Biomechanical Evaluation of Elliptical Leaf Spring Prosthetics for Unilateral Transtibial Amputees During Dynamic Activities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
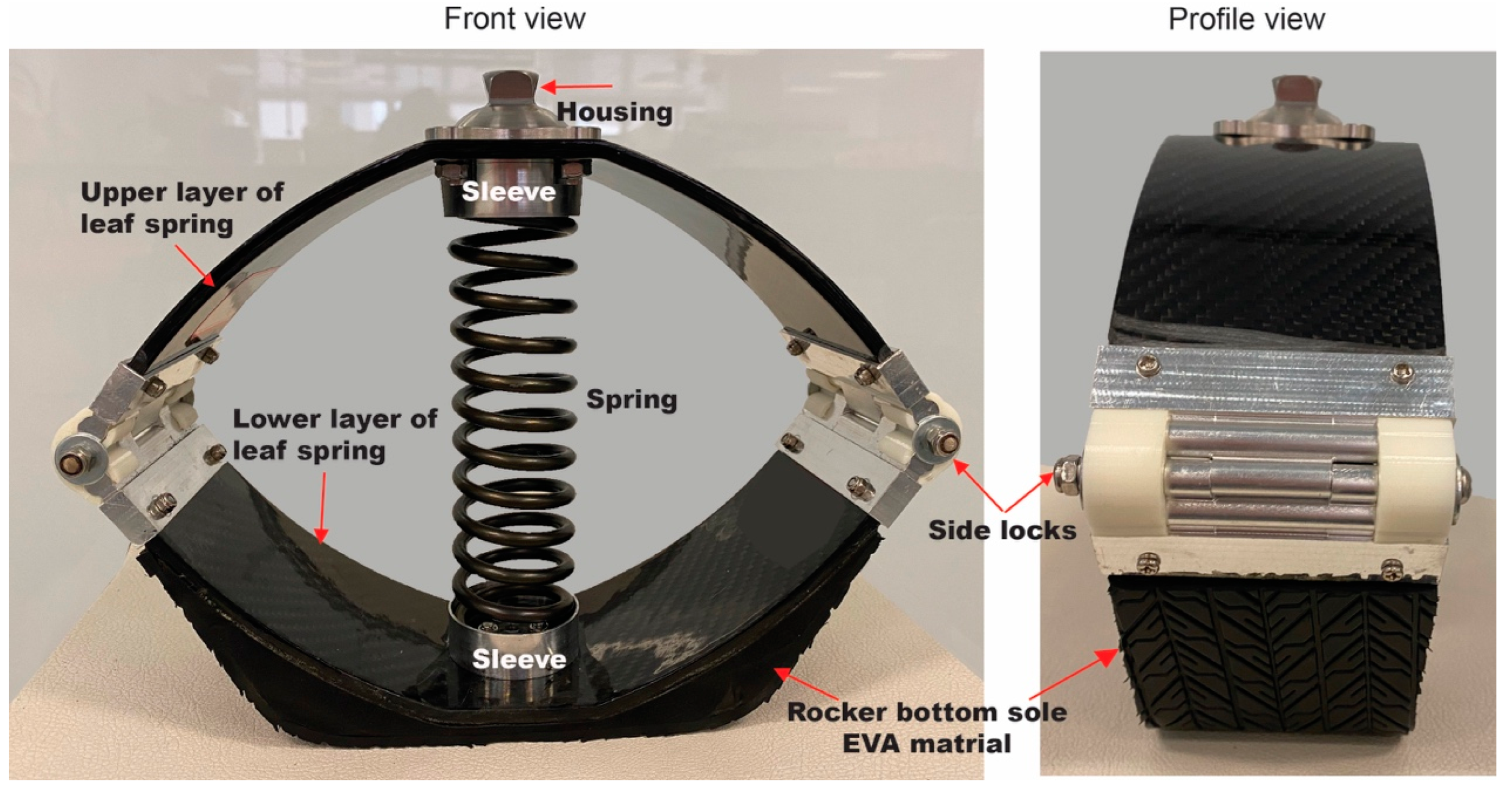
2.1. Design of a Novel ELS-Foot Prosthesis
2.2. Participants
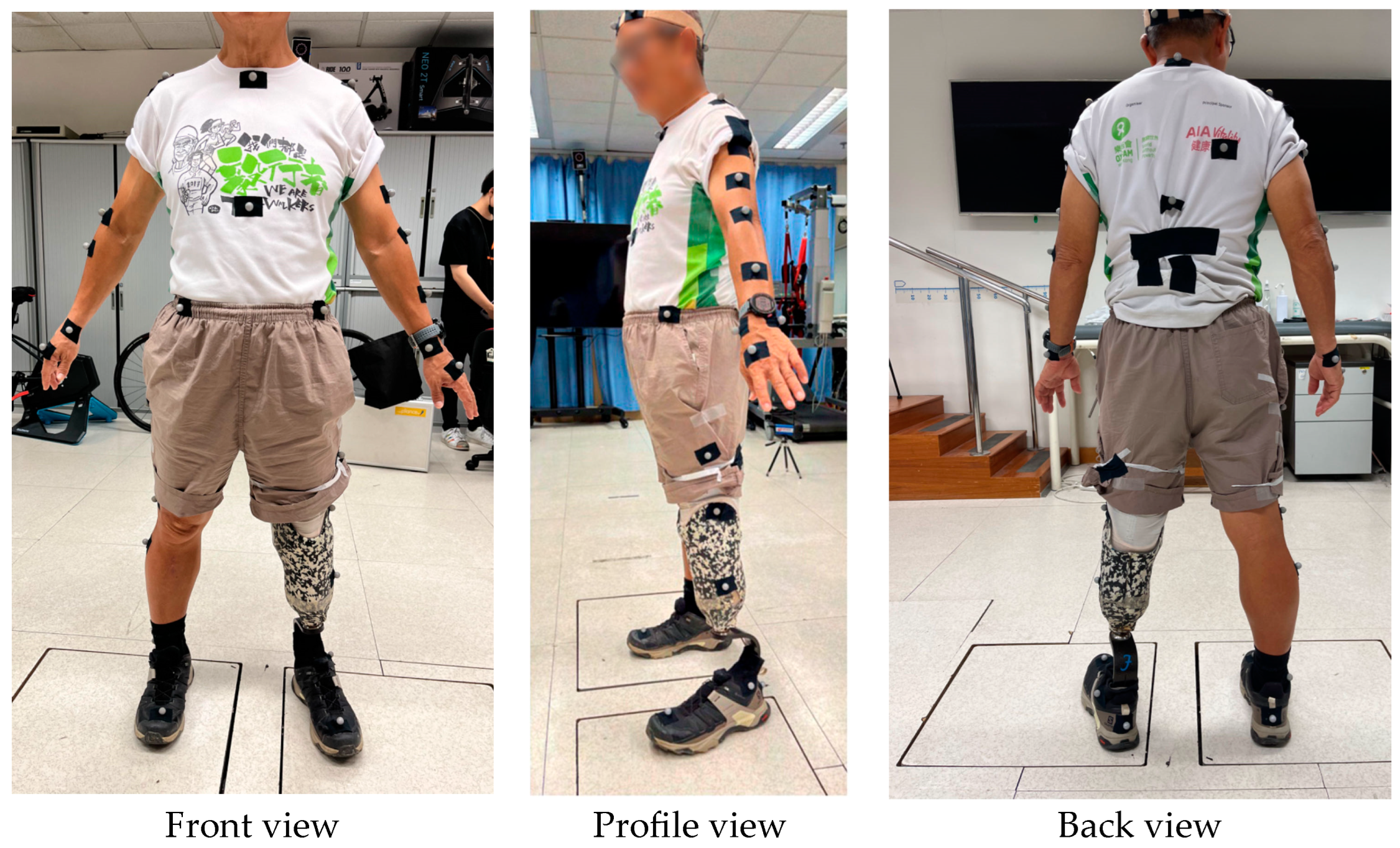
2.3. Experimental Protocols
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Mobility, Balance, Jumping, and Subjective Evaluation
3.2. Gait Analysis with Different Prostheses
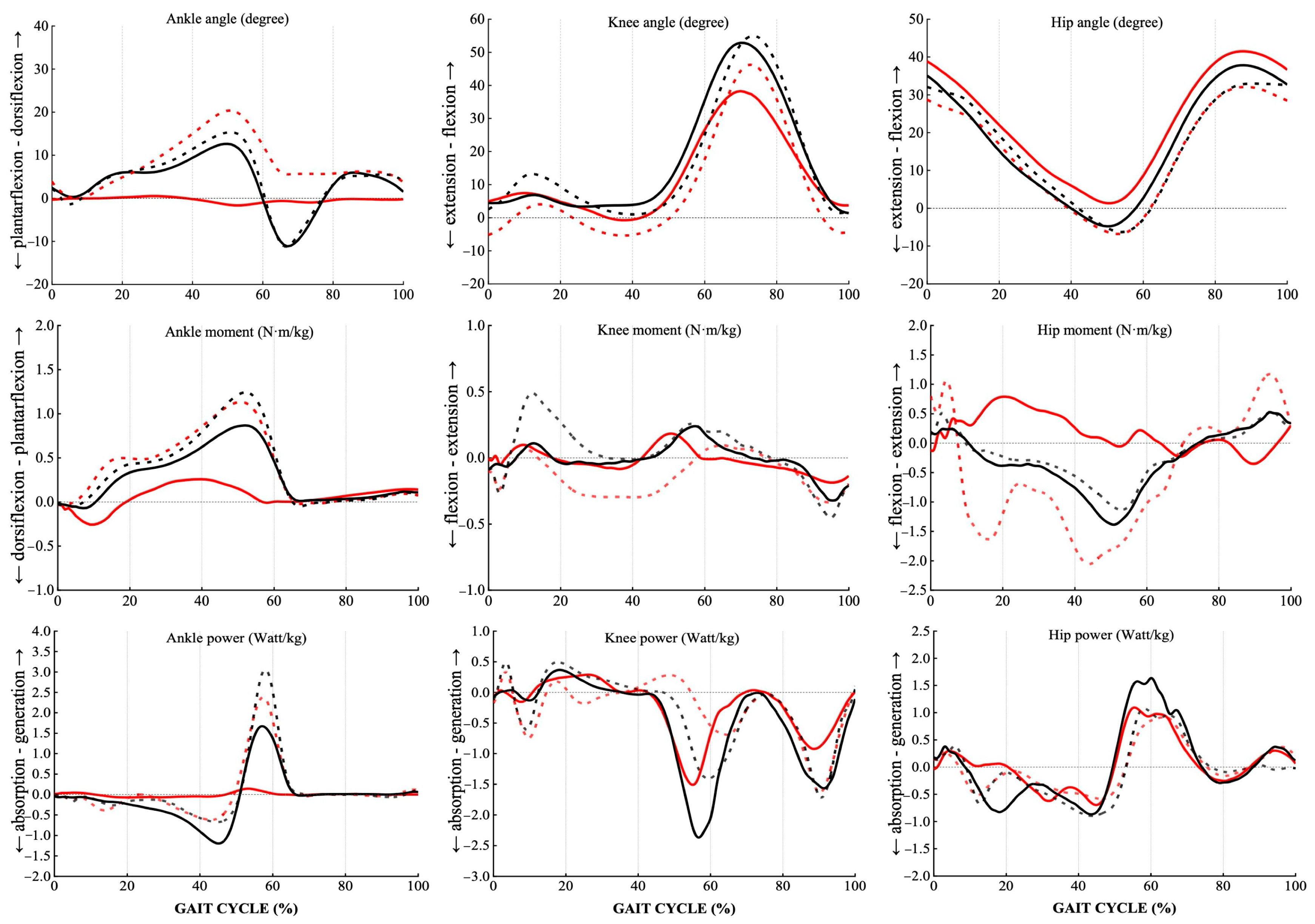
3.2.1. Kinematic Outcomes
3.2.2. Kinetic Outcomes
4. Discussion
4.1. Mobility
4.2. Balance
4.3. Jumping Performance
4.4. Gait Pattern with Different Prostheses
4.5. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| APSI | Anterior–posterior stability index |
| BBS | Berg Balance Scale |
| ELS | Elliptical leaf spring |
| EVA | Ethylene-vinyl acetate |
| FSST | Four Square Step Test |
| LCI | Locomotor Capabilities Index |
| MLSI | Medial–lateral stability index |
| TUG | Timed Up and Go |
References
- Price, M.A.; Beckerle, P.; Sup, F.C. Design optimization in lower limb prostheses: A review. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2019, 27, 1574–1588. [Google Scholar]
- Winter, D.A.; Sienko, S.E. Biomechanics of below-knee amputee gait. J. Biomech. 1988, 21, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bateni, H.; Olney, S.J. Kinematic and kinetic variations of below-knee amputee gait. JPO J. Prosthet. Orthot. 2002, 14, 2–10. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Q.-Q.; Yick, K.-L.; Wu, J.; Huang, X.; Tse, C.-Y.; Chan, M.-K. A Scientometric Analysis and Visualization of Prosthetic Foot Research Work: 2000 to 2022. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolan, L. Carbon fibre prostheses and running in amputees: A review. Foot Ankle Surg. 2008, 14, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Q.-Q.; Chan, M.-k.; Yick, K.-L.; Li, P.-L.; Yip, J.; Tse, C.-Y. Biomechanical Analysis of Unilateral Transtibial Amputees Using Prosthetic Foot During Treadmill Walking at Varying Slopes: 1721. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2023, 55, 581. [Google Scholar]
