An Image-Based Double-Smoothing Cohesive Finite Element Framework for Particle-Reinforced Materials
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Method of Image-Based Reconstruction
- (1)
- The uneven illumination and noises in digital image give rise to the loss of particles and the appearance of unreasonable voids;
- (2)
- The meshes with square elements lead to the appearance of jagged interfaces.
2.1. Smoothing Process for Digital Image
2.2. Pixel-to-Element Mapping
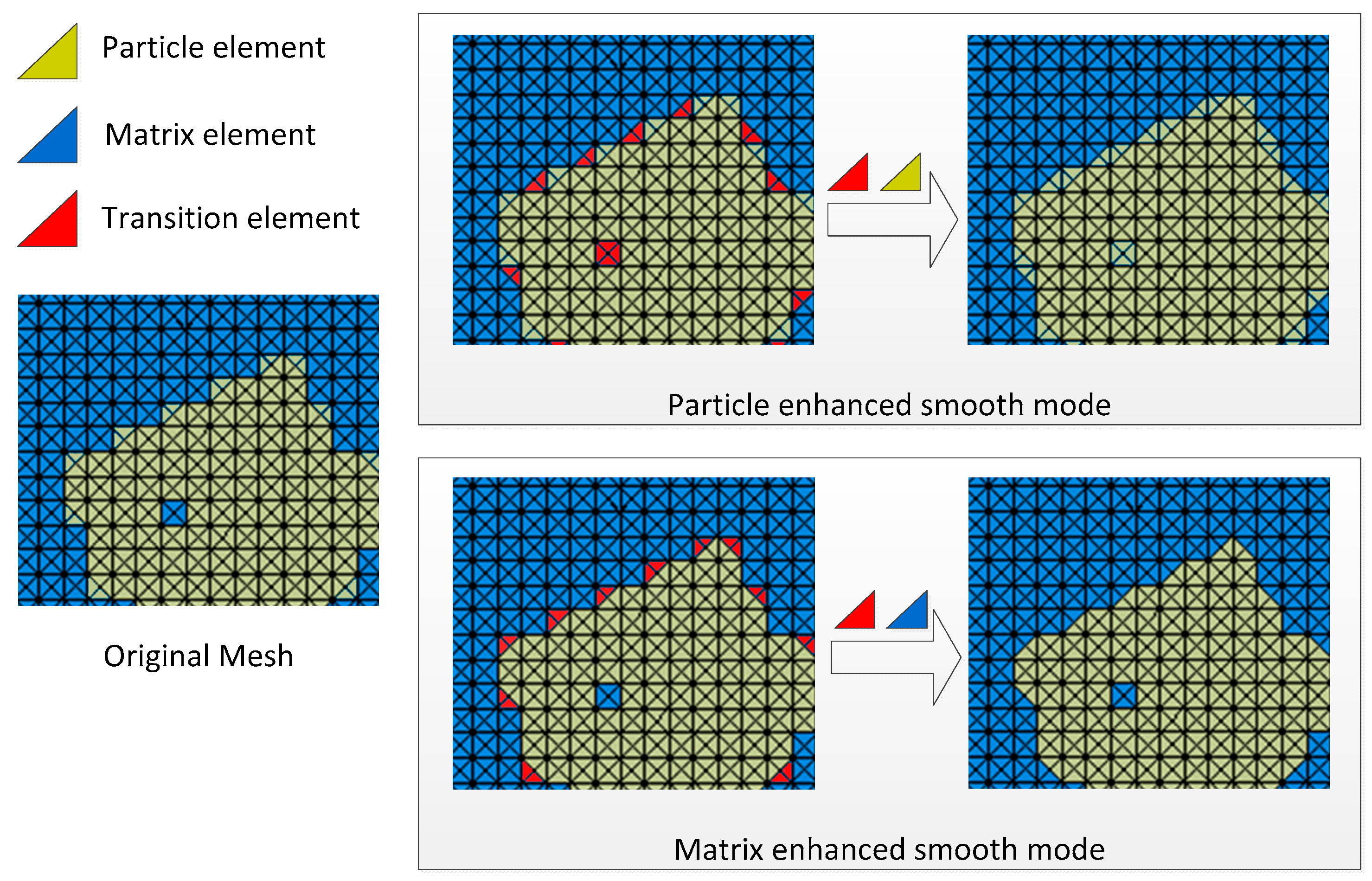
- Since triangular elements are used to smooth the meshes, the rough interfaces caused by square elements are improved effectively;
- The present model can be expanded to an cohesive finite element framework, a significant model for the simulation of damage and fracture, easily.
