Abstract
Process capability indices are widely utilized to evaluate process performance and drive continuous improvements in quality and productivity. Among these indices, the the-larger-the-better lifetime performance index is particularly noteworthy. For products with multiple components, an overall lifetime performance index is used, since it is a monotonically increasing function of the overall conforming rate and the relationship with each individual lifetime performance index can be determined. For products with the lifetime of the ith component following the Chen distribution, we investigate the maximum likelihood estimator for the overall lifetime performance index and the individual lifetime performance index based on the progressive type I interval censoring sample. Their asymptotic distributions for all lifetime performance indices are also derived. Once the target level for the overall lifetime performance index is specified, the desired level of individual lifetime performance index can be specified. By using the maximum likelihood estimator as the test statistic, a testing procedure to test whether the overall lifetime performance index has reached the target level is developed. The power analysis of the testing procedure is shown with figures, and some findings are summarized. At last, we use one practical example with two components to demonstrate how to implement this testing algorithmic procedure to test if the overall production process has reached the pre-assigned target level.
Keywords:
Chen distribution; multiple components; progressive type I interval censoring; maximum likelihood estimator; overall lifetime performance index; testing procedure MSC:
62P30
1. Introduction
This study focuses on examining the lifetimes of components across various production lines, emphasizing the “the-larger-the-better” characteristic of product lifetimes. Unlike many process capability indices (PCIs) that assume a normal distribution for quality characteristics, product lifetimes frequently follow distributions like exponential, gamma, or Chen distributions. In this study, we assume a Chen distribution for the lifetime of components. Given the preference for longer product lifetimes, we utilize the lifetime performance index CL recommended by Montgomery [1] defined as where u denotes the process mean, σ denotes the process standard deviation, and L is the specified lower specification limit.
For products with a single component produced in a single production line, Tong et al. [2] utilized the uniformly minimum variance unbiased estimator for the index of CL as the test statistic to conduct a hypothesis-testing procedure assuming exponential products based on the complete sample. In practical settings, researchers may not consistently have the means to observe the lifetimes of all tested items due to various constraints, such as time limitations, financial and material resources, oversight by typists or recorders, mechanical or experimental challenges, and so forth. Consequently, incomplete data, such as progressive censoring data, might be gathered. Please refer to Balakrishnan [3], Aggarwala [4], Balakrishnan and Aggarwala [5], Wu et al. [6], Sanjel and Balakrishnan [7], and Lee et al. [8] for inferences on progressive censoring data. For the convenience of collecting data, the progressive type I interval censoring scheme has arisen. Progressive type I interval censoring is a method used in survival analysis, particularly in reliability engineering, to handle situations where the exact failure time of an event of interest is not observed, but the number of failure units are observed at each inspection time point. Wu [9] assessed the lifetime performance index of products following a Chen lifetime distribution based on the progressive type I interval censored sample. The sampling design for this testing procedure to reach given test power or minimize the total experimental cost for Chen products is proposed in Wu and Song [10]. The previous studies are suitable for products with a single component. For products with multiple components or products produced in multiple production lines, Wu and Chiang [11] investigated the assessment of the overall lifetime performance index of Weibull products in multiple production lines. This study extends research from products with one component as in Wu [9] to products with multiple components with lifetimes following the Chen lifetime distribution.
Our attention is directed towards the progressive type I interval censoring scheme by subjecting n products to a life test with m inspection intervals. Let us assume that () are the predefined inspection time points, where is the termination time of this experiment. We only observe the number of failure units at the ith inspection time interval; then, product is removed from the rest of the test units with removal probability at the ith inspection time point, i = 1,…, m. At the end of the experiment, the progressive type I interval censored sample () under the progressive censoring scheme of () is collected, and we utilize these sample data to draw inferences on the lifetime performance index.
For products with multiple components whose lifetimes follow the Chen distribution, we use the overall lifetime performance index proposed in Wu and Chiang [11] to evaluate the comprehensive performance of the production processes to produce the multiple components of products. In order to test if the overall lifetime performance index reaches the goal target level for the progressive type I interval censored sample for Chen lifetime products, the maximum likelihood estimator and its asymptotic distribution are utilized. Referring to the method of maximum likelihood estimators, Chengyuan et al. [12] derived the maximum likelihood estimator under the constraint that the hazard is non-negative for all covariate values in their domain and show that this estimator has smaller mean squared error than the ordinary least-squares estimator for the additive hazards model. Aït-Sahalia et al. [13] proposed and implemented an efficient and flexible method to compute maximum likelihood estimators of continuous-time models when part of the state vector is latent. The Bayesian approach is another commonly used method for estimating parameters. This approach provides a methodology for incorporating previous information with the current data. Please refer to Chang [14], Zhuang et al. [15], and Ran and Bai [16] for the Bayesian approach.
The subsequent sections of this paper are arranged as follows: In Section 2, the overall lifetime performance index is introduced for products with multiple components produced in multiple production lines. Its connection with the conforming rate and the individual lifetime performance index are clarified. The derivation of the maximum likelihood estimator and the asymptotic distribution for the overall lifetime performance and the individual lifetime performance indices based on a progressive type I interval censored sample are presented in Section 3.1. We develop a testing procedure for the overall lifetime performance index by conducting the multiple testing procedures for all individual lifetime performance indices in Section 3.2. In Section 3.3, we examine the influence of different parameter configurations, particularly the number of production lines, on the test power. Additionally, Section 3.4 presents a numerical example to demonstrate the proposed testing procedure for products with two components, while Section 4 summarizes the findings.
The research motivation of this study is to extend the testing procedure for the lifetime performance index for products with a single component to the overall lifetime performance index for products with multiple components, where lifetimes follow the Chen distribution under progressive type I interval censoring. This extended work is pioneering in its field, as no relevant research has been conducted on this topic. We aim to contribute to and address the gap in the literature regarding this topic. Our study seeks to enhance the comprehensiveness of research on this topic. The contribution of this work is the accomplishment of this extended work to propose a testing procedure for the overall lifetime performance index to see if the overall production process for products with multiple components is viable. Additionally, we analyze the impact of the number of production lines, the sample size, the number of inspection intervals, the removal probability, and the level of significance on the test power and give an example of products with two components to illustrate the proposed testing procedure.
2. The Overall Lifetime Performance Index and the Conforming Rate
Let us suppose that we consider producing products with d components produced in d independent production lines. The lifetime of the ith component follows a Chen distribution with the probability density function (PDF), cumulative distribution function (CDF), and failure rate function (FRF) as follows:
and
where is the scale parameter and is the shape parameter, with i = 1, …, d. The failure rate function is defined as the conditional probability density function of failure at time u, given survival up to time u. Mathematically, it can be expressed as The Chen distribution is a continuous probability distribution frequently employed to model lifetimes or survival times. The failure rate function for = 2, 1, 0.5, 0.2 under = 1, 2 is displayed in Figure 1a,b in Wu [9]. It is shown that the failure rate function is increasing when ≥ 1 and it has a bathtub shape when < 1. The advantages and adaptability of the Chen distribution in simulating the lifespan data of specific types of products are due to the ability of its failure rate function to either be increasing or having a bathtub shape. Comparing this distribution to the exponential distribution, the failure rate of the exponential distribution is always constant. Comparing this distribution to Weibull distribution, the shape of the failure rate of the Weibull distribution can only be increasing, decreasing, or constant. This study focuses on the Chen lifetime distribution. In this study, we use the the-larger-the-better type lifetime performance index proposed by Montgomery [1]:
where denotes the mean lifetime of the ith component, denotes the standard deviation of the lifetime of the ith component, and is the specified lower specification limit for the lifetime of the ith component. Through the transformation of , the new lifetime Yi has a one-parameter exponential distribution, with PDF and CDF as
with i = 1, …, d. The mean and standard deviation of the new lifetime of the ith component of products are obtained as The lower limit becomes . The lifetime performance index for the lifetime of the ith component is reduced to
When the failure rate ki is large, the lifetime performance index CLi is small. The conforming rate for the ith component is defined as the probability of the lifetime of the ith component of the product surpassing the lower specification limit (i.e., ). The conforming rate for the ith component denoted by is obtained as
Evidently, the conforming rate for the lifetime of the ith component increases while the lifetime performance index CLi increases. By Equation (8), if users desire the conforming rate Pri to exceed 0.9048, they can determine the lower bound for the value of CLi to be 0.9. For products with d components produced in d independent production lines, the overall conforming rate is obtained as follows:
We utilize the overall lifetime performance index CT defined in Wu and Chiang [11], which satisfies the following equation:
As can be observed in the above equation, the overall lifetime performance index CT is set up to be an increasing function of the overall conforming rate By solving Equations (9) and (10) simultaneously, we observe the following relationship:
Let us suppose that the capabilities of the production lines for all components of products are equally important for quality engineers. The consideration of equal individual lifetime performance indices as should be reasonable. Under this assumption, the relationship between CT and can be obtained by solving Equation (11) as
If the quality engineer wishes the overall lifetime performance index to surpass the target level = , the goal level for each individual lifetime performance index for the lifetime of the ith component can be determined as from Equation (12). The corresponding values of for a given value of are given in Table A1 for d = 2, 3, 4, 5, 6. From Table A1, if the quality engineers want the overall conforming rate to be Pr = 0.8607, it can be found that = 0.85 and the corresponding values for each lifetime performance index of component are determined as = 0.9250, 0.9500, 0.9625, 0.9700, 0.9750 for d = 2, 3, 4, 5, 6.
3. The Testing Procedure for the Overall Lifetime Performance Index
In this section, we derive the maximum likelihood estimator and the asymmetric distribution for each individual lifetime performance index as well as the overall lifetime performance index in Section 3.1. The testing procedure to assess whether the overall lifetime performance index meets the desired target level is outlined in Section 3.2. The power analysis is presented in Section 3.3. Section 3.4 provides a numerical example to illustrate our proposed testing procedure.
3.1. Maximum Likelihood Estimation for All Lifetime Performance Indices
In the production line of the ith component of products, the progressive type I interval censored sample is collected at the inspection time points . The likelihood function for this type of censored sample is
where j = 1, , m, and i = 1, , d. The log-likelihood function is
According to Casella and Berger [14], by taking the derivative of the log-likelihood function with respect to the parameter and setting it to zero, we obtain the log-likelihood equation as follows:
By solving the log-likelihood Equation (15), the maximum likelihood estimator of ki denoted by can be obtained numerically. Based on the asymptotic properties of maximum likelihood estimators, the asymptotic variance of the distribution of is the inverse of the Fisher information number, and the Fisher information number is defined as . The second derivative of the log-likelihood function is obtained as
It is observed that
where
Hence, we have
Therefore, the Fisher information number becomes
The asymptotic variance is denoted by . Based on the asymptotic properties of maximum likelihood estimators, we have .
In the special case, we consider the case of equal interval lengths as and , where the value of t0 is specified to be 0. We also consider pj = p, . Equation (15) is rewritten as
By solving for numerically, we can obtain the maximum likelihood estimator .
Based on the property of the invariance of maximum likelihood estimators, the maximum likelihood estimator of is obtained as
By making use of the Delta method, we can show that
where .
Based on the property of the invariance of maximum likelihood estimators, the maximum likelihood estimator of CT is obtained as
with the variance of Its approximate distribution for is
3.2. The Assessment of the Overall Lifetime Performance Index
To evaluate whether the overall lifetime performance index surpasses the desired target value , we develop a statistical testing procedure in this section. That is, we want to test the null hypothesis (production process for producing d components is not viable) vs. the alternative hypothesis (production process for producing d components is viable). For the setup of , the alternative hypothesis for the overall lifetime performance index is equivalent to the hypothesis of , where . Thererfore, the null and alternative hypotheses can be rewritten as follows: vs. . This is the so-called Intersection–Union test in Casella and Berger [17]. For the ith test vs. , we use the maximum likelihood estimator as the test statistic, and the critical value is determined as where (see Wu [9]). The rejection region for the ith test is For testing the capability of the overall lifetime performance index, the joint rejection region is with the test size of α.
The implementation for the testing procedure for the overall lifetime performance index is enumerated as shown in Algorithm 1.
| Algorithm 1: The implementation of the testing procedure for the overall lifetime performance index. |
|
3.3. Test Power and Power Analysis
The test power function is the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis, and it is a function of the value of . For the testing procedure outlined in the algorithm, the test power function at the point of or in the parameter space of the alternative hypothesis is derived as follows:
where is the CDF for the standard normal distribution, , and .
