Abstract
The pervasiveness of technologies leads us to talk about a code society. From an educational point of view, coding, computational thinking, and educational robotics are an open possibility. Nevertheless, new elements such as artificial intelligence are rapidly changing educational technology perspectives. In this work, we will analyze school policies and theoretical bases in order to understand if, and under what kind of, condition coding, computational thinking, and educational robotics still represent the qualifying elements of a framework for digital literacy and digital citizenship.
1. Introduction
When broadly and properly underlined [1], our world has changed in the past few decades with an acceleration that has never been seen before. We are seeing what, until the last century, was the subject of science fiction—from Isaac Asimov to Philip K. Dick to the Wachowski brothers—or was the speculation of philosophers and scientists—such as Alan Turing, John Searle, and Hilary Putnam—who built a framework that had its boundaries in the limits of their contemporary technology.
Our reality has reshaped sub specie tecnologica to such an extent that multiple perspectives can coexist and intertwine in an increasingly complex framework. We are acquainted with categories such as the infosphere [1] and docusphere [2] in order to support knowledge processes in the information society [1]. Currently, programming has taken on an increasingly pervasive role in our lives, and this has led us to deal with new categories such as the code society [3] and software society [4]. These expressions define the software and the code with which they are written as embedded in everyday life. They are an integral part of our reality to such an extent that their presence is not perceived [4]. They are transparent and opaque at the same time: they are not noticed and, in most cases, they are not understood. This can make everything around us as functional as it is unintelligible.
From the pervasiveness of this cluster of computational mechanisms encoded through algorithms [5] emerges artificial intelligence as an element that is filling the media and records. And a further category is also forming: the unconscious. This concept seems to combine different perspectives on coding and artificial intelligence in the same landscape. Accoto [4] defines software as the technological unconscious by virtue of its opacity, and Ferraris [2] analyzed the connection between writing and the construction of the unconscious, where they defined artificial intelligence as the artificial unconscious.
In order to face this complex reality and its cultural challenges, the code society can look at the increasing the relevance of coding in all educational contexts [3]. Through school and education, it is possible to outline learning paths that provide students with the cultural foundations and technological skills to be aware citizens in this new reality. If understood in depth, and used not to create mere ability but to build knowledge, they can be keystones for understanding reality, including emerging issues regarding artificial intelligence.
In this contribution, we will analyze the state of the art of coding, computational thinking, and educational robotics in national and supranational educational policies, up to the interpretation of artificial intelligence in schools. We will then propose an analysis of the fundamental elements of human–robot interactions, connecting it to the fundamental theoretical reflections that have characterized the birth of the debate on artificial intelligence. From this point of view, we will propose an interpretation of robotics and robot programming as a driving element of education in technology and citizenship.
2. The Context: Digital Competence under International and National Government Policies
Preparing students for the challenges of the twenty-first century, encompassing work, citizenship, and life, is a significant undertaking shaped by globalization, technological progress, migration, international competition, and environmental and political complexities [6,7]. In 1999, the American government proposed the report “21st century skills for 21st century jobs” [8], while in 2000, the European Commission promoted the Lisbon Strategy (https://www.europarl.europa.eu/summits/lis1_en.htm, accessed on 7 July 2024), envisioning a future where the rise of new jobs, especially in technological fields, necessitates workers with new skills. These initial actions were followed by global initiatives aimed at preparing future citizens for jobs with undefined requirements, leading to broad and increasingly technical skill sets.
In 2006, the European Commission developed the European Reference Framework of Key Competences for Lifelong Learning [9], identifying eight key competencies essential for full participation in the knowledge society. This framework emphasizes digital competence, and it is defined as the ability to use information society technologies with familiarity and critical thinking. Over time, the European Commission has launched numerous initiatives to promote digital competencies, evolving from technical to more technological characteristics. Initiatives such as the Digital Education Action Plan 2021–2027 [10] aim to enhance digital literacy, skills, and capacity across all levels of education, starting from early childhood. This involves fostering problem solving, creativity, and collaboration, providing basic knowledge of emerging technologies like AI and training teachers to facilitate a conscious use of technologies among learners.
In Italy, the evolution of digital skill education has been influenced by international educational directives and national guidelines. The National Digital School Plan (PNSD) in 2015 [11] and in 2018 (the Updated National Guidelines [12]) recognized the growing importance of digital skills and computational thinking, emphasizing the need to equip students with the ability to understand and create digital content, including basic programming concepts and problem-solving skills. Computational thinking was highlighted as a competence to be acquired across disciplines, including unplugged activities.
In this general overview on national and international policies regarding the development of digital skills and soft skills in students, a brief mention cannot be omitted regarding how they are currently responding to the emerging prominence of artificial intelligence in the field of education. In analyzing some of the documents disseminated by major organizations such as the EU council [13], OECD [14], and UNESCO [15,16], it is possible to identify some trends and initiatives that emerge globally.
Artificial Intelligence: Introduction in an Educational Context
Regarding the integration of AI in teaching and learning, many countries are exploring the use of AI to improve educational processes. This may include the use of virtual tutors to provide personalized support to students, automated assessment systems to evaluate student work, and learning platforms that use AI algorithms to adapt educational materials to students’ individual needs. The issue of teacher training is certainly consequential to the previous one: governments must provide training for teachers on the effective use of AI in the classroom. This is both to help teachers understand how to integrate AI-based tools and resources into their teaching and to develop the digital skills necessary to do so effectively. Finally, two social considerations. Firstly, it is necessary to ensure equitable access to AI-based educational resources and tools for all students. It is crucial to guarantee that the integration of these technologies does not exacerbate existing educational inequalities. Instead, the use of AI in education should promote accessibility and equity, providing every student with fair opportunities to benefit from these innovative tools. Secondly, clear guidelines for the collection, use, and protection of student data in the use of AI should be developed while ensuring compliance with existing privacy laws.
3. Aims and Research Questions
As we have seen, in our cultural context code, software and artificial intelligence are considered fundamental for our society and coding, where computational thinking and robotics are proposed as the educational key to access this reality. Nevertheless, the guidance documents consider skills for technological and digital citizenship in such a broad sense that, though it certainly includes the competencies of the code society, it does not help us to define them.
Our aim is to outline a theoretical framework that can support future transformative [17] educational research in-field by proposing coding, computational thinking, and educational robotics as learning paths for support citizenship in the emerging society. We propose to face some of the questions beyond the rhetoric as follows:
- Does the evolution of policy and skill frameworks and their application support a consistent integration of coding, computational thinking, and educational robotics at school?
- Does an analysis of the theoretical themes underlying human–machine interaction provide us with elements for understanding educational robotics and design its educational use?
