1. Introduction
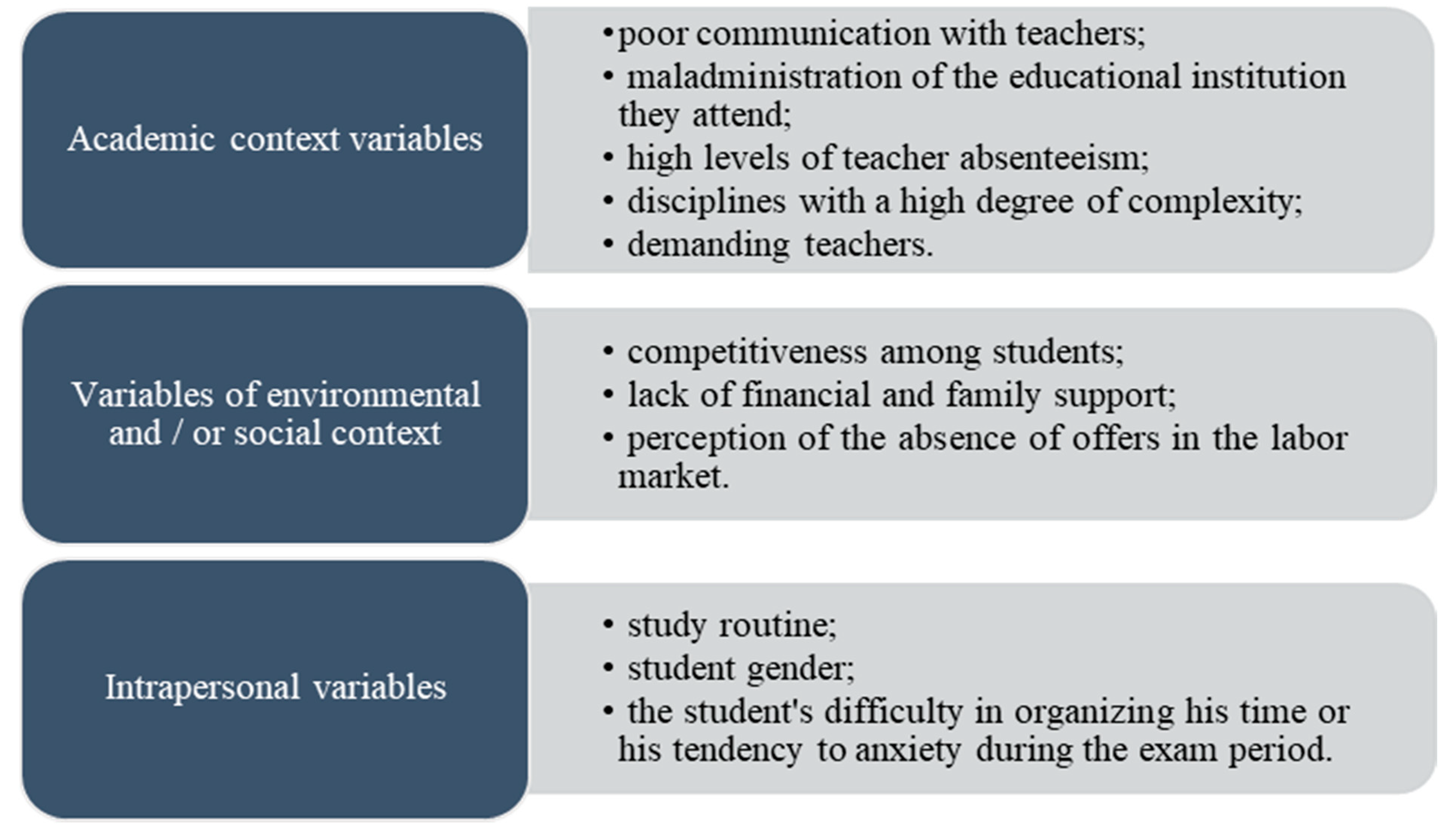
All individuals need to acquire fundamental knowledge and skills throughout their lives, and in particular, to exercise a profession. In an increasingly demanding world, the attendance of higher education is, for many, essential. However, nowadays, there are high levels of stress associated with university life and the environment of higher education institutions [
1], and university students, exposed to highly competitive environments and sometimes precarious working conditions (in the case of student workers), are among the large portion of society that suffers from this complex state of mind.
According to [
2], it seems frequent that, when entering university, students start by feeling only low levels of stress, caused, above all, by the uncertainties associated with the chosen training path and the type of instruction they face in the University education. The author states that this same stress tends, however, to increase with the progression in the academic path and with the intensification of the required work. The growing burden of study and responsibility also tends to add social and family pressures related to the desire for students to finish their study cycles successfully [
3], as well as pressures derived from economic factors, cultural factors, and even aspects related to the personality of each student [
4].
Among the factors that cause stress in young people are the significant changes that students go through in the transition periods from primary to basic education, from basic to secondary education and, of course, from secondary to university education. It is known that it is precisely during these transition periods that students are most concerned with failure, with the future and with aspects such as the expectations of their parents, the possible end of a relationship or the distance from friends [
5], all sources of pressure that can generate conflicts within your family.
On the other hand, among the various factors that generate stress and anxiety in modern society, there are also issues related to employability, namely, the unemployment rate of individuals with a higher education degree, which can have severe social, economic, and political consequences [
6].
It is therefore imperative not only to understand what the consequences of stress are in a university context, but also to study how the growing concern of these students can cause harmful effects on their academic performance.
It is known that, today, one of the most common negative effects in the university community is academic burnout [
7,
8], which is a response to stress related to this specific environment, and which affects “the development, understanding and satisfaction of the student with their education and academic life” ([
9], p. 4).
The academic burnout syndrome can be understood as the state in which a person is when subjected to long periods of work and stress, particularly caused by the questionable working conditions that he faces in the environment of the university institution in which he is inserted. These conditions can materialize in the lack of resources, in the high competitiveness among colleagues and in so many other factors that negatively influence the performance of any activities carried out in this area [
10].
