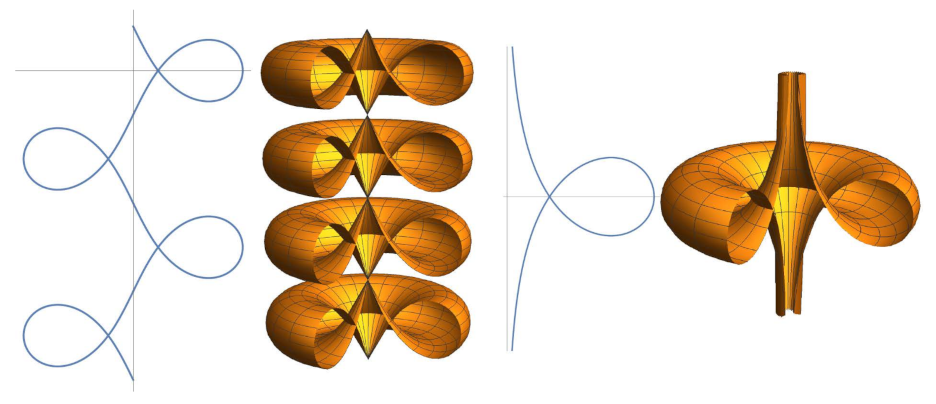Abstract
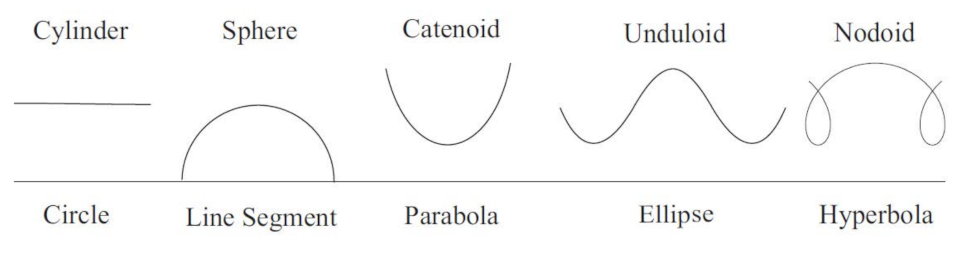
Weingarten surfaces are those whose principal curvatures satisfy a functional relation, whose set of solutions is called the curvature diagram or the W-diagram of the surface. Making use of the notion of geometric linear momentum of a plane curve, we propose a new approach to the study of rotational Weingarten surfaces in Euclidean 3-space. Our contribution consists of reducing any type of Weingarten condition on a rotational surface to a first-order differential equation on the momentum of the generatrix curve. In this line, we provide two new classification results involving a cubic and an hyperbola in the W-diagram of the surface characterizing, respectively, the non-degenerated quadric surfaces of revolution and the elasticoids, defined as the rotational surfaces generated by the rotation of the Euler elastic curves around their directrix line. As another application of our approach, we deal with the problem of prescribing mean or Gauss curvature on rotational surfaces in terms of arbitrary continuous functions depending on distance from the surface to the axis of revolution. As a consequence, we provide simple new proofs of some classical results concerning rotational surfaces, such as Euler’s theorem about minimal ones, Delaunay’s theorem on constant mean curvature ones, and Darboux’s theorem about constant Gauss curvature ones.
1. Introduction
Following [1], the Weingarten surfaces are those whose principal curvatures and satisfy a certain functional relation . The set of solutions of this equation is also called the curvature diagram or the W-diagram of the surface (see [2]). These surfaces were introduced by Weingarten in [3] and their study plays an important role in classical differential geometry (see e.g., [2,4]). Applications of Weingarten surfaces on computer aided design can be found in [5].
In particular, the ones satisfying a linear relation , , , are called linear Weingarten surfaces. In this case, the W-diagram is contained in a straight line or degenerates to one point. This class of Weingarten surfaces include umbilical surfaces, isoparametric surfaces, constant mean curvature, and minimal surfaces or those surfaces where one of the principal curvatures is constant. On the other hand, some types of thin axial symmetric shells subjected to uniform normal pressure are modeled on rotational surfaces whose principal curvatures obey some specific quadratic relations (see e.g., [6,7]). Concretely, the W-diagram is contained in a certain parabola in this case. The general case that the curvature diagram is a standard parabola was studied in [8].
Among the invariant surfaces, precisely the rotational ones are probably the most studied surfaces in Euclidean 3-space. Perhaps the main reason could be they are a nice family where interesting geometric properties can attach on any surface, because its geometry can be controlled by the geometry of the generatrix curve. As an illustration, we can mention the classical theorems of Euler [9], Delaunay [10], and Darboux [11] classifying minimal, constant mean curvature, and constant Gauss curvature rotational surfaces in 1744, 1841, and 1890, respectively. However, the complete classification of rotational linear Weingarten surfaces has not been achieved surprisingly until 2020 in [12]. Some other interesting rotational Weingarten surfaces have been also recently studied in [13,14]. We refer to [8] (and references therein) for the study of closed rotational Weingarten surfaces satisfying , generalizing results of Hopf [2] when and the case of ellipsoids of revolution when . These may be good reasons why rotational surfaces are probably one of the main classes of Weingarten surfaces and continue to deserve attention. We propose in this paper a new approach for their study, inspired mainly by [15].
In order to explain our focus, we start recalling that plane curves are uniquely determined, up to rigid motions, by its intrinsic equation giving its curvature as a function of its arc length. It is well known that one needs three quadratures in the integration process. In [16], David A. Singer considered a different sort of problem, proposing to determine a plane curve if its curvature is given in terms of its position. Probably, the most interesting solved case in this setting corresponds to the Euler elastic curves (see [17]), whose curvature is proportional to one of the coordinate functions, e.g., for curves in the -plane. Motivated by the above question and by the classical elasticae, the authors studied in [15] the plane curves whose curvature depends on the distance to a line (say the z-axis and so ) and in [18] the plane curves whose curvature depends on the distance from a point (say the origin, and so , ) requiring in both cases the computation of three quadratures too. They also considered the analogous problems in Lorentz–Minkowski plane in [19,20].
The key tool for the study of plane curves whose curvature depends on distance to a line is the notion of geometric linear momentum of a plane curve (see [21] or Section 2). It is a smooth function associated to any plane curve, which completely determines it (up to a family of distinguished translations) in relation to its relative position with respect to a fixed line (see Corollary 1). Geometrically, the geometric linear momentum controls the angle of the Frenet frame of the curve with this fixed line and receives that name because, in physical terms, it can be described as the linear momentum (with respect to the fixed line) of a particle of unit mass with unit speed and trajectory the path of the plane curve. Moreover, it can be interpreted as an anti-derivative of the curvature of the curve when this is expressed as a function of the distance to the fixed line.
