Abstract
Recently, there has been growing educational interest in competency. Global organizations, such as the United Nations (UN) and Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), which are leading the discourse on education reform, are undertaking the lead in spreading awareness regarding competency education. Since 2015, the number of published articles on competency education has been rapidly increasing. This paper aims to provide significant implications for creating a sustainable future of competency education. A topic modeling method was used to empirically analyze latent topics and international research trends in 26,532 articles published on competency-based education (CBE). As a result of the analysis, 15 topics were derived, including “approach to competency development.” In addition, five topics including “learning skills” and “teacher training” were found to be hot topics with the increasing article publication. The rapidly changing modern society is calling for a transformation in education. We hope that the results of this study paves the way for further research exploring new directions for education, such as competency education.
1. Introduction
Education essentially aims to cultivate competent talent under the premise of a sustainable future. Accordingly, the rapid advancement of scientific technologies, such as Artificial Intelligence, and the generalization of global issues, such as the COVID-19 pandemic, require fundamental reflection on the paradigm of education. Indeed, education necessitates a new approach for the purpose, content, and methods of education as the notion of sustainable society and competent people continue to evolve.
In response, the United Nations (UN) adopted “Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development” in 2015 as a resolution and proposed 17 sustainable development goals [1]. In the education sector, the suggested new aim for the future of education is to “ensure inclusive and equitable quality education and promote lifelong learning opportunities for all” [1]. Moreover, the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) laid out Learning Compass 2030 through the Education 2030 project, which started in 2015, saying that it is necessary to take the center of life in navigating one’s path in the rapidly changing world with increasing uncertainty [2]. The Center for Curriculum Redesign and their Partnership for 21st Century Skills also reiterate that in the 21st century, the so-called VUCA (volatility, uncertainty, complexity, and ambiguity) era asks not just for mere knowledge, but competency-based education (CBE) that ensures proper utilization of competencies in social life [3,4].
CBE has emerged as an alternative education for future society, transitioning the essential question of conventional knowledge of education from “What will you teach?” to “What kind of student will you teach to be? [5]” Despite the emergence of CBE as an alternative education that can overcome the limitations of traditional knowledge-based education, it still exposes many educational issues.
The supporters of CBE, such as OECD, criticize traditional education as “inert knowledge” education, contending that the social utilization of education should be advanced through “useful knowledge” needed in the 21st century and accountability of education should be reinforced through the efficient management of educational outcomes [6,7]. In particular, they are interested in measuring tools that can evaluate their core competencies.
On the other hand, the negative side of CBE criticizes that behavioristic CBE treats education as a tool, focuses solely on practical outcomes, and has a bias toward job preparation and vocational education. Furthermore, they point out the ambiguity of the concept of competence itself as well as expressing concerns about the possibility of weakening knowledge-oriented education [8,9,10,11].
Concerning the issues regarding CBE’s historical background, on the one hand, CBE’s origin is founded in traditions of liberal education of the ancient Greek era, emphasizing general abilities [12]. On the other hand, its origin is founded in the theory of social efficiency developed mainly in the United States in the early 1900s [8]. Some scholars contend its origin as competency-based teacher training, which started in the 1960s in the United States in the field of teacher education [13,14].
However, in fact, the concept of CBE started to emerge in the direction of being a catalyst for school curriculum change in the mid-1990s [15]. In particular, the OECD has been leading the CBE discourse since the 1990s. First, the OECD has delineated the meaning of competency from the educational perspective through the DeSeCo (defining and selecting key competencies) project (1997–2003), re-examined competencies in the context of school education, and selected three “key competencies” for an individual’s successful life and a prosperous society [16]. The DeSeCo project that facilitates ‘acting autonomously, interacting in socially heterogeneous groups, using tools interactively’ has tremendously affected CBE worldwide [17].
The OECD did not stop there and took another leap forward. It has promoted “The Future of Education and Skills: OECD Education 2030” project called “DeSeCo 2.0” since 2015, suggesting new competencies as “transformative competencies” that aim to reinforce “inclusive growth” to ensure “well-being” [2]. This project describes and systematically categorizes “knowledge,” “skills,” and “attitude and value,” which facilitates in “creating new values,” “reconciling tensions and dilemmas,” and “taking responsibility” through the future learning framework, and thus attempts to reflect them in CBE’s design and implementation [2].
