H∞ Differential Game of Nonlinear Half-Car Active Suspension via Off-Policy Reinforcement Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
- To enhance the vibration control performance of active suspension systems, a more realistic half-car suspension dynamics model is established, and a nonlinear H∞ differential game method is proposed;
- A neural network-based approach is utilized to derive an off-policy RL algorithm for solving the HJI equation, providing an optimal solution without requiring any model parameters;
- A hardware-in-the-loop simulation platform is developed, validating the effectiveness and feasibility of the proposed method through numerical simulations.
2. Mathematical Model
3. Methodology
3.1. H∞ Differential Game
3.2. Off-Policy RL Algorithm
| Algorithm 1. Off-policy RL algorithm for nonlinear active suspension H∞ differential game. |
| Step 1: set , initialize parameters and , apply any reachable and , and collect data ; |
| Step 2: Solve the Equation (32) to obtain NN weight coefficients and if the Equation (33) holds; |
| Step 3: Update the actor , and critic using (15) and (27); |
| Step 4: Set , repeat steps 2–3 until ( is a small positive number). |
4. Numerical Simulation
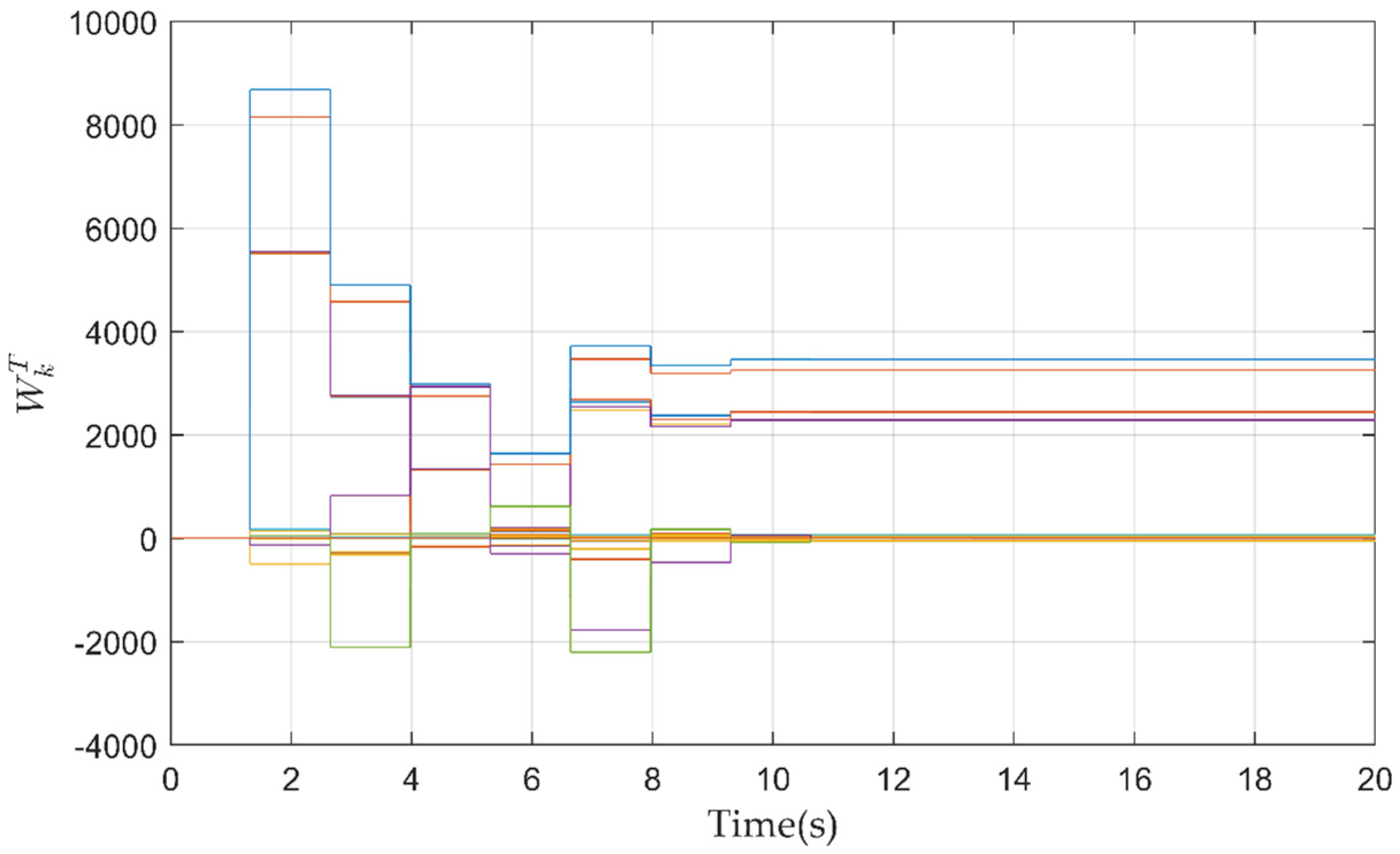
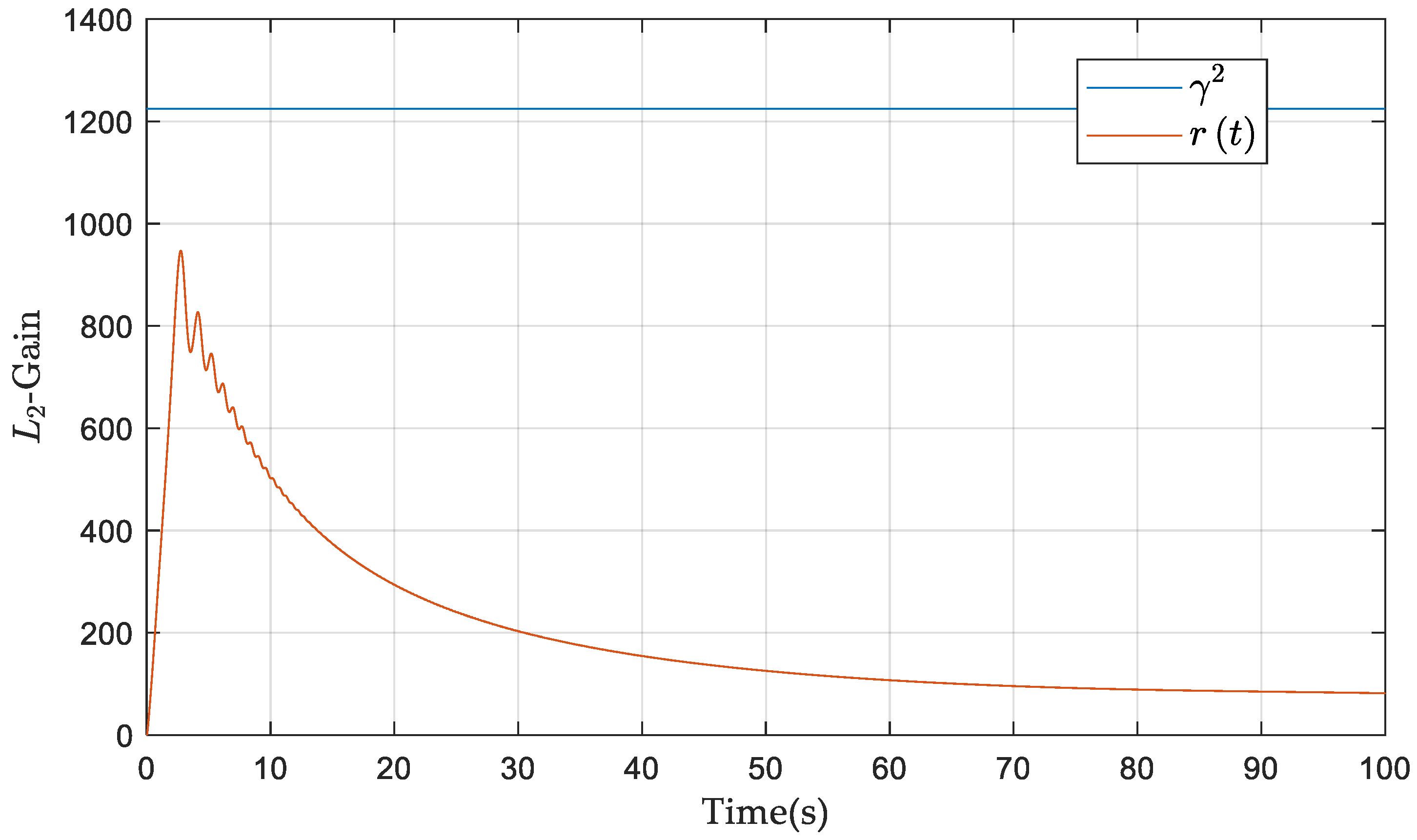
4.1. Implementation of Algorithm 1
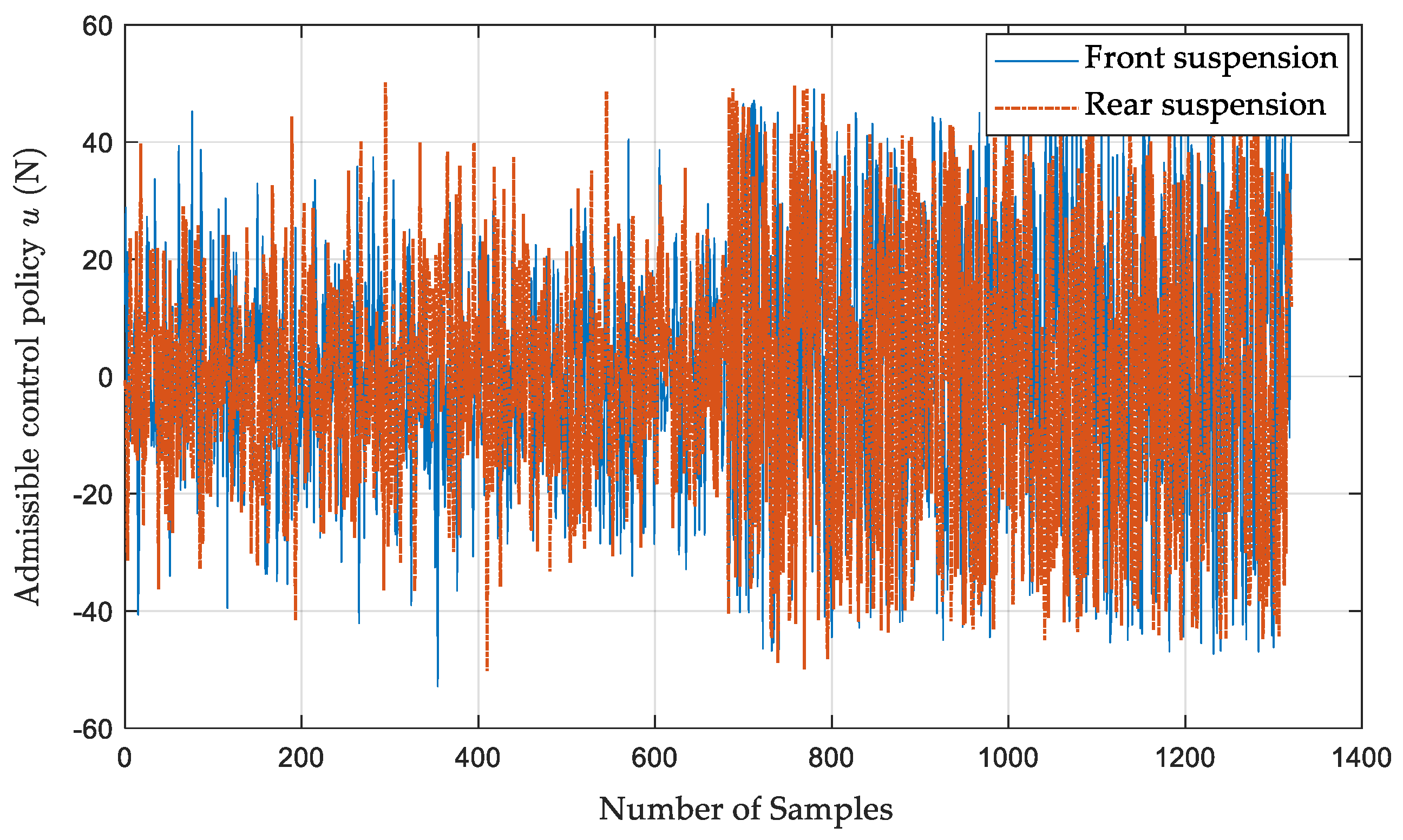
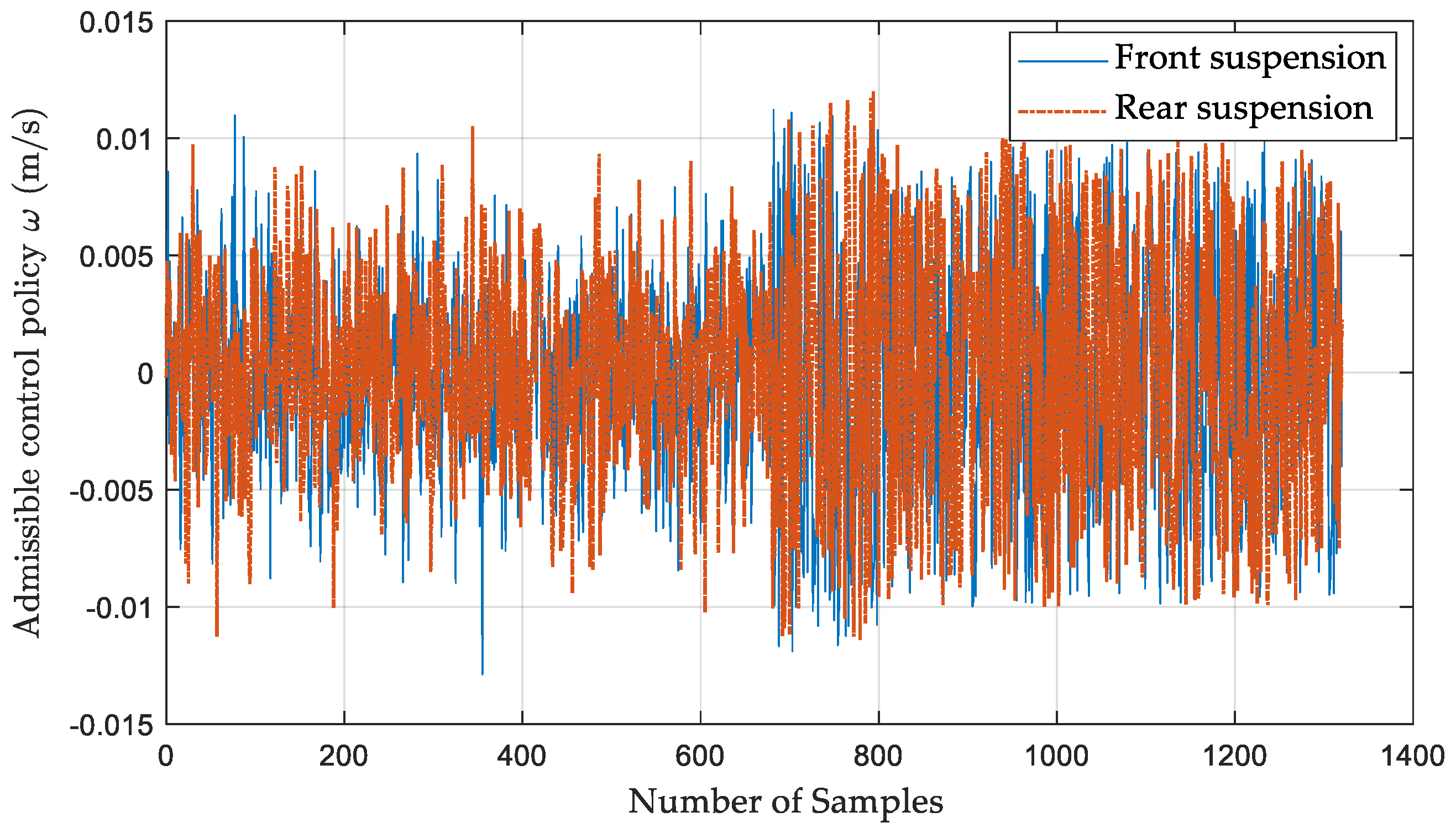