To answer the first question, we will consider the competency frameworks that are usually taken as a reference in education. We will take into account some of the insights provided by the literature relating to coding, computational thinking, and educational robotics as tools used in schools to support the acquisition of these skills. Then, we will consider the emerging elements through a SWOT analysis.
To consider the second question, we look at the pairing of robot/artificial intelligence from a philosophical point of view to find epistemological bases in order to characterize the so-called human–robot interaction (HRI) and its specification—the child–robot iteration (cHRI) [18]. According to this premise, we will try to construct useful grounds for a pedagogical approach. Our focus is to analyze these topics in order define their impact in the contexts that, according to Marchive [19], we can call “learning situations”. That is why will look at a topic that seems to have a strong impact on educational robotics: the Theory of Mind. In particular, we will investigate its declination, viz. the Theory of the Artificial Mind.
Finally, we will address one last question:
- Can we find elements that lead us to enhance the paths already completed in these fields for AI education?
In educational research, the relationship between theory and practice must be narrow and continuous. Here, we are setting “tentative hypotheses” [20] that must be validated by practice. According to a transformative research model—which we have already taken as a reference model—the experience will then transform both theory and practice.
Answering these questions will not give us guarantees or findings, but it will allow us to propose advice to teachers and researchers and to have elements that can facilitate the design of future research on these themes in an educational context.
4. Coding, Computational Thinking, and Educational Robotics in Education: An Overview
4.1. A Competencies’ Framework and Computational Thinking Strategies
In the past twenty years, at least ten different entities, including international bodies, governments, and private groups, have suggested various educational frameworks and skill sets to tackle the demands of the 21st century [21]. Several research works [22,23,24] have examined a range of these frameworks to discern the progression of key themes and shared characteristics. Although there is no universally accepted method for educating the youth for today’s world, a diverse set of competencies and skills has been highlighted as important. Despite variations in their complexity, each framework has its significance for the particular situation it was designed to address. Moreover, the aforementioned comparative studies highlight the lack of these key competencies and skills in the existing educational paradigms [25].
In 2010, the American Association of Colleges of Teacher Education and the Partnership for 21st Century Skills introduced a framework aimed at guiding educators in integrating 21st century skills into classroom practice to meet the challenges of the century [21]. These skills include critical thinking, problem solving, communication, collaboration, creativity, and innovation. The OECD Framework [26] emphasizes the importance of tailored learning environments, proficiency in reading and arithmetic, and the development of digital and data literacy skills. The International Labour Organization (ILO) [27] highlights the need for ongoing learning to adapt to emerging occupations focused on cognitive and metacognitive domains, and this is achieved via proposing a framework based on social and emotional skills, cognitive and metacognitive skills, basic digital skills, and green job skills. In the European context, the Digital Competence Framework for Citizens (Digcomp) [23] provides a reference for digital skills in education and training, emphasizing the confident, critical, and responsible use of digital technologies. However, there is a recognized gap between the current education and necessary skills, urging reflection and revision of educational curricula to address this deficiency.
Acknowledging and integrating essential competencies into educational curricula [28,29,30,31] requires a shift toward dynamic, student-centered approaches emphasizing real-world problem solving and interdisciplinary learning. This involves redesigning learning environments, updating instructional methods, and prioritizing competencies through systemic changes. Leveraging student proficiency in digital technologies can enhance engagement and facilitate inquiry-based learning, thus ultimately preparing individuals for success in the modern era [8,25,32].
The pandemic period, in which schools were forced to find alternative solutions to face-to-face classrooms, highlighted the the shortcomings of the traditional educational method in these situations as this method was, in fact, ineffective when mediated by a screen and distance: “emergency confirmed the need for all educators to be skilled in using digital technologies effectively in their teaching and training process and to ensure that all children can participate in digital education. It has also confirmed that different pedagogical approaches are needed when teaching online. Teachers and learners also need to develop the skills and know-how for this different mode of learning” [10] (p. 3).
Assuming that, therefore, the acquisition of skills such as critical thinking, problem solving, communication, collaboration, creativity, and innovation is one of the main targets of Agenda 2030, then international research is required to investigate in depth and with a wide variety of resources in order to determine what activities enable the acquisition of digital skills.
4.2. Computational Thinking, Coding, and Educational Robotics at School
There is a broad literature that agrees that coding and educational robotics (RE) are effective methodologies for the acquisition of digital skills, as defined by the aforementioned frameworks, especially for the computational thinking competency. Though there is no agreed definition in the literature of what CT is, the one proposed by J. Wing [33] is now well established. Computational thinking (CT) involves breaking down complex problems into smaller, more manageable parts, identifying patterns and trends, and creating algorithms to solve these problems. The discussion, which has led to the writing of the guidelines, has been relevant and finds support in the impending need to train today’s future workers and students with digital skills to cope with increasingly technology- and computer-oriented activities [34,35]. Even in the pedagogical academic landscape of the last century, the discussion on critical, algorithmic, or creative thinking skills has been relevant [36].
Beginning with J. Dewey and the ‘learning by doing’ theory [37], Vigotsky and his reality of the imagination, and adopting a viewpoint grounded in Piagetian constructivist theories, the act of grasping one’s world is seen as an interplay between the individual’s active cognition and their experiential encounters.
Furthermore, Papert [38] has emphasized the role of technology in the educational journey, not merely as a supplement to learning, but also as an enabler for the simulation of real-world scenarios. Papert suggests that, rather than knowledge being directly transferred in its entirety from one individual to another, each person reinterprets and reimagines knowledge in a unique manner. Consequently, technological tools such as computers, tablets, and robots serve as potent avenues for the amalgamation of theoretical understanding with practical application. Moreover, engaging with tangible technological instruments catalyzes a dynamic educational experience that prompts learners to contemplate and employ their knowledge upon the very fabric of their operational world. Papert’s investigations further reveal that robotics kits, beyond imparting computing prowess, awaken a zest for knowledge and foster creative, motivated learning environments where individuals can engage with transformative concepts. Additionally, the belief in learning as an action-oriented process, one that is shaped by experiential learning and augmented by social interplay, underpins the argument for technology to enhance collaborative educational interactions, thus allowing for the discovery and utilization of novel pedagogical approaches [39].
When learners engage with educational technology, it is not only about interacting with a device, it is also an immersive experience that reshapes their approach to knowledge acquisition. The use of robotics and other digital tools in learning environments does not just pass down information from teacher to student, but also allows the direct construction of knowledge through active participation and iterative practice.
As Papert has pointed out: “the essence of learning with technology is not the acquisition of more information, but the ability to do something with it—to transform it, integrate it, and apply it in new and creative ways” [40]. The presence of an interactive tool, such as a robot, acts as more than just a instructional aid, it becomes a catalyst for deeper intellectual engagement [41]. By challenging students to analyze and apply what they know in a tangible context, these tools foster a sense of ownership and personal relevance in the learning process [41].
