Abstract
Fine-tuning a pre-trained sequence-to-sequence-based language model has significantly advanced the field of abstractive summarization. However, the early models of abstractive summarization were limited by the gap between training and inference, and they did not fully utilize the potential of the language model. Recent studies have introduced a two-stage framework that allows the second-stage model to re-rank the candidate summary generated by the first-stage model, to resolve these limitations. In this study, we point out that the supervision method performed in the existing re-ranking model of the two-stage abstractive summarization framework cannot learn detailed and complex information of the data. In addition, we present the problem of positional bias in the existing encoder–decoder-based re-ranking model. To address these two limitations, this study proposes a hierarchical supervision method that jointly performs summary and sentence-level supervision. For sentence-level supervision, we designed two sentence-level loss functions: intra- and inter-intra-sentence ranking losses. Compared to the existing abstractive summarization model, the proposed method exhibited a performance improvement for both the CNN/DM and XSum datasets. The proposed model outperformed the baseline model under a few-shot setting.
MSC:
68T50
1. Introduction
Text summarization aims to create a concise summary containing the key information of a given document. Text summarization is divided into extractive and abstractive summarization, when generating a summary. In extractive summarization, the model extracts part of the document and then concatenates it to create a summary. An abstractive summarization model generates a summary using a combination of new words. This study focuses on abstractive summarization. Abstractive summarization has rapidly progressed through the introduction of sequence-to-sequence [1] models. A sequence-to-sequence model receives a token-level sequence as the input to an encoder and generates a token-level sequence as the output of the decoder. In the training phase, the teacher-forcing method is used to input the correct answer token into the decoder, rather than the token generated by the model, for efficient training. By contrast, in the inference phase, the tokens generated by the model are input into the decoder. Transfer learning [2], involving pre-training a language model and then fine-tuning it, is a widely used training method for abstractive summarization models. In the pre-training step, the language model learns general text generation through conducting self-supervised learning with a large unlabeled corpus. Subsequently, the pre-trained language model is fine-tuned using a human-written downstream summarization dataset.
However, the early single-stage abstractive summarization model based on a language model with a encoder–decoder structure has several limitations. The first is the training–evaluation gap. The objective function of the generative language model is based on token-level prediction. However, the evaluation metric judges the overall similarity between the gold summary and the summary generated by the model. In addition, the sequence-to-sequence model adopts the teacher-forcing method during training, and auto-regressively generates sequences in the inference phase. Therefore, a discrepancy occurs between the training and inference phases, which is known as the exposure bias [3] problem. Second, the single-stage abstractive summarization model has an insufficient ability for selecting the optimal output summary from among candidate summaries. SimCLS [4] pointed out that current studies on abstractive summarization do not fully utilize the potential of language models. SimCLS demonstrated a significant difference in evaluation scores between the summary chosen by the model as the final output and the summary most similar to the gold summary among the candidate summaries. SimCLS revealed a difference of over 10 points in ROUGE-1 [5] score based on fine-tuned BART [6] with a CNN/DM [7] dataset.
To overcome these limitations, research on a two-stage framework for abstractive summarization is being conducted. A recent two-stage framework generated candidate summaries in the first-stage model. The second-stage model then re-ranks the candidate summaries to determine the final output summary. The two-stage framework uses the sequence-level loss to train the second-stage model. Therefore, the training–inference gap of the existing single-stage models can be resolved. This also allows the model to learn optimal summary selection from a range of candidates. In a second-stage model, either a differently structured model is introduced, or the first-stage model is reused. SimCLS and others used an encoder-only model as the second-stage model, whereas BRIO [8] and others reused the first-stage model, which is the encoder–decoder model, as the second-stage model.
In this study, we highlight two limitations of the existing second-stage re-rank model of a two-stage abstractive summarization framework and propose a novel training method to resolve them. First, the existing studies did not consider complex information in the candidate summary. The candidate summary is the result generated by the deep learning model. Therefore, as shown in Figure 1, well-generated and poorly generated sentences coexist in the candidate summary. However, the existing re-ranking models generally perform summary-level supervision, in which the loss is calculated using only one value for a single-candidate summary. If only summary-level supervision is performed during model training, it becomes difficult for the model to learn complex information from the candidate summary. In this study, we argue that using only summary-level supervision for training the re-ranking model is not an appropriate method.

Figure 1.
Example of similarity between the gold summary and each sentence in the candidate summary. The higher the ROUGE-1 recall score of the gold summary and the sentence, the darker the sentence is highlighted.
The second limitation is the bias in the position of the sentence in the existing encoder–decoder-based re-ranking models. The training and inference of the encoder–decoder-based re-ranking models are executed based on a generation probability value for each token in the candidate summary. The average of the generation probability values for all the tokens constituting a single candidate summary is used as the predicted score for the corresponding candidate summary. In this study, we confirmed that the existing encoder–decoder-based re-ranking model tends to allocate lower prediction scores to sentences located toward the end of the candidate summary.
In this study, we propose a re-ranking model that uses hierarchical supervision during training to address these two limitations of the existing re-ranking model of the two-stage abstract summary framework. The proposed model jointly uses sentence and summary-level supervision during training. We designed two types of alternative sentence-level loss for sentence-level supervision. Through the joint objective function, the model learns not only the rank between the candidate summaries, but also the rank between the sentences constituting the candidate summary. Our proposed method can resolve the limitation of the existing re-ranking model, which overlooks the complex information in the candidate summary. In addition, we can alleviate the positional bias problem of the existing encoder–decoder-based re-ranking models. In experiments using two datasets, CNN/DM and XSum [9], the proposed model showed a performance improvement over the existing models in both fully supervised and few-shot settings. Through an additional analysis, we confirmed that the proposed method enables effective learning of the rank between sentences and alleviates positional bias.
2. Related Work
2.1. Re-Ranking Model for Abstractive Summarization
The two-stage framework for abstractive summarization has made significant progress in abstractive summarization by alleviating the train–inference gap and enhancing the potential of language models through a re-ranking model. SimCLS [4] proposes a model for re-ranking candidate summaries using RoBERTa [10], an encoder-only pre-training language model. SimCLS independently derives the representation of the source document, gold summary, and each candidate summary. The model learns that the more similar the candidate summary is to the gold summary, the closer it is to the corresponding source document.Margin ranking loss is used as the loss function. SummaReranker [11] proposed a multi-task learning model based on an encoder-only RoBERTa model, SimCLS. SummaReranker used a multi-gate mixture-of-experts [12] to jointly learn the rank of the candidate summary base on the ROUGE score [5], BART score [13], and BERT score [14]. Multi-label binary cross-entropy was used as the loss function for model training. BRIO [8] reused the first-stage model as a second-stage re-ranking model. BRIO used the encoder–decoder models BART [6] and PEGASUS [15] as re-ranking models. The model was trained to assign a higher generation probability, because the candidate summary was similar to the gold summary. A loss function based on the margin ranking loss was used for training.