If we consider the case of L1 = … = Ld = L, the power function is simplified as
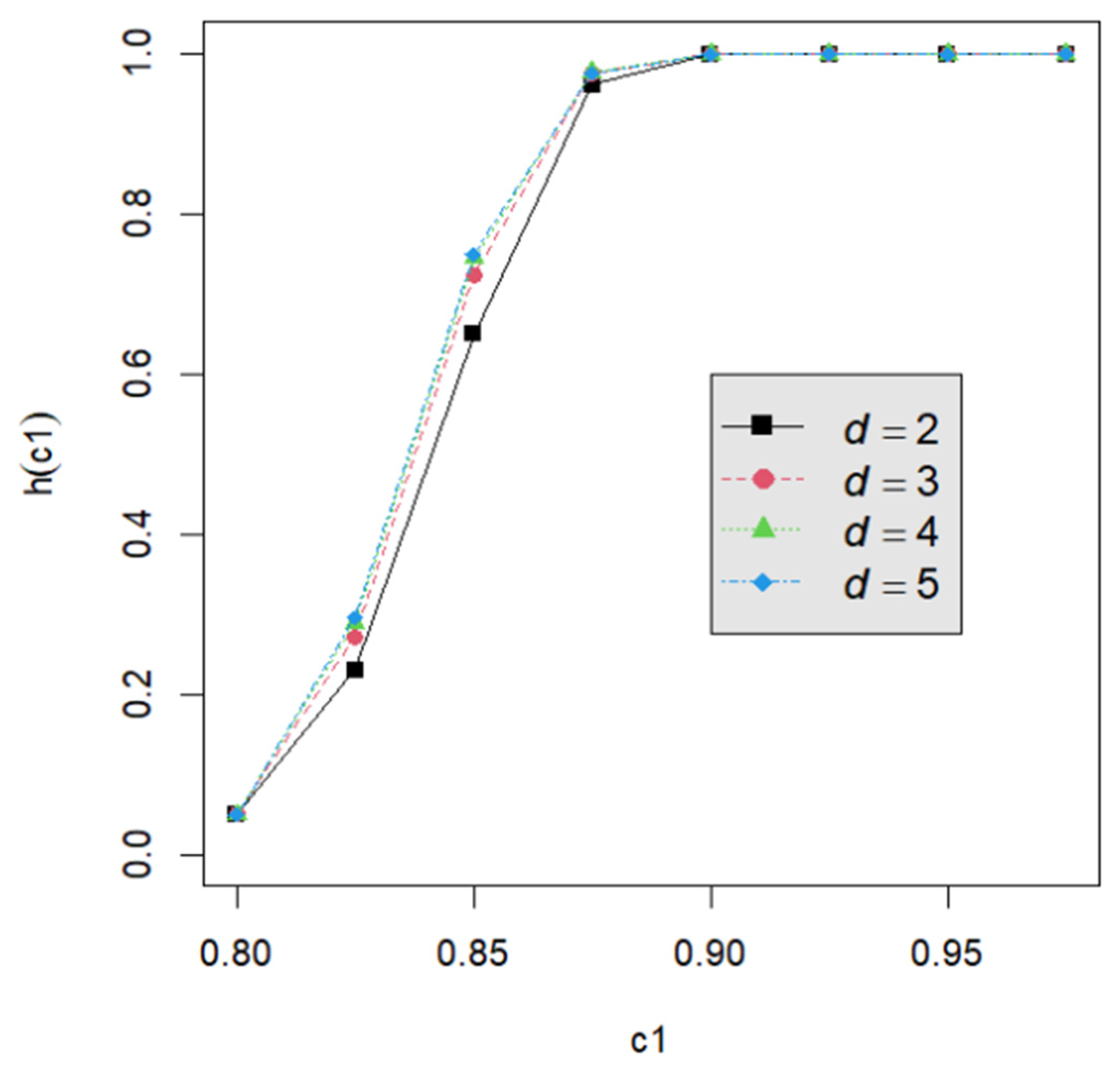
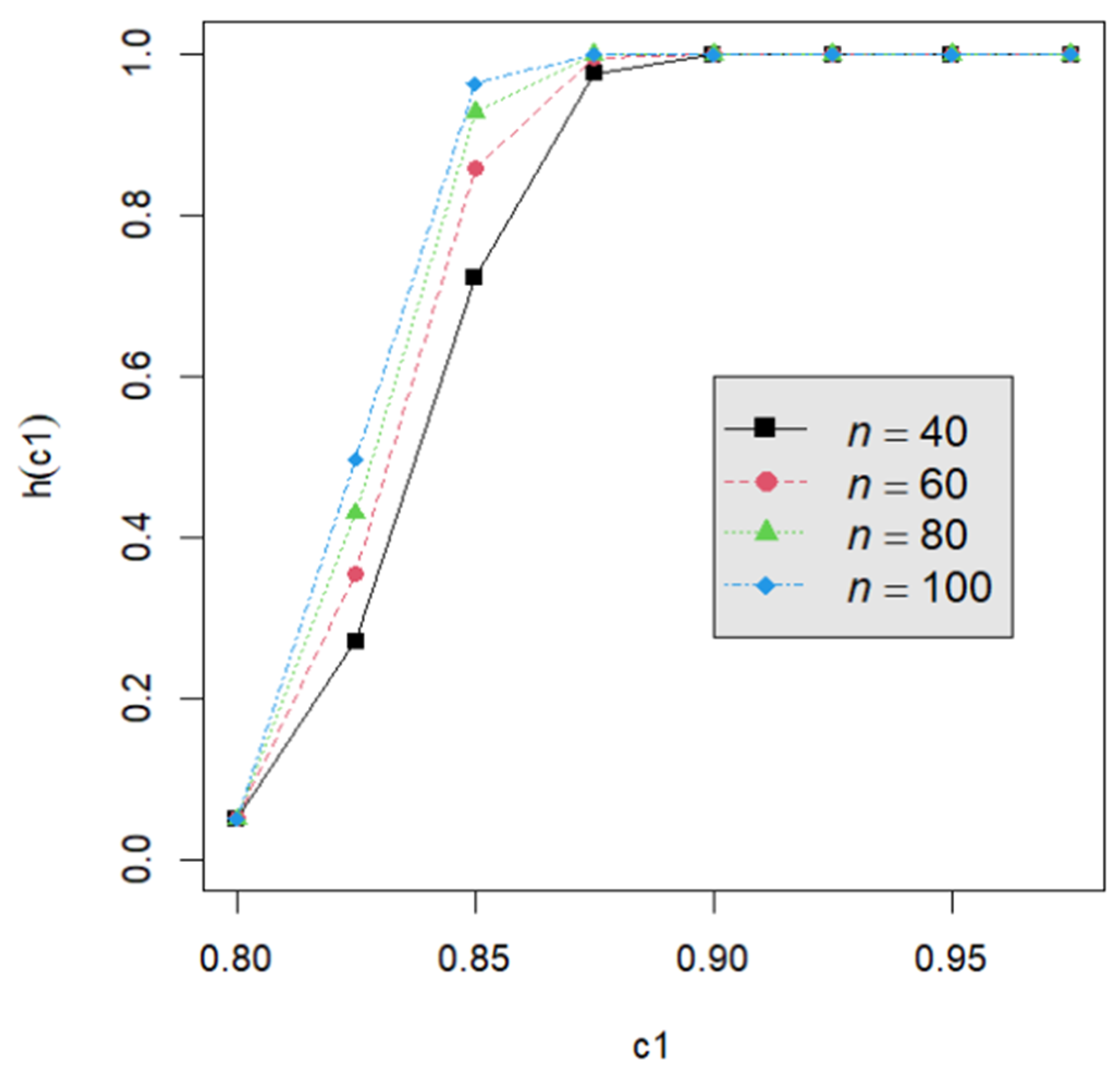
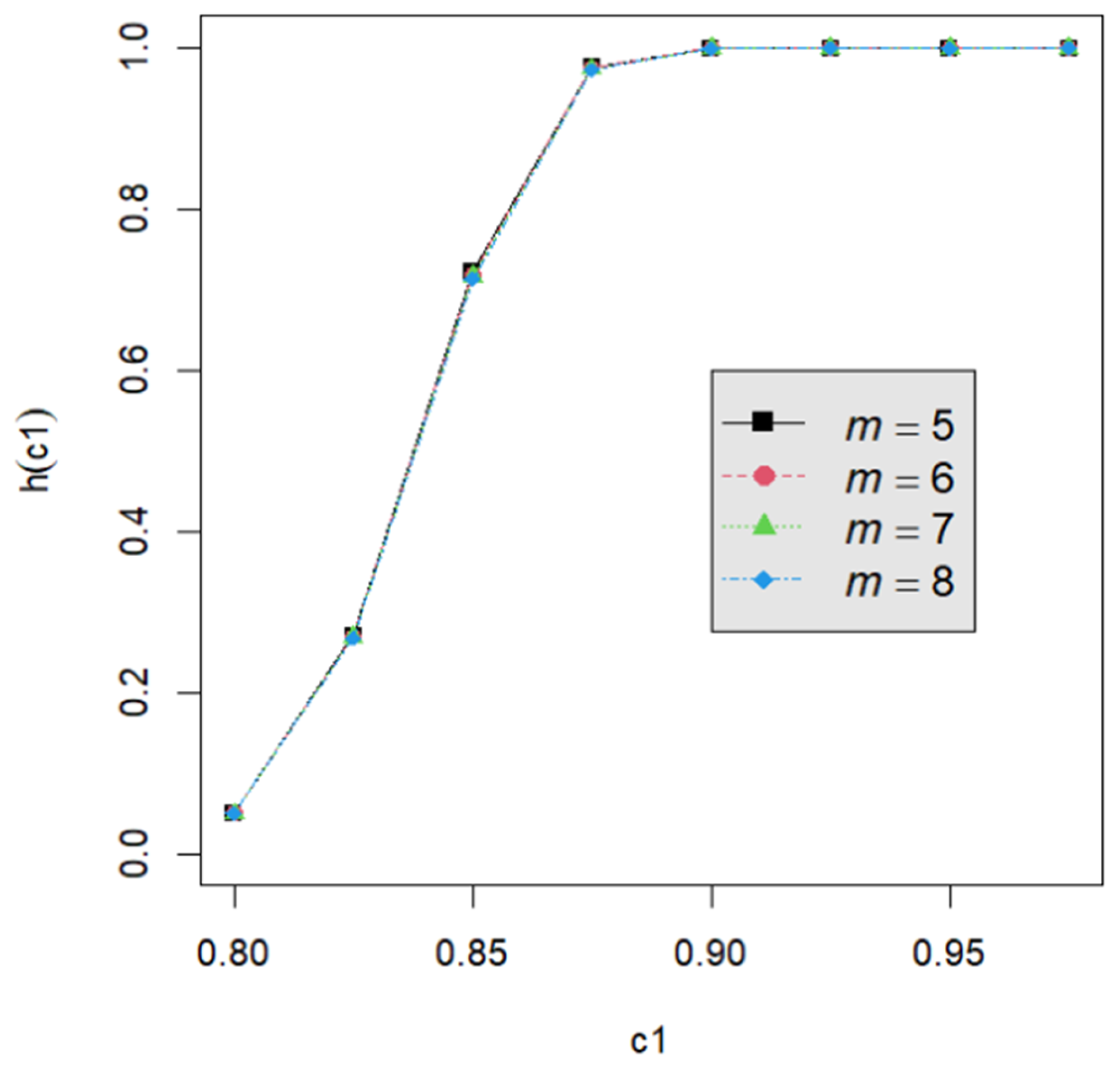
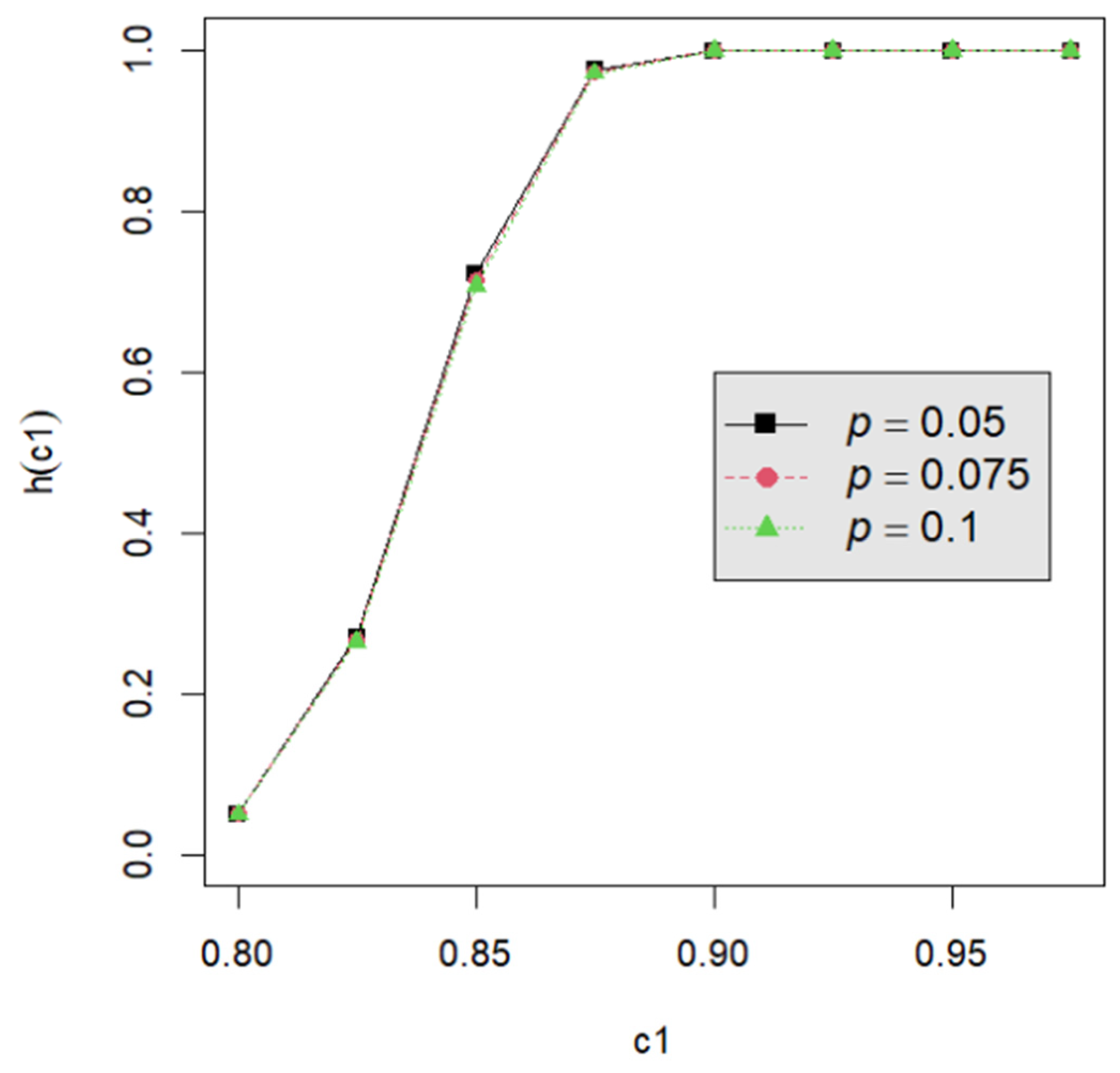
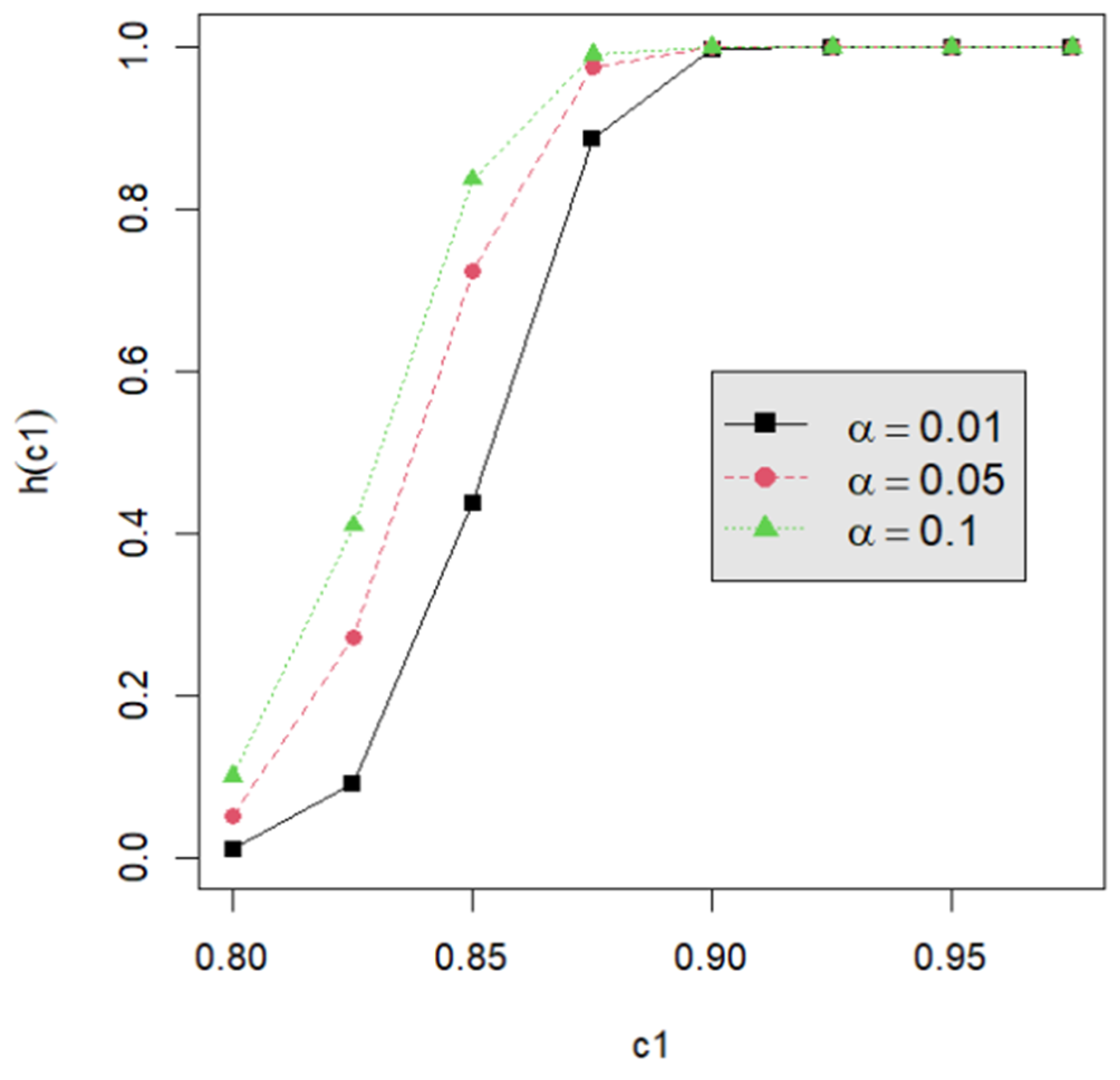
Let us assume that quality engineers want to test vs. with the lower specification limit L = 0.05 and the termination time T = 0.5. The powers h() are calculated by Equation (24) for the proposed testing procedure. They are tabulated for d = 2, 3, 4, 5 with c1 = 0.800, 0.825, 0.850, 0.875, 0.900, 0.925, 0.950; m = 5, 6, 7, 8; n = 40, 60, 80, 120; and p = 0.050, 0.075, 0.100 in Table A2, Table A3, Table A4, Table A5, Table A6, Table A7, Table A8, Table A9 and Table A10. Figure 1, Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5 provide a depiction of the power values for various typical cases. Our observations are as follows: (1) From Figure 1, the power increases with an increase in d under n = 40, m = 5, p = 0.05, and α = 0.05. This behavior is consistent across other combinations of n, m, p, and α. The difference in power for different d decreases when d is greater than 4. (2) From Figure 2, the power increases as n increases, holding d = 3, α = 0.05, m = 5, and p = 0.05 constant. This trend is