Moreover, this hands-on engagement with tech-based learning tools dovetails with the idea that understanding is bolstered not in isolation but in the company of peers. Social interaction is not just a supplement to learning; it is a vital component that enriches the experience, making comprehension more robust. In that spirit, technological innovations in the educational space should be leveraged to expand opportunities for collaborative learning, thus encouraging students and educators alike to break new ground in educational methodologies and strategies. This collaborative approach to learning underscores the importance of educational technology as a means to not just impart knowledge, but to also inspire a collective journey of discovery and intellectual growth.
While government guidelines use the word coding and programming interchangeably, it is not so obvious in the academic world: coding is not merely about learning a programming language; in fact, we can say that programming is only the last aspect and that its relevance, especially in the early educational stakes, is entirely functional to the acquisition of other competencies than developing software. Unplugged coding, which is widely used in preschool, fundamentally revolves around developing computational thinking: students learn to break down complex problems into manageable units, discern patterns, abstract from specific details to general concepts, and design algorithms to process information.
This structured way of thinking is universally applicable, extending beyond computer science to subjects such as mathematics, science, literature, and even the arts. By learning to code, students enhance their logical thinking and gain the ability to automate solutions, thus reinforcing their problem-solving capabilities and skills, which are paramount in their importance in nearly every discipline. Educational robotics transforms theoretical knowledge into tangible outcomes that engage and inspire P-12 students. Building and programming robots provide learners with a playful yet educational experience, where abstract coding concepts become concrete. These robotic systems serve as platforms where STEM concepts are not only understood, but are also seen in action, thus reinforcing learning through interactive play and experimentation [42].
The integration of educational robotics in classrooms fosters an interdisciplinary learning environment. It helps students connect the dots between various subject areas while also promoting essential 21st-century skills such as creativity, adaptability, and systems thinking [43,44], which is also Goal 5 of Agenda 2030 “Gender equality” and the fight against stereotypes [45].
The collaborative context in which coding and robotics are typically used naturally encourages students to engage in teamwork. Projects often require brainstorming, assigning roles, and collective troubleshooting, closely mimicking real-world collaborative scenarios. As teamwork and communication are key components of 21st-century skills, these collaborative experiences are invaluable. They foster a community learning atmosphere where students can exchange ideas and learn from peers, thus preparing them for the collaborative work environment of the future. The integration of coding and educational robotics into P-12 education is more than an enrichment of the learning process; it is a conduit for empowering young minds with the tools required to succeed in the 21st century. This approach nurtures not only the technical skills that are increasingly in demand in the workforce, but also the critical soft skills of problem solving, teamwork, and adaptability. As the educational landscape evolves to meet the needs of a changing world, coding and robotics education stand out as essential components of a future-ready education system that aims to harness technology for creative and collaborative learning. To equip students with the prowess to excel in this new era, educators and policymakers must prioritize the incorporation of these dynamic fields into the education of the young pioneers of tomorrow. Over the last twenty years, there have been many initiatives carried out in schools to institute a constructivist approach to their didactics by carrying out educational robotics and coding courses, and the literature is full of papers and proceedings that classify these experiences, as well as analyses their effects, their learning effects, and highlights any limits or gaps still to be filled [46,47,48,49,50,51]. Most agree that the development of computational thinking is fostered by experiences related to coding and educational robotics at various age levels when considering both pure and multidisciplinary activities [42,52,53,54,55,56,57]. In students who have carried out coding or educational robotics activities, the learning benefits are greater if these activities are conducted with active teaching modes such as collaborative learning, project-based learning, and embodied learning [52]; other studies have discussed how RE and coding can be integrated into education as a curricular activity, as integrated into other disciplines, or in cross-disciplinary learning [58,59]. In particular, Murat et al. expressed the need to define a curriculum for educational robotics as follows: “collaborative curriculum, where the integration of educational robotics is due to an interdisciplinary approach” (p. 1287).
As the aforementioned authors have suggested that integrating robotics into education positively influences student behavior and development, it is important to recognize that simply introducing robots into classrooms does not automatically enhance learning outcomes. Extensive research has underscored various critical factors [60,61]. Firstly, studies have indicated that, without appropriate pedagogical strategies, integrating robotics activities into education can even potentially hinder learning indicators. Furthermore, the beneficial effects of educational robotics are contingent upon specific conditions, including activity design, robot quality, and teacher guidance. To cultivate metacognitive skills—such as self-assessment and adaptive learning strategies—teachers must employ tailored pedagogical approaches. These approaches may involve designing activities that prompt students to evaluate their progress, monitor their learning, and adjust their strategies accordingly.
Finally, some studies have also focused on how to train teachers [62,63] as a prerequisite for the skills to then be properly elicited in students.
4.3. SWOT Analysis
To summarize, from a critical approach that includes coding and educational robotics in school, we can consider the following SWOT analysis. Figure 1. This kind of analysis can give a comprehensive overview of the opportunities and challenges related to integrating coding and educational robotics into the educational context in order to develop effective strategies to maximize benefits and mitigate threats.
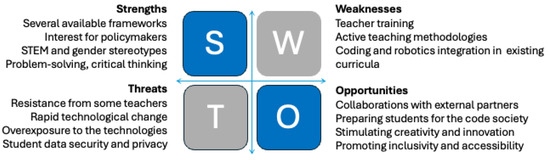
Figure 1.
SWOT analysis.
As the strengths, we identified five key points: from the international and national policies, it is evident that digital skills in the contemporary educational context is important, as is the growing interest and support from educational institutions and policymakers [9,13,14,15,16]; the reflections arising from these policies has led to the availability of established frameworks and resources for teaching coding and robotics [28,29,64,65]. From a learning point of view, coding and robotics have potential in enhancing student interest in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) through the use of these technologies [56,66,67] (even in overcoming stereotypes [45,68]), as well as in developing cross-cutting skills such as problem solving, critical thinking, and collaboration [33].
The following weaknesses were found to mainly center around boundary issues when compared with the acquisition of skills and learning: the lack of adequate training for teachers on the effective use of coding and robotics in the classroom [10,63], the lack in the use of active teaching methodologies by teachers as the best support for coding and robotics activities [52], and the potential challenges in integrating coding and robotics into existing curricula without overburdening students and teachers [58,59]. As pointed out by several frameworks, it is critical to address the possible exclusion of students with limited access to digital technologies and necessary resources.
As opportunities we identified the following four elements: the need for providing teacher training and technological support can lead to collaborations with companies and institutions, as well as a view to integrate them with territorial activities; the incorporation of coding and educational robotics as integral parts of the educational curricula can be the means to prepare students for the code society [6,43,44]. Coding and educational robotics are an opportunity to engage students in hands-on projects and collaborative activities that stimulate creativity and innovation [39], and this is possible precisely because of their nature of reconciling creative aspects with formal learning. Coding and robotics can be used to promote inclusivity and accessibility in education.
