Abstract
Disassembly is one of the most time-consuming and labor-intensive activities during the value recovery of end-of-life (EOL) products. The completion time (makespan) of disassembling EOL products is highly associated with the allocation of operators, especially in parallel disassembly. In this paper, asynchronous parallel disassembly planning (APDP), which avoids the necessity to synchronize disassembly tasks of manipulators during the parallel disassembly process, is studied to optimize the task assignment of manipulators for minimal makespan. We utilize four mixed integer linear programming (MILP) formulations to identify the optimal solutions. A set of different-sized instances are used to test and compare the performance of the proposed models, including some real-world cases. Finally, the proposed exact algorithm is further compared with the existing approach to solving APDP. Results indicate that a significant difference exists in terms of the computational efficiency of the MILP models, while three of four MILP formulations can efficiently achieve better solutions than that of the existing approach.
Keywords:
demanufacturing; disassembly planning; asynchronous parallel disassembly; mixed integer linear programming; exact algorithm MSC:
90B30
1. Introduction
As sustainable manufacturing and circular economy become popular in the industry, demanufacturing has recently attracted increasing attention. In demanufacturing, the first step is to disassemble end-of-life (EOL) products into components or parts and retrieve usable or repairable subassemblies. In addition to economic benefits, the disassembly of EOL products can bring environmental benefits due to the subsequent treatment of subassemblies (e.g., reuse, remanufacturing, and recycling) [1,2], especially toxic materials including solid, liquid, and gas. Disassembly planning (DP) aims to select the optimal disassembly sequence of an EOL product with maximum recovery value and/or processing efficiency [3].
According to the disassembly process, DP can be classified into two categories: (1) sequential disassembly, where parts are disassembled one by one; (2) parallel disassembly, where multiple parts can be disassembled by multiple manipulators simultaneously [4,5]. Sequential disassembly is a typical disassembly problem that has been studied for decades [6], in which only one part or component is disassembled at a time. Obviously, this one-by-one processing could incur a longer makespan to disassemble a product, especially for large or complex products. Parallel disassembly is thus developed that allows multiple manipulators to simultaneously perform disassembly operations. However, parallel disassembly must consider not only the precedence relationships among parts/disassembly operations but also the coordination among manipulators [4]. For parallel disassembly, two challenges need to be addressed: (1) which manipulator is selected for disassembling each part (allocation problem), (2) how to assign parts or disassembly tasks to each manipulator (sequencing problem). Therefore, parallel disassembly is more complicated than sequential disassembly, where sequential disassembly only involves a sequencing problem of disassembling parts/disassembly tasks.
To date, the existing literature on parallel disassembly largely focuses on synchronous manipulator processing, that is, synchronous parallel disassembly planning (SPDP) [3,7,8,9], which requires that the starting time of manipulators are synchronized in each parallel disassembly process. This synchronization simplifies parallel disassembly planning but increases the idle time of manipulators, which affects the disassembly efficiency. Recently, Ren et al. [4] presented a novel parallel disassembly, called asynchronous parallel disassembly, to eliminate the synchronous restriction and strengthen the collaboration among manipulators. Asynchronous parallel disassembly allows a manipulator to continuously work after completing a task as long as precedence (and other) constraints are not violated. In Ren et al.’s work, asynchronous parallel disassembly planning (APDP) was first studied and solved by an improved genetic algorithm (IGA). However, the authors did not describe APDP mathematically and there is no guarantee that the optimal disassembly solutions can be found by IGA. In order to make up for this shortcoming, this paper will make an improvement in terms of mathematical models and methodology based on [4]. Moreover, the proposed method in this work can solve the problems more optimally than the IGA in Ren et al.’s work.
This paper aims at developing an exact method based on the APDP, in which the minimum completion time (makespan) of disassembling a product can be identified. First, we propose a basic mathematical model (i.e., Model 1) for the APDP. Then, three extended models (i.e., Model 2, Model 3, and Model 4) are further developed. To evaluate the performance of the proposed models, a set of different-sized instances are tested. The results of these four formulations are presented and analyzed. Finally, the proposed approach is compared with the IGA used in [4]. Experimental results demonstrate that three of four MILP formulations outperform IGA, specifically, the solutions obtained from IGA are improved in 5 out of 11 test instances. In summary, the key contributions of this work can be summarized as follows:
- (1)
- A nonlinear mathematical model is formulated to demonstrate the APDP.
- (2)
- Four MILP formulations are developed based on the nonlinear model.
- (3)
- The branch-and-cut algorithm of the CPLEX solver is employed to search for exact solutions. The results demonstrate that the exact solutions of three MILP models are able to improve the current best solutions in the test instances.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows. Section 2 provides a literature review, primarily focusing on DP. Section 3 describes the APDP and Section 4 presents four MILP formulations for the APDP. Section 5 first presents the computational results of the models in terms of the problem complexity and the computational performance. Then, the computational results obtained from the proposed approach are compared with that of the existing IGA method. Finally, concluding remarks and future directions are covered in Section 4.
2. Literature Review
The DP is a combinatorial optimization problem and it can be solved by both exact algorithms and heuristic/metaheuristic approaches [10,11,12,13,14]. In terms of exact methods, branch-and-bound algorithms [5,15] and mathematical programming [16] are commonly used, especially the latter. For example, Johnson and Wang [17] established an integer linear programming model based on a two-commodity network flow formulation to find an optimal solution with maximum profit. Kang et al. [18] presented an integer programming model for disassembly sequence planning by modifying the shortest path problem. Lambert [19] formulated a binary integer linear programming approach to maximize profit by applying an AND/OR graph for enumerating the complete set of possible disassembly operations. Ren et al. [16] presented a MILP model to maximize the profit of a partial disassembly process. Edis et al. [20] proposed a MILP model for the disassembly line balancing problem. In addition, several extensions on the MILP model regarding line balancing, hazardousness and demand of parts, and direction changes are proposed.
The exact algorithms perform well when solving relatively small-sized problem instances [21]. However, with the increase in the problem size, their computational times grow exponentially. Therefore, approximate methods are widely used to solve DP problems [22]. Approximate methods mainly refer to heuristics and meta-heuristic algorithms. Smith and Hung [8] studied selective parallel disassembly planning and aimed to maximize product quality and minimize product cost and environmental impacts. Sanchez and Haas [23] studied building disassembly and designed a rule-based recursive method to obtain a near-optimal solution. Seo et al. [24] aimed to optimize the disassembly sequence considering economic and environmental aspects and proposed a genetic algorithm (GA). Kongar and Gupta [25] proposed a weighted multi-objective model to solve the DP problem with consideration of disassembly time, the penalty for direction changes, and the penalty for disassembly method changes. Tian et al. [26] studied the disassembly planning considering uncertainty and proposed a GA to minimize disassembly cost. Based on that, they proposed a hybrid intelligent algorithm that integrates fuzzy simulation and artificial bee colony [27]. Kheder et al. [28] designed a GA to optimize a disassembly process considering several criteria such as maintainability of components and disassembly direction changes. Ren et al. [3] proposed a hierarchical disassembly tree to model selective SPDP and a multi-objective evolutionary algorithm to simultaneously minimize disassembly time and maximize profit. Guo et al. [29] used a scatter search algorithm to simultaneously maximize disassembly profit and minimize time using the weighted coefficient method. Recently, Pistolesi and Lazzerini [9] studied a multi-objective SPDP and proposed a Tensorial Memetic Algorithm (TeMA) to maximize the degree of parallelism, the level of ergonomics, and the balance of workers’ workload, while minimizing the disassembly time and the number of rotating the product.