- Houdijk, H.; Wezenberg, D.; Hak, L.; Cutti, A.G. Energy storing and return prosthetic feet improve step length symmetry while preserving margins of stability in persons with transtibial amputation. J. NeuroEng. Rehabil. 2018, 15, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehara, Y.; Beppu, M.; Nomura, S.; Kunimi, Y.; Takahashi, S. Energy storing property of so-called energy-storing prosthetic feet. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 1993, 74, 68–72. [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesan, M.; Devaraj, D.H. Design and analysis of composite leaf spring in light vehicle. Int. J. Mod. Eng. Res. 2012, 2, 213–218. [Google Scholar]
- Petrone, N.; Costa, G.; Foscan, G.; Gri, A.; Mazzanti, L.; Migliore, G.; Cutti, A.G. Development of instrumented running prosthetic feet for the collection of track loads on elite athletes. Sensors 2020, 20, 5758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leblouba, M.; Altoubat, S.; Ekhlasur Rahman, M.; Palani Selvaraj, B. Elliptical leaf spring shock and vibration mounts with enhanced damping and energy dissipation capabilities using lead spring. Shock. Vib. 2015, 2015, 482063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradeep, S.A.; Iyer, R.K.; Kazan, H.; Pilla, S. Automotive applications of plastics: Past, present, and future. In Applied Plastics Engineering Handbook; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 651–673. [Google Scholar]
- Zajac, F.E. Understanding muscle coordination of the human leg with dynamical simulations. J. Biomech. 2002, 35, 1011–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubley-Kozey, C.; Deluzio, K.; Dunbar, M. Muscle co-activation patterns during walking in those with severe knee osteoarthritis. Clin. Biomech. 2008, 23, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zmitrewicz, R.J.; Neptune, R.R.; Walden, J.G.; Rogers, W.E.; Bosker, G.W. The effect of foot and ankle prosthetic components on braking and propulsive impulses during transtibial amputee gait. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2006, 87, 1334–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, D.; Bao, Z.; Han, W.; Wang, X.; Huang, S.; Huang, L.; Chen, Q.; Zhao, H.; Xu, Y. Effect of strain rate on tensile properties of carbon fiber-reinforced epoxy laminates with different stacking sequences and ply orientations. Polymers 2023, 15, 2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafner, B.J.; Smith, D.G. Differences in function and safety between Medicare Functional Classification Level-2 and-3 transfemoral amputees and influence of prosthetic knee joint control. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 2009, 46, 417–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kent, J.A.; Stergiou, N.; Wurdeman, S.R. Dynamic balance changes within three weeks of fitting a new prosthetic foot component. Gait Posture 2017, 58, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenka, P.; Kumar, R. Gait comparisons of trans tibial amputees with six different prosthetic feet in developing countries. Indian J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2010, 21, 8–14. [Google Scholar]
- Wijekoon, A.; Dona, D.G.; Jayawardana, S. Prevalence of physical health comorbidities and long-term functional outcomes among community-reintegrated veterans following lower limb amputation in Sri Lanka. BMJ Mil. Health 2023, 171, e002578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shumway-Cook, A.; Brauer, S.; Woollacott, M. Predicting the probability for falls in community-dwelling older adults using the Timed Up & Go Test. Phys. Ther. 2000, 80, 896–903. [Google Scholar]
- Dite, W.; Temple, V.A. A clinical test of stepping and change of direction to identify multiple falling older adults. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2002, 83, 1566–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batten, H.R.; McPhail, S.M.; Mandrusiak, A.M.; Varghese, P.N.; Kuys, S.S. Gait speed as an indicator of prosthetic walking potential following lower limb amputation. Prosthet. Orthot. Int. 2019, 43, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Berg, K.O.; Wood-Dauphinee, S.L.; Williams, J.I.; Maki, B. Measuring balance in the elderly: Development and validation of an instrument. Can. J. Public Health 1992, 83 (Suppl. 2), S7–S11. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Arifin, N.; Abu Osman, N.A.; Ali, S.; Wan Abas, W.A.B. The effects of prosthetic foot type and visual alteration on postural steadiness in below-knee amputees. Biomed. Eng. Online 2014, 13, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Gremeaux, V.; Damak, S.; Troisgros, O.; Feki, A.; Laroche, D.; Perennou, D.; Benaim, C.; Casillas, J.-M. Selecting a test for the clinical assessment of balance and walking capacity at the definitive fitting state after unilateral amputation: A comparative study. Prosthet. Orthot. Int. 2012, 36, 415–422. [Google Scholar]
