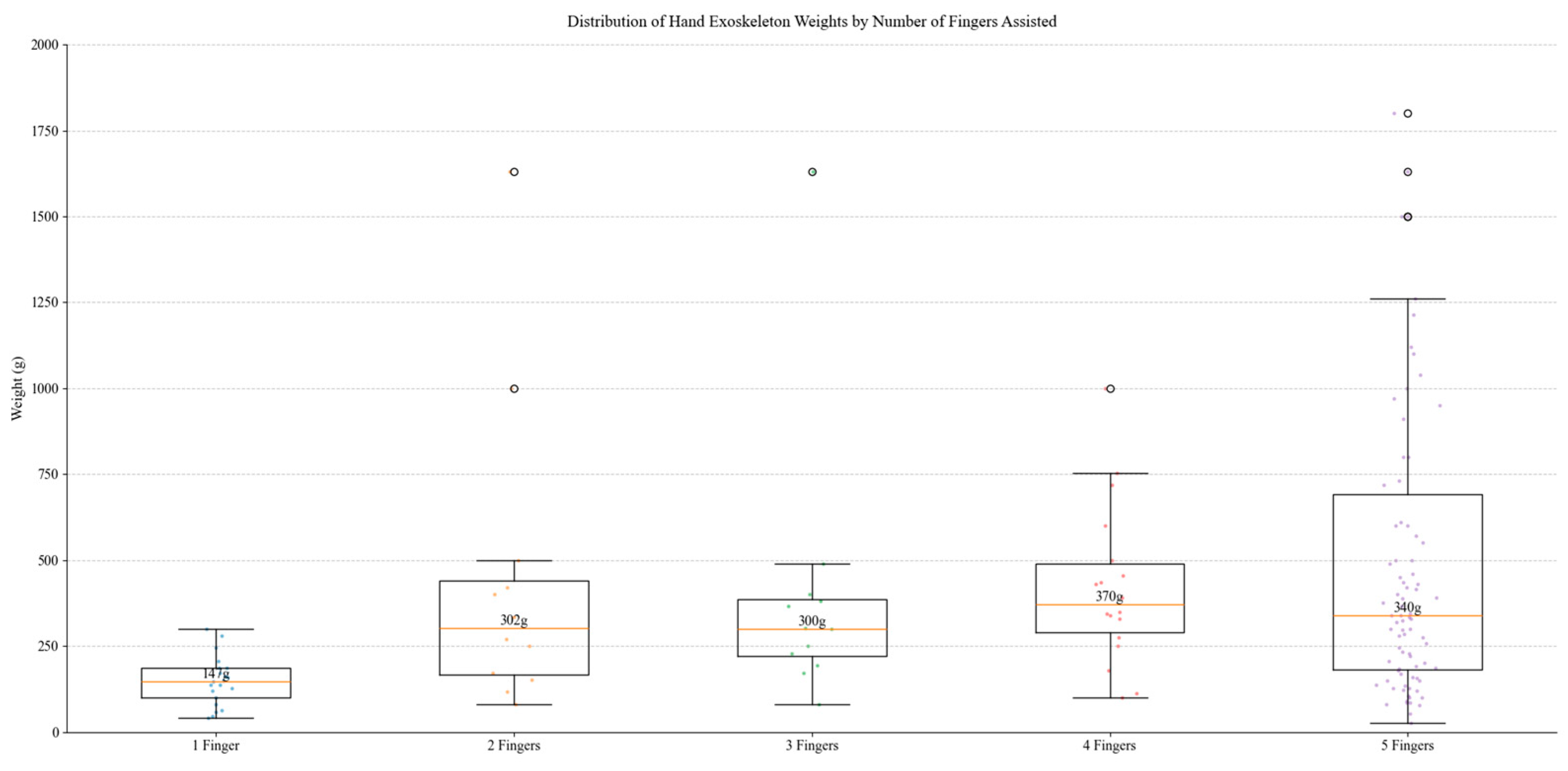
Box plot analysis illustrated in Figure 34 reveals a systematic relationship between device complexity, functionality, and weight across studied hand exoskeleton designs. The observed weight range, from 25 g to 3700 g, demonstrates significant variation across designs, with median values showing progressive increases from single-finger configurations with a mass of 138 g to five-finger configurations with a mass of 320 g. Single-finger devices exhibit minimal weight variance, whereas five-finger systems display broader distribution patterns, reflecting diverse design approaches from assistive to rehabilitation applications. Mechanical complexity represents a key weight determinant.
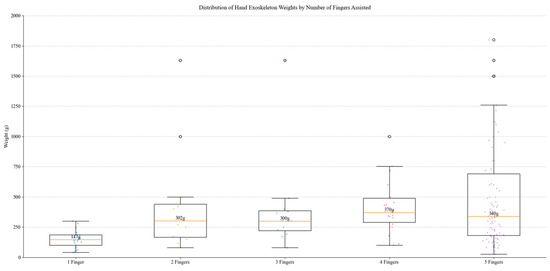
Figure 34.
Distribution of weights by number of fingers assisted.
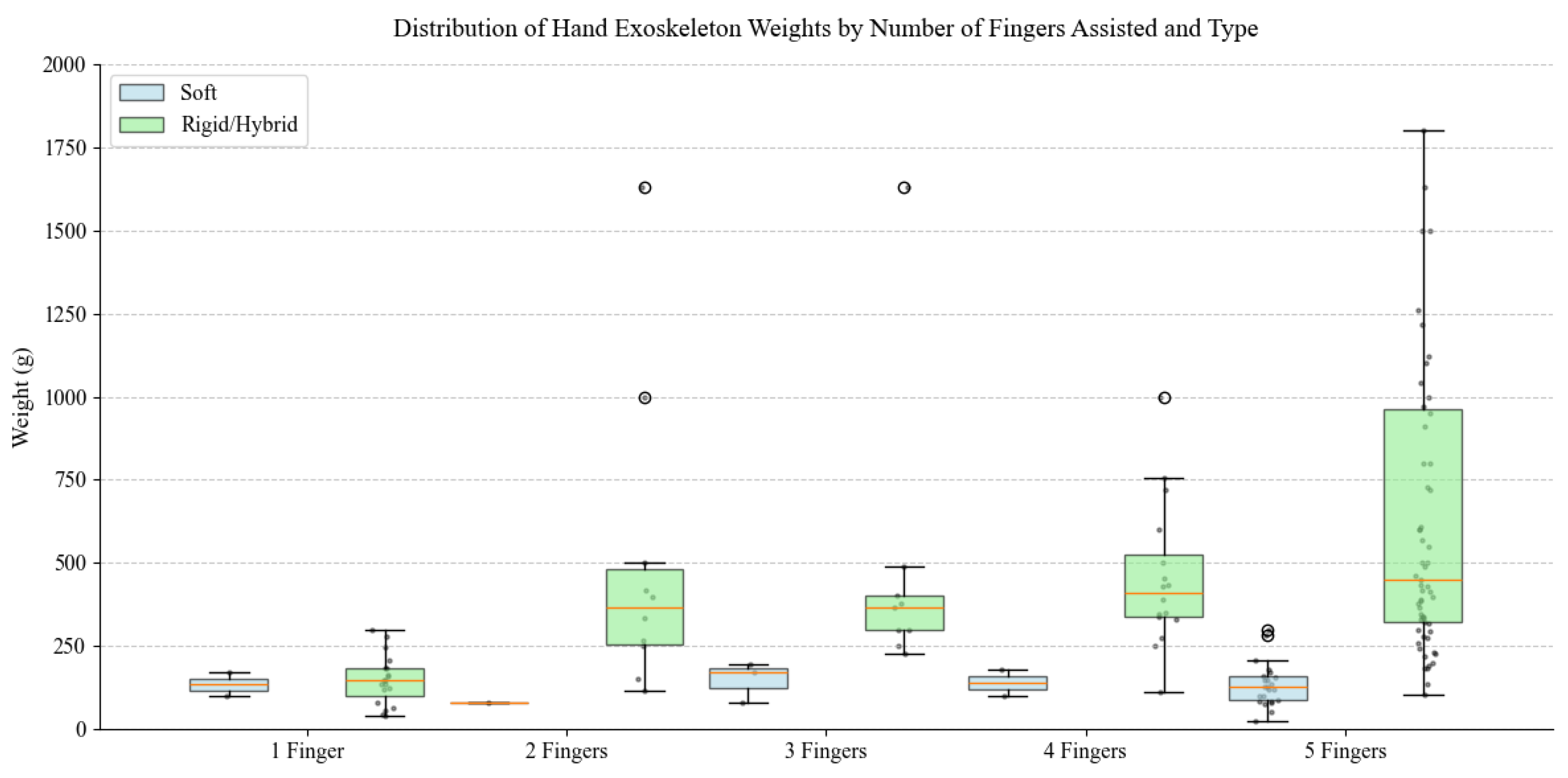
The boxplot analysis depicted in Figure 35 demonstrates distinct weight characteristics between soft and rigid/hybrid hand exoskeletons across different finger assistance configurations. Soft exoskeletons maintain consistently low weights, predominantly below 300 g, regardless of assisted finger count, with five-finger designs ranging from 25 g to 300 g. In contrast, rigid/hybrid systems show substantially higher weights and broader distribution patterns, particularly in multi-finger configurations. While soft exoskeletons maintain relatively stable weights across categories, rigid/hybrid devices exhibit marked weight increases with additional finger assistance, suggesting a direct correlation between mechanical complexity and mass.
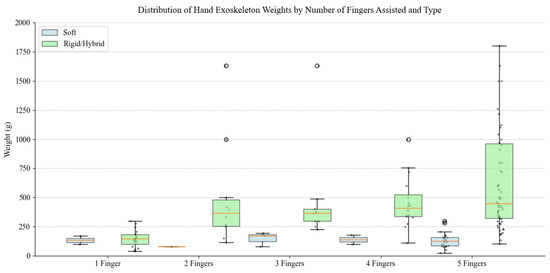
Figure 35.
Distribution of Hand exoskeleton weights by number of fingers assisted and type.
6. Conclusions
This paper presents a detailed analysis of hand rehabilitation devices based on a review of over 300 systems developed between 2002 and 2024, aiming to reveal the most relevant trends in the development of such devices. The analysis demonstrates a clear trend toward more complex and user-centered designs, with research output peaking between 2016 and 2020. While rigid exoskeletons remain dominant, representing 50% of all designs, there has been substantial growth in soft (35%), and hybrid (15.5%) systems, reflecting increasing attention to user comfort and natural movement patterns and revealing future possible development trends.
In terms of technical implementation, electric actuation remains the predominant choice, representing 55.8% of all systems, with DC motors being the most common actuator type. This might be because of their simpler control systems and their size, which allow these devices to be wearable. The required actuation torque is not high, which is one of the reasons for which the preference for electric actuation is followed by pneumatic systems. Device complexity varies significantly, with 29.4% of designs using five or more actuators while 24.8% employ only one or two actuators, indicating diverse approaches to movement assistance. It also shows that hand rehabilitation can be performed, at least in the initial stages, using underactuated devices, with several fingers performing the same motion together. This approach seems sometimes preferred for practical reasons. Dorsal mechanism placement emerged as the most common configuration, followed by glove-based designs, with most systems implementing independent finger actuation to enable precise control and versatile movements.
Weight analysis demonstrated a clear correlation between functionality and mass. Lighter soft exoskeletons prioritize comfort and mild impairment assistance, while heavier rigid designs offer higher force output and more complex joint control for severe rehabilitation needs.
Analysis of the rehabilitation devices revealed clear relationships between mechanism design choices and clinical applications. Rigid designs usually deliver higher forces that are suitable for severe impairments requiring substantial assistance, while soft systems are suitable for mild to moderate conditions. Hybrid approaches offer moderate force capabilities while maintaining acceptable comfort for medium-term rehabilitation sessions.
Despite these advances, several challenges remain to be addressed in future research. There is a clear need for further investigation into optimal actuation strategies, such as assistive, active-assistive, or resistive ones, targeting different rehabilitation scenarios and the development of standardized evaluation metrics for device performance and therapeutic effectiveness. Integration of advanced sensing and control systems for more personalized rehabilitation approaches represents another crucial area for development.
The field has key challenges that need to be addressed, with missing or incomplete data from source materials being a major concern, a lack of standardized terminology and metrics for direct comparisons, limited long-term clinical studies evaluating therapeutic effectiveness, and the ongoing challenge of developing improved power sources for portable devices. These findings suggest that while significant progress has been made in hand rehabilitation robotics, substantial opportunities remain for improving device functionality, usability, and therapeutic effectiveness.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.P. and C.V.; Methodology, I.B.; Software, P.T.; Validation, D.P. and J.M.; Formal Analysis, B.G.; Investigation, I.Z.; Resources, B.G.; Data Curation, A.P.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, I.Z.; Writing—Review and Editing, I.Z. and B.G.; Visualization, C.V.; Supervision, D.P.; Project Administration, C.V.; Funding Acquisition, J.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the project New Frontiers in Adaptive Modular Robotics for Patient-centered Medical Rehabilitation—ASKLEPIOS, funded by the European Union—NextGenerationEU, and the Romanian Government under the National Recovery and Resilience Plan for Romania, contract no. 760071/23 May 2023, code CF 121/15 November 2022, with the Romanian Ministry of Research, Innovation and Digitalization within Component 9, investment I8.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- The Top 10 Causes of Death. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/the-top-10-causes-of-death (accessed on 9 November 2024).
- Murray, C.J.L.; Vos, T.; Lozano, R.; Naghavi, M.; Flaxman, A.D.; Michaud, C.; Ezzati, M.; Shibuya, K.; Salomon, J.A.; Abdalla, S.; et al. Disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) for 291 diseases and injuries in 21 regions, 1990–2010: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2012, 380, 2197–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Major, Z.; Vaida, C.; Major, K.; Tucan, P.; Brusturean, E.; Gherman, B.; Birlescu, I.; Craciunas, R.; Ulinici, I.; Simori, G.; et al. Comparative Assessment of Robotic versus Classical Physical Therapy Using Muscle Strength and Ranges of Motion Testing in Neurological Diseases. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wafa, H.A.; Wolfe, C.D.A.; Emmett, E.; Roth, G.A.; Johnson, C.O.; Wang, Y. Burden of Stroke in Europe: Thirty-Year Projections of Incidence, Prevalence, Deaths, and Disability-Adjusted Life Years. Stroke 2020, 51, 2418–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaida, C.; Carbone, G.; Major, K.A.; Major, Z.; Plitea, N.; Pisla, D. On Human Robot Interaction Modalities in the Upper Limb Rehabilitation After Stroke. Acta Tech. Napoc. Ser. Appl. Math. Mech. Eng. 2017, 60, 91–102. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, G.; Zhang, S.; Wang, H.; Zhou, W.; Ren, F.F.; Liang, H.; Wu, D.D.; Ji, X.Y.; Hashimoto, M.; et al. Efficacy and evaluation of therapeutic exercises on adults with Parkinson’s disease: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. BMC Geriatr. 2022, 22, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selph, S.S.; Skelly, A.C.; Wasson, N.; Dettori, J.R.; Brodt, E.D.; Ensrud, E.; Elliot, D.; Dissinger, K.M.; McDonagh, M. Physical Activity and the Health of Wheelchair Users: A Systematic Review in Multiple Sclerosis, Cerebral Palsy, and Spinal Cord Injury. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2021, 102, 2464–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKevitt, C.; Fudge, N.; Redfern, J.; Sheldenkar, A.; Crichton, S.; Rudd, A.R.; Forster, A.; Young, J.; Nazareth, I.; Silver, L.E.; et al. Self-reported long-term needs after stroke. Stroke 2011, 42, 1398–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfe, C.D.A.; Crichton, S.L.; Heuschmann, P.U.; McKevitt, C.J.; Toschke, A.M.; Grieve, A.P.; Rudd, A.G. Estimates of outcomes up to ten years after stroke: Analysis from the prospective South London Stroke Register. PLoS Med. 2011, 8, e1001033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Burden of Stroke in Europe Report; King’s College London for the Stroke Alliance for Europe: London, UK, 2019; ISBN 978-1-5272-0858-2.
