A Simplified Two-Fluid Model Based on Equilibrium Closure for a Dilute Dispersion of Small Particles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
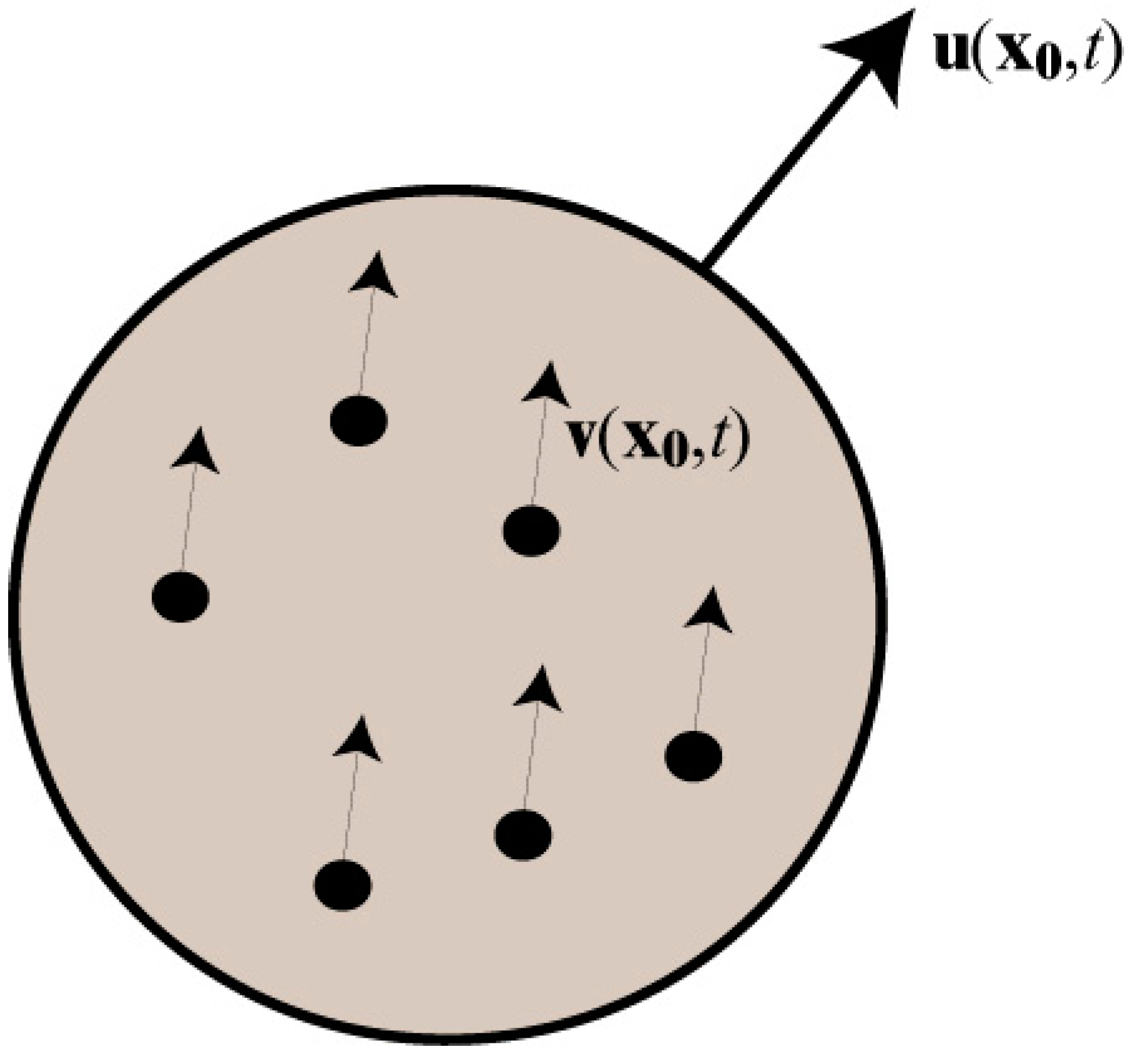
2. Theoretical Framework and Ensemble Average
3. Mathematical Formulation
3.1. Particle Velocity Field
Particle Velocity Field at Equilibrium
3.2. Particle Angular Velocity Field
Particle Angular Velocity Field at Equilibrium
3.3. Simple Estimates
3.4. Conservation Equations
3.4.1. Mass Conservation
3.4.2. Momentum Equation
3.4.3. Enhanced Dissipation
3.4.4. Scaling Analysis
4. Discussion
Inter-Particle Interaction
5. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| particle diameter | |
| E | strain rate tensor |
| acceleration due to gravity | |
| Heaviside (or step) function | |
| mean inter-particle spacing | |
| L | integrodifferential operator |
| m | mass |
| n | particle number density |
| p | fluid pressure |
| R | Reynolds stress tensor |
| Re | Reynolds number |
| St | Stokes number |
| time | |
| u | fluid velocity field |
| composite velocity | |
| particle velocity field | |
| averaging volume | |
| scaled settling velocity vector | |
| W | rotation rate tensor |
| position vector | |
| density ratio parameter | |
| turbulent dissipation | |
| volume fraction | |
| Kolmogorov length scale | |
| density or density ratio | |
| fluid viscosity | |
| maximal compression rate | |
| time scale | |
| fluid vorticity | |
| particle angular velocity | |
| D/Dt | time rate of change following the fluid |
| d/dt | time rate of change following particle |
| Subscript | |
| + | normalized by Kolmogorov scale |
| eff | effective |
| hyd | hydrodynamic |
| ine | inertial |
| pertains to Kolmogorov scale | |
| particle | |
| fluid | |
| L | integral scale |
| ms | meso/macroscale |
| mass-weighted mixture property | |
| ss | small scale |
| mass-weighted mixture property | |
| pertains to particle rotation | |
| Superscript | |
| surface average | |
| volume average | |
| ′ (prime) | perturbation |
Appendix A
Appendix A.1. Particle Settling in Couette Flow
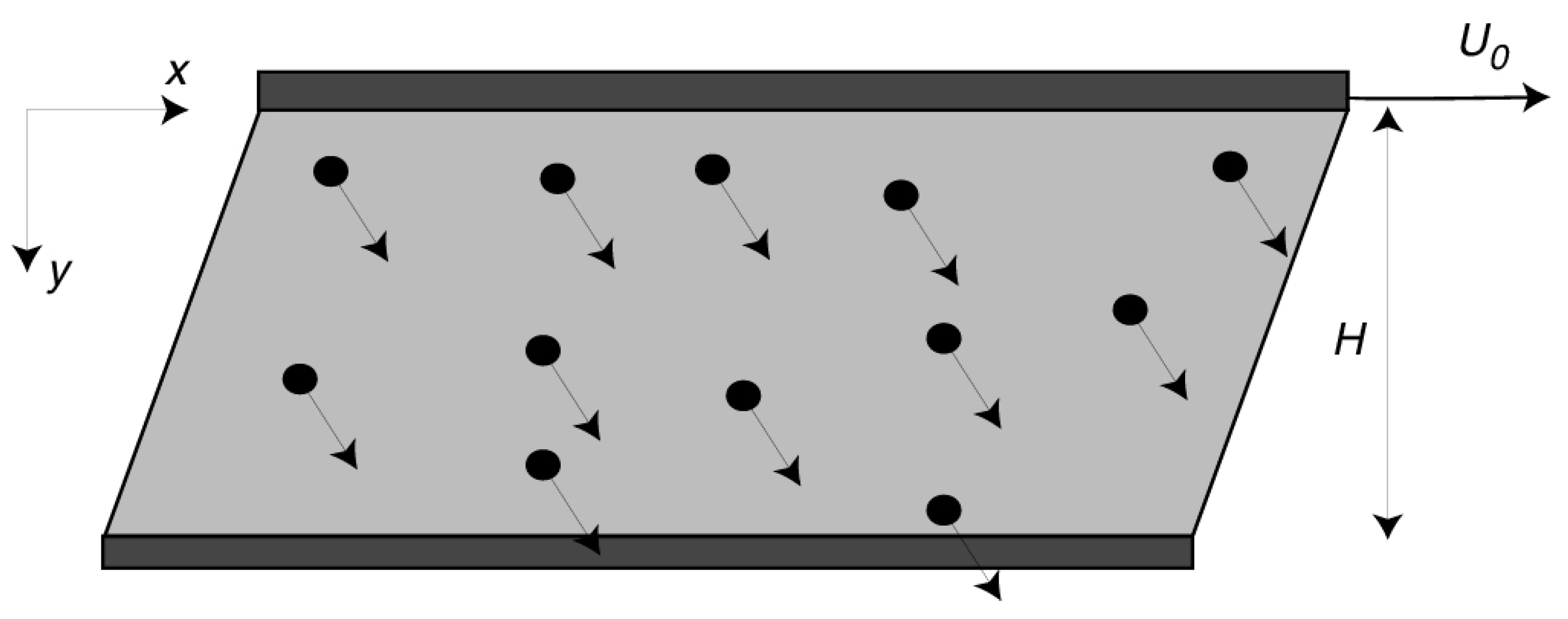
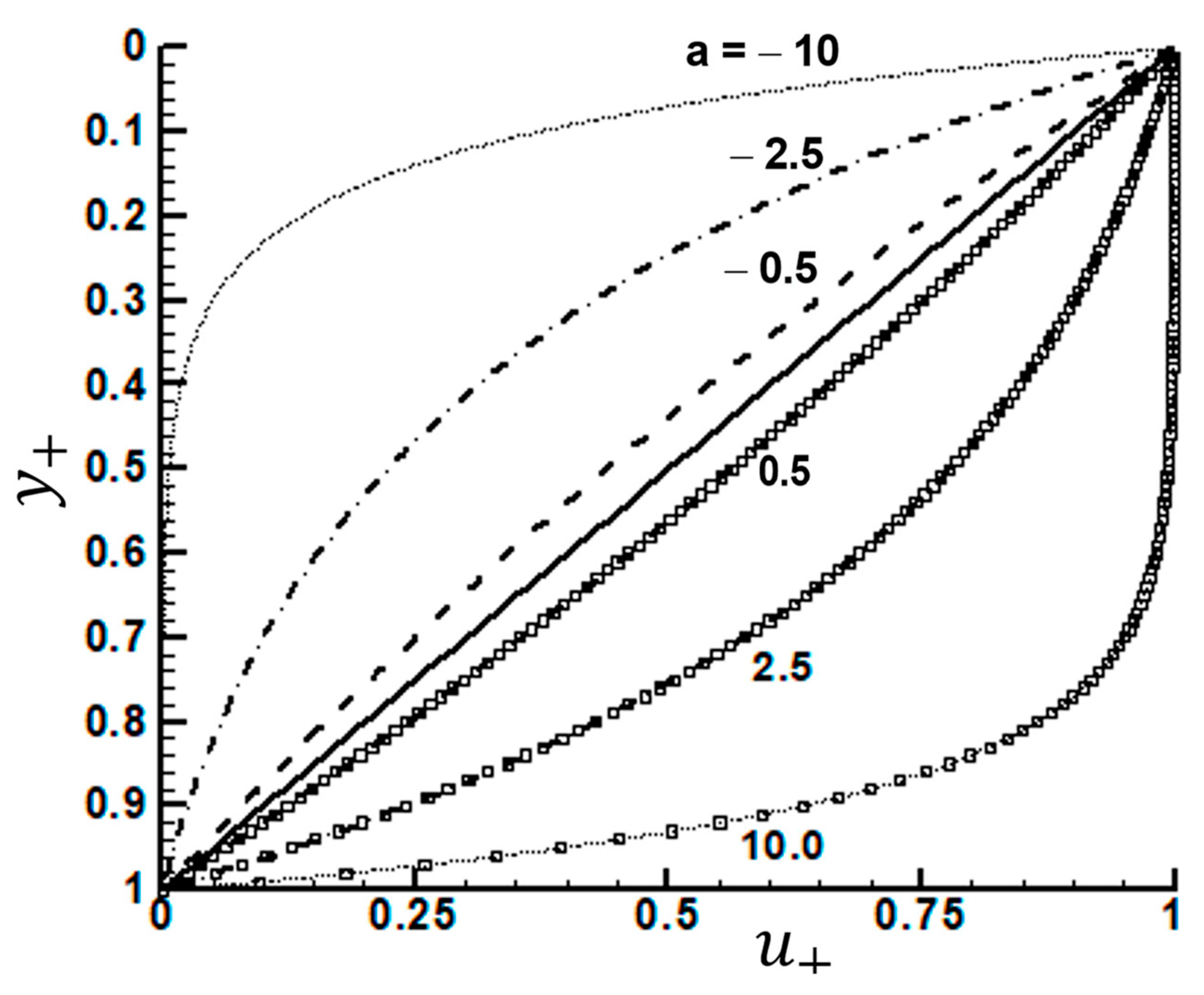
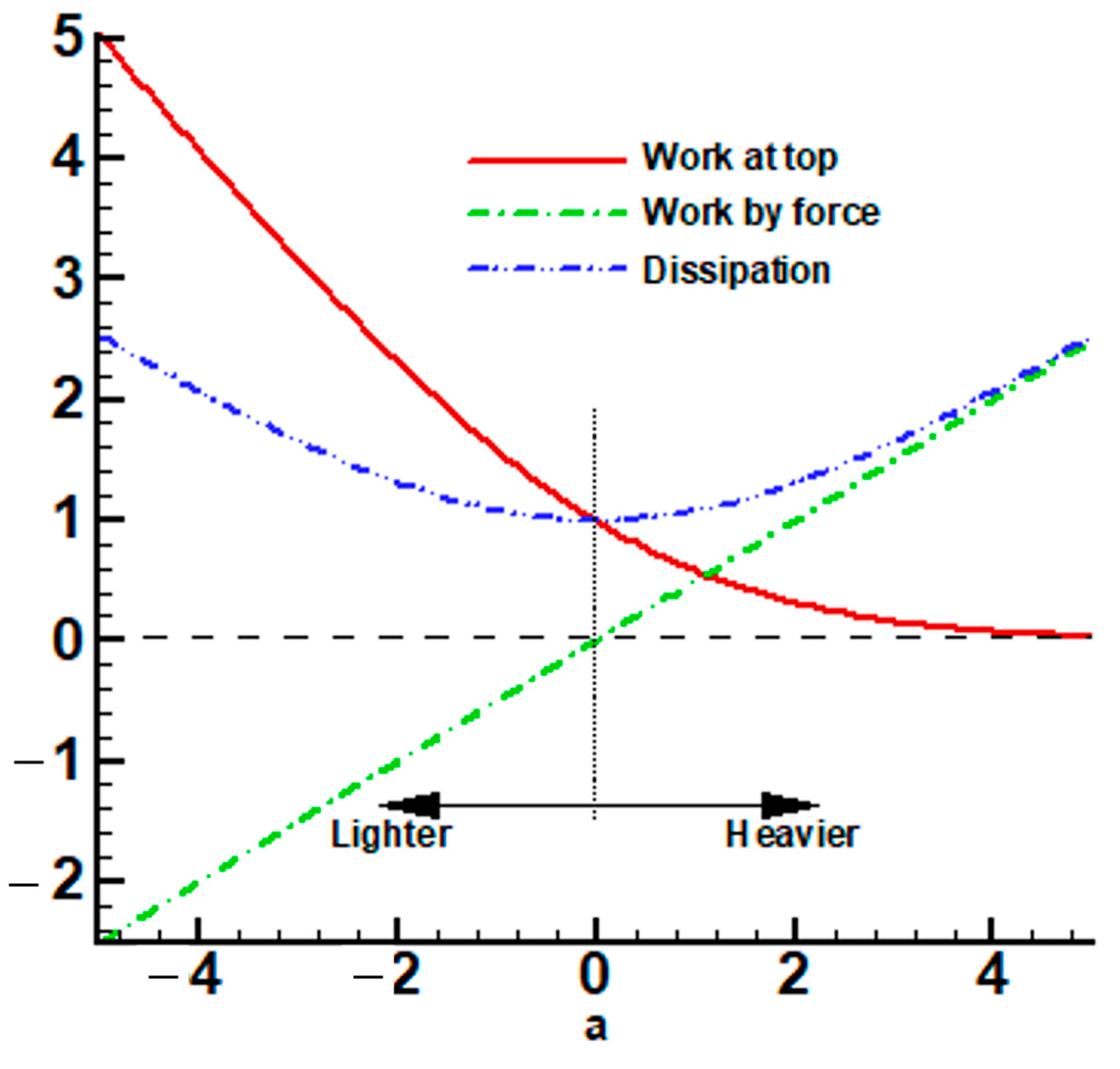
Appendix A.2. Centrifuge
References
