Direct Yaw Moment Control for Distributed Drive Electric Vehicles Based on Hierarchical Optimization Control Framework
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Vehicle Dynamics Model
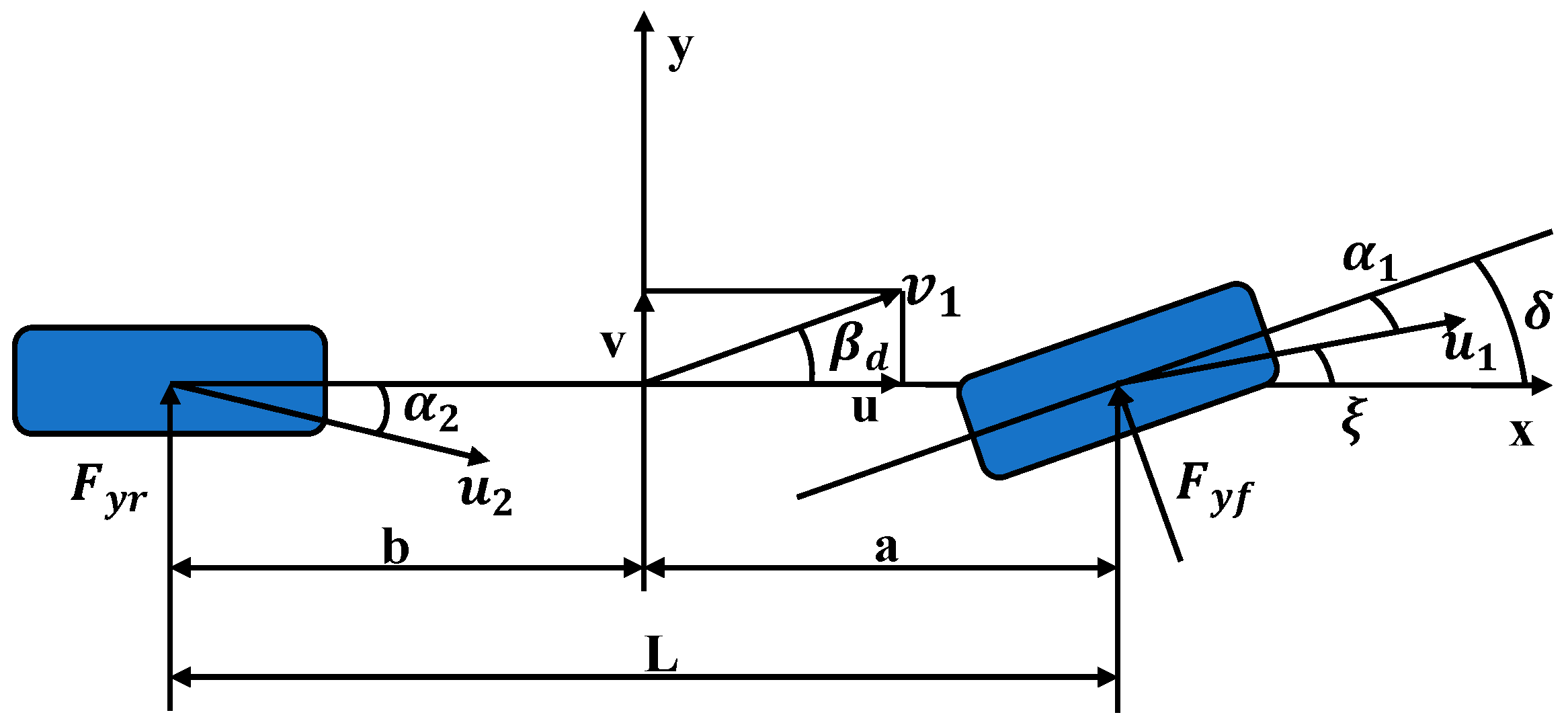
2.1. 2-DOF Reference Model
2.2. Full Vehicle Model
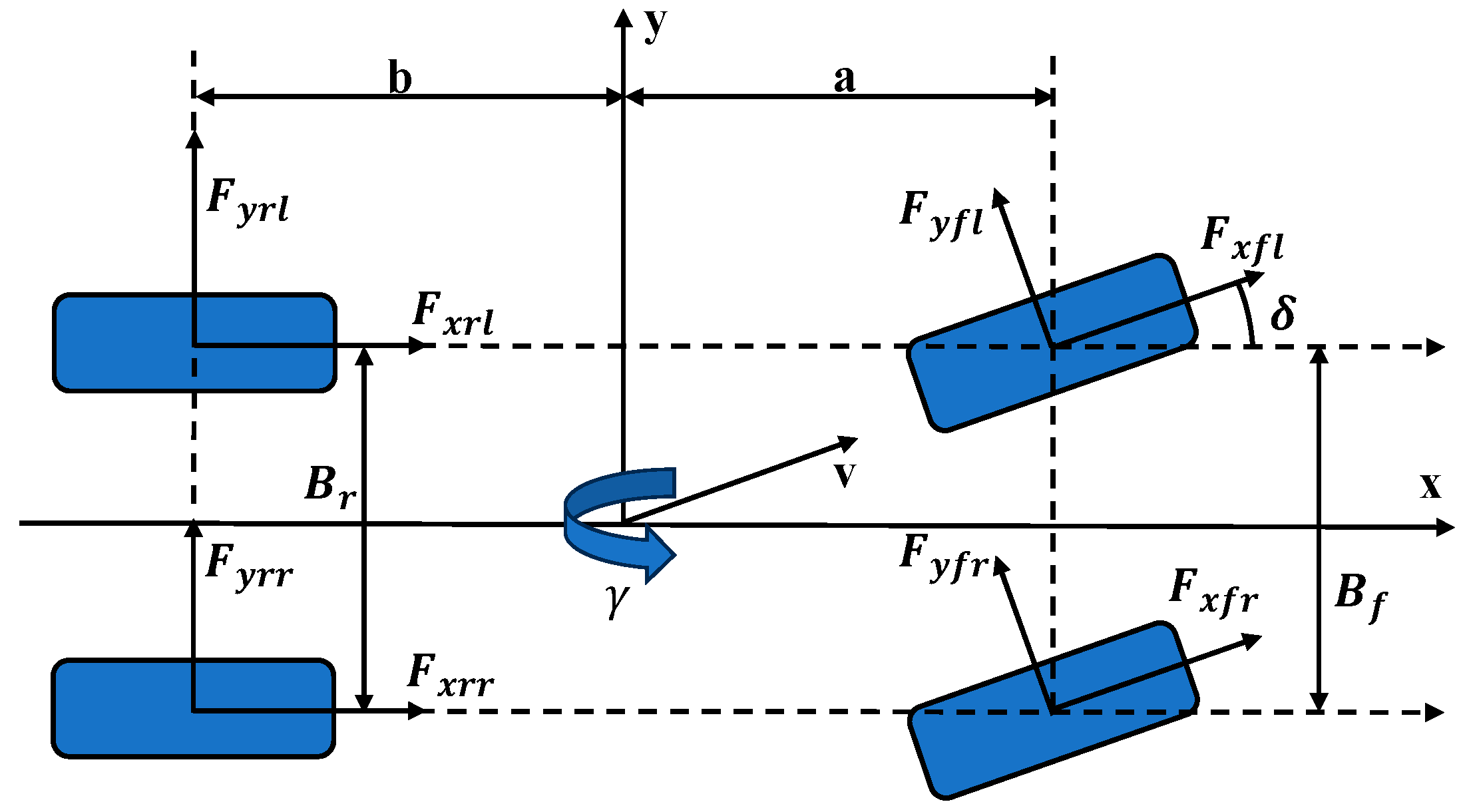
2.2.1. 7-DOF Vehicle Model
2.2.2. Tire Model
2.2.3. Motor Model
2.3. Driver Model
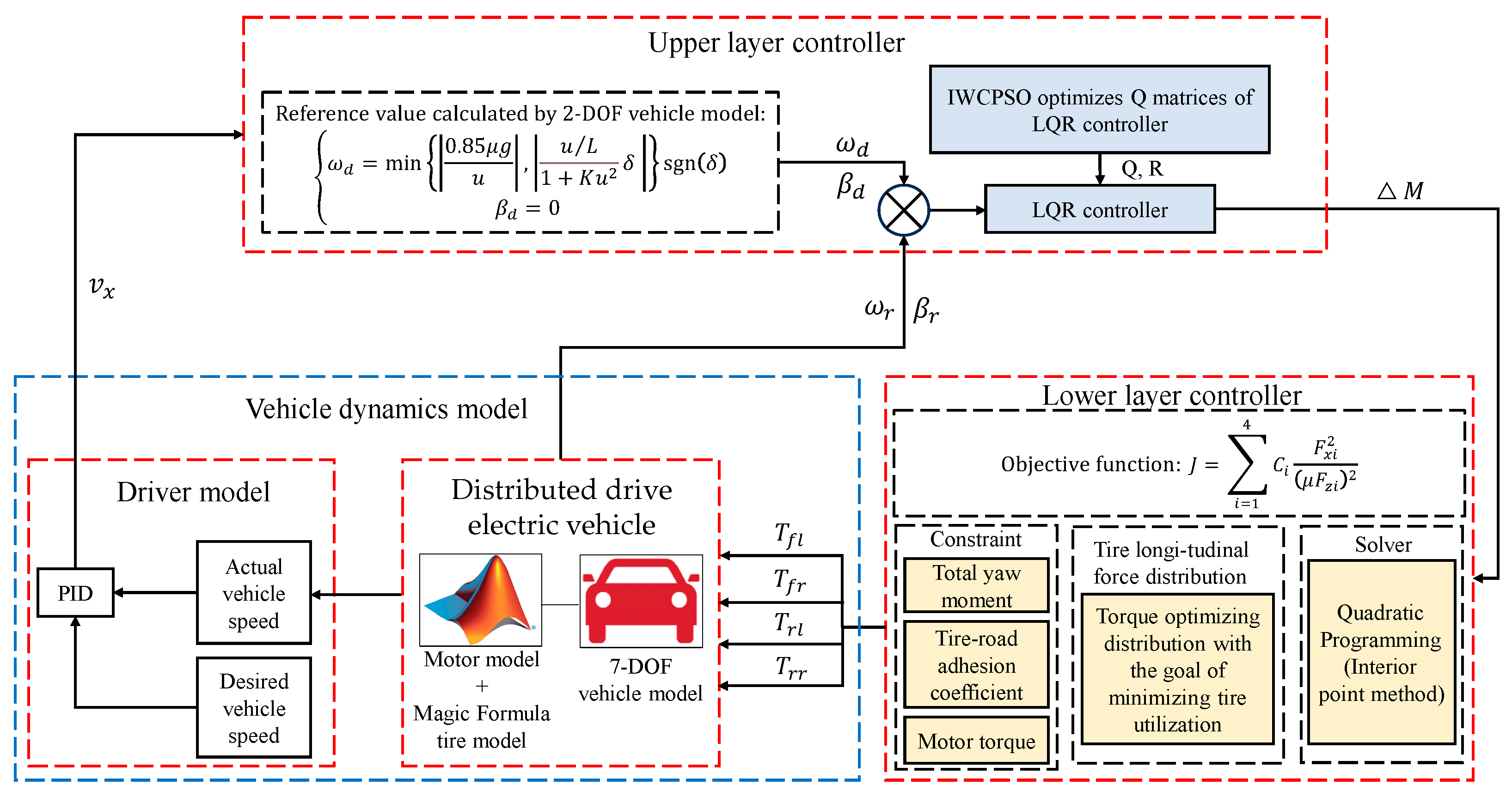
3. Design of Hierarchical Controller for Yaw Stability
3.1. Upper Layer Controller Based on IWCPSO-LQR Algorithm
3.1.1. Conventional LQR Controller
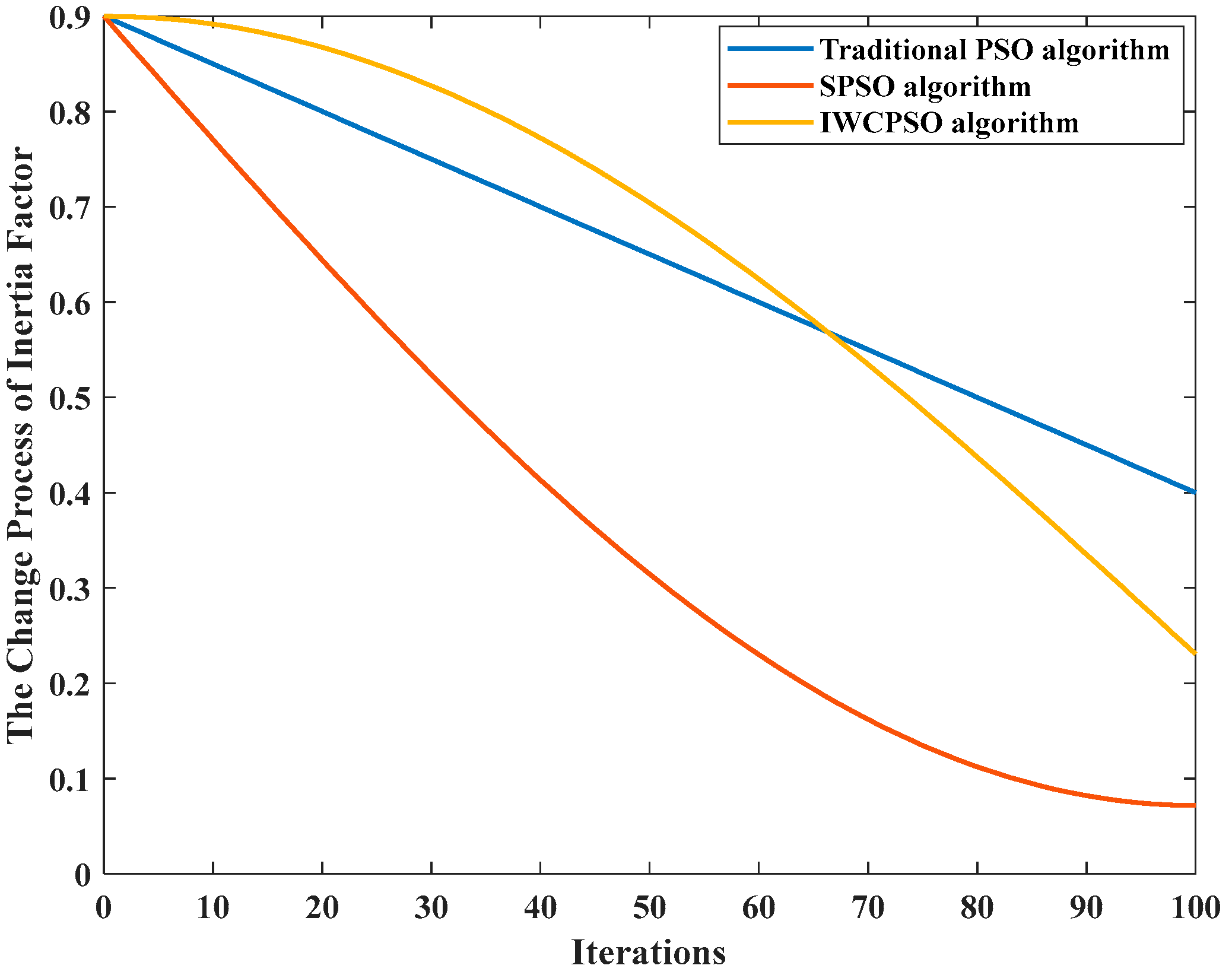
3.1.2. IWCPSO-LQR Controller
3.2. Lower Layer Controller for Optimal Torque Distribution
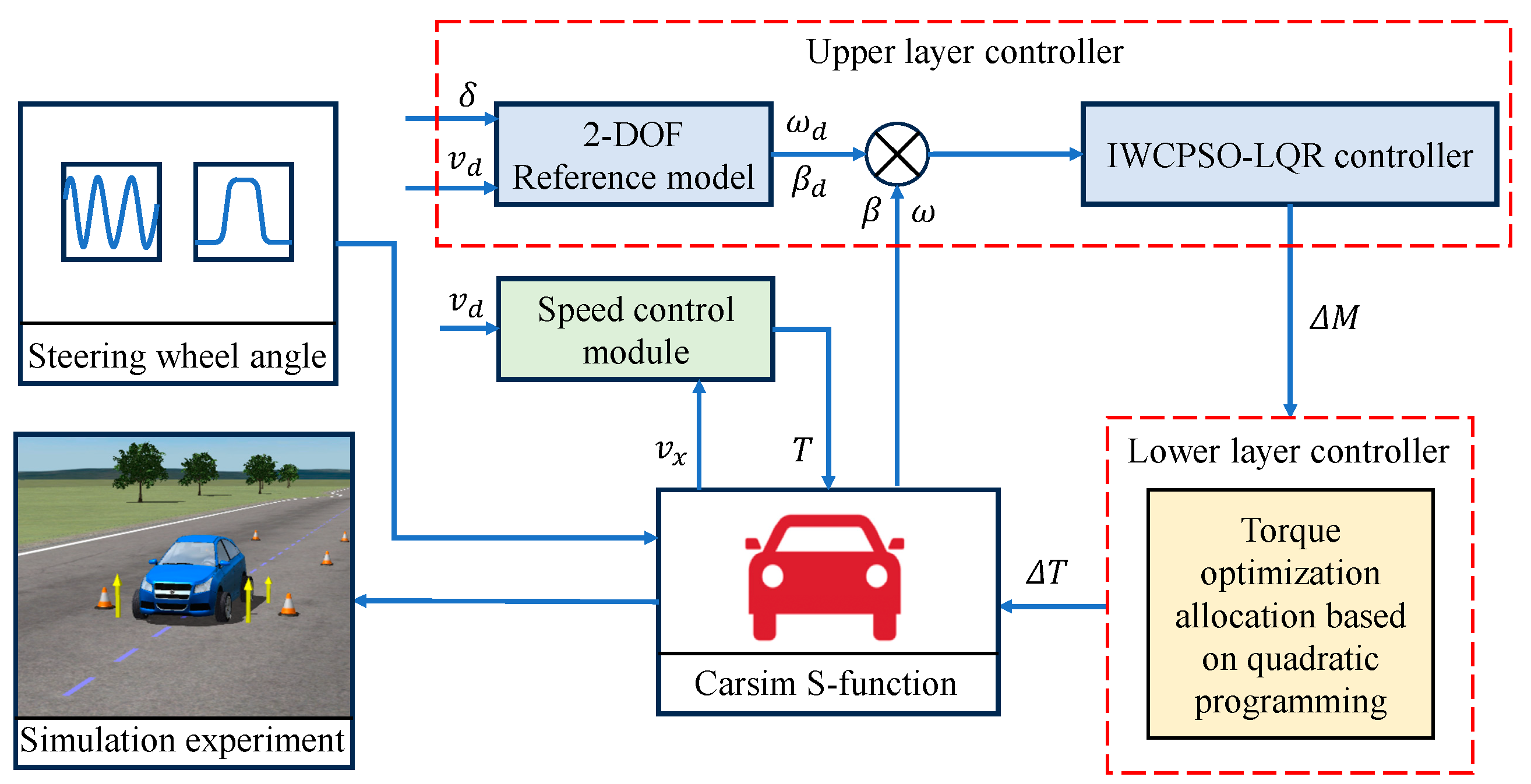
4. Simulation Results and Analysis
4.1. Simulation Setup and Performance Metrics
4.1.1. Simulation Setup
4.1.2. Performance Metrics
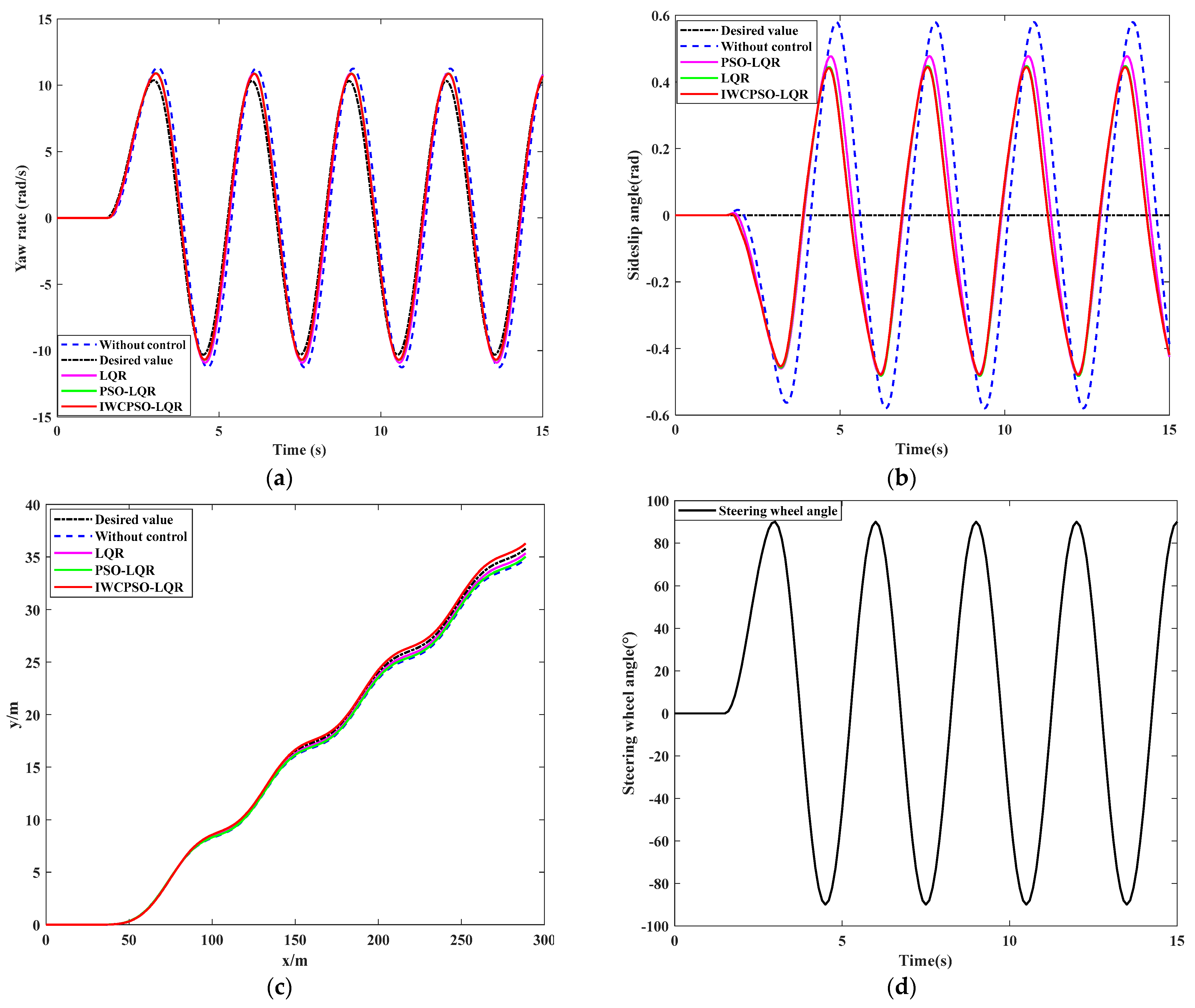
4.2. Simulation on Low Adhesion Road Surfaces
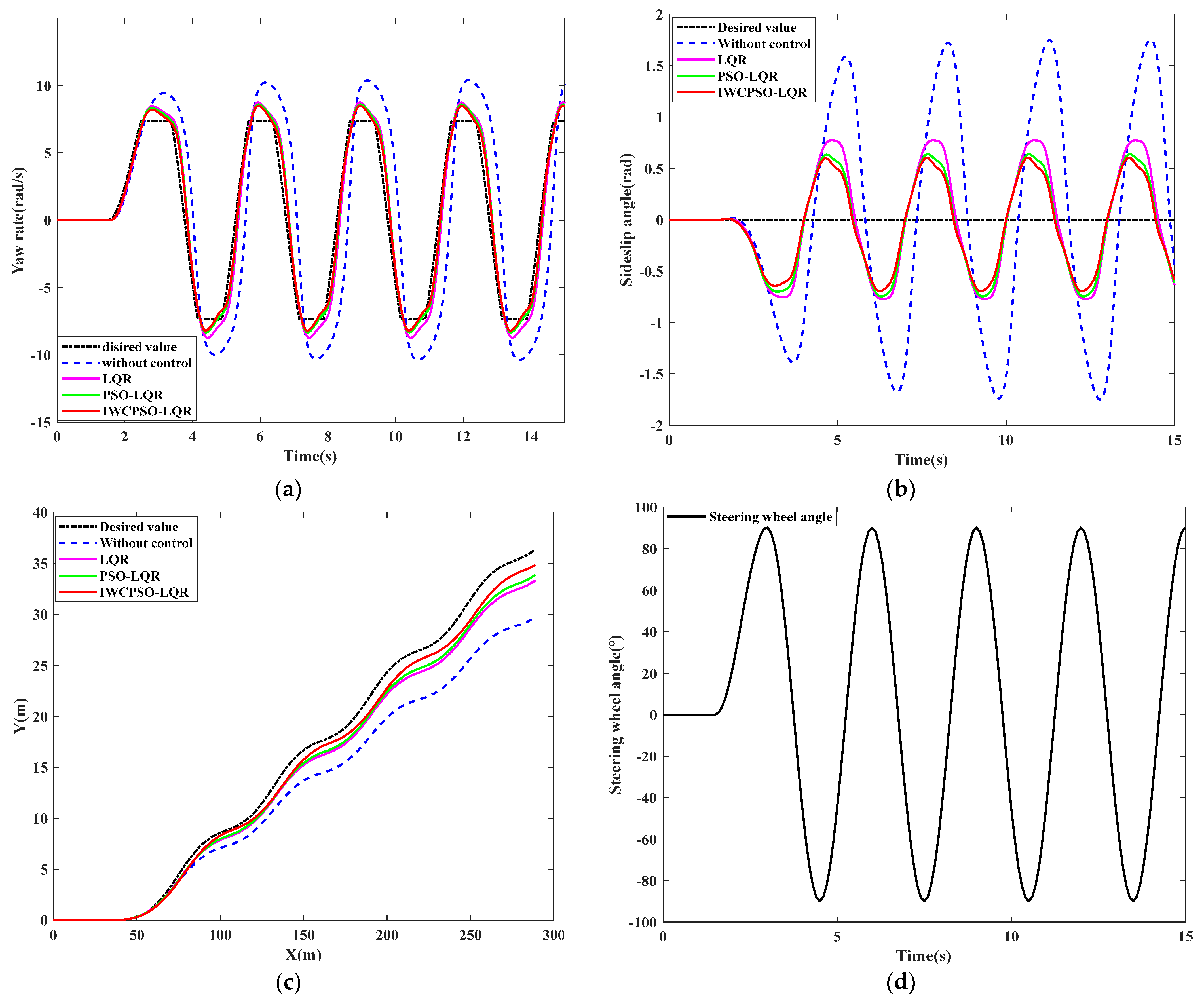
4.2.1. Sinusoidal Test on Low Adhesion Road Surfaces
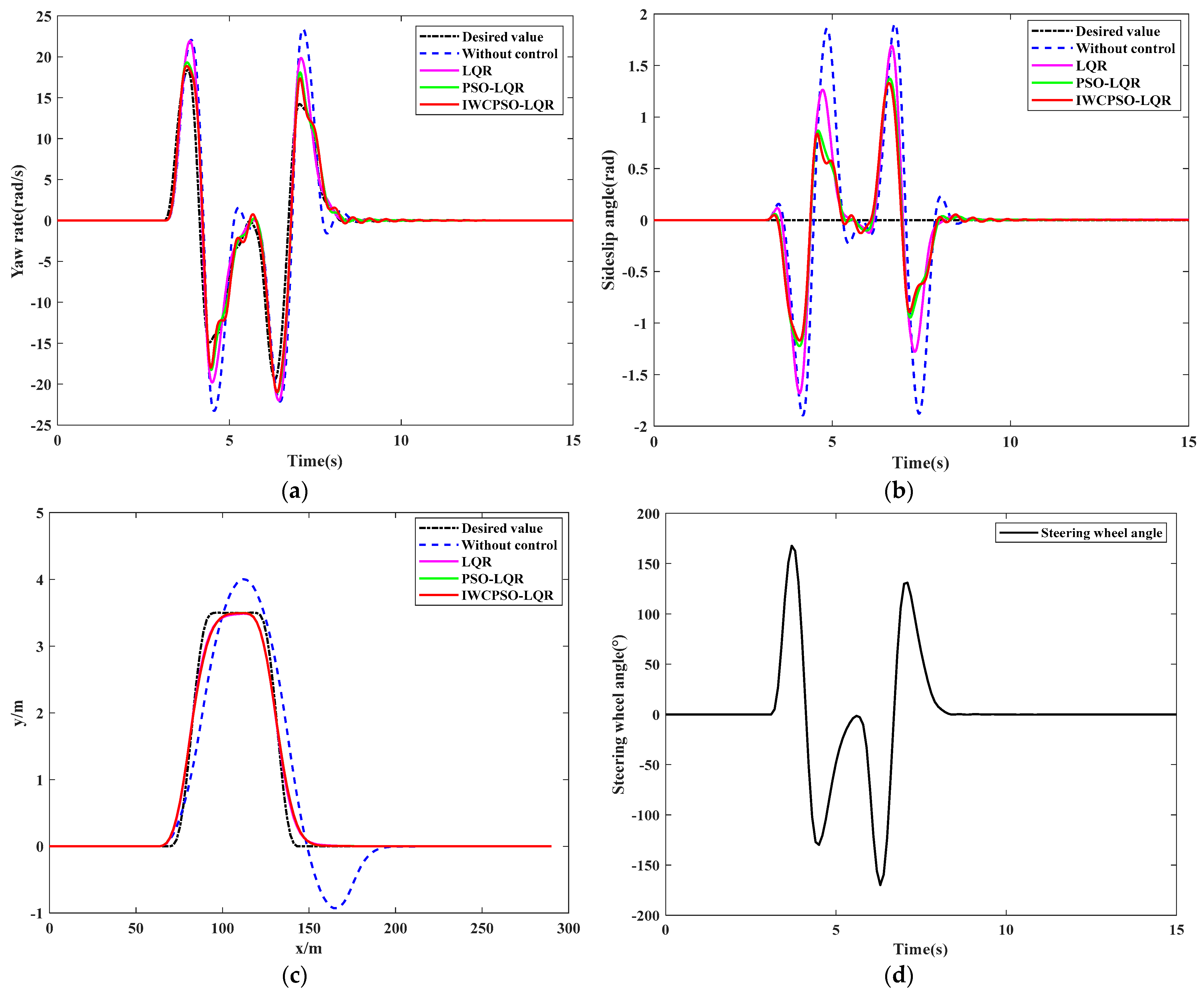
4.2.2. DLC Test on Low Adhesion Road Surfaces
4.3. Simulation on High Adhesion Road Surfaces
4.3.1. Sinusoidal Test on High Adhesion Road Surfaces
4.3.2. DLC Test on High Adhesion Road Surfaces
4.4. Comparison Analysis of Different Algorithms under Different Simulation Conditions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Lv, C. Coordinated control of the steering system and the distributed motors for comprehensive optimization of the dynamics performance and the energy consumption of an electric vehicle. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part D J. Automob. Eng. 2017, 231, 1605–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.F.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Nguyen, A.T. Fault-tolerance-ant predictive control with deep-reinforcement-learning-based torque distribution for four in-wheel motor drive electric vehicle. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2023, 28, 668–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, M.; Zhang, C.W.; Yang, Z.; Chang, B.; Wang, J.L. Research on steering coordination control strategy for distributed drive electric vehicles. AIP Adv. 2023, 13, 025261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Cheng, C.; Guo, J.F.; Shi, B.H.; Ding, S.Y.; Mei, K.Q. Direct yaw-moment control of electric vehicles based on adaptive sliding mode. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2023, 20, 13334–13335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Wang, J.S.; Li, Z.H.; Xu, N.; Ding, H.T.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, K.H.; Xu, H.C. Coordinated optimal control of AFS and DYC for four-wheel independent drive electric vehicles based on MAS model. Sensors 2023, 23, 3505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Pang, H.; Wang, P.; Liu, M.H.; Hu, C. A yaw stability-guaranteed hierarchical coordination control strategy for four-wheel drive electric vehicles using an unscented Kalman filter. J. Frankl. Inst. 2023, 360, 9663–9688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Zhao, F.K.; Zhang, Y. Research on yaw stability control strategy for distributed drive electric trucks. Sensors 2023, 23, 7222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.R.; Bei, S.Y.; Li, B.; Sun, X.Q.; Huang, C.; Tian, J.; Hu, H.Z. Mechanism analysis and control of lateral instability of 4WID vehicle based on phase plane analysis considering front wheel angle. Actuators 2023, 12, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.Q.; Wang, Y.J.; Cai, Y.F.; Wong, P.K.; Chen, L. NFTSM control of direct yaw moment for autonomous electric vehicles with consideration of tire nonlinear mechanical properties. Bull. Pol. Acad. Sci. Tech. Sci. 2021, 69, e137065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viktor, S.; Paulius, K.; Eldar, Š.; Barys, S.; Valentin, I. Review of integrated chassis control techniques for automated ground vehicles. Sensors 2024, 24, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.M.; Xie, L.; Lu, S.; Wu, X.L.; Su, H.Y. Vehicle yaw stability control with a two-layered learning MPC. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 2023, 61, 423–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Liu, H.; Han, L.J.; Wang, W.D.; Guo, C.S. Multi-level coordinated yaw stability control based on sliding mode predictive control for distributed drive electric vehicles under extreme conditions. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2023, 72, 280–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, P.S.; Guo, L.; Feng, J.D.; Zhou, X.Y. Adaptive stability control based on sliding model control for BEVs driven by in-wheel motors. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhang, Q.J.; Wan, Y.D.; Liu, P.; Yu, Y.; Guo, J. Yaw stability control of automated guided vehicle under the condition of centroid variation. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2022, 44, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Y.; Ling, R. Hierarchical control scheme of direct yaw moment control system based on second-order sliding mode control. In Proceedings of the 2022 34th Chinese Control and Decision Conference (CCDC), Hefei, China, 21–23 May 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.; Mei, K.Q.; Ding, S.H. Direct yaw-moment control design for in-wheel electric vehicle with composite terminal sliding mode. Nonlinear Dyn. 2023, 111, 17141–17156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.K.; Shen, X.F.; Ling, H.P. Analysis and design of direct yaw-moment control for distributed drive electric vehicles considering. In Proceedings of the 8th Asia-Pacific Conference on Intelligent Robot Systems, Xi’an, China, 7–9 July 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.M.; Zou, T.; Su, L.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, Y. Optimal coordinated control of active front steering and direct yaw moment for distributed drive electric bus. Machines 2023, 11, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yu, L.Y.; Pan, N.; Liu, X.Y.; Song, J. Vehicle direct yaw moment control based on tire cornering stiffness estimation. In Proceedings of the ASME 2014 Dynamic Systems and Control Conference, San Antonio, TX, USA, 22–24 October 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, K.; Joa, E.; Lee, J.; Yun, J.; Yi, K. Yaw Stability control of 4WD vehicles based on model predictive torque vectoring with physical constraints. Int. J. Automot. Technol. 