- Duncan, P.W.; Weiner, D.K.; Chandler, J.; Studenski, S. Functional reach: A new clinical measure of balance. J. Gerontol. 1990, 45, M192–M197. [Google Scholar]
- Ranker, A.; Gutenbrunner, C.; Eckhardt, I.; Giordano, A.; Burger, H.; Franchignoni, F. Rasch validation and comparison of the German versions of the Locomotor Capabilities Index-5 and Prosthetic Mobility Questionnaire 2.0 in lower-limb prosthesis users. Int. J. Rehabil. Res. 2021, 44, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McErlain-Naylor, S.; King, M.; Pain, M.T.G. Determinants of countermovement jump performance: A kinetic and kinematic analysis. J. Sports Sci. 2014, 32, 1805–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddas, R.; Ju, K.L.; Belanger, T.; Lieberman, I.H. The use of gait analysis in the assessment of patients afflicted with spinal disorders. Eur. Spine J. 2018, 27, 1712–1723. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Q.-Q.; Li, P.-L.; Yick, K.-L.; Jiao, J.; Liu, Q.-L. Influence of Contoured Insoles with Different Materials on Kinematics and Kinetics Changes in Diabetic Elderly during Gait. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2022, 19, 12502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.; Yick, K. Evaluating the Impact of Prosthetics on Gait Symmetry in Unilateral Lower Limb Amputees. In Human Dynamics, Product Evaluation and Quality, Proceedings of the AHFE (2024) International Conference, Nice, France, 24–27 July 2024; Xu, S., Zalio, M., Li, Z., Eds.; AHFE Open Access: Orlando, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Petrovic, M.; Maganaris, C.N.; Deschamps, K.; Verschueren, S.M.; Bowling, F.L.; Boulton, A.J.; Reeves, N.D. Altered Achilles tendon function during walking in people with diabetic neuropathy: Implications for metabolic energy saving. J. Appl. Physiol. 2018, 124, 1333–1340. [Google Scholar]