2.2. Sentence-Level Supervision
For several NLP tasks that primarily use document or passage-level supervision, studies have been conducted to perform sentence-level supervision and document/passage-level supervision. Open-domain passage retrieval aims to determine the most appropriate passage in a passage pool to respond to a given query. Document-level supervision is commonly used for training open-domain passage retrieval. DCSR [16] pointed out that using only document-level supervision for training is not the optimal method, because one passage has multiple sentences containing different information, and they suggested performing sentence-level supervision. A similar approach was studied using a document-level relation extraction task, which aimed to determine the relationship between two entities in a document with multiple sentences. In existing studies, an entire document is generally represented as a sequence or graph-based model to predict the relationship of the entity pair. SIEF [17] designed a sentence focusing loss to ensure that the document from which non-evidence sentences are removed and the original document have the same output distribution. Through sentence focusing loss, the model learned to focus on evidence sentences that are directly related to the relational information of the entity pair.
2.3. Approaches to Reflecting Detailed Information in Text Summarization
In text summarization tasks, various attempts have been made to enable models to learn detailed information contained in a text. SEASON [18] introduced a salience-aware cross-attention module to allow the model to better focus on key sentences in the source document. The model was learned by jointly performing extractive and abstractive summarization. Some studies have emphasized that the summary should not change the meaning of the source document. Thus, a model has been proposed that produces a wide range of summaries, from completely extracted to highly abstractive summaries, by allowing it control over copying [19]. There was also a study to make a more accurate and realistic summary of life events by analyzing the role of sentiment in the generated text [20].
3. Methodology
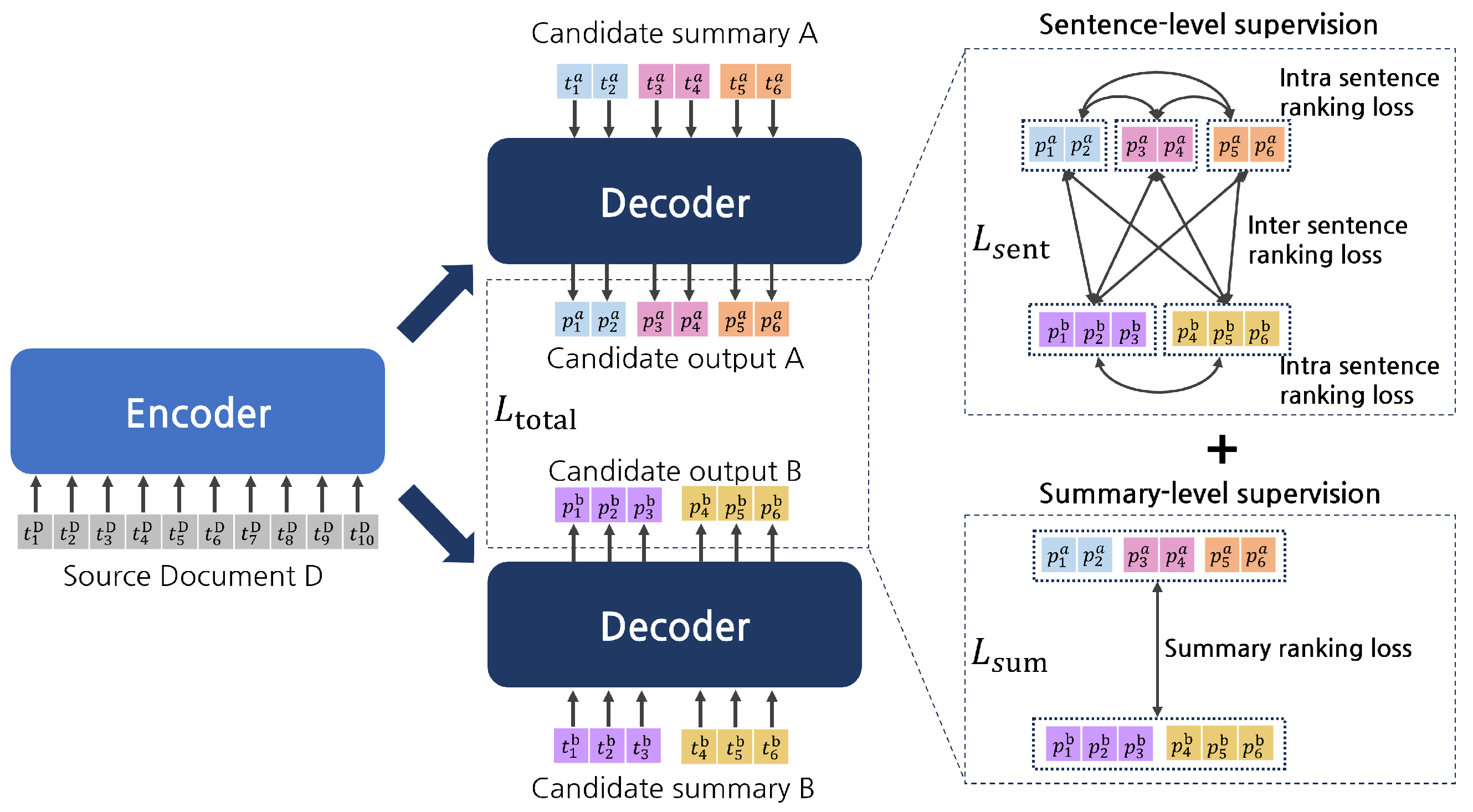
In this study, we propose a hierarchical supervision method that jointly performs sentence-level supervision and summary-level supervision to train a re-ranking model for abstractive summarization. In other words, the proposed model in this study aims to re-rank the candidate summary generated by the first-stage generation model by learning to assign higher scores to the summary or sentence most similar to the gold summary. Figure 2 illustrates the overall structure of the proposed model. The encoder takes the source document as input, and the decoder takes a single candidate summary as input. Subsequently, the decoder outputs a generation probability value for each token that constitutes a candidate summary. The average of the generation probability values of all tokens constituting the candidate summary is considered the predicted score of the corresponding candidate summary. Similarly, the predicted score of a sentence is the average of the generation probabilities of the tokens constituting the sentence. During training, summary-level supervision and sentence-level supervision are performed for the candidate summary and sentence scores predicted by the model, respectively. The model learns the ranking of the candidate summaries through summary-level supervision. The proposed method performs sentence-level supervision using two types of sentence ranking loss: (1) Intra-sentence ranking loss, which aims to learn the ranking between sentences that consist of the same candidate summary. (2) Inter-sentence ranking loss allows the model to learn the ranking between the sentences that constitute the different candidate summaries.
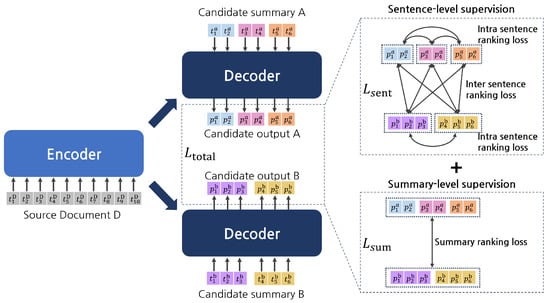
Figure 2.
Overall architecture of the proposed model. The proposed model performs sentence and summary-level supervision simultaneously during training. Superscripts and subscripts associated with the elements are the source document/candidate summary index and token index, respectively. Generation probability values for tokens constituting the same sentence are expressed in uniform colors.