The debate over competency education is not new. As education is a complex notion that synthesizes questions on “why, what, and how,” various educational viewpoints coexist according to their perspectives and contexts. In competency education, there exist diverse contentions, which may include issues on the characteristic of knowledge in the educational aim, such as inert or useful knowledge, practical or theoretical knowledge, as well as issues regarding the meaning and features of competencies, such as behaviorist or humanistic competence and general or domain-specific competence. In addition, various names and definitions for competency education, such as outcome-based learning, mastery-based learning, problem-based learning, performance-based learning, and discipline-based learning, also reflect the complex circumstances of competency education [6,18].
Furthermore, CBE is a comprehensive educational paradigm that needs an extensive and holistic approach requiring a virtuous cycle of reconfirming educational goals, redefining talented human resources, core competency modeling, developing competency-based curriculum, developing competency-based courses and mapping competencies, implementing curriculum and teaching, developing competency-based instructional methods, evaluating competency-based educational achievements, and managing quality of competency-based education [19]. Educational perspectives of professional fields, such as medical and nursing education, should be considered as well.
In this context, analyzing the global research trends and discourses of CBE is pertinent and meaningful. The topic modeling approach applied in this study is a useful algorithm for mechanically identifying potential topics in a vast range of unstructured documents [20]. The topic modeling method will provide a useful framework for grasping international research trends because it utilizes measurement-oriented quantitative methods and interpretation-oriented qualitative methods at the same time [21].
Through this study, we aim to find answers to the following three research questions (RQ).
- What are the major topics being covered in articles on CBE?
- What changes in the trends can be observed in articles on CBE by period(s)?
- What trends can be observed in countries that publish articles on CBE?
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Trend Analysis and LDA Topic Model
Many methods have been attempted to analyze the research trend. Among them, manual allocation is a method of reading documents by professional experts and classifying them according to predetermined topics; however, it has some limitations. First, it is unsuitable for large documents. It is time consuming, and thus errors can occur. Second, classifying topics according to predetermined topics can likely ignore relatively new or emerging topics. Lastly, an article can have various topics. In an article, the research method and the application domain may appear as individual topics. Assigning an article to a single topic cannot reflect such aspects.
The clustering approach uses co-occurrence networks [22], so the first two issues mentioned above may be resolved. However, because one article is usually clustered into a single topic, the multiple topics in a single article cannot be captured.
Topic models are statistical models that automatically find various topics in large documents [23]. In topic models, it is assumed that several topics are mixed in each document, and that each topic has a word distribution. Therefore, document labeling is not needed. It provides a theoretical background that can help understand the document creation mechanism, and documents can be automatically organized and summarized. Topic models have been used to analyze research trends in various fields, such as education [24,25], statistics [26], machine learning [27], biochemistry [28], and manufacturing [29].
Latent Dirichlet allocation (LDA) is the most representative topic model [30]. LDA assumes that words are generated from the document as follows: given Corpus with documents, one document consists of words.
Document has a distribution of topics , and when creating the nth word one topic () from the topics is selected according to the distribution , and the word is generated according to the word distribution of in the topic.
Here, the topic distribution of the document and the word distribution for topic follow the Dirichlet distribution, and and are the parameters of the Dirichlet prior, respectively. This can be expressed as a picture shown in Figure 1.
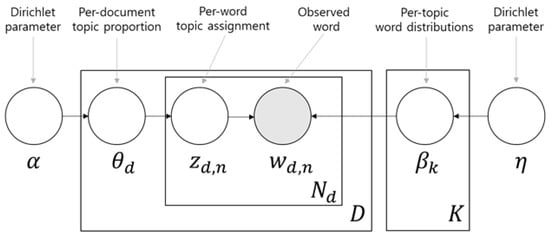
Figure 1.
Graphical model representation of the LDA model.
In the document, only generated words are observed, and the rest becomes latent variables (, , ) and hyper parameters (, ). By maximizing the joint probability of the words in a document in the corpus as indicated in Equation (1), the latent variables , can be obtained.