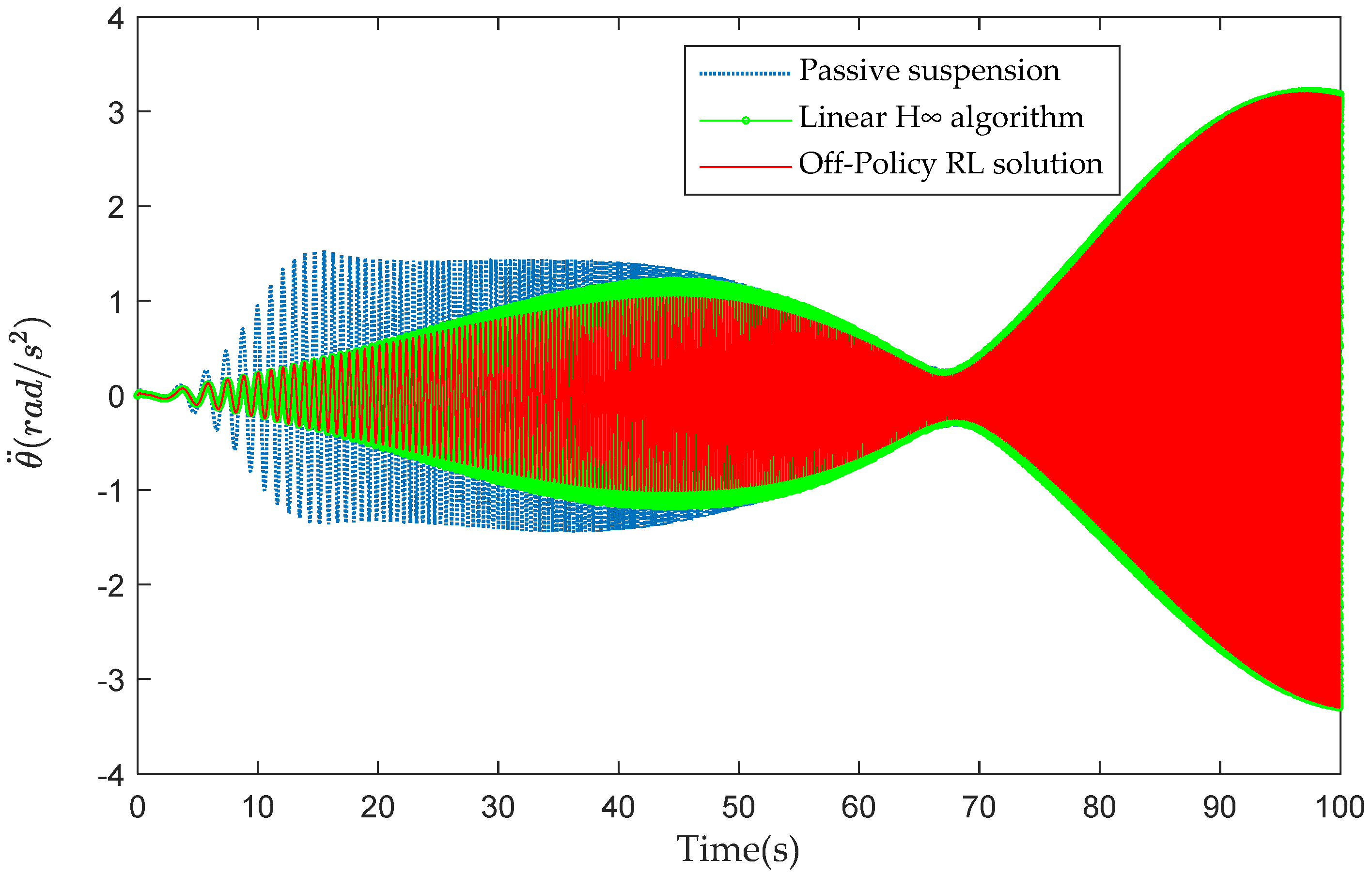
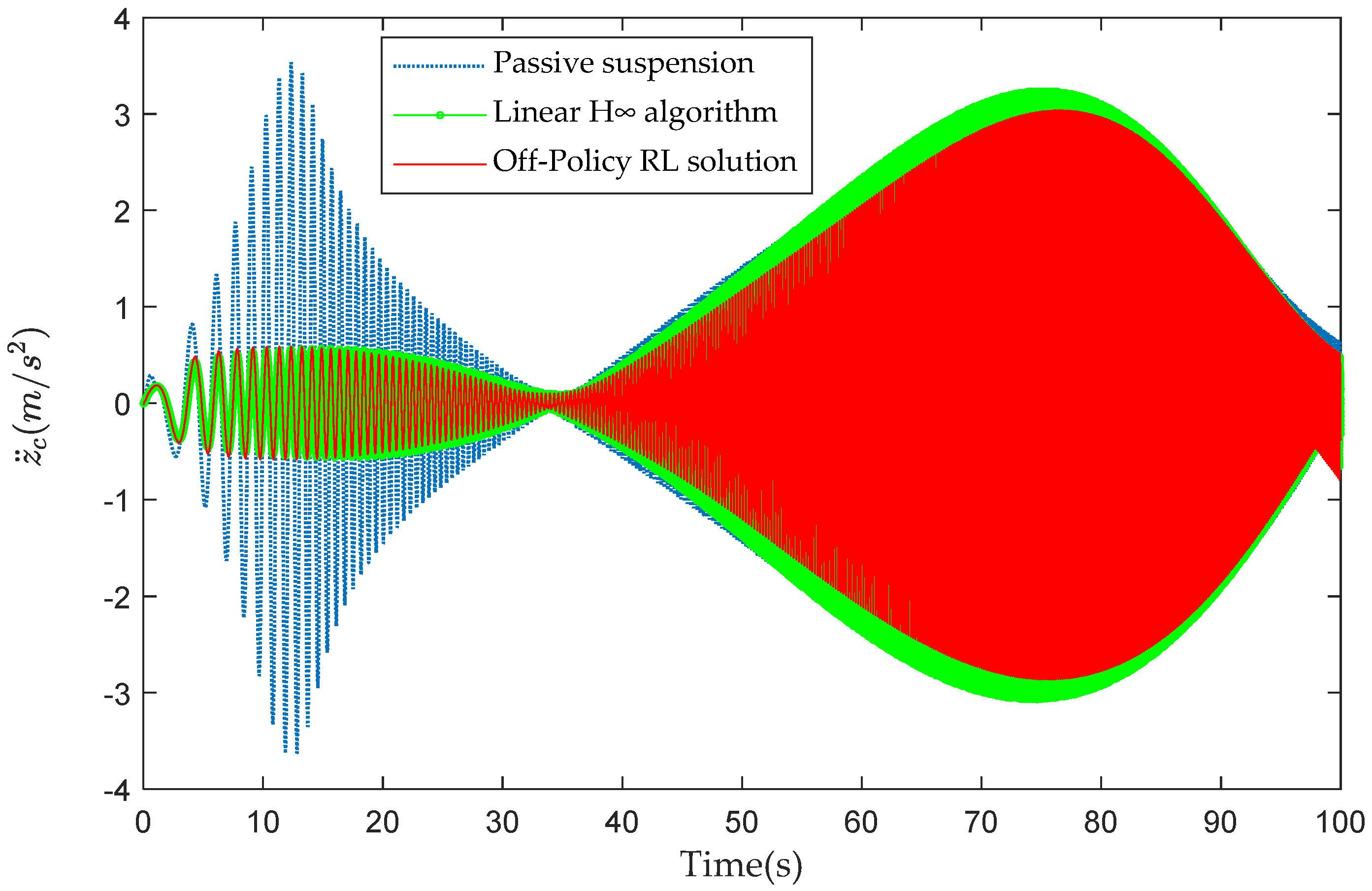
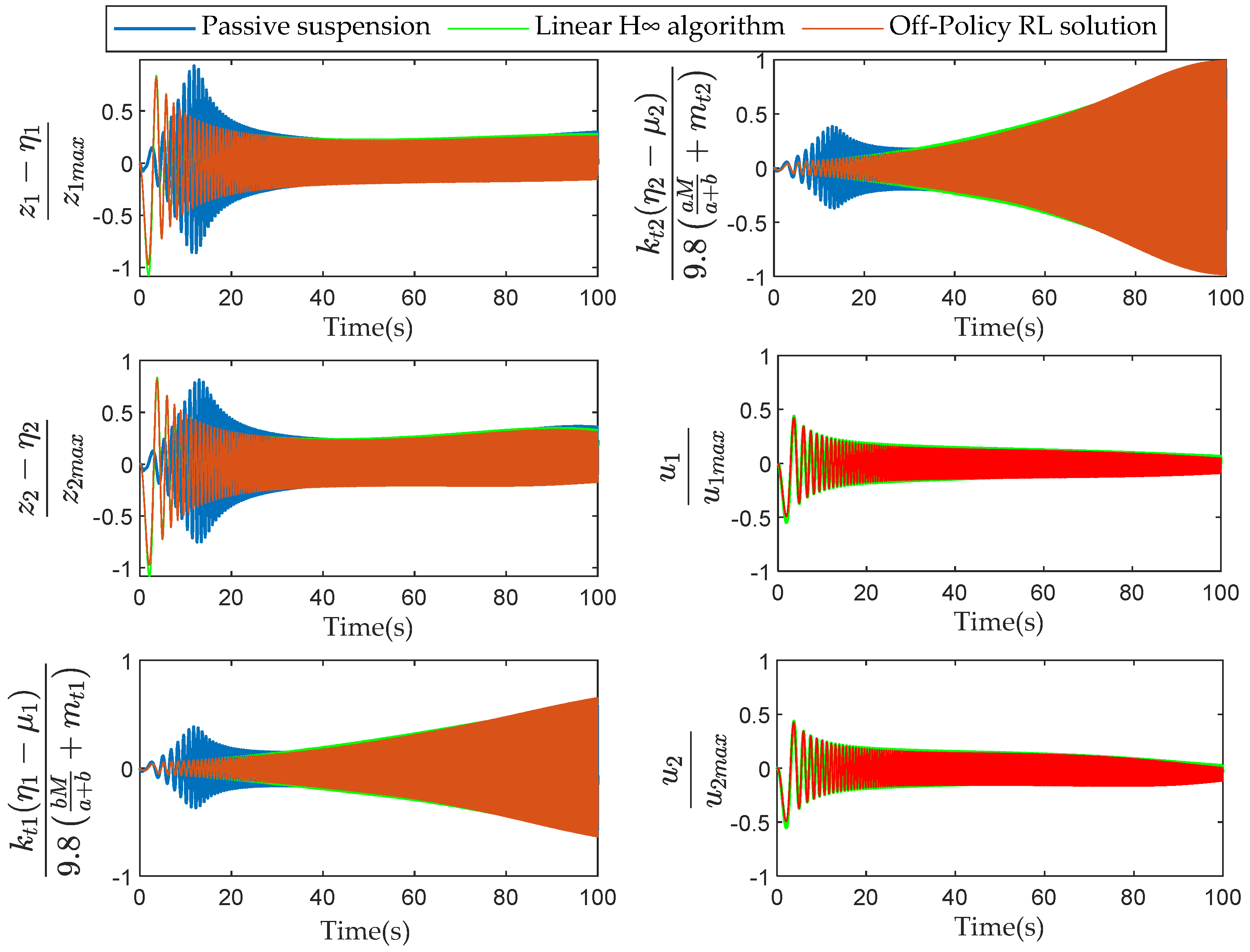
4.2. Vibration Control Performance Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, M.; Evangelou, S.A.; Dini, D. Advances in Active Suspension Systems for Road Vehicles. Engineering 2023, 33, 160–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Zhang, C.; Sun, W. Fault-tolerant multiplayer tracking control for autonomous vehicle via model-free adaptive dynamic programming. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 2022, 72, 1395–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Chen, Z.; Song, H.; Dong, Y. Model predictive control for speed-dependent active suspension system with road preview information. Sensors 2024, 24, 2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, Y.; Hu, C. An adaptive controller design for nonlinear active air suspension systems with uncertainties. Mathematics 2023, 11, 2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Yang, X.; Shi, P.; Wu, L. Fuzzy control of nonlinear electromagnetic suspension systems. Mechatronics 2014, 24, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humaidi, A.J.; Sadiq, M.E.; Abdulkareem, A.I.; Ibraheem, I.K.; Azar, A.T. Adaptive backstepping sliding mode control design for vibration suppression of earth-quaked building supported by magneto-rheological