As threats, we identified the following four categories of problems: the resistance from some teachers or parents who may consider coding and robotics as non-essential or as too complex, even when linked to the need of using the learning by doing methodology to make these activities productive [25,60,61]; the rapid technological change requiring frequent updates and ongoing investments in educational resources; the potential over-reliance on digital technologies at the expense of other aspects of learning; and the concerns about student data security and privacy in the context of using digital technologies [23].
5. Looking for a Different Understanding of Child–Robot Interactions
As we have seen, in the emerging society, interactions with code and everything written with it will probably become increasingly more common. On the one hand, as was properly underlined, code is becoming more prevalent in everyday life; on the other hand, it risks remaining a distant reality in understanding. Four reasons [4] for this were identified:
- Coding requires particular skills, such as engineering and programming, from which non-specialists are excluded;
- It is constantly evolving and, for this reason, it is difficult to understand;
- It has a commercial dimension subject to market laws and logic;
- It is made up of a set of processes and languages that are complex, even for those who create them.
This is also consistent with frameworks and policies, as emerged through the SWOT analysis and with our reflection on Theory of Mind and child–robot interactions. Naya and Varela [69] argued that coding and educational robotics can expose students to a real world, where—as Dennett showed us—algorithms do not usually work as intended. Some authors [70] have suggested using robotics for this purpose as a branch of AI that includes design thinking, mathematics, and computational thinking. Frameworks, policies, and the literature seem to indicate coding, computational thinking, and educational robotics as educational opportunities to prepare young people for the code society in which artificial intelligence is gaining a crucial role. This path requires a theoretical basis that we are going to identify.
5.1. Humans, Robots, and Artificial Intelligence: An Almost Ancient Story
Particular attention seems to be paid to the pairing of robot/artificial intelligence [71]. If we look at the history of contemporary philosophy, this is not surprising. In 1964, the American Philosophical Association dedicated a symposium to the theme “Minds and Machine”. In this occasion, Hilary Putnam opened his contribution recalling science fiction literature in defining robots as “hypothetical machines that simulate human behavior, often with an at least roughly human appearance” [72] (p. 668). Putnam’s point was to explore whether it is possible for a robot to “have feelings, thoughts, attitudes, and character traits”, and, if so, what necessary and sufficient conditions would enable this. In just a page, we faced complex themes such as the following: mind/body dualism; robot mental states and robot bodies; intentionality; and artificial intelligence and the debate between “strong” and “wake” form. These themes are fundamental and steadily connected at varying degrees in so-called human–robot interactions.
It is hard to define human–robot interaction (HRI). What we can assume about it is that the research focus is neither the human nor the robot, but rather the relationship and the interactions between them [73]. Sometimes it is intended as a disciplinary complex [18], as a discipline linked to philosophy and robotics, or as a technology in general and for design [74]. It is also defined as a field of intersection between engineering, psychology, and design [73]. In this contribution, as a first approximation, we will assume a human–robot interaction as a field grounded on a disciplinary complex that includes philosophy and robotics.
Similarities and dissimilarities between humans and machines are one of the basic points that underlie to the topics we are analyzing. Analogy—in all its forms—be it positive, negative, or neutral [75], can also be a powerful tool in this field for knowledge building, as well as for explanations. As we will see, the reflections on similarities and dissimilarities between humans and robots concern both appearance and capabilities (or, as one could say, the body and the mind). We must consider that reflections in the mind precede the ones in the body. The possibility of a human body apparency remains in Fritz Lang movie and in Asimov novel longer than the possibility of thinking. The analogies between humans and machines, concerning the mind and the ability to think and act, come first.
5.1.1. “Can Machines Think?”
It is important to underline the relevance of the context in HRI studies [74]. We must pay equal attention to the context in which the interaction is studied (school, work, etc.) and to the cultural context of the people involved in the interaction. In particular, regarding Alan Turing, we have a large scale of misconceptions, generated, in large part, from pop culture sources. Let us consider, for instance, the two most widespread misconceptions. The so-called “Turing machine” is an imaginary virtual machine, not a huge old computing machine, and the so-called “Turing test” is a thought experiment; neither has anything to do with the description of the code produced by Enigma, the encryption machine used by the German Army during World War II. In Computing Machinery and Intelligence [76], a paper published in 1950, Turing proposed a variant of the “imitation game”. This thought experiment was set to recognize if an unknown speaker is male or female. First, the structure of the game. There are three players: an interrogator (indifferently male or female); (A) a man; and (B) a woman. The interrogator, who asks and writes questions and analyzes the written answers of A and B, must guess who the man is and who is the woman without using any other form of information or contact. The Turing proposal is to replace A with a machine. In this scenario, the original question “Can machines think?” is related with “What will happen when a machine takes the part of A in this game?” and “Will the interrogator decide wrongly as often when the game is played like this as he does when the game is played between a man and a woman?” [76] (p. 434). From this new starting point, Turing set the argument to deal with several objections. We take into account Turing’s consideration that these are particularly significant for the purpose of the present contribution. According to Turing, if a machine is construed to play the imitation game, it can realize something that can be defined as thinking even though it is different from human thinking. Furthermore, a digital computer can be built to perform actions that imitate those of a human computer. This perspective brings us to most discussed topic at the present time: artificial intelligence. John Searle, in his fundamental paper Minds, Brains, as Programs [77], defines defines both weak AI and strong AI. The former, which Searle endorses, is a computer that is defined as “a very powerful tool” [77] (p. 235) of study, where the mind formulates and tests hypotheses with rigorous methods. A very similar position that sees computers and computer concepts as powerful tools for thinking will be presented many years later by Dennett. Searle defines strong AI as a computer that “literally has cognitive states and […] the programs thereby explain human cognition” [77] (p. 235) with another famous counterexample of the “Chinese room”. This experiment is a variation of the imitation game. In extreme simplification, a native English speaker, despite not knowing Chinese, but thanks to instructions in English, is able to hold a conversation with a native Chinese speaker. As Dennett highlights in [78], the counterexample of the Chinese room has endured several decades. At the present time, when we can talk about AI [3] in terms of machine learning (in which an algorithm allows a machine to learn what is necessary to complete an action for which it has not been previously programmed) and deep learning (in which algorithms prepare neural networks), the discussion set up by Searle seems still open and relevant.