2.2. Data Collection and Pre-Processing
The information about articles used in this research was collected from Web of Science, a citation index web database provided by Clarivate Analytics. The Web of Science Core collection provides comprehensive citation information of diverse disciplines, such as SCIE, SSCI, and A&HCI. To collect articles relevant to CBE, the search conditions as shown in Table 1 were used (Search date: 21 March 2021). Articles were retrieved through a topic search using the term “competency,” “competence,” “competencies,” or “21st century skills” from Web of Science core collection. To be specific to the field of education, we have limited the Web of Science Categories to the following three categories: “Education Scientific Disciplines,” “Education Educational Research,” or “Psychology Educational.”

Table 1.
Search conditions.
Under the above conditions, 26,778 articles were searched, and among them, 26,532 articles were left excluding articles without an abstract. We collected “Article Title,” “Abstract”, “Author Keywords”, “Keywords Plus”, “Addresses”, “Publication Year”, “Early Access Date”, “Journal Abbreviation” for the articles.
The collection of “Article Title”, “Abstract”, “Author Keywords” and “Keywords Plus” was used for LDA to discover the research topics. Keywords Plus, index terms automatically generated from the titles of cited articles, is as effective as Author Keywords in terms of bibliometric analysis investigating the knowledge structure of scientific fields [31].
The following pre-processing was performed on the collected texts. First, python NLTK’s regular expression tokenizer was used to tokenize. Then, numbers, punctuations, and stop words were removed. In addition, general words used in research articles, such as “paper,” “study,” “article,” “research,” and “result,” as well as words with a word length of two or less, rare words with a frequency of less than 20, and common words used more than 50% of the entire document were removed. To reduce the size of the vocabulary set, lemmatization was utilized. Lemmatization and stemming are two methods used to reduce the size of the vocabulary set, but lemmatization creates words that are easier to interpret than stemming, thus is more preferable in LDA where semantic interpretation is important. In addition, some studies show that stemming has no significant effect on LDA [32,33]. For lemmatization, python’s spaCy library was used. In the analysis, only nouns, verbs, and adverbs were used. A dictionary was created for the lemmatization data, and the documents were vectorized with bag-of-words that calculated the frequency of words in each document. The dictionary was created through Gensim’s corpora.dictionary, and corpus was created through the integer encoding of dictionary.doc2bow.
2.3. Topic Anlysis
The LDA model was applied to the text data that had been previously pre-processed. Using Genism’s LDA Model, LDA analysis was conducted. To find the optimal hyper parameter values, the setting as shown in Table 2 was used by referring to related papers [27,34].

Table 2.
LDA experiment settings.
To determine K, the number of topics was varied from 10 to 30, and the coherence and perplexity values were compared. As a result, it was found that 15 topics were consistently shown to be good. The number of topics was then set to 15 and hyper parameters were adjusted to create the LDA model. The selected hyper parameter value was alpha = “auto,” eta = “auto,” passes = 35, iterations = 10,000, and num topics = 15. For passes, the performance at 30 was better than at 10 and 20, and from 30 to 35 tended to improve steadily but there was no significant difference, so 35 was used for passes. The value of coherence displayed high when “auto” was used for alpha and eta, which is automatically obtained from corpus.
3. Results
3.1. Analysis on Current Trends
To understand the basic status of article production, trends by year, country, and journal were analyzed. Figure 2 represents the number of articles published by year for a total of 26,532 collected articles. For articles without a publication year, early access date was used. It appeared that the number of published articles increased gradually. This number t has increased rapidly since 2015, and the trend has continued to the present year. The UN declared “The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development” and OECD launched the “Education 2030 project” in 2015, and thus, it can be explained that competency education took a step forward and was upgraded to be known worldwide.
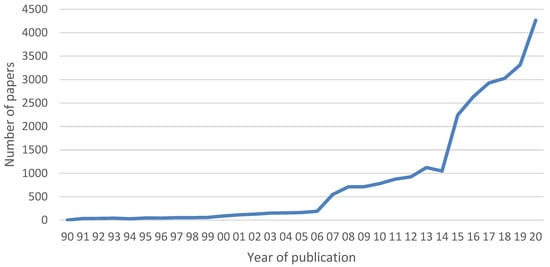
Figure 2.
Number of papers published by year.
