Joint Models for Incomplete Longitudinal Data and Time-to-Event Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
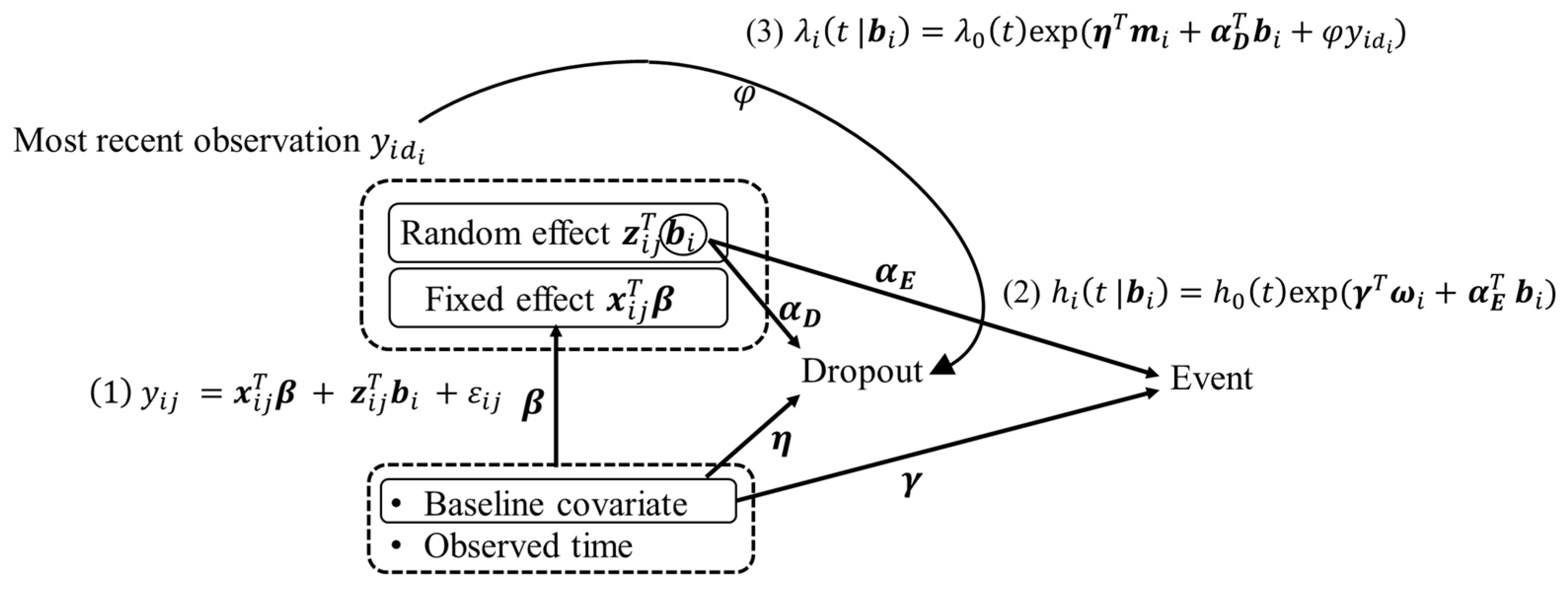
2. Proposed Model and Estimation
2.1. Proposed Model
2.2. Estimation
3. Numerical Results
3.1. Simulation
3.2. PBC2 Data Analysis
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wulfsohn, M.S.; Tsiatis, A.A. A joint model for survival and longitudinal data measured with error. Biometrics 1997, 53, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsiatis, A.; Davidian, M. An overview of joint modeling of longitudinal and time-to-event data. Stat. Sin. 2004, 14, 793–818. [Google Scholar]
- Molenberghs, G.; Beunckens, C.; Sotto, C.; Kenward, M.G. Every missingness not at random model has a missingness at random counterpart with equal fit. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Stat. Methodol. 2008, 70, 371–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, D.B. Inference and missing data. Biometrika 1976, 63, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, R.J.A.; Rubin, D.B. Statistical Analysis with Missing Data, 2nd ed.; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Little, R.J. Pattern-mixture models for multivariate incomplete data. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1993, 88, 125–134. [Google Scholar]
- Little, R.J. A class of pattern-mixture models for normal incomplete data. Biometrika 1994, 81, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, R.J. Modeling the drop-out mechanism in repeated-measures studies. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1995, 90, 1112–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.C.; Carroll, R.J. Estimation and comparison of changes in the presence of informative right censoring by modeling the censoring process. Biometrics 1988, 44, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.C.; Bailey, K.R. Estimation and comparison of changes in the presence of informative right censoring: Conditional linear model. Biometrics 1989, 45, 939–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Follmann, D.; Wu, M. An approximate generalized linear model with random effects for informative missing data. Biometrics 1995, 51, 151–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molenberghs, G.; Vereke, G. Models for Discrete Longitudinal Data; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Molenberghs, G.; Kenward, M.G. Missing Data in Clinical Studies; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Creemers, A.; Hens, N.; Aerts, M.; Molenberghs, G.; Verbeke, G.; Kenward, M.G. A sensitivity analysis for shared-parameter models for incomplete longitudinal outcomes. Biom. J. 2010, 52, 111–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creemers, A.; Hens, N.; Aerts, M.; Molenberghs, G.; Verbeke, G.; Kenward, M.G. Generalized shared-parameter models and missingness at random. Stat. Model. 2011, 11, 279–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njagi, E.N.; Molenberghs, G.; Kenward, M.G.; Verbeke, G.; Rizopoulos, D. A characterization of missingness at random in a generalized shared-parameter joint modeling framework for longitudinal and time-to-event data, and sensitivity analysis. Biom. J. 2014, 56, 1001–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papageorgiou, G.; Rizopoulos, D. An alternative characterization of MAR in shared parameter models for incomplete longitudinal data and its utilization for sensitivity analysis. Stat. Model. 2021, 21, 95–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomadakis, C.; Meligkotsidou, L.; Pantazis, N.; Touloumi, G. Longitudinal and time-to-drop-out joint models can lead to seriously biased estimates when the drop-out mechanism is at random. Biometrics 2019, 75, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizopoulos, D. The R Package JMbayes for Fitting Joint Models for Longitudinal and Time-to-Event Data Using MCMC. J. Stat. Softw. 2016, 72, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, J.C.; Bates, D.M. Mixed-Effects Models in S and S-PLUS; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