Now, all the peculiarities inherent to university life can cause students to develop syndromes such as burnout, directly associated with fatigue and emotional exhaustion [
11], or other disorders of psychological well-being, related to the level of happiness and ideal personal development of students [
12], a path that, in turn, must be free of psychological diseases and that implies reaching its full potential.
In the specific case of burnout, the student ends up facing academic life feeling disinterest and frustration, which, according to [
4], has physical and emotional manifestations that are often accompanied by evasive behaviors and symptoms that mirror this discomfort. Some of these symptoms are identified: constant tiredness and fatigue; mental exhaustion; lack of ability to nurture their personal relationships; social distancing; complex mood states (such as anxiety, irritability and, in some cases, mild depression); difficulty in being focused or attentive during any task; weight loss and muscle spasms; hormonal and metabolic disorders; allergies and migraines; and insomnia and abuse of psychotropic and narcotic substances, alcohol or other drugs [
10].
As can be seen from the symptoms linked to the aforementioned physical and psychological suffering, burnout is a worrying state of health, with many harmful effects [
13]. Many of these symptoms are associated, in the case of university students, with a worse understanding of the subjects taught, with the low expectations of these students, with the (eventual) failure to obtain the desired academic degree and with the growing tendency to abandon the professional career for which the degree was initially chosen, as mentioned by authors such as [
14,
15].
However, and although it is difficult to avoid stress in some scenarios, certain authors, such as [
5], believe that it is possible to learn to live with it, reducing the harmful social consequences and the pathologies that so often result from it.
In this sense, higher education institutions have an essential role in preserving the health of their students, since they are the key element in the higher education sector. Students participate in the process of producing scientific knowledge and are, at the same time, users of the teaching processes involved in it, representing an important part of today’s society, considered to have a critical spirit and creativity [
5].
Study Objectives and Research Questions
In view of the introduction above, with regard to burnout, the aim of this study is to fill a gap in the scientific literature on this topic. Thus, an analysis of academic burnout in a Portuguese public university is carried out and the frequency with which university students of that institution take medication, from multivitamins to stimulants and/or hypnotics, hypnotics are sleeping pills [
16], is investigated in order to try to respond to the demands inherent to that environment.
When tracing the current scenario, it appears that the impact of academic burnout is one of the main factors that affect the professional and personal success of students. For this reason, it is intended to propose, following this analysis, some important recommendations to reduce burnout and to improve the quality of life of students, through the implementation of reforms in higher education.
Ref. [
17] refer that, in an empirical study, it is crucial to clarify the research question that is intended to be answered and that will lead to the research work. With this in mind, in order to achieve the empirical knowledge objectives listed above, the following research question are defined: ”Do students at the Portuguese public university experience burnout and take or have they taken any medication during their academic career?”.
The subject of the present investigation is relevant, since, in Portugal, a significant number of investigations directed to this theme has not been carried out, still less focusing on the public institution studied herein, according to the research carried out in the database SciVerse Scopus (Elsevier) (bibliographic database). Its relevance is also shown by the growing challenge that burnout and taking medication represent for universities, as will be seen below. Both phenomena have relevant economic and social implications, since students who are in a state of burnout are more likely to give up their studies and, therefore, will not be able to make a good contribution to society, as they will not develop their skills and capabilities to their full potential.
In this sense, the main research objectives of the present study are
- (1)
quantify the degree of academic burnout among students at the Portuguese public university;
- (2)
assess the prevalence of taking antidepressant, anxiolytic, multivitamin, stimulating and/or hypnotic medication among students at the Portuguese public university, during their academic career;
- (3)
list the main factors that determine the taking of the same medication;
- (4)
to analyze the relationship between the sociodemographic characteristics of the community under study and the academic burnout experienced by it;
- (5)
identify the way students perceive academic burnout and taking medication throughout their university career, identifying the sensations they try to reduce by taking medication;
- (6)
to propose some important solutions to reduce burnout, as well as improve quality of life and increase student satisfaction;
- (7)
understand how researchers in the field interpret burnout and academic burnout;
The objectives are achieved through the application of a quantitative data collection methodology, more precisely through the application of a questionnaire to students of the Portuguese public university under analysis and through a literature review on the subject, based on a previous documentary survey.
4. Materials and Methods
We shall now present the methodology and procedures adopted in the present study.
Thus, the present work follows a quantitative data collection methodology, more precisely through the application of a questionnaire to students of the Portuguese public university in question.
The literature review on the topic was made based on a previous documentary research.
The objective of the study was to verify how many students experience academic burnout and take (or have already taken) medication due to the requirements of the academic environment.
In the first question of the questionnaire, it was questioned whether the participants studied (or not) at the analyzed public institution. If the participants did not study at that institution, they were sent to the end of the questionnaire and could not answer any more questions. Only participants who studied at the public institution analyzed could complete the entire questionnaire and were sent to the following questions.
The sample of this study is non-probabilistic and is also a convenience sample (not entirely random as the authors used their connections and networks to reach as many students as possible, in the Portuguese public university, having also been aided by various student bodies and associations, as described below); its approach was intended to provide a broad view of the academic environment in question, in order to achieve the objective of the study.
4.1. Participants
In total, 207 students from the analyzed university participated in the study, who were asked to answer a questionnaire, of which, 90% of the participants were between 18 and 25 years old and about 8% were between 26 and 35 years old, with about 31% of the participants being male and 69% female. It should also be noted that 91% of respondents were of Portuguese nationality, and 100% were resident in Portugal, with around 74% attending the university under analysis and the remaining 26% of respondents attending polytechnics at the same institution (the institution has four polytechnics). Of these students, the majority, 61%, have a first cycle (degree).
Regarding the study area, it was decided to divide the courses into four main study areas, namely, Biological Sciences, Health Sciences, Exact Sciences, and Human/Social Sciences, to facilitate the interpretation of the results by the reader, as well as the statistical analysis, and in order to meet the study carried out by [
88], with whose investigation it is intended, in the end, to compare the results.
