Dynamic Behavior Analysis and Synchronization of Memristor-Coupled Heterogeneous Discrete Neural Networks
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. LADM
2.1. LADM Model
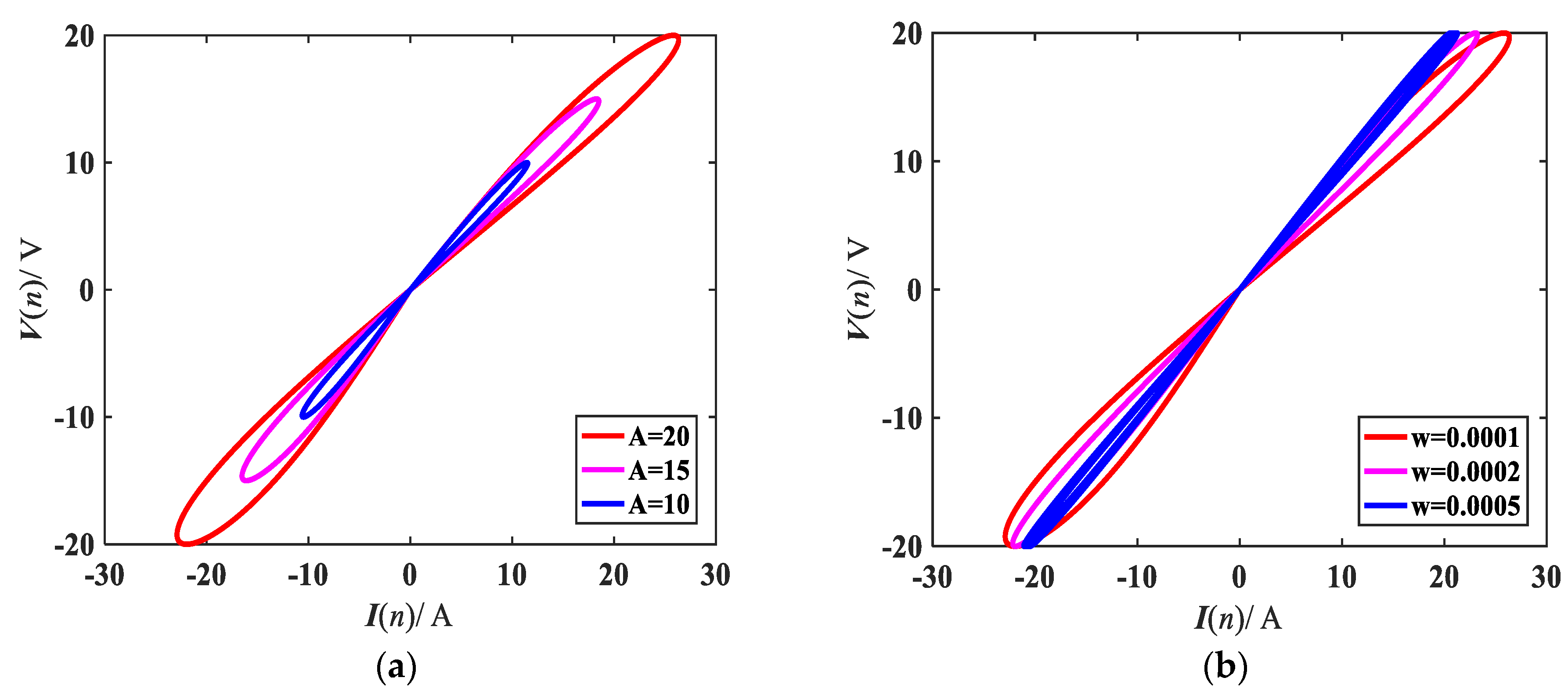
2.2. Pinched Hysteresis Loops
2.3. Nonvolatility and Local Activity
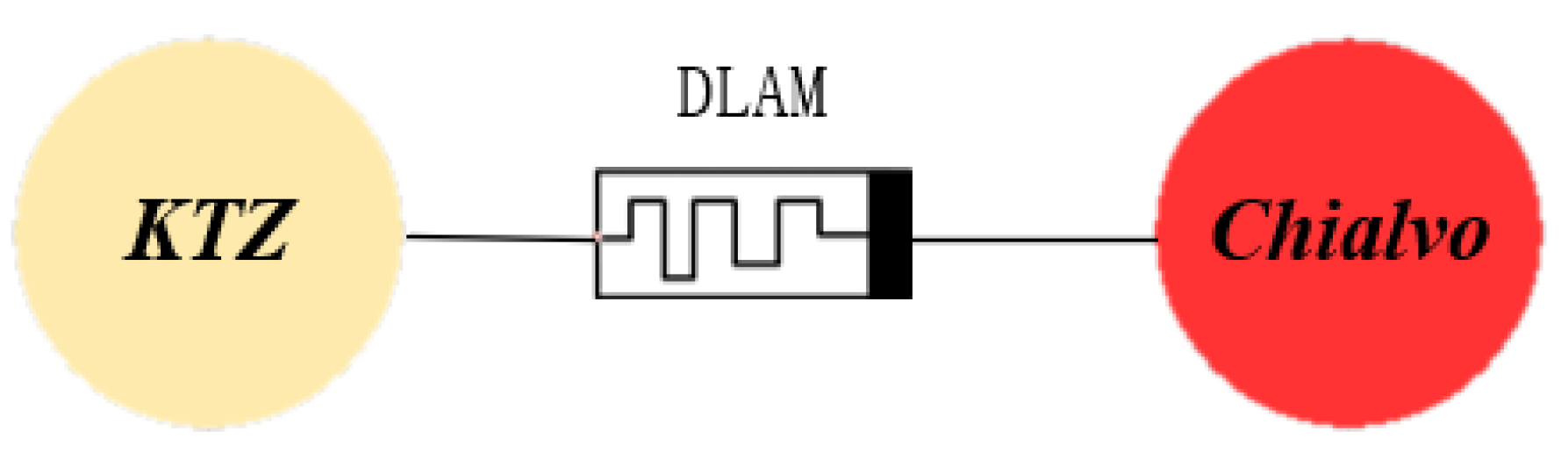
3. LADM Coupled HDNN
3.1. LADM-Coupled HDNN Model
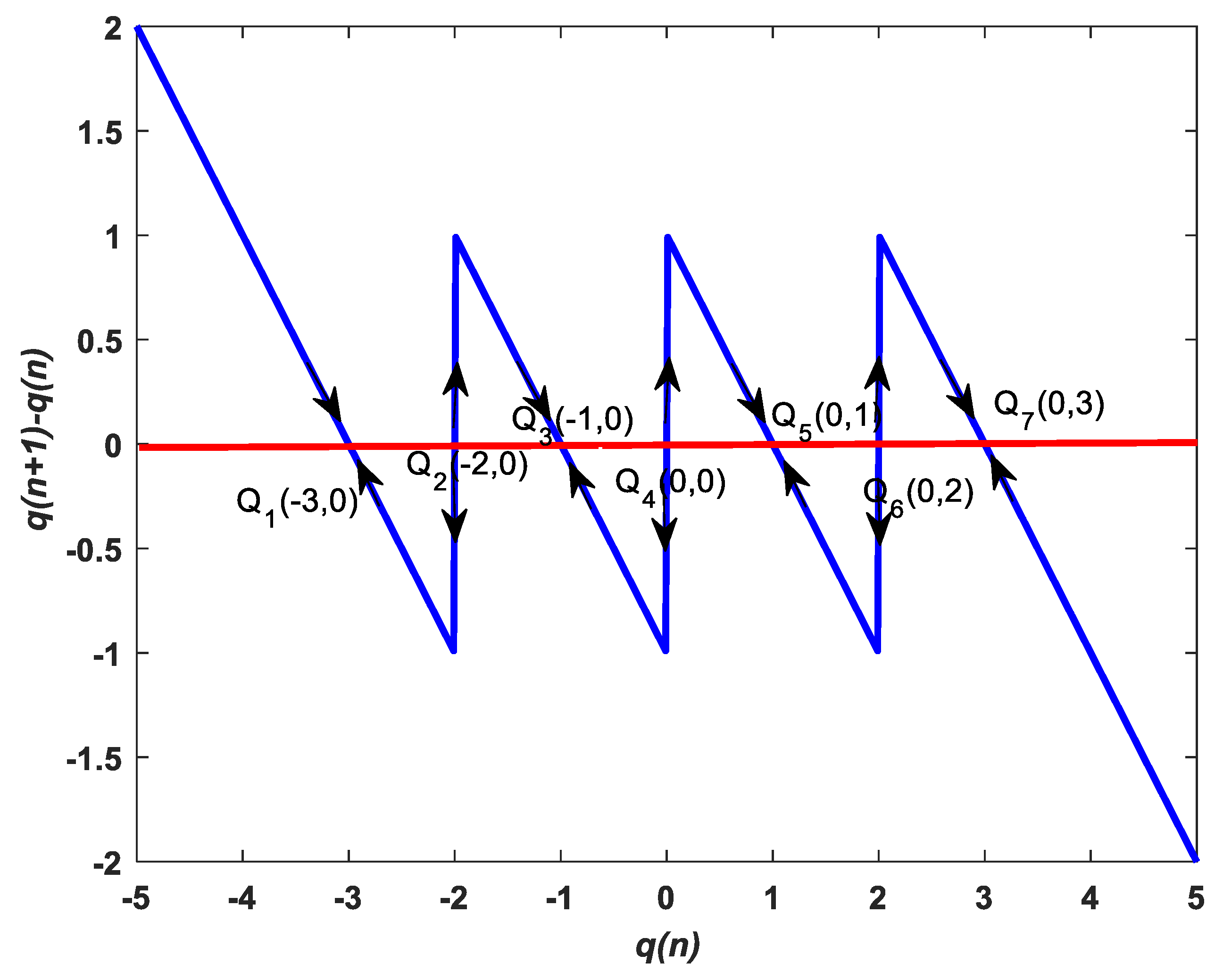
3.2. Stability Analysis of Equilibrium Points
4. Dynamic Behavior Analysis of the LADM-Coupled HDNN
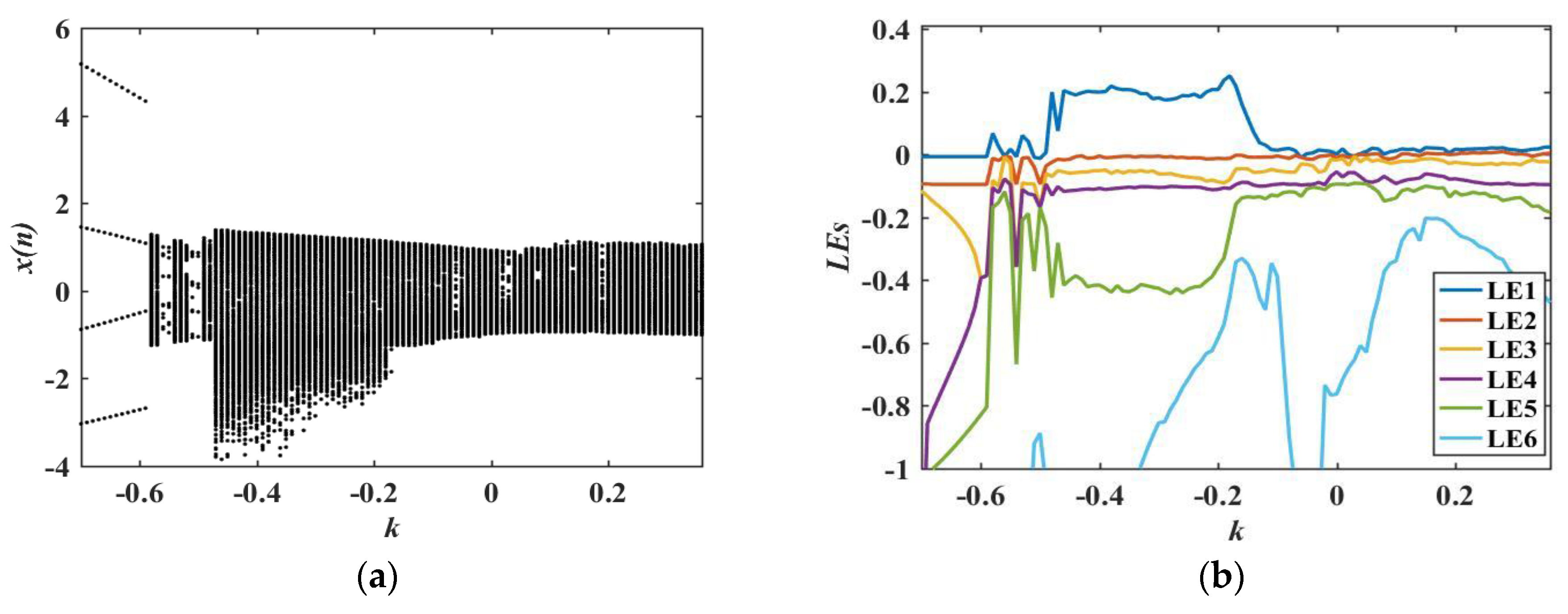
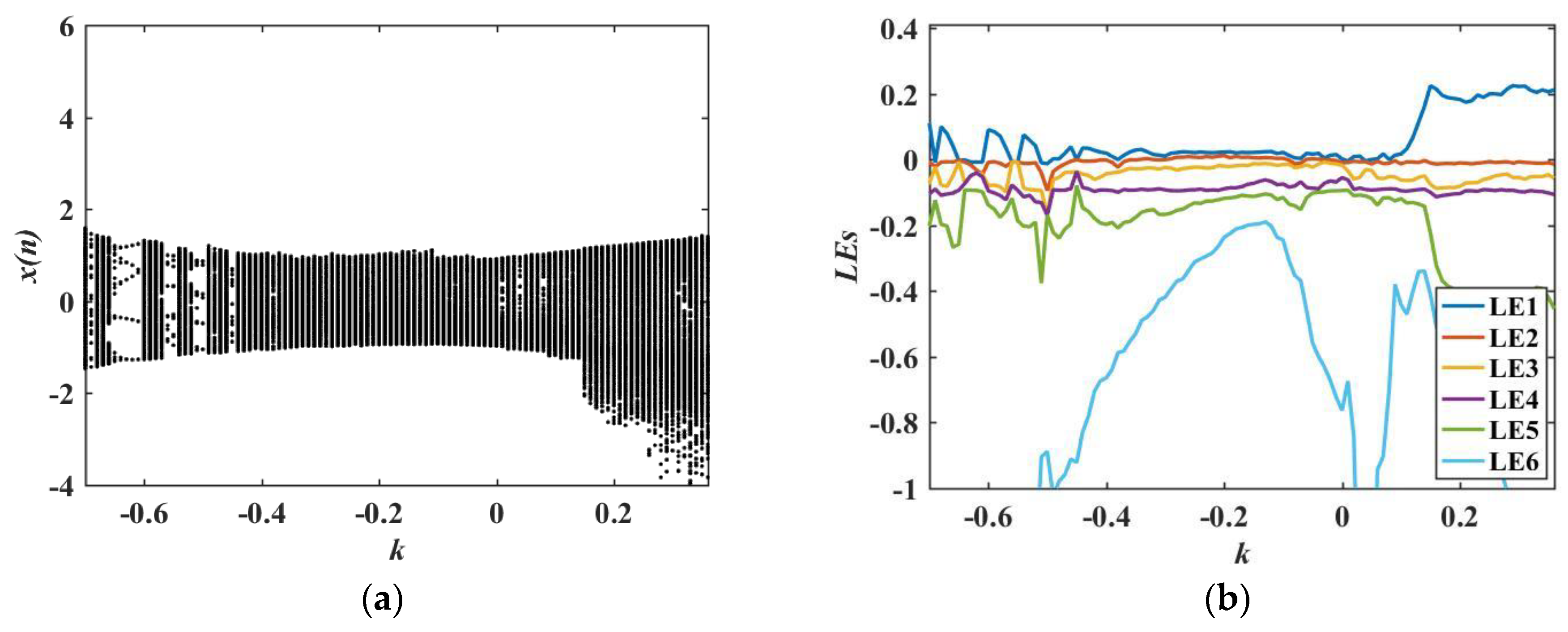
4.1. Bifurcation and Lyapunov Exponent
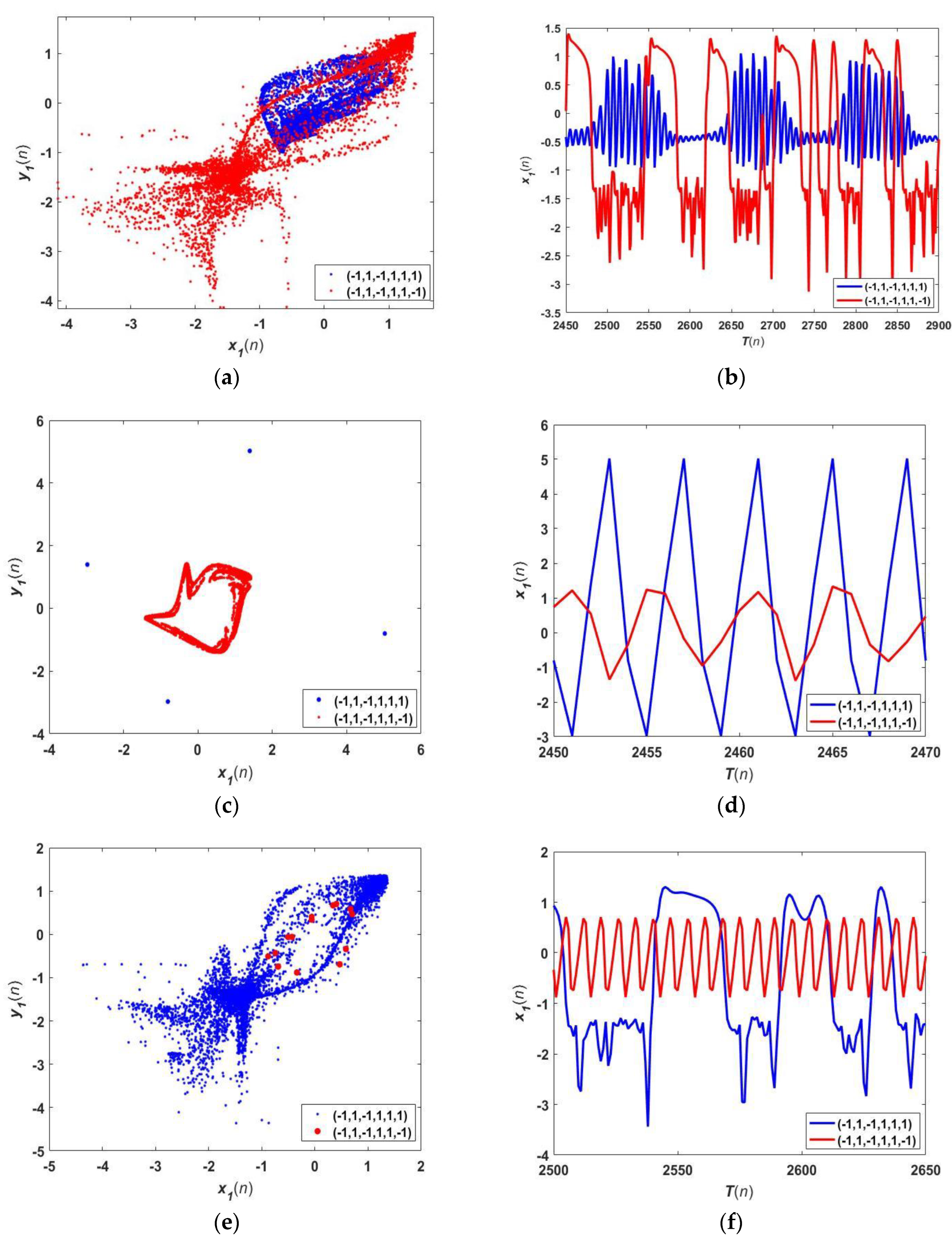
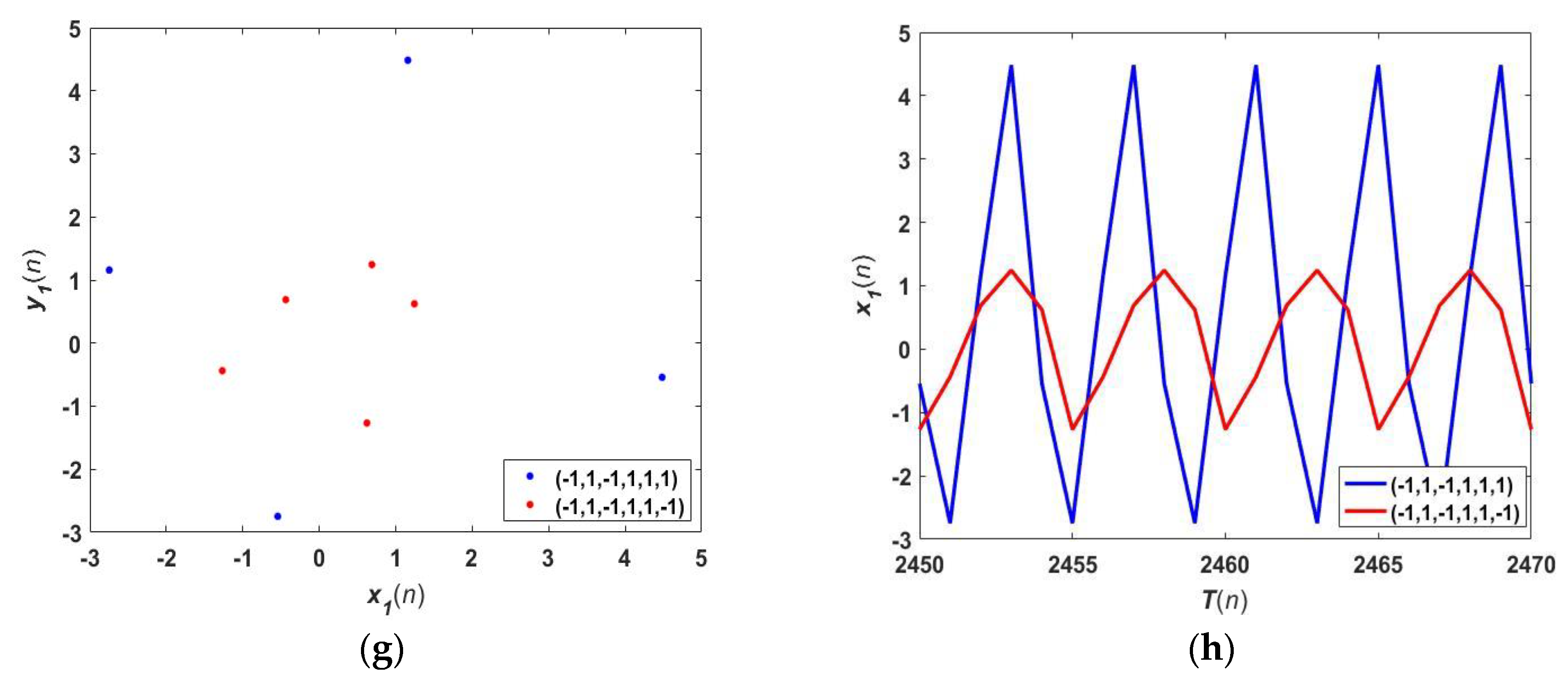
4.2. Coexisting Attractors
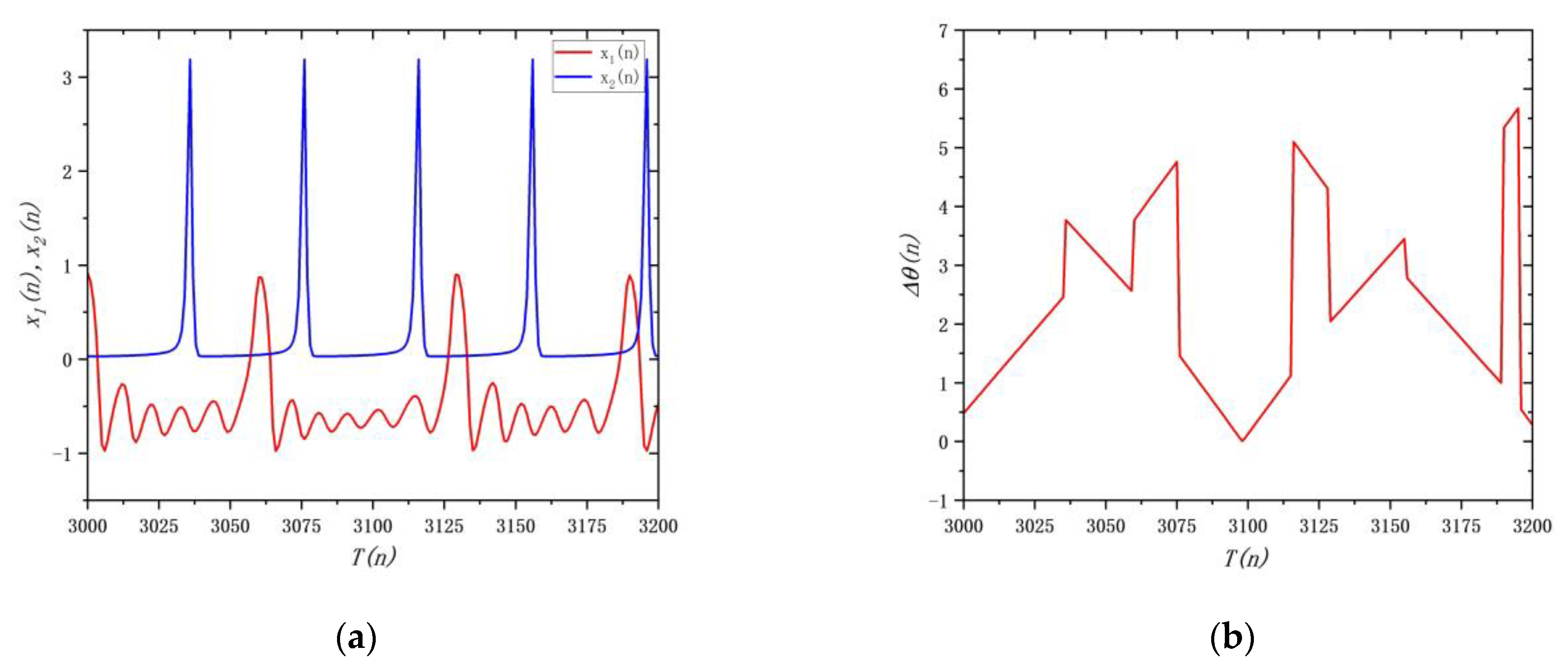
5. Phase Synchronization and Synchronization Transition
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stein, R.B.; Gossen, E.R.; Jones, K.E. Neuronal variability: Noise or part of the signal? Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2005, 6, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, K.; Nagao, H.; Yoshihara, Y. The olfactory bulb: Coding and processing of odor molecule information. Science 1999, 286, 711–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hormuzdi, S.G.; Filippov, M.A.; Mitropoulou, G.; Monyer, H.; Bruzzone, R. Electrical synapses: A dynamic signaling system that shapes the activity of neuronal networks. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Biomembr. 2004, 1662, 113–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Majhi, S.; Bera, B.K.; Ghosh, D.; Perc, M. Chimera states in neuronal networks: A review. Phys. Life Rev. 2019, 28, 100–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kriegeskorte, N. Deep Neural Networks: A New Framework for Modeling Biological Vision and Brain Information Processing. Annu. Rev. Vis. Sci. 2015, 1, 417–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khan, A.; Sohail, A.; Zahoora, U.; Qureshi, A.S. A survey of the recent architectures of deep convolutional neural networks. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2020, 53, 5455–5516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, S.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, X.; Nie, R. Extreme learning machine: Algorithm, theory and applications. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2015, 44, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgkin, A.L.; Huxley, A.F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J. Physiol. 1952, 117, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FitzHugh, R. Impulses and physiological states in theoretical models of nerve membrane. Biophys. J. 1961, 1, 445–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hindmarsh, J.L.; Rose, R.M. A model of neuronal bursting using three coupled first order differential equations. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 1984, 221, 87–102. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, H.; Hua, Z.; Liu, W.; Bao, B. Discrete memristive neuron model and its interspike interval-encoded application inmage encryption. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2021, 64, 2281–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Q.; Yan, Z.; Li, F.; Liu, J.; Chen, S. Multistable dynamics in a Hopfield neural network under electromagnetic radiation and dual bias currents. Nonlinear Dyn. 2022, 109, 2085–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Q.; Yan, Z.; Li, F.; Chen, S.; Liu, J. Complex dynamics in a Hopfield neural network under electromagnetic induction and electromagnetic radiation. Chaos Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 2022, 32, 073107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.; Kong, X.; Mokbel, A.A.M.; Yao, W.; Cai, S. Complex Dynamics, Hardware Implementation and Image Encryption Application of Multiscroll Memeristive Hopfield Neural Network with a Novel Local Active Memeristor. