Neural Network-Based Distributed Consensus Tracking Control for Nonlinear Multi-Agent Systems with Mismatched and Matched Disturbances
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Preliminaries
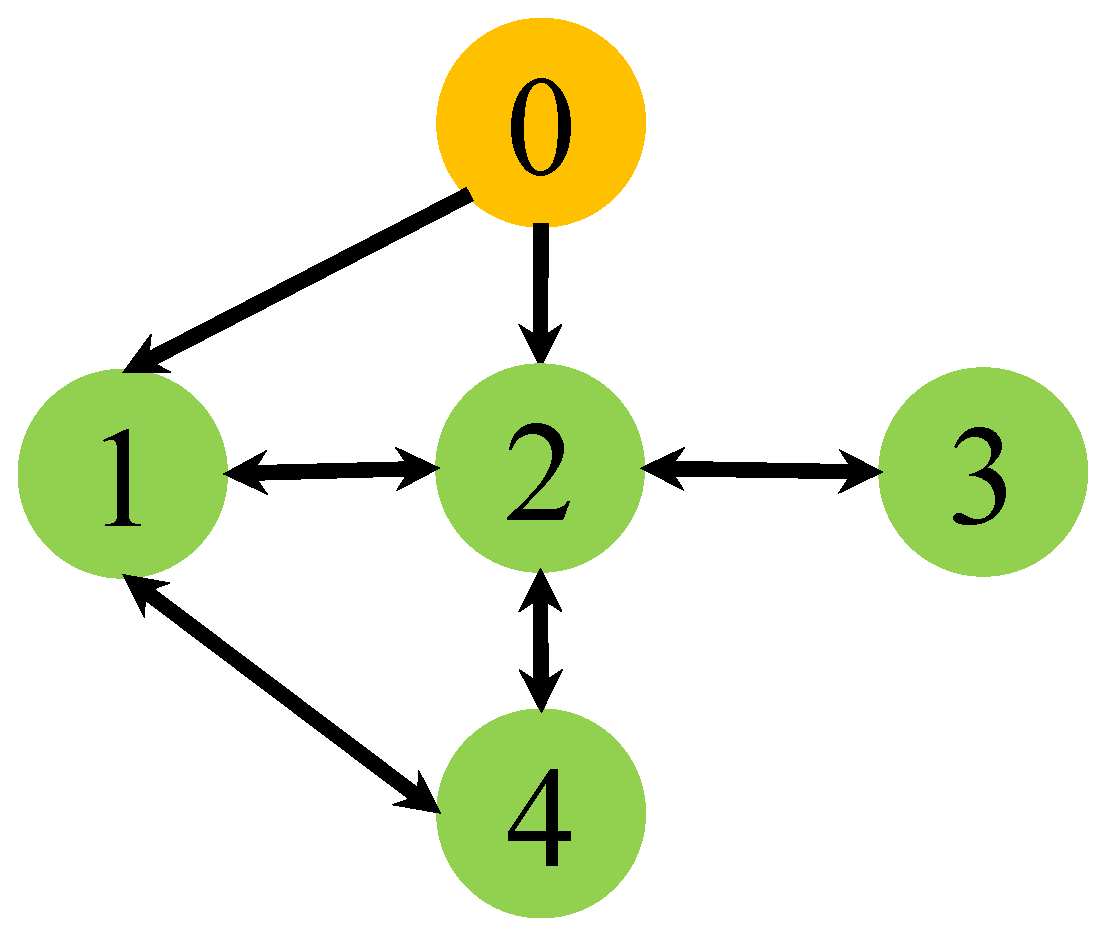
2.1. Graph Theories
2.2. Barrier Function
- is strictly increasing in the interval .
- .
- The function has a unique minimum as .
