A Time-Series Feature-Extraction Methodology Based on Multiscale Overlapping Windows, Adaptive KDE, and Continuous Entropic and Information Functionals
Abstract
1. Introduction
- The proposal of a methodology for feature extraction to transform a time series into a sequence of continuous entropic and information functionals.
- The introduction of a new algorithm to optimize the bandwidth of the Kernel Density Estimation, based on the Jensen–Shannon divergence, to balance the overfitting–underfitting trade-off across multiple PDFs.
- The implementation of the methodology for time-series anomaly detection, including:
- –
- A synthetic experiment, where a contextual collective anomaly is transformed into a new series where the anomaly can be simply detected with upper and lower control bands.
- –
- The final application in a real case of seizure detection using Scalp-EEG.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Theory Background
2.1.1. Kernel Density Estimation
2.1.2. Entropic Functionals and Fisher Non-Parametric Information
2.1.3. Jensen–Shannon Divergences Measure
2.2. Methodology
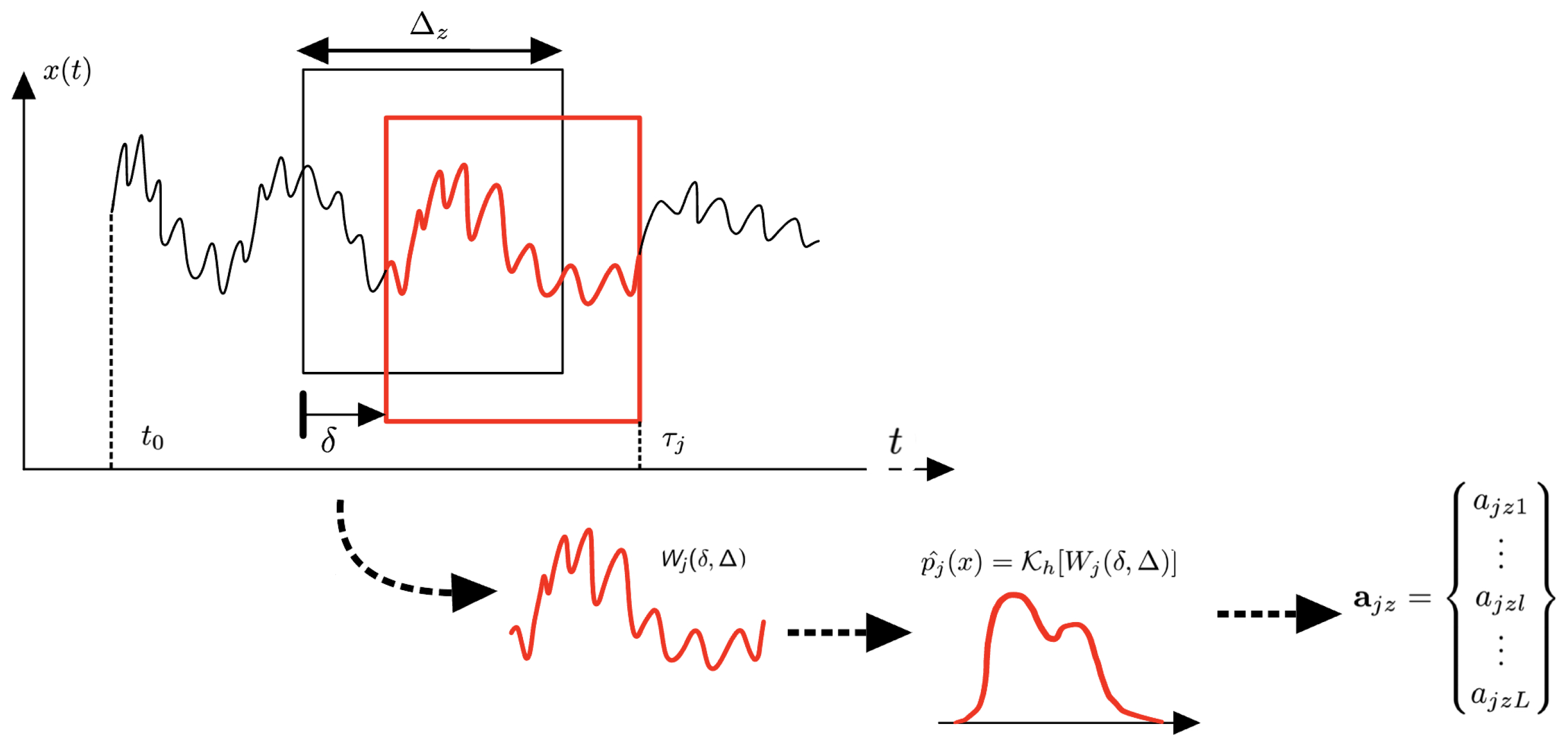
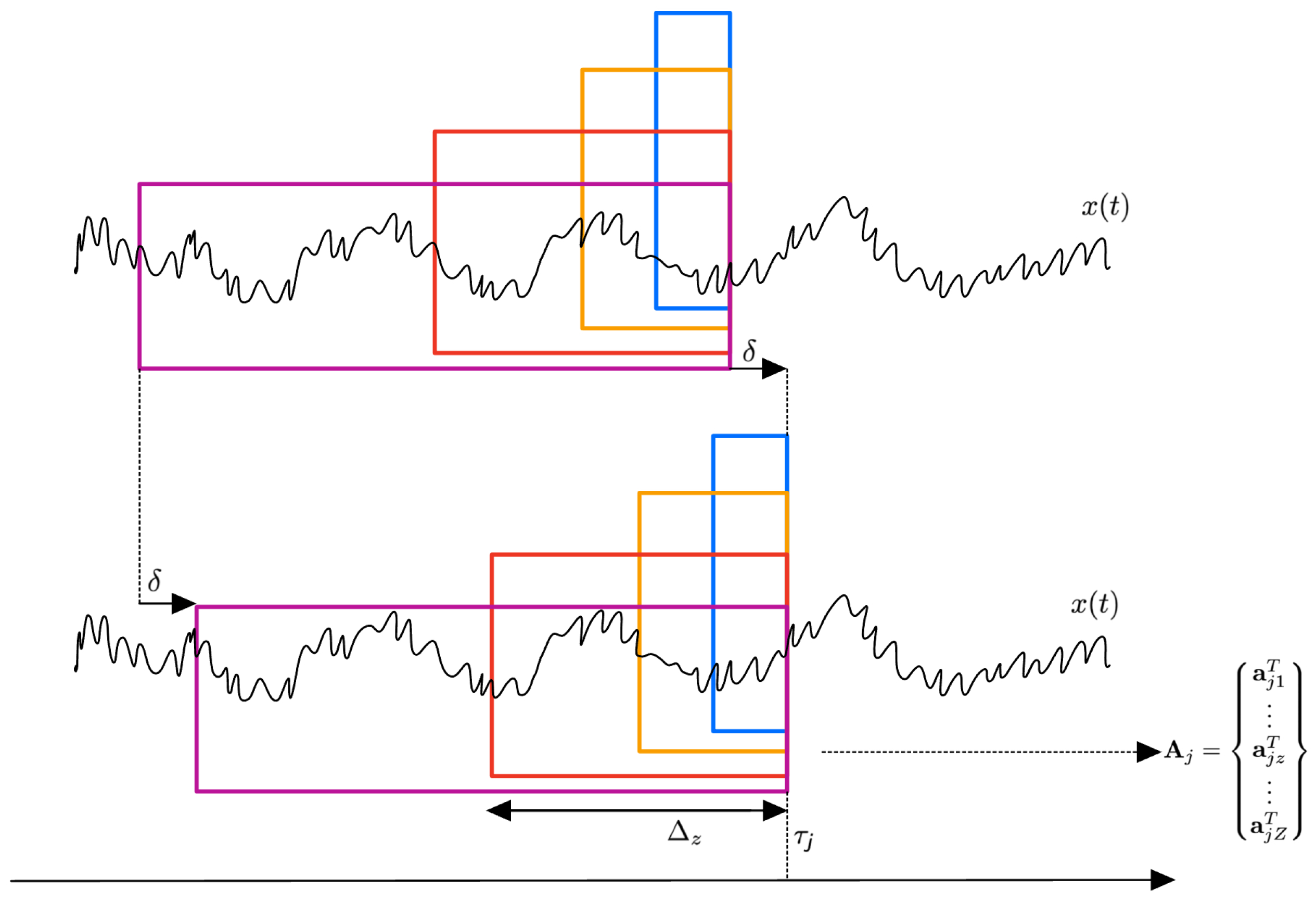
2.2.1. Overlapping Window Divisions
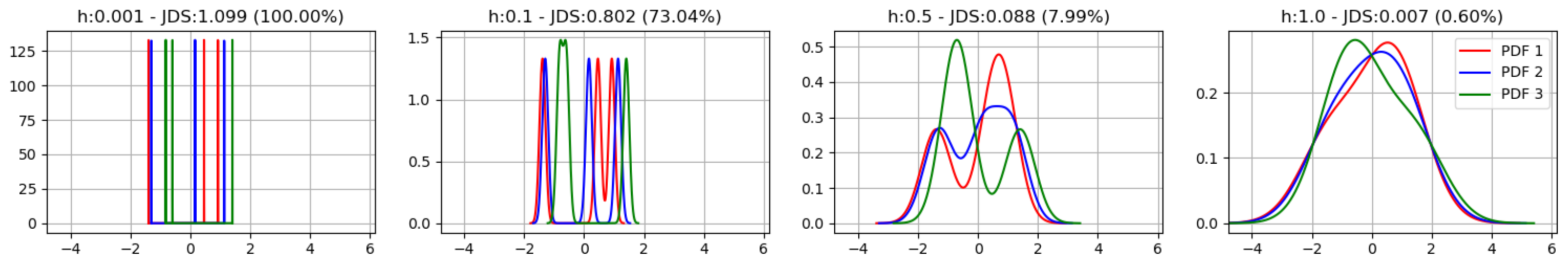
2.2.2. Jensen–Shannon Divergence H-Selection Algorithm
2.2.3. Time Dependent Multiscale Entropy
3. Results
3.1. Synthetic Signal Generation
3.2. Synthetic Experiment Settings
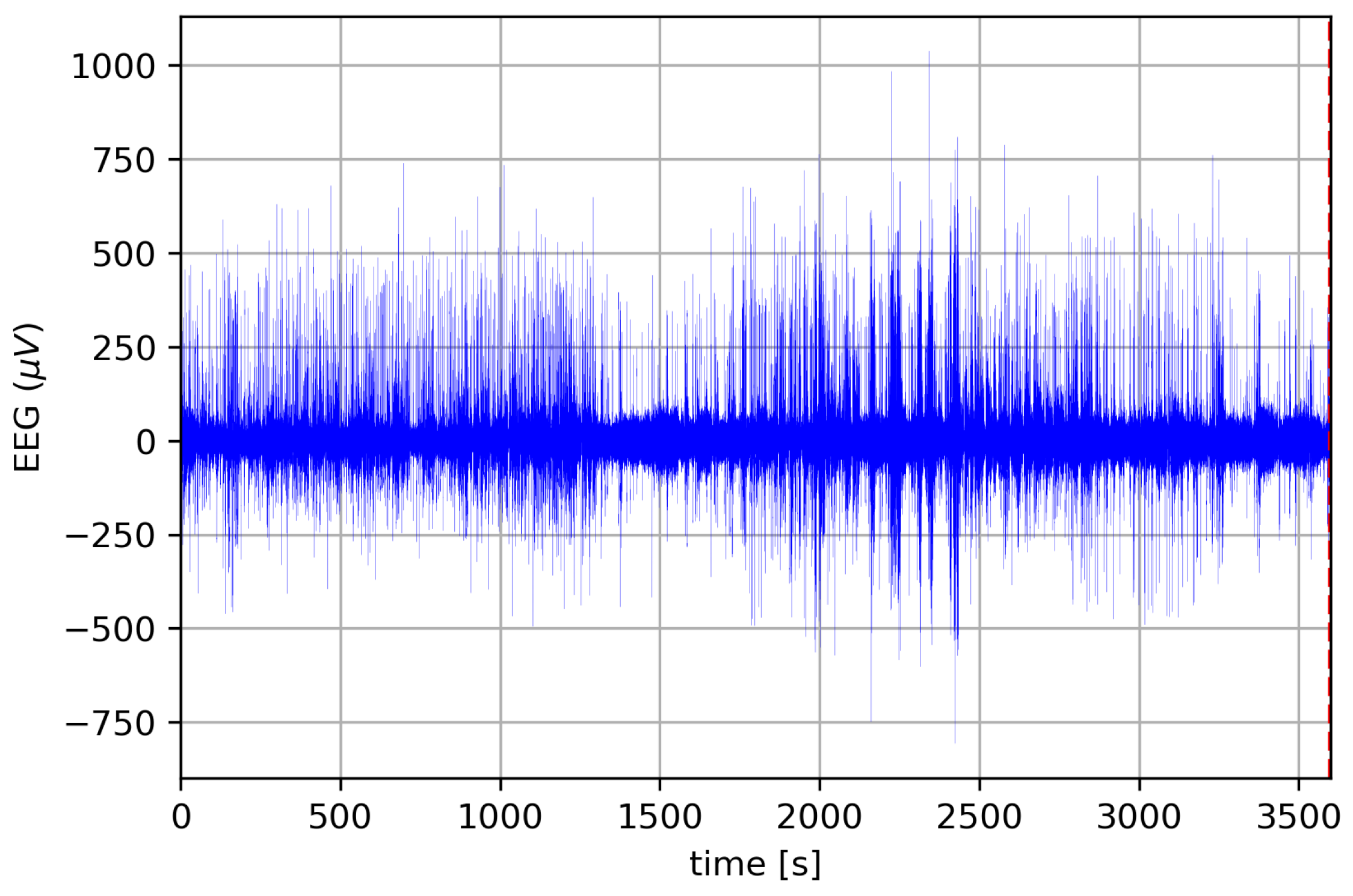
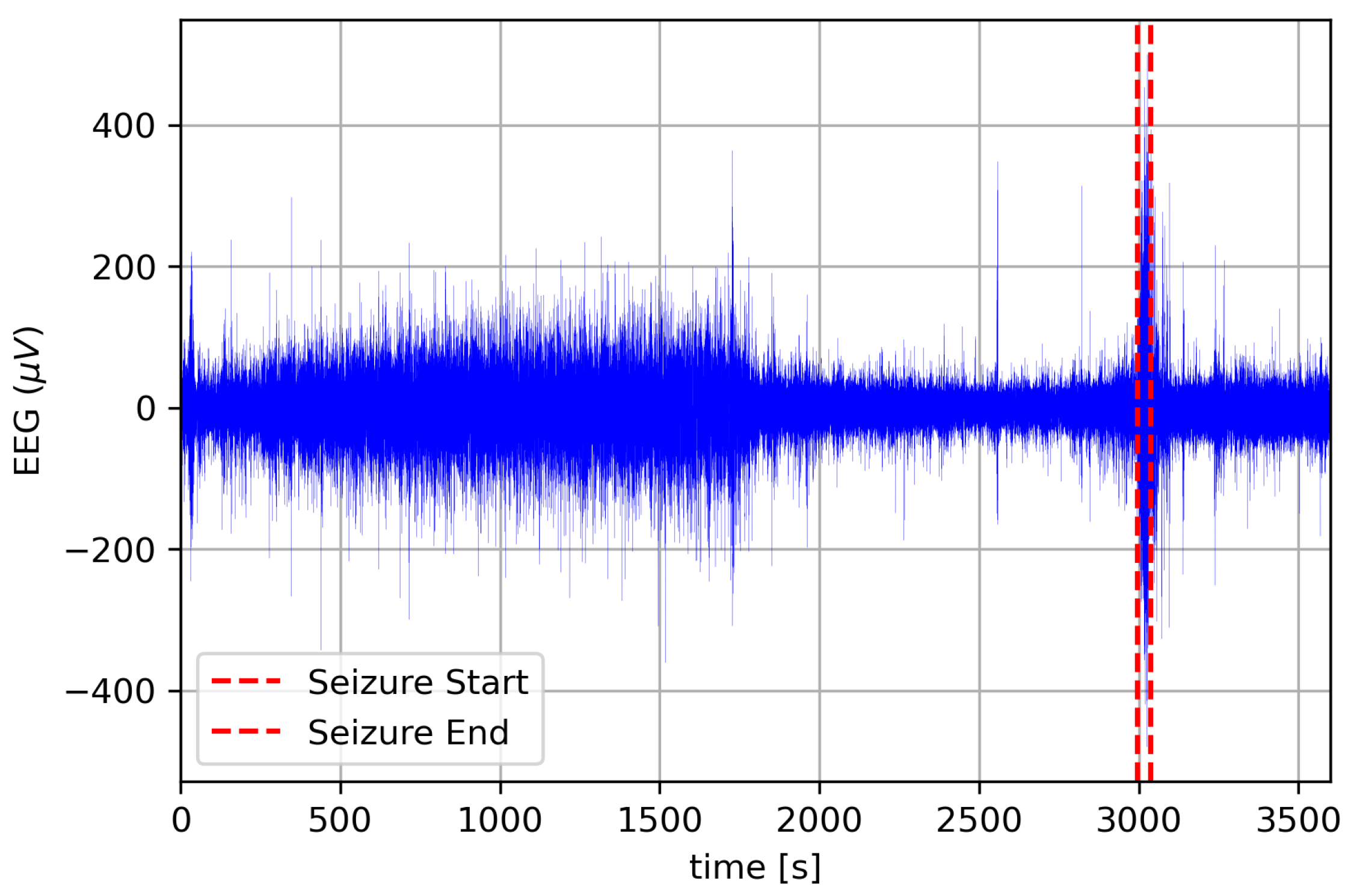
3.3. Real-Case Scenario Application: Scalp-EEG Seizure Detection
4. Discussion and Conclusions
5. Limitations and Future Works
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| i.i.d. | independently and identically distributed |