Meta-heuristic approaches also include the artificial bee colony (ABC) algorithm [27,30,31,32], the particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm [33], the gravitational search algorithm (GSA) [16], and the discrete flower pollination algorithm [34]. They are highly dependent on solution encoding and decoding, parameter setting, and evolutionary operators [35]. On the other hand, it is difficult to guarantee both robustness and optimality of the solutions obtained from a meta-heuristic method [36].
From the literature review above, it is noted that (1) the meta-heuristic algorithms are commonly used to solve DPs, especially for large instances; (2) few studies are available on APDP. In particular, no work exists that models and solves APDP optimally. To fill these gaps, this work is focused on modeling and developing an efficient exact algorithm for APDP. Except for that, this work attempts to optimally solve APDP with medium-/large-sized instances.
3. Problem Description
3.1. Representation of DP
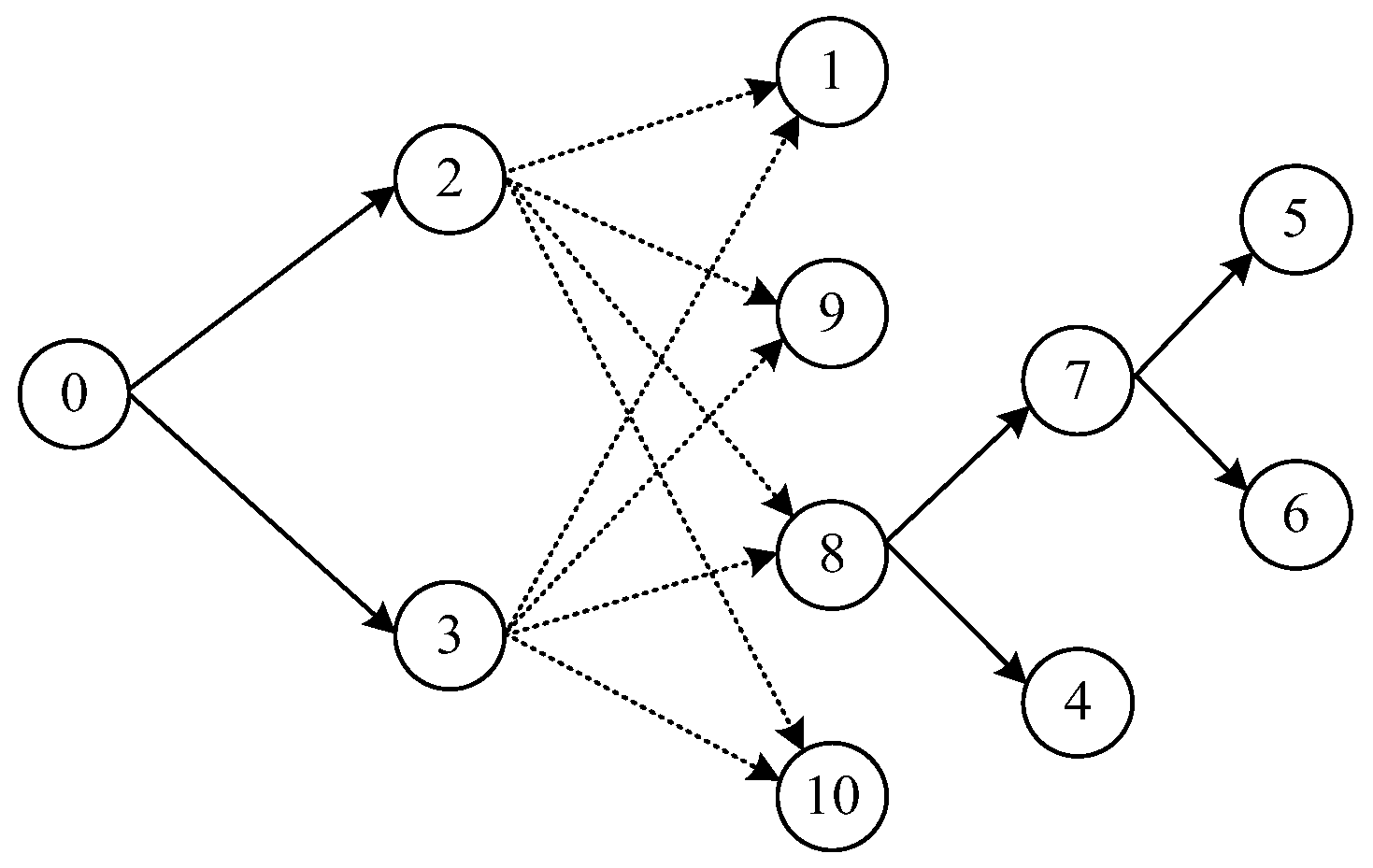
To model a DP problem, we first draw a disassembly precedence diagram to represent the prior relationships among disassembly operations/parts in a product. In a precedence diagram, each part of a product is indexed by j, j = 0, 1, …, N. N is the number of parts and part 0 is a dummy part that denotes an initial point of the disassembly process. Figure 1 shows an example of the disassembly precedence diagram, in which there are 10 parts and a directed edge is used to represent the precedence relationship between pairwise adjacent parts. The edge can be viewed as a disassembly operation, which means that part j will be removed after traversing the edge pointing to it. In Figure 1, the disassembly operations are either solid lines (indicating AND precedence relationships) or dotted lines (indicating OR precedence relationships). A part that is an AND predecessor of part j must be disassembled before removing part j. For example, part 7 is the AND predecessor of parts 5 and 6 so it has to be removed before part 5 or 6 can be disassembled. Before disassembling part j, not less than one of the parts that are OR predecessors of part j must be done. For example, part 3 is one of OR predecessors of parts 1 and the other is part 2, so either part 2 or part 3 has to be removed before part 1 can be disassembled.