- Li, S. Spasticity, Motor Recovery, and Neural Plasticity after Stroke. Front. Neurol. 2017, 8, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sommerfeld, D.K.; Eek, E.U.-B.; Svensson, A.-K.; Holmqvist, L.W.; von Arbin, M.H. Spasticity After Stroke: Its Occurrence and Association With Motor Impairments and Activity Limitations. Stroke 2004, 35, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worsnopp, T.T.; Peshkin, M.A.; Colgate, J.E.; Kamper, D.G. An Actuated Finger Exoskeleton for Hand Rehabilitation Following Stroke. In Proceedings of the IEEE 10th International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics, Noordwijk, The Netherlands, 13–15 June 2007; pp. 896–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demarin, V.; Morovic, S.; Béné, R. Neuroplasticity. Period. Biol. 2014, 116, 209–211. [Google Scholar]
- Alhamad, R.; Seth, N.; Abdullah, H. Initial Testing of Robotic Exoskeleton Hand Device for Stroke Rehabilitation. Sensors 2023, 23, 6339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.S.; Veeravagu, A.; Grant, G. Neuroplasticity after Traumatic Brain Injury. In Translational Research in Traumatic Brain Injury; Laskowitz, D., Grant, G., Eds.; CRC Press/Taylor and Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; Chapter 8. [Google Scholar]
- Nahmani, M.; Turrigiano, G. Adult Cortical Plasticity Following Injury: Recapitulation of Critical Period Mechanisms? Neuroscience 2014, 283, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmichael, S.T. Plasticity of Cortical Projections after Stroke. Neuroscientist 2003, 9, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keci, A.; Tani, K.; Xhema, J. Role of Rehabilitation in Neural Plasticity. Open Access Maced. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 7, 1540–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleim, J.A. Neural Plasticity and Neurorehabilitation: Teaching the New Brain Old Tricks. J. Commun. Disord. 2011, 44, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisla, D.; Tarnita, D.; Tucan, P.; Tohanean, N.; Vaida, C.; Geonea, I.D.; Bogdan, G.; Abrudan, C.; Carbone, G.; Plitea, N. A Parallel Robot with Torque Monitoring for Brachial Monoparesis Rehabilitation Tasks. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 9932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, R.; Sunny, M.S.H.; Ahmed, H.U.; Rahman, M.H. Hand Rehabilitation Devices: A Comprehensive Systematic Review. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langhorne, P.; Bernhardt, J.; Kwakkel, G. Stroke Rehabilitation. Lancet 2011, 377, 1693–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maceira-Elvira, P.; Popa, T.; Schmid, A.C.; Hummel, F.C. Wearable Technology in Stroke Rehabilitation: Towards Improved Diagnosis and Treatment of Upper-Limb Motor Impairment. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2019, 16, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teasell, R.; Salbach, N.M.; Foley, N.; Mountain, A.; Cameron, J.I.; Jong, A.; Acerra, N.E.; Bastasi, D.; Carter, S.L.; Fung, J.; et al. Canadian Stroke Best Practice Recommendations: Rehabilitation, Recovery, and Community Participation following Stroke. Part One: Rehabilitation and Recovery Following Stroke; 6th Edition Update 2019. Int. J. Stroke 2020, 15, 763–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orthopedic Associates of Hartford. Hand Home Exercises. Available online: https://oahct.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/05/OAH-HAND-EXERCISES.pdf (accessed on 9 November 2024).
- Peveler, R.; Carson, A.; Rodin, G. ABC of Psychological Medicine: Depression in Medical Patients. BMJ 2002, 325, 149–152. Available online: http://www.jstor.org/stable/25451876 (accessed on 14 November 2024). [CrossRef]
- Edwards, D.J. On the Understanding and Development of Modern Physical Neurorehabilitation Methods: Robotics and Non-Invasive Brain Stimulation. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2009, 6, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Major, Z.Z.; Vaida, C.; Major, K.A.; Tucan, P.; Simori, G.; Banica, A.; Brusturean, E.; Burz, A.; Craciunas, R.; Ulinici, I.; et al. The Impact of Robotic Rehabilitation on the Motor System in Neurological Diseases. A Multimodal Neurophysiological Approach. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plitea, N.; Hesselbach, J.; Pisla, D.; Raatz, A.; Vaida, C.; Wrege, J.; Burisch, A. Innovative Development of Parallel Robots and Microrobots. Acta Teh. Napoc. Ser. Appl. Math. Mec. 2006, 49, 5–26. [Google Scholar]
- Pisla, D.; Nadas, I.; Tucan, P.; Albert, S.; Carbone, G.; Antal, T.; Banica, A.; Gherman, B. Development of a Control System and Functional Validation of a Parallel Robot for Lower Limb Rehabilitation. Actuators 2021, 10, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J. Hand Rehabilitation Robotics on Poststroke Motor Recovery. Behav. Neurol. 2017, 2017, 3908135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feine, J.S.; Widmer, C.G.; Lund, J.P. Physical Therapy: A Critique. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 1997, 83, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landry, M.D.; Hack, L.M.; Coulson, E.; Freburger, J.; Johnson, M.P.; Katz, R.; Kerwin, J.; Smith, M.H.; Wessman, H.C.; Venskus, D.G.; et al. Workforce Projections 2010–2020: Annual Supply and Demand Forecasting Models for Physical Therapists Across the United States. Phys. Ther. 2016, 96, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marek, K.; Redlicka, J.; Miller, E.; Zubrycki, I. Objectivizing Measures of Post-Stroke Hand Rehabilitation Through Multi-Disciplinary Scales. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 7497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafsson, L.A.; Turpin, M.J.; Dorman, C.M. Clinical Utility of the Chedoke Arm and Hand Activity Inventory for Stroke Rehabilitation. Can. J. Occup. Ther. 2010, 77, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikbali Afsar, S.; Mirzayev, I.; Umit Yemisci, O.; Cosar Saracgil, S.N. Virtual Reality in Upper Extremity Rehabilitation of Stroke Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2018, 27, 3473–3478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, C.S.; Almeida, C.S.; Freitas, L.C.; Santana, R.; Fernandes, G.; Fonseca Junior, P.R.; Moura, R.C.F. Use of the Box and Block Test for the Evaluation of Manual Dexterity in Individuals with Central Nervous System Disorders: A Systematic Review. Man. Ther. Posturology Rehabil. J. 2016, 14, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solaro, C.; Di Giovanni, R.; Grange, E.; Mueller, M.; Messmer Uccelli, M.; Bertoni, R.; Brichetto, G.; Tacchino, A.; Patti, F.; Pappalardo, A.; et al. Box and Block Test, Hand Grip Strength and Nine-Hole Peg Test: Correlations Between Three Upper Limb Objective Measures in Multiple Sclerosis. Eur. J. Neurol. 2020, 27, 2523–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beebe, J.A.; Lang, C.E. Relationships and Responsiveness of Six Upper Extremity Function Tests During the First Six Months of Recovery After Stroke. J. Neurol. Phys. Ther. 2009, 33, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Morente, G.; Hurtado-Pomares, M.; Terol Cantero, M.C. Bibliometric Analysis of Research on the Use of the Nine Hole Peg Test. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 10080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krumlinde-Sundholm, L.; Lindkvist, B.; Plantin, J.; Hoare, B. Development of the Assisting Hand Assessment for Adults Following Stroke: A Rasch-Built Bimanual Performance Measure. Disabil. Rehabil. 2019, 41, 472–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunnstrom, S. Motor Testing Procedures in Hemiplegia: Based on Sequential Recovery Stages. Phys. Ther. 1966, 46, 357–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arwert, H.; Schut, S.; Boiten, J.; Vliet Vlieland, T.; Meesters, J. Patient Reported Outcomes of Hand Function Three Years After Stroke. Top. Stroke Rehabil. 2018, 25, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arcidiacone, S.; Panuccio, F.; Tusoni, F.; Galeoto, G. A Systematic Review of the Measurement Properties of the Michigan Hand Outcomes Questionnaire (MHQ). Hand Surg. Rehabil. 2022, 41, 542–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jebsen, R.H.; Taylor, N.; Trieschmann, R.B.; Trotter, M.J.; Howard, L.A. An Objective and Standardized Test of Hand Function. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 1969, 50, 311–319. [Google Scholar]
- Resnik, L.; Adams, L.; Borgia, M.; Delikat, J.; Disla, R.; Ebner, C.; Walters, L.S. Development and Evaluation of the Activities Measure for Upper Limb Amputees. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2013, 94, 488–494.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sezer, N.; Yavuzer, G.; Sivrioglu, K.; Basaran, P.; Koseoglu, B.F. Clinimetric Properties of the Duruoz Hand Index in Patients with Stroke. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2007, 88, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duruöz, M.T.; Poiraudeau, S.; Fermanian, J.; Menkes, C.J.; Amor, B.; Dougados, M.; Revel, M. Development and Validation of a Rheumatoid Hand Functional Disability Scale that Assesses Functional Handicap. J. Rheumatol. 1996, 23, 1167–1172. [Google Scholar]
- Lefevre-Colau, M.M.; Poiraudeau, S.; Fermanian, J.; Etchepare, F.; Alnot, J.Y.; Le Viet, D.; Leclercq, C.; Oberlin, C.; Bargy, F.; Revel, M. Responsiveness of the Cochin Rheumatoid Hand Disability Scale After Surgery. Rheumatology 2001, 40, 843–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Brower, L.M.; Poole, J.L. Reliability and Validity of the Duruoz Hand Index in Persons with Systemic Sclerosis (Scleroderma). Arthritis Rheum. 2004, 51, 805–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duruöz, M.T.; Cerrahoglu, L.; Dincer-Turhan, Y.; Kürsat, S. Hand Function Assessment in Patients Receiving Haemodialysis. Swiss Med. Wkly. 2003, 133, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penta, M.; Tesio, L.; Arnould, C.; Zancan, A.; Thonnard, J.L. The ABILHAND Questionnaire as a Measure of Manual Ability in Chronic Stroke Patients: Rasch-Based Validation and Relationship to Upper Limb Impairment. Stroke 2001, 32, 1627–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekstrand, E.; Alt Murphy, M.; Sunnerhagen, K.S. Clinical Interpretation and Cutoff Scores for Manual Ability Measured by the ABILHAND Questionnaire in People with Stroke. Top. Stroke Rehabil. 2023, 30, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alt Murphy, M.; Resteghini, C.; Feys, P.; Lamers, I. An Overview of Systematic Reviews on Upper Extremity Outcome Measures After Stroke. BMC Neurol. 2015, 15, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mordor Intelligence. Rehabilitation Robots Market|2022-27|Industry Share, Size, Growth. Available online: https://www.mordorintelligence.com/industry-reports/rehabilitation-robots-market (accessed on 9 November 2024).
- Fortune Business Insights. Rehabilitation Robots Market Size, Share|Global Analysis 2026. Available online: https://www.fortunebusinessinsights.com/industry-reports/rehabilitation-robots-market-101013 (accessed on 9 November 2024).
- Ghosh, S. Capturing Human Hand Kinematics for Object Grasping and Manipulation. Master’s Thesis, Texas A&M University, College Station, TX, USA, May 2013. Available online: https://oaktrust.library.tamu.edu/items/e966525a-6fa2-4a93-a4e0-7bea33c725ee (accessed on 9 November 2024).