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2022, 70, 326–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Wang, C.; Xu, C.; Zhang, X.; Iu, H.H.C. A memristive synapse control method to generate diversified multi-structure chaotic attractors. IEEE Trans. Comput.-Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2022, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xiao, L.; Wei, Z.; Zhang, W. Zero-Hopf bifurcation analysis in an inertial two-neural system with delayed Crespi function. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 2020, 229, 953–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Wang, C.; Cui, L.; Sun, Y.; Xu, C.; Yu, F. Brain-like initial-boosted hyperchaos and application in biomedical image encryption. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2022, 18, 8839–8850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.; Wang, C.; Deng, Q.; Lin, H. Regulating memristive neuronal dynamical properties via excitatory or inhibitory magnetic field coupling. Nonlinear Dyn. 2022, 110, 3823–3835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Yu, F.; Wang, C.; Sun, J.; Cai, S. Firing Mechanism Based on Single Memristive Neuron and Double Memristive Coupled Neurons. Nonlinear Dyn. 2022, 110, 3807–3822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, S.; Hu, X.; Dong, Z.; Wang, L.; Mazumder, P. Memristor-based cellular nonlinear/neural network: Design, analysis, and applications. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2014, 26, 1202–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Shen, H.; Yu, Q.; Kong, X.; Sharma, P.K.; Cai, S. Privacy Protection of Medical Data Based on Multi-scroll Memristive Hopfield Neural Network. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2022, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chialvo, D.R. Generic excitable dynamics on a two-dimensional map. Chaos Solitons Fractals 1995, 5, 461–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rulkov, N.F. Regularization of synchronized chaotic bursts. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 86, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kinouchi, O.; Tragtenberg, M.H.R. Modeling neurons by simple maps. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 1996, 6, 2343–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuva, S.M.; Lima, G.F.; Kinouchi, O.; Tragtenberg, M.H.; Roque, A.C. A minimal model for excitable and bursti elements. Neurocomputing 2001, 38, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenblatt, F. Principles of Neurodynamics. Perceptrons and the Theory of Brain Mechanisms; Cornell Aeronautical Lab Inc.: Buffalo, NY, USA, 1961. [Google Scholar]
- Rulkov, N.F.; Timofeev, I.; Bazhenov, M. Oscillations in large-scale cortical networks: Map-based model. J. Comput. Neurosci. 2004, 17, 203–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izhikevich, E.M. Which model to use for cortical spiking neurons? IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2004, 15, 1063–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; An, M.; Zhang, X.; Iu, H.H.-C. Two-variable boosting bifurcation in a hyperchaotic map and its hardware implementation. Nonlinear Dyn. 2022, 111, 1871–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.M.; Wang, C.H.; Deng, Q.L.; Xu, C. The dynamics of a memristor-based Rulkov neuron with the fractional-order difference. Chin. Phys. B 2022, 31, 60502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; He, S.; Sun, K. Parameter identification for discrete memristive chaotic map using adaptive differential evolution algorithm. Nonlinear Dyn. 2022, 107, 1263–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, L. Memristor-the missing circuit element. IEEE Trans. Circuit Theory 1971, 18, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strukov, D.B.; Snider, G.S.; Stewart, D.R.; Williams, R.S. The missing memristor