| EEG | Electroencephalogram |
| KDE | Kernel Density Estimation |
| TDE | Time-Dependent Entropy |
| PMF | Probability Mass Function |
| probability density function | |
| JSD | Jensen–Shannon Divergence |
| AMISE | Asymptotic Mean Integrated Squared Error |
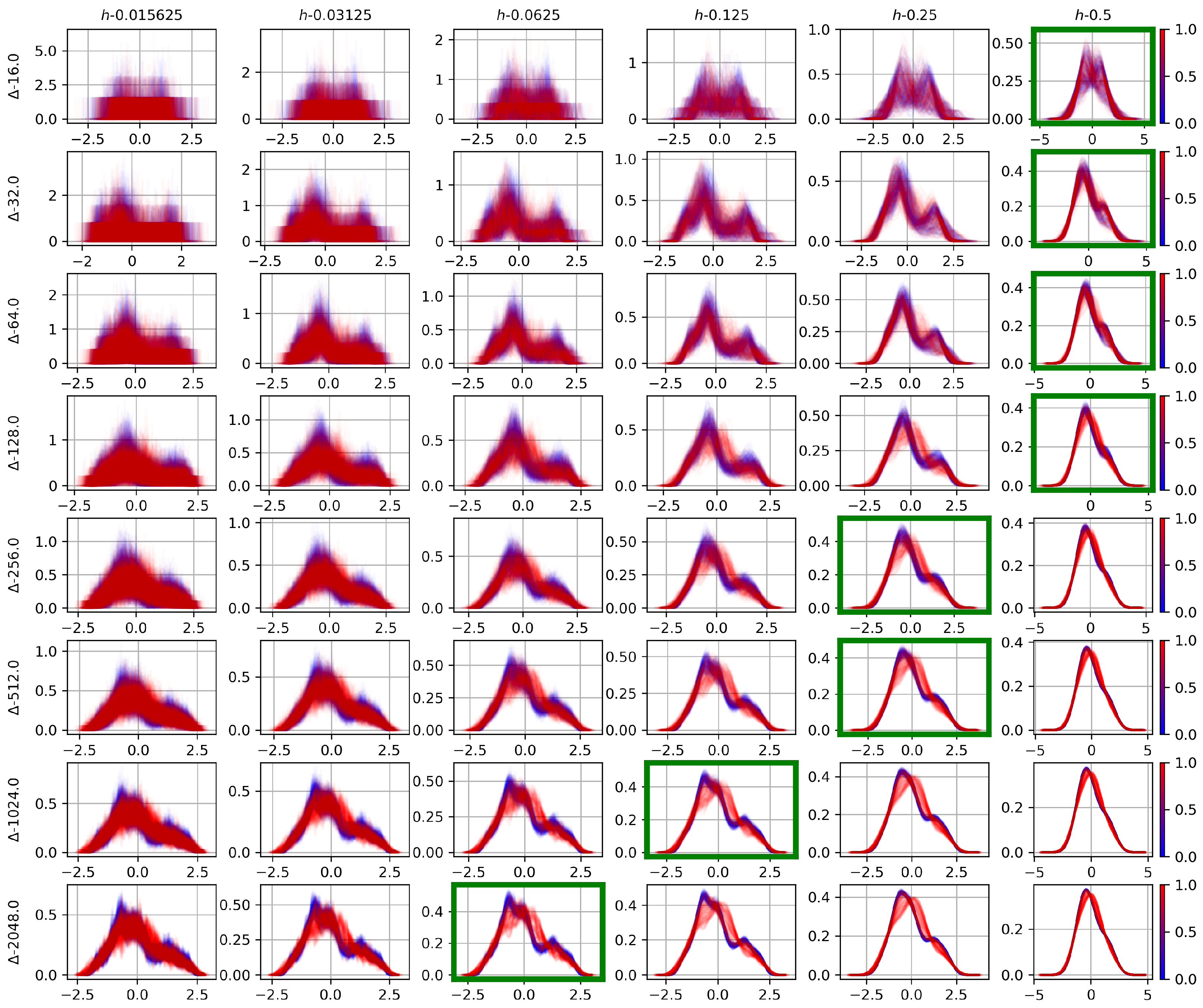
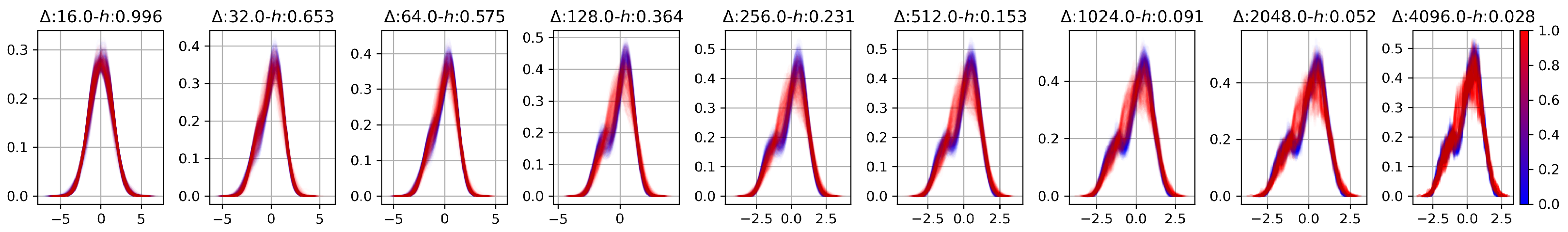
Appendix A. JSD Scores: Relation with h
Appendix B. Further Experiments
References
- Cover, T.M.; Thomas, J.A. Elements of Information Theory; Wiley-Interscience: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006; p. 774. [Google Scholar]
- Rényi, A. On Measures of Entropy and Information. In Proceedings of the Fourth Berkeley Symposium on Mathematical Statistics and Probability, Volume 1: Contributions to the Theory of Statistics, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 20 June–30 July 1960; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1961; Volume 4, pp. 547–562. [Google Scholar]
- Tsallis, C. Entropic Nonextensivity: A Possible Measure of Complexity. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2002, 13, 371–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.; Pachori, R.B. Epileptic Seizure Identification Using Entropy of FBSE Based EEG Rhythms. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2019, 53, 101569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosso, O.; Martin, M.; Figliola, A.; Keller, K.; Plastino, A. EEG Analysis Using Wavelet-Based Information Tools. J. Neurosci. Methods 2006, 153, 163–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mateos, D.M.; Guevara Erra, R.; Wennberg, R.; Perez Velazquez, J.L. Measures of Entropy and Complexity in Altered States of Consciousness. Cogn. Neurodyn. 