Thus, most students, about 32%, attend courses related to the area of Human/Social Sciences, 28% attend courses in the area of the Exact Sciences, 23% in the area of Biological Sciences, and about 17% are in the Health Sciences area. Most students, 29%, are in the 1st year and around 24% are in the 2nd year of higher education (in their degree). About 56% of the students have an arithmetic average of between 13 and 15.
Only 27% of the surveyed students had a paid professional occupation. Most of the students in this study, 33%, have a gross monthly income between 1000 and 1499 euros. However, about 25% have a gross monthly income between 1500 and 2499 euros and 24% have an income between 600 and 999 euros.
4.2. Data Collection Instruments
In order to understand if university students of the chosen educational institution experience academic burnout, as well as if they take (or have already taken) medication during their academic career and to identify their feelings regarding the course and the institution they attend, a questionnaire was applied to university students from a Portuguese public higher education institution. The survey consists of 55 closed-answer questions and four open-answer questions (
Appendix A).
This questionnaire uses some questions from the Maslach Burnout Inventory—Student Survey (MBI-SS), adapted by [
51], translated and adapted to the Portuguese language by [
31]. It is a self-report scale consisting of 15 questions referring to the three subscales of academic burnout (emotional exhaustion, disbelief, and professional effectiveness) and the feelings and emotions that students experience in the school context.
Here, respondents express how often they feel what each of the 15 questions suggests, on an ordinal seven-point scale, which ranges from 0, “never” to 6, “always”. The reliability of the factors was assessed by measuring the internal consistency of the Cronbach’s alpha coefficient (α) and, in its entirety, the MBI-SS scale presents an α = 0.79 [
89].
Since the central point of the scale is “regularly”, the total of the burnout score was calculated using the average of the questions of the three subscales, considering that the students presented burnout when this total score was higher than three, as defended by [
88]. Regarding the three subscales, for the purposes of this study, questions 38 to 42 refer to the emotional exhaustion subscale, questions 43 to 46 refer to disbelief and, finally, questions 49 to 54 refer to professional effectiveness.
In the subscale dedicated to professional effectiveness, the higher the values, the lower the levels of burnout; that is, the higher the values, the lower the ineffectiveness of individuals. For this reason, the response scale for the items in this subscale has been inverted, as suggested by the study by [
90] and as is done in the study by [
88], a study with which we intend, in the final stretch, to compare the results of the present study. The remaining questions were elaborated from scratch, based on the consulted literature.
It should also be noted that, initially, sociodemographic information was collected through the questionnaire.
4.3. Data Collection Procedures
In the study, a questionnaire on burnout and taking medication was distributed to university students.
After elaborating the questionnaire, tests were carried out on the data collection instruments, asking education specialists to evaluate the questionnaire in terms of the time to fill it in and the clarity of the questions, and they were also asked whether or not they had learned anything useful in order to understand whether it would be necessary to make any changes to the questionnaire.
After validation and the elaboration of the necessary corrections, the associative nuclei of the various courses, sports nuclei and administrative services of the university and the polytechnics under analysis were contacted, as well as organizations created in the academic environment, in order to request the dissemination of the questionnaire to the students. The questionnaire was disseminated through social networks via the centers and services mentioned.
It should also be noted that the data collection was carried out respecting all applicable ethical principles, especially with regard to the anonymity of the respondents and the confidentiality of the investigation. There was an incentive for student participation through the drawing of tickets for the RFM SOMNII summer festival at Praia do Relógio in Figueira da Foz (a three-day general pass).
The questionnaire was online (online Google form format) since 30 March 2020 and until 30 April 2020, having obtained 207 responses, all of which valid.
4.4. Statistical Procedures
To perform the analysis of the quantitative data, the program IBM SPSS Statistics, version 25 was used. Inferential statistics were used, namely, Student’s t-test and one-way ANOVA (parametric tests), Spearman’s correlation coefficient, and the Chi-square test to test previously defined research hypotheses.
The variables were characterized using the mean and standard deviation. The level of significance was set at a value of
p < 0.05. Regarding Spearman’s Correlation Coefficient, it is also worth noting that [
91] refers that correlations above 0.40 are considered strong, while correlations that vary between 0.20 and 0.40 are considered moderate. Correlations below 0.20 are considered weak. This was precisely the criterion considered in the analysis carried out in the present investigation.
5. Results
As the values of the asymmetry (
Sk = 0.219) and kurtosis (
Ku = −0.522) coefficients of the burnout score are less than one, it is possible to assume that the data have an approximately normal distribution, as can be seen in
Table 1. Thus, parametric tests can be used, such as Student’s
t-test and ANOVA [
92,
93].
Regarding the reliability analysis, the Alfa Cronbach coefficients were calculated for the burnout score (α = 0.901) and for the respective subscales: emotional exhaustion (α = 0.929), disbelief (α = 0.916) and professional effectiveness (α = 0.830).
The values of the coefficients are above the cut-off line (0.70) and the values of the item-total correlations corrected above 0.30. It was also verified whether the output of an item improved the internal consistency of the scale (Cronbach’s Alpha without the item), as suggested by [
92], as shown in
Table 2.
As mentioned, it was considered that students had burnout when the average score of all questions was higher than three. It is concluded that, in the total sample, 29% of the students surveyed have burnout. It is also observed that about 37% of the students are cognitively and emotionally exhausted, 17% have a cynical attitude towards their studies, colleagues and teachers, and about 36% feel incapacity and professional inefficiency.
5.1. Relationship between Burnout and Sociodemographic Variables
Student’s t-test was used to verify if there were differences in academic burnout due to sociodemographic variables.
There are no statistically significant differences between men (M = 2.54; SD = 0.94) and women (M = 2.45; SD = 0.92) regarding burnout (p = 0.531). Thus, it is concluded that sex does not influence the levels of burnout.
