A Visual Analytics Environment for Navigating Large Conceptual Models by Leveraging Generative Artificial Intelligence
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (Q1)
- How can a user interact with large, complex conceptual models using generative AI?
- (Q2)
- Does the inclusion of generative AI into visual analytics support precise investigations into a conceptual model?
2. Mathematical Foundations
2.1. Text Embeddings
[...] the text first undergoes an embedding process (24 to 36 million parameters depending on the model), followed by transformers (each of which adds 7 or 12.5 million parameters depending on the model), ending with a pooling layer (0.5 or 1 million more parameters depending on the model).
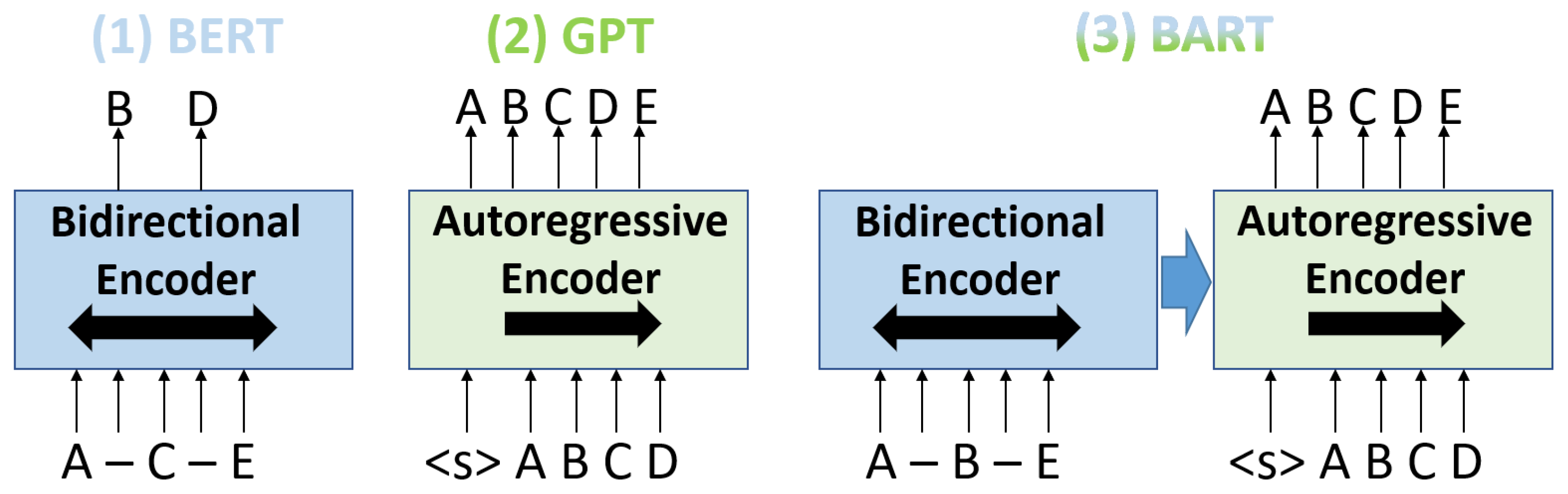
2.2. Natural Language Generation
2.3. Text-to-Image Generation
3. Background
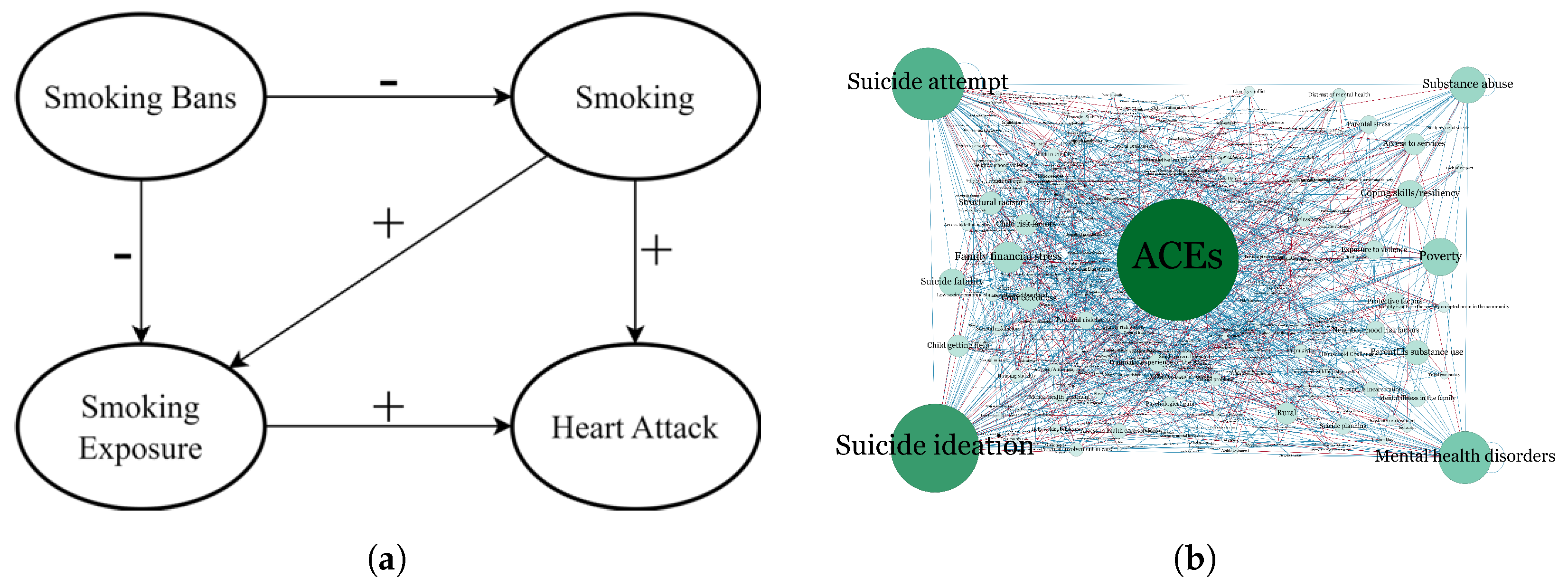
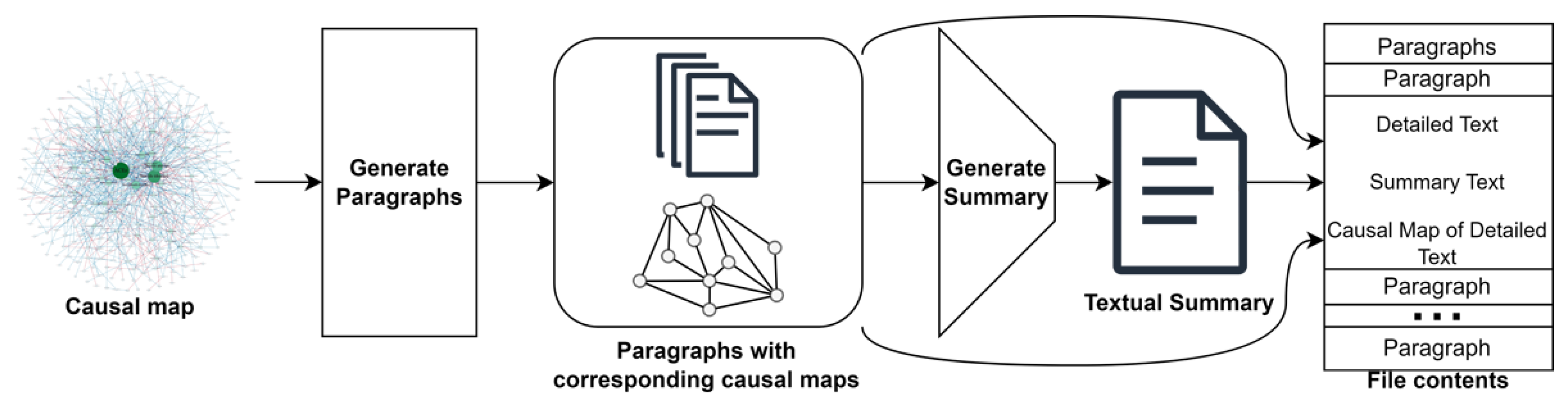
3.1. From Large Causal Maps to Text
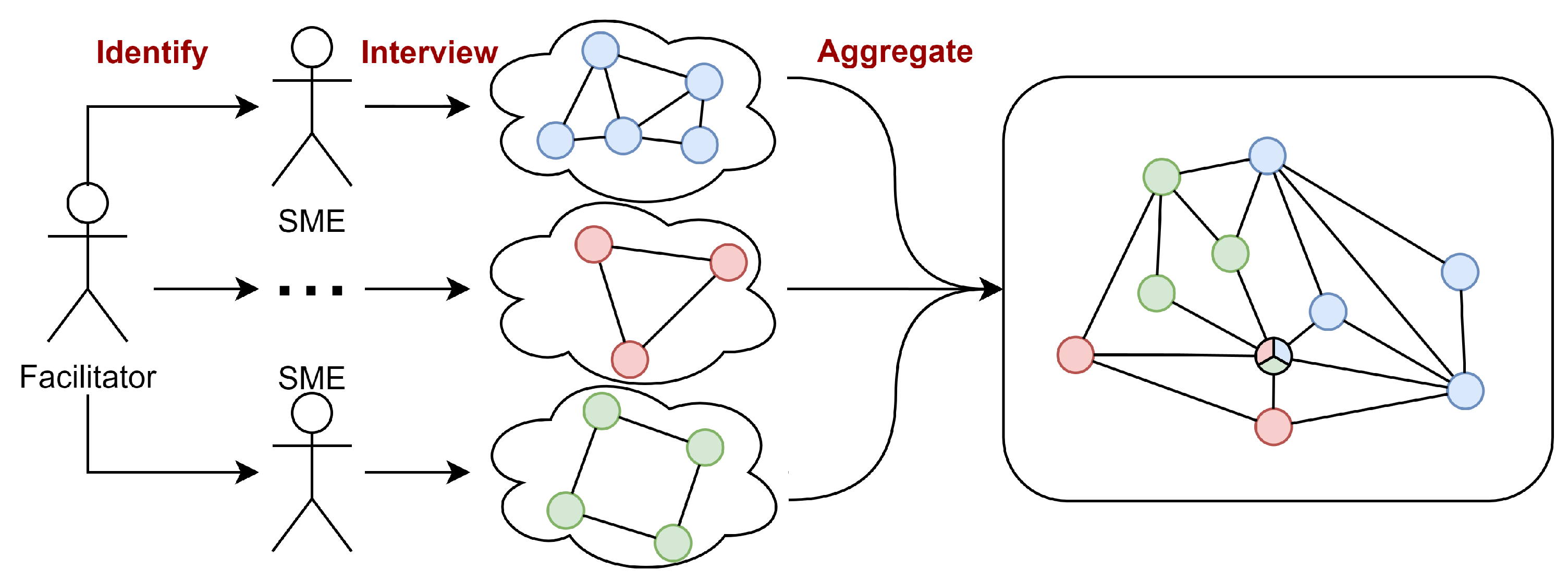
3.1.1. Why Causal Maps Become Large: Elicitation and Aggregation
3.1.2. Preprocessing: Preparing Two Levels of Text and Subgraphs
3.1.3. Leveraging AI to Enable Transformations
3.2. Combating Information Overload with Visual Analytics
4. Methods
4.1. Overview: A User’s Workflow
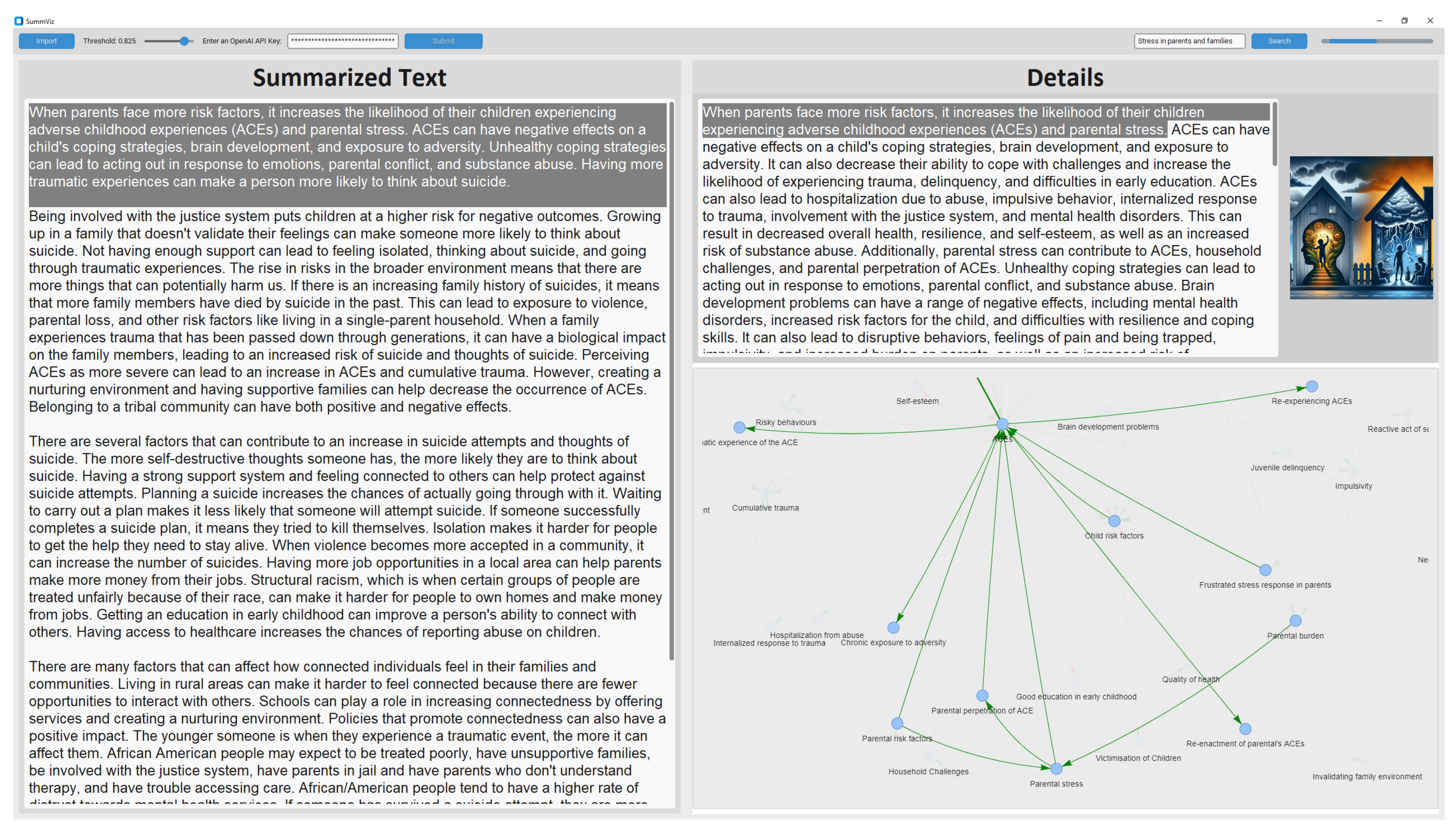
4.2. Visualization

4.3. Interactive Environment
5. Case Study: Suicide and Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACEs) in Youth
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BERT | Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers |
| GPT | Generative Pretrained Transformer |
| LLM | Large Language Model |
| LPAM | Label Propagation Algorithm |
References
- Gill, S.S.; Xu, M.; Patros, P.; Wu, H.; Kaur, R.; Kaur, K.; Fuller, S.; Singh, M.; Arora, P.; Parlikad, A.K.; et al. Transformative effects of ChatGPT on modern education: Emerging Era of AI Chatbots. Internet Things-Cyber-Phys. Syst. 2024, 4, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, M.; Roe, J.; Postma, D.; McGaughran, J.; Hickerson, D. Detection of GPT-4 generated text in higher education: Combining academic judgement and software to identify generative AI tool misuse. J. Acad. Ethics 2024, 22, 89–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frieder, S.; Pinchetti, L.; Griffiths, R.R.; Salvatori, T.; Lukasiewicz, T.; Petersen, P.; Berner, J. Mathematical capabilities of chatgpt. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2024, 36. [Google Scholar]