2018, 12, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, M.T.; Pennini, F.; Plastino, A. Fisher’s Information and the Analysis of Complex Signals. Phys. Lett. A 1999, 256, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M.; Plastino, A.; Plastino, A. Tsallis-like Information Measures and the Analysis of Complex Signals. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2000, 275, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerga, J.; Saulig, N.; Stanković, L.; Seršić, D. Rule-Based EEG Classifier Utilizing Local Entropy of Time–Frequency Distributions. Mathematics 2021, 9, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkahtani, H.; Aldhyani, T.H.H.; Ahmed, Z.A.T.; Alqarni, A.A. Developing System-Based Artificial Intelligence Models for Detecting the Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder. Mathematics 2023, 11, 4698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezerianos, A.; Tong, S.; Thakor, N. Time-Dependent Entropy Estimation of EEG Rhythm Changes Following Brain Ischemia. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2003, 31, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalimeri, M.; Papadimitriou, C.; Balasis, G.; Eftaxias, K. Dynamical Complexity Detection in Pre-Seismic Emissions Using Nonadditive Tsallis Entropy. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2008, 387, 1161–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guignard, F.; Laib, M.; Amato, F.; Kanevski, M. Advanced Analysis of Temporal Data Using Fisher-Shannon Information: Theoretical Development and Application in Geosciences. Front. Earth Sci. 2020, 8, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conejero, J.A.; Velichko, A.; Garibo-i-Orts, Ò.; Izotov, Y.; Pham, V.T. Exploring the Entropy-Based