In order to carry out this analysis, age was recoded in only two classes: from “18 to 25 years” and “26 years or more”, since the respondents were concentrated in the greatest number in these age groups and to facilitate the organization of data; additionally, there are also no statistically significant differences with regard to burnout according to the age group (p = 0.156), which means that students between 18 and 25 years old do not have higher levels of burnout (M = 2.51; SD = 0.91) than students aged 26 or older (M = 2.20; SD = 1.01).
To carry out this analysis, the variable educational qualifications was recoded into two categories: “Degree” and “Other higher qualifications”. With regard to educational qualifications, the differences are close to statistical significance (p = 0.065), that is, there seems to be a trend towards higher levels of burnout in undergraduate students than in students of other study cycles. However, it cannot be considered that there are statistically significant differences between the first cycle (M = 2.57; SD = 0.96) and the academically higher study cycles (M = 2.33; SD = 0.85), in the levels of burnout.
Finally, note that there are differences in academic burnout depending on the student’s professional situation, and students who do not work (M = 2.56; SD = 0.94) have higher levels of burnout (p = 0.046) than students who are student workers (M = 2.27; SD = 0.85).
5.2. Relationship between Burnout and Student Participation in Extracurricular Activities and Physical Exercise
Student’s t-test was used to verify if there were differences in academic burnout due to the participation of students in extracurricular activities and due to the practice of physical exercise.
As it turns out, there are statistically significant differences in academic burnout according to the participation of students in extracurricular activities (p = 0.015). Students who do not participate in extracurricular activities have higher levels of burnout (M = 2.70; SD = 0.96) than students who participate in these activities (M = 2.37; SD = 0.89).
As far as physical exercise is concerned, there are statistically significant differences in academic burnout (p = 0.021). Students who participate in sports activities show lower levels of burnout (M = 2.42; SD = 0.87) than those who do not practice any type of physical exercise (M = 2.70; SD = 1.07).
5.3. Relationship between Burnout and the Transition from Secondary Education to Higher Education, Choice of Course, and Professional Future
Student’s t-test was used to check if there were differences in academic burnout regarding the transition from secondary education to higher education and the choice of course and professional future.
In fact, there are statistically significant differences in burnout due to the students’ perception of the negative impact of sudden freedom brought on by the transition from secondary education to higher education (p = 0.015). Students who consider that this freedom has affected them negatively while students have higher levels of burnout (M = 2.88; SD = 0.84) than students who consider that this aspect has not affected them negatively (M = 2.42; SD = 0.92).
In addition, there are statistically significant differences in academic burnout according to the reasons that led students to choose the course they attend. Students who chose the course they attend based on the employability rate (M = 2.49; SD = 0.86) do not have higher levels of burnout (p = 0.917) than those who did not choose this option (M = 2.47; DP = 0.95). However, students who choose the course by vocation and/or taste (M = 2.42; DP = 0.92) have lower levels of burnout (p = 0.038) than those who did not choose the course for this reason (M = 2.80; SD = 0.93).
There are also statistically significant differences in the levels of burnout according to the uncertainty felt in relation to the professional future (p = 0.004). After all, students who feel uncertain about their future work show higher levels of burnout (M = 2.56; SD = 0.93) than those who do not feel any uncertainty (M = 2.04; SD = 0.79).
5.4. Relationship between Burnout and the Existence of a Recent Diagnosis of Depression, Intake, and Type of Medication
Student’s t-test was used to verify if there were differences in academic burnout due to the existence of a recent diagnosis of depression and taking medication.
Therefore, it was observed that there are statistically significant differences in burnout due to the presence of a diagnosis of depression (p < 0.001), since students who were recently diagnosed with depression have a higher prevalence of this syndrome (M = 3.40; SD = 0.73).
There are also statistically significant differences in academic burnout due to taking medication (p < 0.001), with students taking medication having higher levels of burnout (M = 2.72; SD = 0.90). Students who take antidepressants have higher levels of burnout than those who do not take this type of medication (p < 0.001). In turn, students who take anxiolytics (p < 0.001), food supplements/multivitamins (p = 0.024), and sleeping medication (p = 0.046) have higher levels of burnout compared to those who do not take this type of medication.
In addition, there are statistically significant differences in academic burnout according to the reason for taking medication. For example, students who take medication to combat symptoms of emotional exhaustion (p < 0.001) and to improve their academic achievement (p = 0.010) have higher levels of burnout when compared to students who do not take it for these reasons.
It should also be noted that there are statistically significant differences in academic burnout due to the fact that students know (or do not know) other colleagues who take sleeping pills, since students who do not know colleagues who take this type of medication have higher levels burnout (p = 0.021).
5.5. Relationship between Burnout and the Tendency to Drop Out of the Course or Studies and Aspects to Improve Psychological Well-Being
Student’s t-test was used to check if there were differences in academic burnout due to the tendency of students to drop out of the course or studies and the aspects to improve their level of psychological well-being in the school they attend.
In fact, it is noticed that there are statistically significant differences in burnout according to the fact that the student has considered giving up the course or studies, concluding that students who have considered giving up the course (p < 0.001) or studies (p < 0.001) have higher levels of burnout.
There are also differences in burnout due to the aspects that students consider that would help to improve their level of psychological well-being at the university. In fact, students who report that the reduction in the number of hours of daily and weekly classes (p = 0.005), the reformulation of teaching methods (p < 0.001), and a wider range of curricular options (p = 0.048) would improve their psychological well-being have higher levels of burnout.
Regarding the option concerning the availability of other means that provide psychological support to students, the differences are close to statistical significance (p = 0.071).
5.6. Relationship between Burnout and Study Areas, Year of Higher Education and Arithmetic Mean of Course
ANOVA was used to check if there were differences in academic burnout according to the areas of study of the students, the year of higher education they attend and their arithmetic average (grades) of their course.
There are no statistically significant differences between the study areas regarding burnout (F = 1.379; p = 0.250). In other words, the study area has no influence on burnout levels, which means that students in the areas of Biological Sciences, Exact Sciences, and Health do not have higher levels of academic burnout than the rest.