2019, 20, 923–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.Y.; Wang, Z.P.; Zhang, L. Unbiased-estimation-based and computation-efficient adaptive MPC for four-wheel-independently-actuated electric vehicles. Mech. Mach. Theory 2020, 154, 104100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altork, B.; Yazici, H. Robust static output feedback H∞-controller design for three degree of freedom integrated bus lateral, yaw, roll dynamics model. Trans. Inst. Meas. Control 2019, 41, 4545–4568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.R.; Jing, H.; Hu, C.; Yan, F.J.; Chen, N. Robust H∞ path following control for autonomous ground vehicles with delay and data dropout. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2016, 17, 2042–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Z.L.; Cai, L.C.; Li, J.Q.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Liu, C.G. Direct yaw moment control of eight-wheeled distributed drive electric vehicles based on super-twisting sliding mode control. Front. Mech. Eng. 2023, 9, 1347852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Yuan, X.F.; Huang, G.M.; Zhang, X.Z.; Shen, Y.P. DLMPCS-based improved yaw stability control strategy for DDEV. IET Intell. Transp. Syst. 2019, 13, 1329–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.T.; Shu, H.Y.; Chen, X.B.; Luo, S. Direct-yaw-moment control of four-wheel-drive electrical vehicle based on lateral tire-road forces and sideslip angle observer. IET Intell. Transp. Syst. 2019, 13, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hang, P.; Chen, X.B. Integrated chassis control algorithm design for path tracking based on four-wheel steering and direct yaw-moment control. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. 2019, 233, 625–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, N.Y.; Lenzo, B.; Zhang, X.D.; Zou, Y.; Zhai, R.Q.; Zhang, T. A real-time nonlinear model predictive controller for yaw motion optimization of distributed drive electric vehicles. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 4935–4946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.H.; Feng, J.W.; Lu, Y.B.; Yin, G.D.; Zhuang, W.C.; Mao, X. A direct yaw moment control framework through robust T-S fuzzy approach considering vehicle stability margin. IEEE-ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2024, 29, 166–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.J.; Zhou, B.; Wu, T.Y.; Pan, Q.X. Research on intervention criterion and stability coordinated control of AFS and DYC. Int. J. Veh. Des. 2022, 90, 116–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.Y.; Shih, M.C. Application of the Pacejka magic formula tyre model on a study of a hydraulic anti-lock braking system for a light motorcycle. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 2004, 41, 431–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khasawneh, L.; Das, M. A robust electric power-steering-angle controller for autonomous vehicles with disturbance rejection. Electronics 2022, 11, 1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J. Integrated control of brake pressure and rear-wheel steering to improve lateral stability with fuzzy logic. Int. J. Automot. Technol. 2012, 13, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clerc, M.; Kennedy, J. The particle swarm—Explosion, stability, and convergence in a multidimensional complex space. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2002, 6, 58–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.S.; Tan, D.P.; Liu, L. Particle swarm optimization algorithm: An overview. Soft Comput. 2018, 22, 387–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, A.P.; Liu, D.; Li, Z.Q.; Hasanien, H.M.; Shi, Y.T. Heterogeneous differential evolution particle swarm optimization with local search. Complex Intell. Syst. 2023, 9, 6905–6925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.H.; Zhang, C.Q.; Yi, J.P. Time-optimal trajectory planning for woodworking manipulators using an improved PSO algorithm. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 10482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO3888-2:2018; Passenger Cars–Test Track for A Severe Lane–Change Manoeuvre–Part 1: Double Lane–Change. International Organization for Standardization (ISO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2018.