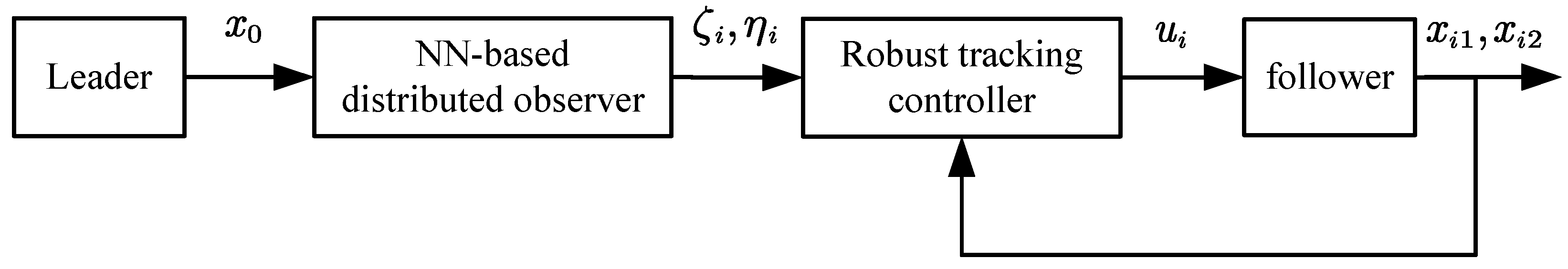
3. Problem Statement
4. Main Results
4.1. Neural Network-Based Distributed Observer Design
4.2. Robust Tracking Controller Design
4.2.1. Step 1
4.2.2. Step 2
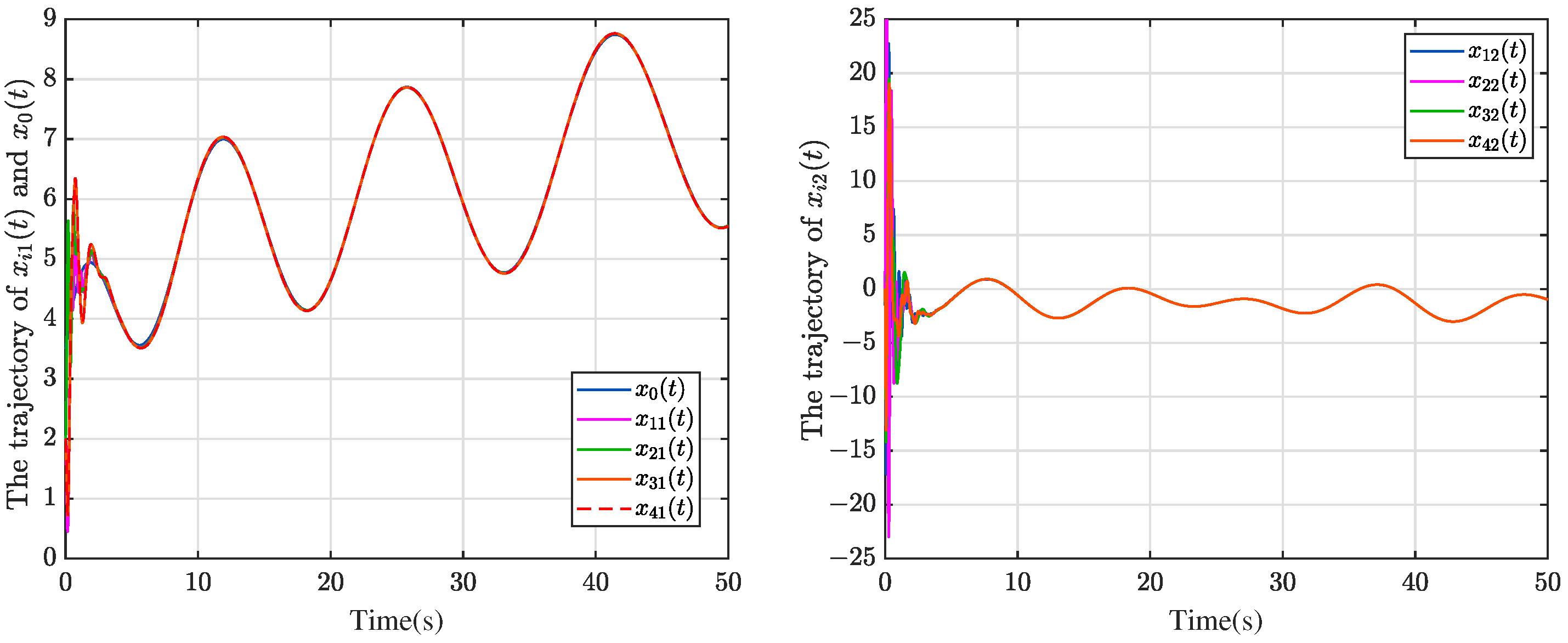
5. Simulation Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, J.; Yan, J.; Zhang, P. Multi-UAV formation control based on a novel back-stepping approach. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 2437–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madridano, A.; Al-Kaff, A.; Martín, D.; De La Escalera, A. Trajectory planning for multi-robot systems: Methods and applications. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 173, 114660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Govindarasu, M. Multi-agent based attack-resilient system integrity protection for smart grid. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2020, 11, 3447–3456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, D.E. Multi-sensor network information for linear-Gaussian multi-target tracking systems. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2021, 69, 4312–4325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Tang, Y.; Karimi, H.R. Consensus of multi-agent systems via fully distributed event-triggered control. Automatica 2020, 116, 108898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G. Global synchronization and asymptotic stability of complex dynamical networks. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2006, 53, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Li, Z. Finite-time consensus for multi-agent systems with directed dynamically changing topologies. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 2023, 33, 8657–8669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdifar, F.; Bechlioulis, C.P.; Hashemzadeh, F.; Baradarannia, M. Prescribed performance distance-based formation control of multi-agent systems. Automatica 2020, 119, 109086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Shi, Z.; Gao, Z. Neural-network-based finite-time bipartite containment control for fractional-order multi-agent systems. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2022, 34, 7418–7429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; An, Q.; Miao, S.; Chen, S.; Wang, X.; Su, H. Flocking of uncertain nonlinear multi-agent systems via distributed adaptive event-triggered control. Neurocomputing 2021, 465, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Guan, S. Diffusion normalized Huber adaptive filtering algorithm. J. Frankl. Inst. 2018, 355, 3812–3825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.H.; Yoo, S.J. Neural-network-based distributed asynchronous event-triggered consensus tracking of a class of uncertain nonlinear multi-agent systems. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2021, 33, 2965–2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, J.; Feng, J.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Y. Tracking consensus of multi-agent systems under switching topologies via novel SMC: An event-triggered approach. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2022, 9, 2150–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.; Li, H.; Ma, H.; Lu, R. Finite-time consensus tracking neural network FTC of multi-agent systems. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2020, 32, 653–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, P.; Han, Q.L.; Lan, W. Finite-time consensus tracking for incommensurate fractional-order nonlinear multiagent systems with directed switching topologies. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2020, 52, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Cao, Y.; Niu, B.; Song, Y. A novel bipartite consensus tracking control for multiagent systems under sensor deception attacks. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2022, 53, 5984–5993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, B.; Han, Q.L.; Zuo, Z. Bipartite consensus tracking for second-order multiagent systems: A time-varying function-based preset-time approach. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2020, 66, 2739–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Peng, C.; Tian, E. Finite-time and fixed-time bipartite consensus tracking of multi-agent systems with weighted antagonistic interactions. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2020, 68, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Ye, D. Observer-based fixed-time secure tracking consensus for networked high-order multiagent systems against DoS attacks. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2020, 52, 2018–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Jiang, B.; Zhang, K.; Patton, R.J. Distributed fault-tolerant consensus tracking control of multi-agent systems under fixed and switching topologies. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2021, 68, 1646–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W. Multi-vehicle consensus with a time-varying reference state. Syst. Control Lett. 2007, 56, 474–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, G.; Duan, Z.; Chen, G.; Yu, W. Consensus tracking of multi-agent systems with Lipschitz-type node dynamics and switching topologies. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2013, 61, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, X.; Ren, W.; Xie, L. Distributed tracking control for linear multiagent systems with a leader of bounded unknown input. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2012, 58, 518–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Ding, Z. Distributed adaptive consensus and output tracking of unknown linear systems on directed graphs. Automatica 2015, 55, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, B.; Lin, C.; Shang, Y. Fuzzy adaptive fixed-time consensus tracking control of high-order multi-agent systems. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2020, 30, 567–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, G.; Wang, H.; Yu, X.; Yu, W. Bipartite tracking consensus of linear multi-agent systems with a dynamic leader. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2017, 65, 1204–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.; Zheng, W.X.; Shi, L.; Cheng, Y. Bipartite tracking consensus of generic linear agents with discrete-time dynamics over cooperation–competition networks. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2020, 51, 5225–5235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, R.; He, W.; Du, W.; Lang, Z.; He, S. Dynamic event-triggered SMC of multi-agent systems for consensus tracking. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2021, 69, 1188–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.; Shi, P.; Zhao, Y.; Pan, Q.; Wang, S. Fixed-time event-triggered output consensus tracking of high-order multiagent systems under directed interaction graphs. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2020, 52, 6391–6405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Lan, W. Adaptive robust tracking control for multiple unknown fractional-order nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2018, 49, 1365–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Xu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhong, W. Adaptive consensus tracking of multi-robotic systems via using integral sliding mode control. Neurocomputing 2021, 455, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yang, G.H. Distributed H-infty consensus tracking control for multi-agent networks with switching directed topologies. Neurocomputing 2016, 207, 693–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wu, Z.H.; Deng, F.; Guo, B.Z. Active Disturbance Rejection Control