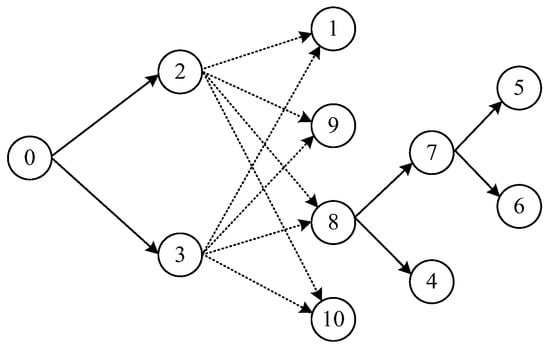
Figure 1.
An example of the disassembly precedence diagram for a product.
3.2. Synchronous Parallel Disassembly and Asynchronous Parallel Disassembly
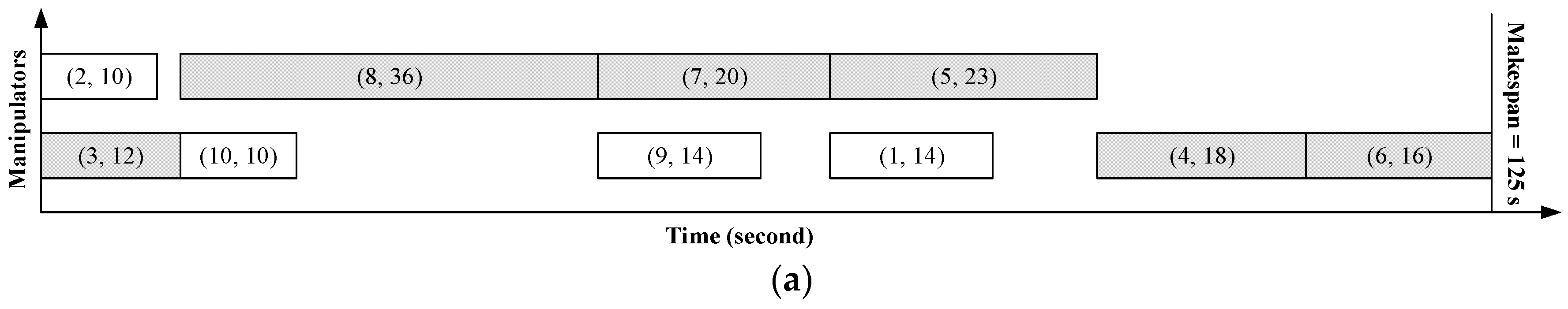
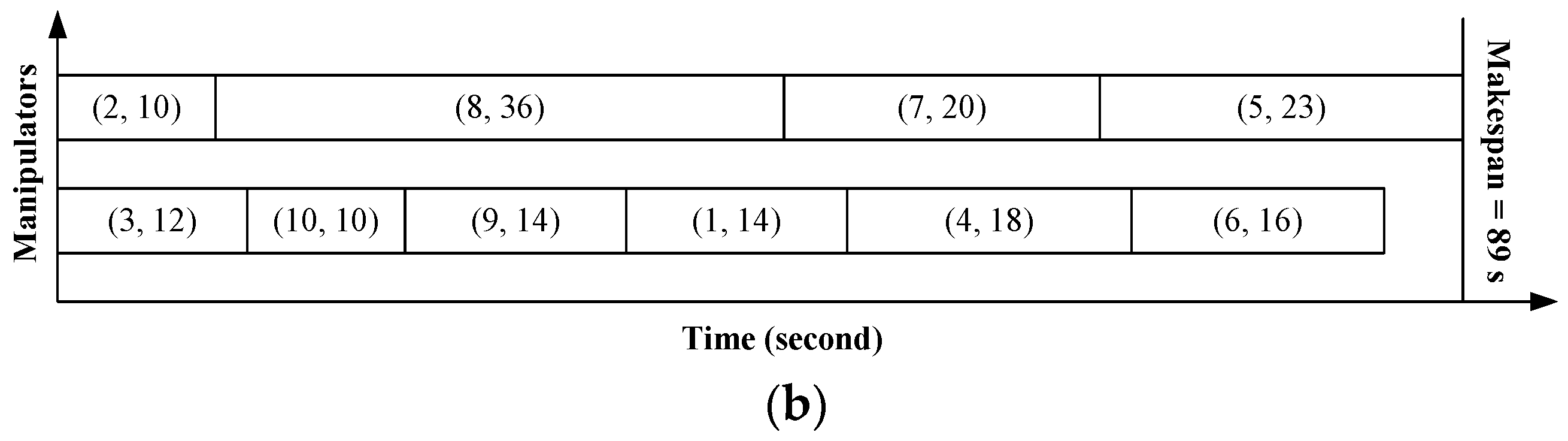
Here, we adapt the example in Figure 1 to differentiate synchronous and asynchronous disassembly processes, which are illustrated in Figure 2a,b, respectively. In Figure 2, the numbers labeled in the parentheses denote the indices of parts and the disassembly time of parts, respectively. Two manipulators are employed to perform the same disassembly sequences in both Figure 2a,b, that is, {2, 8, 7, 5} and {3, 10, 9, 1, 4, 6}. The projection of each rectangle denotes the disassembly time of the corresponding part. From Figure 2a, it is observed that the beginning time of disassembling parts of manipulators is synchronous and a manipulator cannot start a new disassembly task until all other manipulators complete their current ones. The makespan of the synchronous disassembly process is the sum of the maximum disassembly time among parts in each parallel disassembly, which are marked in shadows in Figure 2a. It can be seen that little idle time exists in the asynchronous disassembly process, that is, Figure 2b but a large amount of idle time occurs in synchronous manipulator processing, that is, Figure 2a.
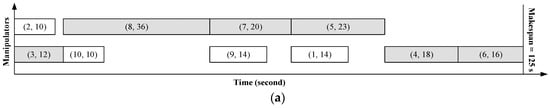
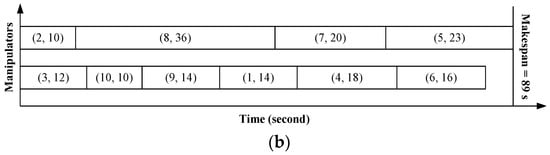
Figure 2.
The comparison between two parallel disassembly processes. (a) Synchronous parallel disassembly process. (b) Asynchronous parallel disassembly process.
In this work, the following assumptions or specifications are considered:
- AND precedence and OR precedence relationships are ensured.
- Work area collisions among manipulators are considered.
- Once a part begins, it cannot be interrupted.
- Each part is exactly removed once by one manipulator.
- Disassembly times of parts are determined in advance.
- A manipulator can remove at most one part at the same time.