3.1. Problem Statement
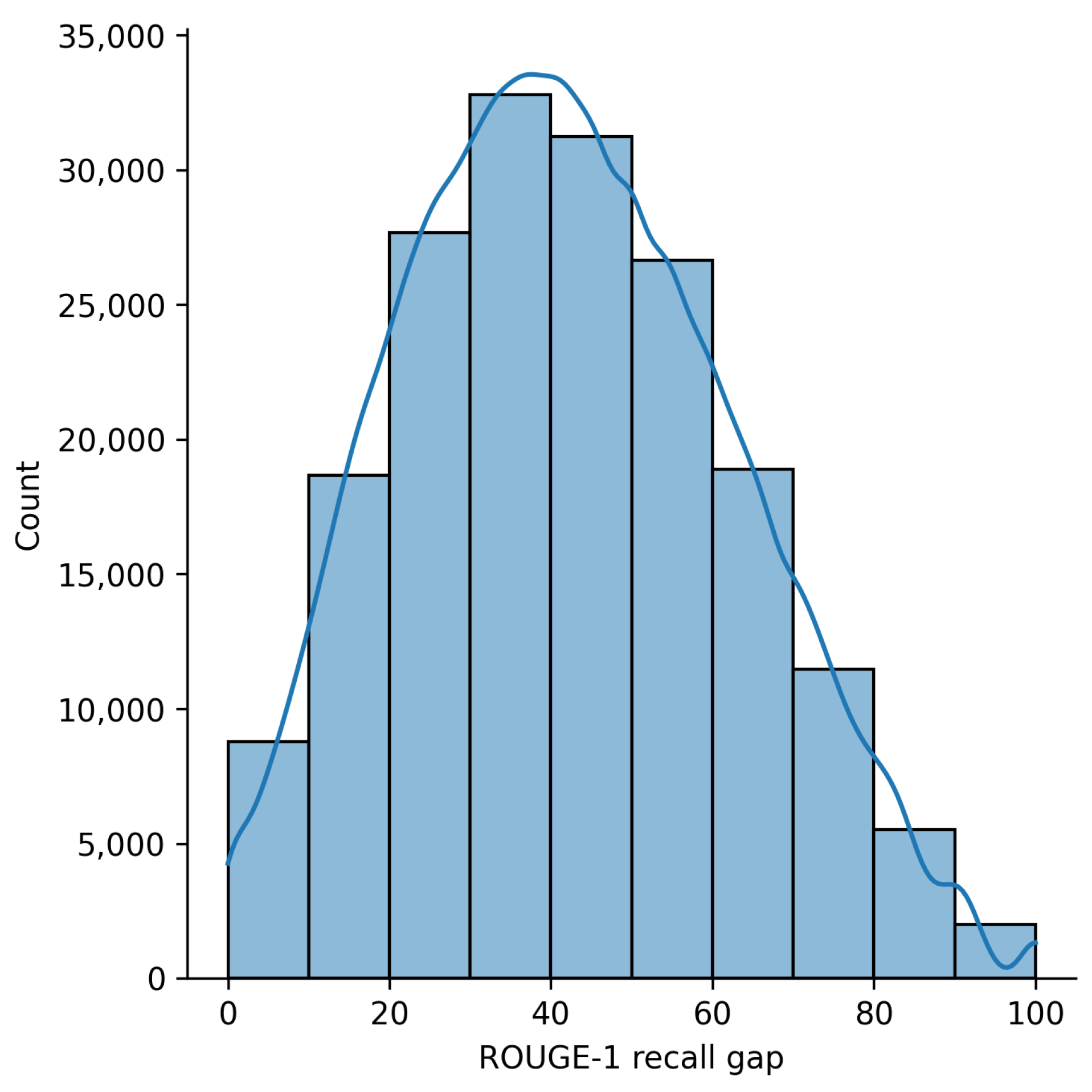
In this study, we present two problems with the existing abstractive summarization re-ranking model. The first problem is that complex information in the candidate summary can be overlooked if the model is trained using only summary-level supervision. The existing re-ranking models are typically trained using summary-level supervision. Re-ranking models with encoder-only structures such as SimCLS [4], independently encode documents and summaries to represent an entire single document or summary as a single vector representation. In encoder–decoder re-ranking models, such as BRIO [8], the average of the generated probability values of the tokens constituting the candidate summary is used as the predicted score for the corresponding candidate summary. Therefore, model supervision is performed using only one value for a candidate summary in existing studies. However, as shown in Figure 1, well and poorly generated sentences coexist in the model-generated candidate summary. Figure 3 shows a distribution plot of the score difference between the sentence with the highest ROUGE-1 recall score and the sentence with the lowest ROUGE-1 recall score for the gold summary among all sentences constituting a single candidate summary. Candidate summaries generated for the CNN/DM [7] test dataset through fine-tuned BART [6] were used for statistical analysis. According to this distribution plot, we can confirm that the quality of sentences generated by the model was diverse, even for a single candidate summary. If the model is supervised using only summary-level supervision, it becomes difficult to learn qualitative differences between sentences. In other words, it becomes difficult to determine whether summary-level supervision is suitable for the characteristics of candidate summaries with a combination of positive (well-summarized) and negative (poorly summarized) elements.

Figure 3.
Distribution plot of the maximum evaluation score gap of a sentence pair in a single candidate summary. The plot shows the diversity of the quality of sentences in the single candidate summary that the model generated. For the evaluation score of each sentence, the ROUGE-1 recall score between the sentence and the gold summary was used. Candidate summaries generated for the test dataset of CNN/DM through fine-tuned BART were used.