5.1.2. Anthropomorphizing Machines
In the previous paragraph, we talked about machines and computers and the possibility of their thinking. Since our focus is on robots, we will assume that the considerations made thus far are also valid for this particular category. In addition, we will delve into the aspect that specifies robots and distinguishes them from other machines: their appearance. We wondered about the similarity between the human mind and the machine; what can we say about the appearance of robots? Does being a machine with a particular appearance similar to humans have a role in HRI? This leads us to analyze a broad theme: the anthropomorphization of machines. We will treat it from several points of view: the appearance, strictly understood; the movement; and the behavior. In 1970, while the debate triggered by the imitation game proposed by Turing continued, Mori published a paper proposing the so-called concept of uncanny valley, which was renewed in English translation in 2012 [79]. This is a prediction, rather than a theory. According to Mori, the more human-like a robot is in appearance, the more favorably it is perceived. When this similarity is too strong and the robot’s appearance is almost indistinguishable from that of a human, it is rejected. Some authors [80,81] have broadened the concept beyond human being to nature in general and have defined the uncanny valley through the categories of aesthetics, specifically as a phenomenon whereby an inaccurate resemblance to natural beings can generate observer repulsion. As noted in [74], the uncanny valley is just a proposal, and its author presented it as such and did not support it with empirical data; nonetheless, it has often been inappropriately advanced as a justification for the human rejection of robots without an analysis of the correlations with appearance.
5.2. Stance, Explanation, and HRI
We focused on anthropomorphizing from an embodiment perspective.
We will try to consider it in terms of interaction processes and underling explanations that we can assume as mentalistic or non-mentalistic [82]. As noted in [83], according to some authors, human beings tend to anthropomorphize what they do not fully understand and to attribute human characteristics to non-human agents or to real or imaginary objects. When we lack specific knowledge, as in the case of machines and robots, we choose “human” models. From this point of view, Marchesi and colleagues argued that an intentional stance is a concept similar to, but not identical to, anthropomorphism.
This bring us to consider Dennett and his studies on stance [84], which remain, to this day, the fundamental background of most of the explanation of artificial agents’ behavior from a mentalistic point of view [82].
Dennett identified three kinds of stance that can be determined by explaining and predicting computer behaviors: the design stance; the physical stance; and the intentional stance. The design stance is generally used to explain mechanical objects. The design stance works when a computer and all its parts perform exactly as they are designed to function. Clearly enough, design stances are strictly related to the concept of function, they can imply proper function as base of warrant [85], and they are a peculiar form of teleology [86]. From a design stance, we cannot explain any kind of breakdown or malfunction since this stance does not take into account “the physical constitution or condition of the innards of the particular object” [84] (p. 88). The physical stance results from what we know about the laws of nature, and it allows us to take into account the current state of an object. Given the complexity of computers, it is rarely adopted for them, and it only usually happens in cases of breakdown. Turing in [76] believed in a possibility of machines being able to compete with humans in intellectual activity. In addition, Dennett also set an example based on a chess-playing computer. In an hypothetical chess game, a human can win only when considering the computer as an “intelligent human opponent” [84] (p. 89) because it has a level of complexity such that its behavior is not explained or predicted through a knowledge of physics (physical stance) and/or of a programming (design stance).
This assumption brings us to the intentional stance, which allows us to see computer as intentional systems.
From this perspective, according to Dennett, “it is a small step to calling the information possessed the computer’s beliefs, its goals and subgoals its desires” [84] (p. 90), which, in our path, is “a giant leap” forward for facing the HRI.
We know that, in the HRI, the context plays a crucial role [73]. This encourages us to consider not only the point of view of scientists, but also that of the people who are operating in our main context: a school with teaching and learning processes. In the code society, teachers, students, parents, and a large variety of people involved as stakeholders, can form mental models of agents as robot or AI. This is why we considered recent studies that, in taking into account non-specialist people, propose a folk-cognitivist stance related to forms of input–output regularity and to algorithms [82].
5.3. Theory of Mind and Child–Robot Interactions
A deeper compression of HRI with respect to all of the components of a school community, i.e., teachers, pupils, and parents, can help us in several aspects. Under this perspective, it is important to consider people as part of a society with different attitudes, beliefs, cultural schemes, and values, which are all factors the researcher must consider and respect when introducing robots [74]. Coding, computational thinking, and educational robotics bring machines and robots forward as physical objects, as well as concepts in the classroom. In teaching and learning activities, we will also consider child–robot interactions (cHRIs), which represent a specific domain of the broader research, as shown in [18]. As was properly underlined by Belpaeme and colleagues [87]: “children are not just small adults”, which is why cHRIs are deeply different from the HRI (as the latter occurs for adult subjects).
What is the educational focus in cHRIs? On the one hand, we can say that robots are often produced for children with a particular attention to the educational context, where a deeper comprehension of cHRIs could help in designing robots. On the other hand, and more relevant for our purposes, a significant impact can be had in the teaching–learning process. This type of interactions can help teachers to choose language, robot, and design activities, and it can help researchers to identify content, structures, and methods for learning path proposals.
The appearance of a robot is an important element in its interaction. As noted in the reflection on the uncanny valley concept [74], the appearance marks the human expectations and the explanation of robot behavior. As recently analyzed in a learning context [88], it is particularly relevant in a pupil’s construction of a robot’s mental model. Nevertheless, regarding the mental aspect, recent studies [89] have highlighted the ability to attribute mental states as a basis for the construction of HRI.
This leads us to the following two topics: stances, which have already been discussed; and the Theory of Mind (ToM). Here, as a provisional definition, we will assume that having a ToM means having the ability to understand mental states, as well as to predict and explain the behavior of other human beings. In our discussion, the ToM is important from two points of view: in the analysis of cHRIs and in the pedagogical value that is given to the ToM itself and its variant, i.e., the Theory of Artificial Mind (ToAM).
Analyzing the ToM in cHRIs is relevant in a society in which we can imagine that children will increasingly interact with robots and robotic agents in every aspect of life [83,89], including at school and in education. The studies carried out in this field [87,89,90] allow us to understand if and when children use the ToM in their interaction with robots and what differences there are compared to the attribution of mental states to other human beings. These elements are fundamental for the construction of educational paths that are oriented toward the use of both educational robotics and artificial intelligence, which take a child’s abilities, cognitive development, and learning needs into due consideration.
Ten years ago, Spektor and Mioduser noted [91] that although we live in a world of “behavioral artifacts”, we have little knowledge regarding our perception of these and the interactions we have with them. This is particularly relevant to perception of children regarding these artifacts. In a quali-quantitative research, Spektor and Mioduser [91] found that, through programming robot activities, children develop what the researchers presented as a new theoretical scheme called the Theory of Artificial Mind (ToAM), which is distinct from their conception of the Theory of Mind (ToM). In another recent quali-quantitative research, Mioduser and Kuperman [92] noted that, through programming, children seem to perceive robots as a rule-based system. This kind of awareness became fundamental in a scenario [89] in which the children interacted with robots and robotic agents in an ever-increasing number and variety of areas and aspects in their lives.