to Consensus of Second-Order Stochastic Multi-Agent Systems. IEEE Trans. Control Netw. Syst. 2022, 10, 993–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, H.; Guo, R.; Zhou, J.; Zhu, X.; Li, N.; Miao, Z. Robust consensus tracking control for switched multiple Lagrangian systems by UDE-based control method. J. Frankl. Inst. 2023, 360, 14372–14387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.; Chen, J.; Wei, Q.; Zhang, W. Robust global consensus tracking of linear multi-agent systems with input saturation via scheduled low-and-high gain feedback. IET Control Theory Appl. 2019, 13, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, X.; Yu, J.; Jia, Z.; Yang, D.; Xu, X.; Shen, Y. Disturbance observer–based consensus tracking for nonlinear multiagent systems with switching topologies. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 2018, 28, 2144–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obeid, H.; Fridman, L.M.; Laghrouche, S.; Harmouche, M. Barrier function-based adaptive sliding mode control. Automatica 2018, 93, 540–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, L.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, L.; Li, G. Disturbance Observer-Based Finite-Time Tracking Control for a Class of Second-Order Nonlinear Systems with Mismatched and Matched Uncertainties. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Guidance, Navigation and Control, Tianjin, China, 5–7 August 2022; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 3981–3990. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Hua, S.; Ge, S.S. Consensus-based distributed cooperative learning control for a group of discrete-time nonlinear multi-agent systems using neural networks. Automatica 2014, 50, 2254–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Lu, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Efe, M.Ö.; Hong, K.S. Single parameter adaptive neural network control for multi-agent deployment with prescribed tracking performance. Automatica 2023, 156, 111207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, H.K. Nonlinear Systems, 3rd ed.; Prentice Hall: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 134–180. [Google Scholar]
- Aboudonia, A.; Rashad, R.; El-Badawy, A. Composite hierarchical anti-disturbance control of a quadrotor UAV in the presence of matched and mismatched disturbances. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2018, 90, 201–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Qin, K.; Liang, J.; Liu, J. Distributed control of uncertain multiagent systems for tracking a leader with unknown fractional-order dynamics. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 2019, 29, 2254–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 100 | 0.1 | |||
| 10 | 100 | 0.02 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, L.; Qin, K. Neural Network-Based Distributed Consensus Tracking Control for Nonlinear Multi-Agent Systems with Mismatched and Matched Disturbances. Mathematics 2024, 12, 1319. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12091319
Xu L, Qin K. Neural Network-Based Distributed Consensus Tracking Control for Nonlinear Multi-Agent Systems with Mismatched and Matched Disturbances. Mathematics. 2024; 12(9):1319. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12091319
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Linxi, and Kaiyu Qin. 2024. "Neural Network-Based Distributed Consensus Tracking Control for Nonlinear Multi-Agent Systems with Mismatched and Matched Disturbances" Mathematics 12, no. 9: 1319. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12091319
APA StyleXu, L., & Qin, K. (2024). Neural Network-Based Distributed Consensus Tracking Control for Nonlinear Multi-Agent Systems with Mismatched and Matched Disturbances. Mathematics, 12(9), 1319. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12091319