- Gandolfi, A. GPT-4 in Education: Evaluating Aptness, Reliability, and Loss of Coherence in Solving Calculus Problems and Grading Submissions. Int. J. Artif. Intell. Educ. 2024, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshareef, A.; Keller, N.; Carbo, P.; Zeigler, B.P. Generative AI with Modeling and Simulation of Activity and Flow-Based Diagrams. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Simulation Tools and Techniques, Seville, Spain, 14–15 December 2023; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 95–109. [Google Scholar]
- Giabbanelli, P.J. GPT-Based Models Meet Simulation: How to Efficiently use Large-Scale Pre-Trained Language Models Across Simulation Tasks. In Proceedings of the 2023 Winter Simulation Conference (WSC), San Antonio, TX, USA, 10–13 December 2023; pp. 2920–2931. [Google Scholar]
- Akhavan, A.; Jalali, M.S. Generative AI and simulation modeling: How should you (not) use large language models like ChatGPT. Syst. Dyn. Rev. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinichimeh, N.; Majumdar, A.; Williams, R.; Ghaffarzadegan, N. From Text to Map: A System Dynamics Bot for Constructing Causal Loop Diagrams. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.11400. [Google Scholar]
- Jalali, M.S.; Akhavan, A. Integrating AI Language Models in Qualitative Research: Replicating Interview Data Analysis with ChatGPT. Syst. Dyn. Rev. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giabbanelli, P.; Witkowicz, N. Generative AI for Systems Thinking: Can a GPT Question-Answering System Turn Text into the Causal Maps Produced by Human Readers? In Proceedings of the 57th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, Waikiki Beach, HI, USA, 3–6 January 2024; pp. 7540–7549. [Google Scholar]
- Phatak, A.; Mago, V.K.; Agrawal, A.; Inbasekaran, A.; Giabbanelli, P.J. Narrating Causal Graphs with Large Language Models. In Proceedings of the Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences (HICSS), Waikiki Beach, HI, USA, 3–6 January 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Shrestha, A.; Mielke, K.; Nguyen, T.A.; Giabbanelli, P.J. Automatically Explaining a Model: Using Deep Neural Networks to Generate Text From Causal Maps. In Proceedings of the Winter Simulation Conference, Singapore, 11–14 December 2022; pp. 2629–2640. [Google Scholar]
- Apvrille, L.; Sultan, B. System Architects Are not Alone Anymore: Automatic System Modeling with AI. In Proceedings of the 12th Internaitonal Conference on Model-Based Software and Systems Engineering (INSTICC), Rome, Italy, 21–23 February 2024; pp. 27–38. [Google Scholar]