found. Nature 2008, 453, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yi, Z. A memristor-based associative memory circuit considering synaptic crosstalk. Electron. Lett. 2022, 58, 539–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; Deng, Q.; Hong, Q.; Li, J.; Liu, H.; Wang, C. A memristor-based circuit design and implementation for blocking on Pavlov associative memory. Neural Comput. Appl. 2022, 34, 14745–14761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Zhu, J.; Zhao, L.; Chen, L.; Chen, L.; Gong, J. A Robust Predefined-Time Convergence Zeroing Neural Network for Dynamic Matrix Inversion. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2022, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Min, F.; Zhang, Y.; Bao, B. Memristive electromagnetic induction effects on Hopfield neural network. Nonlinear Dyn. 2021, 106, 2559–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Mou, J.; Yan, H.; Cao, Y. A new class of Hopfield neural network with double memristive synapses and its DSP implementation. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2022, 137, 1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Zhan, D.; Wang, H.; Sun, K.; Peng, Y. Discrete Memristor and Discrete Memristive Systems. Entropy 2022, 24, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Ju, Z.; Ding, S.; Feng, C.; Chen, M.; Bao, B. Electromagnetic induction effects on electrical activity within a memristive Wilson neuron model. Cogn. Neurodynamics 2022, 16, 1221–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Xing, G.; Deng, Y. Flexible cascade and parallel operations of discrete memristor. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2023, 166, 112888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; You, Z.; Liang, X.; Li, X. A Memristor-Based Colpitts Oscillator Circuit. Mathematics 2022, 10, 4820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Q.; Lai, C.; Zhang, H.; Li, C. Hidden coexisting hyperchaos of new memristive neuron model and its application in image encryption. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2022, 158, 112017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, Y.; Fardad, M.; Varshney, P.K. A memristor-based optimization framework for artificial intelligence applications. IEEE Circuits Syst. Mag. 2018, 18, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Shen, Z.J.; Zhou, G.Y.; Zhao, C.Z.; Yang, L.; Man, K.L.; Lim, E.G. Neuromorphic Properties of Memristor towards Artificial Intelligence. In Proceedings of the 2018 International SoC Design Conference (ISOCC), Daegu, Republic of Korea, 12–15 November 2018; pp. 172–173. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, D.; Xiao, H.; Yang, Z.; Luo, H.; Hu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, M. Fractional-Order Heterogeneous Neuron Network with Hr Neuron and Fhn Neuron Based on Coupled Locally-Active Memristors: Super Coexisting Firing Behaviors, Bursting Behaviors and its Application. Bursting Behav. Its Appl. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhou, H.; Wang, M.; Ma, M. Coexisting firing patterns and phase synchronization in locally active memristor coupled neurons with HR and FN models. Nonlinear Dyn. 2021, 104, 1455–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, H.; Hu, A.; Liu, W.; Bao, B. Hidden bursting firings and bifurcation mechanisms in memristive neuron model with threshold electromagnetic induction. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2019, 31, 502–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, L. If it’s pinched it’s a memristor. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2014, 29, 104001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.J.; Qin, Y.H. Dynamics of Discrete Memristor-Based Rulkov Neuron. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 72051–72056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Bao, H.; Li, H.; Ma, J.; Hua, Z.; Bao, B. Memristive Rulkov neuron model with magnetic induction effects. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2021, 18, 1726–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, B.; Rong, K.; Li, H.; Li, K.; Hua, Z.; Zhang, X. Memristor-coupled logistic hyperchaotic map. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2021, 68, 2992–2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, C.; Du, J. Discretized locally active memristor and application in logarithmic map. Nonlinear Dyn. 2022, 111, 2895–2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Wang, C.; Deng, Q. Rulkov neural network coupled with discrete memristors. Netw. Comput. Neural Syst. 2022, 33, 214–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Rajagopal, K.; Karthikeyan, A.; Srinivasan, A. A discrete Huber-Braun neuron model: From nodal properties to network performance. Cogn. Neurodynamics 2022, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, J.; Bao, H.; Chen, M.; Bao, B. Coexisting multi-stable patterns in memristor synapse-coupled Hopfield neural network with two neurons. Nonlinear Dyn. 2019, 95, 3385–3399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Yang, Y.; Qiu, Z.; Peng, Y.; Sun, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, M. A locally active discrete memristor model and its application in a hyperchaotic map. Nonlinear Dyn. 2022, 107, 2935–2949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, C.; He, S.; Rajagopal, K.; Wang, H.; Sun, K. Dynamics and chimera state in a neural network with discrete memristor coupling. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 2022, 231, 4065–4076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Lu, Y.; Li, Z.; Sun, Y.; Wang, C. Multistability and Phase Synchronization of Rulkov Neurons Coupled with a Locally Active Discrete Memristor. Fractal Fract. 2023, 7, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefański, A.; Kapitaniak, T. Estimation of the dominant Lyapunov exponent of non-smooth systems on the basis of maps synchronization. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2003, 15, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