consistent across other combinations of d, m, p, and α. (3) From Figure 3, the power increases with an increase in m for given d = 3, n = 40, p = 0.05, and α = 0.05. This pattern is also seen with other combinations of d, n, p, and α. (4) From Figure 4, as p increases, the power increases, with d = 3, n = 40, m = 5, and α = 0.05 held fixed. This trend holds for different combinations of d, n, m, and α. (5) From Figure 5, the power increases when α is increased, given d = 3, n = 40, m = 5, and p = 0.05. Similar patterns are observed for various combinations of d, n, m, and p. (6) From Figure 1, Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5, the power increases as the value c1 increases for any combination of d, n, m, p, and α.
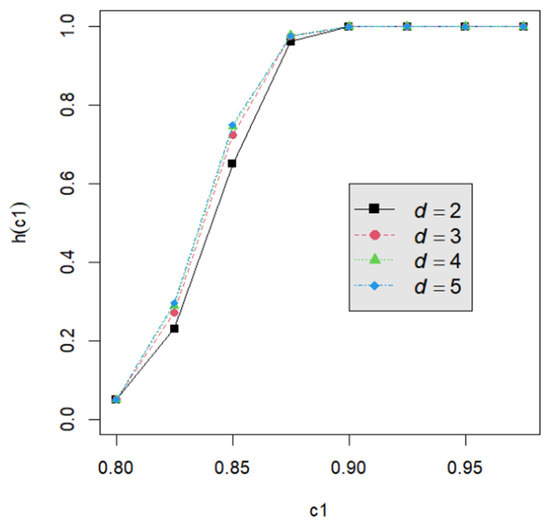
Figure 1.
The power curve for n = 40, m = 5, p = 0.05, α = 0.05, and d = 2, 3, 4, 5.
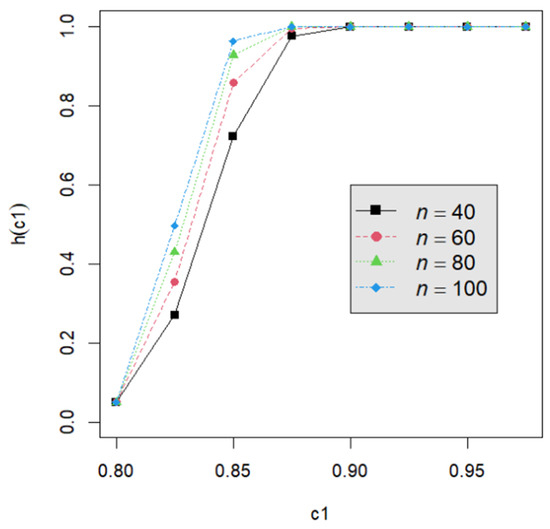
Figure 2.
The power curve for d = 3, α = 0.05, m = 5, p = 0.05, and n = 40, 60, 80, 100.
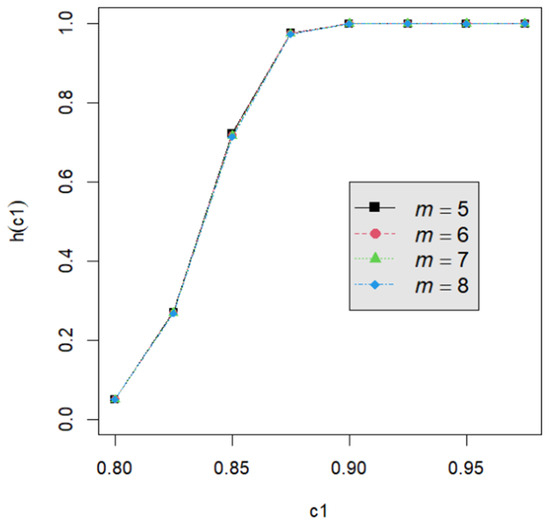
Figure 3.
The power curve for d = 3, α = 0.05, n = 40, p = 0.05, and m = 5, 6, 7, 8.
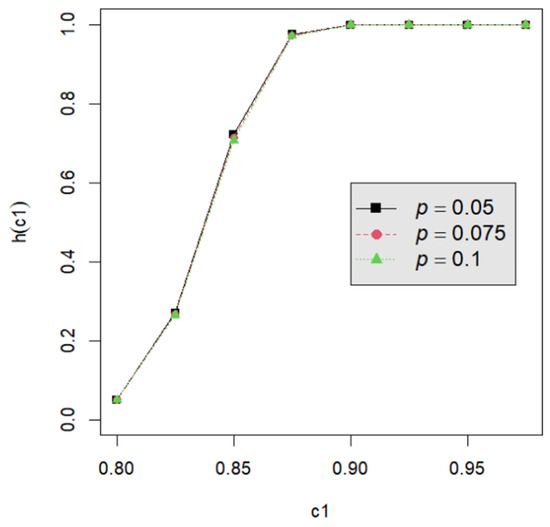
Figure 4.
The power curve for d = 3, α = 0.05, n = 40, m = 5, and p = 0.050, 0.075, 0.100.
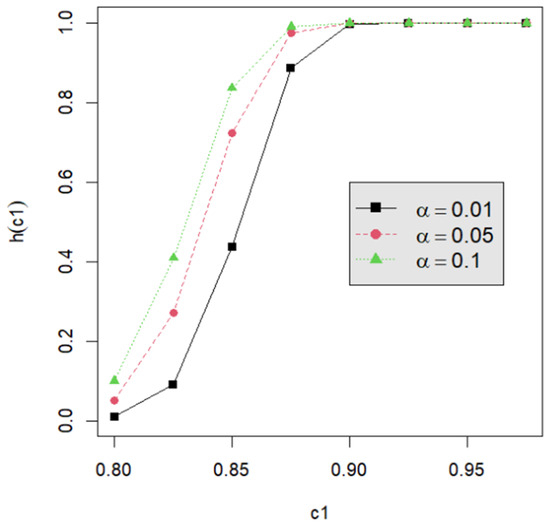
Figure 5.