In addition, there are also no statistically significant differences in academic burnout according to the year of higher education they attend. Students in the first and last years of college do not have higher levels of burnout (F = 0.776; p = 0.542), when compared to students who attend the remaining years. In other words, the year of higher education does not influence the levels of burnout.
Regarding the arithmetic mean of course, there are statistically significant differences in academic burnout (F = 3.369; p = 0.036). Thus, students with a low average, from 10 to 12 points (M = 2.71; SD = 0.98) have higher levels of burnout than students with a higher average, from 16 to 20 points (M = 2.22; SD = 0.96). In sum, the multiple comparisons tests show that there is a trend towards a decrease in burnout levels with the increase in the arithmetic mean of the course (p = 0.029).
Note, however, that, for this analysis, the arithmetic mean variable of the course was recoded into three categories: “From 10 to 12 points”, “From 13 to 15 points” and “From 16 to 20 points” given the classes in which the greatest number of responses were concentrated and to facilitate the organization of the data.
5.7. Relationship between Burnout and the Frequency with Which You Take Medication
ANOVA was used to check if there were differences in academic burnout depending on the frequency with which he takes medication.
There are statistically significant differences in academic burnout according to the frequency of taking medication (F = 5.449; p < 0.001). Multiple comparison tests show that students who take this type of medication about once a month or once a week have significantly higher levels of burnout than students who do not take it (p = 0.006).
It should be noted that in order to carry out this analysis, the variable of the frequency with which students take medication was recoded into four categories: “Only during the assessment periods”, “About once a month or once a week”, “ I do not take any medication” and “Every day” as these are the categories in which the greatest number of responses were concentrated and to facilitate the organization of the data.
5.8. Correlation between Academic Burnout and Students’ Gross Monthly Income, Frequency with Which They Practice Physical Exercise, and Their Initial Expectations Regarding the Course
Spearman’s Correlation Coefficient was used to check if there was a correlation between academic burnout and the students’ gross monthly income, the frequency with which they practice physical exercise, and their initial expectations in relation to the course.
In view of the data obtained, it was concluded that there is no statistically significant association between gross monthly income (rsp = −0.020; p = 0.776) and burnout; that is, that a lower gross monthly income is not necessarily associated with higher burnout levels.
On the other hand, there is a weak negative correlation, statistically significant, between the frequency with which students practice physical exercise and the levels of burnout (rsp = −0.170, p = 0.014); that is, the higher the frequency with which they exercise, the lesser are their burnout levels.
It can also be said that there is a moderate negative correlation, statistically significant, between the classification that students attribute to the course they entered in view of their initial expectations and academic burnout. In fact, the higher the student’s initial expectations, the lower the levels of burnout (rsp = −0.267; p < 0.001).
5.9. Correlation between Academic Burnout and the Perception of the University’s Material Conditions, the Classification Given by Students to Teachers, and Their Relationship with Them
The Spearman Correlation Coefficient was used to check if there was a correlation regarding academic burnout due to the perception, on the part of students, of the material conditions of the university attended, as well as the burnout and the classification they attribute to their teachers and their relationship with them.
There is a weak, statistically significant negative correlation between burnout and the perception of the material conditions of the university attended; that is, when students have a perception that the material conditions of their university are superior, they suffer less from burnout (rsp = −0.137; p = 0.048).
In addition, there is a moderate, statistically significant, negative correlation between burnout and the rating that students assign to their teachers (rsp = −0.349; p < 0.001). It can therefore be said that students who give teachers better ratings have lower levels of burnout.
On the other hand, there is no association between burnout and the classification that students attribute to the relationship with their teachers (rsp = 0.023; p = 0.745). This means that higher ratings regarding the relationship between students and teachers are not associated with lower levels of burnout.
5.10. Correlation between Academic Burnout and the Relationship of Students with Their Colleagues, the Ability to Withstand the Pressure of Studies, and the Classification of Their Performance
Spearman’s Correlation Coefficient was used to check if there was a correlation regarding academic burnout and the way students classify their relationship with colleagues, their ability to withstand the pressure caused by studies and the way they classify their academic performance.
There is a weak, statistically significant negative correlation between burnout and the rating given by students to their relationship with colleagues (rsp = −0.188; p = 0.007), that is, the higher the rating, the lower the levels of student burnout.
In addition, there is a strong, statistically significant negative correlation between burnout and the fact that students know (or do not know how) to withstand the pressures of their study cycle. That is, the more students think they are able to withstand the pressures of their study cycle, the lower the levels of burnout (rsp = −0.522; p < 0.001).
There is also a moderate, statistically significant negative correlation between burnout and the classification of students’ academic performance. This means that the lower the rating of their academic performance, the higher the levels of burnout (rsp = −0.366; p < 0.001) that they suffer.
5.11. Relationship between Medication Intake and Course Arithmetic Mean
The Chi-square test was used to check if there was an association between taking medication and the course arithmetic mean (the grades of the student) (
Table 3 and
Table 4).
Degrees of freedom: 2.
Critical value from the table at the 5% level: 5.991 (which is greater than the calculated critical value 3.44).
Conclusion: there is no association between the variables. The variables are independent—there is no statistically significant relationship between the arithmetic mean of the course obtained by the students and medication intake.
6. Discussion
Among the sociodemographic variables studied, the potential effects on the burnout levels of sex (H1), age (H2), and gross monthly income (H8) were investigated based on the formulated hypotheses.
For the sample analyzed, it was not possible to attribute an influence of the gender variable to the levels of burnout. Thus, hypothesis 1 was not validated, contrary to the results of [
9,
88]. Note, however, that the former found only marginally higher levels of burnout in females, and that the latter attributed risk factors associated with personality characteristics to the sexes, namely, greater perceived effectiveness on the part of women, and more cynical about studies by men. Although both studies may indicate an apparent trend towards their results, the influence of sex on burnout levels does not seem clear, which was also evident in the present study. To confirm this trend, further studies would be needed, with larger and standardized samples.