- Švehlík, M.; Zwick, E.B.; Steinwender, G.; Linhart, W.E.; Schwingenschuh, P.; Katschnig, P.; Ott, E.; Enzinger, C. Gait analysis in patients with Parkinson’s disease off dopaminergic therapy. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2009, 90, 1880–1886. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dillon, M.P.; Major, M.J.; Kaluf, B.; Balasanov, Y.; Fatone, S. Predict the Medicare Functional Classification Level (K-level) using the Amputee Mobility Predictor in people with unilateral transfemoral and transtibial amputation: A pilot study. Prosthet. Orthot. Int. 2018, 42, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Major, M.J.; Fatone, S.; Roth, E.J. Validity and reliability of the Berg Balance Scale for community-dwelling persons with lower-limb amputation. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2013, 94, 2194–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willwacher, S.; Funken, J.; Heinrich, K.; Müller, R.; Hobara, H.; Grabowski, A.M.; Brüggemann, G.-P.; Potthast, W. Elite long jumpers with below the knee prostheses approach the board slower, but take-off more effectively than non-amputee athletes. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16058. [Google Scholar]
- Hobara, H.; Tominaga, S.; Umezawa, S.; Iwashita, K.; Okino, A.; Saito, T.; Usui, F.; Ogata, T. Leg stiffness and sprint ability in amputee sprinters. Prosthet. Orthot. Int. 2012, 36, 312–317. [Google Scholar]
- Su, P.-F.; Gard, S.A.; Lipschutz, R.D.; Kuiken, T.A. Gait characteristics of persons with bilateral transtibial amputations. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 2007, 44, 491–501. [Google Scholar]
- Devan, H.; Carman, A.; Hendrick, P.; Hale, L.; Ribeiro, D.C. Spinal, pelvic, and hip movement asymmetries in people with lower-limb amputation: Systematic review. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 2015, 52, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Michaud, S.B.; Gard, S.A.; Childress, D.S. A preliminary investigation of pelvic obliquity patterns during gait in persons with transtibial and transfemoral amputation. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 2000, 37, 1–10. [Google Scholar]

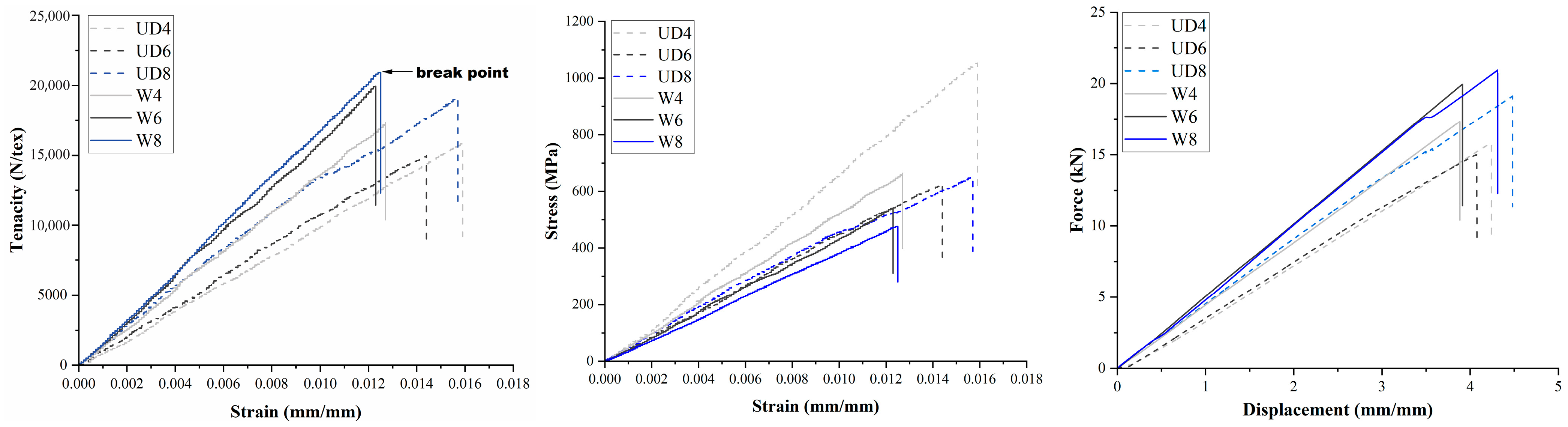



| Unidirectional Carbon Fiber | Woven Carbon Fiber | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Fiber |  |  | ||||