- Xia, K.; Chen, X.; Chang, X.; Liu, C.; Guo, L.; Xu, X.; Lv, F.; Wang, Y.; Sun, H.; Zhou, J. Hand Exoskeleton Design and Human–Machine Interaction Strategies for Rehabilitation. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez-Escobar, M.; Rendon-Velez, E. An Overview of Robotic/Mechanical Devices for Post-Stroke Thumb Rehabilitation. Disabil. Rehabil. Assist. Technol. 2018, 13, 683–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Meydan, T.; Williams, P.I. A Two-Axis Goniometric Sensor for Tracking Finger Motion. Sensors 2017, 17, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarque-Bou, N.J.; Atzori, M.; Müller, H. A Large Calibrated Database of Hand Movements and Grasps Kinematics. Sci. Data 2020, 7, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, J.; Baizid, K. Stroke rehabilitation using exoskeleton-based robotic exercisers: Mini Review. Biomed. Res. India 2014, 26, 197–201. [Google Scholar]
- Heo, P.; Gu, G.M.; Lee, S.; Rhee, K.; Kim, J. Current Hand Exoskeleton Technologies for Rehabilitation and Assistive Engineering. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2012, 13, 807–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaida, C.; Birlescu, I.; Pisla, A.; Carbone, G.; Plitea, N.; Ulinici, I.; Gherman, B.; Puskas, F.; Tucan, P.; Pisla, D. RAISE—An Innovative Parallel Robotic System for Lower Limb Rehabilitation. Adv. Theory Pract. 2019, 4, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisla, D.; Plitea, N.; Gherman, B.; Pisla, A.; Vaida, C. Kinematical Analysis and Design of a New Surgical Parallel Robot. In Computational Kinematics; Kecskeméthy, A., Müller, A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaida, C.; Plitea, N.; Carbone, G.; Birlescu, I.; Ulinici, I.; Pisla, A.; Pisla, D. Innovative Development of a Spherical Parallel Robot for Upper Limb Rehabilitation. Int. J. Mech. Robot. Syst. 2018, 4, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewer, B.R.; McDowell, S.K.; Worthen-Chaudhari, L.C. Poststroke upper extremity rehabilitation: A review of robotic systems and clinical results. Top. Stroke Rehabil. 2007, 14, 22–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopura, R.A.R.C.; Bandara, D.S.V.; Kiguchi, K.; Mann, G.K.I. Developments in hardware systems of active upper-limb exoskeleton robots: A review. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2016, 75, 203–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krebs, H.I.; Hogan, N.; Aisen, M.L.; Volpe, B.T. Robot-aided neurorehabilitation. IEEE Trans. Rehabil. Eng. 1998, 6, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todorov, E.; Shadmehr, R.; Bizzi, E. Augmented Feedback Presented in a Virtual Environment Accelerates Learning of a Difficult Motor Task. J. Mot. Behav. 1997, 29, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarac, M.; Solazzi, M.; Frisoli, A. Design Requirements of Generic Hand Exoskeletons and Survey of Hand Exoskeletons for Rehabilitation, Assistive, or Haptic Use. IEEE Trans. Haptics 2019, 12, 400–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, I.; Hawkes, E.; Christensen, D.; Ploch, C.; Follmer, S. Wolverine: A wearable haptic interface for grasping in virtual reality. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Daejeon, Republic of Korea, 9–14 October 2016; pp. 986–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchholz, B.; Armstrong, T.J. A Kinematic Model of the Human Hand to Evaluate Its Prehensile Capabilities. J. Biomech. 1992, 25, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggogeri, F.; Mikolajczyk, T.; O’Kane, J. Robotics for Rehabilitation of Hand Movement in Stroke Survivors. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2019, 11, 168781401984192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achilli, G.M.; Amici, C.; Dragusanu, M.; Gobbo, M.; Logozzo, S.; Malvezzi, M.; Tiboni, M.; Valigi, M.C. Soft, Rigid, and Hybrid Robotic Exoskeletons for Hand Rehabilitation: Roadmap with Impairment-Oriented Rationale for Devices Design and Selection. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 11287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiboni, M.; Amici, C. Soft Gloves: A Review on Recent Developments in Actuation, Sensing, Control and Applications. Actuators 2022, 11, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, T.; Gouwanda, D.; Nurzaman, S.G.; Gopalai, A.A. Moving Toward Soft Robotics: A Decade Review of the Design of Hand Exoskeletons. Biomimetics 2018, 3, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, B.B.; In, H.; Cho, K. Force Transmission in Joint-less Tendon Driven Wearable Robotic Hand. In Proceedings of the 2012 12th International Conference on Control, Automation and Systems, Jeju Island, Republic of Korea, 17–21 October 2012; pp. 1853–1858. [Google Scholar]
- Noronha, B.; Accoto, D. Exoskeletal Devices for Hand Assistance and Rehabilitation: A Comprehensive Analysis of State-of-the-Art Technologies. IEEE Trans. Med. Robot. Bionics 2021, 3, 525–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, G.; Pei, X.; Yu, J.; Bi, S. Classification and Type Synthesis of 1-DOF Remote Center of Motion Mechanisms. Mech. Mach. Theory 2008, 43, 1585–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, P.W.; Shen, Y.; Rosen, J. Hand Exoskeleton Systems—Overview. In Wearable Robotics; Rosen, J., Ferguson, P.W., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 149–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nava-Téllez, I.A.; Elias-Espinosa, M.C.; Cervantes-Culebro, H.; Flores-González, A.E. Parametric Design of a Finger Rehabilitation Mechanism with Double Action and Two Degrees of Freedom. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 10701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, D.; Centracchio, J.; Andreozzi, E.; Savino, S.; Gargiulo, G.D.; Naik, G.R.; Bifulco, P. Design of a 3D-Printed Hand Exoskeleton Based on Force-Myography Control for Assistance and Rehabilitation. Machines 2022, 10, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, T.-H.; Chiang, Y.-C.; Chan, W.-T.; Chen, S.-J. A Finger Exoskeleton Robot for Finger Movement Rehabilitation. Inventions 2017, 2, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickmann, T.; Wilhelm, N.J.; Glowalla, C.; Haddadin, S.; van der Smagt, P.; Burgkart, R. An Adaptive Mechatronic Exoskeleton for Force-Controlled Finger Rehabilitation. Front. Robot. AI 2021, 8, 716451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troncossi, M.; Mozaffari Foumashi, M.; Carricato, M.; Parenti Castelli, V. Feasibility Study of a Hand Exoskeleton for Rehabilitation of Post-Stroke Patients. In Proceedings of the ASME 2012 International Design Engineering Technical Conferences and Computers and Information in Engineering Conference, Nantes, France, 2–4 July 2012; pp. 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Huang, J.; Wang, Y.; Xing, K. A Wearable Rehabilitation Robotic Hand Driven by PM-TS Actuators. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Robotics and Applications (ICIRA), Shanghai, China, 10–12 November 2010; pp. 440–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Guo, S.; Zhang, F.; Guo, J.; Ji, Y.; Wang, Y. A Novel Upper Limb Rehabilitation System with Hand Exoskeleton Mechanism. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation, Takamatsu, Japan, 4–7 August 2013; pp. 285–290. [Google Scholar]
- Gasser, B.W.; Goldfarb, M. Design and Performance Characterization of a Hand Orthosis Prototype to Aid Activities of Daily Living in a Post-Stroke Population. In Proceedings of the 37th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Milan, Italy, 25–29 August 2015; pp. 3877–3880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lince, A.; Celadon, N.; Battezzato, A.; Favetto, A.; Appendino, S.; Ariano, P.; Botta, A.M. Design and Testing of an Under-Actuated Surface EMG-Driven Hand Exoskeleton. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR), London, UK, 17–20 July 2017; pp. 670–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosselin, F.; Jouan, T.; Brisset, J.; Andriot, C. Design of a Wearable Haptic Interface for Precise Finger Interactions in Large Virtual Environments. In Proceedings of the First Joint Eurohaptics Conference and Symposium on Haptic Interfaces for Virtual Environment and Teleoperator Systems, Pisa, Italy, 18–20 March 2005; pp. 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Tzvi, P.; Ma, Z. Sensing and force-feedback exoskeleton (SAFE) robotic glove. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2015, 23, 992–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Xie, Z.; Liu, H. An Exoskeleton Master Hand for Controlling DLR/HIT Hand. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, St. Louis, MO, USA, 10–15 October 2009; pp. 3703–3708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, J.; Tsagarakis, N.G.; Caldwell, D.G. A Multi-DOF Robotic Exoskeleton Interface for Hand Motion Assistance. In Proceedings of the 33rd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Boston, MA, USA, 30 August–3 September 2011; pp. 1575–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarakoglou, I.; Brygo, A.; Mazzanti, D.; Hernandez, N.G.; Caldwell, D.G.; Tsagarakis, N.G. HEXOTRAC: A highly under-actuated hand exoskeleton for finger tracking and force feedback. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Daejeon, Republic of Korea, 9–14 October 2016; pp. 1033–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertas, I.H.; Hocaoglu, E.; Barkana, D.E.; Patoglu, V. Finger exoskeleton for treatment of tendon injuries. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR), Kyoto, Japan, 23–26 June 2009; pp. 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarac, M.; Solazzi, M.; Sotgiu, E.; Bergamasco, M.; Frisoli, A. Design and kinematic optimization of a novel underactuated robotic hand exoskeleton. Meccanica 2017, 52, 749–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buryanov, A.; Kotiuk, V. Proportions of Hand Segments. Int. J. Morphol. 2010, 28, 755–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarrasse, N.; Morel, G. Connecting a Human Limb to an Exoskeleton. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2012, 28, 697–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.J.; Sugano, S.; Iwata, H. A novel, MRI compatible hand exoskeleton for finger rehabilitation. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE/SICE International Symposium on System Integration (SII), Kyoto, Japan, 20–22 December 2011; pp. 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiCicco, M.; Lucas, L.; Matsuoka, Y. Comparison of control strategies for an EMG controlled orthotic exoskeleton for the hand. In Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), New Orleans, LA, USA, 26 April–1 May 2004; pp. 1622–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cempini, M.; Cortese, M.; Vitiello, N.; Giovacchini, F.; Moise, M.; Posteraro, F.; Carrozza, M.C. Kinematics and design of a portable and wearable exoskeleton for hand rehabilitation. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE 13th International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR), Seattle, WA, USA, 24–26 June 2013; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.A.; Al-Jumaily, A. Design and Development of a Hand Exoskeleton for Rehabilitation Following Stroke. In Proceedings of the 2012 International Conference on Biomedical Engineering (ICBE), Penang, Malaysia, 27–28 February 2012; pp. 1705–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Yang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wang, J. Structure Design of a Wearable Device for Hand Rehabilitation. In Proceedings of the 2016 9th International Symposium on Computational Intelligence and Design (ISCID), Hangzhou, China, 10–11 December 2016; pp. 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Zhang, W.; Guo, J.; Gao, J.; Hu, Y. Design and kinematic simulation of a novel exoskeleton rehabilitation hand robot. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation (ICMA), Harbin, China, 7–10 August 2016; pp. 1125–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaura, H.; Matsushita, K.; Kato, R.; Yokoi, H. Development of hand rehabilitation system for paralysis patient—Universal design using wire-driven mechanism. In Proceedings of the 2009 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 3–6 September 2009; pp. 7122–7125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontana, M.; Dettori, A.; Salsedo, F.; Bergamasco, M. Mechanical design of a novel Hand Exoskeleton for accurate force displaying. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Kobe, Japan, 12–17 May 2009; pp. 1704–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, T.M.W.; Vaidyanathan, R.; Burgess, S.C.; Turton, A.J.; Melhuish, C. Development of a parametric kinematic model of the human hand and a novel robotic exoskeleton. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR), Zurich, Switzerland, 29 June–1 July 2011; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Yang, C.; Bi, Q.; Yang, W. A Grasp Strategy with Flexible Contacting for Multi-fingered Hand Rehabilitation Exoskeleton. In Wearable Sensors and Robots; Yang, C., Virk, G., Yang, H., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering; Springer: Singapore, 2017; Volume 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, P.; Deshpande, A.D. Impedance and force-field control of the index finger module of a hand exoskeleton for rehabilitation. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR), Singapore, 11–14 August 2015; pp. 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arata, J.; Ohmoto, K.; Gassert, R.; Lambercy, O.; Fujimoto, H.; Wada, I. A new hand exoskeleton device for rehabilitation using a three-layered sliding spring mechanism. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Karlsruhe, Germany, 6–10 May 2013; pp. 3902–3907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiboni, M.; Borboni, A.; Vérité, F.; Bregoli, C.; Amici, C. Sensors and Actuation Technologies in Exoskeletons: A Review. Sensors 2022, 22, 884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Zhang, F.; Yang, L.; Fu, Y. Design and Modeling of a Hybrid Soft-Rigid Hand Exoskeleton for Poststroke Rehabilitation. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2021, 209, 106831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achilli, G.M.; Logozzo, S.; Valigi, M.C.; Dragusanu, M.; Malvezzi, M. Theoretical and Experimental Characterization of a New Robotic gripper’s Joint. In Advances in Italian Mechanism Science; Niola, V., Gasparetto, A., Quaglia, G., Carbone, G., Eds.; Mechanisms and Machine Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; Volume 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Xu, G.; Xie, J.; Chen, C. A Soft Robotic Glove for Hand Rehabilitation Training Controlled by Movements of the Healthy Hand. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Ubiquitous Robots (UR), Kyoto, Japan, 24–27 June 2020; pp. 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serbest, K.; Eldoğan, O. Design, Development and Evaluation of a New Hand Exoskeleton for Stroke Rehabilitation at Home. Politeknik Derg. 2021, 24, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Cheng, L.; Sun, N. Design, manipulability analysis and optimization of an index finger exoskeleton for stroke rehabilitation. Mech. Mach. Theory 2022, 167, 104526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bützer, T.; Lambercy, O.; Arata, J.; Gassert, R. Fully wearable actuated soft exoskeleton for grasping assistance in everyday activities. Soft Robot. 2021, 8, 128–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vertongen, J.; Kamper, D. Design of a 3D printed hybrid mechanical structure for a hand exoskeleton. Curr. Dir. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 6, 20202003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Wen, L.; Xu, W.; Zhang, Y. A Three-Fingered Force Feedback Glove Using Fiber-Reinforced Soft Bending Actuators. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 67, 7681–7690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, C.; O’Malley, M. A Hybrid Rigid-Soft Hand Exoskeleton to Assist Functional Dexterity. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2018, 3, 516–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertas, I.H.; Hocaoglu, E.; Patoglu, V. AssistOn-Finger: An Under-Actuated Finger Exoskeleton for Robot-Assisted Tendon Therapy. Robotica 2014, 32, 1363–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Miao, X.; Li, X. Design of a Bidirectional Force Feedback Dataglove Based on Pneumatic Artificial Muscles. In Proceedings of the 2009 International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation, Changchun, China, 9–12 August 2009; pp. 1767–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wege, A.; Kondak, K.; Hommel, G. Development and Control of a Hand Exoskeleton for Rehabilitation. In Human Interaction with Machines; Hommel, G., Huanye, S., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Wang, P.; Wang, S.; Liu, H.; Zhang, F. Design and Development of a Portable Exoskeleton Based CPM Machine for Rehabilitation of Hand Injuries. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO), Sanya, China, 15–18 December 2008; pp. 1476–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubin, P.; Petersen, K.; Sallum, H.; Walsh, C.; Correia, A.; Stirling, L. A pediatric robotic thumb exoskeleton for at-home rehabilitation: The isolated orthosis for thumb actuation (IOTA). Int. J. Intell. Comput. Cybern. 2014, 7, 233–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.L.; Wang, F.; Osswald, C.; Kang, X.; Sarkar, N.; Kamper, D.G. Control and kinematic performance analysis of an Actuated Finger Exoskeleton for hand rehabilitation following stroke. In Proceedings of the 2010 3rd IEEE RAS & EMBS International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics (BioRob), Tokyo, Japan, 26–29 September 2010; pp. 282–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polotto, A.; Modulo, F.; Flumian, F.; Xiao, Z.G.; Boscariol, P.; Menon, C. Index finger rehabilitation/assistive device. In Proceedings of the 2012 4th IEEE RAS & EMBS International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics (BioRob), Rome, Italy, 24–27 June 2012; pp. 1518–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S. Design of an Exoskeleton for Index Finger Rehabilitation. In Proceedings of the 2009 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Minneapolis, MN, USA, 3–6 September 2009; pp. 5957–5960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, P.; Kuo, P.H.; Neptune, R.R.; Deshpande, A.D. A novel framework for virtual prototyping of rehabilitation exoskeletons. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE 13th International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR), Seattle, WA, USA, 24–26 June 2013; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, Q.; Reinkensmeyer, D.J. Design and Preliminary Evaluation of a Soft Finger Exoskeleton Controlled by Isometric Grip Force. Machines 2024, 12, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhafiz, M.H.; Andreasen Struijk, L.N.S.; Dosen, S.; Spaich, E.G. Biomimetic Tendon-Based Mechanism for Finger Flexion and Extension in a Soft Hand Exoskeleton: Design and Experimental Assessment. Sensors 2023, 23, 2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiboni, M.; Loda, D. Monolithic PneuNets Soft Actuators for Robotic Rehabilitation: Methodologies for Design, Production and Characterization. Actuators 2023, 12, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.; Li, G.; Cheng, L. Design and Validation of a Self-Aligning Index Finger Exoskeleton for Post-Stroke Rehabilitation. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2021, 29, 1513–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Zheng, R.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z. Development of a Hand Exoskeleton System for Index Finger Rehabilitation. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2012, 25, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, J.; Tsagarakis, N.G.; Caldwell, D.G. Design of a Wearable Direct-Driven Optimized Hand Exoskeleton Device. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advances in Computer-Human Interaction, Gosier, Guadeloupe, France, 23–28 February 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, A.; Qiu, J.; Wang, F.; Hou, L. An Adaptive and Jointless Hand Exoskeleton System Design. In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Control, Automation, Robotics and Vision (ICARCV), Singapore, 18–21 November 2018; pp. 579–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, M.B.; Kim, S.J.; Ihn, Y.S.; Jeong, G.C.; Kim, K. KULEX-Hand: An Underactuated Wearable Hand for Grasping Power Assistance. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2019, 35, 420–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, J.; Tsagarakis, N.G.; Caldwell, D.G. A human hand compatible optimised exoskeleton system. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics, Tianjin, China, 14–18 December 2010; pp. 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, P.; Fox, J.; Yun, Y.; O’Malley, M.K.; Deshpande, A.D. An Index Finger Exoskeleton with Series Elastic Actuation for Rehabilitation: Design, Control and Performance Characterization. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2015, 34, 1747–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Shastri, M.; Jones, C.L.; Kamper, D.G.; Sarkar, N. Design and Control of an Actuated Thumb Exoskeleton for Hand Rehabilitation Following Stroke. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Shanghai, China, 9–13 May 2011; pp. 3688–3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wege, A.; Hommel, G. Development and Control of a Hand Exoskeleton for Rehabilitation of Hand Injuries. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Edmonton, AB, Canada, 2–6 August 2005; pp. 3046–3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, G.; Gerding, E.C.; Corves, B.; Cafolla, D.; Russo, M.; Ceccarelli, M. Design of a Two-DOFs Driving Mechanism for a Motion-Assisted Finger Exoskeleton. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erden, M.S.; McColl, W.; Abassebay, D.; Haldane, S. Hand Exoskeleton to Assess Hand Spasticity. In Proceedings of the 8th IEEE RAS/EMBS International Conference for Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics (BioRob), New York, NY, USA, 29 November–1 December 2020; pp. 1004–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, Y.-K.; Wang, Y.-L.; Chang, H.-C.; Chen, C.-C. Design and Development of a Wearable Exoskeleton System for Stroke Rehabilitation. Healthcare 2020, 8, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orlando, M.F.; Akolkar, H.; Dutta, A.; Saxena, A.; Behera, L. Optimal Design and Control of a Hand Exoskeleton. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Conference on Robotics, Automation and Mechatronics (RAM), Singapore, 28–30 June 2010; pp. 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surakijboworn, M.; Wannasuphoprasit, W. Design of a Novel Finger Exoskeleton with a Sliding Six-Bar Joint Mechanism. In Proceedings of the 6th Augmented Human International Conference (AH’15), New York, NY, USA, 9 March 2015; pp. 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortoletto, R.; Mello, A.N.; Piovesan, D. A Springs Actuated Finger Exoskeleton: From Mechanical Design to Spring Variables Evaluation. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR), London, UK, 17 July 2017; pp. 1319–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabardi, M.; Solazzi, M.; Leonardis, D.; Frisoli, A. Design and Evaluation of a Novel 5 DoF Underactuated Thumb-Exoskeleton. IEEE Robotics Autom. Lett. 2018, 3, 2322–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, P.; Kim, J. Power-Assistive Finger Exoskeleton With a Palmar Opening at the Fingerpad. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2014, 61, 2688–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, H.K.; Cho, J.; Yeow, R.C.-H. Design and Characterization of Soft Actuator for Hand Rehabilitation Application. IFMBE Proc. 2014, 45, 367–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; Tang, J.; Guo, H.; Hong, J. Modeling and Design of a Soft Pneumatic Finger for Hand Rehabilitation. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Information and Automation (ICInfA), Lijiang, China, 8–10 August 2015; pp. 2460–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, J.; Zheng, R. Active and Passive Control Algorithm for an Exoskeleton with Bowden Cable Transmission for Hand Rehabilitation. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO), Tianjin, China, 14–18 December 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vithanage, I.; Wanasinghe, A.; Kavindya, P.; Kulasekera, A.; Chathuranga, D. A Novel Soft Glove for Hand Tremor Suppression: Evaluation of Layer Jamming Actuator Placement. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Soft Robotics (RoboSoft), New Haven, CT, USA, 15–19 May 2020; pp. 440–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, W.; Bian, Y.; Zhou, D.; Kristensson, P. Dexmo: An Inexpensive and Lightweight Mechanical Exoskeleton for Motion Capture and Force Feedback in VR. In Proceedings of the CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI), San Jose, CA, USA, 7–12 May 2016; pp. 1991–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortese, M.; Cempini, M.; Ribeiro, P.; Soekadar, S.; Carrozza, M.; Vitiello, N. A Mechatronic System for Robot-Mediated Hand Telerehabilitation. IEEE ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2015, 20, 1753–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cempini, M.; Cortese, M.; Vitiello, N. A Powered Finger–Thumb Wearable Hand Exoskeleton With Self-Aligning Joint Axes. IEEE ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2015, 20, 705–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri, H.; Rowe, J.B.; Gardner, D.; Chan, V.; Gray, K.; Bower, C.; Reinkensmeyer, D.J.; Wolbrecht, E.T. Design and preliminary evaluation of the FINGER rehabilitation robot: Controlling challenge and quantifying finger individuation during musical computer game play. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2014, 11, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zheng, R.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, J. iHandRehab: An interactive hand exoskeleton for active and passive rehabilitation. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR), Zurich, Switzerland, 29 June–1 July 2011; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, Y.; Tokita, J.; Kamibayashi, K.; Sankai, Y. Evaluation of fingertip force accuracy in different support conditions of exoskeleton. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Shanghai, China, 9–13 May 2011; pp. 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, P.; Machado, J.; Vaida, C.; Pisla, D.; Miranda, D.; Martins, N.; Carvalho, V.; Matos, D. Design of Wearable Prostheses: A New Approach. In Advances in Service and Industrial Robotics; Pisla, D., Carbone, G., Condurache, D., Vaida, C., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; Volume 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiralerspong, T.; Heung, H.; Tong, R.K.Y.; Li, Z. A Novel Soft Robotic Glove for Daily Life Assistance. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics (BioRob), Enschede, The Netherlands, 26–29 August 2018; pp. 671–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mckinney, Z.; Marconi, D.; Baldoni, A.; Cempini, M.; Crea, S.; Vitiello, N. A Novel Hand Exoskeleton with Series Elastic Actuation for Modulated Torque Transfer. Mechatronics 2019, 61, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, G.A.; Williamson, M.M. Series Elastic Actuators. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 5–9 August 1995; pp. 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, J.; Khan, H.; Tsagarakis, N.G.; Caldwell, D.G. A Novel Exoskeleton Robotic System for Hand Rehabilitation—Conceptualization to Prototyping. Biocybern. Biomed. Eng. 2014, 34, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Desplenter, T.; Chinchalkar, S.; Trejos, A.L. A Wearable Mechatronic Glove for Resistive Hand Therapy Exercises. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 16th International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR), Toronto, ON, Canada, 24–28 June 2019; pp. 1097–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haarman, C.J.W.; Hekman, E.E.G.; Rietman, J.S.; Van Der Kooij, H. Mechanical Design and Feasibility of a Finger Exoskeleton to Support Finger Extension of Severely Affected Stroke Patients. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2023, 31, 1268–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, R.; Li, J. Kinematics and Workspace Analysis of an Exoskeleton for Thumb and Index Finger Rehabilitation. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO), Tianjin, China, 14–18 December 2010; pp. 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, J.; Tsagarakis, N.; Fiorilla, A.; Caldwell, D. A Portable Rehabilitation Device for the Hand. In Proceedings of the 2010 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Buenos Aires, Argentina, 31 August–4 September 2010; pp. 3694–3697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.L.; Huang, J.J.; Pu, S.W.; Chen, H.P.; Hsu, S.C.; Chang, J.Y.; Pei, Y.C. Usability Assessment of a Cable-Driven Exoskeletal Robot for Hand Rehabilitation. Front. Neurorobot. 2019, 13, e00003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Lee, J.; Park, W.; Bae, J. Quantitative evaluation of hand functions using a wearable hand exoskeleton system. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR), London, UK, 17–20 July 2017; pp. 1488–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- In, H.; Lee, D.; Cho, K.-J. Investigation of friction characteristics of a tendon-driven wearable robotic hand. In Proceedings of the ICCAS 2010, Gyeonggi-do, Republic of Korea, 27–30 October 2010; pp. 568–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Wu, Q.; Zhu, Y. Development of a soft cable-driven hand exoskeleton for assisted rehabilitation training. Ind. Robot 2021, 48, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- In, H.; Cho, K.-J.; Kim, K.; Lee, B. Jointless structure and under-actuation mechanism for compact hand exoskeleton. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics, Zurich, Switzerland, 29 June–1 July 2011; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, B.B.; Lee, H.; In, H.; Jeong, U.; Chung, J.; Cho, K.-J. Development of a polymer-based tendon-driven wearable robotic hand. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Stockholm, Sweden, 16–21 May 2016; pp. 3750–3755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radder, B.; Prange, G.; Kottink, A.; Holmberg, J.; Sletta, K.; Dijk, M.; Meyer, T.; Melendez-Calderon, A.; Buurke, J.; Rietman, J. Home Rehabilitation Supported by a Wearable Soft-Robotic Device for Improving Hand Function in Older Adults: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0220544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Q.; Shen, Z.; Nie, Z.; Meng, Q.; Wu, Z.; Yu, H. Modeling and Evaluation of a Novel Hybrid-Driven Compliant Hand Exoskeleton Based on Human-Machine Coupling Model. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osuagwu, B.; Timms, S.; Peachment, R.; Dowie, S.; Thrussell, H.; Cross, S.; Shirley, R.; Segura-Fragoso, A.; Taylor, J. Home-Based Rehabilitation Using a Soft Robotic Hand Glove Device Leads to Improvement in Hand Function in People with Chronic Spinal Cord Injury: A Pilot Study. J. NeuroEng. Rehabil. 2020, 17, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, L.; Olaloye, O.; Talarico, M.; Shah, S.; Arends, R.; BuSha, B. A Power-Assisted Exoskeleton Optimized for Pinching and Grasping Motions. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE 36th Annual Northeast Bioengineering Conference (NEBEC), New York, NY, USA, 26–28 March 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierotowicz, M.; Lotti, N.; Nell, L.; Missiroli, F.; Alicea, R.; Zhang, X.; Xiloyannis, M.; Rupp, R.; Papp, E.; Krzywinski, J.; et al. EMG-Driven Machine Learning Control of a Soft Glove for Grasping Assistance and Rehabilitation. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2022, 7, 1566–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, B.; Choi, H.; Lee, H.; Cho, K.-J. Exo-Glove Poly II: A Polymer-Based Soft Wearable Robot for the Hand with a Tendon-Driven Actuation System. Soft Robot. 2018, 6, 214–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, U.; In, H.-K.; Cho, K.-J. Implementation of Various Control Algorithms for Hand Rehabilitation Exercise Using Wearable Robotic Hand. Intell. Serv. Robot. 