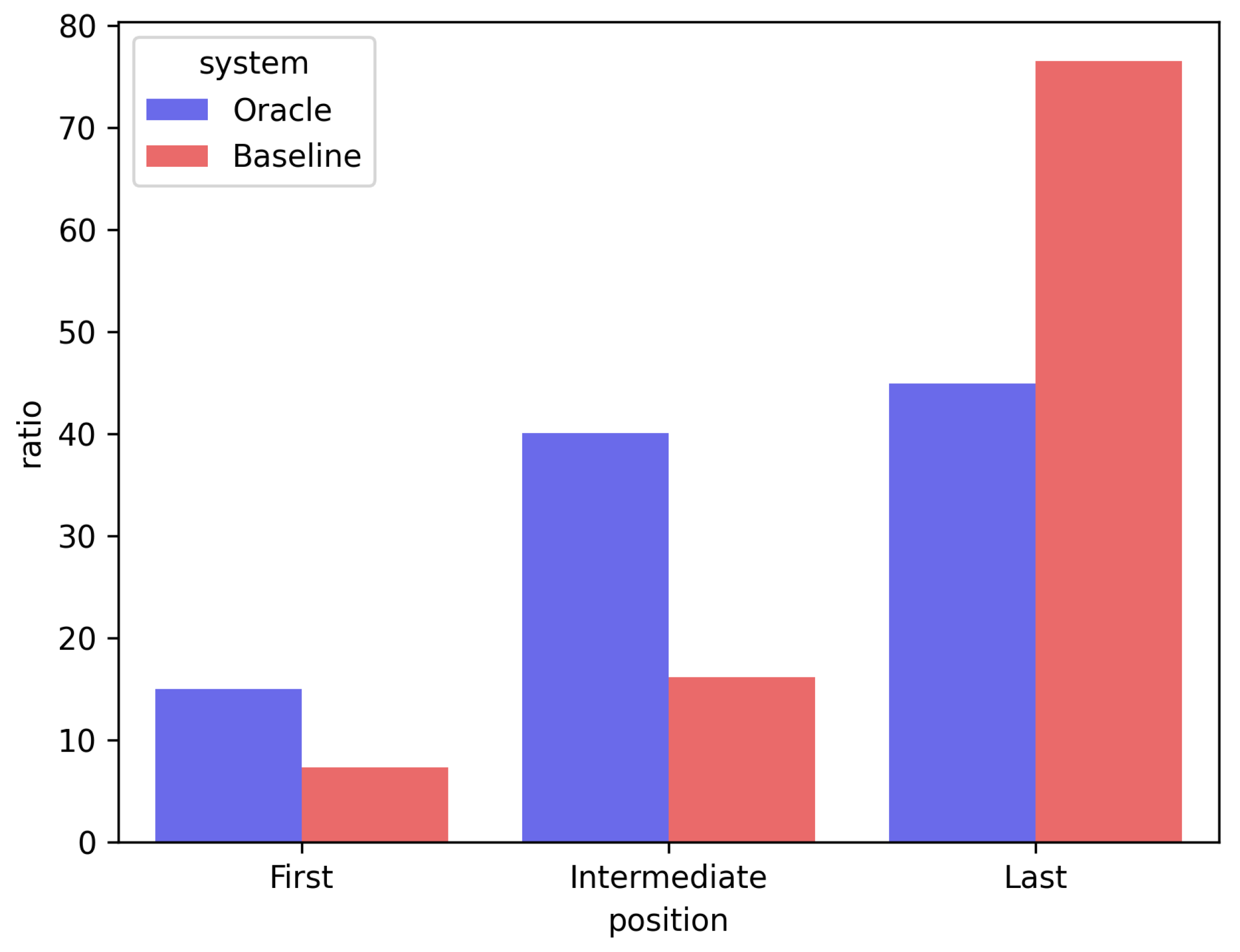
The second limitation is the bias according to sentence position in the encoder–decoder-based abstractive summarization re-ranking model. Existing encoder–decoder re-ranking models tend to allocate a lower predicted score when the sentence is located behind the candidate summary. Figure 4 confirms the positional bias of the existing encoder–decoder re-ranking model using the CNN/DM test set. Figure 4 is a bar chart comparing the position of the sentence to which the existing model (expressed as “Baseline”) assigned the lowest prediction score in one candidate summary and the position of the sentence that least resembled the gold summary (expressed as “Oracle”). “First” means the first sentence of the summary, “Last” means the last sentence, and “Intermediate” means all the sentences located between the first and last sentences. To confirm this bias, we stored the ROUGE score with a gold summary for all the sentences constituting each candidate summary. We then compared the ground-truth score of the sentence with the sentence score predicted by the model (average of the generation probability values of all tokens that made up the sentence). The analysis indicated that the probability of the last sentence of the candidate summary having the lowest ground-truth score was approximately 45%. By comparison, the rate at which the existing model (BRIO) allocated the lowest prediction score to the last sentence was approximately 76%, which is a considerable difference. The analysis results confirmed that the existing encoder–decoder re-ranking model has a bias in assigning lower prediction scores to sentences toward the end of the candidate summary.
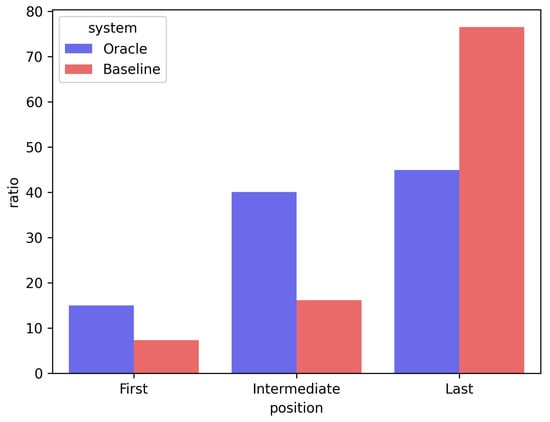
Figure 4.
Bar chart of the positional bias of the existing encoder–decoder-based re-ranking model. Oracle: ground-truth, baseline: existing model. First: first sentence of summary, last: last sentence of summary, intermediate: all sentences located between first sentence and last sentence. Analysis was conducted with the test dataset from CNN/DM.
This study proposes a hierarchical supervision method that concurrently executes supervision across both narrow and wide ranges. The model learns the complex information of sentences constituting the candidate summary through sentence-level supervision. Furthermore, by independently supervising the predicted score of each sentence, we attempt to alleviate the positional bias of existing encoder–decoder-based re-ranking models.
3.2. Problem Formulation
The re-ranking model of the two-stage abstractive summarization framework aims to select the best summary among candidate summaries. Given a source document D and m candidate summaries , the model is trained to select the candidate summary that most resembles the gold summary; the proposed model aims to identify the best candidate summary , which has the highest ROUGE score for the gold summary G, based on the encoder–decoder structure. Therefore, the training objective of the model is as follows:
In Equation (1), is the ROUGE score of two sequences X, Y. In Equation (2), is a learnable model parameter.
In this study, we propose a training method that uses hierarchical supervision to simultaneously perform summary and sentence-level supervision. Therefore, a ground-truth ranking is required between all candidate summaries and between all sentences in each source document to train the model. Furthermore, we labeled the gold scores of the candidate summaries and sentences as follows and used the corresponding ground-truth ranking for training.
Summary gold score: The gold score of the candidate summary used for summary-level supervision was labeled according to BRIO. Gold scores of the candidate summaries were labeled using the mean of the ROUGE-1,2,L score or the harmonic mean of the ROUGE-1,2 score.
Sentence gold score: The ROUGE-1 recall score of the gold summary for each sentence was labeled as the gold score of the sentences used in sentence-level supervision. If the summary comprised a single sentence, it was divided into two spans. We treated the first half of the words as one sentence and the other half as another sentence.
3.3. Summary-Level Supervision
The model learns the ranks of candidate summaries by performing summary-level supervision, which is a supervisory method, over a relatively wide range. Summary-level supervision ensures that the summary score predicted by the model is consistent with the ground-truth rank. The summary score is derived using the encoder–decoder model. To obtain the summary score of the i-th candidate summary, the encoder takes the source document D as the input, and the decoder takes the i-th candidate summary as the input (t is a token, l is the length of the candidate summary). The summary score of a specific candidate summary is the average of the generation probability values for all tokens that constitute the corresponding candidate summary. Thus, the summary score of the i-th candidate summary is
In Equation (3), is the length of the i-th candidate summary. is a hyperparameter that represents a penalty for the length of the candidate summary.
The summary ranking loss for summary-level supervision is defined based on the margin ranking loss. By optimizing the summary ranking loss, the model learns to allocate the summary score of the candidate summary based on the ground-truth rank. The equation for the summary ranking loss is as follows:
in Equation (4) is the hyperparameter that refers to the base margin for the summary ranking loss, and is the gap of the ground-truth rank for the candidate summary pair and . The loss is calculated by assigning a larger margin to the candidate summary pair with a large rank gap and a relatively small margin to the pair with a small rank gap.