- Ferry, J.; Balachandar, S. A fast Eulerian method for disperse two-phase Flow. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2001, 27, 1199–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferry, J.; Balachandar, S. Equilibrium expansion for the Eulerian velocity of small particles. Powder Technol. 2002, 125, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferry, J.; Rani, S.L.; Balachandar, S. A locally implicit improvement of the equilibrium Eulerian method. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2003, 29, 869–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferry, J.; Balachandar, S. Equilibrium Eulerian approach for predicting the thermal field of a dispersion of small particles. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2005, 48, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balachandar, S.; Liu, K.; Lakhote, M. Self-induced velocity correction for improved drag estimation in Euler–Lagrange point-particle simulations. J. Comput. Phys. 2019, 376, 160–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balachandar, S. Fundamentals of Dispersed Multiphase Flows; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Drew, D.A. Mathematical modeling of two-phase Flow. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 1983, 15, 261–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, M. Thermo Fluid Dynamic Theory of Two-Phase Flow; Eyrolles: Paris, France, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Joseph, D.D.; Lundgren, T.S.; Jackson, R.; Saville, D. Ensemble averaged and mixture theory equations for incompressible fluid-particle suspensions. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 1990, 16, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigmatulin, R.I. Spatial averaging in the mechanics of heterogeneous and dispersed systems. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 1979, 5, 353–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallis, G.B. The averaged Bernoulli equation and macroscopic equations of motion for the potential flow of a two-phase dispersion. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 1991, 17, 683–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.Z.; Prosperetti, A. Averaged equations for inviscid disperse two-phase Flow. J. Fluid Mech. 1994, 267, 185–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.Z.; Prosperetti, A. Momentum and energy equations for disperse two-phase flows and their closure for dilute suspensions. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 1997, 23, 425–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-P.; Maxey, M.R. Settling velocity and concentration distribution of heavy particles in homogeneous isotropic turbulence. J. Fluid Mech. 1993, 256, 27–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batchelor, G.K. The Stress system in a suspension of force-free particles. J. Fluid Mech. 1970, 41, 545–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batchelor, G.K. Transport properties of two-phase materials with random structure. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 1974, 6, 227–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acrivos, A. Shear-induced particle diffusion in concentrated suspensions of noncolloidal particles. J. Rheol. 1995, 39, 813–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Mauri, R.; Acrivos, A. Transverse shear-induced gradient diffusion in a dilute suspension of spheres. J. Fluid Mech. 1998, 357, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Karrila, S.J. Microhydrodynamics: Principles and Selected Applications; Butterworth-Heinemann: Boston, MA, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Balachandar, S. A scaling analysis for point–particle approaches to turbulent multiphase flows. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2009, 35, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Y.; Parmar, M.; Balachandar, S. A scaling analysis of added-mass and history forces and their coupling in dispersed multiphase flows. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2013, 57, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balachandar, S.; Najjar, F.M. Optimal two-dimensional models for wake flows. Phys. Fluids 2001, 13, 157–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langford, J.A.; Moser, R.D. Optimal LES formulations for isotropic turbulence. J. Fluid Mech. 1999, 398, 321–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundgren, T.S. Slow flow through stationary random beds and suspensions of spheres. J. Fluid Mech. 1972, 51, 273–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saffman, P.G. On the boundary condition at the surface of a porous medium. Stud. Appl. Math. 1971, 50, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatignol, R. The Faxen formulae for a rigid particle in an unsteady non-uniform Stokes Flow. J. Mec. Theor. Appl. 1983, 1, 143. [Google Scholar]