| Structure | Uni-directional | Woven Twill | ||||
| Fabrication | Pre-Preg Layup | |||||
| Layers and Stacking Sequence |  | |||||
| Composite Code | UD4 | UD6 | UD8 | W4 | W6 | W8 |
| Thickness (mm) | 0.4 | 0.97 | 1.24 | 1.06 | 1.48 | 1.92 |
| Weight (g) | 108 | 136.8 | 190.18 | 148.3 | 190.1 | 256.3 |
| Type of Material | Component | Unit | Total Weight (g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon fiber | Semi-elliptical leaf spring | 2 | 284.0 |
| Metal | Side joint | 4 | 116.0 |
| Holder | 4 | 15.2 | |
| Rotational pyramid | 1 | 50.0 | |
| Spring sleeve | 2 | 57.6 | |
| Spring | 1 | 32.3 | |
| Steel | Screws for side joints | 6 | 32.0 |
| Screws for pyramid | 4 | 14.4 | |
| Screws for spring sleeves | 2 | 32.0 | |
| Total | 633 | ||
| Participant Number | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | Mean (SD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | F | M | M | M | F | M | |
| Age (years old) | 52 | 70 | 46 | 51 | 64 | 36 | 53.2 (12.3) |
| Body mass (kg) | 67.1 | 63.5 | 76.0 | 72.3 | 69.0 | 82.0 | 71.7 (6.6) |
| Height (cm) | 157 | 165 | 182 | 171 | 158 | 181 | 169.1 (10.8) |
| Residual limb side | R | L | R | L | R | L | |
| Years of using prosthetic foot | 21 | 42 | 17 | 30 | 48 | 6 | 27.3 (15.8) |
| Type of prosthetic foot used | Pro-Flex® XC | AllPro fillauer | Pro-Flex® XC | Pro-Flex® XC | Triton | Rush Lo-Pro | |
| MFCL | K3 | K4 | K3 | K3 | K2 | K2 | |
| Average daily walking speed (km/h) | 4.2 | 4.0 | 6.1 | 4.0 | 4.1 | 4.1 | 4.4 (0.8) |
| Test Items | Control | ELS-Foot | F | p | h2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mobility Function | TUG (s) | 9.62 ± 0.60 | 9.75 ± 1.97 | 0.91 | 0.02 * | 0.01 | |
| FSST (s) | 9.75 ± 1.87 | 8.67 ± 2.53 | 5.15 | 0.15 | 0.72 | ||
| 10 m walk test (s) | 4.48 ± 0.06 | 5.08 ± 1.32 | 0.57 | 0.53 | 0.22 | ||
| Balance Function | BBS (score) | 56 | 56 | ||||
| Eyes-closed standing (mm) | APSI | 39.77 ± 4.52 | 32.30 ± 15.92 | 0.52 | 0.23 | 0.23 | |
| MLSI | 27.98 ± 11.47 | 23.38 ± 6.50 | 0.53 | 0.22 | 0.22 | ||
| Tandem Test (mm) | APSI | 45.58 ± 9.91 | 39.60 ± 8.25 | 0.13 | 0.75 | 0.75 | |
| MLSI | 36.54 ± 2.57 | 33.42 ± 3.84 | 0.34 | 0.43 | 0.43 | ||
| Functional Reach test (cm) | 35.03 ± 8.56 | 32.73 ± 4.69 | 0.52 | 0.55 | 0.21 | ||