3.4. Sentence-Level Supervision
Sentence-level supervision enables the model to learn the ranking of sentences that comprise the candidate summary. Similarly to the summary score, the sentence score used in sentence-level supervision is the generation probability value of each token constituting the sentence derived using the encoder-decoder model. Here, each sentence is not input into the decoder independently; rather, the entire single candidate summary is input into the decoder. Subsequently, the average of the generation probability values of the tokens corresponding to each sentence is used as the sentence score. The sentence score of the j-th sentence in the i-th candidate summary is
In Equation (5), mean the position of the first token of the j-th sentence of the i-th candidate summary and the position of the last token, respectively. is the length of the j-th sentence in the i-th candidate summary; is a hyperparameter that represents a penalty for the length of the sentence.
In this study, two types of sentence ranking loss were designed to perform sentence-level supervision. During training, one of the two sentence ranking losses was selected and used. For each candidate summary, a set of sentences was organized based on the type of sentence ranking loss, and the loss was calculated for all sentence pairs within this set.
3.4.1. Intra-Sentence Ranking Loss
One of the losses designed for sentence-level supervision is the intra-sentence ranking loss. The intra-sentence ranking loss allows the model to learn the rank of sentences in a single candidate summary. The intra-sentence set for the i-th candidate summary is defined as . refers to the number of sentences in i-th candidate summary. The model learns to assign the sentence score according to the ground-truth rank by optimizing the intra-sentence ranking loss. The intra-sentence ranking loss is expressed as follows:
in Equation (6) is a hyperparameter that signifies the base margin for the sentence ranking loss, and is the gap of the ground-truth rank for the candidate sentence pair and . Similarly to for the summary ranking loss, the loss is calculated by assigning a larger margin to a sentence pair with a large rank gap and a relatively small margin to a pair with a small rank gap.
3.4.2. Inter-Intra-Sentence Ranking Loss
Another loss designed for sentence-level supervision is the inter-intra-sentence ranking loss. Inter-intra-sentence ranking loss allows the model to learn not only the rank between sentences in a single candidate summary, but also the rank of sentences constituting different candidate summaries. To balance the number of intra- and inter-sentence pairs, we sampled r external sentences per candidate summary. Therefore, the inter-intra-sentence set for the i-th candidate summary consists of all sentences in the corresponding candidate summary and r sentences randomly sampled from the external candidate summary. The inter-intra-sentence set of the i-th candidate summary is defined as . refers to the number of sentences in i-th candidate summary. and are a randomly sampled candidate summary index and sentence index, respectively. Similarly to the intra-sentence ranking loss, the inter-intra-sentence ranking loss is defined based on the margin ranking loss. By optimizing the inter-intra-sentence ranking loss, the model learns to allocate the sentence score according to the ground-truth rank. The equation for the inter-intra-sentence ranking loss is as follows:
in Equation (7) is a hyperparameter that signifies the base margin for the sentence ranking loss, and is the gap of the ground-truth rank for the candidate sentence pair and . The loss calculation is also varied based on the rank gap between sentence pairs: a larger margin is assigned to pairs with a large rank gap, and a smaller margin to those with a small rank gap.
The weighted sum of the summary ranking loss and sentence ranking loss is the final loss used for training. For the sentence ranking loss, the intra-sentence ranking loss or inter-intra-sentence ranking loss is used as an alternative. The final objective function is as follows:
in Equation (8) is the hyperparameter of the weight of the sentence ranking loss. is or . As shown in the above equation, the model is trained using hierarchical supervision, which not only uses summary-level loss but also sentence-level loss. Therefore, the proposed method enables the model to learn the ranking between sentences such that complex information in the candidate summary is considered during training. In addition, because each sentence score is independently supervised, the positional bias of the existing encoder–decoder-based re-ranking model can be alleviated.
4. Experiments
4.1. Experimental Settings
4.1.1. Datasets
In this study, we used two summarization datasets with a different average number of sentences in the gold summary. We conducted experiments on a CNN/DM [7] dataset with a multi-sentence gold summary and an XSum [9] dataset with only a single-sentence gold summary. The CNN/DM and XSum datasets are some of the most commonly used datasets in summarization tasks. In addition, the CNN/DM dataset has a relatively extractive summary, and the XSum has a relatively abstractive summary, allowing experiments with various types of summary. We explored the impact of hierarchical supervision through two experimental setups: one using a dataset with multi-sentence summaries, and another where all summaries consisted of single sentences. This approach aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of hierarchical supervision with different summary structures.
CNN/DM contains news articles paired with highlights obtained from the CNN and DailyMail newspapers. The average number of sentences constituting the gold summary is approximately 3.6, which is relatively large. There are 287,227 document–summary pairs for training, 13,368 for validation, and 11,490 for testing.
XSum consists of online articles with highly abstractive summaries from the BBC. All the gold summaries are composed of a single sentence. There are 204,045 document–summary pairs for training, 11,332 for validation, and 11,334 for testing.
Data statistics are specified in Table 1.

Table 1.
Statistics of the two datasets. Doc.: document, Summ.: summary.
4.1.2. Implementation Details
We used the same backbone model in the first-stage generation model and the second-stage re-ranking model of the two-stage abstractive summarization framework in the experiment. The parameters of the backbone model were initialized using fine-tuned BART-large and PEGASUS for the CNN/DM and XSum datasets, respectively. Using the first-stage generation model, we generated 16 candidate summaries per source document for the training, validation, and test sets, and then used them for training and inference of the second-stage re-ranking model. A diverse beam search [21] was used as the decoding strategy for the first-stage generation model.
Adam [22] was used as the optimizer and the learning rate was tuned using the validation set. We followed BRIO for the summary length penalty and summary margin. The summary length penalty was 2.0 and 0.6 for CNNDM and XSum, respectively. The summary margin was 0.001 for CNNDM and 0.1 for XSum. For both datasets, the sentence length penalty and the sentence margin used 1.0 and 0.4, respectively. was set to 0.007 on CNNDM and 0.01 on XSum (when was set like this, note that the average summary ranging loss and average sentence ranging loss had an actual quantitative ratio between 3:1 and 1:1). In the few-shot setting experiment, datasets were set to 100 and 1000 data sizes. For each size, a dataset was randomly sampled through 3 random seeds.
4.2. Main Results
In the main experiment, various abstractive summarization models were used as baselines for comparison with the proposed model. The baseline could be divided into three types. First, the single-stage models. BERTSumExtAbs [23] is a BERT [2]-based model that first fine-tunes the encoder with the extractive summarization task and then fine-tunes the decoder with the abstractive summarization task. BART [6] and PEGASUS [15] are encoder–decoder-based pre-trained language models. SEASON [18] is a model that jointly learns extractive and abstractive summarization based on BART. Second, SimCLS [4] and SummaReranker [11] are two-stage models that use encoder-only models as second-stage re-ranking models. The BRIO [8] is a two-stage model that uses a re-ranking model based on the encoder-decoder model. The performance listed in the table is the ROUGE score between the gold summary and the final output summary selected by each model. We did not compare the proposed model with ChatGPT [24], which has received a lot of attention recently. The first reason for this is that ChatGPT has not disclosed its performance. In addition, a comparison between the proposed model and ChatGPT is not suitable because of the difference in parameter size. The parameter size of the backbone model of the other baseline models and the proposed model is less than 500 million, while the parameter size of ChatGPT is about 175 billion, so a comparison with the proposed model was considered inappropriate.