2013, 6, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radder, B.; Prange, G.; Kottink, A.; Gaasbeek, L.; Holmberg, J.; Meyer, T.; Melendez-Calderon, A.; Ingvast, J.; Buurke, J.; Rietman, J. A Wearable Soft-Robotic Glove Enables Hand Support in ADL and Rehabilitation: A Feasibility Study on the Assistive Functionality. J. Rehabil. Assist. Technol. Eng. 2016, 3, 2055668316670553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biggar, S.; Yao, W. Design and Evaluation of a Soft and Wearable Robotic Glove for Hand Rehabilitation. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2016, 24, 1071–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiloyannis, M.; Cappello, L.; Khanh, D.B.; Yen, S.-C.; Masia, L. Modelling and Design of a Synergy-Based Actuator for a Tendon-Driven Soft Robotic Glove. In Proceedings of the 2016 6th IEEE International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics (BioRob), Singapore, 26–29 June 2016; pp. 1213–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouzit, M.; Burdea, G.; Popescu, G.; Boian, R. The Rutgers Master II-new design force-feedback glove. IEEE-ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2002, 7, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allotta, B.; Conti, R.; Governi, L.; Meli, E.; Ridolfi, A.; Volpe, Y. Development and experimental testing of a portable hand exoskeleton. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Hamburg, Germany, 28 September–2 October 2015; pp. 5339–5344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, D.; Gaponov, I.; Ryu, J.H. Portable Exoskeleton Glove With Soft Structure for Hand Assistance in Activities of Daily Living. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2016, 22, 865–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.W.; Landers, K.A.; Park, H.S. Biomimetic hand exotendon device (BiomHED) for functional hand rehabilitation in stroke. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE 13th International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR), Seattle, WA, USA, 24–26 June 2013; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Guo, Z.; Tang, W. Design of wearable hand rehabilitation glove with soft hoop-reinforced pneumatic actuator. J. Cent. South Univ. 2019, 26, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setiawan, J.D.; Ariyanto, M.; Nugroho, S.; Munadi, M.; Ismail, R. A soft exoskeleton glove incorporating motor-tendon actuator for hand movements assistance. IREACO 2023, 13, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, Z.; Wen, Y. A Soft Exoskeleton Glove for Hand Bilateral Training via Surface EMG. Sensors 2021, 21, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birouaș, F.I.; Țarcă, R.C.; Dzitac, S.; Dzitac, I. Preliminary Results in Testing of a Novel Asymmetric Underactuated Robotic Hand Exoskeleton for Motor Impairment Rehabilitation. Symmetry 2020, 12, 1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Li, J.Z.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, L.Q.; Ding, L.; Zhang, X.; Lan, Y.; Kamper, D.G. User-Driven Functional Movement Training With a Wearable Hand Robot After Stroke. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2020, 28, 2265–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Götzelmann, T. A 3D Printable Hand Exoskeleton for the Haptic Exploration of Virtual 3D Scenes. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on PErvasive Technologies Related to Assistive Environments (PETRA), Island of Rhodes, Greece, 21–23 June 2017; pp. 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, S.W.; Tsai, S.Y.; Chang, J.Y. Design and Development of the Wearable Hand Exoskeleton System for Rehabilitation of Hand Impaired Patients. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Automation Science and Engineering (CASE), Taipei, Taiwan, 18–22 August 2014; pp. 996–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polygerinos, P.; Lyne, S.; Wang, Z.; Nicolini, L.; Mosadegh, B.; Whitesides, G.; Walsh, C. Towards a Soft Pneumatic Glove for Hand Rehabilitation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Tokyo, Japan, 3–7 November 2013; pp. 1512–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, M.; Cempini, M.; Conti, R.; Meli, E.; Ridolfi, A.; Vitiello, N.; Allotta, B. Design of a Series Elastic Transmission for Hand Exoskeletons. Mechatronics 2018, 51, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, A.; Malkin, R. HANDLINK: A Dexterous Robotic Hand Exoskeleton Controlled by Motor Imagery (MI). J. Adv. Med. Med. Res. 2022, 34, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Fahaam, H.; Davis, S.; Nefti-Meziani, S.; Theodoridis, T. Novel Soft Bending Actuator-Based Power Augmentation Hand Exoskeleton Controlled by Human Intention. Intell. Serv. Robot. 2018, 11, 247–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wege, A.; Kondak, K.; Hommel, G. Force Control Strategy for a Hand Exoskeleton Based on Sliding Mode Position Control. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Beijing, China, 9–15 October 2006; pp. 4615–4620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Fahaam, H. Power Assistive and Rehabilitation Wearable Robot Based on Pneumatic Soft Actuators. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Methods and Models in Automation and Robotics (MMAR), Miedzyzdroje, Poland, 29 August–1 September 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhao, L.; Yu, P.; Yang, T.; Li, N.; Yang, Y.; Liu, L. A Wearable Bionic Soft Exoskeleton Glove for Stroke Patients. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Cyber Technology in Automation, Control, and Intelligent Systems (CYBER), Tianjin, China, 19–23 July 2018; pp. 932–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, R.; Meli, E.; Ridolfi, A.; Bianchi, M.; Governi, L.; Volpe, Y.; Allotta, B. Kinematic Synthesis and Testing of a New Portable Hand Exoskeleton. Meccanica 2017, 52, 2873–2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, B.; Choi, Y. Soft Pneumatic Glove for Grasping Power Improvement. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Ubiquitous Robots and Ambient Intelligence (URAI), Jeju, Republic of Korea, 28 June–1 July 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, R.K.Y.; Ho, S.K.; Pang, P.; Hu, X.; Tam, W.K.; Fung, K.; Wei, X.J.; Chen, P.; Chen, M. An Intention Driven Hand Functions Task Training Robotic System. In Proceedings of the 32nd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Buenos Aires, Argentina, 31 August–4 September 2010; pp. 3406–3409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, P.; Heyer, L.; Munte, T.F.; Heldmann, M.; Schweikard, A.; Maehle, E. Towards a parameterizable exoskeleton for training of hand function after stroke. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR), Seattle, WA, USA, 24–26 June 2013; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roccella, S.; Cattin, E.; Vitiello, N.; Giovacchini, F.; Chiri, A.; Vecchi, F.; Carrozza, M.C. Design of a Hand Exoskeleton (Handexos) for the Rehabilitation of the Hand. Gerontechnology 2008, 7, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonardis, D.; Barsotti, M.; Loconsole, C.; Solazzi, M.; Troncossi, M.; Mazzotti, C.; Parenti Castelli, V.; Procopio, C.; Lamola, G.; Chisari, C.; et al. An EMG-Controlled Robotic Hand Exoskeleton for Bilateral Rehabilitation. IEEE Trans. Haptics 2015, 8, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Meng, Q.; Meng, Q.; Li, X.; Yu, H. Design and Development of a Portable Exoskeleton for Hand Rehabilitation. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2018, 26, 2376–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secciani, N.; Brogi, C.; Pagliai, M.; Buonamici, F.; Gerli, F.; Vannetti, F.; Bianchini, M.; Volpe, Y.; Ridolfi, A. Wearable Robots: An Original Mechatronic Design of a Hand Exoskeleton for Assistive and Rehabilitative Purposes. Front. Neurorobot. 2021, 15, 750385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borboni, A.; Mor, M.; Faglia, R. Gloreha—Hand Robotic Rehabilitation: Design, Mechanical Model, and Experiments. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 2016, 138, 111003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, H.C.; Triandafilou, K.M.; Thielbar, K.O.; Ochoa, J.M.; Lazzaro, E.D.C.; Pacholski, K.A.; Kamper, D.G. Use of a Portable Assistive Glove to Facilitate Rehabilitation in Stroke Survivors With Severe Hand Impairment. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2016, 24, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- du Plessis, T.; Djouani, K.; Oosthuizen, C. A Review of Active Hand Exoskeletons for Rehabilitation and Assistance. Robotics 2021, 10, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.Y.; Patterson, R.M. Soft Robotic Devices for Hand Rehabilitation and Assistance: A Narrative Review. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2018, 15, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Cheng, Y.; Zheng, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, C. Design and Optimization of Actuator for Multi-Joint Soft Rehabilitation Glove. Ind. Robot 2021, 48, 877–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, D.Y.L.; Lai, H.S.; Yeow, R.C.H. A Bidirectional Fabric-Based Soft Robotic Glove for Hand Function Assistance in Patients with Chronic Stroke. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2023, 20, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souhail, A.; Vessakosol, P. Low Cost Soft Robotic Gloves for At-Home Rehabilitation and Daily Living Activities. J. Autom. Mobile Robot. Intell. Syst. 2019, 13, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Chen, D.; Que, J.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Xu, Y. Soft Robotic Glove for Hand Rehabilitation Based on a Novel Fabrication Method. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO), Macau, China, 5–8 December 2017; pp. 817–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Fei, Y.; Pang, W. Design, Modeling, and Testing of a Soft Pneumatic Glove With Segmented PneuNets Bending Actuators. IEEE ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2019, 24, 990–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radder, B.; Prange, G.; Kottink, A.; Melendez-Calderon, A.; Buurke, J.; Rietman, J. Feasibility of a Wearable Soft-Robotic Glove to Support Impaired Hand Function in Stroke Patients. J. Rehabil. Med. 2018, 50, 598–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, M.; Vinjamuri, R. Design of a Soft Glove-Based Robotic Hand Exoskeleton with Embedded Synergies. In Advances in Motor Neuroprostheses; Vinjamuri, R., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 71–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.-S.; Kang, B.; Cho, K.-J. Exo-Glove PM: An Easily Customizable Modularized Pneumatic Assistive Glove. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2017, 2, 1725–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Xu, F.; Song, Y.; Cao, X.; Meng, F. A Soft Robotic Glove for Hand Rehabilitation Using Pneumatic Actuators with Variable Stiffness. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Intelligent Robotics and Applications (ICIRA), Shenyang, China, 2 August 2019; pp. 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.M.; Wagner, D.; Nuckols, R.; Heimgartner, R.; Correia, C.; Clarke, M.; Orzel, D.; O’Neill, C.; Solinsky, R.; Paganoni, S.; et al. Soft Robotic Glove with Integrated Sensing for Intuitive Grasping Assistance Post Spinal Cord Injury. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 May 2019; pp. 9059–9065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, S.-W.; Chang, J.-Y. Robotic Hand System Design for Mirror Therapy Rehabilitation After Stroke. Microsyst. Technol. 2020, 26, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernocchi, P.; Mulè, C.; Vanoglio, F.; Taveggia, G.; Luisa, A.; Scalvini, S. Home-Based Hand Rehabilitation with a Robotic Glove in Hemiplegic Patients After Stroke: A Pilot Feasibility Study. Top. Stroke Rehabil. 2017, 25, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seçkin, M.; Yaman Turan, N. Rehabilitation Glove Device Design. J. Eng. Technol. Appl. Sci. 2018, 3, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandolla, M.; Ferrante, S.; Baldassini, D.; Cottini, M.; Seneci, C.; Molteni, F.; Guanziroli, E.; Pedrocchi, A. EMG-Controlled Robotic Hand Rehabilitation Device for Domestic Training. In Proceedings of the XIV Mediterranean Conference on Medical and Biological Engineering and Computing, Paphos, Cyprus, 31 March–2 April 2016; pp. 644–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Tzvi, P.; Danoff, J.; Ma, Z. The Design Evolution of a Sensing and Force-Feedback Exoskeleton Robotic Glove for Hand Rehabilitation Application. J. Mech. Robot. 2016, 8, 051019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randazzo, L.; Iturrate, I.; Perdikis, S.; Millán, J.R. mano: A Wearable Hand Exoskeleton for Activities of Daily Living and Neurorehabilitation. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2018, 3, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, I.; Lee, J.; Park, Y.; Bae, J. Design of a wearable hand exoskeleton for exercising flexion/extension of the fingers. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR), London, UK, 17–20 July 2017; pp. 1615–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, Y.; Mikami, Y.; Watanabe, K.; Sankai, Y. Five-fingered assistive hand with mechanical compliance of human finger. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Pasadena, CA, USA, 19–23 May 2008; pp. 718–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulas, M.; Folgheraiter, M.; Gini, G. An EMG-controlled exoskeleton for hand rehabilitation. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR), Chicago, IL, USA, 28 June–1 July 2005; pp. 371–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brokaw, E.B.; Black, I.; Holley, R.J.; Lum, P.S. Hand Spring Operated Movement Enhancer (HandSOME): A portable, passive hand exoskeleton for stroke rehabilitation. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2011, 19, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasser, B.W.; Bennett, D.A.; Durrough, C.M.; Goldfarb, M. Design and preliminary assessment of Vanderbilt hand exoskeleton. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR), London, UK, 17–20 July 2017; pp. 1537–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Cheng, L. Preliminary study on the design and control of a pneumatically-actuated hand rehabilitation device. In Proceedings of the IEEE Youth Academic Annual Conference (YAC), Hefei, China, 19–21 May 2017; pp. 860–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refour, E.M.; Sebastian, B.; Chauhan, R.J.; Ben-Tzvi, P. A General Purpose Robotic Hand Exoskeleton With Series Elastic Actuation. J. Mech. Robot. 2019, 11, 060902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.W.; Landers, K.A.; Park, H.-S. Development of a biomimetic hand exotendon device (BiomHED) for restoration of functional hand movement post-stroke. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2014, 22, 886–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coffey, A.; Leamy, D.; Ward, T. A Novel BCI-Controlled Pneumatic Glove System for Home-Based Neurorehabilitation. In Proceedings of the 2014 36th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Chicago, IL, USA, 26–30 August 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Xie, H.-L.; Shi, J. A Novel Motion-Coupling Design for a Jointless Tendon-Driven Finger Exoskeleton for Rehabilitation. Mech. Mach. Theory 2016, 99, 83–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kline, T.; Kamper, D.; Schmit, B. Control System for Pneumatically Controlled Glove to Assist in Grasp Activities. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE 9th International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR), Chicago, IL, USA, 28 June–1 July 2005; pp. 78–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochoa, J.; Narasimhan, Y.; Kamper, D. Development of a Portable Actuated Orthotic Glove to Facilitate Gross Extension of the Digits for Therapeutic Training after Stroke. In Proceedings of the 2009 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Minneapolis, MN, USA, 3–6 September 2009; pp. 6918–6921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foumashi, M.; Troncossi, M.; Parenti Castelli, V. Design of a New Hand Exoskeleton for Rehabilitation of Post-Stroke Patients. In Proceedings of the Romansy 19-Robot Design, Dynamics and Control, Udine, Italy, 2013; pp. 