Classification of Time Series Using Visibility Graphs from Chaotic Maps. Mathematics 2024, 12, 938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Qiu, T.; Ding, Y.; Gao, S.; Zhao, N.; Liu, F.; Zhou, X.; Gururajan, R. Detecting Depression Using Single-Channel EEG and Graph Methods. Mathematics 2022, 10, 4177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.; Yi, J.; Park, C.; Yoon, S. Deep Learning for Anomaly Detection in Time-Series Data: Review, Analysis, and Guidelines. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 120043–120065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandola, V.; Banerjee, A.; Kumar, V. Anomaly Detection: A Survey. Acm Comput. Surv. 2009, 41, 1–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bently, D.E.; Hatch’Charles, T. Fundamentals of Rotating Machinery Diagnostics. Mech. Eng.-CIME 2003, 125, 53–54. [Google Scholar]
- Eftaxias, K.; Minadakis, G.; Athanasopoulou, L.; Kalimeri, M.; Potirakis, S.M.; Balasis, G. Are Epileptic Seizures Quakes of the Brain? An Approach by Means of Nonextensive Tsallis Statistics. arXiv 2011, arXiv:1110.2169. [Google Scholar]
- Farashi, S. A Multiresolution Time-Dependent Entropy Method for QRS Complex Detection. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2016, 24, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Yang, B.; Huang, L. Feature Extraction of EEG Signals Using Power Spectral Entropy. In Proceedings of the 2008 International Conference on BioMedical Engineering and Informatics, Sanya, China, 27–30 May 2008; Volume 2, pp. 435–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocak, H. Automatic Detection of Epileptic Seizures in EEG Using Discrete Wavelet Transform and Approximate Entropy. Expert Syst. Appl. 2009, 36, 2027–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Lin, C.T. Inherent Fuzzy Entropy for the Improvement of EEG Complexity Evaluation. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2018, 26, 1032–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Ding, W.; Wang, Y.K.; Hussain, F.K.; Al-Jumaily, A.; Lin, C.T. Effects of Repetitive SSVEPs on EEG Complexity Using Multiscale Inherent Fuzzy Entropy. Neurocomputing 2020, 389, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, J.; Li, C.; Li, H.; Cao, R.; Wang, B.; Han, X.; Chen, J. The Detection of Epileptic Seizure Signals Based on Fuzzy Entropy. J. Neurosci. Methods 2015, 243, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patidar, S.; Panigrahi, T. Detection of Epileptic Seizure Using Kraskov Entropy Applied on Tunable-Q Wavelet Transform of EEG Signals. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2017, 34, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambom, A.Z.; Dias, R. A Review of Kernel Density Estimation with Applications to Econometrics. Int. Econom. Rev. 2013, 5, 20–42. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Moreno, P.; Yanez, R.; Dehesa, J. Discrete Densities and Fisher Information. In Difference Equations and Applications; Bahçesehir University Press: Istanbul, Turkey, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Tabass, M.S.; Borzadaran, G.R.M.; AmiNi, M. Renyi Entropy in Continuous Case Is Not the Limit of Discrete Case. Math. Sci. Appl. E-Notes 2016, 4, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telesca, L.; Lovallo, M. On the Performance of Fisher Information Measure and Shannon Entropy Estimators. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2017, 484, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, A.; Oryshchenko, V. Kernel Density Estimation for Time Series Data. Int. J. Forecast. 