2.3. Smoothing Process for FE Mesh
3. Comparison of the Smoothed and Unsmoothed Model
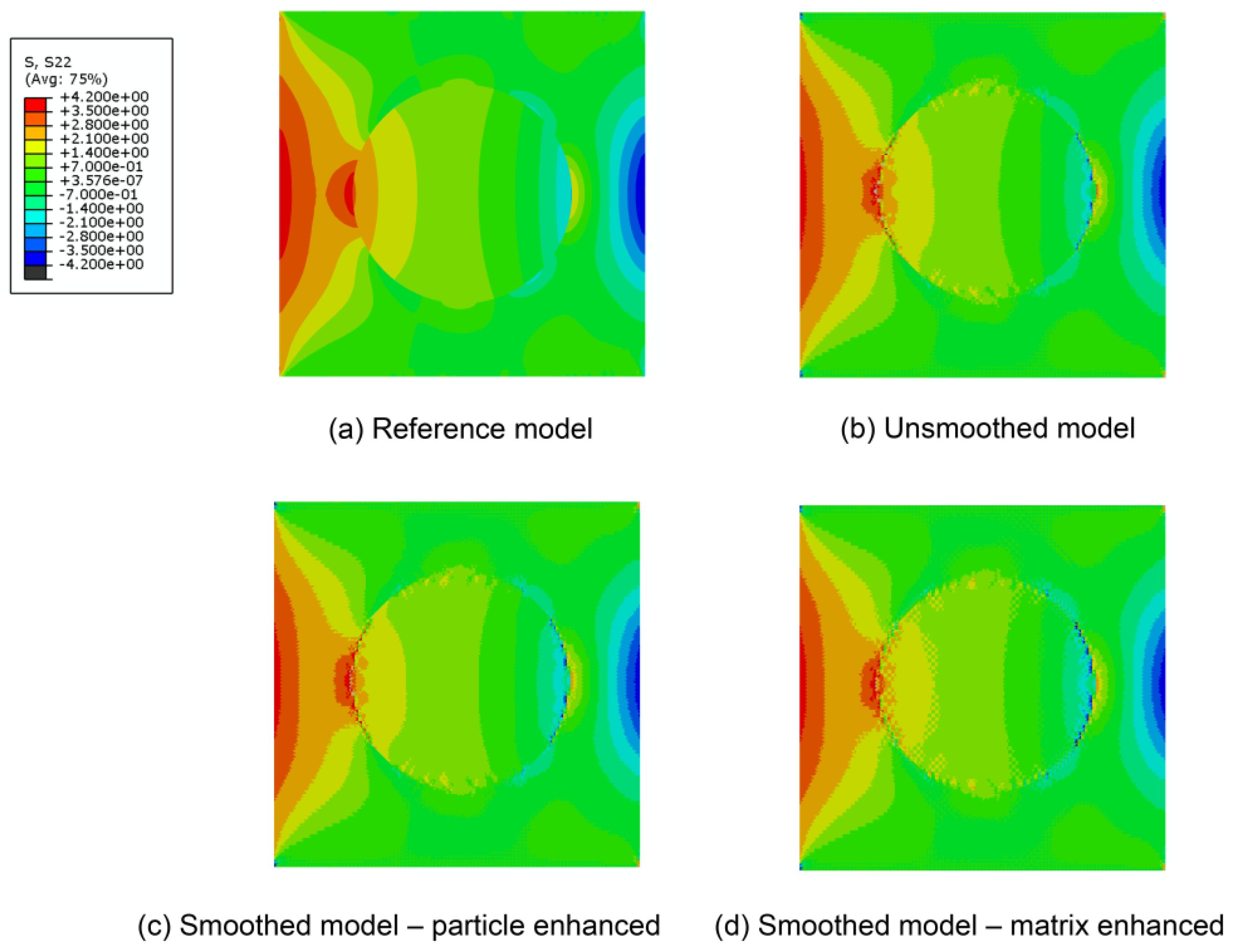
3.1. One Circular Particle Model
3.1.1. Models without the Consideration of Damage
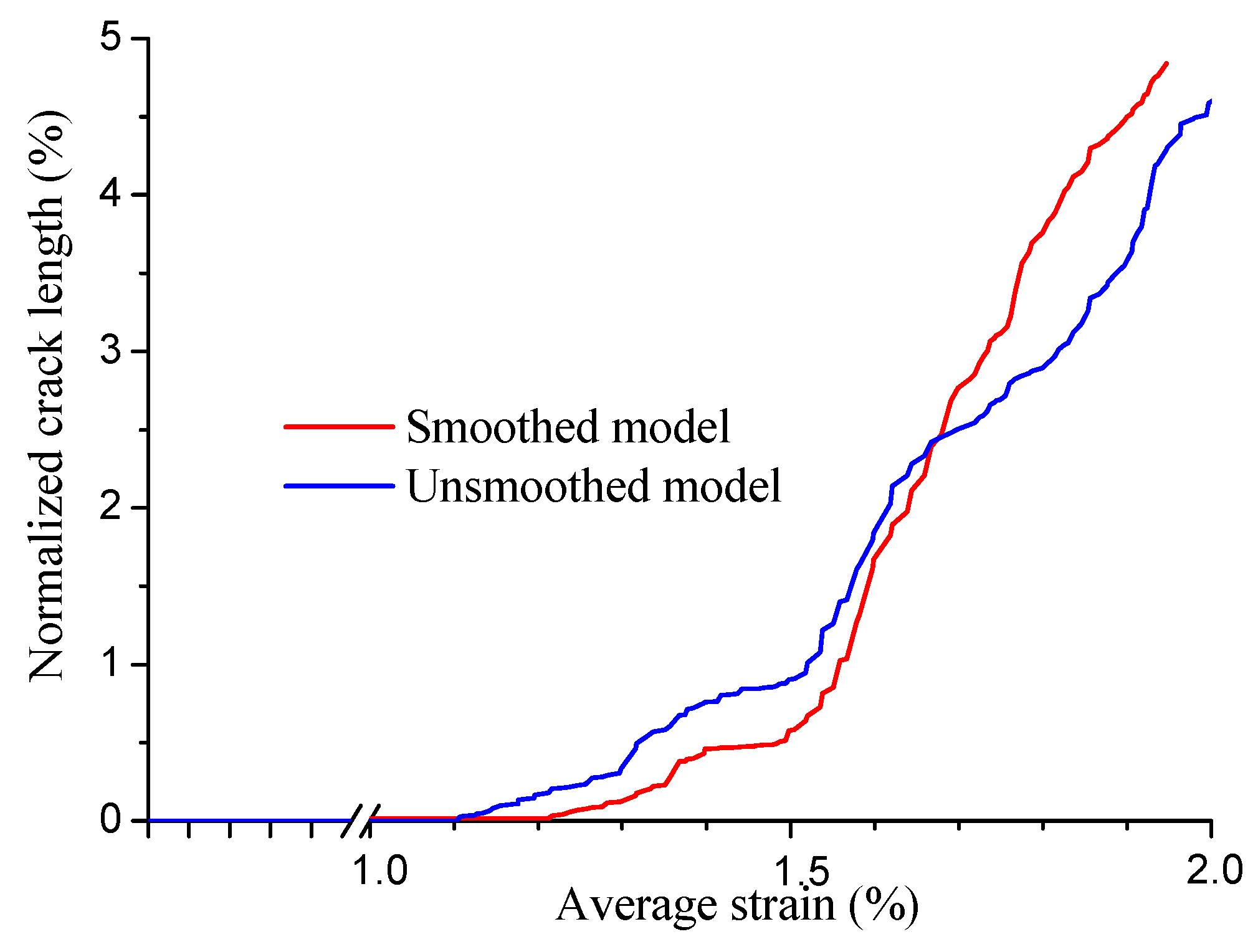
3.1.2. Models with the Consideration of Damage
4. Application in Polymer Binder Explosive Model
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahmed, S.; Jones, F. A review of particulate reinforcement theories for polymer composites. J. Mater. Sci. 1990, 25, 4933–4942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, I.; Mohamed, F.; Lavernia, E. Particulate reinforced metal matrix composites—A review. J. Mater. Sci. 1991, 26, 1137–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keiser, D.D.; Robinson, A.B.; Jue, J.-F.; Medvedev, P.; Wachs, D.M.; Finlay, M.R. Microstructural development in irradiated U-7Mo/6061 Al alloy matrix dispersion fuel. J. Nucl. Mater. 2009, 393, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cebral, J.R.; Löhner, R. From medical images to anatomically accurate finite element grids. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 2001, 51, 985–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, N.; Chawla, K. Microstructure-based modeling of the deformation behavior of particle reinforced metal matrix composites. J. Mater. Sci. 2006, 41, 913–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babout, L.; Maire, E.; Fougeres, R. Damage initiation in model metallic materials: X-ray tomography and modelling. Acta Mater. 2004, 52, 2475–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, A.; El-Danaf, E.; Kalidindi, S.R.; Doherty, R.D. Evolution of grain-scale microstructure during large strain simple compression of polycrystalline aluminum with quasi-columnar grains: OIM measurements and numerical simulations. Int. J. Plast. 