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Kline, T.; Fischer, H.; Stubblefield, K.; Kenyon, R.; Kamper, D. Integration of Augmented Reality and Assistive Devices for Post-Stroke Hand Opening Rehabilitation. In Proceedings of the 2005 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Shanghai, China, 1–4 September 2005; pp. 6855–6858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troncossi, M.; Mozaffari, M.; Mazzotti, C.; Zannoli, D.; Parenti Castelli, V. Design and Manufacturing of a Hand-and-Wrist Exoskeleton Prototype for the Rehabilitation of Post-Stroke Patients. In Quaderni del DIEM–GMA. Atti della Sesta Giornata di Studio Ettore Funaioli; Asterisco: Rome, Italy, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Gerez, L.; Dwivedi, A.; Liarokapis, M. A hybrid, soft exoskeleton glove equipped with a telescopic extra thumb and abduction capabilities. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Paris, France, 31 May–31 August 2020; pp. 9100–9106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappello, L.; Meyer, J.T.; Galloway, K.C.; Peisner, A.; Granberry, R.; Wagner, D.A.; Walsh, C.J. Assisting Hand Function After Spinal Cord Injury with a Fabric-Based Soft Robotic Glove. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2018, 15, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, P.H.; Lee, S.H.; Gu, G.M.; Lee, S.H.; Jin, S.H.; Yeo, S.S.; Seo, J.P.; Jang, S.H. The cortical activation pattern by a rehabilitation robotic hand: A functional NIRS study. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wege, A.; Zimmermann, A. Electromyography Sensor-Based Control for a Hand Exoskeleton. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics, Sanya, China, 15–18 December 2007; pp. 1470–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, L.; Chen, F.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Han, D.; Wang, T.; Gu, G. Design, Modeling, and Evaluation of Fabric-Based Pneumatic Actuators for Soft Wearable Assistive Gloves. Soft Robot. 2020, 7, 583–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, I.; Bae, J. A Force-Controllable Compact Actuator Module for a Wearable Hand Exoskeleton. IFAC Proc. Vol. 2014, 47, 4453–4458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delph, M.A.; Fischer, S.A.; Gauthier, P.W.; Luna, C.H.M.; Clancy, E.A.; Fischer, G.S. A soft robotic exomusculature glove with integrated sEMG sensing for hand rehabilitation. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE 13th International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR), Seattle, WA, USA, 24–26 June 2013; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Chen, M.; Li, Z. Design and Control of a Wearable Hand Rehabilitation Robot. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 41884–41896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiri, A.; Vitiello, N.; Giovacchini, F.; Roccella, S.; Vecchi, F.; Carrozza, M.C. Mechatronic Design and Characterization of the Index Finger Module of a Hand Exoskeleton for Post-Stroke Rehabilitation. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2012, 17, 884–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, M.; Lim, J.; Yeow, R.C.-H. Design and Characterization of a Soft Robotic Therapeutic Glove for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Assist. Technol. 2017, 31, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trott, R.; Kleinig, T.; Hillier, S.; Hobbs, D.; Reynolds, K. A Modular Hybrid Exoskeletal-Soft Glove for High Degree of Freedom Monitoring Capability. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR), Toronto, ON, Canada, 24–28 June 2019; pp. 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Bae, J. Design of a hand exoskeleton for biomechanical analysis of the stroke hand. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR), Singapore, 11–14 August 2015; pp. 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Phan, A.; Allison, G. Design and fabrication of a three dimensional printable non-assembly articulated hand exoskeleton for rehabilitation. In Proceedings of the 37th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Milan, Italy, 25–29 August 2015; pp. 4627–4630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, P.W.; Dimapasoc, B.; Shen, Y.; Rosen, J. Design of a Hand Exoskeleton for Use with Upper Limb Exoskeletons. In Wearable Robotics: Challenges and Trends; Carrozza, M., Micera, S., Pons, J., Eds.; Biosystems & Biorobotics; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeder-York, P.; Clites, T.; Boggs, E.; Neff, R.; Polygerinos, P.; Holland, D.; Stirling, L.; Galloway, K.; Wee, C.; Walsh, C. Biologically Inspired Soft Robot for Thumb Rehabilitation. J. Med. Devices 2014, 8, 020933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorilla, A.E.; Tsagarakis, N.G.; Nori, F.; Sandini, G. Design of a 2-finger hand exoskeleton for finger stiffness measurements. Appl. Bion. Biomech. 2009, 6, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decker, M.; Kim, Y. A hand exoskeleton device for robot assisted sensory-motor training after stroke. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE World Haptics Conference (WHC), Munich, Germany, 6–9 June 2017; pp. 436–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polygerinos, P.; Wang, Z.; Galloway, K.C.; Wood, R.J.; Walsh, C.J. Soft Robotic Glove for Combined Assistance and at-Home Rehabilitation. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2015, 73, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, F.; Ikai, G.; Fukui, W.; Nakamoto, H.; Kojima, F. Multipoint haptic device for robot hand teleoperation. In Proceedings of the 2012 International Symposium on Micro-NanoMechatronics and Human Science (MHS), Nagoya, Japan, 4–7 November 2012; pp. 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, K.; Kobayashi, F.; Nakamoto, H.; Kojima, F. Development of haptic device for five-fingered robot hand teleoperation. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE/SICE International Symposium on System Integration (SII), Kobe, Japan, 15–17 December 2013; pp. 820–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triolo, E.; BuSha, B. Design and Experimental Testing of a Force-Augmenting Exoskeleton for the Human Hand. J. NeuroEngineering Rehabil. 2022, 19, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.L.; Tong, K.Y.; Wei, X.J.; Rong, W.; Susanto, E.A.; Ho, S.K. The effects of post-stroke upper-limb training with an electromyography (EMG)-driven hand robot. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2013, 23, 1065–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojek, I.; Kaczmarek, M.; Kotlarz, P.; Kempiński, M.; Mikołajewski, D.; Szczepański, Z.; Kopowski, J.; Nowak, J.; Macko, M.; Szczepańczyk, A.; et al. Hand Exoskeleton—Development of Own Concept. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 3238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, G.; Abdullah, H.A. Development and Testing of a Soft Exoskeleton Robotic Hand Training Device. Sensors 2023, 23, 8395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, N.; Furuya, S.; Koike, H. Soft Exoskeleton Glove with Human Anatomical Architecture: Production of Dexterous Finger Movements and Skillful Piano Performance. IEEE Trans. Haptics 2020, 13, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, S.K.; Tong, R.K.Y.; Hu, X.; Fung, K.; Wei, X.J.; Rong, W.; Susanto, E. An EMG-driven Exoskeleton Hand Robotic Training Device on Chronic Stroke Subjects: Task Training System for Stroke Rehabilitation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR), Zurich, Switzerland, 29 June–1 July 2011; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertani, R.; Melegari, C.; De Cola, M.C.; Bramanti, P.; Bramanti, A.; Calvo, A. Effects of Robot-Assisted Upper Limb Rehabilitation in Stroke Patients: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Neurol. Sci. 2017, 38, 1561–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Hua, L.; Fu, Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, S. Design and Development of a Hand Exoskeleton for Rehabilitation of Hand Injuries. Mech. Mach. Theory 2014, 73, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazari, V.; Pouladian, M.; Zheng, Y.-P.; Alam, M. A Compact and Lightweight Rehabilitative Exoskeleton to Restore Grasping Functions for People with Hand Paralysis. Sensors 2021, 21, 6900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, F.; Gan, Z. Design and Development of a Hand Rehabilitation Robot for Patient-Cooperative Therapy Following Stroke. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation (ICMA), Beijing, China, 7–10 August 2011; pp. 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Ben-Tzvi, P.; Danoff, J. Hand Rehabilitation Learning System with an Exoskeleton Robotic Glove. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2016, 24, 1323–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval-Gonzalez, O.; Jacinto-Villegas, J.; Herrera-Aguilar, I.; Portilla-Flores, E.A.; Tripicchio, P.; Hernandez-Ramos, M.; Flores-Cuautle, A.; Avila-Vilchis, J.C. Design and Development of a Hand Exoskeleton Robot for Active and Passive Rehabilitation. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2016, 13, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triwiyanto, T.; Luthfiyah, S.; Pawana, P.; Ahmed, A.A.; Andrian, A. Bilateral Mode Exoskeleton for Hand Rehabilitation with Wireless Control Using 3D Printing Technology Based on IMU Sensor. HardwareX 2023, 14, e00432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, I.B.; Bouteraa, Y.; Rekik, C. Design and Development of 3D Printed Myoelectric Robotic Exoskeleton for Hand Rehabilitation. Int. J. Smart Sens. Intell. Syst. 2017, 10, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceccarelli, M.; Morales-Cruz, C. A Prototype Characterization of ExoFinger, a Finger Exoskeleton. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2021, 18, 172988142110248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, R.; Meli, E.; Ridolfi, A. A Novel Kinematic Architecture for Portable Hand Exoskeletons. Mechatronics 2016, 35, 192–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.L.; Wang, F.; Morrison, R.; Sarkar, N.; Kamper, D.G. Design and Development of the Cable Actuated Finger Exoskeleton for Hand Rehabilitation Following Stroke. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2014, 19, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, T.; Assad-Uz-Zaman, M.; Islam, M.R.; Gottheardt, D.; McGonigle, E.; Brahmi, B.; Rahman, M.H. Flexohand: A Hybrid Exoskeleton-Based Novel Hand Rehabilitation Device. Micromachines 2021, 12, 1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, D.; Georgilas, I.; Dagnino, G.; Dogramadzi, S. Powered Exoskeleton with Palm Degrees of Freedom for Hand Rehabilitation. In Proceedings of the 2015 37th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Milan, Italy, 25–29 August 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahit, M.A.A.; Ahmad, S.A. Design and Development of Low-Cost Exoskeleton Hand Robot Structure. In Proceedings of the IEEE 15th Student Conference on Research and Development (SCOReD), Putrajaya, Malaysia, 13–14 December 2017; pp. 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghshenas-Jaryani, M.; Nothnagle, C.; Patterson, R.M.; Bugnariu, N.; Wijesundara, M.B.J. Soft Robotic Rehabilitation Exoskeleton (REHAB Glove) for Hand Therapy. In Proceedings of the ASME International Design Engineering Technical Conferences and Computers and Information in Engineering Conference (IDETC-CIE), Cleveland, OH, USA, 6–9 August 2017. Paper No. DETC2017-68291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumphoo, T.; Uthansakul, M.; Duangmanee, P.; Khan, N.; Uthansakul, P. Soft Robotic Glove Controlling Using Brainwave Detection for Continuous Rehabilitation at Home. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2021, 66, 961–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerges, F.; Desai, J.; Watkins, J.M.; Burugupally, S.P. Master-Slave Control for a Pneumatically Actuated Low Pressure Soft Robotic Glove to Facilitate Bilateral Training for Stroke Patients. In Proceedings of the 23rd International Symposium on Measurement and Control in Robotics (ISMCR), Budapest, Hungary, 22–24 October 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Y.; Li, Q.; Li, D.; Hong, J. A Novel Soft Robotic Glove with Positive-Negative Pneumatic Actuator for Hand Rehabilitation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics (AIM), Boston, MA, USA, 6–9 July 2020; pp. 1840–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, N.; Sun, Z.; Wang, X.; Yeung, E.; To, M.; Li, X.; Hu, Y. Simulation Analysis for Optimal Design of Pneumatic Bellow Actuators for Soft-Robotic Glove. Biocybern. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 40, 1507–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, M.; Yang, D.; Gu, G. High-Force Fabric-Based Pneumatic Actuators with Asymmetric Chambers and Interference-Reinforced Structure for Soft Wearable Assistive Gloves. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2021, 6, 3105–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noritsugu, T.; Takaiwa, M.; Sasaki, D. Development of Power Assist Wear Using Pneumatic Rubber Artificial Muscles. J. Robot. Mechatron. 2009, 21, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjahyono, A.P.; Aw, K.C.; Devaraj, H.; Surendra, W.; Haemmerle, E.; Travas-Sejdic, J. A Five-Fingered Hand Exoskeleton Driven by Pneumatic Artificial Muscles with Novel Polypyrrole Sensors. Ind. Robot 2013, 40, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadi, A.; Alipour, K.; Kazeminasab, S.; Elahinia, M. ASR Glove: A Wearable Glove for Hand Assistance and Rehabilitation Using Shape Memory Alloys. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2018, 29, 1575–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.; Zhang, D.; Tao, X.; Zhu, X. An Exoskeleton System for Hand Rehabilitation Driven by Shape Memory Alloy. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO), Shenzhen, China, 12–14 December 2013; pp. 756–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitney, J.P.; Glisson, M.F.; Brockmeyer, E.L.; Hodgins, J.K. A Low-Friction Passive Fluid Transmission and Fluid-Tendon Soft Actuator. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Chicago, IL, USA, 14–18 September 2014; pp. 2801–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.; Al-Jumaily, A. Design and Development of a Bilateral Therapeutic Hand Device for Stroke Rehabilitation. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2013, 10, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Lum, P.S. Hand Rehabilitation After Stroke Using a Wearable, High DOF, Spring Powered Exoskeleton. In Proceedings of the 2016 38th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Orlando, FL, USA, 16–20 August 2016; pp. 578–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casas, R.; Sandison, M.; Chen, T.; Lum, P.S. Clinical Test of a Wearable, High DOF, Spring Powered Hand Exoskeleton (HandSOME II). IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2021, 29, 1877–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yap, H.K.; Ang, B.W.K.; Lim, J.H.; Goh, J.C.H.; Yeow, C.-H. A Fabric-Regulated Soft Robotic Glove with User Intent Detection Using EMG and RFID for Hand Assistive Application. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Stockholm, Sweden, 16–21 May 2016; pp. 3537–3542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Xiong, C.; Huang, Y.; Chen, W.; Chen, W. Design of a Compact Finger-Integrated Mechanism with Robust Kinematics for Hand Exoskeleton. In Intelligent Robotics and Applications; Liu, H., Kubota, N., Zhu, X., Dillmann, R., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 9246, pp. 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, S.-W.; Chang, J.-Y.; Pei, Y.-C.; Kuo, C.-C.; Wang, M.-J. Anthropometry-Based Structural Design of a Hand Exoskeleton for Rehabilitation. In Proceedings of the 2016 23rd International Conference on Mechatronics and Machine Vision in Practice (M2VIP), Nanjing, China, 28–30 November 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Festo, ‘‘ExoHand Festo,” 2022. Available online: https://www.festo.com/PDF_Flip/corp/Festo_ExoHand/en/index.html (accessed on 12 November 2024).