2012, 28, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, E.; Schuetz, A.; Stewart, W.F.; Sun, J. Using Recurrent Neural Network Models for Early Detection of Heart Failure Onset. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 2017, 24, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoeb, A.H.; Guttag, J.V. Application of Machine Learning To Epileptic Seizure Detection. In Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Machine Learning, ICML 2019, Long Beach, CA, USA, 9–15 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Izenman, A.J. Review Papers: Recent Developments in Nonparametric Density Estimation. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1991, 86, 205–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Scott, D.W. Nonparametric Density Estimation for High-dimensional Data—Algorithms and Applications. WIREs Comput. Stat. 2019, 11, e1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parzen, E. On Estimation of a Probability Density Function and Mode. Ann. Math. Stat. 1962, 33, 1065–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raykar, V.C.; Duraiswami, R. Fast Optimal Bandwidth Selection for Kernel Density Estimation. In Proceedings of the 2006 SIAM International Conference on Data Mining (SDM), Bethesda, MD, USA, 20–22 April 2006; pp. 524–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheather, S.J.; Jones, M.C. A Reliable Data-Based Bandwidth Selection Method for Kernel Density Estimation. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B (Methodol.) 1991, 53, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcin, M. Complexity Measure, Kernel Density Estimation, Bandwidth Selection, and the Efficient Market Hypothesis. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.13123. [Google Scholar]