| Scenario 1 | Scenario 2 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| True Value | Mean | MCSE | Bias | CV(%) | Mean | MCSE | Bias | CV(%) | |
| Proposed Model | |||||||||
| Intercept | 0.5 | 0.48 | 0.3110−2 | −0.02 | 94.7 | 0.48 | 0.3110−2 | −0.02 | 95.2 |
| Slope | 0.8 | 0.79 | 0.0910−2 | −0.01 | 88.4 | 0.78 | 0.0910−2 | −0.01 | 89.3 |
| Baseline Covariate | 0.8 | 0.86 | 0.3610−2 | 0.05 | 94.5 | 0.85 | 0.4010−2 | 0.05 | 93.8 |
| Survival Model Baseline | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.7610−2 | 0.00 | 93.7 | 0.04 | 0.8010−2 | 0.01 | 94.0 |
| Association Intercept | 1 | 0.69 | 2.0610−2 | −0.31 | 97.4 | 0.70 | 2.0610−2 | −0.29 | 98.1 |
| Association Slope | 3 | 3.67 | 4.9610−2 | 0.66 | 98.4 | 3.68 | 5.01 × 10−2 | 0.65 | 98.6 |
| Joint Model | |||||||||
| Intercept | 0.5 | 0.49 | 0.3610−2 | −0.01 | 97.0 | 0.50 | 0.3610−2 | −0.00 | 97.0 |
| Slope | 0.8 | 0.81 | 0.2210−2 | 0.01 | 99.8 | 0.82 | 0.2210−2 | 0.02 | 99.6 |
| Baseline Covariate | 0.8 | 0.81 | 0.4910−2 | 0.01 | 96.4 | 0.81 | 0.4910−2 | 0.01 | 95.8 |
| Survival Model Baseline | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.8510−2 | 0.01 | 97.4 | 0.05 | 0.8510−2 | 0.02 | 97.2 |
| Association Intercept | 1 | 1.33 | 0.7610−2 | 0.33 | 50.4 | 1.34 | 0.7610−2 | 0.34 | 49.2 |
| Association Slope | 3 | 2.17 | 1.7910−2 | −0.83 | 49.4 | 2.18 | 1.8310−2 | −0.82 | 50.6 |
| Linear Mixed model | |||||||||
| Intercept | 0.5 | 0.50 | 0.2710−2 | −0.00 | 96.2 | 0.50 | 0.2710−2 | 0.00 | 95.3 |
| Slope | 0.8 | 0.78 | 0.1310−2 | −0.02 | 83.0 | 0.78 | 0.0910−2 | −0.02 | 85.2 |
| Baseline Covariate | 0.8 | 0.80 | 0.2710−2 | 0.00 | 93.4 | 0.81 | 0.2710−2 | 0.01 | 93.5 |
| Estimate | Std.Error | 95%CI | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Proposed Model | |||
| Intercept | 0.56 | 1.210−3 | (0.39, 0.72) |
| Year | 2.65 | 2.310−3 | (2.34, 2.96) |
| Drug | −0.12 | 1.710−3 | (−0.35, 0.11) |
| Survival Model Drug | −0.01 | 2.410−3 | (−0.34, 0.33) |
| Association Intercept | 0.91 | 1.510−3 | (0.71, 1.12) |
| Association Year | 0.37 | 0.710−3 | (0.27, 0.47) |
| Joint Model | |||
| Intercept | 0.57 | 2.010−3 | (0.40, 0.73) |
| Year | 2.77 | 7.810−3 | (2.44, 3.11) |
| Drug | −0.13 | 2.710−3 | (−0.33, 0.08) |
| Survival Model Drug | −0.10 | 7.510−3 | (−0.46, 0.27) |
| Association Intercept | 0.92 | 5.710−3 | (0.69, 1.15) |
| Association Year | 0.48 | 9.710−3 | (0.33, 0.66) |
| Linear Mixed Model | |||
| Intercept | 0.56 | 0.810−1 | (0.40, 0.72) |
| Year | 2.50 | 1.710−1 | (2.15, 2.84) |
| Drug | −0.13 | 1.110−1 | (−0.35, 0.09) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Takeda, Y.; Misumi, T.; Yamamoto, K. Joint Models for Incomplete Longitudinal Data and Time-to-Event Data. Mathematics 2022, 10, 3656. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10193656
Takeda Y, Misumi T, Yamamoto K. Joint Models for Incomplete Longitudinal Data and Time-to-Event Data. Mathematics. 2022; 10(19):3656. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10193656
Chicago/Turabian StyleTakeda, Yuriko, Toshihiro Misumi, and Kouji Yamamoto. 2022. "Joint Models for Incomplete Longitudinal Data and Time-to-Event Data" Mathematics 10, no. 19: 3656. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10193656
APA StyleTakeda, Y., Misumi, T., & Yamamoto, K. (2022). Joint Models for Incomplete Longitudinal Data and Time-to-Event Data. Mathematics, 10(19), 3656. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10193656