2001, 17, 861–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terada, K.; Miura, T.; Kikuchi, N. Digital image-based modeling applied to the homogenization analysis of composite materials. Comput. Mech. 1997, 20, 331–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindez, J.M.; Molinero, J. Assessment of the long-term stability of cementitious barriers of radioactive waste repositories by using digital-image-based microstructure generation and reactive transport modelling. Cem. Concr. Res. 2010, 40, 1278–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barua, A.; Zhou, M. A Lagrangian framework for analyzing microstructural level response of polymer-bonded explosives. Model. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2011, 19, 055001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Ooi, E.; Saputra, A.; Yang, Z.; Natarajan, S.; Ooi, E.; Song, C. A quadtree-polygon-based scaled boundary finite element method for image-based mesoscale fracture modelling in concrete. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2019, 211, 420–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trawiński, W.; Tejchman, J.; Bobiński, J. A three-dimensional meso-scale modelling of concrete fracture, based on cohesive elements and X-ray μCT images. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2018, 189, 27–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trawiński, W.; Bobiński, J.; Tejchman, J. Two-dimensional simulations of concrete fracture at aggregate level with cohesive elements based on X-ray μCT images. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2016, 168, 204–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saputra, A.; Talebi, H.; Tran, D.; Birk, C.; Song, C. Automatic image-based stress analysis by the scaled boundary finite element method. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 2017, 109, 697–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Yang, Z.; Sharma, R.; Zhang, C.; Withers, P.J. Two-dimensional X-ray CT image based meso-scale fracture modelling of concrete. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2015, 133, 24–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, W.