Darcy–Brinkman–Forchheimer Model for Nano-Bioconvection Stratified MHD Flow through an Elastic Surface: A Successive Relaxation Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
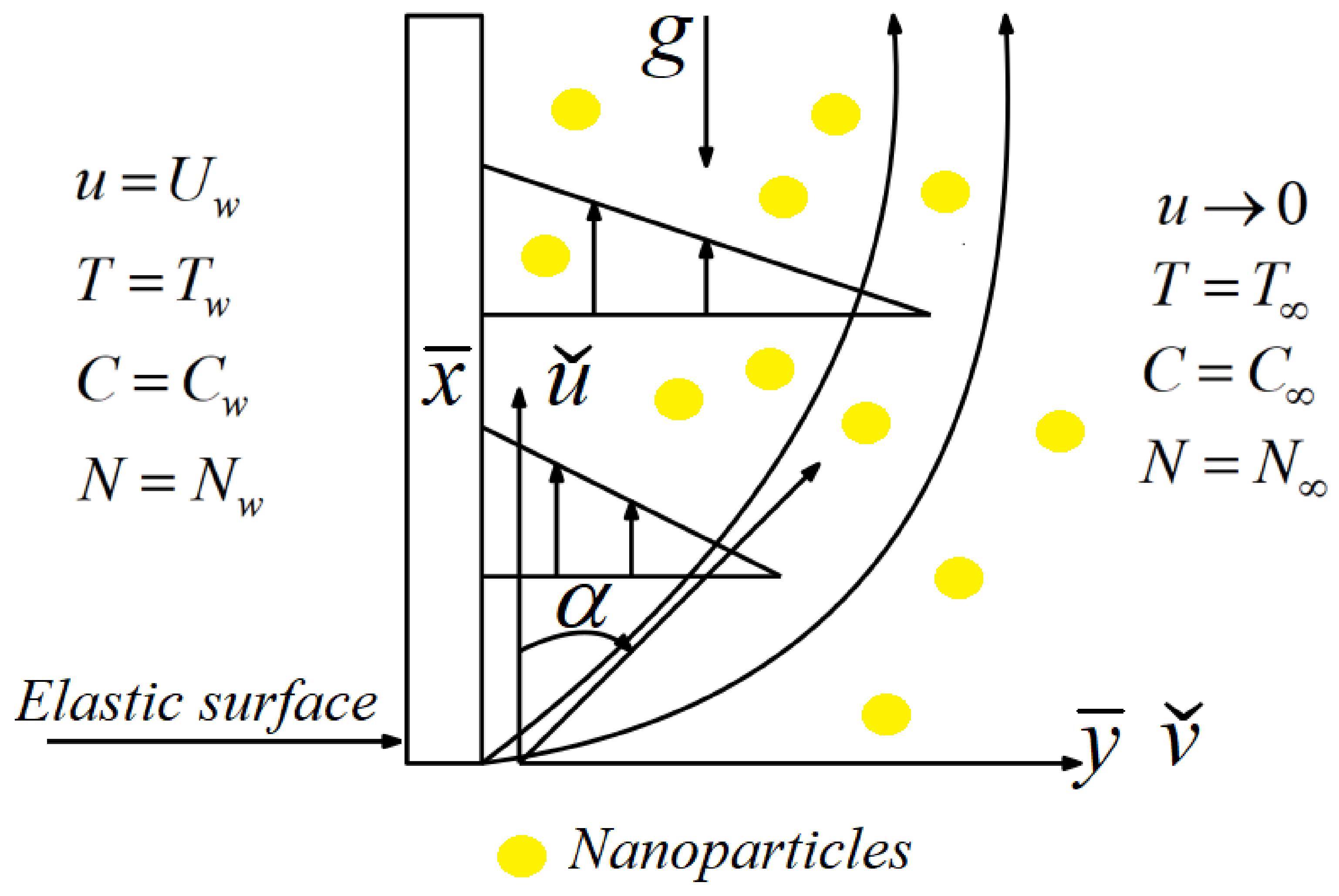
2. Mathematical Model
3. Numerical Method
3.1. The SRM Scheme and Its Elementary Notion
3.2. Solutions by SRM Technique
4. Convergence, Error, and Stableness of the Iteration Scheme