4. MILP Modeling of APDP
The notations are shown as follows:
| the number of parts | |
| position indices of manipulators, where | |
| the number of manipulators | |
| the disassembly time of part | |
| index set of AND predecessors of part | |
| index set of OR predecessors of part | |
| index set of parts that have work area collisions with part in the parallel disassembly process | |
| a large positive number | |
| a binary decision variable, , if part occupies position of the disassembly sequence of manipulator ; otherwise, | |
| a binary decision variable,, if part is removed by manipulator ; otherwise, | |
| a binary decision variable, , if part is removed immediately before part by manipulator ; otherwise, | |
| a binary decision variable, , if part is removed before (adjacent or non-adjacent) part ; otherwise, , part is removed before (adjacent or non-adjacent) part | |
| a continuous decision variable, the starting time of disassembling part | |
| a continuous decision variable, the time when manipulator starts to remove the part | |
| a continuous decision variable, the maximum completion time (makespan) of the disassembly process |
As shown in Equation (1), the objective of our APDP is to minimize the makespan of completely disassembling a product, in which the assignment of disassembly tasks and the sequence of removing parts are integrally determined for each manipulator. In the following, we will illustrate the MILP formulations of the APDP.
4.1. Model 1
As aforementioned, two subproblems, that is, the allocation problem and sequencing problem need to be addressed. Here, we introduce a binary decision variable that represents whether part is the part removed by manipulator . Moreover, two continuous decision variables, that is, and , are employed to denote the starting time of removing part i and the makespan of the disassembly process, respectively. The constraint sets of Model 1 are described in Equations (2)–(10):
Constraint (2) denotes that each part must be exactly removed once by one manipulator during the disassembly process. Constraint (3) denotes that a manipulator can remove at most one part simultaneously. Constraint (4) ensures that a manipulator can begin to disassemble the next part only after the current part is completely disassembled. To be more specific, if and are equal to 1, parts j and i are successively disassembled by manipulator m, which indicates that the completion time of removing part j is no more than the starting time of removing part i; otherwise, both sides of inequation (4) are equal to 0. Constraint (5) denotes that there is no idle position in each disassembly sequence until the last part of each disassembly sequence is removed by the manipulator. Constraint (6) and (7) guarantee the AND, and OR precedence relationships among parts, respectively. Constraint set (7) can also be formulated as , among which returns 1 or 0. Constraint (8) excludes the work area collisions between manipulators when they work at the same time. Constraint (9) means that the makespan of a disassembly process must be more than the completion time of disassembling each part. Constraint (10) defines the decision variable .
Equations (1)–(10) are linear except constraint (4). Constraint (4) includes the product of binary and continuous variables, which is typically non-convex and difficult to be solved. Here, we use the big M method to linearize formulation (4). Then, constraint (4) is converted to constraint (11). The MILP of Model 1 can be depicted by formulations (1)–(3) and (5)–(11).
4.2. Model 2
Although constraint (11) is linear, it involves four indices (i.e., i, j, m, and p) and consists of a large number of constraints. This could incur an increase in the computational complexity of Model 1. To avoid the complex computation, we attempt to simplify constraint (11) in this segment.
First, a continuous variable is defined that denotes the starting time of removing the part by manipulator . With , , and , we can obtain the following equations:
Equation (12) illustrates the relationships among the decision variables, which denotes that if part is the part removed by manipulator , that is, , must be equal to . Constraint (13) is used to replace constraint (11), where the number of constraints becomes small. However, the right-hand side of Equation (12) is nonlinear. To linearize it, we formulate constraints (14)–(16), which are equivalent to constraint (12). To be more specific, if , constraint (14) enforces to be no less than and constraint (15) enforces to be no more than . Therefore, is equal to . If , constraint (14) and (15) are relaxed and holds, and constraint (16) guarantee that is equal to 0.
4.3. Model 3
Decision variable is indispensable and crucial in both Model 1 and Model 2. Here, is simplified to be to reduce the solution space and it determines whether part is removed by manipulator without considering the position p. Nevertheless, can only deal with the allocation problem of removal parts, and additional binary variable is thus introduced. If equals 1, part i is removed before part j; otherwise, part i is removed after part j, by which the disassembly sequence of parts can be determined.
The relationships among , , and are formulated as:
Constraint (17) denotes that the disassembly task of each part must be exactly assigned to one manipulator. Constraints (18) and (19) are equivalent to constraint (11). Specifically, inequation (18) requires that the starting time of removing part j is later than the completion time of removing part i when . Instead, inequation (19) denotes that the starting time of removing part i is later than the completion time of removing part j when . Notably, constraints (18) and (19) are dual with respect to i and j. Hence, both indices can be subjected to i < j, which helps reduce the number of constraints in constraints (18) and (19).
Due to the nonconvexity and nonlinearity of constraints (18) and (19), we further transform them into constraints (20) and (21), respectively. The MILP of Model 3 is obtained by Equations (1), (6)–(10), (17), and (20)–(21).
4.4. Model 4
As presented in Model 3, is integrated with to address the allocation and sequencing problems of APDP. Herein, we combine and into a binary decision variable, i.e., . Let = 1 mean that part i is removed immediately before part j for the same manipulator m, and otherwise = 0 [37]. Clearly, can simultaneously decide on the task assignment of manipulators and the disassembly sequence of parts. Furthermore, a dummy part, that is, part 0 is assumed to start and terminate each disassembly sequence. This implies that part 0 is disassembled twice by each manipulator, that is, the starting and the completion time of each disassembly sequence. It should be noted that the disassembly time of part 0 is zero.
Based on decision variables , and , Model 4 can be formulated as follows.
Constraint (22) is equivalent to constraint (17), which indicates that each part has exactly one immediate predecessor that is disassembled by the same manipulator. Constraint (23) guarantees the equilibrium of in-degree and out-degree, that is, each part has exactly one immediate predecessor and follower in the disassembly sequence. Actually, the disassembly sequence of each manipulator is a tour that starts from part 0 and terminates at part 0. Constraint (24) is formulated to eliminate the subtour, that is, each manipulator can at most complete one disassembly sequence. Similar to constraint (4), constraint set (25) denotes that the immediate predecessor of each part must be earlier removed before it. Constraint (26) denotes that the starting time of part 0 is equal to zero.
Finally, inequation (25) is linearized to (27) using the big M method, and the MILP of Model 4 is formulated by Equations (1), (6)–(10), (22)–(24), and (26)–(27).
5. Computational Results
The Branch-and-Cut (B&C) algorithm of IBM ILOG CPLEX 12.7.1 is used to solve the proposed MILP formulations. The B&C algorithm is embodied in the CPLEX software (i.e., IBM ILOG CPLEX 12.7.1, IBM International Business Machines Corporation, New York, NY, USA), which is very popular in solving mixed integer programming (MIP), especially for mixed integer linear programming (MILP). In this section, four product cases previously used in [4] are applied to test our models and evaluate the exact solutions found by the B&C. Except Case 1 with 10 parts as presented in Figure 1, others are real-world cases, that is, a valve cover head fixture with 22 parts (Case 2), an engine block with 35 parts (Case 3), and a five-speed mechanical transmission with 40 parts (Case 4). Also, the maximum CPU time (timelimit) used by the B&C is set to be 600 s and other configurations of the algorithm adopt the default settings in the CPLEX software. The algorithm is implemented on a desktop computer equipped with Intel Core i5-4460 CPU@3.20 GHz.