The main results for the CNN/DM are listed in Table 2. In the experiment on CNN/DM, compared to the baseline models, ROUGE-1 improved by 0.07, ROUGE-2 by 0.24, and ROUGE-L by 0.14 points with the proposed model. Table 3 lists the main results for XSum. For the XSum dataset, the proposed model surpassed the baseline model in performance, achieving improvements of 0.12, 0.09, and 0.03 points for ROUGE-1, ROUGE-2, and ROUGE-L scores, respectively. The results showed that the performance of the model improved for both the experiment on CNN/DM, which has a multi-sentence gold summary, and the experiment on XSum, which only has a single-sentence gold summary. Therefore, it is effective to use hierarchical supervision to train an abstractive summarization re-ranking model. In addition, this result suggests that, not only is is effective to perform sentence-level supervision, but also to perform span-level supervision, which is a supervision method with a smaller unit. Additionally, we performed a t-test to prove the reliability of the performance improvement of the proposed model. We derived the model performance using five random seeds for the proposed model and the existing encoder–decoder-based re-ranking model(BRIO), respectively, and performed a t-test with the average values of the ROUGE-1, 2, and L scores. As the result of the t-test, the p-value was calculated as 0.004 in CNN/DM and 0.011 in XSum. As the p-value was lower than the alpha level = 0.05 in both datasets, we confirmed that the results of this experiment were statistically significant.

Table 2.
Results on CNN/DM. *: outperformed the baseline model results reported in the original papers. proposed-intra: intra-sentence ranking loss used, proposed-inter + intra: inter-intra-sentence ranking loss used. The highest performance for each metric is indicated in bold text.

Table 3.
Results on XSum. *: outperformed the baseline model results reported in the original papers. proposed-intra: intra-sentence ranking loss used, proposed-inter + intra: inter-intra-sentence ranking loss used. The highest performance for each metric is indicated in bold text.
In both datasets, the model using intra-sentence ranking loss outperformed the model using inter-intra-sentence ranking loss. This is because sentence pairs constituting different candidate summaries often contain similar meanings. It is rare for the meaning to duplicate sentences constituting a candidate summary. However, sentences containing different candidate summaries often have overlapping meanings. If the model encounters two sentences with similar meanings but different assigned gold scores, it learns to recognize a quality difference between them. This capability is crucial for nuanced understanding and ranking of a content. Therefore, these experimental results were obtained because these sentence pairs could act as noise when using the inter-intra-sentence ranking loss.
4.3. Few-Shot Results
In this study, we performed a few-shot experiment on a re-ranking model of abstractive summarization using two data sizes: 100-shot and 1000-shot. We sampled the training and validation sets thrice using three random seeds for each data size. The experiment was conducted with three sampled datasets, and we describe the average performance derived from the three experiments. We compared the proposed model with BRIO [8], which is a two-stage model that uses a re-ranking model with an encoder–decoder structure as the baseline. We also compared the proposed model to BART [6] and PEGASUS [15], which are single-step models that do not use a re-ranking model (this can be considered as a 0-shot setting because a re-ranking model does not exist). In this experiment, the few-shot setting was only applied to the second stage re-ranking model based on the first-stage generation model trained on the entire dataset.
The few-shot results for the CNN/DM, Xsum are presented in Table 4. In the experiments with 100-shot and 1000-shot settings for CNN/DM, the proposed model showed a higher performance for both settings compared with the baseline. In the experiment on XSum, the proposed model outperformed the baseline model in both the 100-shot and 1000-shot settings. The results indicated that the proposed method is effective, not only in conditions where the amount of training data is large, but also in conditions where there is a small amount of training data.

Table 4.
Few-shot results on CNN/DM, XSum. proposed-intra: intra-sentence ranking loss used, proposed-inter + intra: inter-intra-sentence ranking loss used. The highest performance for each metric is indicated in bold text.
In the few-shot setting, the model using inter-intra-sentence ranking loss generally showed a better performance than the model using intra-sentence ranking loss. This was because, in the few-shot setting, the gain from the additional information played a greater role than the loss from noise. Furthermore, the amount of information that could be obtained from the data was failry small because the model was trained with a small amount of data. Therefore, because the sentence pairs used in the inter-intra-sentence ranking loss were more diverse than those in the intra-sentence ranking loss, the model using the former loss function was able to learn more information than the model using the latter loss function. The gains obtained through having more information outweighed the noise caused by the inter-sentence pairs.
In addition, when comparing the performance of the proposed model and the baseline, CNN/DM, which has multiple sentences, showed a significant performance improvement compared to XSum, where the summary consists of a single sentence. These results can also be interpreted as showing that it is effective to learn as many sentence pairs as possible using a small amount of training data.
5. Analysis
In this section, we demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method by performing an additional analysis using a CNN/DM [7] test dataset. Through this analysis, we check whether the proposed method resolves the two limitations of the existing re-ranking model, as pointed out in this paper.
5.1. Sentence Ranking Performance
The first limitation is that the complex information of the sentences constituting the candidate summary was overlooked in the existing studies. In previous studies that performed summary-level supervision, it was difficult to determine whether a particular sentence in a candidate summary was well-generated. To address this limitation, the proposed method uses hierarchical supervision methods that perform sentence-level and summary-level supervision together in the training of the re-ranking model. Thus, the proposed method allows the model to learn whether a particular sentence in a candidate summary contains an important part of the original document.
Table 5 lists the accuracy when distinguishing the most or least similar sentences from the gold summary among the sentences constituting the candidate summary. This study attempted to confirm whether the proposed model effectively learned the superior relationships between sentences through analysis. We compared the performance of the proposed model with that of BRIO [8], which uses a re-ranking model with the same encoder–decoder structure as the proposed model. Compared with the baseline, the proposed model showed a performance improvement of approximately 7% in both cases. The analysis results confirmed that the proposed model can learn the ranking of sentences constituting the candidate summary. Regarding the type of sentence ranking loss, the model showed a higher accuracy when using inter-intra-sentence ranking loss than when using intra-sentence ranking loss. The reason for this is that the model learns more diverse sentence pairs when using inter-intra-sentence ranking loss than when using intra-sentence ranking loss. Thus, we can assume that the inter-intra-sentence ranking loss allows the model to learn the ranking between sentences that consist of a single candidate summary more effectively.

Table 5.
Analysis results for the accuracy of identifying the best-generated sentence and worst-generated sentence in a single candidate summary. Proposed-intra: intra-sentence ranking loss used, proposed-inter + intra: inter-intra-sentence ranking loss used. Analysis was conducted for CNN/DM. The highest performance for each metric is indicated in bold text.