damper. J. Low Freq. Noise Vib. Act. Control 2022, 41, 768–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Sun, M.; Wang, R.; Zhu, C.; Zeng, Q. Finite-Time Neural Control of Stochastic Active Electromagnetic Suspension System with Actuator Failure. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 2024, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Yim, S. Design of Static Output Feedback Suspension Controllers for Ride Comfort Improvement and Motion Sickness Reduction. Processes 2024, 12, 968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Lam, J.; Cheung, K.C. Multi-objective control for active vehicle suspension with wheelbase preview. J. Sound Vib. 2014, 333, 5269–5282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Z. Robust state-feedback control design for active suspension system with time-varying input delay and wheelbase preview information. J. Frankl. Inst. 2019, 356, 1899–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Si, Y.; Sun, W. Ride comfort oriented integrated design of preview active suspension control and longitudinal velocity planning. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2024, 208, 110992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Guevara, D.; Favela-Contreras, A.; Beltran-Carbajal, F.; Sotelo, C.; Sotelo, D. A Differential Flatness-Based Model Predictive Control Strategy for a Nonlinear Quarter-Car Active Suspension System. Mathematics 2023, 11, 1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Zhang, J.; Sun, W. Robust saturated fault-tolerant control for active suspension system via partial measurement information. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2023, 191, 110116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, W.; Li, K.; Chen, Q.; Liu, G. Mixed FTS/H∞ control of vehicle active suspensions with shock road disturbance. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 2019, 57, 841–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Jing, X.; Lam, H.K.; Shi, P. Fuzzy sampled-data control for uncertain vehicle suspension systems. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2013, 44, 1111–1126. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, W.; Gao, H.; Kaynak, O. Finite frequency H∞ control for vehicle active suspension systems. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2010, 19, 416–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogruer, C.U. Constrained model predictive control of a vehicle suspension using Laguerre polynomials. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2020, 234, 1253–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeili, J.S.; Akbari, A.; Farnam, A.; Azad, N.L.; Crevecoeur, G. Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Control of Active Vehicle Suspension Based on H2 and H∞ Synthesis. Machines 2023, 11, 1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Zhao, X.; Karimi, H.R.; Wang, D.; Zong, G. Adaptive optimal control for unknown constrained nonlinear systems with a novel quasi-model network. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2021, 33, 2867–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Wang, J.; Pan, H. Approximation-free prespecified time bionic reliable control for vehicle suspension. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2023, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.C.; Xin, Y. Data-driven H∞ vibration control design and verification for an active suspension system with unknown pseudo-drift dynamics. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2023, 125, 107397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazouchi, M.; Yang, Y.; Modares, H. Data-driven dynamic multiobjective optimal control: An aspiration-satisfying reinforcement learning approach. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2021, 33, 6183–6193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Li, K.; Liu, S.; Jing, H. Model-Free H∞ Output Feedback Control of Road Sensing in Vehicle Active Suspension Based on Reinforcement Learning. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 2023, 145, 061003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Liao, X.; Dong, T. Event-driven optimal control for uncertain nonlinear systems with external disturbance via adaptive dynamic programming. Neurocomputing 2018, 281, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.N.; Luo, B. Neural Network Based Online Simultaneous Policy Update Algorithm for Solving the HJI Equation in Nonlinear H∞ Control. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2012, 23, 1884–1895. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Luo, B.; Wu, H.N.; Huang, T. Off-policy reinforcement learning for H∞ control design. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2014, 45, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiumarsi, B.; Lewis, F.L.; Jiang, Z.P. H∞ control of linear discrete-time systems: Off-policy reinforcement learning. Automatica 2017, 78, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.N.; Luo, B. Simultaneous policy update algorithms for learning the solution of linear continuous-time H∞ state feedback control. Inf. Sci. 2013, 222, 472–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valadbeigi, A.P.; Sedigh, A.K.; Lewis, F.L. H∞ Static Output-Feedback Control Design for Discrete-Time Systems Using Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2019, 31, 396–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Zhao, Z.; Gao, H. Saturated adaptive robust control for active suspension systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2012, 60, 3889–3896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Du, H.; Feng, Z.; Ning, D.; Li, W.; Sun, S.; Tu, L.; Wei, J. Singular system-based approach for active vibration control of vehicle seat suspension. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 2020, 142, 091003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
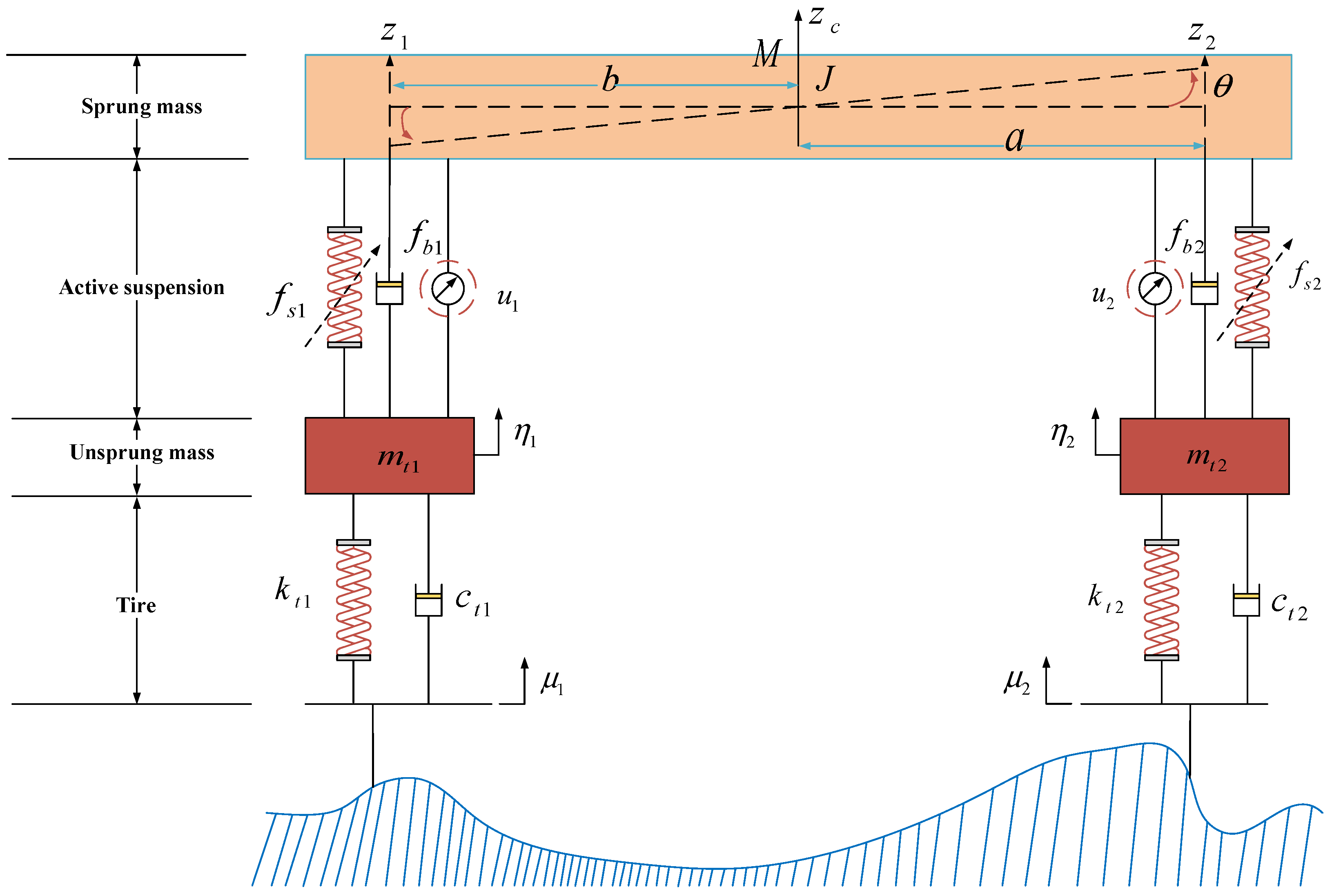





| Symbol | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Sprung mass | |
| Pitch moment of inertia | |
| , | Unsprung mass |
| Distance from front axle to center of mass | |
| Distance from rear axle to center of mass | |
| , | Tire stiffness |
| , | Suspension spring linear stiffness |
| , , , | Suspension spring nonlinear stiffness |
| , | Suspension hydraulic linear damping |
| , | Suspension hydraulic nonlinear damping |
| , | Active control force |
| Vertical displacement of the center of mass | |
| Pitch angle | |
| , | Vertical displacement of unsprung mass |
| , | Road disturbance |
| Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 | 1.25 | ||
| 910 | 1.45 | ||
| 30 | 10,000 | ||
| 40 | 10,000 | ||
| 1000 | 1000 | ||
| 20,000 | 20,000 | ||
| 1000 | 1000 | ||
| 100,000 | 2000 | ||
| 100,000 | 2000 | ||
| 0.1 | 200 | ||
| 0.1 | 200 |
| Method | (m/s2) | (rad/s2) | (N) | (N) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Passive suspension | 1.371 | 1.081 | —— | —— |
| Linear H∞ algorithm | 1.228 | 1.004 | 253.6 | 255.1 |