Further, an analysis of the article publication by country is shown in Table 3. We used authors’ affiliations for country analysis. If there are multiple authors, the countries of affiliation of all authors were checked. It revealed that the United States published the greatest number of articles, followed by Spain, Germany, Canada, the United Kingdom, and Australia. It appeared that countries in North America and Europe took a lead in the article publication.

Table 3.
Top ten countries of article publication.
Additionally, the journals in which the papers were published were analyzed, and it was found that the articles were widely published in a total of 896 journals. In particular, it appeared that medical journals published a noticeable number of articles. Table 4 shows the frequency and proportion of the top 10 journals.

Table 4.
Top 10 journals.
3.2. Topic Discovery
Table 5 shows the names of 15 topics derived from LDA topic modeling, the list of words included in the order of probability of appearance, and the proportion of each topic. Each topic was rearranged in descending order according to the appearance of frequent words, and the number of each topic was assigned.

Table 5.
Topics and Frequent Words.
First, topic names were assigned for each topic classified by the LDA algorithm. To assign topic names, word frequency by each topic extracted through the LDA modeling was also considered with priority. Moreover, the title and abstract of five representative articles, selected by the percentage contribution of the topic in the given document, were reviewed.
The name of Topic 1 (T1) was “Approach to Competency Development” as it explores theories and approaches to competency development and education, such as development, practice, approach, framework, model, process, and need. “Learning skills” in Topic 2 (T2) and “teacher training” in Topic 3 (T3) were words that were noticeably revealed. Topic 4 (T4) was themed “Performance Assessment” as the contents were centered on performance assessment that is important in competency education, including medical education. Topic 5 (T5) was about “Path and Career Development,” where articles reveal the kinds of experiences and work experiences needed to increase the employment rate. Keywords related to “Academic Achievement” in Topic 6 (T6) were easily derived, and Topic 7 (T7) also noticeably conveyed contents about medical education. Topic 8 (T8) was about the “Affective Domain” that affects competency development in the areas of self, motivation, physical, efficacy, perception, autonomy, belief, and goal. Topic 9 (T9) was named “Linguistic Literacy,” as contents about enhancing the linguistic ability, such as language, English, literacy, foreign, and communication, were identified. Topic 10 (T10) reflected various environmental characteristics that affect education, such as child, social and emotional early intervention, parent, school, preschool, behavior, skill, childhood, family, and was named “Characteristics of Child’s Competency Development.” Topic 11 (T11) included frequent keywords, such as scale, factor, test, analysis, model, item, measure, instrument, and questionnaire, and thus was named “Factor Analysis.” Topic 12 (T12) was named “Curriculum Development” as it deals with programs, curriculum, and courses for competency development. Topic 13 (T13) clearly revealed the topic of nursing education. Topic 14 (T14) was named “Competency Development Environment and Policy” as it delved into the sociocultural environment and national policy factors, such as society, culture, international, global, policy, country, and diversity. Topic 15 (T15) was named “Categories and Classifications of Competencies” as it presented various competencies to be considered in the competency model, such as science, problem, knowledge, solving, thinking, mathematics, critical, writing, and ability.
The proportion of each topic is shown in Figure 3. The highest proportion was T1 at 17.7% of the total. As T2 accounted for 12.9%, research in T2 is also being actively conducted. T3 was at 9%, a topic that was widely explored. Meanwhile, the proportion of five topics, including T11, T12, T13, T14, T15, was approximately 3.9–4.3%, showing no significant difference.
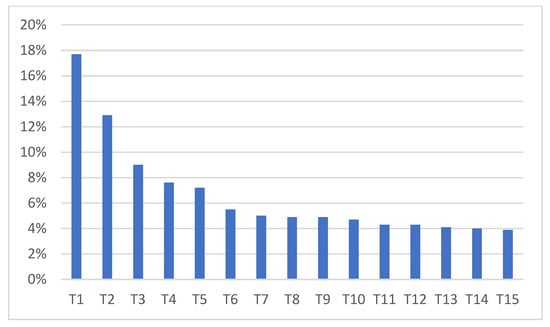
Figure 3.
Proportion of each topic.