- Frydenlund, E.; Martínez, J.; Padilla, J.J.; Palacio, K.; Shuttleworth, D. Modeler in a box: How can large language models aid in the simulation modeling process? Simulation 2024, 00375497241239360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feleki, A.; Apostolopoulos, I.D.; Moustakidis, S.; Papageorgiou, E.I.; Papathanasiou, N.; Apostolopoulos, D.; Papandrianos, N. Explainable Deep Fuzzy Cognitive Map Diagnosis of Coronary Artery Disease: Integrating Myocardial Perfusion Imaging, Clinical Data, and Natural Language Insights. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 11953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, S.; Arbez, G.; Birta, L.G.; Tolk, A.; Wagner, G. Conceptual modeling: Definition, purpose and benefits. In Proceedings of the 2015 Winter Simulation Conference (WSC), Huntington Beach, CA, USA, 6–9 December 2015; pp. 2812–2826. [Google Scholar]
- Voinov, A.; Jenni, K.; Gray, S.; Kolagani, N.; Glynn, P.D.; Bommel, P.; Prell, C.; Zellner, M.; Paolisso, M.; Jordan, R.; et al. Tools and methods in participatory modeling: Selecting the right tool for the job. Environ. Model. Softw. 2018, 109, 232–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooney, S.J. Systems thinking in population health research and policy. In Systems Science and Population Health; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2017; pp. 49–60. [Google Scholar]
- Jack, A. Foresight report on obesity–Author’s reply. Lancet 2007, 370, 1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, S.; Soltani Panah, A.; McCosker, A. Weight-Biased Language across 30 Years of Australian News Reporting on Obesity: Associations with Public Health Policy. Obesities 2022, 2, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drasic, L.; Giabbanelli, P.J. Exploring the interactions between physical well-being, and obesity. Can. J. Diabetes 2015, 39, S12–S13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGlashan, J.; Hayward, J.; Brown, A.; Owen, B.; Millar, L.; Johnstone, M.; Creighton, D.; Allender, S. Comparing complex perspectives on obesity drivers: Action-driven communities and evidence-oriented experts. Obes. Sci. Pract. 2018, 4, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keim, D.; Andrienko, G.; Fekete, J.D.; Gorg, C.; Kohlhammer, J.; Melançon, G. Visual analytics: Definition, process, and challenges. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2008, 4950, 154–176. [Google Scholar]
- Giabbanelli, P.J.; Vesuvala, C.X. Human Factors in Leveraging Systems Science to Shape Public Policy for Obesity: A Usability Study. Information 2023, 14, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hvalshagen, M.; Lukyanenko, R.; Samuel, B.M. Empowering users with narratives: Examining the efficacy of narratives for understanding data-oriented conceptual models. Inf. Syst. Res. 2023, 34, 890–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasegaran, S.; Badam, S.K.; Kisselburgh, L.; Ramani, K.; Elmqvist, N. Integrating visual analytics support for grounded theory practice in qualitative text analysis. In Computer Graphics Forum; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; Volume 36, pp. 201–212. [Google Scholar]