- Maxey, M.R.; Riley, J.J. Equation of motion for a small sphere in a nonuniform Flow. Phys. Fluids 1983, 26, 883–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatom, F.B. The Basset term as a semiderivative. Appl. Sci. Res. 1988, 45, 283–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.; Elghobashi, S.; Sirignano, W.A. On the equation for spherical-particle motion: Effect of Reynolds and acceleration numbers. J. Fluid Mech. 1998, 367, 221–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovalenti, P.M.; Brady, J.F. The force on a sphere in a uniform flow with small-amplitude oscillations at finite Reynolds number. J. Fluid Mech. 1993, 256, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, R.; Adrian, R.J. Flow past a sphere with an oscillation in the free-stream velocity and unsteady drag at finite Reynolds number. J. Fluid Mech. 1992, 237, 323–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Druzhinin, O.A. On the two-way interaction in two-dimensional particle laden flows: The accumulation of particles and flow modification. J. Fluid Mech. 1995, 297, 49–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxey, M.R. The gravitational settling of aerosol particles in homogeneous turbulence and random flow fields. J. Fluid Mech. 1987, 174, 441–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, S.L.; Balachandar, S. Evaluation of the equilibrium Eulerian approach for the evolution of particle concentration in isotropic turbulence. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2003, 29, 1793–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, S.L.; Balachandar, S. Preferential concentration of particles in isotropic turbulence: A comparison of the Lagrangian and the equilibrium Eulerian approaches. Powder Technol. 2004, 141, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shotorban, B.; Balachandar, S. Particle concentration in homogeneous shear turbulence simulated via Lagrangian and equilibrium Eulerian approaches. Phys. Fluids 2006, 18, 065105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shotorban, B.; Balachandar, S. A Eulerian model for large-eddy simulation of concentration of particles with small Stokes numbers. Phys. Fluids 2007, 19, 118107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shotorban, B.; Balachandar, S. Two-fluid