- Tsallis, C.; Baldovin, F.; Cerbino, R.; Pierobon, P. Introduction to Nonextensive Statistical Mechanics and Thermodynamics. arXiv 2003, arXiv:cond-mat/0309093. [Google Scholar]
- Amigó, J.M.; Balogh, S.G.; Hernández, S. A Brief Review of Generalized Entropies. Entropy 2018, 20, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsallis, C.; Mendes, R.; Plastino, A. The Role of Constraints within Generalized Nonextensive Statistics. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 1998, 261, 534–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignat, C.; Bercher, J.F. Analysis of Signals in the Fisher–Shannon Information Plane. Phys. Lett. A 2003, 312, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bercher, J.F. On Escort Distributions, Q-gaussians and Fisher Information. AIP Conf. Proc. 2011, 1305, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J. Divergence Measures Based on the Shannon Entropy. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1991, 37, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endres, D.; Schindelin, J. A New Metric for Probability Distributions. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2003, 49, 1858–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffreys, S.H.; Jeffreys, S.H. The Theory of Probability, 3rd ed.; Oxford Classic Texts in the Physical Sciences; Oxford University Press: Oxford, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Fisher, R.S.; van Emde Boas, W.; Blume, W.; Elger, C.; Genton, P.; Lee, P.; Engel, J. Epileptic Seizures and Epilepsy: Definitions Proposed by the International League Against Epilepsy (ILAE) and the International Bureau for Epilepsy (IBE). Epilepsia 2005, 46, 470–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, V. Outlier Detection with One-class Kernel Fisher Discriminants. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2004; Volume 17. [Google Scholar]







| 4096 | |
| 256 | |
| 0.001 |
| 440.0, 220.0, 22.0 | |
| 1.5, 2.0, 1.0 | |
| 440.0, 220.0, 22.0, 50.0, 1000.0 | |
| 1.0, 1.0, 0.5, 2.0, 0.5 | |
| 0.5 |
| 256 | |
| 256 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Squicciarini, A.; Valero Toranzo, E.; Zarzo, A. A Time-Series Feature-Extraction Methodology Based on Multiscale Overlapping Windows, Adaptive KDE, and Continuous Entropic and Information Functionals. Mathematics 2024, 12, 2396. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12152396
Squicciarini A, Valero Toranzo E, Zarzo A. A Time-Series Feature-Extraction Methodology Based on Multiscale Overlapping Windows, Adaptive KDE, and Continuous Entropic and Information Functionals. Mathematics. 2024; 12(15):2396. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12152396
Chicago/Turabian StyleSquicciarini, Antonio, Elio Valero Toranzo, and Alejandro Zarzo. 2024. "A Time-Series Feature-Extraction Methodology Based on Multiscale Overlapping Windows, Adaptive KDE, and Continuous Entropic and Information Functionals" Mathematics 12, no. 15: 2396. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12152396
APA StyleSquicciarini, A., Valero Toranzo, E., & Zarzo, A. (2024). A Time-Series Feature-Extraction Methodology Based on Multiscale Overlapping Windows, Adaptive KDE, and Continuous Entropic and Information Functionals. Mathematics, 12(15), 2396. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12152396