5.2. Positional Bias
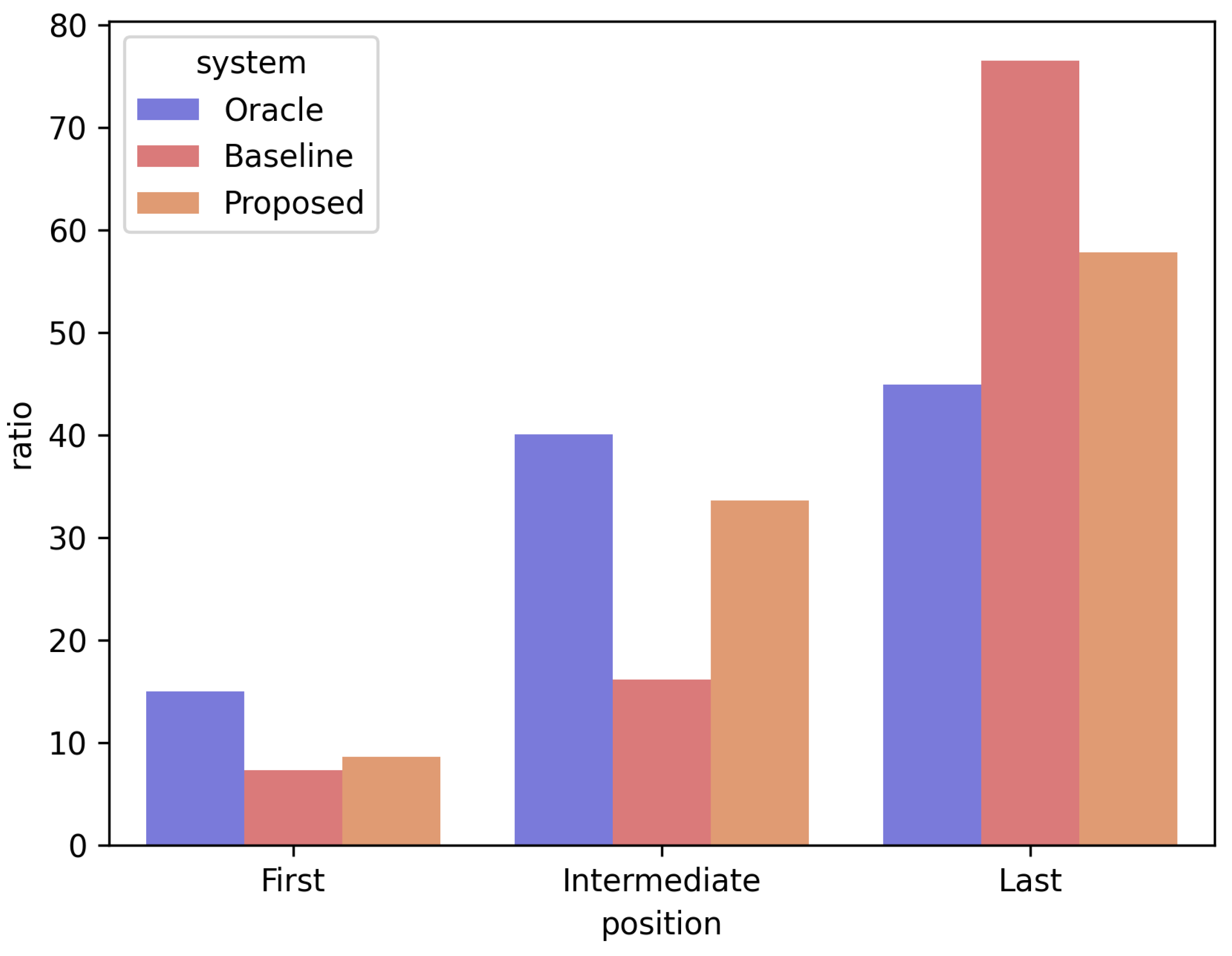
The second limitation highlighted in this study is the bias according to the position of the sentence in the existing encoder–decoder structure re-ranking model. Existing models are biased in assigning a lower prediction score because the sentence is located toward the end of the candidate summary. This study attempted to alleviate this positional bias by supervising the prediction score of a sentence to be aligned with the ground-truth ranking. Figure 5 is a bar chart comparing the position of the sentence to which the existing model BRIO [8] (expressed as “Baseline”) and the proposed model (expressed as “Proposed”) assigned the lowest prediction score in one candidate summary and the gold-truth (expressed as “Oracle”). “First” means the first sentence of the summary, “Last” means the last sentence, and “Intermediate” means all the sentences located between the first and last sentences. When comparing the baseline and proposed models, the probability of predicting the last sentence of the candidate summary as the most poorly-generated sentence was reduced by approximately 20%, from 76% to 57%. In addition, the probability of predicting that the first or intermediate sentence was the least similar to the gold summary increased. Through this analysis, we demonstrated that positional bias is alleviated in the proposed model.

Figure 5.
Analysis result of whether the positional bias of the existing encoder–decoder-based re-ranking model is alleviated. Oracle: ground-truth, baseline: existing model, proposed: proposed model. First: first sentence of summary, last: last sentence of summary, intermediate: all sentences located between first sentence and last sentence. Analysis was conducted for CNN/DM.
6. Conclusions
In this study, we proposed a re-ranking model for a two-stage abstractive summarization framework that performs hierarchical supervision. The proposed method, by concurrently implementing summary-level and sentence-level supervision, enables the model to learn not just the ranking of candidate summaries but also the ranking among sentences within each candidate summary. This dual-level approach enhances the capability of the model to discern the relative importance of both summaries and their constituent sentences. With hierarchical supervision, the model can learn complex information contained in sentences that comprise a candidate summary. The proposed method also alleviates the problem of positional bias in the existing encoder–decoder structure re-ranking model. The proposed model demonstrated the effectiveness of the hierarchical supervision method by outperforming existing studies on both the CNN/DM [7] and XSum [9] datasets. The proposed model, in the few-shot setting experiment, demonstrated improved performance over existing studies, indicating its effectiveness, even with a very small amount of training data. This suggests that the methodology introduced in this study is robust and efficient in data-constrained scenarios.
7. Limitation
The disadvantage of the proposed method is that it is difficult to tune the hyperparameters. The proposed model has various hyperparameters, such as summary sentence margin, summary sentence length penalty, sentence margin, sentence length penalty, and sentence loss function weight. Since there are many types of hyperparameters, it is a disadvantage that it takes a lot of time to adjust hyperparameters. However, the main limitation of this study is that some of the hyperparameters of the proposed model are dependent on each other. Because the sentence prediction score and summary prediction score are derived using the same model output, optimizing the summary ranking loss or sentence ranking loss affects the model’s derivation of both the sentence prediction score and the summary prediction score. Therefore, the hyperparameters of the margin for the summary ranking loss and sentence ranking loss are mutually dependent. In addition, the units of value of the summary prediction score and sentence prediction score vary according to other hyperparameters, the summary length penalty, and the sentence length penalty. In addition, even if the weight of the sentence ranking loss is constant, the ratio of the loss value of the summary ranking loss to that of the sentence ranking loss varies depending on the summary or sentence margins. Table 6 shows the results of hyperparameter tuning on CNN/DM [7]. The results of this experiment show that the performance of the proposed model varies greatly depending on the combination of hyperparameters; therefore, the proposed model has a limitation in that it is very difficult to tune hyperparameters, because they are deeply dependent on each other.

Table 6.
Results of hyperparameter tuning for CNN/DM. : summary length penalty, : summary margin, : sentence length penalty, : sentence margin, : sentence loss function weight. The highest performance is marked in bold text, and the lowest performance is underlined for each sentence ranking loss.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.Y. and G.K.; methodology, E.Y.; software, E.Y. and G.K.; data curation, E.Y.; writing—original draft preparation, E.Y.; writing—review and editing, E.Y. and G.K.; visualization, E.Y. and G.K.; supervision, S.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported in part by the National Research Foundation of Korea(NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT) (2022R1A2C1005316) and in part by Gachon University research fund of 2021 (GCU-202109980001).