- Giabbanelli, P.J.; Rice, K.L.; Galgoczy, M.C.; Nataraj, N.; Brown, M.M.; Harper, C.R.; Nguyen, M.D.; Foy, R. Pathways to suicide or collections of vicious cycles? Understanding the complexity of suicide through causal mapping. Soc. Netw. Anal. Min. 2022, 12, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higham, C.F.; Higham, D.J.; Grindrod, P. Diffusion Models for Generative Artificial Intelligence: An Introduction for Applied Mathematicians. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2312.14977. [Google Scholar]
- Berry, M.W.; Drmac, Z.; Jessup, E.R. Matrices, vector spaces, and information retrieval. SIAM Rev. 1999, 41, 335–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, C. Statistical language models for information retrieval a critical review. Found. Trends® Inf. Retr. 2008, 2, 137–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yoshida, T.; Tang, X. A comparative study of TF* IDF, LSI and multi-words for text classification. Expert Syst. Appl. 2011, 38, 2758–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillutla, V.S.; Tawfik, A.A.; Giabbanelli, P.J. Detecting the depth and progression of learning in massive open online courses by mining discussion data. Technol. Knowl. Learn. 2020, 25, 881–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selva Birunda, S.; Kanniga Devi, R. A review on word embedding techniques for text classification. In Innovative Data Communication Technologies and Application: Proceedings of the ICIDCA 2020, Coimbatore, India, 3–4 September 2020; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 267–281. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Zhou, H.; He, J.; Wang, M.; Yang, Y.; Li, L. On the sentence embeddings from pre-trained language models. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2011.05864. [Google Scholar]
- Galgoczy, M.C.; Phatak, A.; Vinson, D.; Mago, V.K.; Giabbanelli, P.J. (Re) shaping online narratives: When bots promote the message of President Trump during his first impeachment. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2022, 8, e947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, A.; Han, K.; Jadon, A. A Comparative Analysis of Text Embedding Models for Bug Report Semantic Similarity. In Proceedings of the 2024 11th International Conference on Signal Processing and Integrated Networks (SPIN), Noida, India, 21–22 March 2024; pp. 262–267. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Henriksson, A.; Duneld, M.; Nouri, J.; Wu, Y. Evaluating Embeddings from Pre-Trained Language Models and Knowledge Graphs for Educational Content Recommendation. Future Internet 2023, 16, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aperdannier, R.; Koeppel, M.; Unger, T.; Schacht, S.; Barkur, S.K. Systematic Evaluation of Different Approaches on Embedding Search. In Advances in Information and Communication, Proceedings of the Future of Information and Communication Conference, Berlin, Germany, 4–5 April 2024; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 526–536. [Google Scholar]
- Reiter, E.; Dale, R. Building applied natural language generation systems. Nat. Lang. Eng. 1997, 3, 57–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitromanolaki, A. Learning to Order Facts for Discourse Planning in Natural Language. In Proceedings of the 10th Conference of The European Chapter, Budapest, Hungary, 12–17 April 2003; p. 23. [Google Scholar]
- Di Eugenio, B.; Fossati, D.; Yu, D.; Haller, S.; Glass, M. Aggregation improves learning: Experiments in natural language generation for intelligent tutoring systems. In Proceedings of the 43rd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL’05), Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 25–30 June 2005; pp. 50–57. [Google Scholar]
- AlShaikh, F.; Hewahi, N. Ai and machine learning techniques in the development of Intelligent Tutoring System: A review. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Innovation and Intelligence for Informatics, Computing and Technologies (3ICT), Zallaq, Bahrain, 29–30 September 2021; pp. 403–410. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, K. Multi-Context Dependent Natural Text Generation for More Robust NPC Dialogue. Bachelor’s Thesis, Harvard University, Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, Z.; Lee, N.; Frieske, R.; Yu, T.; Su, D.; Xu, Y.; Ishii, E.; Bang, Y.J.; Madotto, A.; Fung, P. Survey of hallucination in natural language generation. ACM Comput. Surv. 2023, 55, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrycks, D.; Gimpel, K. Gaussian error linear units (gelus). arXiv 2016, arXiv:1606.08415. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, M.; Liu, Y.; Goyal, N.; Ghazvininejad, M.; Mohamed, A.; Levy, O.; Stoyanov, V.; Zettlemoyer, L. BART: Denoising Sequence-to-Sequence Pre-training for Natural Language Generation, Translation, and Comprehension. In Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Online, 5–10 July 2020; pp. 7871–7880. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Li, Z.; He, D.; Sun, Z.; Dong, B.; Qin, T.; Wang, L.; Liu, T.Y. Understanding and improving transformer from a multi-particle dynamic system point of view. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1906.02762. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, M.; Yang, Z.; Hong, W.; Zheng, W.; Zhou, C.; Yin, D.; Lin, J.; Zou, X.; Shao, Z.; Yang, H.; et al. Cogview: Mastering text-to-image generation via transformers. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 19822–19835. [Google Scholar]