5.1. Comparisons of MILP Models
This subsection compares four MILP models in both size complexity and computational complexity. Three indicators are employed to evaluate the size complexity, that is, the number of binary decision variables (NBV), the number of constraints (NC), and the number of continuous decision variables (NCV). The performance of the MILP formulations is highly associated with NBV, NC, and NCV [38,39]. Like others, in this paper, the computational complexity is measured by the current solution (CS) found in the B&C, CPU time consumed by the B&C, Gap, and Opt. CPU time is equal to timelimit if the B&C algorithm cannot prove the optimal solution; otherwise, it is the time consumed for proving the optimal solution. Note that Gap is the relative tolerance between CS and BS, where BS is the lower bound obtained from the CPLEX solver, and Gap = |CS − BS|/CS% [40,41,42,43]. Opt represents the total number of problem instances solved to optimality by the B&C algorithm within 600 s.
5.1.1. Size Complexity
Table 1 summarizes the four MILP models, and Table 2 reports the detailed information on NBV, NC, and NCV of each model in the test instances. The first column of Table 2 denotes the number of manipulators employed in each case. It can be seen from Table 2 that Model 3 has the smallest NBV, Model 4 has the smallest NC, and Models 1, 3, and 4 have the smallest NCV. Model 1 has much more constraints than Model 2 since constraint (11) in Model 1 comprises of much more constraints than constraints (13)–(16) in Model 2. Due to decision variable , NCV in Model 2 is larger than that in Model 1. In Model 3, two-dimensional variables and replace the three-dimensional decision variables. Herein, the differences in the MILP models are analyzed with respect to decision variables and constraints, the following subsection will further discuss the relationships between the size complexity and the computational complexity.

Table 1.
Summary of four MILP Models.

Table 2.
Comparison of size complexity.
5.1.2. Computational Complexity
This segment focuses on the analysis of computational complexity among the models and the comparison of the results is shown in Table 3. The first column of Table 3 denotes the number of manipulators employed in each case. It is observed that Model 1 performs worst in both the solution quality and the computational efficiency. It can only find the optimal solutions for 5 out of 12 instances and its Gap values are equal to 0 in 4 instances. For Case 3 and Case 4, Model 1 cannot even find any feasible solutions within 600 s. As described in Table 1, Model 1 includes a three-dimensional binary variable and a complex constraint (11), which results in poor computational performance.

Table 3.
Comparisons of computational complexity.
In terms of computational performance, Model 2 is significantly better than Model 1. Firstly, Model 2 is able to optimally solve 8 out of 12 instances (i.e., Gap = 0). Secondly, its computational cost is much less than that of Model 1. By comparing their size complexities, we can find that constraint (11) is simplified to constraint (13) in Model 2, which highly reduces its complexity.
The Gap values of Models 2 and 3 show that the same instances can be optimally solved by both models. As seen in the CS values, Model 3 can obtain feasible or optimal solutions in each case within 600 s, whereas Model 2 cannot explore a feasible solution in 3 out of 12 instances within 600 s. This demonstrates that the computational efficiency of Model 3 is superior to that of Model 2. By comparing their decision variables in Table 1, we find that Model 3 does not involve a three-dimensional binary variable and a continuous variable . Furthermore, the constraints of Model 3 are much less than those of Model 2 according to the NC values in Table 2. Hence, the simplified decision variables and the reduced constraints might improve the computational performance of the models.
For Model 4, its CS values are slightly different from those of Model 3. Specifically, only two solutions are found in Model 4, which is a little inferior to Model 3 in all tests. On the other hand, the Gap values of Model 4 are significantly bigger than those of Model 3 when both cannot optimally solve the test instances. Therefore, Model 4 is not as good as Model 3 in terms of solution convergence.
The last two rows of Table 3 provide the mean CPU time, the mean Gap, and Opt of each model over all test instances. Notably, we only consider the instances that feasible solutions can be found within 600 s when computing the mean Gap. It is noted that Model 1 finds the least optimal solutions (i.e., Opt = 4), while the other models explore 8 optimal solutions within 600 s. Although Models 2, 3, and 4 have the same Opt, both the mean CPU time and the mean Gap of Model 3 significantly outperform those of Models 2 and 4. Therefore, Model 3 is the best, Models 2 and 4 are secondary, and Model 1 performs worst for solving the APDP.