We used the LDA visualization tool pyLDAvis and assessed topic models [35]. The intertopic distance map can visualize similarity among topics and the relative size of topics as shown in Figure 4. The associated keywords are shown in the right-hand side of the plot. T1 and T3 and, T6 and T8 had considerable overlapping parts, and it is confirmed that some of T9 and T15 also overlapped. Further analysis and discussion will be covered in Section 4.
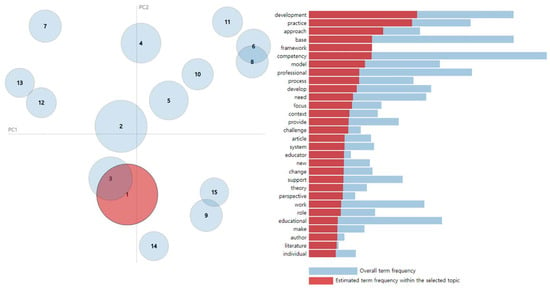
Figure 4.
Intertopic distance map (left) and keywords of topic 1 (right).
3.3. Topic Trend Analysis by Year
To understand the changes of the research trend over time, the publication year was divided into four periods, and the changes in the ranking of each topic were analyzed. The year was divided into 1991–2000, 2001–2010, 2011–2015, and 2016–2020. The publication of articles has increased rapidly in the last 10 years, this period was thus divided into five-year periods. Only two papers were published in 1990, and therefore was excluded.
As shown in Figure 5, it appears that between 1991 and 2000, particularly in the early years of competency education, the research was focused on topics T1, T4, T7, and T13. In the 21st century, research on T1 and T2 were conducted with great importance, showing a consistent pattern among the topics. Indeed, the research proportion by topic during 2011–2015 and 2016–2020 appears to be almost identical. However, it is noteworthy that research on T3 “Teaching Training” has increased considerably since 2016.
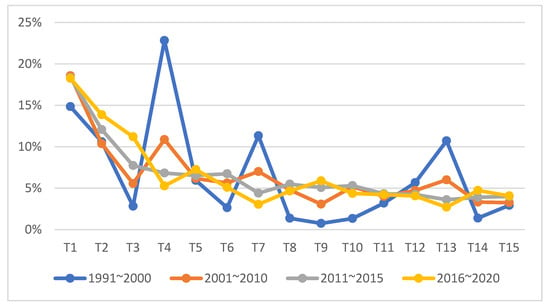
Figure 5.
Topic proportions (%) by period.
Through the above analysis, it was possible to derive that the overall change in the research proportion by topic appeared in the entire period, but to further understand the change by year, hot topics and cold topics were analyzed using data from the recent 10 years.
A simple linear regression model was fit with the year as the predictor and the year’s topic weight as the response, calculating the average weight of topics by year using the data from the recent 10 years, 2011–2020. As shown in Table 6, topics were organized into four categories based on the sign of slope and statistical significance.

Table 6.
Topic categories based on the sign and statistical significance of the slope of the linear regression.
Table 7 shows the result for linear regression. Topics were classified into five hot topics, two warm topics, one cool topic, and seven cold topics.

Table 7.
Topic category.
Figure 6 shows the trend of changes in the proportion of research by topic by year for the recent 10 years. Five topics (T2, T3, T5, T9, and T14) were classified as hot topics, which were topics that have been actively studied over time. These include topics related to “learning” and “teaching,” the essential elements of education, and shows that “Path and Career Development,” “Linguistic Ability,” and “Competency Development Environment and Policy” are fundamental topics that must be explored to enhance the sustainability of competency education. Seven topics (T4, T6, T7, T8, T10, T12, and T13) were categorized as cold topics as the article publication was gradually declining, which included medical education and nursing education, as well as diagnosis, evaluation, and curriculum development. It appeared that CBE, which is a technical and instrumental approach to competency education in the above fields, were gradually being studied less. T1 and T15, classified as warm topics, showed an upward trend, and T11, a cold topic, showed a downward trend.