6. Conclusions
In the present contribution, we underlined that the interest aroused by recent developments in artificial intelligence has brought this debate to the field of education. As always happens with emerging technologies, there is a constant push to make them the object and tool of curricula. We dedicated a deep reflection on the HRI and cHRIs because they are significant from a pedagogical point of view in facing the use of coding, computational thinking, and educational robotics at school. Starting from the results of the same SWOT, we deepened the discussion on the elements that can support the construction of coding, computational thinking, and educational robotics paths that are aimed at an adequate educational situation for eliciting the competencies necessary to operate in the code society. The SWOT analysis also revealed the value of active methodologies and laboratory approaches. This led us to an unblackboxing approach to technology as a broad concept, as well as to educational robotics and artificial intelligence. This approach, as we underlined, is already being considered in media education [3], in the maker movement, in the FabLab tradition [93], and in the philosophical approach to coding and computational thinking [7].
According to this perspective, we tried to demonstrate that understanding the dynamics of HRI and cHRIs can support the creation of educational paths if the relationship with the technological element is deepened as a dimension of the teaching and learning process, and if it is aimed at understanding the technology itself and the world of which it is a part.
If it is necessary to talk about AI literacy, the authors are convinced that coding and robotics, if handled with the awareness that cHRIs can give, can contribute to creating a broad framework of technological literacy and digital citizenship education in which AI can reasonably be inserted.
Author Contributions
Funding
This study was funded by Project HERB-Human Explanation of Robotic Behaviour–CUP Master: H53D23004060006-CUP: B53D23014230008 (Bando 2022-PRIN 20224X95JC-MUR, Segretariato Generale Direzione Generale della Ricerca)-PNRR-Mission 4 “Education and Research”–Component C2–Investment 1.1, “Fund for Research Programmes of National Interest (PRIN)”, FINANCED BY THE EUROPEAN UNION–Next Generation EU.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Floridi, L. Philosophy and Computing: An Introduction; Routledge: London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Ferraris, M. L’inconscio artificiale. Boll. Filos. 2021, 36, 60–68. [Google Scholar]
- Panciroli, C.; Rivoltella, P.C. Pedagogia Algoritmica: Per una Riflessione Educativa Sull’Intelligenza Artificiale; Number 227 in Orso blu; Scholé: Brescia, Italy, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Accoto, C. Il Mondo Dato. Cinque Brevi Lezioni di Filosofia Digitale; Egea: Milano, Italy, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Floridi, L.; Cabitza, F. Intelligenza Artificiale: L’uso delle Nuove Macchine; Bompiani: Milano, Italy, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Di Stasio, M.; Camizzi, L.; Messini, L. Understanding languages and building literacies for citizens education. J. e-Learn. Knowl. Soc. 2022, 18, 117–127. [Google Scholar]
- Di Stasio, M.; Messini, L. Intrecci di culture: Literacies per la consapevolezza della realtà. In La Scuola Come Bene di Tutti, la Scuola per il Bene di Tutti; Pastori, G., Luisa Zecca, F.Z., Eds.; FrancoAngeli: Milan, Italy, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Stuart, L. 21st Century Skills for 21st Century Jobs. A Report of the U.S. Department of Commerce, U.S. Department of Education, U.S. Department of Labor, National Institute for Literacy and Small Business Administration; Technical Report; Department of Commerce: Washington, DC, USA, 1999; ISBN 0-16-049964-X.
- European Commission. Recommendation of the European Parliament and of the Council of 18 December 2006 on Key Competences for Lifelong Learning; Technical Report; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Piano D’Azione per L’Istruzione Digitale 2021–2027 Ripensare L’Istruzione e la Formazione per L’era Digitale; Technical Report; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2020; Available online: https://education.ec.europa.eu/focus-topics/digital-education/action-plan (accessed on 7 July 2024).
- MIUR. Piano Nazionale Scuola Digitale; Technical Report; MIUR: Rome, Italy, 2015. Available online: https://www.miur.gov.it/scuola-digitale (accessed on 7 July 2024).
- MIUR. Indicazioni Nazionali e Nuovi Scenari; Technical Report; MIUR: Rome, Italy, 2018. Available online: https://www.miur.gov.it/documents/20182/0/Indicazioni+nazionali+e+nuovi+scenari/ (accessed on 7 July 2024).
- European Commission. Ethical Guidelines on the Use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Data in Teaching and Learning for Educators; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Recommendation of the Council on Artificial Intelligence; Technical Report OECD/LEGAL/0449; OECD: Paris, France, 2019; Available online: https://legalinstruments.oecd.org/en/instruments/OECD-LEGAL-0449 (accessed on 7 July 2024).
- Educational, U.N. Steering AI and Advanced ICTs for Knowledge Societies: A Rights, Openness, Access, and Multi-Stakeholder Perspective. Available online: https://unesdoc.unesco.org/ark:/48223/pf0000372132 (accessed on 7 July 2024).
- Educational, U.N. K-12 AI Curricula: A Mapping of Government-Endorsed AI Curricula. Technical Report. Available online: https://unesdoc.unesco.org/ark:/48223/pf0000380602 (accessed on 7 July 2024).
- Mortari, L. La ricerca empirica in educazione: Questioni aperte. Studi Form./Open J. Educ. 2009, 12, 33–46. [Google Scholar]
- Damiano, L. Mente, robot ed ecologie sociali miste. Per unépistemologia sperimentale dei robot sociali. Sist. Intelligenti 2020, 1, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchive, A. La Pédagogie à L’épreuve de la Didactique: Approche Historique, Perspectives théOriques et Recherches Empiriques; Paideia, Presses Universitaires de Rennes: Rennes, France, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Dewey, J. Essays in Experimental Logic; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 21st Century Knowledge and Skills in Educator Preparation. Technical Report, American Association of Colleges of Teacher Education and the Partnership for 21st Century Skills (P21). 2010. Available online: https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED519336.pdf (accessed on 7 July 2024).
- Dede, C. Comparing frameworks for 21st century skills. 21st Century Ski. Rethink. How Stud. Learn. 2010, 20, 51–76. [Google Scholar]
- Vuorikari, R.; Kluzer, S.; Punie, Y. DigComp 2.2: The Digital Competence Framework for Citizens; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Law, N.; Woo, D.J.; de la Torre, J.; Wong, K. A Global Framework of Reference on Digital Literacy Skills for Indicator 4.4.2. 2018. Available online: https://uis.unesco.org/sites/default/files/documents/ip51-global-framework-reference-digital-literacy-skills-2018-en.pdf (accessed on 7 July 2024).