Therefore, it seems to be natural that when one deals with rotational surfaces, generated by the rotation of a plane curve (the generatrix curve) around a coplanar fixed line (the axis of revolution), the geometric linear momentum of the generatrix with respect to the axis of revolution plays a predominant role to control the geometry of the rotational surface. We show it in Corollary 2, proving that any rotational surface is uniquely determined, up to translations along the axis of revolution, by the geometric linear momentum of the generatrix curve. This main result is confirmed when we study the geometry of a rotational surface since both its first and second fundamental forms can be expressed only in terms of the geometric linear momentum and, of course, the (non-constant) distance from the surface to the axis of revolution. This allows our main contribution in the paper, which consists of reducing any type of Weingarten condition on a rotational surface to a first-order differential equation on the momentum of the generatrix curve (see Section 3). We illustrate this procedure analyzing under our optics the two types of linear Weingarten surfaces one can find in the literature (see Section 3.2 and Section 3.3) and we emphasize two new classification results involving a cubic and an hyperbola in the W-diagram of the rotational Weingarten surface (see Theorems 2 and 3, respectively) characterizing, respectively, the non-degenerated quadric surfaces of revolution and the elasticoids (defined as the rotational surfaces generated by the rotation of the Euler elastic curves around their directrix line).
As another application, we deal in Section 4 with the problem of prescribing mean or Gauss curvature on rotational surfaces in terms of arbitrary continuous functions depending on distance from the surface to the axis of revolution, providing in Theorem 4 one-parameter families of rotational surfaces with prescribed mean or Gaussian curvature. We point out that Kenmotsu [22] constructed a 3-parameter family of surfaces of revolution admitting as the mean curvature for a given continuous function , s being the arc parameter of the generatrix curve.
As a consequence of Theorem 4, we provide simple new proofs of the above mentioned classical results concerning rotational surfaces such as Euler’s theorem about minimal ones (see Corollary 3), Delaunay’s theorem on constant mean curvature ones (see Corollary 4), and Darboux’s theorem about constant Gauss curvature ones (see Corollary 5).
2. The Geometric Linear Momentum of a Plane Curve
We introduce a smooth function associated to any plane curve, which completely determines it (up to a family of distinguished isometries) in relation with its relative position with respect to a fixed line.
Let be a regular plane curve parametrized by arc length; that is, , where I is some interval in . Here means derivation with respect to s. We denote by the usual inner product in . Let be the unit tangent vector to the curve and let be the vector orthogonal to T such that the frame is positively oriented. The Frenet equations of are given by
where is the (signed) curvature of . Up to sign, , where can be chosen as the angle .
We are interested in the geometric condition that the curvature of depends on the distance to a fixed line of . We choose Cartesian coordinates in and we write . Thus it is enough to study the condition , since x represents the signed distance to the z-axis.
A key role is played then by the geometric linear momentum of the plane curve (with respect to the z-axis). At a given point on the curve, it is defined by
Geometrically, controls the angle of the Frenet frame of the curve with the coordinate axes.
We can also observe a physical interpretation if we write in Cartesian coordinates. Since , then and so the linear momentum at is given by
Hence, in physical terms, may be described as the linear momentum (with respect to the z-axis) of a particle of unit mass with unit speed and trajectory . We point out that assumes values in and it is well defined, up to the sign, depending on the orientation of .
Remark 1.
If the plane curve is not necessarily parametrized by arc length, i.e., , t being any parameter, one can computes the geometric linear momentum by means of
where denotes derivation respect to t.
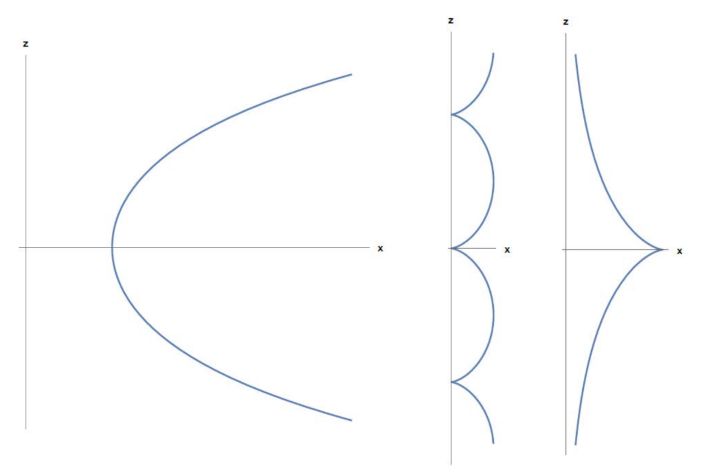
It is an easy exercise to demonstrate the computation of the geometric linear momenta of some distinguished plane curves for our purposes, using Remark 1 if necessary, some of them are located in a determinate position with respect to z-axis, that we collect in the following list (see Figure 1):
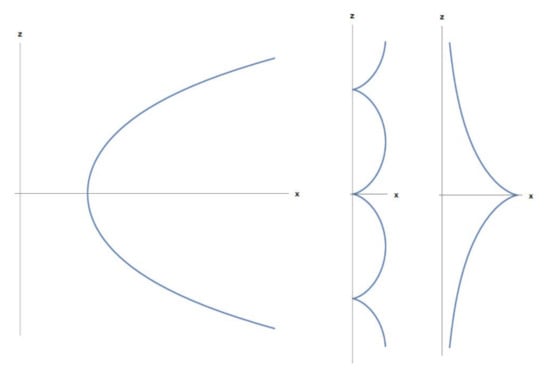
Figure 1.
From left to right: catenary, cycloid, and tractrix.
Example 1.
- (1)
- Vertical lines: .
- (2)
- Line with slope , , given by : .
- (3)
- Circle centered at , , and radius :.
- (4)
- Catenary , : .
- (5)
- Cycloid of radius given by , , : .
- (6)
- Tractrix of height given by , , : .
On the other hand, when is unit speed we have that
Thus, given as an explicit function, looking at (4) one may attempt to compute and in three steps: integrate to obtain , invert to obtain and integrate to obtain .
Therefore, we deduce that can be interpreted as an anti-derivative of . As a summary, we can determine by quadratures in a constructive explicit way the plane curves such that , in the spirit of ([16], Theorem 3.1).
Theorem 1.
Let be a continuous function. Then the problem of determining a curve , with s the arc length parameter, whose curvature is with geometric linear momentum satisfying (5)—x representing the (non-constant) signed distance to the z-axis—is solvable by quadratures where and are obtained through (4) after inverting .
Moreover, such a curve is uniquely determined, up to translations in the z-direction (and a translation of the arc parameter s), by the geometric linear momentum .
If we focus on the determining role of the geometric linear momentum, we can rephrase the above result simply as follows:
Corollary 1.
Any plane curve , with x non-constant, is uniquely determined by its geometric linear momentum as a function of its distance to the z-axis, that is, by . The uniqueness is modulo translations in the z-direction. Moreover, the curvature of α is given by .
Remark 2.
If we prescribe a continuous function as the curvature of a plane curve, the proof of Theorem 1 offers an algorithm to recover the curve through the computation of three quadratures, following the sequence:
- (i)
- A one-parameter family of anti-derivatives of :
- (ii)
- Arc-length parameter s of in terms of x, defined—up to translations of the parameter—by the integral:where , and inverting to obtain .