- ISO15037-1:2019; Road Vehicles–Vehicle Dynamics Test Methods–Part 1: General Conditions for Passenger Cars. International Organization for Standardization (ISO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2019.





| Definition | Symbol | Unit | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vehicle mass | 1400 | ||
| Yaw moment of inertia about z-axis | 1343.1 | ||
| Distance from centroid to front axle | 1.04 | ||
| Distance from centroid to rear axle | 1.56 | ||
| Front track | 1.48 | ||
| Rear track | 1.48 | ||
| Front wheel total lateral stiffness | −108,880 | ||
| Rear wheel total lateral stiffness | −108,880 |
| Algorithm | Yaw Rate | Sideslip Angle | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S | RMSE | Peak Value | S | RMSE | Peak Value | |
| Without control | 15.52 | 17.77 | 10.36 | 20.01 | 20.85 | 1.73 |
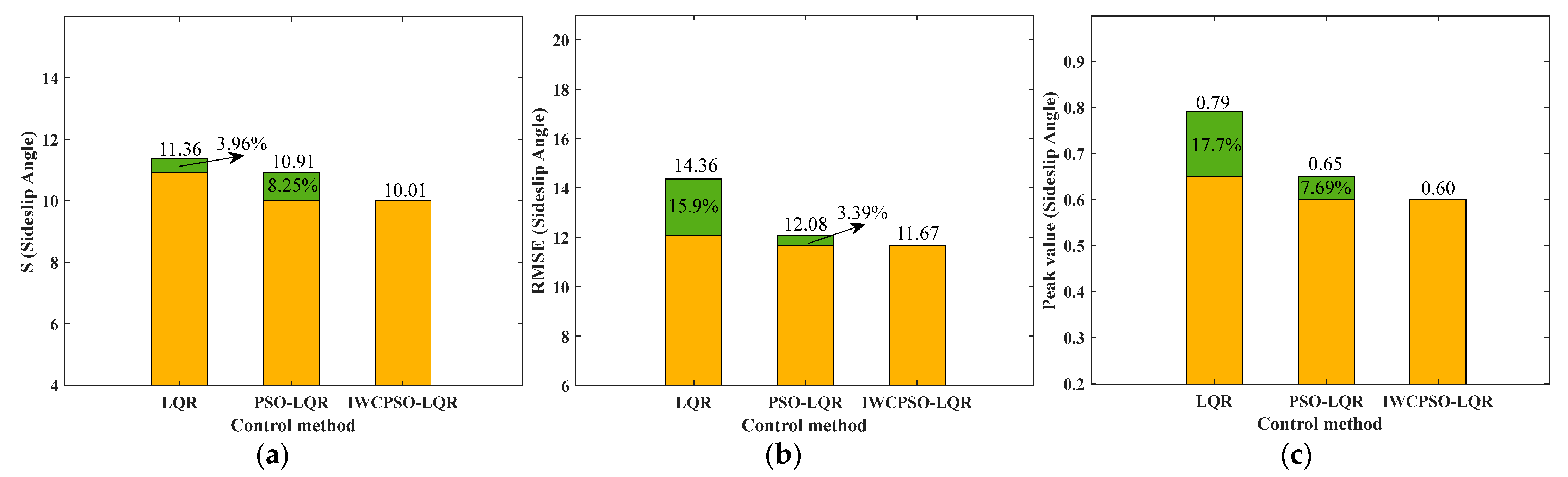
| LQR | 7.04 | 12.34 | 8.74 | 11.36 | 14.36 | 0.79 |
| PSO-LQR IWCPSO-LQR | 6.28 5.99 | 11.69 10.25 | 8.56 8.46 | 10.91 10.01 | 12.08 11.67 | 0.65 0.60 |
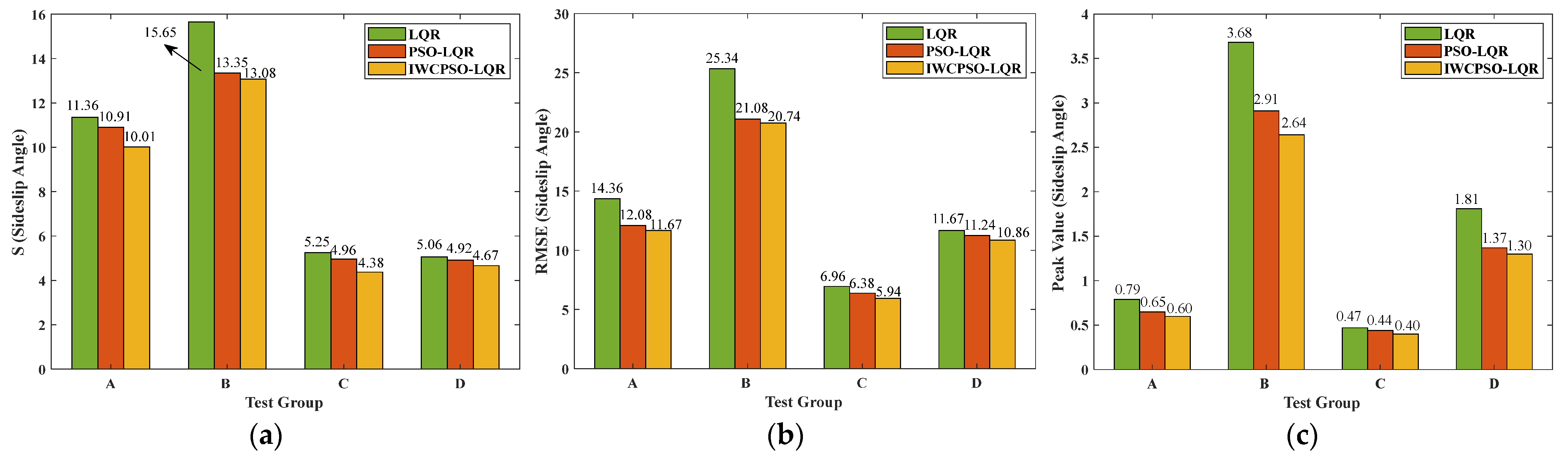
| Algorithm | Yaw Rate | Sideslip Angle | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S | RMSE | Peak Value | S | RMSE | Peak Value | |
| Without control | 317.52 | 546.23 | 71.25 | 408.01 | 427.28 | 178.55 |