| Off-Policy RL solution | 1.131 | 0.964 | 247.2 | 249.2 |
| Method | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Passive suspension | 0.9301 | 0.8131 | 0.5832 | 0.9135 | —— | —— |
| Linear H∞ algorithm | 1.076 | 1.082 | 0.6153 | 0.899 | 0.5484 | 0.5513 |
| Off-Policy RL solution | 0.9725 | 0.9735 | 0.6514 | 0.9894 | 0.4921 | 0.4928 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, G.; Deng, J.; Zhou, T.; Liu, S. H∞ Differential Game of Nonlinear Half-Car Active Suspension via Off-Policy Reinforcement Learning. Mathematics 2024, 12, 2665. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12172665
Wang G, Deng J, Zhou T, Liu S. H∞ Differential Game of Nonlinear Half-Car Active Suspension via Off-Policy Reinforcement Learning. Mathematics. 2024; 12(17):2665. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12172665
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Gang, Jiafan Deng, Tingting Zhou, and Suqi Liu. 2024. "H∞ Differential Game of Nonlinear Half-Car Active Suspension via Off-Policy Reinforcement Learning" Mathematics 12, no. 17: 2665. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12172665
APA StyleWang, G., Deng, J., Zhou, T., & Liu, S. (2024). H∞ Differential Game of Nonlinear Half-Car Active Suspension via Off-Policy Reinforcement Learning. Mathematics, 12(17), 2665. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12172665