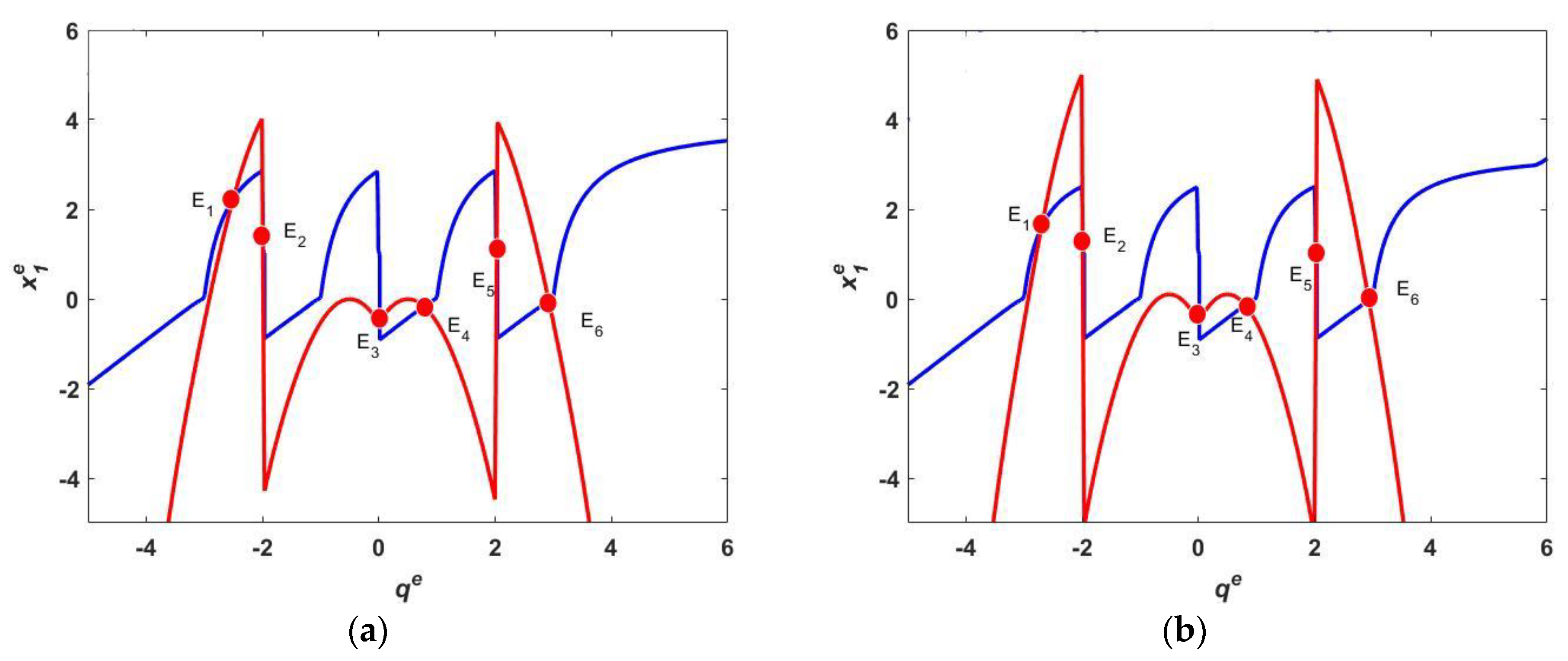

| k | NO. | (x1(e), q(e)) | Eigenvalues | Stabilities |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| E1 | (−0.0337, 2.9189) | 0.6698 + 1.1494i, 0.6698 − 1.1494i 0.5151, 0.9885, 0.8554, 0.9021. | Stable | |
| 0.25 | E4 | (−0.1708, 0.7795) | 0, 0.9920, −0.0024, 0.0024, 0.9004, 0.8996. | Stable |
| E6 | (2.2301, −2.5028) | −2.7047, −2.1365, 1.2382, 0, 1.5248, 1.6534. | Unstable | |
| E1 | (−0.0331, 2.9327) | 0.6830 + 1.2400i, 0.6830 − 1.2400i 0.6666, 0.7710, 0.9894, 0.9018. | Stable | |
| 0.3 | E4 | (−0.1429, 0.8094) | 0.7902 + 0.7365i, 0.7902 − 0.7365i, 0.2326, 0.9770, 0.9113, 0.8998. | Stable |
| E6 | (1.5934, −2.7005) | −1.4298, −1.6982, 2.1698, 1.9782, 0, 2.3712. | Unstable |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, M.; Xiong, K.; Li, Z.; Sun, Y. Dynamic Behavior Analysis and Synchronization of Memristor-Coupled Heterogeneous Discrete Neural Networks. Mathematics 2023, 11, 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11020375
Ma M, Xiong K, Li Z, Sun Y. Dynamic Behavior Analysis and Synchronization of Memristor-Coupled Heterogeneous Discrete Neural Networks. Mathematics. 2023; 11(2):375. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11020375
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Minglin, Kangling Xiong, Zhijun Li, and Yichuang Sun. 2023. "Dynamic Behavior Analysis and Synchronization of Memristor-Coupled Heterogeneous Discrete Neural Networks" Mathematics 11, no. 2: 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11020375
APA StyleMa, M., Xiong, K., Li, Z., & Sun, Y. (2023). Dynamic Behavior Analysis and Synchronization of Memristor-Coupled Heterogeneous Discrete Neural Networks. Mathematics, 11(2), 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11020375