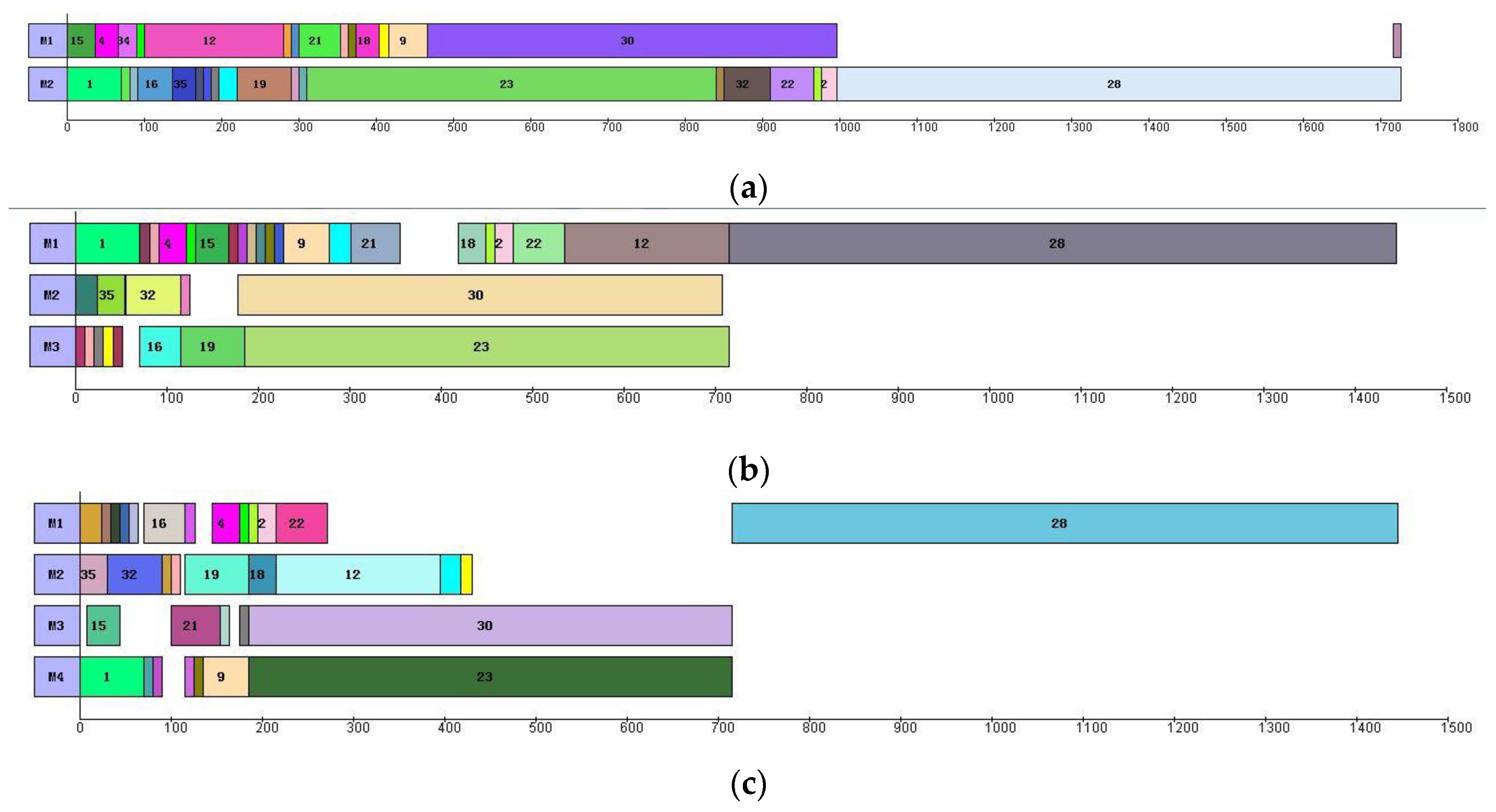
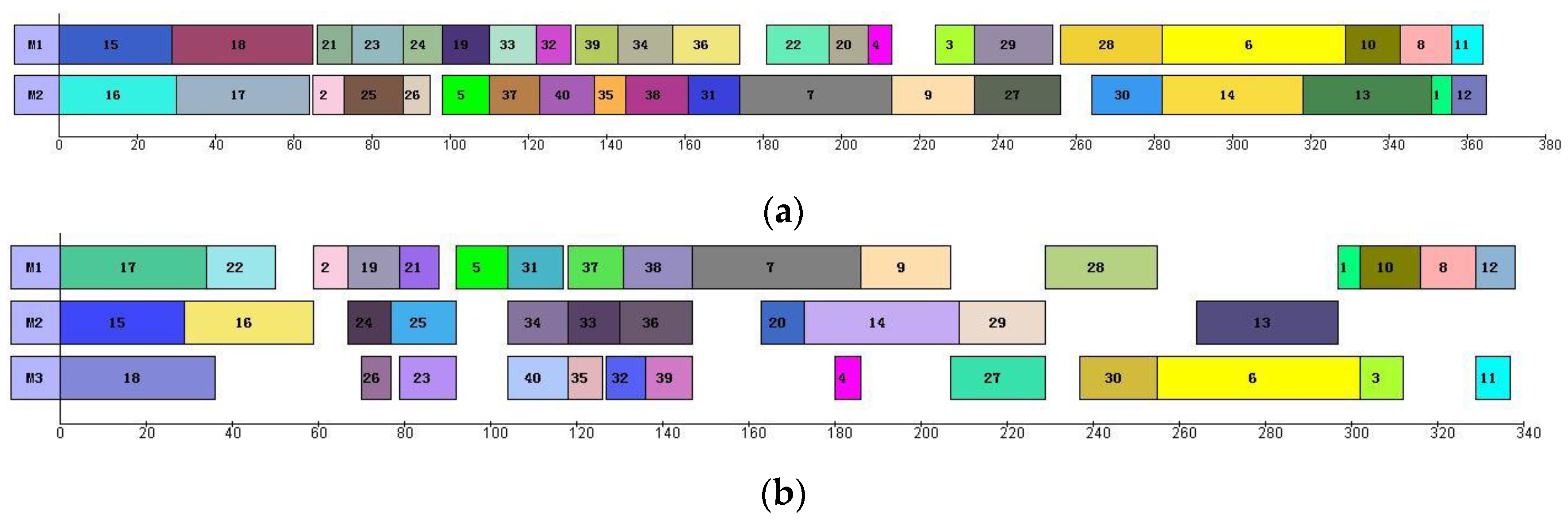
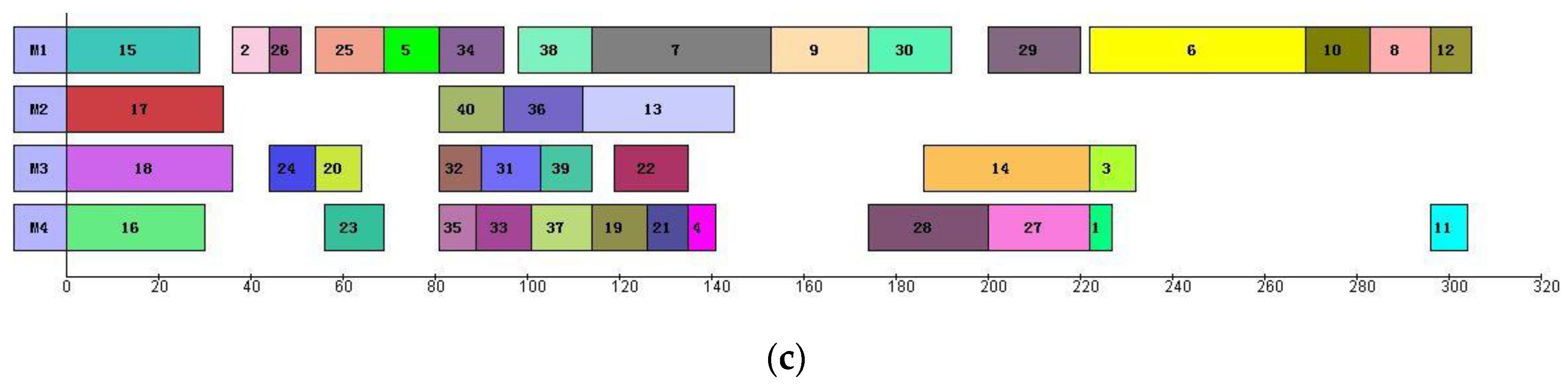
Table 4 presents the best solutions for Cases 3 and 4 with Nm = 2, 3, and 4, respectively. Figure 3 and Figure 4 present the Gantt charts of the best solutions for Cases 3 and 4, respectively. As seen in Table 4, Figure 3 and Figure 4, the makespan gets some extent improvement with the increase of manipulators. However, there exists a threshold with respect to Nm. In other words, the makespan of the disassembly process will not be reduced once the manipulators are redundant. For example, Case 3 with 3 and 4 manipulators are able to find the same optimal solution (i.e., 1445). This situation also usually happens in practice. Our proposed method can help decision-makers select the ideal manipulator configuration, where trade-offs have to be made between the makespan and the cost of manipulators. With regard to the case with considering unlimited manipulators, the four MILP mod-els can be seen in Appendix A.