Additionally, the age of the students did not reveal any influence on the burnout levels, although the literature refers that one of the groups most affected by the syndrome is the millennials [
94]. In this study, higher levels of burnout were not found among students aged 18 to 25 years, when compared with those of students aged 26 or older, so research hypothesis 2 was not validated. Remember that the definition of millennial is not consensual, so the age range considered in this study may not be representative of that generation. On the other hand, the entire sample consisted of university students and, regardless of the age range referring to millenials, not all will be university students, so it would be necessary to extend the study universe to extra-university realities in order to be able to correctly measure the levels of the generation as a whole.
According to the research hypothesis 8, it was expected that lower gross monthly income would be associated with higher levels of burnout, as suggested by [
33], who emphasize that the lack of financial support is a variable associated with academic burnout. Studies such as those by [
32] point to the fact that the related social and professional pressures with higher education funding being a factor that makes university students more vulnerable to academic burnout. However, this was not verified in this study, since a lower gross monthly income was not significantly associated with higher levels of burnout; thus, not validating hypothesis 8. The financial support that the University in analysis provides and the fact that it is located in a geographical area where the cost of living is not high can explain this result.
With regard to academic variables, the educational qualifications (H3), the study areas (H4), the year of higher education attended (H5), the arithmetic average of the course (H6) and the professional situation were considered for analysis (H7).
No significant differences were found in the burnout syndrome between educational qualifications, areas of study or year of higher education attended; therefore, hypotheses 3, 4, and 5 were not validated. The fact that there are no significant differences in relation to educational qualifications and the year in higher education can be explained by the possible uniformity of academic load throughout the university course; that is, students continue with the same workload and suffer from stress throughout the course. As it turned out, in the course of their training, it is understood that students are, on the one hand, reformulating their goals, and, on the other, being confronted with the reality of their course and the profession they intend to exercise as mentioned by the authors [
69,
71,
95]. These perceptions that are being fed may lead students to continually renew the pressure on themselves, or that, on the contrary, they will gradually lose their motivation and enthusiasm for the path they have been following. In any case, stress levels can be replenished and thus maintained, for different reasons, throughout the course.
Ref. [
88] found that students of courses in the area of Biological and Exact Sciences are the ones who reveal the highest levels of burnout among the various areas of study and that those in the Humanities are those who suffer less from burnout; this was not evidenced by the present study. This result can be explained by the distribution of the study areas in the sample, it being verified that the majority of respondents, about 32%, were studying in the area of Human/Social Sciences, 28% in the area of Exact Sciences, around 17% in the area of Health Sciences and the remaining 23% were in areas related to Biological Sciences. In the study by [
88], 33% attended courses in the Humanities area, about 30% in the Exact Sciences area, 27% in the Health Sciences area, and only about 10% in the Biological Sciences area. The main differences in the two distributions are, therefore, in the areas of Health Sciences and Biological Sciences; that is, in the present study there was an excess of 13% of students in the area of Biological Sciences and 10% less in the area of Health Sciences.
As for the arithmetic mean, it was found that students with a lower average, from 10 to 12 points, have higher levels of burnout than students with higher averages, from 16 to 20 points. This result validates hypothesis 6 and is in line with what is reported by the authors [
45,
46], who indicate that the syndrome is related to poor cognitive performance and decreased academic achievement. It is understandable that this is the case, since academic burnout, as we have seen, is characterized precisely by a lack of motivation to study and perform the required tasks, in addition to physical symptoms such as constant tiredness and fatigue and migraines, thus impacting the output of students who suffer from it.
The influence on burnout levels was also analyzed according to the professional situation, verifying that students who do not work have higher levels of burnout than those who are worker-students. Thus, hypothesis 7 has not been validated. It would be plausible to consider that student workers could have higher levels of burnout, compared to students who do not engage in any paid professional activity, because they have to reconcile their studies with their profession, and are therefore faced with more challenges. However, according to the results obtained in the present study, and since no references to similar analyses were found in the revised literature, the possibility of students with worker-student status having better developed or adapted mechanisms such as coping and emotional intelligence, managing to better manage stress in relation to students who have less challenges to manage.
In addition to the sociodemographic and academic variables analyzed above, we tried to understand the impact that students’ perceptions about the transition from secondary to higher education, and their options regarding the course, can have on the level of burnout, considering that the transition experience is an imminent cause of stress during the first year of post-secondary studies [
28]. In fact, it was proven that there are differences in the manifestations of academic burnout due to the students’ perception about the negative impact of the sudden freedom brought by the transition from secondary education to higher education, thus validating hypothesis 12. Students who consider that this freedom has affected them in a negative way have higher levels of burnout, as [
28] refer. Freedom brings responsibility and, in this sense, young people may not yet be mature enough to properly manage emotions, relationships and even studies, without a support network as tight as up until then; that is, there are lower levels of emotional intelligence and resilience that, as mentioned earlier, act as a kind of protection against the syndrome.
The conditions of the educational institution itself are also pointed out in the literature as factors related to the burnout syndrome [
9,
10,
33]. It was found, in the present investigation, that students who have a perception that the material conditions of their university are superior suffer less from burnout. Additionally, the higher (better) the relationship with their colleagues, the lower the burnout levels of students. Thus, hypotheses 15 and 18 were validated, which is in agreement with the conclusions of [
36], regarding the contribution to the appearance of burnout of factors such as reduced solidarity and companionship, competition and disagreements with colleagues. However, higher classifications regarding the relationship between students and teachers were not, in this study, associated with lower levels of burnout, contrary to what was indicated by the authors [
36], who report that poor relationships between students and teachers and the lack of feedback from teachers, are academic social risk factors that can precede or predict the appearance of burnout. Therefore, hypothesis 17 was not validated.