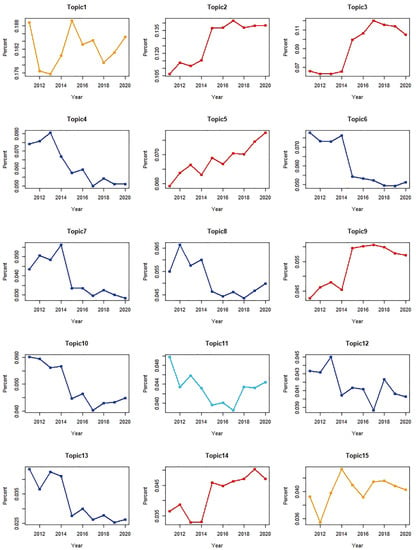
Figure 6.
Hot (red), warm (orange), cool (sky blue), and cold (blue) topics and their proportion changes over time from 2011 to 2020.
3.4. Topic Trend Analysis by Country
Next, research trends were compared by country. Among the top 10 countries for article publication, five countries including the Unites States, Spain, Germany, Australia, and China were selected to analyze the proportion of research by topic within the country. As shown in Figure 7, most of the countries continuously published articles on T1, which explores approaches to competency development and competency education, and the proportion of articles by topic also showed a similar pattern.
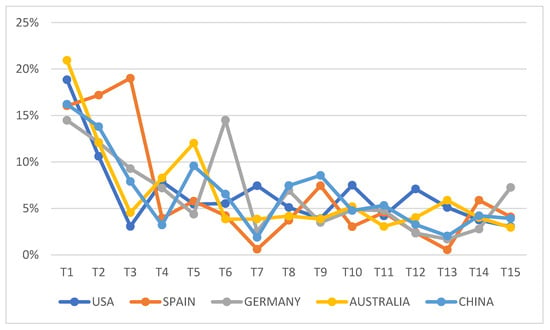
Figure 7.
Topic proportions (%) by country.
By country, it was found that the proportion of research was relatively high in some topics, particularly T7, T10, and T12 for the United States, T3 for Spain, T6 for Germany, T5 for Australia, and T9 for China.
4. Discussion
One of the urgent challenges of mankind to resolve is what and how to learn in the 21st century, as the amount of knowledge is increasing exponentially while the lifespan of knowledge is rapidly decreasing. On the one hand, the full application of competency-based education is insisted, and on the other hand, the strengthening knowledge-based education with a high transfer rate is requested.
In light of this, this study aimed to contribute to the sustainable development of CBE in the future by empirically analyzing international trends using LDA topic modeling for a total of 26,532 articles published from 1990 to 2020.
First, in order to explore research question 1 (RQ1), this study identified the topics that were mainly dealt with in the articles on CBE. Based on the LDA algorithm, 15 topics related to CBE were derived and listed with frequent words in order of topic proportion. We then gave appropriate names for each of 15 topics based on frequent words and representative articles of each topic. Reclassifying the 15 topics into five groups, which is a larger category, will provide a clearer understanding of the CBE’s research trends. The first group consists of topics that have been studied the most. These are groups that influence other topics as research on learners (T2) and instructors (T3) based on their approach to competency (T1). The second group was a group that explored competencies of students’ path and career development (T5) and childhood competency development (T10), as well as its relationship with performance assessment (T4); it showed a relatively close relationship with the first group. The third group delved into linguistic literacy (T9) and Categories and Classifications of Competencies (T15), and also showed interest in the competency development, environment and policy (T14). This group had a relatively close relationship with the first group as well. The fourth group was concerned with the affective domain (T8), a group that aimed to improve academic achievement (T6) through examining relevant factors (T11). The fifth group was a topic group in which CBE and curriculum development (T12) were carried out in the professional disciplines of medical (T7) and nursing fields (T13). Through this relationship, it was revealed that the development of competency-based curriculum is mainly centered on medicine and nursing. Through the topic trend analysis on CBE, it was empirically confirmed that almost all topics that should be dealt with CBE were being studied.
Further, to delve into research question 2 (RQ2), the yearly trend of articles was examined. It was found that, in terms of quantity, article publication was trivial from 1990 to 2005, but started to increase in 2006, and showed an exponential increase starting in 2015. It appeared that the OECD’s Education 2030 project had a great impact. In addition, as a result of conducting a regression analysis on the changes by topic for the recent 10 years, the research trend by topic was revealed clearly. It may be possible to predict the trend of CBE research in the future by the five topics classified as hot topics (T2, T3, T5, T9, and T14) and seven topics classified as cold topics (T4, T6, T7, T8, T10, T12, and T13). As seen in topics that increased rapidly since 2015 (T2, T3, and T9), it is expected that topics related to the “future learning framework”, such as “student agency, emphasized by the Education 2030 project, will continually increase.