The power curve for d = 3, n = 40, m = 5, p = 0.05, and α = 0.01, 0.05, 0.10.
3.4. Example
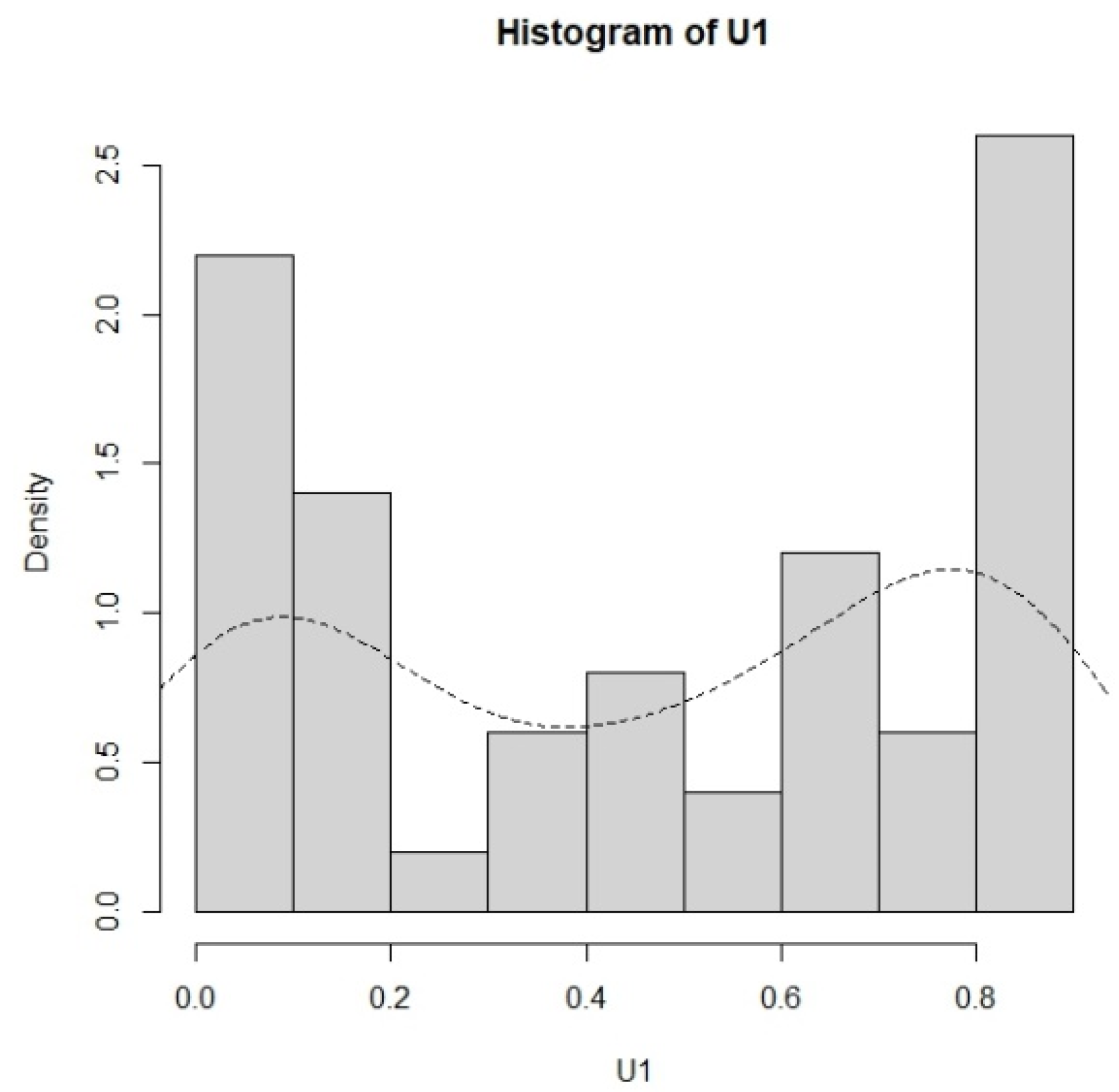
For the production of products with two components (d = 2), the lifetime data of the first component are the failure times in Aarset [18]. The data of 50 failure times U1j, j = 1, …, 50, are as follows: 0.001, 0.002, 0.010, 0.010, 0.010, 0.010, 0.010, 0.020, 0.030, 0.060, 0.070, 0.110, 0.120, 0.180, 0.180, 0.180, 0.180, 0.180, 0.210, 0.320, 0.360, 0.400, 0.450, 0.450, 0.470, 0.500, 0.550, 0.600, 0.630, 0.630, 0.670, 0.670, 0.670, 0.670, 0.720, 0.750, 0.790, 0.820, 0.820, 0.830, 0.840, 0.840, 0.840, 0.850, 0.850, 0.850, 0.850, 0.850, 0.860, and 0.860. The histogram and the density curve for this dataset are displayed in Figure 6.
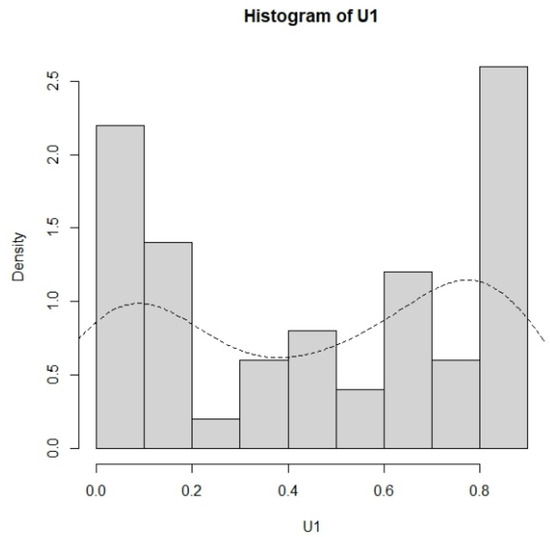
Figure 6.
The histogram and the density curve for the first dataset.
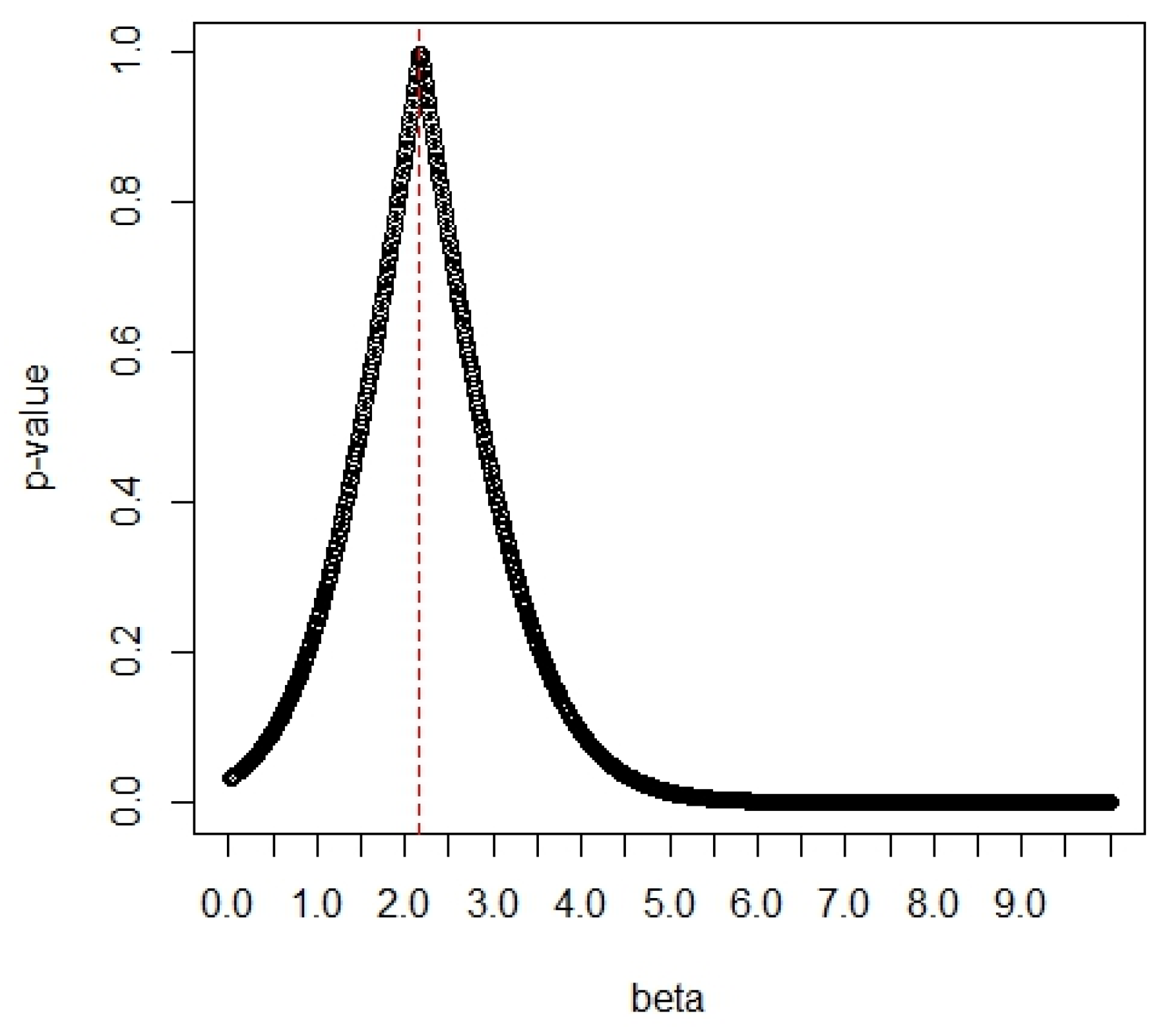
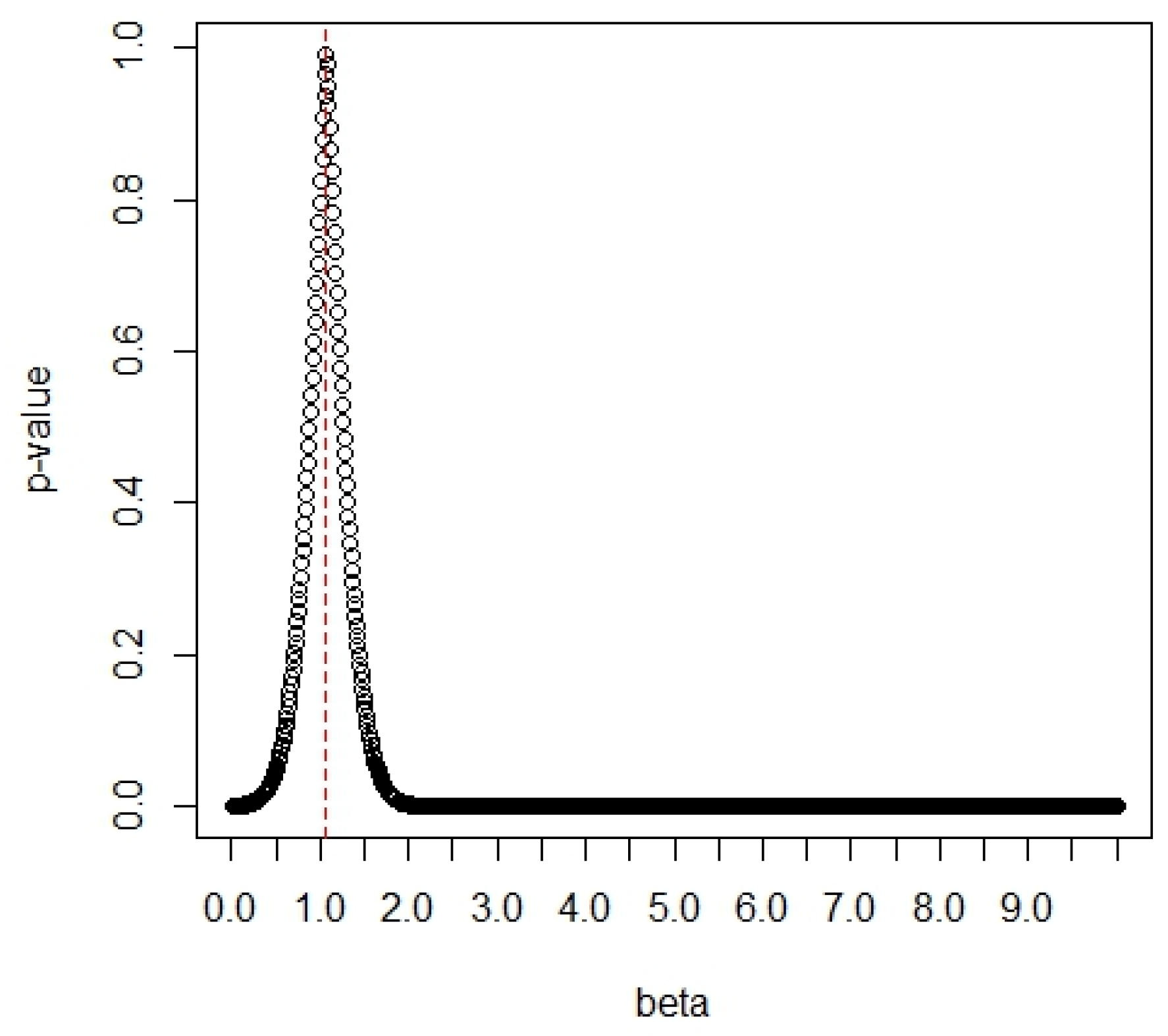
The p-values of the G test based on the Gini statistic (see Gail and Gastwirth [19]) are a function of the values of δ1, and they are displayed in Figure 7. The Gini statistic is obtained as where and j = 1, …, 25. From Figure 7, we can find the maximum p-value of 0.9966 at the value of δ1 = 2.17. The large p-value indicates that the data fit the Chen distribution very well, so the value of δ1 is determined as δ1 = 2.17.