Another factor that is pointed out in the literature as a predictor of academic burnout felt by students is the competence of their teachers [
96]. Further, in the present study, it was concluded that students who attribute better ratings to their teachers show lower levels of burnout, which validates hypothesis 16. Students who feel that teachers are not competent may tend to develop a more cynical attitude towards the course, and/or become discouraged, feeling that the discipline or course does not meet expectations, which, in turn, may influence your motivation and commitment to studies. Students who are unmotivated and with worse academic performance are more susceptible to developing the syndrome.
The impact that the reasons for choosing the course can have on the levels of burnout was also analyzed, concluding that the students who chose the course they attend taking into account the employability rate do not present significantly higher levels of burnout than those for which the choice did not consider this criterion. However, students who chose the course by vocation and/or taste have lower burnout levels than those who did not choose the course they are attending for that reason. Therefore, hypothesis 13 was partially validated, and the assumption that the vocation or taste for the course may be linked to greater motivation on the part of the students, and thus constitute a protective factor against this syndrome as mentioned in the literature seems plausible. Remember that [
95] affirm that the choice of the profession to be exercised is not fully conscious, ending up not being a factor directly linked to the students’ decision. Factors which do weigh, the authors point out, for example, are economic reasons, reputation or the desire to help others.
In the present study, the correlation between burnout and the fact that students feel they know (or not) how to withstand the pressures of their study cycle was also assessed. The more students think they are able to withstand the pressures of their study cycle, the lower their burnout levels. In addition, students who report that the reduction in the number of hours of daily and weekly classes, the reformulation of teaching methods and a wider range of curricular options as factors that would improve their psychological well-being, in the university context, present greater burnout levels. Hypotheses 28 and 30 have therefore been validated.
Ref. [
96] refer to the low expectations of students with regard to their course as one of the factors that most result in burnout in Portuguese university students. Ref. [
95] state that, by understanding, during their academic career, that the course or future profession does not meet the expectations created, the student develops a sense of disappointment that, consequently, can also lead to frustration, discontent and stress, with a tendency to increase continuously, and lead to a burnout scenario. If the scenario gets worse, and if effective coping strategies and their implementation are neglected, a burnout scenario will most likely arise. Similar results were obtained in the present study, since it was concluded that the higher the initial expectations of the student, the lower the levels of burnout, therefore hypothesis 14 was validated.
Issues related to employability and the perception of the absence of offers in the labor market were also pointed out as factors that generate stress and anxiety in modern society and associated with academic burnout [
6,
33]. The present study also found that students who feel uncertain about their future work show higher levels of burnout than those who do not manifest this uncertainty, thus validating hypothesis 19. This uncertainty felt by students may be partly explained by the crisis that we are facing, as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic, namely, regarding its repercussions in the labor market, in which it was already difficult for graduates to enter.
In Portugal, young people have more and more academic training, according to the data in [
97], which show that, in 2019, there were 83,193 individuals with recent degrees (students who completed their bachelor’s, master’s, doctorate, or specialization course in that year). In Portuguese society, until the 1980s, having a higher education was associated with ensuring a well-paid job. However, the widespread entry into higher education and the resulting increase in graduated individuals caused significant changes in this scenario. Portugal has a small and diversified economy, there is little labor, and this reality, combined with constant advances in technology and automation, contributes to the difficulty of finding jobs by young people. Most young people are unable to obtain employment in their area of training, or if they do, it is poorly paid. Nowadays, the number of young people who have a regular full-time job is decreasing, and those who have it are hardly able to achieve a degree of security in the long term; that is, a large part survives through occasional jobs in the short term (part-time), with little or no guarantees and contractual rights, which results in the possibility of losing jobs unexpectedly due to economic crises and/or the employer (being fired with no forewarning). These situations provoke feelings of insecurity, uncertainty and fear in this generation, with serious psychological consequences. Due to the social and economic aspects mentioned, most young people postpone the decisions and responsibilities inherent in adult life, remaining for long periods semi-dependent on their parents, with all the social and personal repercussions that arise from it [
98]. According to [
99], the youth unemployment rate in the European Union increased by two percentage points between 2019 and 2020, reaching 17%.
Other factors considered important in preventing burnout are extracurricular activities and physical exercise. This study points in this direction, since it was concluded that students who participate in extracurricular activities or practice physical exercise have lower levels of burnout, and, in addition, the greater the frequency with which they practice physical exercise, the lower these levels are. These results allow us to validate the research hypotheses 9, 10 and 11, and are congruent with those obtained by [
36], who showed that non-participation in cultural or recreational activities can precede or predict the appearance of burnout.
As already mentioned, burnout syndrome is related to depressive symptoms [
47] and even suicidal thoughts [
13]. The analysis of the data in the present study showed that students who were recently diagnosed with depression have higher levels of burnout, so hypothesis 20 was validated.
The need to take medication was pointed out by [
96] as a predictor of academic burnout experienced by university students. In the present study, it was found that students who take medication show higher levels of burnout, and those who take it about once a month or once a week have significantly higher levels of burnout than students who do not take any medication. Regarding the type of medication, those who take antidepressants have higher levels of burnout than those who do not; those who take anxiolytics or sleeping medication, or food supplements/multivitamins, have higher levels of burnout compared to those who do not take this type of medication. In this study, it was also determined that students who take medication to combat the symptoms of emotional exhaustion (related to burnout) and to improve their academic performance have higher levels of burnout when compared to students who do not take it for these reasons. Thus, research hypotheses 21, 22, 23, and 24 were validated. This result can be justified by the social pressure that is exerted by society and by family members (related to the desire that the students conclude their study cycles successfully), and also by the increasing responsibility [
3], economic pressures, cultural, and even aspects related to the students’ personality [
4]. It would be pertinent to understand if the levels of burnout are higher in students who take more than one type of medication at the same time.
It should also be noted that students who do not know other colleagues who take sleeping medication have been shown to have higher levels of burnout, which validates hypothesis 25. A possible explanation for these results may be the fact that difficulty in sleeping and/or the medication taken are felt as taboo topics, and not knowing specific coping strategies via such medication may be detrimental (given the importance of a good night’s sleep).