- Reed, S.; Akata, Z.; Yan, X.; Logeswaran, L.; Schiele, B.; Lee, H. Generative adversarial text to image synthesis. In Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Machine Learning, New York, NY, USA, 20–22 June 2016; pp. 1060–1069. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.; Ye, J.C.; Bresler, Y. Generative Models for Inverse Imaging Problems: From mathematical foundations to physics-driven applications. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2023, 40, 148–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatkhulin, T.; Leokhin, Y.; Mentus, M.; Kulikova, A.; Alshawi, R. Analysis of the Basic Image Generation Methods by Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2023 Intelligent Technologies and Electronic Devices in Vehicle and Road Transport Complex (TIRVED), Moscow, Russia, 15–17 November 2023; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Podell, D.; English, Z.; Lacey, K.; Blattmann, A.; Dockhorn, T.; Müller, J.; Penna, J.; Rombach, R. Sdxl: Improving latent diffusion models for high-resolution image synthesis. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2307.01952. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.; Meng, C.; Ermon, S. Denoising diffusion implicit models. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.02502. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, S. A Survey of Data-Driven 2D Diffusion Models for Generating Images from Text. EAI Endorsed Trans. AI Robot. 2024, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betker, J.; Goh, G.; Jing, L.; Brooks, T.; Wang, J.; Li, L.; Ouyang, L.; Zhuang, J.; Lee, J.; Guo, Y.; et al. Improving Image Generation with Better Captions. 2023. Available online: https://cdn.openai.com/papers/dall-e-3.pdf (accessed on 21 May 2024).
- Yang, L.; Yu, Z.; Meng, C.; Xu, M.; Ermon, S.; Cui, B. Mastering text-to-image diffusion: Recaptioning, planning, and generating with multimodal llms. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.11708. [Google Scholar]
- Pinho, H.D. Generation of systems maps. In Systems Science and Population Health; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2017; pp. 61–76. [Google Scholar]