- (iii)
- z-coordinate of the curve—up to translations along z-axis—by the integral:
We note that we obtain a one-parameter family of plane curves satisfying according to the linear momentum chosen in (i) and verifying . It will distinguish geometrically the curves inside the same family by their relative position with respect to z-axis. We recall that we can easily recover κ from simply by means of . In some sense, can be interpreted as the extrinsic equation of α in this setting, in contrast to the classical intrinsic equation .
We now show two illustrative examples applying steps (i)-(iii) of the algorithm described in Remark 2:
Example 2
(). Then , and easily , . Writing , , we arrive at Example 1(2). Up to z-translations, we obtain all the (non vertical) lines in the plane.
Example 3
(). Then , and it is not difficult to obtain that , . Writing we arrive at Example 1(3). Up to z-translations, we obtain all the circles with radius in the plane.
Remark 3.
The main difficulties one can find carrying on the strategy described in Remark 2 (or in Theorem 1) to determine a plane curve whose curvature is are the following:
- (1)
- The integration of : Even in the case that were polynomial, the corresponding integral is not necessarily elementary. For example, when is a quadratic polynomial, it can be solved using Jacobian elliptic functions (see, e.g., [23]). This last case is equivalent to be linear, i.e., , , and . These are precisely the Euler elastic curves (see [15], [Section 3]).
- (2)
- The previous integration gives us ; it is not always possible to obtain explicitly , what is necessary to determine the curve.
- (3)
- Even knowing explicitly , the integration to obtain may be impossible to perform using elementary or known functions.
We finish this section with an example illustrating the difficulty (2) in Remark 3.
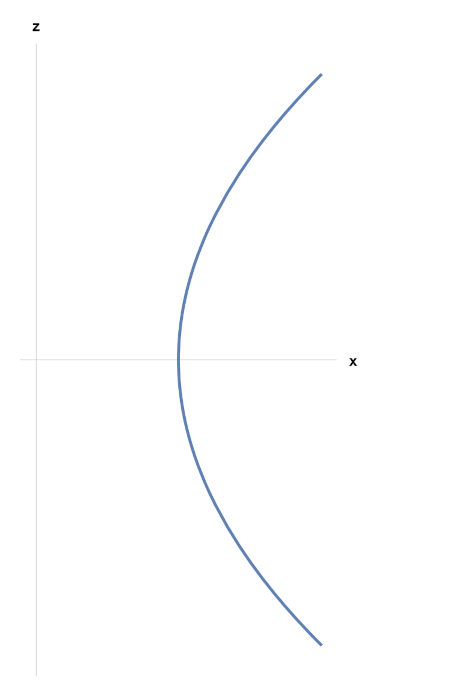
Example 4.
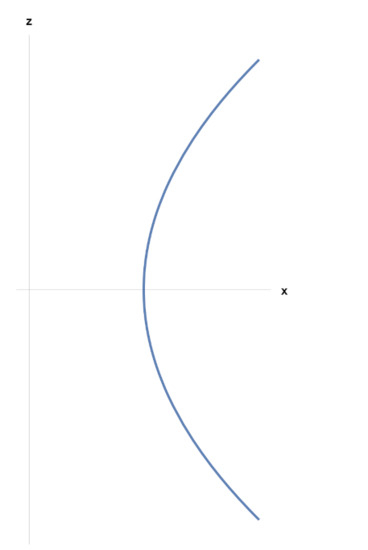
Consider , . Then and it is not possible to invert to obtain ; however, eliminating in Remark 2(ii) and (iii), we obtain:
Applying the above formula in this example, we arrive at that corresponds with the parabola with vertex and focus (see Figure 2).

Figure 2.
Parabola of Example 4.
3. Rotational Weingarten Surfaces
We start this section considering rotational surfaces, also called surfaces of revolution. They are surfaces globally invariant under the action of any rotation around a fixed line called axis of revolution. The rotation of a curve (called generatrix) around a fixed line generates a surface of revolution. The sections of a surface of revolution by half-planes delimited by the axis of revolution, called meridians, are special generatrices. The sections by planes perpendicular to the axis are circles called parallels of the surface.
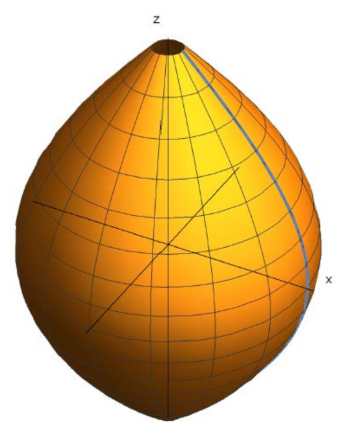
We denote the rotational surface in generated by the rotation around z-axis of a plane curve in the -plane (see Figure 3). That is, is the generatrix curve that we consider parametrized by arc length, with parametric equations given by , , , and . Then is parametrized by
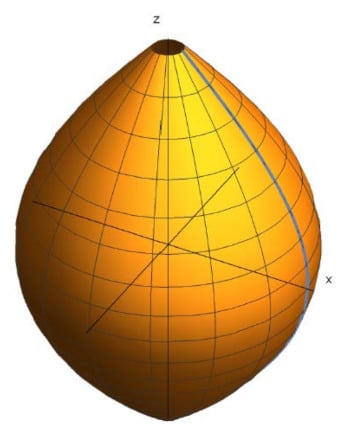
Figure 3.
: rotational surface generated by .
It is obvious that if we translate the generatrix curve of a rotational surface along z-axis, we obtain a congruent surface to . Then, as an immediate consequence of Corollary 1, we deduce the following key result:
Corollary 2.
Any rotational surface , with generatrix curve , is uniquely determined, up to z-translations, by the geometric linear momentum of its generatrix curve, where x is non-constant.
Remark 4.
The only rotational surface excluded in Corollary 2 is the right circular cylinder, corresponding to x being constant. We recall that it is a flat rotational surface and its principal curvatures are 0 (along generatrices) and (along parallel circles), being the radius of the cylinder.