Note, however, that no relationship was found between the arithmetic mean obtained by students and taking medication. Therefore, hypothesis 26 has not been validated. Considering, as indicated above, that taking medication can be enhanced by the social pressure exerted, this result can be justified by the idea that this pressure is exerted on students whatever their course average; that is, if the student has a lower average, you will feel pressure to go up; if it is average, you may be required to improve it to reach the highest level; if it is already high, you will feel pressure to maintain it.
Ref. [
96] point out the student’s subjective academic performance and the intention to give up his study cycle as relevant predictive factors for the academic burnout felt by students. In this sense, it was found, in the present study, that students who consider giving up the course or studies have higher levels of burnout, and therefore hypothesis 27 was validated. Regarding the classification of their academic performance, it was proved that the better they classify their academic performance, the lower the burnout levels of the students, which validates the hypothesis 29.
Finally, hypothesis 30 was also validated. There are differences between academic burnout and the fact that students consider that improving some aspects of the university’s functioning would help to increase their level of psychological well-being, with students considering that reducing the number of hours of daily and weekly classes, the reformulation of teaching methods, a wider range of curricular options, and the availability of other means that provide psychological support would improve their psychological well-being are the students who have higher levels of burnout.
7. Conclusions
Based on the results obtained, it was not possible to establish a relationship between the occurrence of burnout and sociodemographic variables, such as gender, age group, and gross monthly income, or academic variables, such as educational qualifications, areas of study, year in higher education, and the relationship with teachers.
However, there are statistically significant differences between burnout and the following factors: the arithmetic mean of the students' course; your professional situation; the way they perceive the transition to higher education; the material conditions of the educational institution; their assessment of their relationship with colleagues; the rating they attribute to the competence of teachers; the reasons for choosing the course; students' ability to withstand the pressure of their study cycle; the aspects that they believe can improve their level of psychological well-being at the university; your expectations regarding the course; uncertainty regarding the professional future; their participation in extracurricular activities; the practice of physical exercise (and the frequency of this practice); a recent depressive clinical condition; taking medication (in particular antidepressants, anxiolytics, multivitamins and/or hypnotics) and the frequency with which they take it; the reason for taking medication (alleviating symptoms of emotional exhaustion and improving school performance); the knowledge of colleagues who take sleeping medication; consider giving up the course or studies; and the way they rate their own academic performance.
In contrast, among the factors that seem to protect students from experiencing burnout are academic involvement, intrinsic motivation, coping strategies and social support, emotional intelligence, and resilience.
It should be noted that the present study showed that about 29% of the university students at the analyzed university show signs of burnout. Higher education institutions urgently need to take measures to remedy this situation, which constitutes a serious public health problem and which has several consequences, namely that of hampering the training of young people. Among these measures, rethinking, and reformulating teaching will be essential.
The results obtained provide an important practical contribution to the management of the satisfaction of university students and to improve their quality of life, since they alert to several factors that can serve as a basis for correcting failures and implementing improvements, increasing permanence and success in the analyzed higher education institution and, potentially, in other institutions.
In terms of practical contribution, it is suggested that the educational institution analyzed and the other higher education institutions implement some of the suggestions listed below to increase student satisfaction and students’ quality of life:
Reformulation of teaching methods, creating new methods of assessment (not just exams and/or tests) and promoting dynamic classes to stimulate students’ creativity and motivation (taking, for example, occasional classes outdoors or with music);
The reduction in the number of hours of daily and weekly classes; Portugal is one of the European countries where students have a greater number of hours, on average, about 21 h of classes per week (similar to Poland). The European average is only 17 h. However, there are countries in the North where these numbers are lower, for example, in Sweden (10 h) and/or Norway (13 h). However, if study time is added to this time, a national university student spends, on average, about 46 h in class and in study. Regarding worker-students, the number rises to the 63 h per week that worker-students occupy between classes, study, and their profession, which justifies that it is very hard to work and study simultaneously in such a national context [
100];
Provide a wider range of curriculum options so that students can study what they really like, and think is appropriate for their vocational pathways;
Providing more free workshops to learn how to deal with anxiety, pressure, stress, time management, as well as sessions on emotional intelligence and resilience aimed at the entire academic community;
Reduction of waiting lists for psychology appointments;
Greater dissemination of mental illness and psychology consultations;
Make the exam schedule available at the beginning of the semester, so that students can choose the assessment method in an organized manner and reduce students’ stress and anxiety during the assessment period;
Greater coordination by the university’s Rectory to avoid accumulating exams on the same day;
Have a lower load of group work and, on the other hand, more individual work, since it was an aspect mentioned by the students;
The reduction in the number of students per class in order to promote greater teacher–student interaction;
Reformulation of the program of most curricular units, giving more importance to the practical aspect of teaching, the promotion of short-term paid internships and, in general, the preparation of students for the imperfections of the working world (which is the main mission of teaching at university). In the same sense, the courses could be divided into two phases: one held at the university and the other at a company (having access to real problems), with the company paying students for their time, knowledge and availability or, alternatively, paying for their tuition fees (as occurs in Germany). This measure would increase the students' intrinsic motivation, which, as verified in the present study, is a burnout protection factor;
Consideration of student feedback regarding the topics taught and the topics not taught that may be really relevant to them;
Creation of an extracurricular physical exercise activity to promote individual and team work to relieve stress and promote interpersonal relationships;
Improving the comfort of leisure spaces and increasing the number of social spaces to relieve stress and promote interpersonal relationships;
Improving material conditions to increase comfort in classrooms, as material conditions have an influence on burnout;
Individual and group orientation programs as suggested by the authors [
57];
If the success of higher education institutions and their students is related to the well-being of teachers, it is crucial to analyze the predominance of stress and burnout in this profession to understand the problems and some of the causes behind stress and implement measures [
101].
In short, future research may relate the variables burnout and taking medication with others not addressed in this study, such as student personality traits (anxiety, rigidity, perfectionism, and self-efficacy), the social support system in which he/she is inserted, and the coping strategies used by him/her.