- Ueki, S.; Kawasaki, H.; Ito, S.; Nishimoto, Y.; Abe, M.; Aoki, T.; Ishigure, Y.; Ojika, T.; Mouri, T. Development of a Hand-Assist Robot With Multi-Degrees-of-Freedom for Rehabilitation Therapy. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2012, 17, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schabowsky, C.; Godfrey, S.; Holley, R.; Lum, P. Development and pilot testing of HEXORR: Hand EXOskeleton Rehabilitation Robot. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2010, 7, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Legeng, L.; Yang, L.; Fu, Y. Design of an Active and Passive Control System of Hand Exoskeleton for Rehabilitation. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuswanto, D.; Iskandriawan, B.; Mahardhika, P. Power Grip Exoskeleton Design as Rehabilitation Devices for Post-Stroke Survivors. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics (BIOMIC), Bali, Indonesia, 26–29 August 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragusanu, M.; Iqbal, M.Z.; Lisini, T.; Prattichizzo, D.; Malvezzi, M. Design, Development, and Control of a Hand/Wrist Exoskeleton for Rehabilitation and Training. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2022, 38, 1472–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Cruz Sánchez, B.; Arias-Montiel, M.; Lugo, E. EMG-Controlled Hand Exoskeleton for Assisted Bilateral Rehabilitation. Biocybern. Biomed. Eng. 2022, 42, 596–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, H.K.; Kamaldin, N.; Lim, J.; Nasrallah, F.; Cho, J.; Yeow, R.C.-H. A Magnetic Resonance Compatible Soft Wearable Robotic Glove for Hand Rehabilitation and Brain Imaging. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2016, 25, 782–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heung, H.; Tong, R.K.-Y.; Lau, A.; Li, Z. Robotic Glove with Soft-Elastic Composite Actuators for Assisting Activities of Daily Living. Soft Robot. 2019, 6, 289–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, B.; Yeow, R.C.-H. Print-it-Yourself (PIY) Glove: A Fully 3D Printed Soft Robotic Hand Rehabilitative and Assistive Exoskeleton for Stroke Patients. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–28 September 2017; pp. 1219–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghshenas-Jaryani, M.; Carrigan, W.; Nothnagle, C.; Wijesundara, M. Sensorized Soft Robotic Glove for Continuous Passive Motion Therapy. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics (BIOROB), Singapore, 26–29 June 2016; pp. 815–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, H.K.; Lim, J.; Nasrallah, F.; Low, F.-Z.; Cho, J.; Yeow, R.C.-H. MRC-Glove: A fMRI Compatible Soft Robotic Glove for Hand Rehabilitation Application. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR), Singapore, 11–14 August 2015; pp. 735–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serpelloni, M.; Tiboni, M.; Lancini, M.; Pasinetti, S.; Vertuan, A.; Gobbo, M. Preliminary Study of a Robotic Rehabilitation System Driven by EMG for Hand Mirroring. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Symposium on Medical Measurements and Applications (MeMeA), Benevento, Italy, 15–18 May 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, D.; Noritsugu, T.; Takaiwa, M.; Yamamoto, H. Wearable Power Assist Device for Hand Grasping Using Pneumatic Artificial Rubber Muscle. In Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO), Shenyang, China, 22–26 August 2004; pp. 655–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadano, K.; Akai, M.; Kadota, K.; Kawashima, K. Development of Grip Amplified Glove Using Bi-Articular Mechanism with Pneumatic Artificial Rubber Muscle. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Anchorage, AK, USA, 3–8 May 2010; pp. 2363–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toya, K.; Miyagawa, T.; Kubota, Y. Power-Assist Glove Operated by Predicting the Grasping Mode. J. Syst. Des. Dyn. 2011, 5, 94–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, J.; Ahmad, O.; Malik, A. HEXOSYS II—Towards Realization of Light Mass Robotics for the Hand. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO), Sanya, China, 7–10 December 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Sugano, S.; Iwata, H. Design and Evaluation of an One DOF Finger Rehabilitation Device. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics (AIM), Wollongong, NSW, Australia, 9–12 July 2013; pp. 822–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, H.K.; Lim, J.; Cho, J.; Yeow, R.C.-H. Design of a Soft Robotic Glove for Hand Rehabilitation of Stroke Patients With Clenched Fist Deformity Using Inflatable Plastic Actuators. J. Med. Devices 2016, 10, 044504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, J.; Caldwell, D.; Tsagarakis, N. Four-Fingered Lightweight Exoskeleton Robotic Device Accommodating Different Hand Sizes. Electron. Lett. 2015, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irimia, D.C.; Poboroniuc, M.S.; Hartopanu, S.; Sticea, D.; Paicu, G.; Ignat, B.E. Post-Stroke Hand Rehabilitation Using a Hybrid FES-Robotic Glove. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference and Exposition on Electrical and Power Engineering (EPE), Iasi, Romania, 20–22 October 2016; pp. 356–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; McDaid, A.; Biglari-Abhari, M.; Aw, K. Design and Development of a Glove for Post-Stroke Hand Rehabilitation. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics (AIM), Munich, Germany, 3–7 July 2017; pp. 1047–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Kang, B.; In, H.; Cho, K.-J. Design Improvement of a Polymer-Based Tendon-Driven Wearable Robotic Hand (Exo-Glove Poly). In Proceedings of the Wearable Robotics: Challenges and Trends, Segovia, Spain, 18–20 October 2016; pp. 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, J.-H.; Ang, M.H.; Yeow, R.C.-H. Customizable Soft Pneumatic Finger Actuators for Hand Orthotic and Prosthetic Applications. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR), Singapore, 11–14 August 2015; pp. 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, P.; Yun, Y.; Fox, J.; Madden, K.; Deshpande, A. Design, Control, and Testing of a Thumb Exoskeleton with Series Elastic Actuation. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2017, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.; Shen, Z.; Song, C.; Wang, Z. A Soft Robotic Glove for Hand Motion Assistance. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Real-time Computing and Robotics (RCAR), Angkor Wat, Cambodia, 6–10 June 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemerle, S.; Nozaki, T.; Ohnishi, K. Design and Evaluation of a Remote Actuated Finger Exoskeleton Using Motion-Copying System for Tendon Rehabilitation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. 2018, 14, 5167–5177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, P.; Kim, S.; Kim, J. Powered Finger Exoskeleton Having Partially Open Fingerpad for Flexion Force Assistance. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics (AIM), Wollongong, NSW, Australia, 9–12 July 2013; pp. 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Chen, D.; Liu, P.; Jiao, X.; Ping, Z.; Xu, Z.; Li, J.; Xu, Y. Fishbone-Inspired Soft Robotic Glove for Hand Rehabilitation with Multi-Degrees-of-Freedom. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Soft Robotics (RoboSoft), Livorno, Italy, 24–28 April 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.; Chen, X.; Wang, Z. A 3D-Printed Soft Robotic Glove with Enhanced Ergonomics and Force Capability. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2017, 3, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, Y.; Dancausse, S.; Esmatloo, P.; Serrato, A.; Merring, C.; Agarwal, P.; Deshpande, A. Maestro: An EMG-Driven Assistive Hand Exoskeleton for Spinal Cord Injury Patients. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Singapore, 29 May–3 June 2017; pp. 2904–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Zhang, F.; Wei, W.; Zhao, F.; Wang, Y. Kinematic Analysis of a Novel Exoskeleton Finger Rehabilitation Robot for Stroke Patients. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation (ICMA), Tianjin, China, 3–6 August 2014; pp. 924–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, M.; Hafeez, U.; Shehzad, M.; Awais, M.N.; Elahi, H. A Soft Robotic Glove for Assistance and Rehabilitation of Stroke Affected Patients. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Frontiers of Information Technology (FIT), Islamabad, Pakistan, 16–18 December 2019; pp. 110–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, A.; Lavranos, J.; Choong, P.; Oetomo, D. Flexo-Glove: A 3D Printed Soft Exoskeleton Robotic Glove for Impaired Hand Rehabilitation and Assistance. In Proceedings of the 2018 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Honolulu, HI, USA, 17–21 July 2018; pp. 2120–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-J.; Jeong, Y.-J.; Jeon, H.-S.; Lee, D.-W.; Kim, J.-I. Development of a Soft Robotic Glove with High Gripping Force Using Force Distributing Compliant Structures. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–28 September 2017; pp. 3883–3890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Zhang, D. Soft Robotic Glove with Integrated sEMG Sensing for Disabled People with Hand Paralysis. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO), Qingdao, China, 3–7 December 2016; pp. 714–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuckols, R.; Hohimer, C.; Glover, C.; Lucena, D.; Moyo, W.; Wagner, D.; Cloutier, A.; Lin, D.; Walsh, C. Effects of a Soft Robotic Glove Using a High Repetition Protocol in Chronic Stroke: A Pilot Study. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics (BioRob), New York, NY, USA, 29 June–2 July 2020; pp. 428–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Agroudy, M.; Awad, M.; Rehan, A.; Maged, S. Assistive Exoskeleton Hand Glove Using Soft Pneumatic Actuators: Design Optimization. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 973, 012041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akgun, G.; Cetin, A.E.; Kaplanoglu, E. Exoskeleton Design and Adaptive Compliance Control for Hand Rehabilitation. Trans. Inst. Meas. Control 2019, 014233121987497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Ji, J.; Yang, G.; Yang, Y. A Novel Robotic Exoskeleton for Finger Rehabilitation: Kinematics Analysis. Appl. Bionics Biomech. 2022, 2022, 1751460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Santos, C.; Davizón, Y.A.; Said, A.R.; Soto, R.; Félix-Herrán, L.C.; Vargas-Martínez, A. Development of a Wearable Finger Exoskeleton for Rehabilitation. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.-H.; Koh, C.-L.; Hsu, C.-H.; Chen, P.-C.; Chen, J.-W.; Lan, Y.-H.; Yang, Y.; Lin, Y.-D.; Wu, C.-H.; Liu, H.-K.; et al. An Instrumented Glove-Controlled Portable Hand-Exoskeleton for Bilateral Hand Rehabilitation. Biosensors 2021, 11, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Jiazhou, C.; He, G.; Cui, L.; Chen, C.; Secco, E.L.; Yao, W.; Xie, J.; Xu, G.; Wurdemann, H. Attention Enhancement for Exoskeleton-Assisted Hand Rehabilitation Using Fingertip Haptic Stimulation. Front. Robot. AI 2021, 8, 602091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yihun, Y.; Miklos, R.; Perez-Gracia, A.; Reinkensmeyer, D.; Denney, K.; Wolbrecht, E. Single Degree-of-Freedom Exoskeleton Mechanism Design for Thumb Rehabilitation. In Proceedings of the 2012 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), San Diego, CA, USA, 28 August–1 September 2012; pp. 1916–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragusanu, M.; Troisi, D.; Villani, A.; Prattichizzo, D.; Malvezzi, M. Design and Prototyping of an Underactuated Hand Exoskeleton with Fingers Coupled by a Gear-Based Differential. Front. Robot. AI 2022, 9, 862340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandison, M.; Phan, K.; Casas, R.; Nguyen, L.; Lum, M.; Pergami-Peries, M.; Lum, P. HandMATE: Wearable Robotic Hand Exoskeleton and Integrated Android App for At Home Stroke Rehabilitation. In Proceedings of the 2020 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 July 2020; pp. 4867–4872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Park, W.; Kim, S.; Bae, J. Design of a Wearable Hand Rehabilitation System for Quantitative Evaluation of the Stroke Hand. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Control, Automation and Systems (ICCAS), Gyeongju, Republic of Korea, 16–19 October 2016; pp. 419–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-SanJuan, V.; Cisnal, A.; Fraile, J.-C.; Pérez-Turiel, J.; Fuente-Lopez, E. Design and Characterization of a Lightweight Underactuated RACA Hand Exoskeleton for Neurorehabilitation. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2021, 143, 103828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malvezzi, M.; Lisini, T.; Villani, A.; Ciccarese, F.; Prattichizzo, D. Design, Development, and Preliminary Evaluation of a Highly Wearable Exoskeleton. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Robot and Human Interactive Communication (RO-MAN), Naples, Italy, 31 August–4 September 2020; pp. 1055–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, D.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, B.; Niu, J. Mechanism Design and Performance Analysis of a Wearable Hand Rehabilitation Robot. Machines 2022, 10, 1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nycz, C.; Butzer, T.; Lambercy, O.; Arata, J.; Fischer, G.; Gassert, R. Design and Characterization of a Lightweight and Fully Portable Remote Actuation System for Use With a Hand Exoskeleton. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2016, 1, 976–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ockenfeld, C.; Tong, R.K.; Susanto, E.A.; Ho, S.K.; Hu, X.L. Fine Finger Motor Skill Training with Exoskeleton Robotic Hand in Chronic Stroke: Stroke Rehabilitation. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR), Seattle, WA, USA, 24–26 June 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wege, A.; Kondak, K.; Hommel, G. Mechanical Design and Motion Control of a Hand Exoskeleton for Rehabilitation. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation (ICMA), Niagara Falls, ON, Canada, 29 July–1 August 2005; pp. 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kladovasilakis, N.; Kostavelis, I.; Sideridis, P.; Koltzi, E.; Piliounis, K.; Tzetzis, D.; Tzovaras, D. A Novel Soft Robotic Exoskeleton System for Hand Rehabilitation and Assistance Purposes. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connelly, L.; Jia, Y.; Toro, M.L.; Stoykov, M.E.; Kenyon, R.V.; Kamper, D.G. A Pneumatic Glove and Immersive Virtual Reality Environment for Hand Rehabilitative Training After Stroke. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2010, 18, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, H.K.; Lim, J.H.; Nasrallah, F.A.; Goh, J.C.H.; Yeow, R.C.H. A soft exoskeleton for hand assistive and rehabilitation application using pneumatic actuators with variable stiffness. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Seattle, WA, USA, 26–30 May 2015; pp. 4967–4972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, D.; Moon, K.W.; Nam, H.; Lee, Y.; Chun, C.; Kang, S.; Song, J.B. Micro hydraulic system using slim artificial muscles for a wearable haptic glove. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Nice, France, 22–26 September 2008; pp. 3028–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polygerinos, P.; Galloway, K.C.; Savage, E.; Herman, M.; O’Donnell, K.; Walsh, C.J. Soft robotic glove for hand rehabilitation and task-specific training. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Seattle, WA, USA, 26–30 May 2015; pp. 2913–2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaid, A.M.; Chean, T.C.; Sukor, J.A.; Hanafi, D. Development of hand exoskeleton for rehabilitation of post-stroke patient. AIP Conf. Proc. 2017, 1891, 020103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridremont, T.; Singh, I.; Bruzek, B.; Jamieson, A.; Gu, Y.; Merzouki, R.; Wijesundara, M.B.J. Pneumatically Actuated Soft Robotic Hand and Wrist Exoskeleton for Motion Assistance in Rehabilitation. Actuators 2024, 13, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudd, G.; Daly, L.; Jovanovic, V.; Cuckov, F. A Low-Cost Soft Robotic Hand Exoskeleton for Use in Therapy of Limited Hand–Motor Function. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.C.; Lourenço, B.G.; Ulhoa, P.H.F.; Dias, E.A.F.; da Cunha, F.L.; Tonetto, C.P.; Villani, L.G.; Vimieiro, C.B.S.; Lepski, G.A.; Monjardim, M.; et al. Biomimetic Design of a Tendon-Driven Myoelectric Soft Hand Exoskeleton for Upper-Limb Rehabilitation. Biomimetics 2023, 8, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, M.K.; Pei, D.; Vinjamuri, R. Myoelectric control of a soft hand exoskeleton using kinematic synergies. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2019, 13, 1351–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aruanno, B.; Covarrubias, M. HANDY: Novel hand exoskeleton for personalized rehabilitation. Comput. Aided Des. Appl. 2021, 19, 405–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Gong, L.; Zheng, L.; Zou, Z. Soft exoskeleton glove for hand assistance based on human-machine interaction and machine learning. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Human-Machine Systems (ICHMS), Rome, Italy, 7–9 September 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamaludin, M.S.; Jamali, A.; Mohamaddan, S. Design and fabrication of finger rehabilitation device for stroke patients-a prototype development. In Proceedings of the 5th Brunei International Conference on Engineering and Technology (BICET 2014), Bandar Seri Begawan, Brunei, 1–3 November 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Xu, Q.; Wu, F. Design of wearable hand rehabilitation glove with bionic fiber-reinforced actuator. IEEE J. Transl. Eng. Health Med. 2022, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birlescu, I.; Tohanean, N.; Vaida, C.; Gherman, B.; Neguran, D.; Horsia, A.; Tucan, P.; Condurache, D.; Pisla, D. Modeling and analysis of a parallel robotic system for lower limb rehabilitation with predefined operational workspace. Mech. Mach. Theory 2024, 198, 105674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado-Mejía, J.C.; Múnera, M.; Diaz, C.A.R.; Wurdemann, H.; Moazen, M.; Pontes, M.J.; Vieira Segatto, M.E.; Monteiro, M.E.; Cifuentes, C.A. A fabric-based soft hand exoskeleton for assistance: The ExHand Exoskeleton. Front. Neurorobot. 