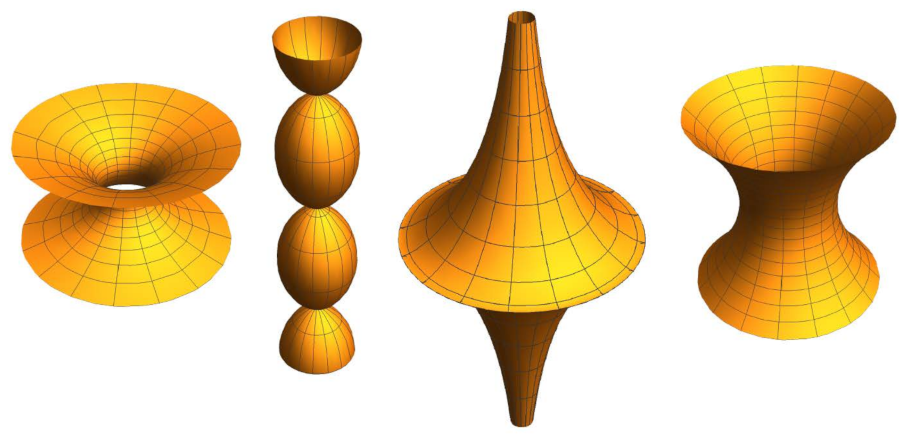
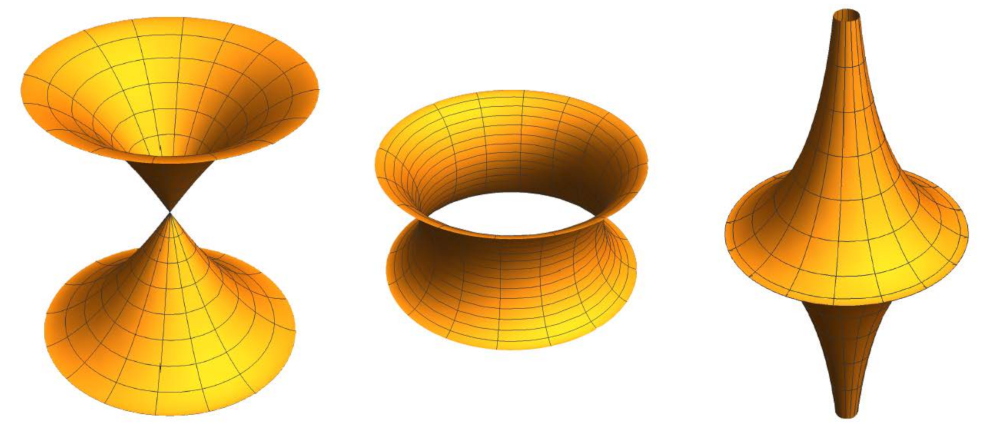
Looking at Examples 1 and 4 and making use of Corollary 2, we can list the following classical and conventional rotational surfaces joint with its determining geometric linear momentum. See Figure 4.
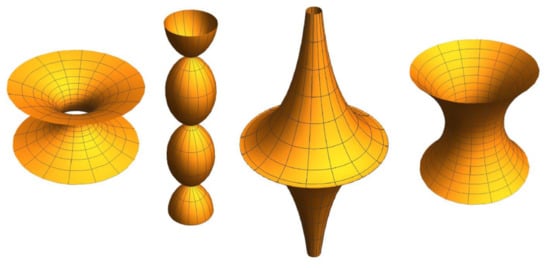
Figure 4.
Rotational surfaces. From left to right: catenoid, onducycloid, pseudosphere, and antiparaboloid.
Proposition 1.
Up to translations in z-direction:
- (1)
- Any horizontal plane is uniquely determined by the geometric linear momentum .
- (2)
- The circular cone with opening , given by , is uniquely determined by the geometric linear momentum .
- (3)
- The sphere of radius , given by , is uniquely determined by the geometric linear momentum .
- (4)
- The torus of revolution with major radius and minor radius , given by , is uniquely determined by the geometric linear momentum .
- (5)
- The catenoid of chord , given by , is uniquely determined by the geometric linear momentum .
- (6)
- The onducycloid of radius , defined as the surface generated by rotation of the cycloid in Example 1(5) around its base, is uniquely determined by the geometric linear momentum .
- (7)
- The pseudosphere of pseudoradius (cf. [24]), defined as the surface generated by the rotation of the tractrix in Example 1(6) around its asymptote, is uniquely determined by the geometric linear momentum .
- (8)
- The antiparaboloid of radius , defined as the surface generated by the rotation of the parabola with vertex and focus , , around its directrix line, given by , is uniquely determined by the geometric linear momentum .
Remark 5.
Recently, biconservative surfaces in 3-dimensional space forms have been studied (in particular, biconservative surfaces in the Euclidean 3-space); see [25,26]. These are rotational Weingarten surfaces. Using their explicit description given in Proposition 4.1 of [25] and (6), it is not difficult to obtain that, up to translations in the z-direction, they are uniquely determined by the geometric linear momentum , with , being the parameter appearing in the statement of Proposition 4.1 of [25].
We can confirm the result established in Corollary 2 when we study the geometry of through its first and second fundamental forms, I and , since a direct computation, using that , shows that both can be expressed only in terms of the geometric linear momentum and, of course, the non-constant distance x from the surface to the axis of revolution:
Therefore, we obtain the following expressions for the principal curvatures and , whose curvature lines are the meridians and parallels, respectively, of the rotational surface :
Thus, the mean curvature H of is given by
and the Gauss curvature of is given by
Now we can pay attention to rotational Weingarten surfaces. Weingarten surfaces must satisfy a functional relation between their principal curvatures. In the case of rotational surfaces, the principal curvatures are reached along meridians and parallel of and, from (7), it is clear that rotational surfaces constitute a distinguish class of Weingarten surfaces. For example, if is invertible, from (7) we arrive at . In general, we just simply write ; however, taking into account (7), we easily deduce that the above functional relation translates into a first-order differential equation for the geometric linear momentum determining according Corollary 2:
If the above equation can be rewritten as or, equivalently , it follows that locally any equation of this type with an arbitrary continuous function F (or ) admits a solution.
We can illustrate the above simple reasoning analyzing some interesting Weingarten-type conditions.
3.1. Rotational Surfaces with Some Constant Principal Curvature
We distinguish two cases. First, if some principal curvature of is null, we have that . If , using (7), we obtain that , . Then, using Corollary 2, Remark 4, and Proposition 1, we conclude that is a circular cylinder, a plane (when ) or a circular cone (when ). Further, if , using (7), we conclude that and is a plane.
We consider now the case that some principal curvature is a nonzero constant. If , using (7), we conclude that , . Then, using Proposition 1, we conclude that is a sphere when or a torus of revolution when . Further, if , using (7), we conclude that and is a sphere or a circular cylinder (see Remark 4).
3.2. Linear Rotational Weingarten Surfaces
They are defined by the linear relation We can assume (see Section 3.1 if ) and we just write
These surfaces have been recently classified in [12] by means of a qualitative study, providing closed (embedded and not embedded) surfaces and periodic (embedded and not embedded) surfaces with a geometric behavior similar to Delaunay surfaces ([10]). In [12], there is a necessary distinction of cases according to or . In fact, when , the generatrix curves are -elastic curves (see [27] for a description of them) generalizing classical elastic curves corresponding to (see [28,29]). Under our optics, (10) translates into the linear o.d.e. , that it is easy to solve. Using Corollary 2, both above mentioned families are uniquely determined, up to z-translations, by the following geometric linear momenta:
and
This can be a reasonable explanation of the commented distinction of cases in [12].
The case , in (10), i.e., , leads obviously to the only umbilical surfaces (planes and spheres) since then , (see Proposition 1(1), (3)).
We now pay attention to the case in (10), i.e., , which leads to . Under our optics, we can localize distinguished rotational surfaces satisfying in this subclass of linear Weingarten surfaces. Using Proposition 1, we obtain catenoids if , onducycloids if and antiparaboloids if .