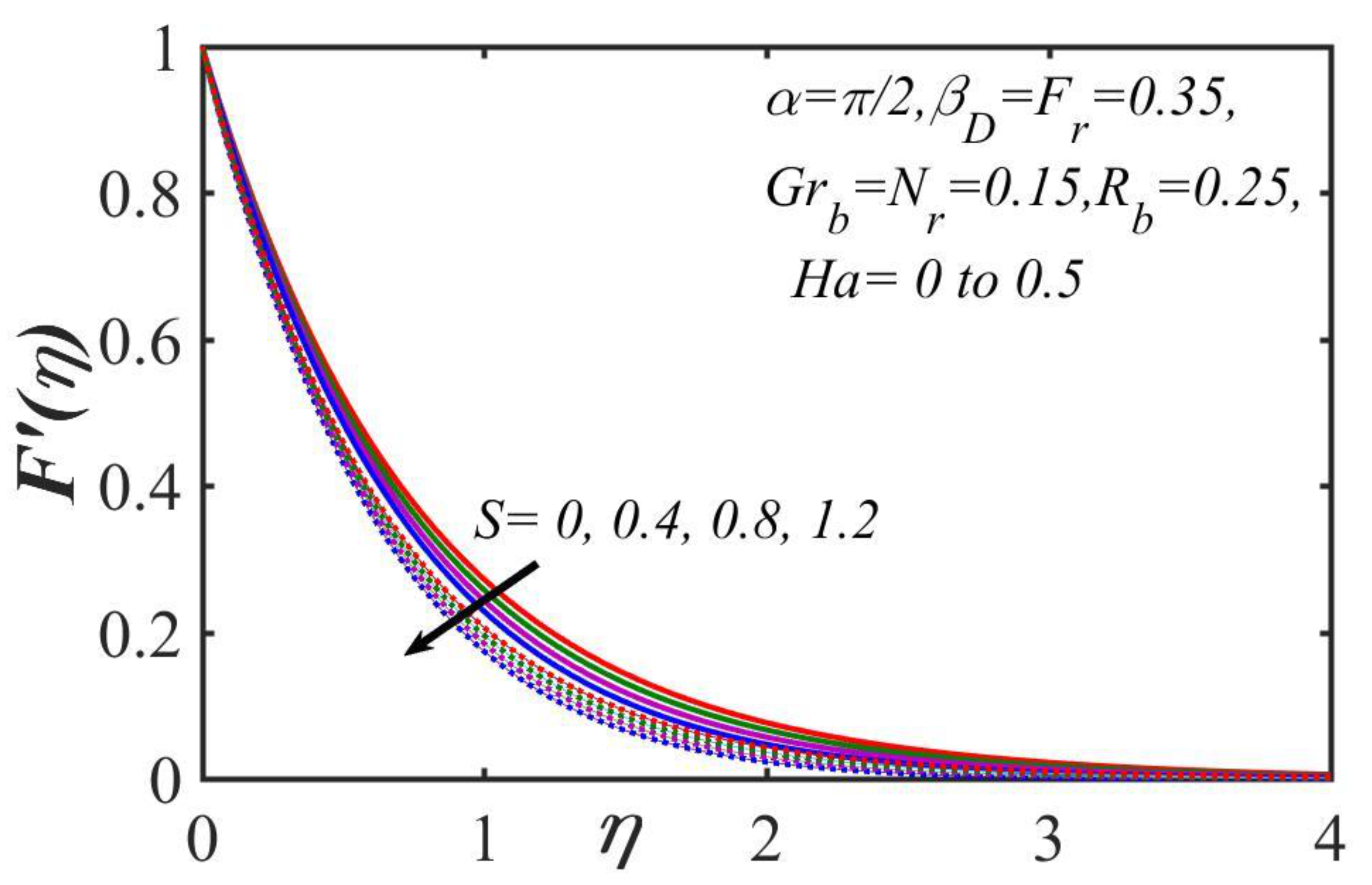
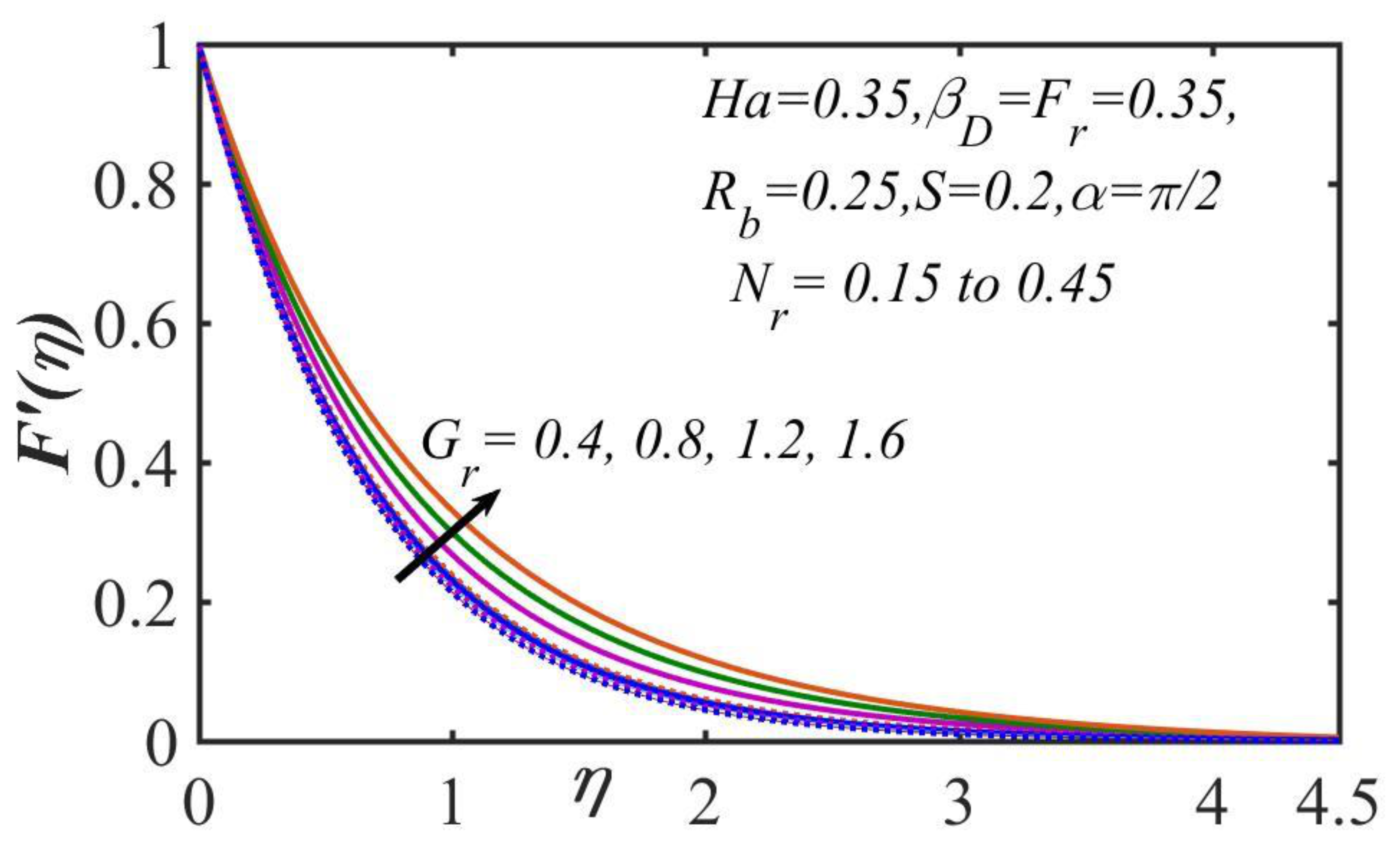
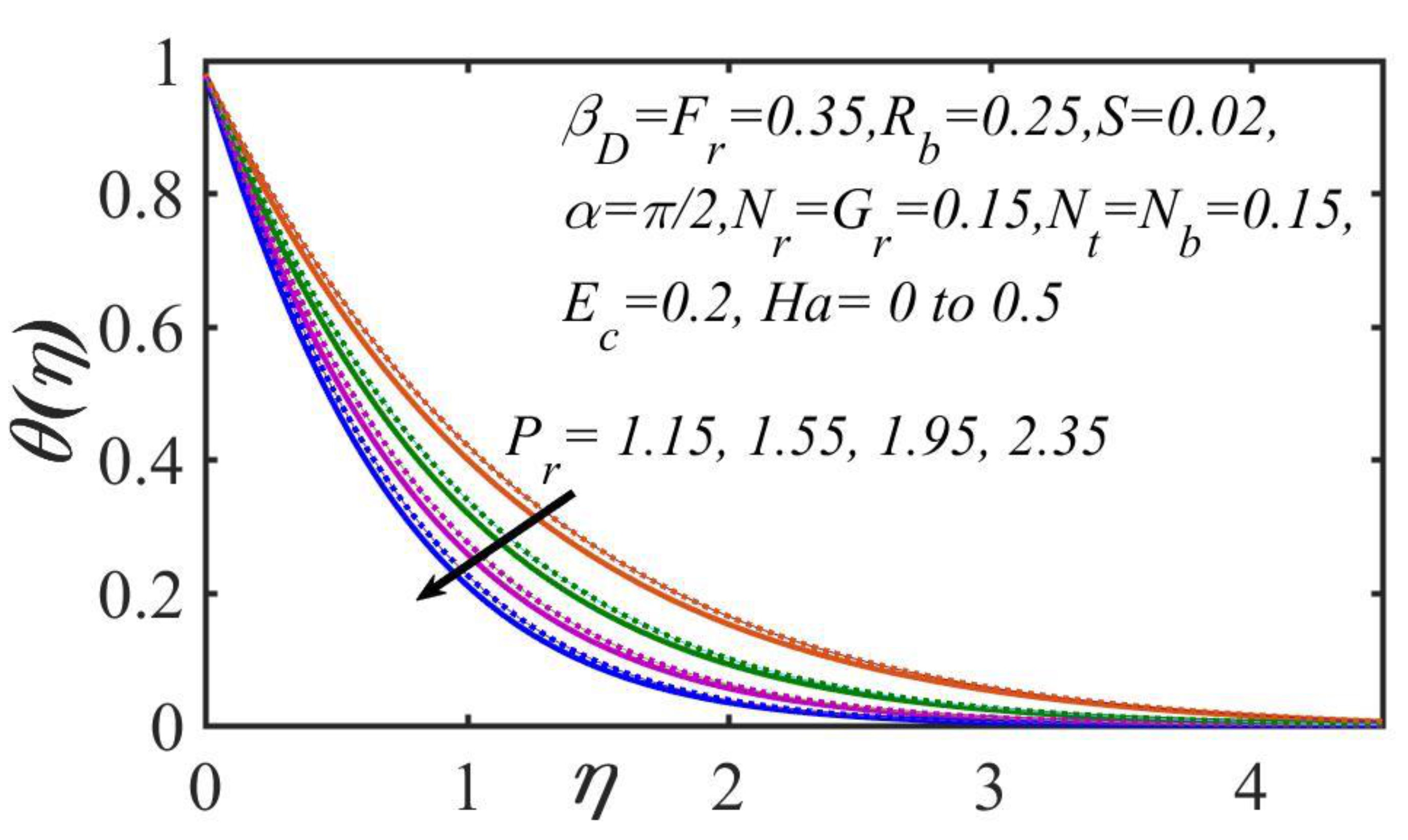
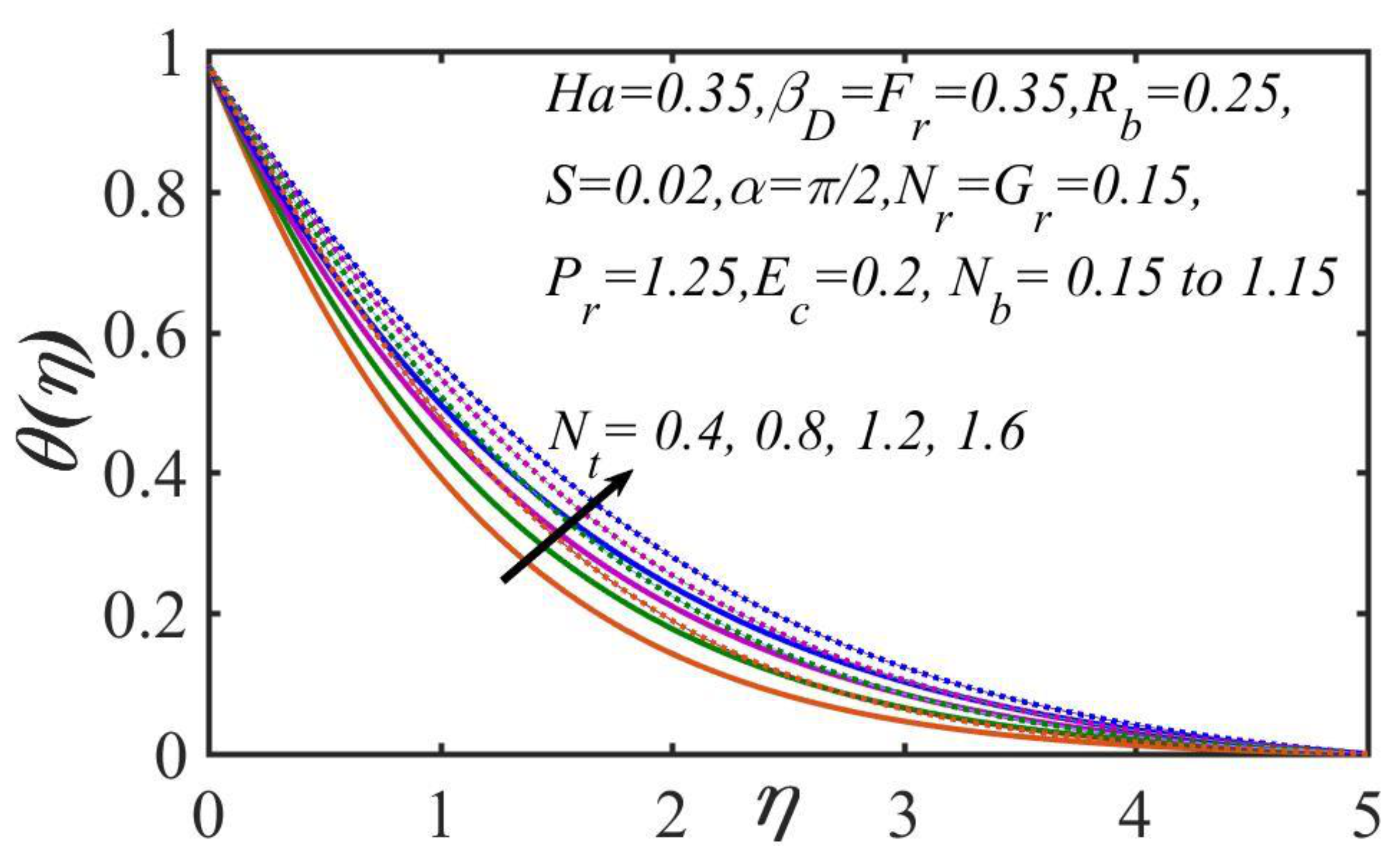
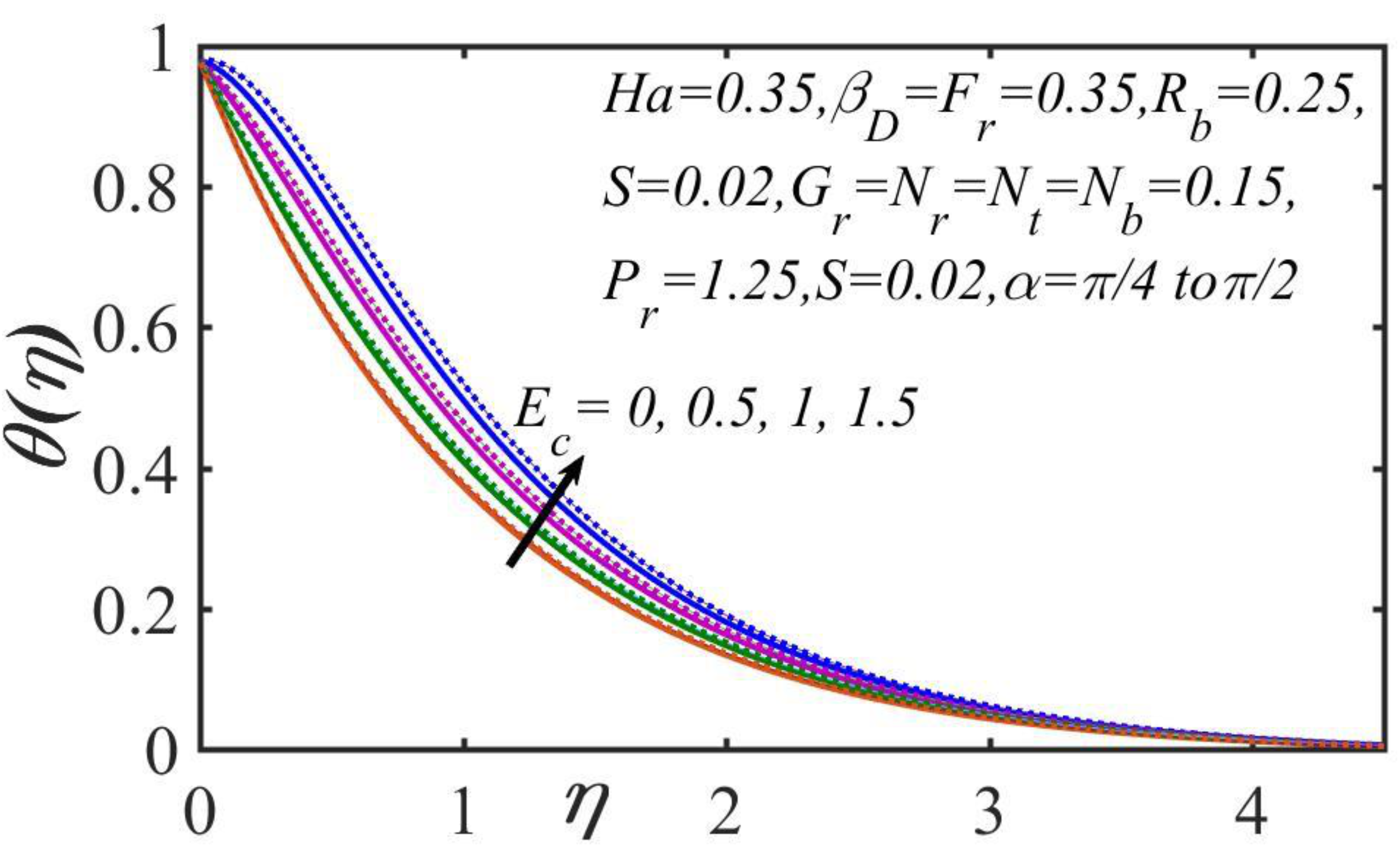
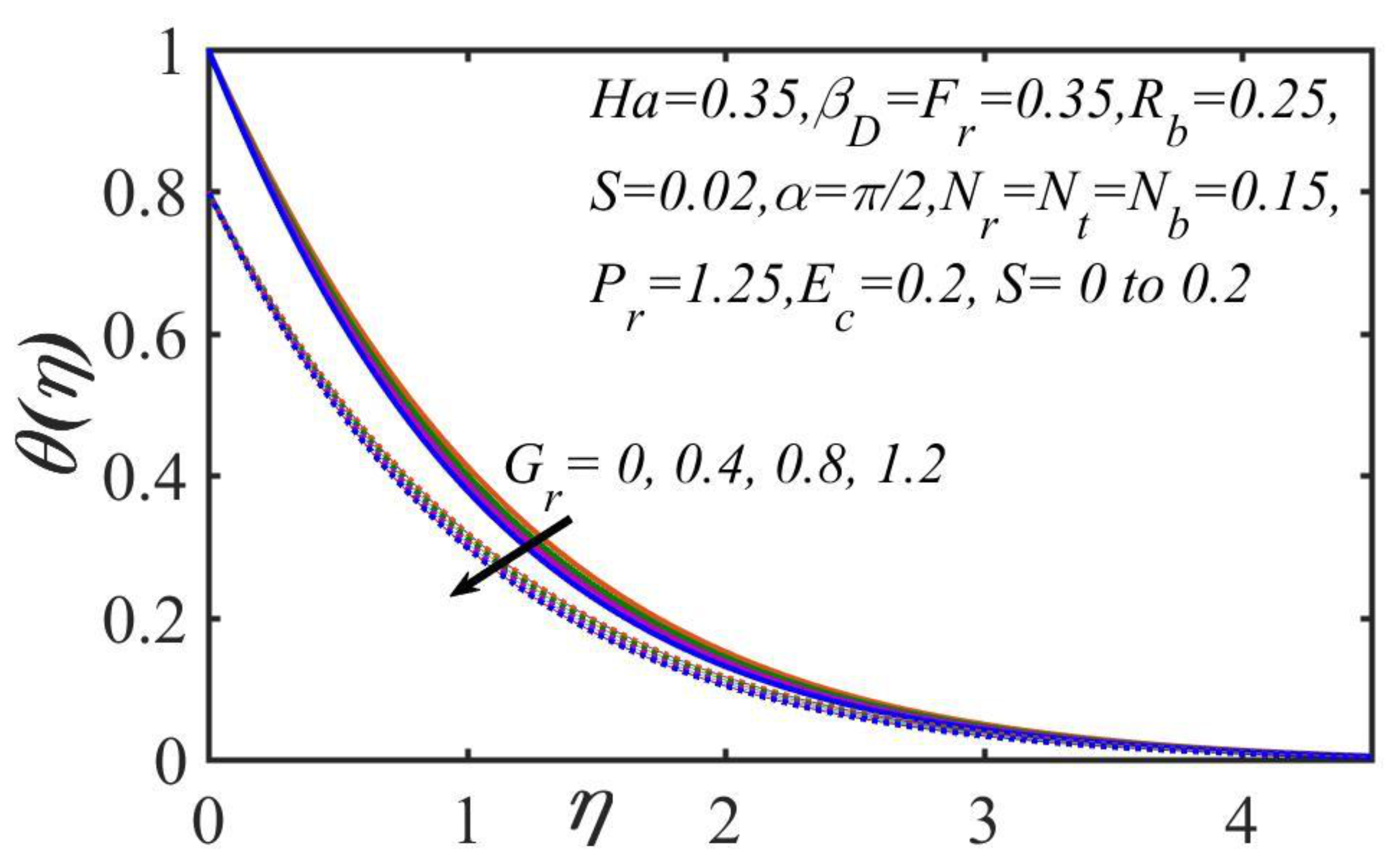
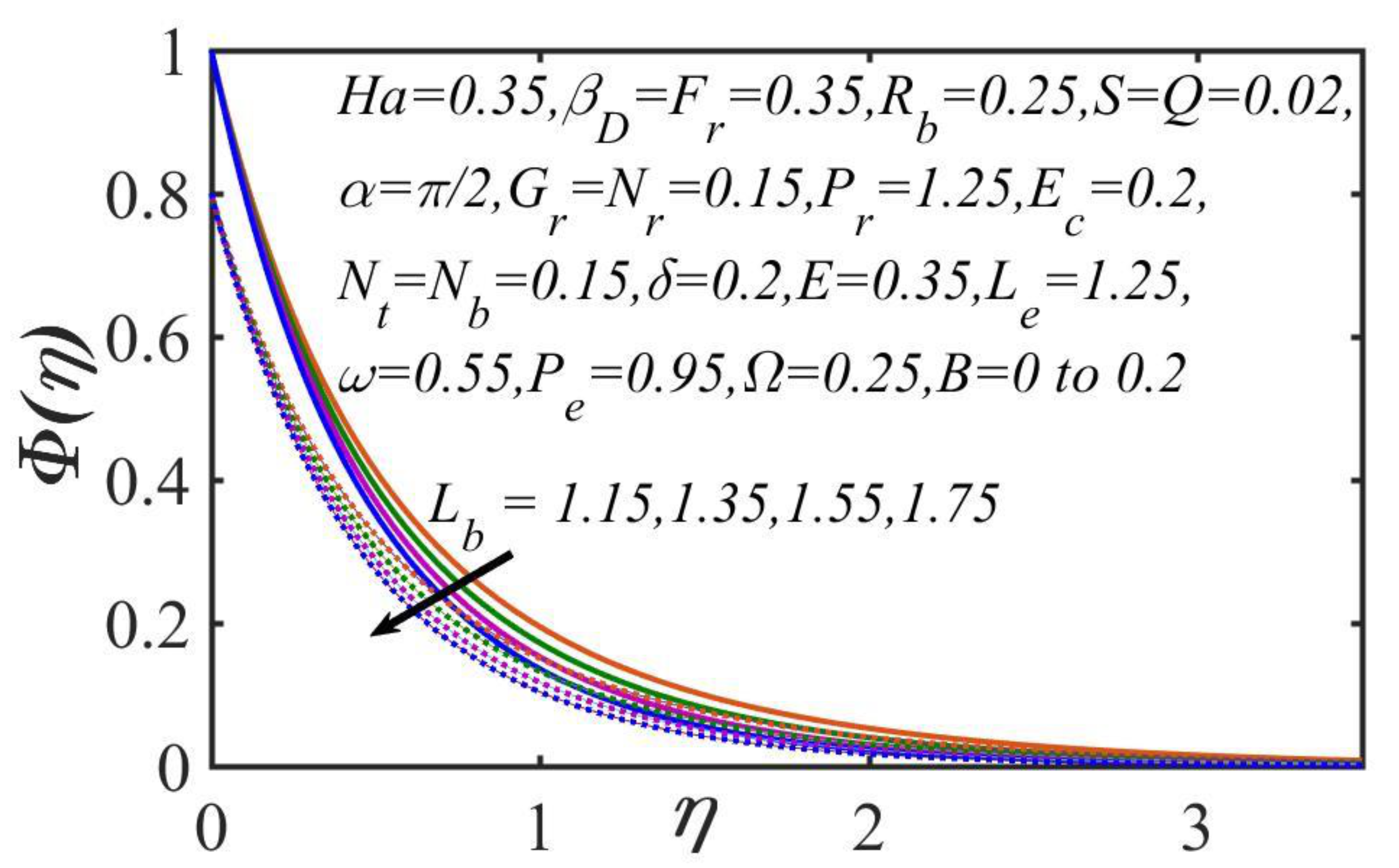
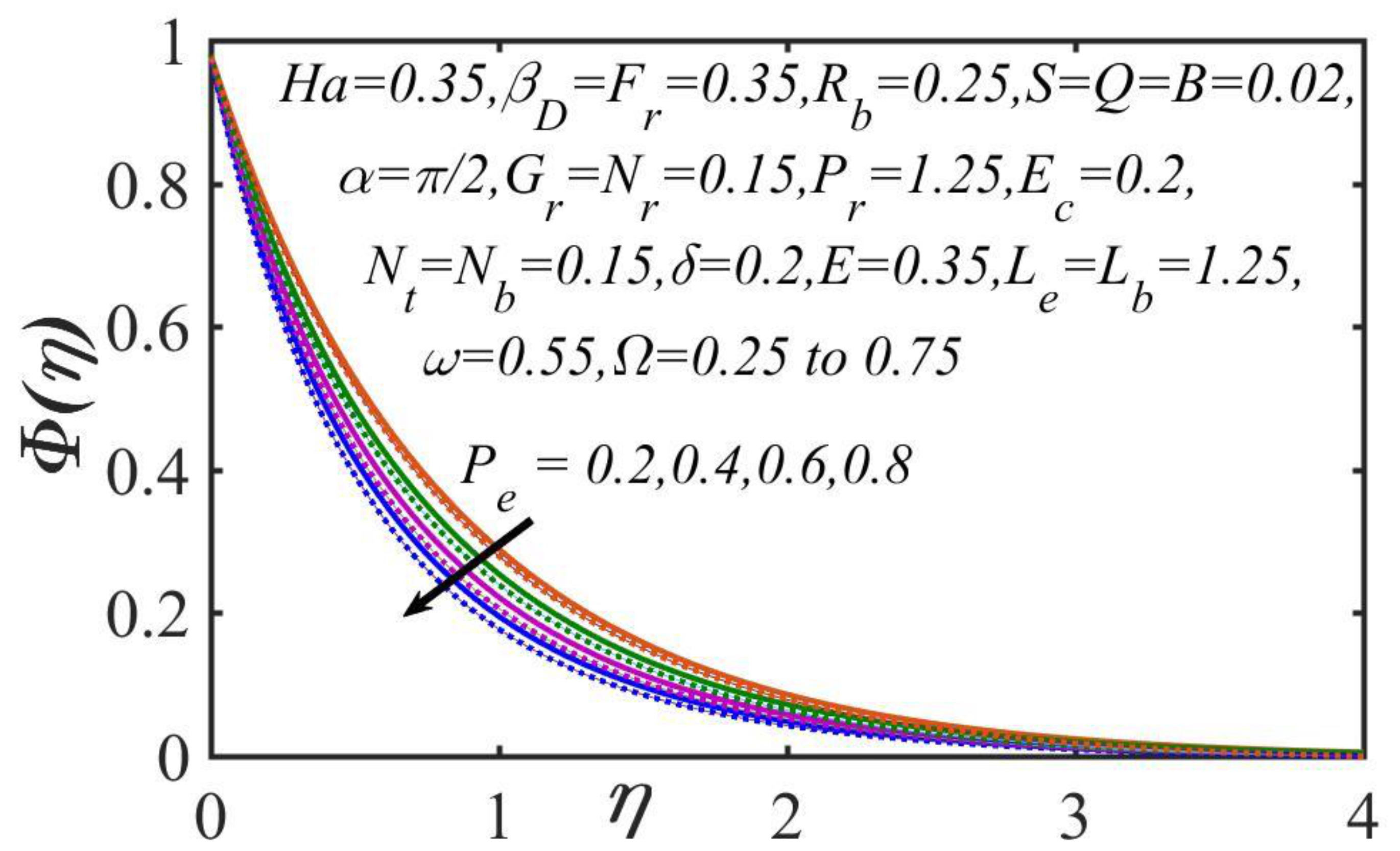
5. Results and Discussion
6. Concluding Remarks
- The velocity showed a decreasing mechanism against the higher values of the inclination angle, thermal stratification, permeability, the Darcy–Brinkman–Forchheimer parameter, the bioconvection Rayleigh number, the buoyancy proportion parameter, and the Hartmann number, as well as thickening the momentum boundary layer over the horizontal stretched surface as it reduces.
- The velocity profiles increased as the numerical value of the mixed convection parametric quantity increased, while the thickness of the momentum boundary layer also increased.
- The temperature magnitude decreased as the Prandtl number, the mixed convection parametric quantity, and the thermal stratification values increased; however, temperature distribution increased as the Brownian motion, Eckert number, and thermophoresis parameters increased.
- The concentration magnitude decreased as the Lewis number and Brownian motion parameter increased, whereas they increased as the activation energy and thermophoresis parameters increased.
- The microorganisms’ magnitudes decelerated with higher values in the bioconvection Lewis number, the motile density stratification, and the bioconvection Peclet number.
- The SRM algorithm’s defining advantage is that it divides a large, coupled set of equations into smaller subsystems that could be handled progressively in a very computationally efficient and effective way. The proposed methodology for SRM showed that this method is accurate, easy to develop, convergent, and highly efficient in solving nonlinear problems.