2023, 17, 1091827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Zhuo, Y.; He, B.; Liang, Z.; Xu, Z.; Xie, J.; Zhang, S. A 3D-printed soft hand exoskeleton with finger abduction assistance. In Proceedings of the 2019 16th International Conference on Ubiquitous Robots (UR), Jeju, Republic of Korea, 24–27 June 2019; pp. 319–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Agroudy, M.N.; Awad, M.I.; Maged, S.A. Soft Finger Modelling and Co-Simulation Control towards Assistive Exoskeleton Hand Glove. Micromachines 2021, 12, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, D.T.G.; Nguyen, L. An efficient force-feedback hand exoskeleton for haptic applications. Int. J. Intell. Robot Appl. 2021, 5, 395–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Gong, W.; Chu, K.; Wang, X.; Hu, Z.; Su, H. A Novel Wearable Soft Glove for Hand Rehabilitation and Assistive Grasping. Sensors 2022, 22, 6294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bressi, F.; Cricenti, L.; Bravi, M.; Pannunzio, F.; Cordella, F.; Lapresa, M.; Miccinilli, S.; Santacaterina, F.; Zollo, L.; Sterzi, S.; et al. Treatment of the Paretic Hand with a Robotic Glove Combined with Physiotherapy in a Patient Suffering from Traumatic Tetraparesis: A Case Report. Sensors 2023, 23, 3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, L.; DiCicco, M.; Matsuoka, Y. An EMG-Controlled Hand Exoskeleton for Natural Pinching. J. Robot. Mechatron. 2004, 16, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, O.; Múnera, M.; Moazen, M.; Wurdemann, H.; Cifuentes, C.A. Assessment of Soft Actuators for Hand Exoskeletons: Pleated Textile Actuators and Fiber-Reinforced Silicone Actuators. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 924888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villoslada, Á.; Rivera, C.; Escudero, N.; Martín, F.; Blanco, D.; Moreno, L. Hand Exo-Muscular System for Assisting Astronauts During Extravehicular Activities. Soft Robot. 2019, 6, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadowaki, Y.; Noritsugu, T.; Takaiwa, M.; Sasaki, D.; Kato, M. Development of Soft Power-Assist Glove and Control Based on Human Intent. J. Robotics Mechatron. 2011, 23, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurkewich, A.; Kozak, I.; Ivanovic, A.; Rossos, D.; Wang, R.; Hebert, D.; Mihailidis, A. Myoelectric Untethered Robotic Glove Enhances Hand Function and Performance on Daily Living Tasks After Stroke. J. Rehabil. Assist. Technol. Eng. 2020, 7, 205566832096405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, U.; In, H.; Lee, H.; Kang, B.; Cho, K.-J. Investigation on the Control Strategy of Soft Wearable Robotic Hand with Slack Enabling Tendon Actuator. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Seattle, WA, USA, 26–30 May 2015; pp. 5004–5009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polygerinos, P.; Galloway, K.; Sanan, S.; Herman, M.; Walsh, C. EMG Controlled Soft Robotic Glove for Assistance During Activities of Daily Living. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR), Singapore, 11–14 August 2015; pp. 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; In, H.; Lee, D.-Y.; Cho, K.-J. Development and Assessment of a Hand Assist Device: GRIPIT. J. NeuroEng. Rehabil. 2017, 14, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamaddan, S.; Komeda, T. Wire-Driven Mechanism for Finger Rehabilitation Device. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation (ICMA), Xi’an, China, 4–7 August 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, C.; Nuckols, R.; Wagner, D.; Zhou, Y.M.; Clarke, M.; Orzel, D.; Solinsky, R.; Paganoni, S.; Walsh, C. Improving Grasp Function After Spinal Cord Injury With a Soft Robotic Glove. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2020, 28, 1407–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiri, A.; Giovacchini, F.; Vitiello, N.; Cattin, E.; Roccella, S.; Vecchi, F.; Carrozza, M.C. HANDEXOS: Towards an Exoskeleton Device for the Rehabilitation of the Hand. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, St. Louis, MO, USA, 10–15 October 2009; pp. 1106–1111. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.; Park, H.-S. Design Optimization of a Soft Robotic Rehabilitation Glove Based on Finger Workspace Analysis. Biomimetics 2024, 9, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brogi, C.; Secciani, N.; Bartalucci, L.; Di Iorio, F.; Meli, E.; Rinchi, M.; Allotta, B.; Ridolfi, A. An Original Hybrid-Architecture Finger Mechanism for Wearable Hand Exoskeletons. Mechatronics 2024, 98, 103117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, J.; Tsagarakis, N.; Caldwell, D.G. Human Hand Compatible Underactuated Exoskeleton Robotic System. Electron. Lett. 2014, 50, 494–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dovat, L.; Lambercy, O.; Gassert, R.; Maeder, T.; Milner, T.; Leong, T.C.; Burdet, E. HandCARE: A Cable-Actuated Rehabilitation System to Train Hand Function After Stroke. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2008, 16, 582–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nycz, C.; Delph, M.; Fischer, G. Modeling and Design of a Tendon Actuated Soft Robotic Exoskeleton for Hemiparetic Upper Limb Rehabilitation. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Milan, Italy, 25–29 August 2015; pp. 3889–3892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, P.; Jeong, S.; Wolf, S.; Desai, J. Patient-Specific, Voice-Controlled, Robotic FLEX-otendon Glove-II System for Spinal Cord Injury. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 898–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemerle, S.; Fukushima, S.; Saito, Y.; Nozaki, T.; Ohnishi, K. Wearable Finger Exoskeleton Using Flexible Actuator for Rehabilitation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics (ICM), Churchill, VIC, Australia, 13–15 February 2017; pp. 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, R.; Ariyanto, M.; Hidayat, T.; Setiawan, J. Design of Fabric-Based Soft Robotic Glove for Hand Function Assistance. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Information Technology, Computer, and Electrical Engineering (ICITACEE), Semarang, Indonesia, 26–27 September 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duanmu, D.; Li, X.; Huang, W.; Hu, Y. Soft Finger Rehabilitation Exoskeleton of Biomimetic Dragonfly Abdominal Ventral Muscles: Center Tendon Pneumatic Bellows Actuator. Biomimetics 2023, 8, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, H.K.; Lim, J.H.; Nasrallah, F.; Yeow, C.H. Design and Preliminary Feasibility Study of a Soft Robotic Glove for Hand Function Assistance in Stroke Survivors. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, H.K.; Khin, P.; Koh, T.; Sun, Y.; Liang, X.; Lim, J.; Yeow, R.C.-H. A Fully Fabric-Based Bidirectional Soft Robotic Glove for Assistance and Rehabilitation of Hand Impaired Patients. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2017, 2, 1383–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koizumi, S.; Shimada, Y.; Chang, T.-H.; Nabae, H.; Endo, G.; Suzumori, K.; Mita, M.; Saitoh, K.; Hatakeyama, K.; Chida, S. Soft Robotic Gloves with Thin McKibben Muscles for Hand Assist and Rehabilitation. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/SICE International Symposium on System Integration (SII), Honolulu, HI, USA, 12–15 January 2020; pp. 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, N.; Takahashi, H.; Koike, H. Soft Exoskeleton Glove Enabling Force Feedback for Human-Like Finger Posture Control with 20 Degrees of Freedom. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE World Haptics Conference (WHC), Tokyo, Japan, 9–12 July 2019; pp. 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhav, S.; Kannanda, V.; Kang, B.; Tolley, M.T.; Schulze, J.P. Soft Robotic Glove for Kinesthetic Haptic Feedback in Virtual Reality Environments. In Proceedings of the IS&T International Symposium on Electronic Imaging: The Engineering Reality of Virtual Reality, Burlingame, CA, USA, 29 January–2 February 2017; pp. 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tondu, B.; Lopez, P. Modeling and Control of McKibben Artificial Muscle Robot Actuators. IEEE Control Syst. Mag. 2000, 20, 15–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, D.; Noritsugu, T.; Takaiwa, M. Development of Active Support Splint Driven by Pneumatic Soft Actuator (ASSIST). In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Barcelona, Spain, 18–22 April 2005; pp. 520–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hand Physical Therapy with the HandMentor™. Available online: http://www.kineticmuscles.com/hand-physicaltherapy-hand-mentor.html (accessed on 12 November 2024).
- Pisla, D.; Nae, L.; Vaida, C.; Oprea, E.; Pisla, A.; Gherman, B.; Antal, T.; Riessenberger, K.; Plitea, N. Development of a Learning Management System for Knowledge Transfer in Engineering. Acta Tech. Napoc. Ser. Appl. Math. Mech. Eng. 2021, 64, 361–368. [Google Scholar]
- Gopura, R.A.R.C.; Kiguchi, K. Mechanical Designs of Active Upper-Limb Exoskeleton Robots: State-of-the-Art and Design Difficulties. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR), Kyoto, Japan, 23–26 June 2009; pp. 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Neri, W.; Zakri, C.; Merzeau, P.; Kratz, K.; Lendlein, A.; Poulin, P. Shape Memory Nanocomposite Fibers for Untethered High-Energy Microengines. Science 2019, 365, 155–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H. Application of Intelligent Materials in the Control System. J. Comput. Theor. Nanosci. 2015, 12, 2830–2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuka, K.; Wayman, C.M. (Eds.) Shape Memory Materials; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Mavroidis, C.; Pfeiffer, C.; Mosley, M. Conventional Actuators, Shape Memory Alloys and Electrorheological Fluids. In Automation, Miniature Robotics and Sensors for Non-Destructive Testing and Evaluation; Bar-Cohen, Y., Ed.; American Society for Nondestructive Testing: Columbus, OH, USA, 2000; pp. 189–214. [Google Scholar]
- Kazeminasab, S.; Hadi, A.; Alipour, K.; Elahinia, M. Force and Motion Control of a Tendon-Driven Hand Exoskeleton Actuated by Shape Memory Alloys. Ind. Robot 2019, 45, 623–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, M.; Ingvast, J.; Wikander, J.; von Holst, H. The Soft Extra Muscle System for Improving the Grasping Capability in Neurological Rehabilitation. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE-EMBS Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Sciences (IECBES), Langkawi, Malaysia, 17–19 December 2012; pp. 412–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Linnenberg, C.; Argubi-Wollesen, A.; Weidner, R.; Wulfsberg, J. Biomimetic Design of an Ultra-Compact and Light-Weight Soft Muscle Glove. Prod. Eng. 2017, 11, 731–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Lagoudas, D. Introduction to Shape Memory Alloys. In Shape Memory Alloys; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2008; Volume 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, C.T.; Hughes, A.M.; Burridge, J.H.; Chappell, P.H.; Lewin, P.L.; Rogers, E. Iterative Learning Control of FES Applied to the Upper Extremity for Rehabilitation. Control Eng. Pract. 2009, 17, 368–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trolier-McKinstry, S.; Zhang, S.; Bell, A.J.; Tan, X. High-Performance Piezoelectric Crystals, Ceramics, and Films. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2018, 48, 191–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesse, S.; Schulte-Tigges, G.; Konrad, M.; Bardeleben, A.; Werner, C. Robot-Assisted Arm Trainer for the Passive and Active Practice of Bilateral Forearm and Wrist Movements in Hemiparetic Subjects. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2003, 84, 915–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesse, S.; Schmidt, H.; Werner, C. Machines to Support Motor Rehabilitation After Stroke: 10 Years of Experience in Berlin. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 2006, 43, 671–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.W.; Lee, S.J.; Yoon, B.R.; Jho, J.Y.; Rhee, K. Preliminary Study on Analysis of Pinching Motion Actuated by Electro-Active Polymers. Int. J. Mech. Mechatron. Eng. 2014, 8, 919–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzger, J.-C.; Lambercy, O.; Gassert, R. High-Fidelity Rendering of Virtual Objects with the ReHapticKnob-Novel Avenues in Robot-Assisted Rehabilitation of Hand Function. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Haptics Symposium (HAPTICS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 4–7 March 2012; pp. 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, I.; Bae, J. Design and Control of a Wearable and Force-Controllable Hand Exoskeleton System. Mechatronics 2017, 41, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullock, I.M.; Borràs, J.; Dollar, A.M. Assessing Assumptions in Kinematic Hand Models: A Review. In Proceedings of the 2012 4th IEEE RAS & EMBS International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics (BioRob), Rome, Italy, 24–27 June 2012; Volume 49, pp. 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, C.H.; Seong, J.W.; Son, D.-S. Individual Finger Synchronized Robot-Assisted Hand Rehabilitation in Subacute to Chronic Stroke: A Prospective Randomized Clinical Trial of Efficacy. Clin. Rehabil. 2012, 26, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ang, K.; Guan, C.; Phua, K.S.; Wang, C.; Zhou, L.; Tang, K.Y.; Joseph, G.; Kuah, C.; Chua, K. Brain-Computer Interface-Based Robotic End Effector System for Wrist and Hand Rehabilitation: Results of a Three-Armed Randomized Controlled Trial for Chronic Stroke. Front. Neuroeng. 2014, 7, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tohanean, N.; Tucan, P.; Vanta, O.-M.; Abrudan, C.; Pintea, S.; Gherman, B.; Burz, A.; Banica, A.; Vaida, C.; Neguran, D.A.; et al. The Efficacity of the NeuroAssist Robotic System for Motor Rehabilitation of the Upper Limb—Promising Results from a Pilot Study. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, B.; In, H.; Cho, K.-J. Modeling of Tendon Driven Soft Wearable Robot for the Finger. In Proceedings of the 2013 10th International Conference on Ubiquitous Robots and Ambient Intelligence (URAI), Jeju, Republic of Korea, 30 October–2 November 2013; pp. 459–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kottink, A.; Nikamp, C.; Buurke, J.; Bos, F.; Sluis, C.; Broek, M.; Onneweer, B.; Stolwijk-Swüste, J.; Brink, S.; Rietman, J.; et al. Six Weeks Use of a Wearable Soft-Robotic Glove During ADL: Preliminary Results of Ongoing Clinical Study. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR), Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 25–29 July 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesse, S.; Kuhlmann, H.; Wilk, J.; Tomelleri, C.; Kirker, S.G.B. A New Electromechanical Trainer for Sensorimotor Rehabilitation of Paralysed Fingers: A Case Series in Chronic and Acute Stroke Patients. J. NeuroEng. Rehabil. 2008, 5, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thielbar, K.O.; Triandafilou, K.M.; Fischer, H.C.; O’Toole, J.M.; Corrigan, M.L.; Ochoa, J.M.; Stoykov, M.E.; Kamper, D.G. Benefits of Using a Voice and EMG-Driven Actuated Glove to Support Occupational Therapy for Stroke Survivors. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2017, 25, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, A.; Haghverd, F.; Behbahani, S. Robotic Home-Based Rehabilitation Systems Design: From a Literature Review to a Conceptual Framework for Community-Based Remote Therapy During COVID-19 Pandemic. Front. Robot. AI 2021, 8, 612331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.C.; Kuo, F.L.; Lin, Y.N.; Liou, T.H.; Lin, J.C.; Huang, S.W. Effects of Robot-Assisted Rehabilitation on Hand Function of People with Stroke: A Randomized, Crossover-Controlled, Assessor-Blinded Study. Am. J. Occup. Ther. 2021, 75, 7501205020p1–7501205020p11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metzger, J.-C.; Lambercy, O.; Chapuis, D.; Gassert, R. Design and Characterization of the ReHapticKnob, a Robot for Assessment and Therapy of Hand Function. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), San Francisco, CA, USA, 25–30 September 2011; Volume 10, pp. 3074–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- In, H.; Kang, B.B.; Sin, M.; Cho, K.-J. Exo-Glove: A Wearable Robot for the Hand with a Soft Tendon Routing System. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2015, 22, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- In, H.K.; Cho, K.J. Evaluation of the Antagonistic Tendon Driven System for SNU Exo-Glove. In Proceedings of the 2012 9th International Conference on Ubiquitous Robots and Ambient Intelligence (URAI), Daejeon, Republic of Korea, 26–28 November 2012; pp. 507–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Q.; Zhao, W.; Cui, X.; Fei, Y. Design, Control and Testing of Soft Pneumatic Rehabilitation Glove. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 3rd World Conference on Mechanical Engineering and Intelligent Manufacturing (WCMEIM), Shanghai, China, 4–6 December 2020; pp. 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Vella, K.; Holmes, D.P. Grasping with Kirigami Shells. Sci. Robot. 2021, 6, eabd6426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).