Table 4.
Best Solutions for cases 3–4 with 2–4 Manipulators.
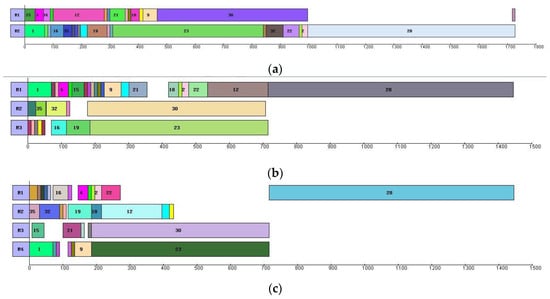
Figure 3.
Gantt charts of Case 3 with 2–4 manipulators. (a) Case 3 with 2 manipulators (). (b) Case 3 with 3 manipulators ( ). (c) Case 3 with 4 manipulators ( ).
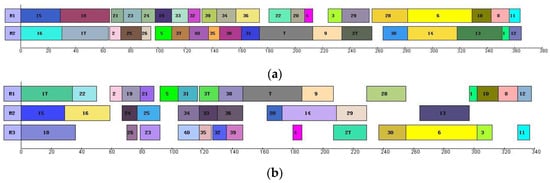
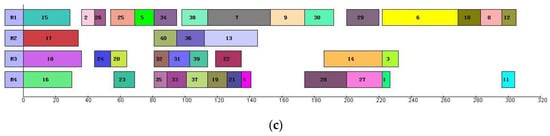
Figure 4.
Gantt charts of Case 4 with 2–4 manipulators. (a) Case 4 with 2 manipulators (). (b) Case 4 with 3 manipulators ( ). (c) Case 4 with 4 manipulators ( ).
5.2. Result Comparisons with IGA
The exact solutions obtained from the proposed MILP models are compared with the solutions from the IGA in [4]. Table 5 shows the result comparisons, in which the best solution for each instance is highlighted. It can be seen that IGA can obtain seven best solutions in 12 test instances. Models 1–4 can identify 5, 9, 12, and 10 best solutions, respectively. Obviously, IGA outperforms Model 1, while it is not as good as Models 2–4. On the other hand, IGA cannot ensure that the same solution is obtained in each test, which can be demonstrated by the difference among the Best, Average and Worst values of IGA. Instead, the proposed method aims to solve the exact solutions of the APDP. Except for that, it can guarantee the robustness of the solution. In summary, three out of four proposed MILP models perform better than the IGA in both the quality and robustness of the solutions. This is because the IGA is one of the approximation algorithms, and it cannot guarantee obtaining the same solution within the same time limit. This is the commonness of most approximation algorithms. With regard to MILP formulation, it is solved by the exact Branch-and-Cut (B&C) algorithm of CPLEX, and the same solution within the same time limit can be obtained.

Table 5.
Computational results of our MILP models and the IGA.
6. Conclusions
This paper is focused on exploring the exact solutions of asynchronous parallel disassembly planning (APDP) with minimal makespan during the disassembly process. A basic nonlinear mathematical model is presented to demonstrate the APDP. To improve the basic model, four MILP models are further developed using linearization or relaxation techniques. We employ the branch-and-cut algorithm embedded in CPLEX to solve the models. In the experimental tests, the four MILP models are analyzed from the perspective of size complexity. Then, the computational performance of each model is evaluated and compared by solving a set of instances. The obtained results indicate that Model 3 performs best, Models 2 and 4 are secondary, and the worst is Model 1. Finally, the obtained exact solutions are compared with the existing solutions from an improved genetic algorithm (IGA). The comparison demonstrates that three out of four proposed models can obtain better solutions than the IGA.
In this paper, only 12 tests are done to evaluate the differences of different MILP models. We welcome related researchers to use our MILP formulations to solve more different-sized instances and find more differences between different MILP models. It is undeniable that the efficiency of IGA (approximation algorithm) will be much higher than the MILP model for solving large-sized instances, this has been proved by much existing research for solving other combinatorial optimization problems [21,40]. This is because, with the increase of the size of the instance, the solution space, the number of decision variables, and the number of constraints will enlarge exponentially, which will result in difficult branching and finding new low bounds of the B&C algorithm.
In future studies, other important factors such as the recovered profit of EOL products and the manipulator configuration will be considered as the objective for APDP, which could help find much better optimal solutions that involve the balance between disassembly efficiency, cost, and profit.
Author Contributions
L.M.: Writing—Original draft, methodology. B.Z.: conceptualization. Y.R.: validation, supervision. H.S.: formal analysis. K.G.: validation. C.Z.: editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research is supported by the Funds for National Natural Science Foundation of China [grant numbers 52205529, 52205526 and 62173356], the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province [grant numbers ZR2021QE195 and ZR2021QF036], the Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation of Guangdong Province of China (Grant No. 2019A1515110399) and Guangyue Youth Scholar Innovation Talent Program support received from Liaocheng University [LCUGYTD2022-03].
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author, upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A
With regard to the case considering unlimited manipulators, the four MILP models are as follows. Model 1 is subjected to constraint sets (A1)–(A8), Model 2 is subjected to constraint sets (A1)–(A12), Model 3 is subjected to constraint sets (A4)–(A8) and (A13)–(A14), and Model 4 is subjected constraint sets (A4)–(A8) and (A15)–(A18).