-D.; Legrain, G.; Cartraud, P. Image-based computational homogenization and localization: Comparison between X-FEM/levelset and voxel-based approaches. Comput. Mech. 2013, 51, 279–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, W.; Tang, L.; Liu, X.; Ma, G.; Chen, M. Mesoscopic simulation of the dynamic tensile behaviour of concrete based on a rate-dependent cohesive model. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2016, 95, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lengsfeld, M.; Schmitt, J.; Alter, P.; Kaminsky, J.; Leppek, R. Comparison of geometry-based and CT voxel-based finite element modelling and experimental validation. Med. Eng. Phys. 1998, 20, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero-Chacón, F.; Marín-Montín, J.; Medina, F. Mesomechanical characterization of porosity in cementitious composites by means of a voxel-based finite element model. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2014, 90, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz-Herrera, J.; Garcia Aznar, J.M.; Doblaré, M. Micro–macro numerical modelling of bone regeneration in tissue engineering. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2008, 197, 3092–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bright, D.S.; Steel, E.B. Two-Dimensional Top Hat Filter for Extracting Spots and Spheres from Digital Images. J. Microsc. 1987, 146, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiener, N. Extrapolation, Interpolation, and Smoothing of Stationary Time Series; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1949. [Google Scholar]
- Rae, P.J.; Goldrein, H.T.; Palmer, S.J.P.; Field, J.E.; Lewis, A.L. Quasi-static studies of the deformation and failure of beta-HMX based polymer bonded explosives. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2002, 458, 743–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rae, P.J.; Palmer, S.J.P.; Goldrein, H.T.; Field, J.E.; Lewis, A.L. Quasi-static studies of the deformation and failure of PBX 9501. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2002, 458, 2227–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero-Chacón, F.; Zaghi, S.; Rossi, R.; Garc’ia-Pérez, E.; Heras, I.; Martinez, X.; Oller, S.; doblaré, M. Multiscale thermo-mechanical analysis of multi-layered materials in solar thermal applications. Finite Elem. Anal. Des. 2017, 127, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, X.P.; Needleman, A. Numerical simulations of dynamic crack growth along an interface. Int. J. Fract. 