- Scott, C.L. The Futures of Learning 2: What Kind of Learning for the 21st Century? Educ. Res. Foresight Work. Pap. 2015, 14, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- OECD. The Future of Education and Skills Education 2030; Technical Report; OECD: Paris, France, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Office, I.L. Global Framework on Core Skills for Life and Work in the 21st Century; Technical Report; International Labour Office: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Bocconi, S.; Chioccariello, A.; Kampylis, P.; Dagienė, V.; Wastiau, P.; Engelhardt, K.; Earp, J.; Horvath, M.; Jasutė, E.; Malagoli, C.; et al. Reviewing Computational Thinking in Compulsory Education; Technical Report; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Balanskat, A.; Engelhardt, K.; Licht, A.H. Strategies to Include Computational Thinking in School Curricula in Norway and Sweden- European Schoolnet’s 2018 Study Visit; Technical Report; European Schoolnet: Brussels, Belgium, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kampylis, P.; Dagienė, V.; Bocconi, S.; Chioccariello, A.; Engelhardt, K.; Stupurienė, G.; Masiulionytė-Dagienė, V.; Jasutė, E.; Malagoli, C.; Horvath, M.; et al. Integrating Computational Thinking into Primary and Lower Secondary Education: A Systematic Review. Educ. Technol. Soc. 2023, 26, 99–117. [Google Scholar]
- K-12 Computer Science Framework Steering Committee. K-12 Computer Science Framework; Technical Report; K-12 Computer Science Framework Steering Committee: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Key Competences for Lifelong Learning; Technical Report; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wing, J. Computational thinking’s influence on research and education for all. Ital. J. Educ. Technol. 2017, 25, 7–14. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Chen, P.; Lin, Z. Artificial Intelligence in Education: A Review. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 75264–75278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goksel, N.; Bozkurt, A. Artificial Intelligence in Education: Current Insights and Future Perspectives. In Advances in Educational Technologies and Instructional Design; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2019; pp. 224–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Stasio, M.; Nulli, G. Nterfacce tangibili per la didattica disciplinare nel Primo Ciclo. Dalla sperimentazione alla formazione. In Interazione Bambini-Robot; Bozzi, G., Luisa Zecca, E.D., Eds.; FrancoAngeli: Milano, Italy, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Dewey, J. Experience and Education. Educ. Forum 1986, 50, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papert, S. Mindstorms; Basic Books: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Benvenuti, M.; Cangelosi, A.; Weinberger, A.; Mazzoni, E.; Benassi, M.; Barbaresi, M.; Orsoni, M. Artificial intelligence and human behavioral development: A perspective on new skills and competences acquisition for the educational context. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2023, 148, 107903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Children’s Machine: Rethinking School in the Age of the Computer; A Member of the Perseus Books Group. 1993. Available online: https://lcl.media.mit.edu/resources/readings/childrens-machine.pdf (accessed on 7 July 2024).
- Merlo, D. La Robotica Educativa Nella Scuola Primaria; StreetLib: Loreto, Italy, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, S.E.; Won, E.S. Systematic Review of Research Trends in Robotics Education for Young Children. Sustainability 2018, 10, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gratani, F.; Giannandrea, L.; Renieri, A.; Annessi, M. Fostering Students’ Problem-Solving Skills through Educational Robotics in Primary School. In Studies in Computational Intelligence; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nulli, G.; Miotti, B.; Stasio, M.D. Robotica Educativa e Coding: Strumenti per la Trasformazione del Curricolo; Indire, Carocci Editore: Firenze, Italy, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Bagattini, D.; Miotti, B. Lavorare sul Genere a Scuola con Coding e Robotica Educativa; Ricerche Indire, Carocci Editore: Firenze, Italy, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Malvezzi, M.; Alimisis, D.; Moro, M. (Eds.) Education in & with Robotics to Foster 21st-Century Skills; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; Volume 982. [Google Scholar]
- Lepuschitz, W.; Merdan, M.; Koppensteiner, G.; Balogh, R.; Obdržálek, D. (Eds.) Robotics in Education: RiE 2022; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; Volume 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balogh, R.; Obdržálek, D.; Christoforou, E. (Eds.) Robotics in Education: Proceedings of the RiE 2023 Conference; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; Volume 747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merdan, M.; Lepuschitz, W.; Koppensteiner, G.; Balogh, R.; Obdržálek, D. (Eds.) Robotics in Education: RiE 2021; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; Volume 1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaradozzi, D.; Guasti, L.; Stasio, M.D.; Miotti, B.; Monteriù, A.; Blikstein, P. (Eds.) Makers at School, Educational Robotics and Innovative Learning Environments: Research and Experiences from FabLearn Italy 2019, in the Italian Schools and Beyond; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilfried Lepuschitz, M.M.; Koppensteiner, G.; Balogh, R.; Obdržálek, D. (Eds.) Robotics in Education: Methodologies and Technologies; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; Volume 1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ching, Y.H.; Hsu, Y.C. Educational Robotics for Developing Computational Thinking in Young Learners: A Systematic Review. TechTrends 2023, 68, 423–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilüfer Atman Uslu, G.Ö.Y.; Usluel, Y.K. A systematic review study on educational robotics and robots. Interact. Learn. Environ. 2023, 31, 5874–5898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montuori, C.; Pozzan, G.; Padova, C.; Ronconi, L.; Vardanega, T.; Arfé, B. Combined Unplugged and Educational Robotics Training to Promote Computational Thinking and Cognitive Abilities in Preschoolers. Educ. Sci. 2023, 13, 858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapti, S.; Sapounidis, T. Critical thinking, Communication, Collaboration, Creativity in kindergarten with Educational Robotics: A scoping review (2012–2023). Comput. Educ. 2024, 210, 104968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.I.; Khordi-moodi, M.; Lohan, K.S. Social Robot for STEM Education. In Proceedings of the Companion of the HRI ’20, 2020 ACM/IEEE International Conference on Human-Robot Interaction, Cambridge, UK, 23–26 March 2020; pp. 90–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangina, E.; Psyrra, G.; Screpanti, L.; Scaradozzi, D. Robotics in the Context of Primary and Preschool Education: A Scoping Review. IEEE Trans. Learn. Technol. 2024, 17, 342–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auyelbek, M.; Ybyraimzhanov, K.; Andasbayev, E.; Abdykerimova, E.; Turkmenbayev, A. Analysis of Studies in the Literature on Educational Robotics. J. Turk. Sci. Educ. 2022, 19, 1267–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapounidis, T.; Alimisis, D. Educational Robotics Curricula: Current Trends and Shortcomings. In Studies in Computational Intelligence; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavo, F.; Campitiello, L.; Todino, M.D.; Di Tore, P.A. Educational Robots, Emotion Recognition and ASD: New Horizon in Special Education. Educ. Sci. 2024, 14, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meral, M.; Altun Yalçin, S. Trends in Studies on Educational Robotics in Recent Years: A Content Analysis. Trak. Eğit. Derg. 2024, 14, 148–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, F.R.; Moriarty, M.A. Robotics and Discovery Learning: Pedagogical Beliefs, Teacher Practice, and Technology Integration. J. Technol. Teach. Educ. 2009, 17, 109–142. [Google Scholar]