| Jumping Performance | Jump height (cm) | 9.88 ± 5.12 | 10.50 ± 4.53 | 1.3 | 0.37 | 0.4 | |
| Subjective Evaluation | LCI (score) | 56 | 54.33 ± 1.53 | ||||
| ELS-Foot (Experiment) | Control | p Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intact | Residual | Intact | Residual | I | R | |
| Hip angle | ||||||
| Max flexion (°) | 32.53 ± 10.97 | 42.00 ± 5.71 | 34.56 ± 13.06 | 38.39 ± 10.22 | 0.70 | 0.27 |
| tmax flexion (%CT) | 89.33 ± 4.14 | 78.39 ± 14.15 | 82.07 ± 24.68 | 78.50 ± 14.41 | 0.56 | 0.99 |
| Max extension (°) | −7.28 ± 6.67 | 0.82 ± 10.10 | −6.51 ± 11.18 | −5.13 ± 12.16 | 0.88 | 0.08 |
| tmax extension (%CT) | 53.17 ± 2.67 | 50.72 ± 1.91 | 53.94 ± 1.32 | 50.89 ± 2.17 | 0.40 | 0.91 |
| ROM (°) | 40.40 ± 7.16 | 50.73 ± 6.58 | 45.97 ± 9.43 | 49.22 ± 7.33 | 0.13 | 0.67 |
| Knee angle | ||||||
| Max flexion (°) | 48.33 ± 13.00 | 39.96 ± 19.01 | 55.53 ± 13.59 | 57.17 ± 8.38 | 0.003 | 0.03 |
| tmax flexion (%CT) | 73.11 ± 2.83 | 71.06 ± 3.70 | 73.44 ± 1.56 | 69.83 ± 4.83 | 0.74 | 0.70 |
| Max extension (°) | −9.48 ± 11.71 | −2.03 ± 10.49 | −3.32 ± 8.39 | 0.31 ± 8.43 | 0.20 | 0.53 |
| tmax extension (%CT) | 60.67 ± 29.15 | 52.17 ± 16.92 | 50.94 ± 35.93 | 70.94 ± 26.79 | 0.19 | 0.14 |
| ROM (°) | 59.35 ± 6.94 | 48.36 ± 19.53 | 62.05 ± 14.39 | 63.93 ± 11.03 | 0.47 | 0.02 |
| Ankle angle | ||||||
| Max dorsiflexion (°) | 15.79 ± 7.57 | 3.74 ± 2.89 | 17.40 ± 4.62 | 21.34 ± 5.43 | 0.40 | 0.001 |
| tmax dorsiflexion (%CT) | 59.53 ± 13.51 | 39.00 ± 11.84 | 52.87 ± 4.60 | 50.73 ± 3.42 | 0.24 | 0.06 |
| Max plantarflexion (°) | −12.17 ± 9.39 | −2.31 ± 5.00 | −13.41 ± 5.55 | −0.71 ± 2.14 | 0.60 | 0.55 |
| tmax plantarflexion (%CT) | 66.80 ± 2.78 | 64.53 ± 13.92 | 54.20 ± 27.53 | 14.27 ± 13.86 | 0.36 | 0.01 |
| ROM (°) | 28.25 ± 3.65 | 8.04 ± 3.09 | 30.82 ± 1.49 | 23.30 ± 5.16 | 0.21 | 0.01 |
| ELS-Foot (Experiment) | Control | p Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intact | Residual | Intact | Residual | Intact | Residual | |
| Power (W/kg) | ||||||
| Hip | ||||||
| Max generation during pre-swing | 1.33 ± 0.30 | 1.54 ± 0.69 | 1.53 ± 0.31 | 2.41 ± 0.72 | 0.29 | 0.005 |
| Max absorption during stance | −0.97 ± 0.57 | −1.29 ± 0.41 | −1.21 ± 0.47 | −1.53 ± 0.78 | 0.55 | 0.30 |
| Knee | ||||||