1996, 74, 289–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.P.; Needleman, A. Numerical Simulations of Fast Crack-Growth in Brittle Solids. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 1994, 42, 1397–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Referenced | Unsmoothed | Smoothed-P | Smoothed-M | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| The volume fraction of particle (%) | 28.27 | 27.56 | 27.18 | 27.92 |
| Radian of the Cracks (Degree) | Errors (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Left Side | Right Side | Left Side | Right Side | |
| Referenced model | 91.57 | 70.17 | 0 | 0 |
| Unsmoothed model | 73.74 | 59.96 | 14.54 | 19.47 |
| Smoothed–P model | 92.73 | 71.08 | 1.29 | 1.26 |
| Smoothed–M model | 87.21 | 65.24 | 7.03 | 4.77 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bai, X.; Mi, X.; Xie, H.; Shi, K.; Xiong, F.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, L. An Image-Based Double-Smoothing Cohesive Finite Element Framework for Particle-Reinforced Materials. Mathematics 2020, 8, 543. https://doi.org/10.3390/math8040543
Bai X, Mi X, Xie H, Shi K, Xiong F, Zhang Y, Guo L. An Image-Based Double-Smoothing Cohesive Finite Element Framework for Particle-Reinforced Materials. Mathematics. 2020; 8(4):543. https://doi.org/10.3390/math8040543
Chicago/Turabian StyleBai, Xiaoming, Xue Mi, Hai Xie, Kaikai Shi, Furui Xiong, Yixiong Zhang, and Licheng Guo. 2020. "An Image-Based Double-Smoothing Cohesive Finite Element Framework for Particle-Reinforced Materials" Mathematics 8, no. 4: 543. https://doi.org/10.3390/math8040543
APA StyleBai, X., Mi, X., Xie, H., Shi, K., Xiong, F., Zhang, Y., & Guo, L. (2020). An Image-Based Double-Smoothing Cohesive Finite Element Framework for Particle-Reinforced Materials. Mathematics, 8(4), 543. https://doi.org/10.3390/math8040543