- Schuerkamp, R.; Giabbanelli, P.; Grandi, U.; Doutre, S. How to Combine Models? Principles and Mechanisms to Aggregate Fuzzy Cognitive Maps. In Proceedings of the Winter Simulation Conference (WSC 2023), San Antonio, TX, USA, 10–13 December 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Gandee, T.J. natural language generation: Improving the Accessibility of Causal Modeling through Applied Deep Learning. Master’s Thesis, Miami University, Oxford, OH, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Ponomarenko, A.; Pitsoulis, L.; Shamshetdinov, M. Overlapping community detection in networks based on link partitioning and partitioning around medoids. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0255717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisz, J.D.; Muller, M.; He, J.; Houde, S. Toward general design principles for generative AI applications. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2301.05578. [Google Scholar]
- Bubeck, S.; Chandrasekaran, V.; Eldan, R.; Gehrke, J.; Horvitz, E.; Kamar, E.; Lee, P.; Lee, Y.T.; Li, Y.; Lundberg, S.; et al. Sparks of artificial general intelligence: Early experiments with gpt-4. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.12712. [Google Scholar]
- Ganguli, D.; Hernandez, D.; Lovitt, L.; Askell, A.; Bai, Y.; Chen, A.; Conerly, T.; Dassarma, N.; Drain, D.; Elhage, N.; et al. Predictability and surprise in large generative models. In Proceedings of the ACM Conference on Fairness, Accountability, and Transparency, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 21–24 June 2022; pp. 1747–1764. [Google Scholar]
- Guerreiro, N.M.; Alves, D.M.; Waldendorf, J.; Haddow, B.; Birch, A.; Colombo, P.; Martins, A.F. Hallucinations in large multilingual translation models. Trans. Assoc. Comput. Linguist. 2023, 11, 1500–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, S.A.; Milios, E.E.; de Oliveira, M.C.F. Evaluating visual analytics for text information retrieval. In Proceedings of the XX Brazilian Symposium on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Virtual, 18–22 October 2021; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Dowling, M.; Wycoff, N.; Mayer, B.; Wenskovitch, J.; House, L.; Polys, N.; North, C.; Hauck, P. Interactive visual analytics for sensemaking with big text. Big Data Res. 2019, 16, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neelakantan, A.; Xu, T.; Puri, R.; Radford, A.; Han, J.M.; Tworek, J.; Yuan, Q.; Tezak, N.; Kim, J.W.; Hallacy, C.; et al. Text and code embeddings by contrastive pre-training. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2201.10005. [Google Scholar]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Suicide Prevention Resource for Action: A Compilation of the Best Available Evidence; Technical Report; National Center for Injury Prevention and Control: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National Vital Statistics System, Mortality 2018–2021 on CDC WONDER Online Database. 2023. Available online: http://wonder.cdc.gov/mcd-icd10-expanded.html (accessed on 10 January 2024).