- Schina, D.; Esteve-González, V.; Usart, M. An overview of teacher training programs in educational robotics: Characteristics, best practices and recommendations. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2021, 26, 2831–2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocconi, S.; Chioccariello, A.; Dettori, G.; Ferrari, A.; Engelhardt, K. Developing Computational Thinking in Compulsory Education—Implications for Policy and Practice; Technical Report; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Balanskat, A.; Engelhardt, K. Computing Our Future: Computer Programming and Coding—Priorities, School Curricula and Initiatives across Europe; Technical Report; European Schoolnet: Brussels, Belgium, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Screpanti, L.; Miotti, B.; Monteriù, A. Robotics in Education: A Smart and Innovative Approach to the Challenges of the 21st Century. In Makers at School, Educational Robotics and Innovative Learning Environments: Research and Experiences from FabLearn Italy 2019, in the Italian Schools and Beyond; Scaradozzi, D., Guasti, L., Di Stasio, M., Miotti, B., Monteriù, A., Blikstein, P., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 17–26. [Google Scholar]
- Bano, S.; Atif, K.; Mehdi, S.A. Systematic review: Potential effectiveness of educational robotics for 21st century skills development in young learners. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2023, 29, 11135–11153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, Y.; George, J.; Samuel, J. Beyond STEM, How Can Women Engage Big Data, Analytics, Robotics and Artificial Intelligence? An Exploratory Analysis of Confidence and Educational Factors in the Emerging Technology Waves Influencing the Role of, and Impact Upon, Women. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.11746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naya-Varela, M.; Guerreiro-Santalla, S.; Baamonde, T.; Bellas, F. Robobo SmartCity: An Autonomous Driving Model for Computational Intelligence Learning Through Educational Robotics. IEEE Trans. Learn. Technol. 2023, 16, 543–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolpe, K.; Hallström, J. Artificial intelligence literacy for technology education. Comput. Educ. Open 2024, 6, 100159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandlhofer, M.; Steinbauer, G.; Lassnig, J.; Menzinger, M.; Baumann, W.; Ehardt-Schmiederer, M.; Bieber, R.; Winkler, T.; Plomer, S.; Strobl-Zuchtriegl, I.; et al. EDLRIS: A European Driving License for Robots and Intelligent Systems. KI—Künstl. Intell. 2021, 35, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putman, H.; Putnam, H. Robots: Machines or Artificially Created Life? J. Philos. 1964, 61, 668–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartneck, C. Godspeed Questionnaire Series: Translations and Usage. In International Handbook of Behavioral Health Assessment; Krägeloh, C.U., Alyami, M., Medvedev, O.N., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartneck, C.; Belpaeme, T.; Eyssel, F.; Kanda, T.; Keijsers, M.; Šabanović, S. Human-Robot Interaction: An Introduction, 1st ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesse, M.B. Models and Analogies in Science, 2nd ed.; Philosophy: Notre Dame, IN, USA, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Turing, A.M. Computing Machinery and Intelligence. Mind 1950, 59, 433–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Searle, J.R. Minds, brains, and programs. Behav. Brain Sci. 1980, 3, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennett, D.C. Intuition Pumps and Other Tools for Thinking, 1st ed.; W. W. Norton & Company: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Mori, M.; MacDorman, K.F.; Kageki, N. The Uncanny Valley [From the Field]. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2012, 19, 98–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDorman, K.F.; Ishiguro, H. The uncanny advantage of using androids in cognitive and social science research. Interact. Stud. Soc. Behav. Commun. Biol. Artif. Syst. 2006, 7, 297–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, D.; Di Nuovo, S.; Buono, S.; Di Nuovo, A. Robots in Education and Care of Children with Developmental Disabilities: A Study on Acceptance by Experienced and Future Professionals. Int. J. Soc. Robot. 2017, 9, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larghi, S.; Datteri, E. Educational Robotics Inclusive and Technology Education. In Proceedings of the CIFMA 2023—5th International Workshop on Cognition: Interdisciplinary Foundations, Models and Applications; Lecture Notes in Compuer Science (LNCS); Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Marchesi, S.; Ghiglino, D.; Ciardo, F.; Perez-Osorio, J.; Baykara, E.; Wykowska, A. Do We Adopt the Intentional Stance Toward Humanoid Robots? Front. Psychol. 2019, 10, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dennett, D.C. Intentional Systems. J. Philos. 1971, 68, 87–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plantinga, A. Warrant and Proper Function; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Di Stasio, M. Plantinga e L’argomento Teleologi: Dalla Critica a Hume al Ruolo del Concetto di “Proper Function”. Annali del dipartimento di filosofia. N. 11-2005. 2005. Available online: https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/228528355.pdf (accessed on 7 July 2024).
- Belpaeme, T.; Baxter, P.; de Greeff, J.; Kennedy, J.; Read, R.; Looije, R.; Neerincx, M.; Baroni, I.; Zelati, M.C. Child-Robot Interaction: Perspectives and Challenges. In Social Robotics; Herrmann, G., Pearson, M.J., Lenz, A., Bremner, P., Spiers, A., Leonards, U., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2013; pp. 452–459. [Google Scholar]
- Storjak, I.; Krzic, A.S.; Jagust, T. Elementary School Pupils’ Mental Models Regarding Robots and Programming. IEEE Trans. Educ. 2022, 65, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dio, C.D.; Manzi, F.; Peretti, G.; Cangelosi, A.; Harris, P.L.; Massaro, D.; Marchetti, A. Come i bambini pensano alla mente del robot. Il ruolo dell’attaccamento e della Teoria della Mente nell’attribuzione di stati mentali ad un agente robotico. Sist. Intelligenti 2020, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Dio, C.; Manzi, F.; Peretti, G.; Cangelosi, A.; Harris, P.L.; Massaro, D.; Marchetti, A. Shall I Trust You? From Child–Robot Interaction to Trusting Relationships. Front. Psychol. 2020, 11, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spektor-Precel, K.; Mioduser, D. 5–7 Year Old Children’s Conceptions of Behaving Artifacts and the Influence of Constructing Their Behavior on the Development of Theory of Mind (ToM) and Theory of Artificial Mind (ToAM). Interdiscip. J. e-Ski. Lifelong Learn. 2015, 11, 329–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mioduser, D.; Kuperman, A. Young Children’s Representational Structures of Robots’ Behaviors. Des. Technol. Educ. 2020, 25, 143–159. [Google Scholar]
- Blikstein, P. Maker Movement in Education: History and Prospects. In Handbook of Technology Education; Springer International: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).