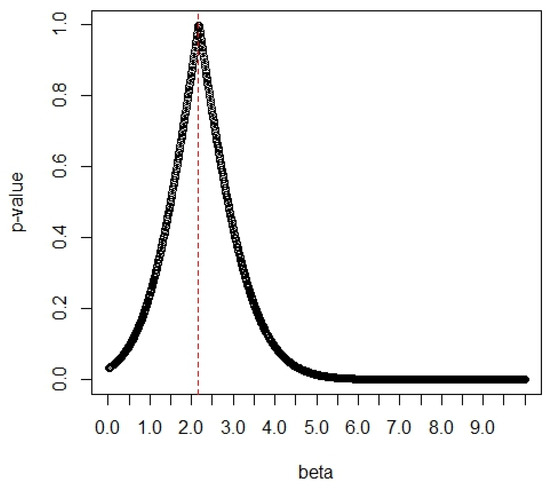
Figure 7.
The p-values vs. the values of δ1.
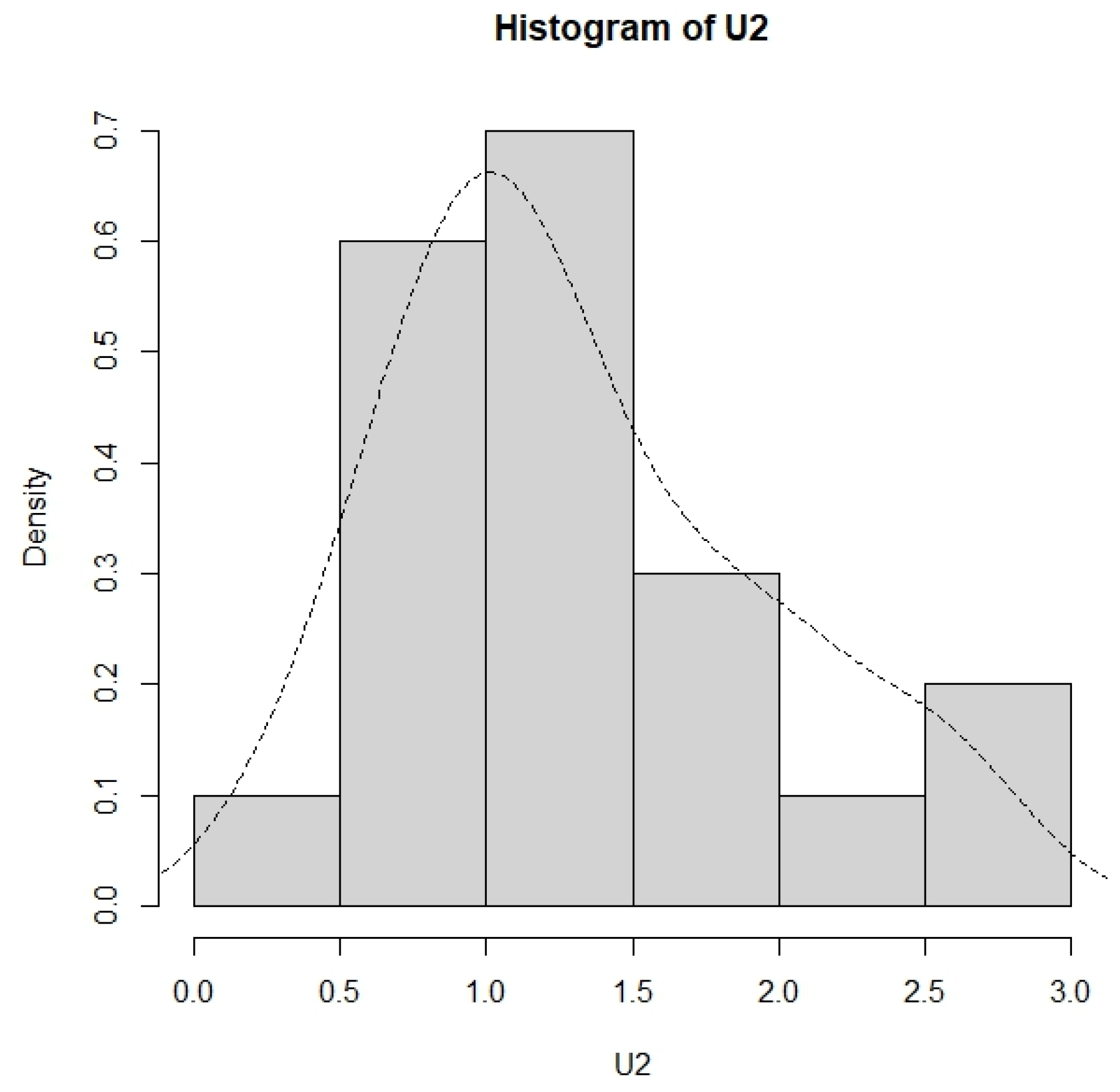
The lifetime of the second component consists of the failure times (number of cycles) of n = 20 ball bearings in Caroni [20]. The data are as follows: 0.3576, 0.5784, 0.6600, 0.8304, 0.8424, 0.9120, 0.9696, 1.0368, 1.0392, 1.0824, 1.1112, 1.3560, 1.3728, 1.3776, 1.6824, 1.8624, 1.9728, 2.1024, 2.5584, and 2.5608. The histogram and the density curve for this dataset are displayed in Figure 8.
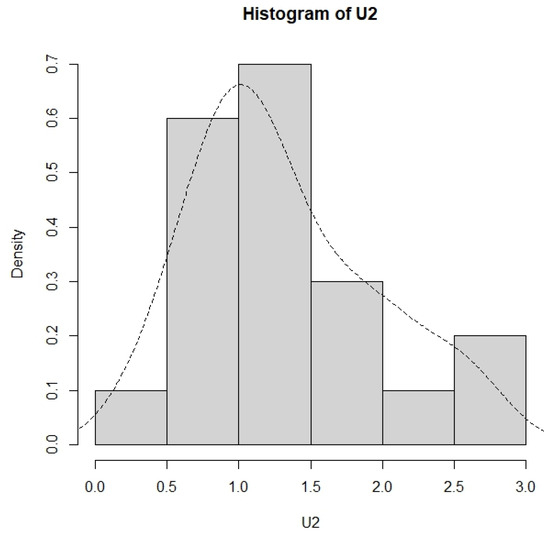
Figure 8.
The histogram and the density curve for the second dataset.
Similarly, we display the p-values of the G test versus the values of δ2 in Figure 9. In Figure 9, the maximum p-value of 0.9925 occurs at the value of δ2 = 1.07. The large p-value indicates the good fit of the data to the Chen distribution. Therefore, the value of δ2 is obtained as δ2 = 1.07.
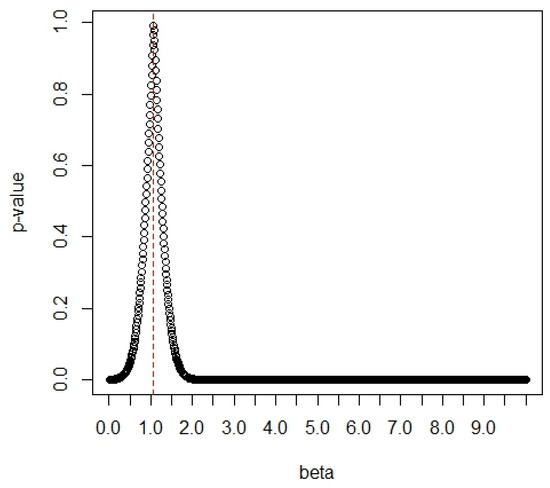
Figure 9.
The p-values vs. the values of δ2.
Let us suppose that we want to test . The progressive type I interval censored samples for the failure times of two components are collected with the termination times of T = 0.5 for the first component and T = 3.0 for the second component with the number of inspections of m = 5 and the pre-specified removal percentages of () = (0.05, 0.05, 0.05, 0.05, 1.00).
The testing procedure is conducted following Algorithm 1 with the steps in Algorithm 2.
| Algorithm 2: The implementation of the testing procedure for the overall lifetime performance index based on this numerical example. |
|
4. Conclusions
In diverse manufacturing sectors, evaluating lifetime performance indices for products, particularly those following a Chen distribution, is paramount. For products with multiple components produced in multiple production lines with Chen-distributed lifetimes, we utilize the overall lifetime performance index, which is a monotonic increasing function of the overall lifetime performance index and all individual lifetime performance indices. By using progressive type I interval censored samples, we develop a hypothesis-testing procedure to evaluate if the overall lifetime performance index meets the target level, which equivalently tests multiple hypotheses for each individual lifetime performance index. This work contributes to the literature by developing a testing procedure to assess the overall lifetime performance index, evaluating the capability of the production process for products with multiple components. Additionally, we examine how factors such as the number of production lines, sample size, number of inspection intervals, removal probability, and significance level influence the test power, presenting the analysis graphically. To illustrate the proposed testing procedure, we provide an example involving products with two components, and their lifetimes fit the Chen distribution very well.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.-F.W.; methodology, S.-F.W.; software, S.-F.W. and Y.-L.H.; validation, Y.-L.H.; formal analysis, S.-F.W.; investigation, S.-F.W. and Y.-L.H.; resources, S.-F.W.; data curation, S.-F.W. and Y.-L.H.; writing—original draft preparation, S.-F.W. and Y.-L.H.; writing—review and editing, S.-F.W.; visualization, Y.-L.H.; supervision, S.-F.W.; project administration, S.-F.W.; funding acquisition, S.-F.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research and the APC were funded by [National Science and Technology Council, Taiwan] NSTC 111-2118-M-032-003-MY2 and NSTC 113-2118-M-032-002-.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available in a publicly accessible repository. The data presented in this study are openly available in Aarset [18] and Caroni [20].
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Appendix A

Table A1.
The goal target values of for given target levels of .
Table A1.
The goal target values of for given target levels of .
| d | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pr | CT | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| 0.6703 | 0.600 | 0.8000 | 0.8667 | 0.9000 | 0.9200 | 0.9333 |
| 0.6873 | 0.625 | 0.8125 | 0.8750 | 0.9063 | 0.9250 | 0.9375 |
| 0.7047 | 0.650 | 0.8250 | 0.8833 | 0.9125 | 0.9300 | 0.9417 |
| 0.7225 | 0.675 | 0.8375 | 0.8917 | 0.9188 | 0.9350 | 0.9458 |
| 0.7408 | 0.700 | 0.8500 | 0.9000 | 0.9250 | 0.9400 | 0.9500 |
| 0.7596 | 0.725 | 0.8625 | 0.9083 | 0.9313 | 0.9450 | 0.9542 |
| 0.7788 | 0.750 | 0.8750 | 0.9167 | 0.9375 | 0.9500 | 0.9583 |
| 0.7985 | 0.775 | 0.8875 | 0.9250 | 0.9438 | 0.9550 | 0.9625 |
| 0.8187 | 0.800 | 0.9000 | 0.9333 | 0.9500 | 0.9600 | 0.9667 |
| 0.8395 | 0.825 | 0.9125 | 0.9417 | 0.9563 | 0.9650 | 0.9708 |
| 0.8607 | 0.850 | 0.9250 | 0.9500 | 0.9625 | 0.9700 | 0.9750 |
| 0.8825 | 0.875 | 0.9375 | 0.9583 | 0.9688 | 0.9750 | 0.9792 |
| 0.9048 | 0.900 | 0.9500 | 0.9667 | 0.9750 | 0.9800 | 0.9833 |
| 0.9277 | 0.925 | 0.9625 | 0.9750 | 0.9813 | 0.9850 | 0.9875 |
| 0.9512 | 0.950 | 0.9750 | 0.9833 | 0.9875 | 0.9900 | 0.9917 |
| 0.9753 | 0.975 | 0.9875 | 0.9917 | 0.9938 | 0.9950 | 0.9958 |
| 1.0000 | 1.000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 |

Table A2.