Author Contributions
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Choi, S.U.; Eastman, J.A. Enhancing Thermal Conductivity of Fluids with Nanoparticles; No. ANL/MSD/CP-84938; CONF-951135-29; Argonne National Lab.: Lemont, IL, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Das, S.K.; Choi, S.U.; Yu, W.; Pradeep, T. Nanofluids: Science and Technology; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Buongiorno, J. Convective transport in nanofluids. J. Heat Transf. 2006, 128, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, R.K.; Das, M.K. Heat transfer augmentation in a two-sided lid-driven differentially heated square cavity utilizing nanofluids. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2007, 50, 2002–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakaç, S.; Pramuanjaroenkij, A. Review of convective heat transfer enhancement with nanofluids. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer. 2009, 52, 3187–3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachok, N.; Ishak, A.; Pop, I. Boundary-layer flow of nanofluids over a moving surface in a flowing fluid. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2010, 49, 1663–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makinde, O.D.; Aziz, A. Boundary layer flow of a nanofluid past a stretching sheet with convective boundary condition. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2011, 50, 1326–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, Z.; Abu-Nada, E.; Oztop, H.F.; Mataoui, A. Natural convection in nanofluids: Are the thermophoresis and Brownian motion effect significant in nanofluids heat transfer enhancement. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2012, 57, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashidi, M.M.; Nasiri, M.; Khezerloo, M.; Laraqi, N. Numerical investigation of magnetic field effect on mixed convection heat transfer of nanofluid in a channel with sinusoidal walls. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2016, 401, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kefayati, G.H.R. Simulation of natural convection and entropy generation of non-Newtonian nanofluid in a porous cavity using Buongiorno’s mathematical model. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2017, 112, 709–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, W.; Shankar, B. MHD boundary layer flow and heat transfer of a nanofluid past a permeable stretching sheet with velocity, thermal and solutal slip boundary conditions. Comp. Fluid. 2013, 75, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, W.; Shankar, B.; Nandeppanavar, M.M. MHD stagnation point flow and heat transfer due to nanofluid towards a stretching sheet. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2013, 56, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabood, F.; Khan, W.A.; Ismail, A.M. MHD boundary layer flow and heat transfer of nanofluids over a nonlinear stretching sheet: A numerical study. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2015, 374, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Malik, M.Y.; Hussain, A.; Khan, M. Magnetohydrodynamics Carreau nanofluid flow over an inclined convective heated stretching cylinder with Joule heating. Results Phys. 2017, 7, 4001–4012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metri, P.G.; Guariglia, E.; Silvestrov, S. Lie group analysis for MHD boundary layer flow and heat transfer over stretching sheet in presence of viscous dissipation and uniform heat source/sink. In AIP Conference Proceedings; American Institute of Physics: College Park, MA, USA, 2017; Volume 1798, p. 020096. [Google Scholar]
- Rauf, A.; Abbas, Z.; Shehzad, S.A. Magnetohydrodynamics slip flow of a nanofluid through an oscillatory disk under porous medium supremacy. Heat Transf. Asian Res. 2019, 48, 3446–3465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subhani, M.; Nadeem, S. Numerical investigation into unsteady magnetohydrodynamics flow of micropolar hybrid nanofluid in porous medium. Phys. Scr. 2019, 94, 105220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zainal, N.A.; Nazar, R.; Naganthran, K.; Pop, I. Stability analysis of MHD hybrid nanofluid flow over a stretching/shrinking sheet with quadratic velocity. Alex. Eng. J. 2021, 60, 915–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Myong, R.S. Critical Review of Fluid Flow Physics at Micro-to Nano-scale Porous Media Applications in the Energy Sector. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 2018, 9565240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.; Marin, M.; Alsharif, A.; Ellahi, R. Convective heat transfer flow of nanofluid in a porous medium over wavy surface. Phys. Lett. A 2018, 382, 2749–2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izadi, M.; Sheremet, M.A.; Mehryan, S.A.M. Natural convection of a hybrid nanofluid affected by an inclined periodic magnetic field within a porous medium. Chin. J. Phys. 2020, 65, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eid, M.R.; Nafe, M.A. Thermal conductivity variation and heat generation effects on magneto-hybrid nanofluid flow in a porous medium with slip condition. Waves Random Complex Media 2020, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, Z.; He, B.; Su, L.; Kuang, Y. Thermo-hydraulic analyses of the absorber tube with molten salt-based nanofluid and porous medium inserts. Sol. Energy 2021, 226, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loganathan, K.; Alessa, N.; Tamilvanan, K.; Alshammari, F.S. Significances of Darcy–Forchheimer porous medium in third-grade nanofluid flow with entropy features. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 2021, 230, 1293–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bees, M.A. Advances in bioconvection. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2020, 52, 449–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashad, A.M.; Nabwey, H.A. Gyrotactic mixed bioconvection flow of a nanofluid past a circular cylinder with convective boundary condition. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2019, 99, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Ashraf, M.; Ali, K. Nanofluid Flow Comprising Gyrotactic Microorganisms through a Porous Medium. J. Appl. Fluid Mech. 2020, 13, 1539–1549. [Google Scholar]