3.3. “Linear” Rotational Weingarten Surfaces
Some authors define linear Weingarten surfaces as those ones such that a linear combination of its mean curvature H and Gauss curvature is constant (see e.g., [30]):
They are also referred as special Weingarten surfaces in [31]. They include CMC (constant mean curvature) surfaces when and CGC (constant Gauss curvature) surfaces when . The closed ones were studied in [1,2] among others. In [32], the authors studied properly embedded surfaces in satisfying , where a and b are positive. For , the curvature diagram corresponding to (11) is given by the rectangular hyperbola
3.4. Cubic Rotational Weingarten Surfaces
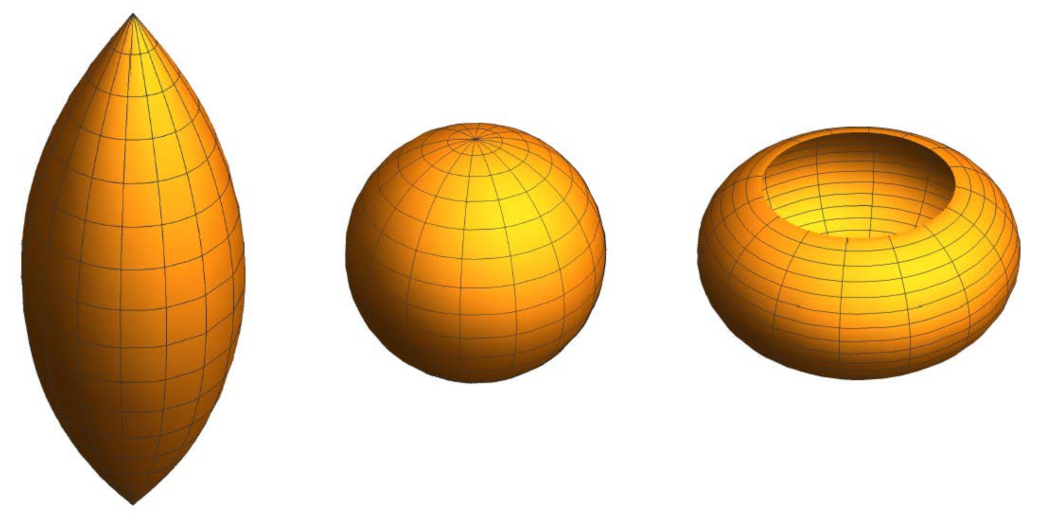
It is known (see [33]) that the ellipsoid of revolution
satisfies the relation
In [8], it is also proved that any closed surface of revolution satisfying , for any positive constant , is congruent to some ellipsoid of revolution. The aim of this section is to generalize this result using our local approach to the study of rotational Weingarten surfaces.
For our purposes, recalling Corollary 2, we need to compute the geometric linear momentum of the ellipsoid (13). We parametrize the generatrix semiellipse by , , , and using Remark 1, it is not difficult to conclude that
We proceed in the same way with the one-sheet hyperboloid of revolution
obtaining, from the generatrix hyperbola , , , and Remark 1, that
and now we can check that the one-sheet hyperboloid of revolution satisfies the relation
However, for the two-sheets hyperboloid of revolution
as now the generatrix hyperbola is , , , we obtain from Remark 1 that
and so we arrive at the following relation satisfied by the two-sheets hyperboloid of revolution:
that it is formally the same than the one (14) of the ellipsoid of revolution.
Finally, for the paraboloid of revolution
we use the generatrix parabola , , , and Remark 1 gives that
and then the paraboloid of revolution satisfies the relation
Now we are in a position to state our main result in this section characterizing all the quadric surfaces of revolution (see Figure 5) in terms of a cubic Weingarten relation.
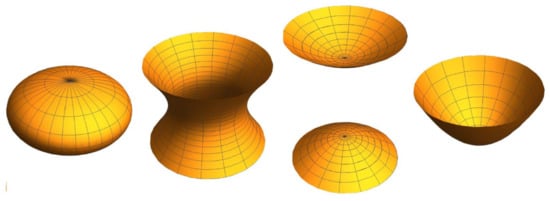
Figure 5.
Quadric surfaces of revolution. From left to right: Ellipsoid, one-sheet hyperboloid, two-sheets hyperboloid, and paraboloid.
Theorem 2.
The only rotational surfaces satisfying , , are the plane and the non-degenerate quadric surfaces of revolution.
Proof.
Using (7), the cubic Weingarten relation translates into the separable o.d.e.
Its constant solution leads to the plane (see Proposition 1(1)). Its non-constant solution is given by
We are going to identify the rotational surfaces uniquely determined, up to z-translations, by the one parameter family of geometric linear momenta (depending on c) given in (25) (see Corollary 2). There is no restriction if we only consider plus sign in (25).
We distinguish two cases according to the sign of .