The power h(c1) for d = 2 and α = 0.01.
Table A2.
The power h(c1) for d = 2 and α = 0.01.
| 0.800 | 0.825 | 0.850 | 0.875 | 0.900 | 0.925 | 0.950 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 40 | 0.050 | 0.0100 | 0.0686 | 0.3330 | 0.8136 | 0.9949 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 |
| 0.075 | 0.0100 | 0.0677 | 0.3268 | 0.8051 | 0.9941 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0100 | 0.0668 | 0.3208 | 0.7967 | 0.9932 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 60 | 0.050 | 0.0100 | 0.1051 | 0.5308 | 0.9564 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0100 | 0.1036 | 0.5224 | 0.9528 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0100 | 0.1020 | 0.5142 | 0.9491 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 80 | 0.050 | 0.0100 | 0.1452 | 0.6903 | 0.9912 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0100 | 0.1428 | 0.6817 | 0.9901 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0100 | 0.1406 | 0.6732 | 0.9890 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 100 | 0.050 | 0.0100 | 0.1877 | 0.8048 | 0.9984 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0100 | 0.1846 | 0.7972 | 0.9981 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0100 | 0.1817 | 0.7897 | 0.9978 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 6 | 40 | 0.050 | 0.0100 | 0.0691 | 0.3342 | 0.8134 | 0.9947 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 |
| 0.075 | 0.0100 | 0.0679 | 0.3265 | 0.8029 | 0.9937 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0100 | 0.0668 | 0.3192 | 0.7925 | 0.9925 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 60 | 0.050 | 0.0100 | 0.1058 | 0.5317 | 0.9561 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0100 | 0.1038 | 0.5213 | 0.9515 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0100 | 0.1019 | 0.5112 | 0.9469 | 0.9998 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 80 | 0.050 | 0.0100 | 0.1459 | 0.6909 | 0.9911 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0100 | 0.1430 | 0.6801 | 0.9897 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0100 | 0.1403 | 0.6697 | 0.9883 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 100 | 0.050 | 0.0100 | 0.1886 | 0.8051 | 0.9984 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0100 | 0.1848 | 0.7956 | 0.9980 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0100 | 0.1811 | 0.7863 | 0.9976 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 7 | 40 | 0.050 | 0.0100 | 0.0692 | 0.3339 | 0.8118 | 0.9945 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 |
| 0.075 | 0.0100 | 0.0679 | 0.3248 | 0.7993 | 0.9932 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0100 | 0.0666 | 0.3163 | 0.7870 | 0.9918 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 60 | 0.050 | 0.0100 | 0.1059 | 0.5310 | 0.9553 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0100 | 0.1036 | 0.5186 | 0.9498 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0100 | 0.1014 | 0.5068 | 0.9442 | 0.9998 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 80 | 0.050 | 0.0100 | 0.1461 | 0.6899 | 0.9908 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0100 | 0.1426 | 0.6771 | 0.9892 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0100 | 0.1394 | 0.6647 | 0.9873 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 100 | 0.050 | 0.0100 | 0.1887 | 0.8040 | 0.9983 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0100 | 0.1841 | 0.7927 | 0.9979 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0100 | 0.1798 | 0.7817 | 0.9974 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 8 | 40 | 0.050 | 0.0100 | 0.0692 | 0.3329 | 0.8095 | 0.9942 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 |
| 0.075 | 0.0100 | 0.0676 | 0.3225 | 0.7950 | 0.9927 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0100 | 0.0662 | 0.3128 | 0.7808 | 0.9909 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 60 | 0.050 | 0.0100 | 0.1058 | 0.5292 | 0.9542 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0100 | 0.1031 | 0.5149 | 0.9477 | 0.9998 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0100 | 0.1006 | 0.5015 | 0.9411 | 0.9998 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 80 | 0.050 | 0.0100 | 0.1458 | 0.6879 | 0.9905 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0100 | 0.1419 | 0.6731 | 0.9885 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0100 | 0.1382 | 0.6590 | 0.9863 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 100 | 0.050 | 0.0100 | 0.1884 | 0.8022 | 0.9982 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0100 | 0.1831 | 0.7891 | 0.9977 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0100 | 0.1782 | 0.7764 | 0.9971 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||

Table A3.
The power h(c1) for d = 2 and α = 0.05.
Table A3.
The power h(c1) for d = 2 and α = 0.05.
| 0.800 | 0.825 | 0.850 | 0.875 | 0.900 | 0.925 | 0.950 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 40 | 0.050 | 0.0500 | 0.2307 | 0.6505 | 0.9619 | 0.9998 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 |
| 0.075 | 0.0500 | 0.2285 | 0.6439 | 0.9592 | 0.9998 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0500 | 0.2263 | 0.6374 | 0.9565 | 0.9997 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 60 | 0.050 | 0.0500 | 0.3053 | 0.8093 | 0.9947 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0500 | 0.3021 | 0.8033 | 0.9941 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0500 | 0.2991 | 0.7975 | 0.9935 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 80 | 0.050 | 0.0500 | 0.3749 | 0.8992 | 0.9993 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0500 | 0.3708 | 0.8948 | 0.9992 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0500 | 0.3670 | 0.8904 | 0.9991 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 100 | 0.050 | 0.0500 | 0.4393 | 0.9478 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0500 | 0.4346 | 0.9449 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0500 | 0.4301 | 0.9418 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 6 | 40 | 0.050 | 0.0500 | 0.2313 | 0.6506 | 0.9615 | 0.9998 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 |
| 0.075 | 0.0500 | 0.2285 | 0.6424 | 0.9581 | 0.9997 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0500 | 0.2259 | 0.6345 | 0.9546 | 0.9997 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 60 | 0.050 | 0.0500 | 0.3060 | 0.8092 | 0.9946 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0500 | 0.3020 | 0.8018 | 0.9939 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0500 | 0.2983 | 0.7945 | 0.9930 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 80 | 0.050 | 0.0500 | 0.3756 | 0.8990 | 0.9993 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0500 | 0.3706 | 0.8935 | 0.9992 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0500 | 0.3658 | 0.8880 | 0.9990 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 100 | 0.050 | 0.0500 | 0.4400 | 0.9477 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0500 | 0.4342 | 0.9439 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0500 | 0.4287 | 0.9402 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 7 | 40 | 0.050 | 0.0500 | 0.2313 | 0.6496 | 0.9608 | 0.9998 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 |
| 0.075 | 0.0500 | 0.2280 | 0.6399 | 0.9567 | 0.9997 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0500 | 0.2249 | 0.6305 | 0.9524 | 0.9996 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 60 | 0.050 | 0.0500 | 0.3059 | 0.8081 | 0.9945 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0500 | 0.3012 | 0.7993 | 0.9935 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0500 | 0.2968 | 0.7907 | 0.9925 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 80 | 0.050 | 0.0500 | 0.3754 | 0.8982 | 0.9993 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0500 | 0.3695 | 0.8916 | 0.9991 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0500 | 0.3639 | 0.8850 | 0.9989 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 100 | 0.050 | 0.0500 | 0.4397 | 0.9471 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0500 | 0.4328 | 0.9426 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0500 | 0.4263 | 0.9380 | 0.9998 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 8 | 40 | 0.050 | 0.0500 | 0.2310 | 0.6479 | 0.9599 | 0.9998 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 |
| 0.075 | 0.0500 | 0.2272 | 0.6367 | 0.9550 | 0.9997 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0500 | 0.2237 | 0.6261 | 0.9500 | 0.9995 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 60 | 0.050 | 0.0500 | 0.3054 | 0.8065 | 0.9942 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0500 | 0.3000 | 0.7963 | 0.9931 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0500 | 0.2950 | 0.7864 | 0.9918 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 80 | 0.050 | 0.0500 | 0.3747 | 0.8969 | 0.9992 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0500 | 0.3679 | 0.8892 | 0.9990 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0500 | 0.3616 | 0.8816 | 0.9987 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 100 | 0.050 | 0.0500 | 0.4389 | 0.9462 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0500 | 0.4309 | 0.9409 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0500 | 0.4235 | 0.9356 | 0.9998 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||

Table A4.
The power h(c1) for d = 2 and α = 0.1.
Table A4.
The power h(c1) for d = 2 and α = 0.1.
| 0.800 | 0.825 | 0.850 | 0.875 | 0.900 | 0.925 | 0.950 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 40 | 0.050 | 0.1000 | 0.3670 | 0.7925 | 0.9873 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 |
| 0.075 | 0.1000 | 0.3642 | 0.7872 | 0.9862 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.1000 | 0.3614 | 0.7821 | 0.9850 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 60 | 0.050 | 0.1000 | 0.4538 | 0.9019 | 0.9987 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.1000 | 0.4501 | 0.8981 | 0.9985 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.1000 | 0.4465 | 0.8942 | 0.9983 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 80 | 0.050 | 0.1000 | 0.5281 | 0.9541 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.1000 | 0.5239 | 0.9516 | 0.9998 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.1000 | 0.5197 | 0.9491 | 0.9998 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 100 | 0.050 | 0.1000 | 0.5924 | 0.9786 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.1000 | 0.5878 | 0.9771 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.1000 | 0.5832 | 0.9757 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 6 | 40 | 0.050 | 0.1000 | 0.3674 | 0.7921 | 0.9870 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 |
| 0.075 | 0.1000 | 0.3639 | 0.7857 | 0.9856 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.1000 | 0.3605 | 0.7793 | 0.9842 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 60 | 0.050 | 0.1000 | 0.4542 | 0.9016 | 0.9986 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.1000 | 0.4497 | 0.8968 | 0.9984 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.1000 | 0.4453 | 0.8921 | 0.9981 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 80 | 0.050 | 0.1000 | 0.5286 | 0.9538 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.1000 | 0.5233 | 0.9508 | 0.9998 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.1000 | 0.5182 | 0.9477 | 0.9998 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 100 | 0.050 | 0.1000 | 0.5928 | 0.9784 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.1000 | 0.5871 | 0.9766 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.1000 | 0.5815 | 0.9747 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 7 | 40 | 0.050 | 0.1000 | 0.3673 | 0.7911 | 0.9867 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 |
| 0.075 | 0.1000 | 0.3631 | 0.7833 | 0.9850 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.1000 | 0.3591 | 0.7759 | 0.9832 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 60 | 0.050 | 0.1000 | 0.4539 | 0.9007 | 0.9986 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.1000 | 0.4485 | 0.8950 | 0.9983 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.1000 | 0.4434 | 0.8894 | 0.9980 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 80 | 0.050 | 0.1000 | 0.5282 | 0.9532 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.1000 | 0.5219 | 0.9496 | 0.9998 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.1000 | 0.5159 | 0.9459 | 0.9998 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 100 | 0.050 | 0.1000 | 0.5924 | 0.9781 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.1000 | 0.5855 | 0.9759 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.1000 | 0.5790 | 0.9736 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 8 | 40 | 0.050 | 0.1000 | 0.3668 | 0.7895 | 0.9863 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 |
| 0.075 | 0.1000 | 0.3619 | 0.7806 | 0.9843 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.1000 | 0.3574 | 0.7720 | 0.9821 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 60 | 0.050 | 0.1000 | 0.4532 | 0.8995 | 0.9985 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.1000 | 0.4470 | 0.8929 | 0.9982 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.1000 | 0.4411 | 0.8864 | 0.9978 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 80 | 0.050 | 0.1000 | 0.5273 | 0.9525 | 0.9998 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.1000 | 0.5201 | 0.9482 | 0.9998 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.1000 | 0.5132 | 0.9438 | 0.9997 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 100 | 0.050 | 0.1000 | 0.5914 | 0.9776 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.1000 | 0.5835 | 0.9750 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.1000 | 0.5760 | 0.9724 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||

Table A5.
The power h(c1) for d = 3 and α = 0.01.
Table A5.