Finally, to delve into research question 3 (RQ3), the trends of each country publishing articles on CBE were examined. The articles were being published in the order of the United States, Spain, Germany, Canada, and the United Kingdom. The topic trend by country appeared almost the same. The proportion of articles on the approach to competency (T1) was high, and showed similar patterns, yet articles on T3 for Spain, T6 for Germany, and T5 for Australia were published more, and thus, we were able to identify topics of interest by country.
5. Limitations
To collect articles for use in our analysis, the topic search and category settings were retrieved on Web of Science. It is possible that the data collected did not include all CBE-related papers or included studies that were not related to CBE.
This study also has general limitations of research trend analysis. In other words, it shows well what the research topic on CBE is, when and where it was conducted, but does not suggest a direction for CBE to go forward. The search for various alternatives for the sustainable development of competency education will have to be addressed in future studies.
6. Conclusions
In this study, core topics of CBE were searched using LDA, and recent international research trends were analyzed using 26,532 related research articles published during the last thirty years. We briefly reviewed the derived topics of CBE and examined the dynamic changes in topics by uncovering the hot and cold topics. Research trends on CBE by country were also examined, and characteristics between countries were identified.
Education is a cultural invention for all mankind’s sustainable future. Education is a complex and comprehensive process that simultaneously pursues the happiness of present life as well as the values of the future. Rapidly evolving globalization changes, such as the Fourth Industrial Revolution, Artificial Intelligence, Big Data, and the COVID-19 pandemic, require changes in education. Whether it is the expansion of quality education or strengthening knowledge education, the search for better education should be continuously carried out.
Better education asks us to re-explore basic questions about what the purpose of education is and what and how to educate in order to achieve that purpose. CBE is no different. It requires a vest and in-depth exploration on education in general. A better future education should be sought through research and discussion that can cross various perspectives and boundaries from character to knowledge education, liberal to professional education, humanities to career education, and elementary to higher education. The international trends in CBE revealed through this study are expected to provide a reference for exploring the sustainable future education.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.P. and N.K.; methodology, T.U. and N.K.; software, T.U.; validation, S.P., T.U. and N.K.; formal analysis, S.P.; investigation, S.P. and N.K.; data curation, T.U.; writing—original draft preparation, S.P. and N.K.; writing—review and editing, N.K.; visualization, T.U.; supervision, N.K.; project administration, S.P.; funding acquisition, S.P. and N.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Gachon University research fund of 2019(GCU-2019-0718).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- United Nations (UN). Resolution Adopted by the General Assembly. Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. A/RES/70/1. 2015. Available online: http://www.un.org/en/ga/search/view_doc.asp?symbol=A/RES/70/1 (accessed on 21 March 2021).
- OECD. Future of Education and Skills 2030: OECD Learning Compass 2030, A Series of Concept Notes. 2019. Available online: https://www.oecd.org/education/2030-project/teaching-and-learning/learning/all-concept-notes/ (accessed on 21 March 2021).
- Trilling, B.; Fadel, C. 21st Century Skills, Enhanced Edition: Learning for Life in Our Times; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Fadel, C.; Bialik, M.; Trilling, B. Four-Dimensional Education: The Competencies Learners Need to Succeed; Center for Curriculum Redesign: MA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Pristley, M.; Biesta, G. Reinventing the Curriculum: New Trends in Curriculum Policy and Practice; Bloomsbury Academic: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Gervais, J. The operational definition of competency-based education. Competency Based Educ. 2016, 1, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, E.A.; Voorhees, R.A. Defining and Assessing Learning: Exploring Competency-Based Initiatives, Report of The National Postsecondary Education Cooperative Working Group on Competency-Based Initiatives in Postsecondary Education; Brochure [and] Report; Council of the National Postsecondary Education Cooperative Working Group on Competency-Based Initiatives: Washington, DC, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Hyland, T. Competence, knowledge, and education. J. Philos. Educ. 1993, 27, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheelahan, L. Why Knowledge Matters in Curriculum: A Social Realist Argument; Routledge: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Young, M. Overcoming the crisis in curriculum theory: A knowledge-based approach. J. Stud. 2013, 45, 101–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christodoulou, D. The Seven Myths about Education; Routledge: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ewens, T. Analyzing the Impact of Competence-Based Approaches on Liberal Education. In On Competence: A Critical Analysis of Competence-Based Reforms in Higher Education; Grant, G., Elbow, P., Ewens, T., Gamson, Z., Kohli, W., Neumann, W., Olesen, V., Riesman, D., Eds.; Jossey-Bass: San Francisco, CA, USA; pp. 160–198.