- . We separate in turn three possibilities:
- (i)
- (ii)
- (iii)
This proves the result. □
Remark 6.
We point out that, although it is not explicitly established in [8] because the authors were interested in closed Weingarten surfaces, the case in Theorem 2 was considered in [8].
3.5. Rotational Weingarten Surfaces Generated by Elastic Curves
The elastic curves are those plane curves whose curvature is, at all points, proportional to the distance to a fixed line, called the directrix. They were studied by Jacques Bernoulli in 1691 who named it elastica, by Euler in 1744, and Poisson in 1833 (cf. [24]). With the elastica in the -plane and the directrix as the z axis, the above condition can be written as , , and then we have a one-parameter family of elastic curves determined, up to z-translations, by the geometric linear momenta
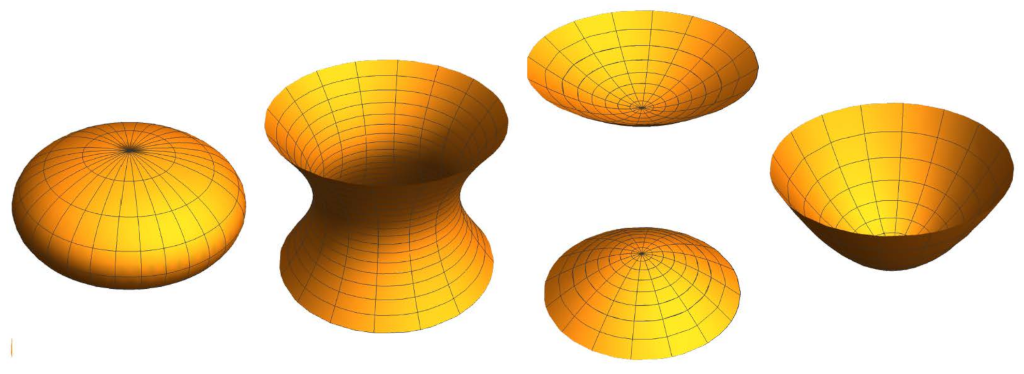
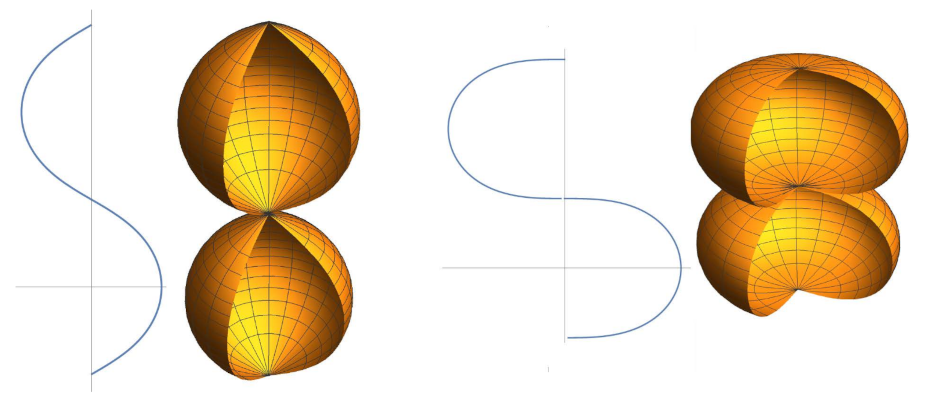
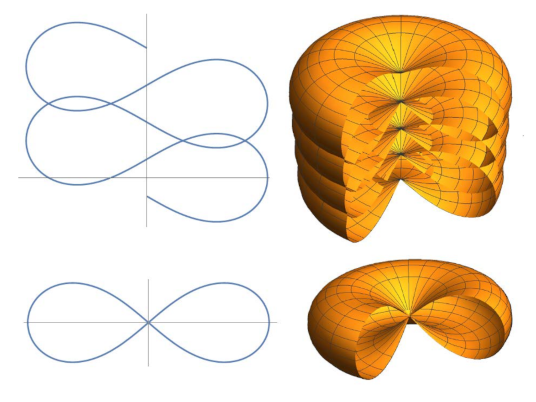
since (see Remark 2). We define the elasticoids as the rotational surfaces generated by the rotation of an elastic curve around its directrix. Using Corollary 2, they are uniquely determined, up to translations along z-axis, by the geometric linear momenta given in (26). Following [24] or [17] for example, we can distinguish seven types of elasticoids according to the seven types of elastic curves depending on the possible ranges of values of the modulus of the elliptic functions which appear in the parametrizations of the elastic curves generating the elasticoids. See Figure 6, Figure 7, Figure 8 and Figure 9 for a description of them.
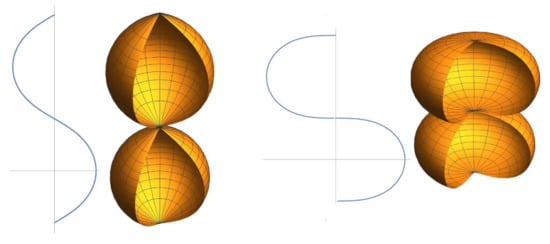
Figure 6.
Elasticoids I: surfaces of revolution generated by, from left to right, the pseudo-sinusoids () and the right lintearia ().
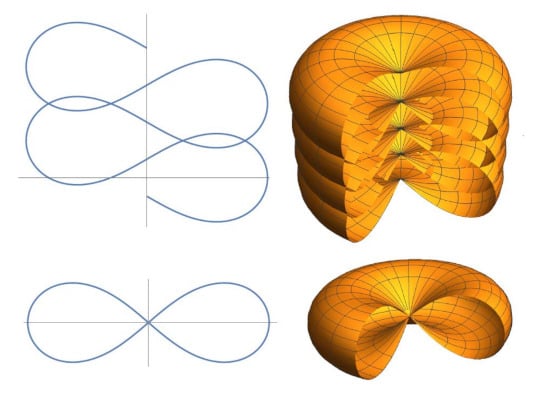
Figure 7.
Elasticoids II: surfaces of revolution generated by, from left to right, the elastic curves with and the pseudolemniscate ().
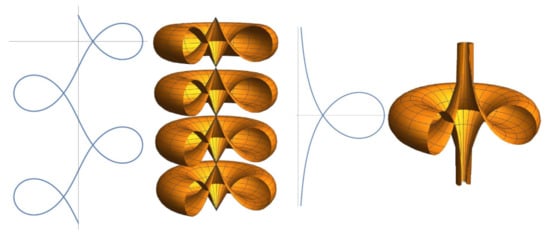
Figure 8.
Elasticoids III: surfaces of revolution generated by, from left to right, the elastic curves with and the convict curve ().
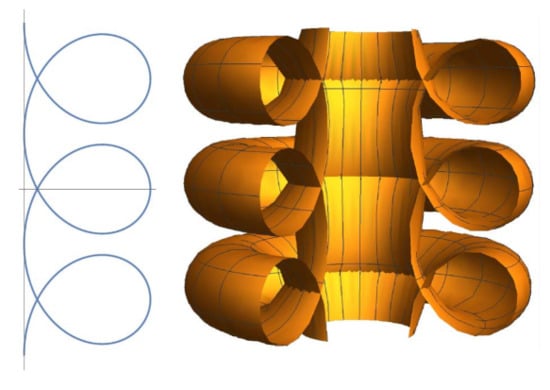
Figure 9.
Elasticoids IV: surfaces of revolution generated by the pseudotrochoids ().
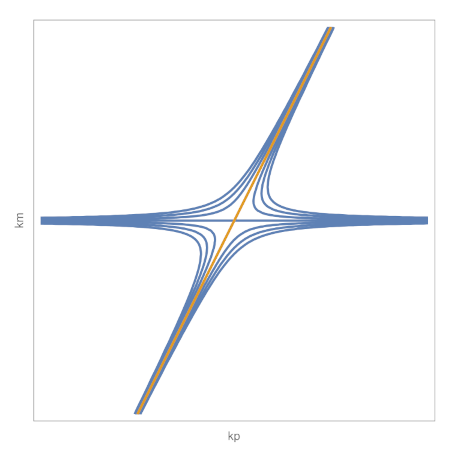
Using (7) and (26), we have that the principal curvatures for the elasticoids are given by and . We can eliminate x since obtaining the W-diagram of the elasticoids:
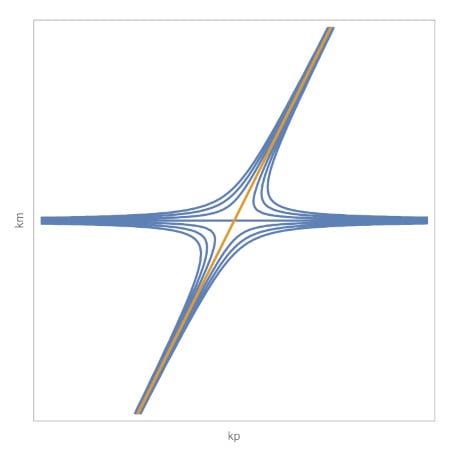
Figure 10.
W-diagram of the elasticoids.
The elasticoids with null modulus, i.e., , are linear Weingarten surfaces since they satisfy (see Section 3.2). Otherwise, we provide the following uniqueness result for Weingarten surfaces involving hyperbolae in the curvature diagram.
Theorem 3.
The only rotational surfaces satisfying , , are the sphere of radius () and the elasticoids with nonzero modulus.
Proof.