Data Availability Statement
Our code is available at: https://github.com/YooEunseok/HiSumRanker, accessed on 7 January 2024. Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. This data can be found here: CNN/DM [7] (https://huggingface.co/datasets/cnn_dailymail, accessed on 7 January 2024), XSum [9] (https://huggingface.co/datasets/EdinburghNLP/xsum, accessed on 7 January 2024).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sutskever, I.; Vinyals, O.; Le, Q.V. Sequence to Sequence Learning with Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the NIPS’14, 27th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, QC, Canada, 8–13 December 2014; Volume 2, pp. 3104–3112. [Google Scholar]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. BERT: Pre-training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding. In Proceedings of the 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2–7 June 2019; (Long and Short Papers). Burstein, J., Doran, C., Solorio, T., Eds.; Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2019; Volume 1, pp. 4171–4186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengio, S.; Vinyals, O.; Jaitly, N.; Shazeer, N. Scheduled Sampling for Sequence Prediction with Recurrent Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the NIPS’15, 28th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, QC, Canada, 7–12 December 2015; Volume 1, pp. 1171–1179. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, P. SimCLS: A Simple Framework for Contrastive Learning of Abstractive Summarization. In Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 11th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing, Online, 1–6 August 2021; (Short Papers). Zong, C., Xia, F., Li, W., Navigli, R., Eds.; Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2021; Volume 2, pp. 1065–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.Y. ROUGE: A Package for Automatic Evaluation of Summaries. In Proceedings of the Text Summarization Branches Out, Barcelona, Spain, 25–26 July 2004; pp. 74–81. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, M.; Liu, Y.; Goyal, N.; Ghazvininejad, M.; Mohamed, A.; Levy, O.; Stoyanov, V.; Zettlemoyer, L. BART: Denoising Sequence-to-Sequence Pre-training for Natural Language Generation, Translation, and Comprehension. In Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Online, 5–10 July 2020; Jurafsky, D., Chai, J., Schluter, N., Tetreault, J., Eds.; Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2020; pp. 7871–7880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermann, K.M.; Kociský, T.; Grefenstette, E.; Espeholt, L.; Kay, W.; Suleyman, M.; Blunsom, P. Teaching Machines to Read and Comprehend. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 28; Curran Associates, Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 1693–1701. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, P.; Radev, D.; Neubig, G. BRIO: Bringing Order to Abstractive Summarization. In Proceedings of the 60th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Dublin, Ireland, 22–27 May 2022; (Long Papers). Muresan, S., Nakov, P., Villavicencio, A., Eds.; Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2022; Volume 1, pp. 2890–2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayan, S.; Cohen, S.B.; Lapata, M. Don’t Give Me the Details, Just the Summary! Topic-Aware Convolutional Neural Networks for Extreme Summarization. In Proceedings of the 2018 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Brussels, Belgium, 31 October–4 November 2018; Riloff, E., Chiang, D., Hockenmaier, J., Tsujii, J., Eds.; Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2018; pp. 1797–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ott, M.; Goyal, N.; Du, J.; Joshi, M.; Chen, D.; Levy, O.; Lewis, M.; Zettlemoyer, L.; Stoyanov, V. RoBERTa: A Robustly Optimized BERT Pretraining Approach. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1907.11692. [Google Scholar]
- Ravaut, M.; Joty, S.; Chen, N. SummaReranker: A Multi-Task Mixture-of-Experts Re-ranking Framework for Abstractive Summarization. In Proceedings of the 60th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Dublin, Ireland, 22–27 May 2022; (Long Papers). Muresan, S., Nakov, P., Villavicencio, A., Eds.; Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2022; Volume 1, pp. 4504–4524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhao, Z.; Yi, X.; Chen, J.; Hong, L.; Chi, E.H. Modeling Task Relationships in Multi-Task Learning with Multi-Gate Mixture-of-Experts. In Proceedings of the KDD’18, 24th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, London, UK, 19–23 August 2018; pp. 1930–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Neubig, G.; Liu, P. BARTScore: Evaluating Generated Text as Text Generation. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 34; Ranzato, M., Beygelzimer, A., Dauphin, Y., Liang, P., Vaughan, J.W., Eds.; Curran Associates, Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2021; Volume 34, pp. 27263–27277. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Kishore, V.; Wu, F.; Weinberger, K.Q.; Artzi, Y. BERTScore: Evaluating Text Generation with BERT. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 26–30 April 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Saleh, M.; Liu, P.J. PEGASUS: Pre-Training with Extracted Gap-Sentences for Abstractive Summarization. In Proceedings of the ICML’20, 37th International Conference on Machine Learning, Virtual, 13–18 July 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, B.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhao, H. Sentence-aware Contrastive Learning for Open-Domain Passage Retrieval. In Proceedings of the 60th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Dublin, Ireland, 22–27 May 2022; (Long Papers). Muresan, S., Nakov, P., Villavicencio, A., Eds.; Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2022; Volume 1, pp. 1062–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Chen, K.; Mou, L.; Zhao, T. Document-Level Relation Extraction with Sentences Importance Estimation and Focusing. In Proceedings of the 2022 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Seattle, WA, USA, 10–15 July 2022; Carpuat, M., de Marneffe, M.C., Meza Ruiz, I.V., Eds.; Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2022; pp. 2920–2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Song, K.; Zhang, H.; Jin, L.; Cho, S.; Yao, W.; Wang, X.; Chen, M.; Yu, D. Salience Allocation as Guidance for Abstractive Summarization. In Proceedings of the 2022 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 7–11 December 2022; Goldberg, Y., Kozareva, Z., Zhang, Y., Eds.; pp. 6094–6106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Wang, B.; Feng, Z.; Liu, R.; Liu, F. Controlling the Amount of Verbatim Copying in Abstractive Summarization. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 2020, 34, 8902–8909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, C.J.; Jensen, E.J.; Zamponi, V.; O’Brien, K.; Frydenlund, E.; Gore, R. A Structured Narrative Prompt for Prompting Narratives from Large Language Models: Sentiment Assessment of ChatGPT-Generated Narratives and Real Tweets. Future Internet 2023, 15, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayakumar, A.K.; Cogswell, M.; Selvaraju, R.R.; Sun, Q.; Lee, S.; Crandall, D.; Batra, D. Diverse Beam Search: Decoding Diverse Solutions from Neural Sequence Models. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1610.02424. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/1610.02424 (accessed on 7 October 2016).
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, San Diego, CA, USA, 7–9 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Lapata, M. Text Summarization with Pretrained Encoders. In Proceedings of the 2019 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing and the 9th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (EMNLP-IJCNLP), Hong Kong, China, 3–7 November 2019; Inui, K., Jiang, J., Ng, V., Wan, X., Eds.; Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2019; pp. 3730–3740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, L.; Wu, J.; Jiang, X.; Almeida, D.; Wainwright, C.L.; Mishkin, P.; Zhang, C.; Agarwal, S.; Slama, K.; Ray, A.; et al. Training language models to follow instructions with human feedback. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.02155. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/2203.02155 (accessed on 4 March 2022).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).