| Max generation in single support | 0.85 ± 0.40 | 0.61 ± 0.26 | 1.22 ± 0.43 | 0.62 ± 0.12 | 0.21 | 0.96 |
| Max absorption during stance | −2.27 ± 0.69 | −2.14 ± 1.16 | −2.53 ± 1.11 | −3.55 ± 0.85 | 0.46 | 0.04 |
| Ankle | ||||||
| Max generation | 2.94 ± 1.49 | 0.22 ± 0.08 | 3.31 ± 1.32 | 2.52 ± 0.58 | 0.39 | <0.001 |
| Max absorption | −0.84 ± 0.38 | −0.18 ± 0.10 | −0.89 ± 0.26 | −1.44 ± 0.45 | 0.80 | 0.002 |
| Moment (N·m/kg) | ||||||
| Hip | ||||||
| Max extension | 0.86 ± 0.24 | 0.64 ± 0.14 | 0.95 ± 0.16 | 0.69 ± 0.22 | 0.52 | 0.61 |
| Max flexion | −0.86 ± 0.56 | −0.77 ± 0.39 | −1.19 ± 0.54 | −1.45 ± 0.43 | 0.46 | 0.02 |
| Knee | ||||||
| Max extension | 0.27 ± 0.11 | 0.40 ± 0.24 | 0.54 ± 0.24 | 0.53 ± 0.20 | 0.10 | 0.26 |
| Max flexion | −0.54 ± 0.17 | −0.44 ± 0.22 | −0.58 ± 0.20 | −0.49 ± 0.22 | 0.76 | 0.69 |
| Ankle | ||||||
| Max plantarflexion | 1.17 ± 0.58 | 0.37 ± 0.16 | 1.27 ± 0.23 | 1.12 ± 0.54 | 0.58 | 0.01 |
| Max dorsiflexion in loading response | −0.12 ± 0.06 | −0.39 ± 0.19 | −0.16 ± 0.10 | −0.36 ± 0.46 | 0.36 | 0.78 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, Q.-Q.; Yick, K.-L.; Li, C.-H.; Tse, C.-Y.; Hui, C.-H. Biomechanical Evaluation of Elliptical Leaf Spring Prosthetics for Unilateral Transtibial Amputees During Dynamic Activities. Technologies 2025, 13, 129. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies13040129
Shi Q-Q, Yick K-L, Li C-H, Tse C-Y, Hui C-H. Biomechanical Evaluation of Elliptical Leaf Spring Prosthetics for Unilateral Transtibial Amputees During Dynamic Activities. Technologies. 2025; 13(4):129. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies13040129
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Qiu-Qiong, Kit-Lun Yick, Chu-Hao Li, Chi-Yung Tse, and Chi-Hang Hui. 2025. "Biomechanical Evaluation of Elliptical Leaf Spring Prosthetics for Unilateral Transtibial Amputees During Dynamic Activities" Technologies 13, no. 4: 129. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies13040129
APA StyleShi, Q.-Q., Yick, K.-L., Li, C.-H., Tse, C.-Y., & Hui, C.-H. (2025). Biomechanical Evaluation of Elliptical Leaf Spring Prosthetics for Unilateral Transtibial Amputees During Dynamic Activities. Technologies, 13(4), 129. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies13040129