Using (7), the Weingarten relation translates into the o.d.e.
We make the change of variable and (28) becomes into the separable o.d.e. for :
The constant solution leads to and Proposition 1(3) gives the sphere of radius . Otherwise, by integrating (29), we obtain , for some constant . From here we easily deduce that . Looking at (26), using Corollary 2, we arrive at the elasticoid of modulus , which is consistent with (27). This finishes the proof. □
4. Prescribing Curvature on a Rotational Surface
Making use of Corollary 2, we present in this section an existence and uniqueness result on prescribing mean or Gauss curvature for a rotational surface with an arbitrary continuous function depending on the distance from the surface to the axis of revolution.
Theorem 4.
- (a)
- Let , , be a continuous function. Then there exists a one-parameter family of rotational surfaces with mean curvature , x being the distance from the surface to the axis of revolution. The surfaces in the family are uniquely determined, up to translations along z-axis, by the geometric linear momenta of their generatrix curves given by
- (b)
- Let , , be a continuous function. Then there exists a one-parameter family of rotational surfaces with Gauss curvature , x being the distance from the surface to the axis of revolution. The surfaces in the family are uniquely determined, up to translations along z-axis, by the geometric linear momenta of their generatrix curves given by
Remark 7.
Proof.
The proof of part (a) simply relies on solving the linear equation
for unknown , coming from (8), and applying Corollary 2.
The same reasoning gives part (b) solving now the immediate equation
coming from (9). □
As a first application of part (a) in Theorem 4, we provide a very short simple proof of a classical result of Euler (cf. [9]) concerning rotational minimal surfaces, i.e., those with vanishing mean curvature.
Corollary 3.
The only minimal rotational surfaces are the plane and the catenoid.
Proof.
If , then (30) leads to , . When , Proposition 1(1) gives the plane, and when , Proposition 1(5) leads to the catenoid. □
Applying again part (a) in Theorem 4, we now deal with a new shorter proof of the classification of rotational CMC surfaces given by Delaunay (cf. [10], see also [34]). We recall (see [24]) that the Delaunay surfaces are the surfaces of revolution generated by the rotation of the Delaunay roulettes around their base. According to [24], the differential equation of these curves in the -plane is given by
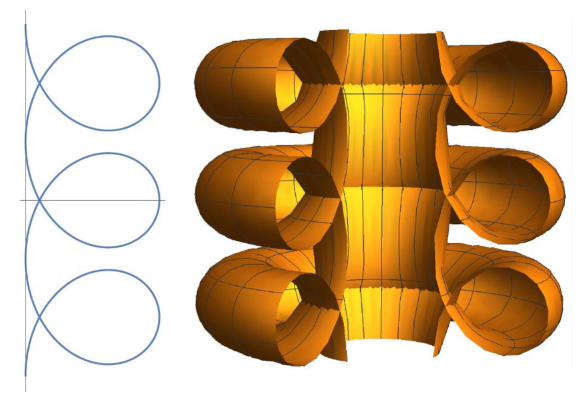
with for the elliptic roulette (ellipse with semi-axes a and b, ), and for the hyperbolic roulette (hyperbola with semi-axes a and b). The surfaces associated to an elliptic roulette are called onduloids and those ones associated to a hyperbolic roulette nodoids. Since the parabolic roulette is the catenary, the associated surface is none other than the catenoid (case of zero mean curvature). The Delaunay surfaces have the remarkable property, apart from the circular cylinder (corresponding to a circular roulette), of being the only surfaces of revolution with nonzero constant mean curvature (if we include the sphere, which is a limit case). See Figure 11.
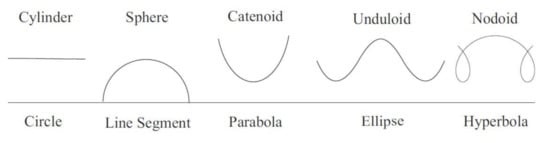
Figure 11.
Delaunay roulettes (the profile curves of the Delaunay surfaces) generated by rolling the conics listed below them; this is Figure 1 in [34].
Corollary 4.
The only nonzero constant mean curvature rotational surfaces are the circular cylinder, the sphere, and the Delaunay surfaces.
Proof.
Assume, without restriction, . Then (30) leads to
If , and we obtain the sphere of radius from Proposition 1(3). We must also take into account the case x constant, because it produces the circular cylinder of radius (see Remark 4). When x is non-constant, we look for the generatrix curve determined by (33) applying Remark 2, and obtain:
and
From the above two expressions, we deduce that
Comparing with (32), we arrive at Delaunay roulettes considering and , that is, if , taking and so and if , taking and so . This finishes the proof. □
Now we deal with some applications of part (b) in Theorem 4. We can immediately obtain the flat rotational surfaces, since implies that must be constant, and we arrive at planes, cones, and cylinders (see Proposition 1 (1), (2), and Remark 4). More interesting is the study (initiated by Darboux in 1890) of rotational surfaces with nonzero constant Gauss curvature. They are called Darboux surfaces and we present them following the description in [24] and references therein.
Let .
- (i)
- Positive Gaussian curvature , .In cylindrical coordinates , the surfaces are defined bywhere denotes the elliptic integral of second kind and modulus ([23]). The case correspond to the sphere and the shapes are different according to or . See Figure 12.
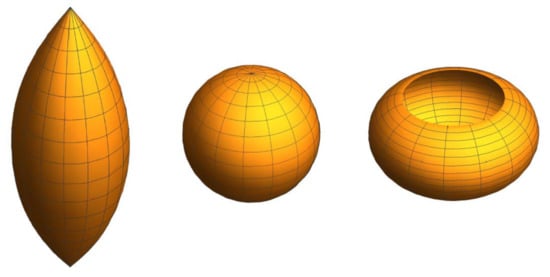 Figure 12. Rotational surfaces with . From left to right: , (sphere), .
Figure 12. Rotational surfaces with . From left to right: , (sphere), . - (ii)
- Negative Gaussian curvature , .There are also three kinds of surfaces, but this time with three different parametrizations. See Figure 13.
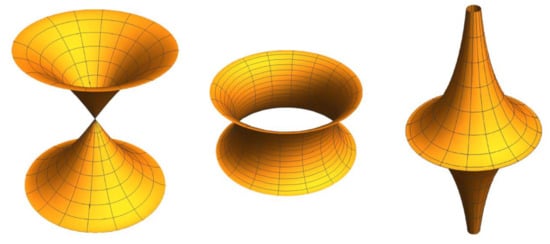 Figure 13. Rotational surfaces with . From left to right: surface with a conical point, surface of hyperboloid-type, and pseudosphere.
Figure 13. Rotational surfaces with . From left to right: surface with a conical point, surface of hyperboloid-type, and pseudosphere.- −
- First type: surfaces with a conical point. In cylindrical coordinates, the surfaces are given by
- −
- Second type: surfaces that look like a hyperboloid. In cylindrical coordinates, the surfaces are described by
- −
- Third type: the pseudosphere. The pseudosphere is the surface of revolution generated by the rotation of a tractrix around its asymptote (see Proposition 1(7)). It was studied by Ferdinand Minding (1806–1885) and Eugene Beltrami in 1868.