The power h(c1) for d = 3 and α = 0.01.
| 0.800 | 0.825 | 0.850 | 0.875 | 0.900 | 0.925 | 0.950 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 40 | 0.050 | 0.0100 | 0.0916 | 0.4380 | 0.8880 | 0.9978 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 |
| 0.075 | 0.0100 | 0.0899 | 0.4288 | 0.8805 | 0.9973 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0100 | 0.0883 | 0.4200 | 0.8729 | 0.9968 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 60 | 0.050 | 0.0100 | 0.1390 | 0.6377 | 0.9764 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0100 | 0.1362 | 0.6272 | 0.9738 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0100 | 0.1335 | 0.6169 | 0.9711 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 80 | 0.050 | 0.0100 | 0.1895 | 0.7780 | 0.9954 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0100 | 0.1855 | 0.7685 | 0.9947 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0100 | 0.1817 | 0.7591 | 0.9939 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 100 | 0.050 | 0.0100 | 0.2416 | 0.8682 | 0.9991 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0100 | 0.2365 | 0.8607 | 0.9990 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0100 | 0.2316 | 0.8532 | 0.9988 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 6 | 40 | 0.050 | 0.0100 | 0.0911 | 0.4349 | 0.8851 | 0.9976 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 |
| 0.075 | 0.0100 | 0.0891 | 0.4236 | 0.8756 | 0.9970 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0100 | 0.0871 | 0.4128 | 0.8661 | 0.9963 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 60 | 0.050 | 0.0100 | 0.1382 | 0.6340 | 0.9754 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0100 | 0.1347 | 0.6209 | 0.9720 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0100 | 0.1315 | 0.6083 | 0.9685 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 80 | 0.050 | 0.0100 | 0.1883 | 0.7746 | 0.9951 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0100 | 0.1834 | 0.7628 | 0.9941 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0100 | 0.1788 | 0.7511 | 0.9931 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 100 | 0.050 | 0.0100 | 0.2400 | 0.8655 | 0.9991 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0100 | 0.2338 | 0.8561 | 0.9988 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0100 | 0.2279 | 0.8467 | 0.9985 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 7 | 40 | 0.050 | 0.0100 | 0.0906 | 0.4313 | 0.8818 | 0.9974 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 |
| 0.075 | 0.0100 | 0.0881 | 0.4179 | 0.8704 | 0.9966 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0100 | 0.0858 | 0.4053 | 0.8589 | 0.9957 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 60 | 0.050 | 0.0100 | 0.1372 | 0.6297 | 0.9742 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0100 | 0.1331 | 0.6142 | 0.9701 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0100 | 0.1293 | 0.5994 | 0.9656 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 80 | 0.050 | 0.0100 | 0.1868 | 0.7707 | 0.9948 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0100 | 0.1811 | 0.7566 | 0.9936 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0100 | 0.1758 | 0.7427 | 0.9922 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 100 | 0.050 | 0.0100 | 0.2381 | 0.8624 | 0.9990 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0100 | 0.2308 | 0.8511 | 0.9987 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0100 | 0.2239 | 0.8398 | 0.9983 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 8 | 40 | 0.050 | 0.0100 | 0.0899 | 0.4274 | 0.8784 | 0.9971 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 |
| 0.075 | 0.0100 | 0.0871 | 0.4121 | 0.8650 | 0.9962 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0100 | 0.0845 | 0.3979 | 0.8515 | 0.9951 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 60 | 0.050 | 0.0100 | 0.1361 | 0.6252 | 0.9730 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0100 | 0.1314 | 0.6073 | 0.9680 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0100 | 0.1272 | 0.5904 | 0.9626 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 80 | 0.050 | 0.0100 | 0.1852 | 0.7665 | 0.9944 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0100 | 0.1787 | 0.7501 | 0.9929 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0100 | 0.1727 | 0.7341 | 0.9912 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 100 | 0.050 | 0.0100 | 0.2361 | 0.8591 | 0.9989 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0100 | 0.2277 | 0.8458 | 0.9985 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0100 | 0.2200 | 0.8326 | 0.9980 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||

Table A6.
The power h(c1) for d = 3 and α = 0.05.
Table A6.
The power h(c1) for d = 3 and α = 0.05.
| 0.800 | 0.825 | 0.850 | 0.875 | 0.900 | 0.925 | 0.950 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 40 | 0.050 | 0.0500 | 0.2711 | 0.7230 | 0.9760 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 |
| 0.075 | 0.0500 | 0.2677 | 0.7153 | 0.9738 | 0.9998 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0500 | 0.2643 | 0.7076 | 0.9715 | 0.9998 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 60 | 0.050 | 0.0500 | 0.3544 | 0.8579 | 0.9966 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0500 | 0.3497 | 0.8517 | 0.9961 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0500 | 0.3451 | 0.8455 | 0.9956 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 80 | 0.050 | 0.0500 | 0.4296 | 0.9279 | 0.9995 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0500 | 0.4239 | 0.9236 | 0.9994 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0500 | 0.4184 | 0.9193 | 0.9993 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 100 | 0.050 | 0.0500 | 0.4973 | 0.9636 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0500 | 0.4909 | 0.9608 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0500 | 0.4847 | 0.9580 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 6 | 40 | 0.050 | 0.0500 | 0.2700 | 0.7201 | 0.9751 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 |
| 0.075 | 0.0500 | 0.2658 | 0.7104 | 0.9723 | 0.9998 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0500 | 0.2617 | 0.7010 | 0.9693 | 0.9998 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 60 | 0.050 | 0.0500 | 0.3529 | 0.8555 | 0.9964 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0500 | 0.3471 | 0.8477 | 0.9958 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0500 | 0.3415 | 0.8400 | 0.9951 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 80 | 0.050 | 0.0500 | 0.4277 | 0.9263 | 0.9995 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0500 | 0.4207 | 0.9208 | 0.9994 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0500 | 0.4140 | 0.9154 | 0.9992 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 100 | 0.050 | 0.0500 | 0.4952 | 0.9625 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0500 | 0.4872 | 0.9590 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0500 | 0.4796 | 0.9554 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 7 | 40 | 0.050 | 0.0500 | 0.2687 | 0.7168 | 0.9741 | 0.9998 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 |
| 0.075 | 0.0500 | 0.2637 | 0.7053 | 0.9706 | 0.9998 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0500 | 0.2590 | 0.6942 | 0.9670 | 0.9997 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 60 | 0.050 | 0.0500 | 0.3511 | 0.8529 | 0.9962 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0500 | 0.3442 | 0.8435 | 0.9954 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0500 | 0.3377 | 0.8343 | 0.9945 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 80 | 0.050 | 0.0500 | 0.4255 | 0.9244 | 0.9994 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0500 | 0.4172 | 0.9179 | 0.9993 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0500 | 0.4094 | 0.9112 | 0.9991 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 100 | 0.050 | 0.0500 | 0.4926 | 0.9613 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0500 | 0.4833 | 0.9571 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0500 | 0.4744 | 0.9527 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 8 | 40 | 0.050 | 0.0500 | 0.2673 | 0.7133 | 0.9730 | 0.9998 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 |
| 0.075 | 0.0500 | 0.2615 | 0.7001 | 0.9689 | 0.9997 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0500 | 0.2562 | 0.6874 | 0.9645 | 0.9996 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 60 | 0.050 | 0.0500 | 0.3491 | 0.8500 | 0.9960 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0500 | 0.3412 | 0.8392 | 0.9950 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0500 | 0.3339 | 0.8285 | 0.9939 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 80 | 0.050 | 0.0500 | 0.4231 | 0.9224 | 0.9994 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0500 | 0.4136 | 0.9147 | 0.9992 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0500 | 0.4047 | 0.9070 | 0.9989 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 100 | 0.050 | 0.0500 | 0.4899 | 0.9601 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0500 | 0.4792 | 0.9550 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0500 | 0.4691 | 0.9498 | 0.9998 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||

Table A7.
The power h(c1) for d = 3 and α = 0.1.
Table A7.
The power h(c1) for d = 3 and α = 0.1.
| 0.800 | 0.825 | 0.850 | 0.875 | 0.900 | 0.925 | 0.950 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 40 | 0.050 | 0.1000 | 0.4094 | 0.8368 | 0.9913 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 |
| 0.075 | 0.1000 | 0.4053 | 0.8311 | 0.9903 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.1000 | 0.4014 | 0.8254 | 0.9893 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 60 | 0.050 | 0.1000 | 0.5003 | 0.9258 | 0.9990 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.1000 | 0.4953 | 0.9220 | 0.9989 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.1000 | 0.4904 | 0.9181 | 0.9987 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 80 | 0.050 | 0.1000 | 0.5760 | 0.9659 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.1000 | 0.5704 | 0.9635 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.1000 | 0.5649 | 0.9611 | 0.9998 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 100 | 0.050 | 0.1000 | 0.6397 | 0.9842 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.1000 | 0.6337 | 0.9828 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.1000 | 0.6279 | 0.9814 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 6 | 40 | 0.050 | 0.1000 | 0.4080 | 0.8345 | 0.9909 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 |
| 0.075 | 0.1000 | 0.4030 | 0.8274 | 0.9896 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.1000 | 0.3982 | 0.8204 | 0.9884 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 60 | 0.050 | 0.1000 | 0.4986 | 0.9243 | 0.9989 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.1000 | 0.4924 | 0.9194 | 0.9987 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.1000 | 0.4864 | 0.9145 | 0.9985 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 80 | 0.050 | 0.1000 | 0.5741 | 0.9649 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.1000 | 0.5671 | 0.9620 | 0.9998 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.1000 | 0.5604 | 0.9589 | 0.9998 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 100 | 0.050 | 0.1000 | 0.6376 | 0.9836 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.1000 | 0.6302 | 0.9819 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.1000 | 0.6231 | 0.9800 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 7 | 40 | 0.050 | 0.1000 | 0.4064 | 0.8320 | 0.9904 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 |
| 0.075 | 0.1000 | 0.4004 | 0.8235 | 0.9889 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.1000 | 0.3949 | 0.8152 | 0.9873 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 60 | 0.050 | 0.1000 | 0.4966 | 0.9226 | 0.9989 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.1000 | 0.4892 | 0.9167 | 0.9986 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.1000 | 0.4822 | 0.9108 | 0.9983 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 80 | 0.050 | 0.1000 | 0.5718 | 0.9639 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.1000 | 0.5635 | 0.9603 | 0.9998 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.1000 | 0.5557 | 0.9565 | 0.9998 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 100 | 0.050 | 0.1000 | 0.6352 | 0.9830 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.1000 | 0.6264 | 0.9809 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.1000 | 0.6181 | 0.9786 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 8 | 40 | 0.050 | 0.1000 | 0.4046 | 0.8294 | 0.9900 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 |
| 0.075 | 0.1000 | 0.3979 | 0.8195 | 0.9881 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.1000 | 0.3915 | 0.8100 | 0.9862 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 60 | 0.050 | 0.1000 | 0.4944 | 0.9208 | 0.9988 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.1000 | 0.4860 | 0.9139 | 0.9984 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.1000 | 0.4781 | 0.9071 | 0.9981 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 80 | 0.050 | 0.1000 | 0.5694 | 0.9628 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.1000 | 0.5599 | 0.9585 | 0.9998 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.1000 | 0.5509 | 0.9541 | 0.9997 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 100 | 0.050 | 0.1000 | 0.6326 | 0.9824 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.1000 | 0.6225 | 0.9798 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.1000 | 0.6130 | 0.9771 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||

Table A8.
The power h(c1) for d = 4 and α = 0.01.
Table A8.