approach for direct numerical simulation of particle-laden turbulent flows at small Stokes numbers. Phys. Rev. E 2009, 79, 056703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feuillebois, F.; Lasek, A. On the rotational historic term in non-stationary Stokes Flow. Q. J. Mech. Appl. Math. 1978, 31, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tennekes, H.; Lumley, J.L. A First Course in Turbulence; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Marchioro, M.; Tanksley, M.; Prosperetti, A. Mixture pressure and stress in disperse two-phase Flow. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 1999, 25, 1395–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prosperetti, A. Ensemble averaging techniques for disperse flows. In Particulate Flows Processing and Rheology; Drew, D.A., Joseph, D.D., Passman, S.L., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Annamalai, S.; Balachandar, S.; Sridharan, P.; Jackson, T.L. Pressure evolution equation for the particulate phase in inhomogeneous compressible disperse multiphase flows. Phys. Rev. Fluids 2017, 2, 024301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.H.; Liou, M.S. A robust and accurate approach to computing compressible multiphase flow: Stratified flow model and AUSM+-up scheme. J. Comput. Phys. 2007, 225, 840–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, R.O. Recent advances in well-posed Eulerian models for polydisperse multiphase flows. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2023, 172, 104715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, D.Z.; Balachandar, S. Numerical calculation of the particle–fluid–particle stress in random arrays of fixed particles. Phys. Rev. Fluids 2021, 6, 104306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.Z.; Wang, M.; Balachandar, S. Evolution of the age-included nearest pair distribution in disperse multiphase flows. Phys. Fluids 2023, 35, 063307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinch, E.J. An averaged equation approach to particle interactions in a fluid suspension. J. Fluid Mech. 1977, 83, 695–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marble, F.E. Dynamics of dusty gases. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 1970, 2, 397–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saffman, P.G. On the stability of laminar flow of a dusty gas. J. Fluid Mech. 1962, 13, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batchelor, G.K. Sedimentation in a dilute dispersion of spheres. J. Fluid Mech. 1972, 52, 245–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, R.H.; Acrivos, A. Sedimentation of noncolloidal particles at low Reynolds numbers. Ann. Rev. Fluid Mech. 1985, 17, 91–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saffman, P.G. On the settling speed of free and fixed suspensions. Stud. Appl. Math. 1973, 52, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchioro, M.; Acrivos, A. Shear-induced particle diffusivities from numerical simulations. J. Fluid Mech. 2001, 443, 101–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nott, P.R.; Brady, J.F. Pressure-driven flow of suspensions: Simulation and theory. J. Fluid Mech. 1994, 275, 157–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, I.M.; Stone, H.A. Axial dispersion via shear-enhanced diffusion in colloidal suspensions. Europhys. Lett. 2012, 97, 58005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leshansky, A.M.; Morris, J.F.; Brady, J.F. Collective diffusion in sheared colloidal suspensions. J. Fluid Mech. 2008, 597, 305–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malipeddi, A.R.; Sarkar, K. Shear-induced collective diffusivity down a concentration gradient in a viscous emulsion of drops. J. Fluid Mech. 2019, 868, 5–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Balachandar, S. A Simplified Two-Fluid Model Based on Equilibrium Closure for a Dilute Dispersion of Small Particles. Mathematics 2024, 12, 3543. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12223543
Balachandar S. A Simplified Two-Fluid Model Based on Equilibrium Closure for a Dilute Dispersion of Small Particles. Mathematics. 2024; 12(22):3543. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12223543
Chicago/Turabian StyleBalachandar, S. 2024. "A Simplified Two-Fluid Model Based on Equilibrium Closure for a Dilute Dispersion of Small Particles" Mathematics 12, no. 22: 3543. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12223543
APA StyleBalachandar, S. (2024). A Simplified Two-Fluid Model Based on Equilibrium Closure for a Dilute Dispersion of Small Particles. Mathematics, 12(22), 3543. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12223543