- Scherer, W.; Tolk, A.; Loper, M.; Barry, P.; Rabadi, G.; Yilmaz, L. Chances and challenges of CHATGPT and similar models for education in M&S. Authorea Prepr. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- du Plooy, C.; Oosthuizen, R. AI usefulness in systems modelling and simulation: Gpt-4 application. S. Afr. J. Ind. Eng. 2023, 34, 286–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touvron, H.; Martin, L.; Stone, K.; Albert, P.; Almahairi, A.; Babaei, Y.; Bashlykov, N.; Batra, S.; Bhargava, P.; Bhosale, S.; et al. Llama 2: Open foundation and fine-tuned chat models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2307.09288. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhery, A.; Narang, S.; Devlin, J.; Bosma, M.; Mishra, G.; Roberts, A.; Barham, P.; Chung, H.W.; Sutton, C.; Gehrmann, S.; et al. Palm: Scaling language modeling with pathways. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2023, 24, 1–113. [Google Scholar]
- Beltagy, I.; Peters, M.E.; Cohan, A. Longformer: The long-document transformer. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.05150. [Google Scholar]
- Raffel, C.; Shazeer, N.; Roberts, A.; Lee, K.; Narang, S.; Matena, M.; Zhou, Y.; Li, W.; Liu, P.J. Exploring the Limits of Transfer Learning With a Unified Text-To-Text Transformer. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2020, 21, 1–67. [Google Scholar]
- Reviriego, P.; Merino-Gómez, E. Text to image generation: Leaving no language behind. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2208.09333. [Google Scholar]
- Lukyanenko, R.; Bork, D.; Storey, V.C.; Parsons, J.; Pastor, O. Inclusive conceptual modeling: Diversity, equity, involvement, and belonging in conceptual modeling. In ER Forum; CEUR Workshop Proceedings, RWTH Aachen University: Aachen, Germany, 2023; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Song, K.; Cho, S.; Wang, X.; Foroosh, H.; Liu, F. DecipherPref: Analyzing Influential Factors in Human Preference Judgments via GPT-4. In Proceedings of the 2023 Conference on Empirical Methods in natural language processing, Singapore, 6–10 December 2023; pp. 8344–8357. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, K.; Shao, A.; Burapacheep, J.; Li, Y. Conversational AI and equity through assessing GPT-3’s communication with diverse social groups on contentious topics. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gandee, T.J.; Glaze, S.C.; Giabbanelli, P.J. A Visual Analytics Environment for Navigating Large Conceptual Models by Leveraging Generative Artificial Intelligence. Mathematics 2024, 12, 1946. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12131946
Gandee TJ, Glaze SC, Giabbanelli PJ. A Visual Analytics Environment for Navigating Large Conceptual Models by Leveraging Generative Artificial Intelligence. Mathematics. 2024; 12(13):1946. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12131946
Chicago/Turabian StyleGandee, Tyler J., Sean C. Glaze, and Philippe J. Giabbanelli. 2024. "A Visual Analytics Environment for Navigating Large Conceptual Models by Leveraging Generative Artificial Intelligence" Mathematics 12, no. 13: 1946. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12131946
APA StyleGandee, T. J., Glaze, S. C., & Giabbanelli, P. J. (2024). A Visual Analytics Environment for Navigating Large Conceptual Models by Leveraging Generative Artificial Intelligence. Mathematics, 12(13), 1946. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12131946