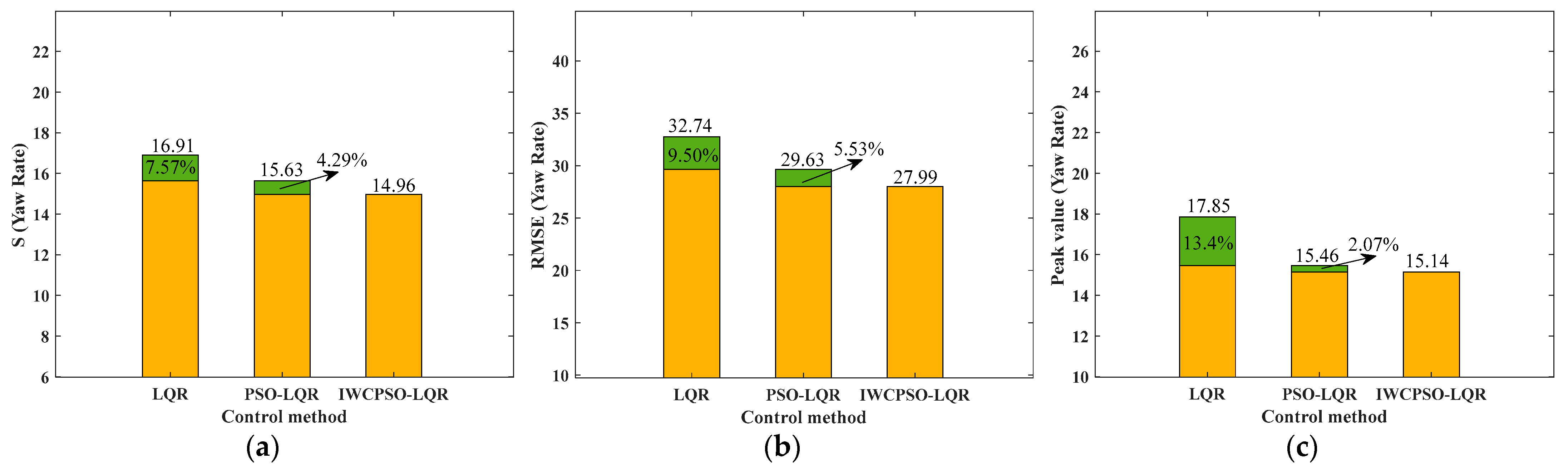
| LQR | 16.91 | 32.74 | 17.85 | 15.65 | 25.34 | 3.68 |
| PSO-LQR | 15.63 | 29.63 | 15.46 | 13.35 | 21.08 | 2.91 |
| IWCPSO-LQR | 14.96 | 27.99 | 15.14 | 13.08 | 20.74 | 2.64 |
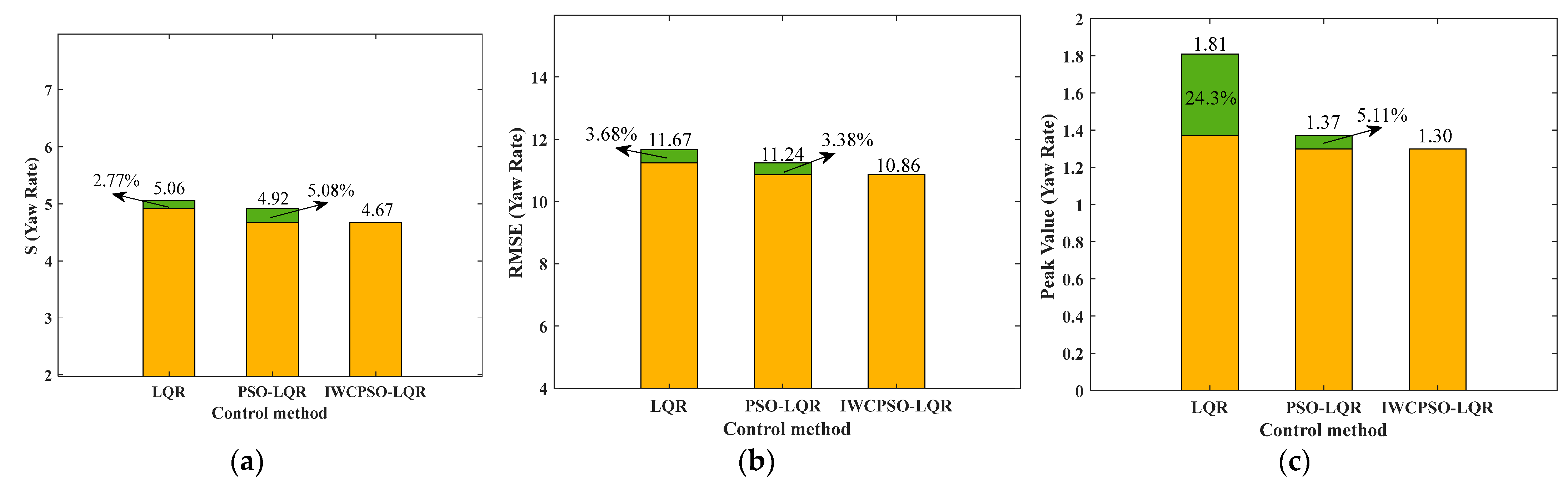
| Algorithm | Yaw Rate | Sideslip Angle | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S | RMSE | Peak Value | S | RMSE | Peak Value | |
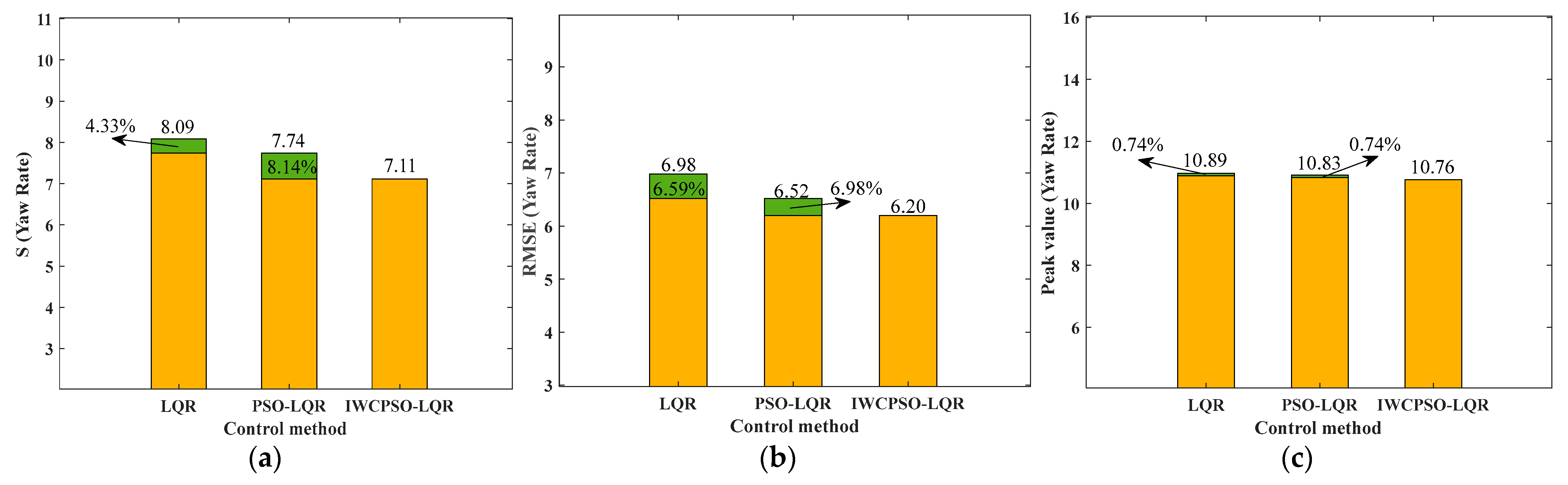
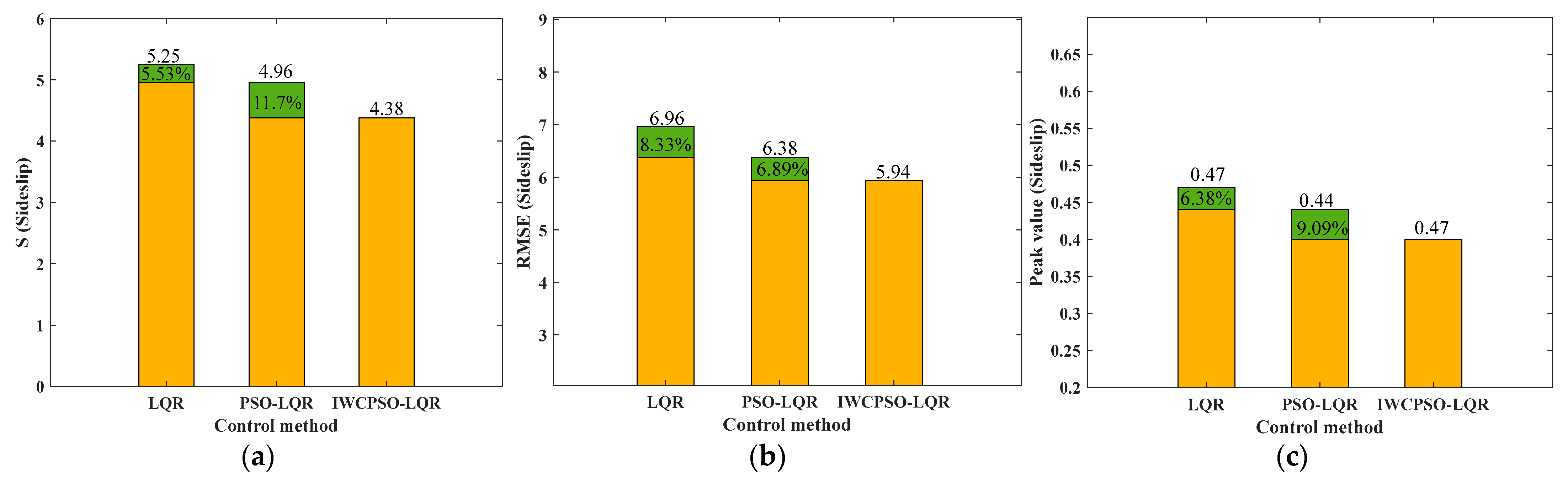
| Without control | 16.77 | 8.25 | 11.25 | 10.25 | 7.85 | 0.58 |
| LQR | 8.09 | 6.98 | 10.89 | 5.25 | 6.96 | 0.47 |
| PSO-LQR | 7.74 | 6.52 | 10.83 | 4.96 | 6.38 | 0.44 |
| IWCPSO-LQR | 7.11 | 6.20 | 10.76 | 4.38 | 5.94 | 0.40 |
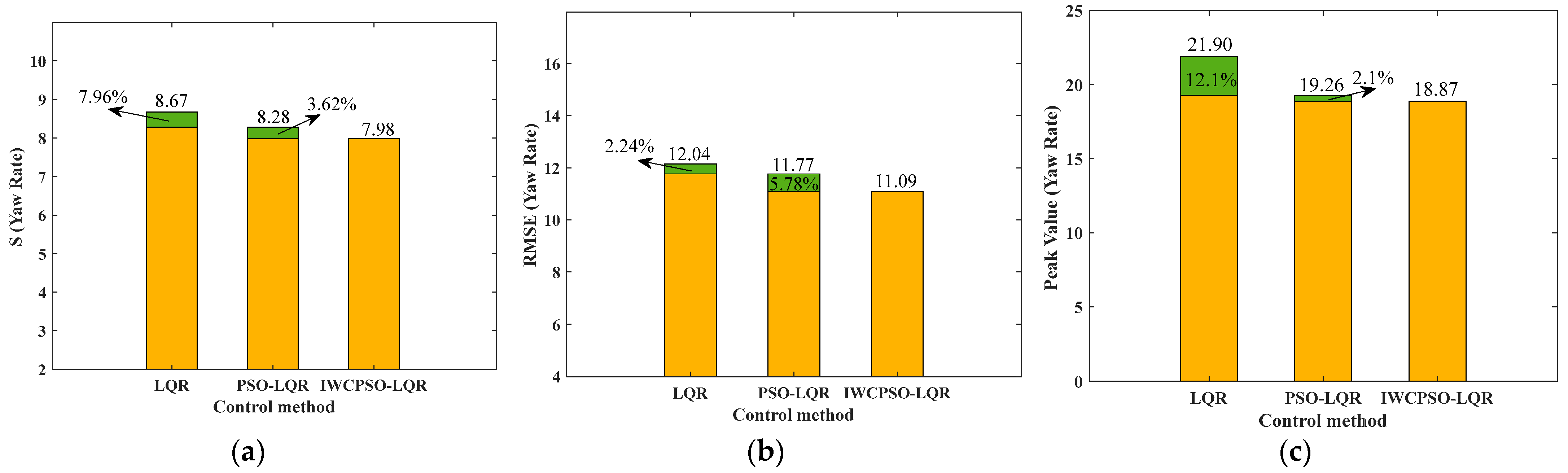
| Algorithm | Yaw Rate | Sideslip Angle | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S | RMSE | Peak Value | S | RMSE | Peak Value | |
| Without control | 20.31 | 15.85 | 23.36 | 12.65 | 14.83 | 1.87 |
| LQR | 8.67 | 12.04 | 21.90 | 5.06 | 11.67 | 1.81 |
| PSO-LQR | 8.28 | 11.77 | 19.26 | 4.92 | 11.24 | 1.37 |
| IWCPSO-LQR | 7.98 | 11.09 | 18.87 | 4.67 | 10.86 | 1.30 |
| Test Group | Test Condition | Road Adhesion Coefficient |
|---|---|---|
| A | Sinusoidal condition | Low (0.3) |
| B | Double-lane-change condition | Low (0.3) |
| C | Sinusoidal condition | High (0.85) |
| D | Double-lane-change condition | High (0.85) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, J.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, P.; Yan, F. Direct Yaw Moment Control for Distributed Drive Electric Vehicles Based on Hierarchical Optimization Control Framework. Mathematics 2024, 12, 1715. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12111715
Hu J, Zhang K, Zhang P, Yan F. Direct Yaw Moment Control for Distributed Drive Electric Vehicles Based on Hierarchical Optimization Control Framework. Mathematics. 2024; 12(11):1715. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12111715
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Jie, Kefan Zhang, Pei Zhang, and Fuwu Yan. 2024. "Direct Yaw Moment Control for Distributed Drive Electric Vehicles Based on Hierarchical Optimization Control Framework" Mathematics 12, no. 11: 1715. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12111715
APA StyleHu, J., Zhang, K., Zhang, P., & Yan, F. (2024). Direct Yaw Moment Control for Distributed Drive Electric Vehicles Based on Hierarchical Optimization Control Framework. Mathematics, 12(11), 1715. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12111715