Applying part (b) in Theorem 4, we provide a new proof of the classification of rotational surfaces with nonzero constant Gaussian curvature.
Corollary 5.
The only nonzero constant Gauss curvature rotational surfaces are the Darboux surfaces.
Proof.
Assume . Then (31) leads to
If , , , and we obtain the sphere of radius from Proposition 1(3).
Now we look for the rotational surface determined by (37) (see Corollary 2). Applying (6), we obtain:
We must distinguish two cases according to the sign of . If , we have that
with in this case. We put , , and make the change of variable in (39). Then we arrive at . Looking at (34), we recover the Darboux surfaces with positive constant Gauss curvature. We point out that (and then ) gives again the sphere of radius as then .
If , from (38) we obtain that
with in this case.
When , we write , . Then we make the change of variable in (40) and so we arrive at . Looking at (35), we recover the first type of Darboux surfaces with negative constant Gauss curvature.
When , we can set , . Now we make the change of variable in (40) and arrive at . Looking at (36), we recover the second type of Darboux surfaces with negative constant Gauss curvature.
When , we simply have that
that is nothing but the Cartesian equation of the tractrix (cf. [24]), the generatrix curve of the pseudosphere. Anyway, from (37) we deduce that in this case. Then Proposition 1(7) also leads to the pseudosphere. This finishes the proof. □
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.C. and I.C.; writing—original draft preparation, P.C. and I.C.; writing—review and editing, P.C. and I.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This publication is part of the R+D+i project PID2020-117868GB-I00, financed by MCIN/AEI/10.13039/501100011033/. The second author is also supported by the EBM/FEDER UJA 2020 project 1380860 and the Junta de Andalucıa grant P18-FR-4049.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Chern, S.S. Some new characterizations of the Euclidean sphere. Duke Math. J. 1945, 12, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopf, H. Über Flächen mit einer Relation zwischen den Hauptkrü. Math. Nachr. 1951, 4, 232–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weingarten, J. Ueber eine Klasse auf einander abwickelbarer Flächen. J. Reine Angew. Math. 1861, 59, 382–393. [Google Scholar]
- Voss, K. Über geschlossene Weingartensche Flächen. Math. Annalen 1959, 138, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van-Brunt, B.; Grant, K. Potential applications of Weingarten surfaces in CAGD, I: Weingarten surfaces and surface shape investigation. Comput. Aided Geom. Des. 1996, 13, 569–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulov, V.I.; Hadzhilazova, M.T.; Mladenov, I.V. Deformations Without Bending: Explicit Examples. Geom. Integr. Quantization 2019, 20, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulov, V.I.; Mladenov, I.V. Further deformations of the axially-symmetric non-bending surfaces. J. Geom. Symmetry Phys. 2020, 55, 51–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kühnel, W.; Steller, M. On closed Weingarten surfaces. Monatsh. Math. 2005, 146, 113–126. [Google Scholar]
- Euler, L. Methodus Inveniendi Lineas Curvas: Maximi Minimive Proprietate Gaudentessive Solutio Problematis Isoperimetrici Latissimo Sensu Accepti; Opera Omnia: Series 1; Marcum-Michaelem Bousquet: Lausanne, Geneva, 1744; Volume 24. (In Latin) [Google Scholar]
- Delaunay, C. Sur la surface de revolution dont la courbure moyenne est constante. J. Math. Pures Appl. 1841, 6, 309–320. [Google Scholar]
- Darboux, G. Sur la surface dont la courbure totale est constante. Ann. Sci. Éc. Norm. Supér. 1890, 7, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- López, R.; Pámpano, A. Clasification of rotational surfaces in Euclidean space satisfying a lineal relation between their principal curvatures. Math. Nachr. 2020, 293, 735–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, R.; Pámpano, A. Rotational surfaces of constant astigmatism in space forms. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 2020, 483, 123602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, R.; Pámpano, A. Classification of rotational surfaces with constant skew curvature in 3-space forms. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 2020, 489, 124195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, I.; Castro-Infantes, I. Plane curves with curvature depending on distance to a line. Differ. Geom. Appl. 2016, 44, 77–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, D. Curves whose curvature depends on distance from the origin. Am. Math. Mon. 1999, 106, 835–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, D. Lectures on elastic curves and rods. Curvature and Variational Modelling in Physics and Biophysics. AIP Conf. Proc. Vol. 2008, 1002, 3–32. [Google Scholar]
- Castro, I.; Castro-Infantes, I.; Castro-Infantes, J. New plane curves with curvature depending on distance from the origin. Mediterr. J. Math. 2017, 14, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, I.; Castro-Infantes, I.; Castro-Infantes, J. Curves in Lorentz-Minkowski plane: Elasticae, catenaries and grim-reapers. Open Math. 2018, 16, 747–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, I.; Castro-Infantes, I.; Castro-Infantes, J. Curves in Lorentz-Minkowski plane with curvature depending on their position. Open Math. 2020, 18, 749–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, I.; Castro-Infantes, I.; Castro-Infantes, J. On a Problem of David Singer about Prescribing Curvature for Curves. Geom. Integr. Quantization 2020, 21, 100–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenmotsu, K. Surfaces of revolution with prescribed mean curvature. Tôhoku Math. J. 1980, 32, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrd, P.F.; Friedman, M.D. Handbook of Elliptic Integrals for Engineers and Physicists, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Ferréol, R. Encyclopédie des Formes Mathématiques Remarquables. Available online: www.mathcurve.com (accessed on 30 December 2021).
- Caddeo, R.; Montaldo, S.; Oniciuc, C.; Piu, P. Surfaces in three-dimensional space forms with divergence-free stress-bienergy tensor. Ann. Mat. Pura Appl. 2014, 193, 529–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nistor, S.; Oniciuc, C. On the uniqueness of complete biconservative surfaces in ℝ3. Proc. Am. Math. Soc. 2019, 147, 1231–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, R.; Pámpano, A. Stationary soap films with vertical potentials. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2111.03293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langer, J.; Singer, D. The total squared curvature of closed curves. J. Differ. Geom. 1984, 20, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mladenov, I.V.; Oprea, J. The Mylar balloon revisited. Am. Math. Mon. 2003, 110, 761–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gálvez, J.A.; Martínez, A.; Milán, F. Linear Weingarten surfaces in ℝ3. Monatsh. Math. 2003, 138, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, R. Special Weingarten surfaces foliated by circles. Monatsh. Math. 2008, 154, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosenberg, H.; Earp, R.S. The geometry of properly embedded special surfaces in ℝ3; e.g., surfaces satisfying aH + bK = 1, where a and b are positive. Duke Math. J. 1994, 73, 291–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van-Brunt, B.; Grant, K. Hyperbolic Weingarten surfaces. Math. Proc. Camb. Philos. Soc. 1994, 116, 489–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulov, V.I.; Mladenov, I.V. Rotating liquid drops and Delaunay surfaces. J. Geom. Symmetry Phys. 2019, 54, 55–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).