References
- Ren, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, F.; Tian, G.; Lin, W.; Meng, L.; Li, H. Disassembly line balancing problem using interdependent weights-based multi-criteria decision making and 2-Optimal algorithm. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 174, 1475–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colledani, M.; Battaïa, O. A decision support system to manage the quality of End-of-Life products in disassembly systems. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 65, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Tian, G.; Zhao, F.; Yu, D.; Zhang, C. Selective cooperative disassembly planning based on multi-objective discrete artificial bee colony algorithm. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2017, 64, 415–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, F.; Xiao, H.; Tian, G. An asynchronous parallel disassembly planning based on genetic algorithm. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2018, 269, 647–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.F.; Zhang, S.Y. Product cooperative disassembly sequence planning based on branch-and-bound algorithm. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2010, 51, 1139–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kara, S.; Pornprasitpol, P.; Kaebernick, H. Selective Disassembly Sequencing: A Methodology for the Disassembly of End-of-Life Products. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 2006, 55, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiu, F.Z.; Gang, Y.; Zhi, Y.H.; Cheng, H.P.; Guo, Q.M. Parallel disassembly sequence planning for complex products based on fuzzy-rough sets. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2014, 72, 231–239. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, S.; Hung, P.-Y. A novel selective parallel disassembly planning method for green design. J. Eng. Des. 2015, 26, 283–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pistolesi, F.; Lazzerini, B. TeMA: A Tensorial Memetic Algorithm for Many-Objective Parallel Disassembly Sequence Planning in Product Refurbishment. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2019, 15, 3743–3753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, F.; Triebe, M.J.; Meng, L. An MCDM-Based Multiobjective General Variable Neighborhood Search Approach for Disassembly Line Balancing Problem. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2020, 50, 3770–3783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Zhou, M.; Tian, G.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Tan, J. Target Disassembly Sequencing and Scheme Evaluation for CNC Machine Tools Using Improved Multiobjective Ant Colony Algorithm and Fuzzy Integral. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2019, 49, 2438–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, H.-P. A Fuzzy Knowledge-Based Disassembly Process Planning System Based on Fuzzy Attributed and Timed Predicate/Transition Net. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2016, 47, 1800–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y. Learning-Based Disassembly Process Planner for Uncertainty Management. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part A Syst. Hum. 2008, 39, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Zhou, M. Fuzzy-Petri-net based disassembly planning considering human factors. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. A Syst. 2004, 26, 718–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güngör, A.; Gupta, S.M. Disassembly sequence plan generation using a branch-and-bound algorithm. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2001, 39, 481–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Yu, D.; Zhang, C.; Tian, G.; Meng, L.; Zhou, X. An improved gravitational search algorithm for profit-oriented partial disas-sembly line balancing problem. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2017, 55, 7302–7316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.R.; Wang, M.H. Economical evaluation of disassembly operations for recycling, remanufacturing and reuse. Int. J. Prod. Res. 1998, 36, 3227–3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.-G.; Lee, D.-H.; Xirouchakis, P.; Persson, J.-G. Parallel Disassembly Sequencing with Sequence-Dependent Operation Times. CIRP Ann. 2001, 50, 343–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, A. Optimizing disassembly processes subjected to sequence-dependent cost. Comput. Oper. Res. 2007, 34, 536–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edis, E.B.; Ilgin, M.A.; Edis, R.S. Disassembly line balancing with sequencing decisions: A mixed integer linear programming model and extensions. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 238, 117826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Zhang, C.; Shao, X.; Ren, Y.; Ren, C. Mathematical modelling and optimisation of energy-conscious hybrid flow shop scheduling problem with unrelated parallel machines. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2018, 57, 1119–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pistolesi, F.; Lazzerini, B.; Mura, M.D.; Dini, G. EMOGA: A Hybrid Genetic Algorithm with Extremal Optimization Core for Multi-objective Disassembly Line Balancing. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2018, 14, 1089–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, B.; Haas, C. A novel selective disassembly sequence planning method for adaptive reuse of buildings. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 183, 998–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, K.-K.; Park, J.-H.; Jang, D.-S. Optimal Disassembly Sequence Using Genetic Algorithms Considering Economic and Environmental Aspects. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2001, 18, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kongar, E.; Gupta, S.M. Disassembly sequencing using genetic algorithm. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2005, 30, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, G.; Zhou, M.; Chu, J. A Chance Constrained Programming Approach to Determine the Optimal Disassembly Sequence. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2013, 10, 1004–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, G.; Zhou, M.; Li, P. Disassembly Sequence Planning Considering Fuzzy Component Quality and Varying Operational Cost. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2017, 15, 748–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheder, M.; Trigui, M.; Aifaoui, N. Disassembly sequence planning based on a genetic algorithm. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C: J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2014, 229, 2281–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Liu, S.; Zhou, M.; Tian, G. Dual-Objective Program and Scatter Search for the Optimization of Disassembly Sequences Subject to Multiresource Constraints. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2017, 15, 1091–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalayci, C.B.; Gupta, S.M. Artificial bee colony algorithm for solving sequence-dependent disassembly line balancing problem. Expert Syst. Appl. 2013, 40, 7231–7241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Ren, Y.; Jin, H.; Meng, L.; Li, L.; Zhang, C.; Sutherland, J.W. A hybrid metaheuristic algorithm for a profit-oriented and ener-gy-efficient disassembly sequencing problem. Robot. Cim. Int. Manuf. 2020, 61, 101828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, G.; Ren, Y.; Feng, Y.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, H.; Tan, J. Modeling and Planning for Dual-Objective Selective Disassembly Using and/or Graph and Discrete Artificial Bee Colony. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2018, 15, 2456–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Xia, K.; Gao, L.; Chao, K.-M. Selective disassembly planning for waste electrical and electronic equipment with case studies on liquid crystaldisplays. Robot. Comput. Manuf. 2013, 29, 248–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Li, X.; Gao, L.; Garg, A. Partial disassembly line balancing for energy consumption and profit under uncertainty. Robot. Comput. Manuf. 2019, 59, 235–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Pan, Q.-K.; Gao, L.; Li, X.; Meng, L.-L.; Peng, K.-K. A multiobjective evolutionary algorithm based on decomposition for hybrid flowshop green scheduling problem. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2019, 136, 325–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Zhang, C.; Shao, X.; Ren, Y. MILP models for energy-aware flexible job shop scheduling problem. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 210, 710–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, P.M.; Grossmann, I.E. Generalized Disjunctive Programming as a Systematic Modeling Framework to Derive Scheduling Formulations. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 5781–5792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Zhang, C.; Shao, X.; Zhang, B.; Ren, Y.; Lin, W. More MILP models for hybrid flow shop scheduling problem and its extended problems. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2019, 58, 3905–3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.-H. A study of integer programming formulations for scheduling problems. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 1997, 28, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, B.; Ren, Y. Mathematical Modeling and Optimization of Energy-Conscious Flexible Job Shop Scheduling Problem with Worker Flexibility. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 68043–68059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, P.M.; Zeballos, L.J.; Méndez, C.A. Hybrid time slots sequencing model for a class of scheduling problems. AIChE J. 2011, 58, 789–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Zhang, C.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, B.; Lv, C. Mixed-integer linear programming and constraint programming formulations for solving distributed flexible job shop scheduling problem. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2020, 142, 106347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Gao, K.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, B.; Sang, H.; Zhang, C. Novel MILP and CP Models for Distributed Hybrid Flowshop Scheduling Problem with Se-quence-Dependent Setup Times. Swarm Evol. Comput. 2022, 71, 101058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).