The power h(c1) for d = 4 and α = 0.01.
| 0.800 | 0.825 | 0.850 | 0.875 | 0.900 | 0.925 | 0.950 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 40 | 0.050 | 0.0100 | 0.1037 | 0.4806 | 0.9049 | 0.9979 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 |
| 0.075 | 0.0100 | 0.1015 | 0.4702 | 0.8979 | 0.9975 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0100 | 0.0994 | 0.4601 | 0.8907 | 0.9970 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 60 | 0.050 | 0.0100 | 0.1555 | 0.6721 | 0.9790 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0100 | 0.1520 | 0.6609 | 0.9765 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0100 | 0.1486 | 0.6499 | 0.9739 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 80 | 0.050 | 0.0100 | 0.2097 | 0.8008 | 0.9955 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0100 | 0.2048 | 0.7911 | 0.9948 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0100 | 0.2002 | 0.7814 | 0.9940 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 100 | 0.050 | 0.0100 | 0.2647 | 0.8816 | 0.9990 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0100 | 0.2585 | 0.8740 | 0.9989 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0100 | 0.2527 | 0.8664 | 0.9986 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 6 | 40 | 0.050 | 0.0100 | 0.1028 | 0.4760 | 0.9017 | 0.9977 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 |
| 0.075 | 0.0100 | 0.1001 | 0.4632 | 0.8927 | 0.9972 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0100 | 0.0976 | 0.4509 | 0.8835 | 0.9965 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 60 | 0.050 | 0.0100 | 0.1540 | 0.6671 | 0.9779 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0100 | 0.1497 | 0.6532 | 0.9747 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0100 | 0.1456 | 0.6397 | 0.9712 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 80 | 0.050 | 0.0100 | 0.2076 | 0.7965 | 0.9952 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0100 | 0.2016 | 0.7843 | 0.9942 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0100 | 0.1960 | 0.7722 | 0.9931 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 100 | 0.050 | 0.0100 | 0.2620 | 0.8782 | 0.9990 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0100 | 0.2545 | 0.8687 | 0.9987 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0100 | 0.2475 | 0.8591 | 0.9984 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 7 | 40 | 0.050 | 0.0100 | 0.1018 | 0.4711 | 0.8983 | 0.9975 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 |
| 0.075 | 0.0100 | 0.0987 | 0.4560 | 0.8874 | 0.9968 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0100 | 0.0957 | 0.4418 | 0.8762 | 0.9959 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 60 | 0.050 | 0.0100 | 0.1524 | 0.6619 | 0.9767 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0100 | 0.1474 | 0.6453 | 0.9726 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0100 | 0.1427 | 0.6294 | 0.9683 | 0.9998 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 80 | 0.050 | 0.0100 | 0.2054 | 0.7919 | 0.9948 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0100 | 0.1984 | 0.7773 | 0.9936 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0100 | 0.1920 | 0.7629 | 0.9921 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 100 | 0.050 | 0.0100 | 0.2593 | 0.8746 | 0.9989 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0100 | 0.2505 | 0.8631 | 0.9985 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0100 | 0.2423 | 0.8516 | 0.9981 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 8 | 40 | 0.050 | 0.0100 | 0.1008 | 0.4662 | 0.8947 | 0.9973 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 |
| 0.075 | 0.0100 | 0.0972 | 0.4490 | 0.8819 | 0.9964 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0100 | 0.0940 | 0.4328 | 0.8688 | 0.9953 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 60 | 0.050 | 0.0100 | 0.1508 | 0.6565 | 0.9754 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0100 | 0.1451 | 0.6375 | 0.9705 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0100 | 0.1398 | 0.6192 | 0.9652 | 0.9998 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 80 | 0.050 | 0.0100 | 0.2032 | 0.7872 | 0.9944 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0100 | 0.1952 | 0.7702 | 0.9929 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0100 | 0.1880 | 0.7536 | 0.9911 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 100 | 0.050 | 0.0100 | 0.2565 | 0.8710 | 0.9988 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0100 | 0.2465 | 0.8575 | 0.9983 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0100 | 0.2373 | 0.8439 | 0.9977 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||

Table A9.
The power h(c1) for d = 4 and α = 0.05.
Table A9.
The power h(c1) for d = 4 and α = 0.05.
| 0.800 | 0.825 | 0.850 | 0.875 | 0.900 | 0.925 | 0.950 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 40 | 0.050 | 0.0500 | 0.2886 | 0.7445 | 0.9776 | 0.9998 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 |
| 0.075 | 0.0500 | 0.2844 | 0.7363 | 0.9755 | 0.9998 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0500 | 0.2805 | 0.7283 | 0.9732 | 0.9997 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 60 | 0.050 | 0.0500 | 0.3735 | 0.8684 | 0.9965 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0500 | 0.3681 | 0.8620 | 0.9959 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0500 | 0.3628 | 0.8556 | 0.9954 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 80 | 0.050 | 0.0500 | 0.4491 | 0.9321 | 0.9994 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0500 | 0.4426 | 0.9277 | 0.9993 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0500 | 0.4363 | 0.9232 | 0.9992 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 100 | 0.050 | 0.0500 | 0.5163 | 0.9648 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0500 | 0.5091 | 0.9619 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0500 | 0.5021 | 0.9590 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 6 | 40 | 0.050 | 0.0500 | 0.2868 | 0.7407 | 0.9766 | 0.9998 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 |
| 0.075 | 0.0500 | 0.2817 | 0.7306 | 0.9738 | 0.9998 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0500 | 0.2769 | 0.7206 | 0.9708 | 0.9997 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 60 | 0.050 | 0.0500 | 0.3711 | 0.8654 | 0.9962 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0500 | 0.3644 | 0.8574 | 0.9955 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0500 | 0.3580 | 0.8494 | 0.9948 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 80 | 0.050 | 0.0500 | 0.4463 | 0.9301 | 0.9994 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0500 | 0.4383 | 0.9245 | 0.9992 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0500 | 0.4306 | 0.9188 | 0.9990 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 100 | 0.050 | 0.0500 | 0.5131 | 0.9635 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0500 | 0.5042 | 0.9598 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0500 | 0.4956 | 0.9561 | 0.9998 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 7 | 40 | 0.050 | 0.0500 | 0.2849 | 0.7368 | 0.9755 | 0.9998 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 |
| 0.075 | 0.0500 | 0.2789 | 0.7247 | 0.9721 | 0.9997 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0500 | 0.2734 | 0.7130 | 0.9684 | 0.9996 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 60 | 0.050 | 0.0500 | 0.3686 | 0.8624 | 0.9959 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0500 | 0.3607 | 0.8527 | 0.9951 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0500 | 0.3532 | 0.8431 | 0.9941 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 80 | 0.050 | 0.0500 | 0.4433 | 0.9279 | 0.9993 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0500 | 0.4338 | 0.9212 | 0.9991 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0500 | 0.4249 | 0.9143 | 0.9989 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 100 | 0.050 | 0.0500 | 0.5098 | 0.9621 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0500 | 0.4993 | 0.9576 | 0.9998 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0500 | 0.4893 | 0.9530 | 0.9998 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 8 | 40 | 0.050 | 0.0500 | 0.2829 | 0.7328 | 0.9744 | 0.9998 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 |
| 0.075 | 0.0500 | 0.2762 | 0.7189 | 0.9703 | 0.9997 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0500 | 0.2699 | 0.7054 | 0.9659 | 0.9995 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 60 | 0.050 | 0.0500 | 0.3660 | 0.8592 | 0.9957 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0500 | 0.3570 | 0.8480 | 0.9946 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0500 | 0.3486 | 0.8368 | 0.9934 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 80 | 0.050 | 0.0500 | 0.4402 | 0.9258 | 0.9992 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0500 | 0.4294 | 0.9178 | 0.9990 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0500 | 0.4193 | 0.9097 | 0.9987 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 100 | 0.050 | 0.0500 | 0.5064 | 0.9607 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.0500 | 0.4943 | 0.9554 | 0.9998 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.0500 | 0.4830 | 0.9498 | 0.9997 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||

Table A10.
The power h(c1) for d = 4 and α = 0.1.
Table A10.
The power h(c1) for d = 4 and α = 0.1.
| 0.800 | 0.825 | 0.850 | 0.875 | 0.900 | 0.925 | 0.950 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 40 | 0.050 | 0.1000 | 0.4256 | 0.8471 | 0.9912 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 |
| 0.075 | 0.1000 | 0.4209 | 0.8412 | 0.9902 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.1000 | 0.4164 | 0.8353 | 0.9892 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 60 | 0.050 | 0.1000 | 0.5160 | 0.9291 | 0.9988 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.1000 | 0.5103 | 0.9251 | 0.9986 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.1000 | 0.5048 | 0.9211 | 0.9984 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 80 | 0.050 | 0.1000 | 0.5904 | 0.9664 | 0.9998 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.1000 | 0.5841 | 0.9639 | 0.9998 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.1000 | 0.5780 | 0.9613 | 0.9998 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 100 | 0.050 | 0.1000 | 0.6523 | 0.9838 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.1000 | 0.6458 | 0.9823 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.1000 | 0.6394 | 0.9807 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 6 | 40 | 0.050 | 0.1000 | 0.4235 | 0.8443 | 0.9907 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 |
| 0.075 | 0.1000 | 0.4178 | 0.8370 | 0.9894 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.1000 | 0.4123 | 0.8297 | 0.9881 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 60 | 0.050 | 0.1000 | 0.5135 | 0.9272 | 0.9987 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.1000 | 0.5065 | 0.9222 | 0.9985 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.1000 | 0.4998 | 0.9171 | 0.9982 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 80 | 0.050 | 0.1000 | 0.5876 | 0.9652 | 0.9998 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.1000 | 0.5798 | 0.9621 | 0.9998 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.1000 | 0.5723 | 0.9588 | 0.9997 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 100 | 0.050 | 0.1000 | 0.6494 | 0.9831 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.1000 | 0.6413 | 0.9812 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.1000 | 0.6334 | 0.9792 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 7 | 40 | 0.050 | 0.1000 | 0.4213 | 0.8415 | 0.9902 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 |
| 0.075 | 0.1000 | 0.4146 | 0.8327 | 0.9886 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.1000 | 0.4082 | 0.8240 | 0.9869 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 60 | 0.050 | 0.1000 | 0.5108 | 0.9253 | 0.9986 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.1000 | 0.5026 | 0.9192 | 0.9983 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.1000 | 0.4947 | 0.9130 | 0.9979 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 80 | 0.050 | 0.1000 | 0.5846 | 0.9640 | 0.9998 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.1000 | 0.5755 | 0.9601 | 0.9997 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.1000 | 0.5667 | 0.9562 | 0.9997 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 100 | 0.050 | 0.1000 | 0.6464 | 0.9824 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.1000 | 0.6367 | 0.9800 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.1000 | 0.6275 | 0.9776 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 8 | 40 | 0.050 | 0.1000 | 0.4191 | 0.8386 | 0.9897 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 |
| 0.075 | 0.1000 | 0.4114 | 0.8283 | 0.9878 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.1000 | 0.4042 | 0.8183 | 0.9857 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 60 | 0.050 | 0.1000 | 0.5081 | 0.9233 | 0.9985 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.1000 | 0.4987 | 0.9161 | 0.9981 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.1000 | 0.4898 | 0.9090 | 0.9977 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 80 | 0.050 | 0.1000 | 0.5817 | 0.9628 | 0.9998 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.1000 | 0.5711 | 0.9582 | 0.9997 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.1000 | 0.5612 | 0.9535 | 0.9996 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 100 | 0.050 | 0.1000 | 0.6432 | 0.9816 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 0.075 | 0.1000 | 0.6322 | 0.9788 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
| 0.100 | 0.1000 | 0.6217 | 0.9759 | 0.9999 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||
References
- Montgomery, D.C. Introduction to Statistical Quality Control; John Wiley and Sons Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, L.I.; Chen, K.S.; Chen, H.T. Statistical testing for assessing the performance of lifetime index of electronic components with exponential distribution. Int. J. Qual. Reliab. Manag. 2002, 19, 812–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, N. Progressive censoring methodology: An appraisal. TEST 2007, 16, 211–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwala, R. Progressive interval censoring: Some mathematical results with applications to inference. Commun. Stat. Theory Methods 2001, 30, 1921–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, N.; Aggarwala, R. Progressive Censoring: Theory, Methods and Applications. Birkhäuser: Boston, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.W.; Lee, W.C.; Lin, L.S.; Hong, M.L. Bayesian test of lifetime performance index for exponential products based on the progressively type II right censored sample. J. Quant. Manag. 2011, 8, 57–77. [Google Scholar]
- Sanjel, D.; Balakrishnan, N. A Laguerre polynomial approximation for a goodness-of-fit test for exponential distribution based on progressively censored data. J. Stat. Comput. Simul. 2008, 78, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.C.; Wu, J.W.; Hong, C.W. Assessing the lifetime performance index of products with the exponential distribution under progressively type II right censored samples. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2009, 231, 648–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.F. The performance assessment on the lifetime performance index of products following Chen lifetime distribution based on the progressive type I interval censored sample. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2018, 334, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.F.; Song, M.Z. The experimental design for the progressive type I interval censoring on the lifetime performance index of Chen lifetime distribution. Mathematics 2023, 11, 1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.F.; Chiang, K.Y. Assessment of the overall lifetime performance index of Weibull products in multiple production lines. Mathematics 2024, 12, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chengyuan, L.; Jelle, G.; Hein, P. Maximum Likelihood Estimation in the Additive Hazards Model. Biometrics 2023, 79, 1646–1656. [Google Scholar]
- Aït-Sahalia, Y.; Li, C.; Li, C. Maximum likelihood estimation of latent Markov models using closed-form approximations. J. Econom. 2024, 240, 105008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.C. Bayesian-inspired minimum contamination designs under a doublepair conditional effect model. Stat. Theory Relat. Fields 2023, 7, 336–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, L.; Xu, A.; Wang, Y.; Tang, Y. Remaining useful life prediction for two-phase degradation model based on reparameterized inverse Gaussian process. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2024; unpublished. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, H.; Bai, Y. Partially fixed bayesian additive regression trees. Stat. Theory Relat. Fields, 2024; unpublished. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casella, G.; Berger, R.L. Statistical Inference, 2nd ed.; Duxbury Press: Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Aarset, M.V. How to identify a bathtub hazard rate. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 1987, 36, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gail, M.H.; Gastwirth, J.L. A scale-free goodness of fit test for the exponential distribution based on the Gini Statistic. J. R. Stat. Soc. B 1978, 40, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caroni, C. The correct “ball bearings” data. Lifetime Data Anal. 2002, 8, 395–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).