- Chappell, C.; Gonczi, A.; Hager, P. “Competency-based education”, Praise for the first edition of Understanding. Adult Educ. Train. 2000, 192–207. [Google Scholar]
- Morcke, A.M.; Dornan, T.; Eika, B. Outcome (competency) based education: An exploration of its origins, theoretical basis, and empirical evidence. Adv. Health Sci. Educ. Theory Pract. 2013, 18, 851–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodge, S. The origins of competency-based training. Aust. J. Adult Learn. 2007, 47, 179–209. [Google Scholar]
- OECD. The Definition and Selection of Key Competencies: Executive Summary; OECD: Paris, France, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Bieber, T.; Martens, K. The OECD PISA study as a soft power in education? Lessons from Switzerland and the US. Eur. J. Educ. 2011, 46, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, J. (Ed.) Competency Based Education and Training; Routledge: London, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Paek, S.S. A Study on the problem and improvement of core competency-based liberal arts education. Korean J. Gen. Educ. 2011, 14, 11–23. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.H.; Wood, J.; Kim, J. Tracing the Trends in sustainability and social media research using topic modeling. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmiedel, T.; Müller, O.; vom Brocke, J. Topic modeling as a strategy of inquiry in organizational research: A tutorial with an application example on organizational culture. Organ. Res. Methods 2019, 22, 941–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, E.; Ding, Y.; Milojević, S.; Sugimoto, C.R. Topics in dynamic research communities: An exploratory study for the field of information retrieval. J. Inf. 2012, 6, 140–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blei, D.M. Probabilistic topic models. Commun. ACM 2012, 55, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daenekindt, S.; Huisman, J. Mapping the scattered field of research on higher education. A correlated topic model of 17,000 articles, 1991–2018. Higher Educ. 2020, 80, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Park, T.; Choi, J. Analyzing Research Trends in University Student Experience Based on Topic Modeling. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Battisti, F.; Ferrara, A.; Salini, S. A decade of research in statistics: A topic model approach. Scientometrics 2015, 103, 413–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Kumar, B.; Chand, S. A trend analysis of machine learning research with topic models and Mann-Kendall test. Int. J. Intell. Syst. Appl. 2019, 11, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.J.; Kim, C.; Kang, K. Analysis of the trends in biochemical research using Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA). Processes 2019, 7, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.; Cheng, Y.; Zhao, W.; Liu, J. Analyzing scientific research topics in manufacturing field using a topic model. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2019, 135, 333–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blei, D.M.; Ng, A.Y.; Jordan, M.I. Latent dirichlet allocation. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2003, 3, 993–1022. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Yu, Q.; Zheng, F.; Long, C.; Lu, Z.; Duan, Z. Comparing keywords plus of WOS and author keywords: A case study of patient adherence research. J. Assoc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2016, 67, 967–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, C.; Cotterell, R.; Van Durme, B. An analysis of lemmatization on topic models of morphologically rich language. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1608.03995. [Google Scholar]
- Schofield, A.; Mimno, D. Comparing apples to apple: The effects of stemmers on topic models. Trans. Assoc. Comp. Linguist. 2016, 4, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kang, P. Analyzing international collaboration and identifying core topics for the “internet of things” based on network analysis and topic modeling. Int. J. Ind. Eng. 2018, 25, 349–369. [Google Scholar]
- Sievert, C.; Shirley, K. LDavis: A method for visualizing and interpreting topics. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Interactive Language Learning, Visualization, and Interfaces, Baltimore, MD, USA, 27 June 2014; pp. 63–70. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).