- Alshomrani, A.S. Numerical investigation for bio-convection flow of viscoelastic nanofluid with magnetic dipole and motile microorganisms. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2021, 46, 5945–5956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, U.; Abdal, S.; Siddique, I.; Ali, R. A comparative study on micropolar, Williamson, Maxwell nanofluids flow due to a stretching surface in the presence of bioconvection, double diffusion and activation energy. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2021, 127, 105551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koriko, O.K.; Shah, N.A.; Saleem, S.; Chung, J.D.; Omowaye, A.J.; Oreyeni, T. Exploration of bioconvection flow of MHD thixotropic nanofluid past a vertical surface coexisting with both nanoparticles and gyrotactic microorganisms. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 16627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bestman, A.R. Natural convection boundary layer with suction and mass transfer in a porous medium. Int. J. Energy Res. 2009, 14, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makinde, O.D.; Olanrewaju, P.O.; Charles, W.M. Unsteady convection with chemical reaction and radiative heat transfer past a flat porous plate moving through a binary mixture. Afr. Mat. 2011, 22, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamid, A.; Khan, M. Impacts of binary chemical reaction with activation energy on unsteady flow of magneto-Williamson nanofluid. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 262, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irfan, M.; Khan, W.A.; Khan, M.; Gulzar, M.M. Influence of Arrhenius activation energy in chemically reactive radiative flow of 3D Carreau nanofluid with nonlinear mixed convection. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2019, 125, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeeshan, A.; Shehzad, N.; Ellahi, R. Analysis of activation energy in Couette-Poiseuille flow of nanofluid in the presence of chemical reaction and convective boundary conditions. Results Phys. 2018, 8, 502–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Bhatti, M.M.; Shahid, A.; Ellahi, R.; Bég, O.A.; Sait, S.M. Nonlinear nanofluid fluid flow under the consequences of Lorentz forces and Arrhenius kinetics through a permeable surface: A robust spectral approach. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2021, 124, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosayebidorcheh, S.; Hatami, M. Analytical investigation of peristaltic nanofluid flow and heat transfer in an asymmetric wavy wall channel (Part II: Divergent channel). Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2018, 126, 800–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhar, M.H.; Fakhar, A.; Tabatabaei, H. Mathematical modeling of pipes reinforced by agglomerated CNTs conveying turbulent nanofluid and application of semi-analytical method for studying the instable Nusselt number and fluid velocity. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2020, 378, 112945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arain, M.B.; Bhatti, M.M.; Zeeshan, A.; Alzahrani, F.S. Bioconvection Reiner-Rivlin Nanofluid Flow between Rotating Circular Plates with Induced Magnetic Effects, Activation Energy and Squeezing Phenomena. Mathematics 2021, 9, 2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaedi, A.; Khan, M.I.; Farooq, M.; Gull, N.; Hayat, T. Magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) stratified bioconvective flow of nanofluid due to gyrotactic microorganisms. Adv. Powder Technol. 2017, 28, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motsa, S.S. A new spectral relaxation method for similarity variable nonlinear boundary layer flow systems. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2013, 201, 241–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, M.Y.; Salahuddin, T.; Hussain, A.; Bilal, S. MHD flow of tangent hyperbolic fluid over a stretching cylinder: Using Keller box method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2015, 395, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, T.; Zhang, J.; Yao, S. Slip MHD viscous flow over a stretching sheet–an exact solution. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2009, 14, 3731–3737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Ha | Alsaedi et al. [40] | Malik et al. [42] | Fang et al. [43] | Current Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | 1.00001 | 1.00000 | - | 1.00001 |
| 0.5 | 1.1180 | 1.1180 | 1.1180 | 1.11804 |
| 1.0 | 1.41421 | 1.41419 | - | 1.41421 |
| 2.0 | - | - | 2.2361 | 2.23612 |
| Alsaedi et al. [40] | Makinde and Aziz [7] | Current Results | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.2 | 0.61913 | 0.6191 | 0.61913 |
| 0.7 | 0.45395 | 0.4539 | 0.45395 |
| 2.0 | 0.91132 | 0.9113 | 0.91132 |
| Alsaedi et al. [40] | Current Results | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1 | 0.5878 | 0.5878 | ||
| 0.3 | 0.9582 | 0.9582 | ||
| 0.2 | 0.8588 | 0.8588 | ||
| 0.3 | −0.3914 | −0.3914 | ||
| 0.4 | 0.4586 | 0.4586 | ||
| 0.6 | 0.3725 | 0.3725 |
| Alsaedi et al. [40] | Current Results | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.7 | 1.3811 | 1.3811 | ||
| 0.9 | 1.4764 | 1.4764 | ||
| 1.2 | 1.5731 | 1.5731 | ||
| 1.6 | 1.7657 | 1.7657 | ||
| 0.3 | 1.4060 | 1.4060 | ||
| 0.5 | 1.2391 | 1.2391 |
| E | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.2 | 0.25 | 0.4 | 0.1 | 1.2 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0 | 1.3 | 1.2 | 0.7 | 2.352715 | 0.752014 | 1.072020 | 1.557273 |
| 0.3 | 2.398654 | 0.742471 | 1.071343 | 1.552463 | ||||||||||
| 0.3 | 0.5 | 2.487139 | 0.726684 | 1.070907 | 1.545084 | |||||||||
| 0.6 | 2.522533 | 0.720207 | 1.070811 | 1.542152 | ||||||||||
| 0.25 | 0.3 | 2.364434 | 0.752439 | 1.069943 | 1.554744 | |||||||||
| 0.5 | 2.431602 | 0.732918 | 1.072817 | 1.550414 | ||||||||||
| 0.4 | 0.2 | 2.368601 | 0.749691 | 1.072003 | 1.556196 | |||||||||
| 0.3 | 2.338548 | 0.756783 | 1.072703 | 1.559920 | ||||||||||
| 0.1 | 1 | - | 0.657802 | 1.103879 | 1.572894 | |||||||||
| 3 | - | 1.309006 | 0.773985 | 1.363474 | ||||||||||
| 1.2 | 0.1 | - | 0.742471 | 1.071343 | 1.552463 | |||||||||
| 0.2 | - | 0.719265 | 1.170932 | 1.614982 | ||||||||||
| 0.1 | 0.2 | - | 0.702976 | 0.899657 | 1.445912 | |||||||||
| 0.3 | - | 0.668042 | 0.735167 | 1.344962 | ||||||||||
| 0.1 | 0.3 | - | - | 1.078053 | 1.556685 | |||||||||
| 0.4 | - | - | 1.080335 | 1.558122 | ||||||||||
| 0.5 | 0.4 | - | - | 0.298772 | 1.114593 | |||||||||
| 0.5 | - | - | 0.422982 | 1.181335 | ||||||||||
| 1.3 | 0.5 | - | - | - | 1.178318 | |||||||||
| 0.6 | - | - | - | 1.240586 | ||||||||||
| 1.2 | 0.8 | - | - | - | 1.642909 | |||||||||
| 1.0 | - | - | - | 1.810811 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shahid, A.; Mohamed, M.S.; Bhatti, M.M.; Doranehgard, M.H. Darcy–Brinkman–Forchheimer Model for Nano-Bioconvection Stratified MHD Flow through an Elastic Surface: A Successive Relaxation Approach. Mathematics 2021, 9, 2514. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9192514
Shahid A, Mohamed MS, Bhatti MM, Doranehgard MH. Darcy–Brinkman–Forchheimer Model for Nano-Bioconvection Stratified MHD Flow through an Elastic Surface: A Successive Relaxation Approach. Mathematics. 2021; 9(19):2514. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9192514
Chicago/Turabian StyleShahid, Anwar, Mohamed S. Mohamed, Muhammad Mubashir Bhatti, and Mohammad Hossein Doranehgard. 2021. "Darcy–Brinkman–Forchheimer Model for Nano-Bioconvection Stratified MHD Flow through an Elastic Surface: A Successive Relaxation Approach" Mathematics 9, no. 19: 2514. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9192514
APA StyleShahid, A., Mohamed, M. S., Bhatti, M. M., & Doranehgard, M. H. (2021). Darcy–Brinkman–Forchheimer Model for Nano-Bioconvection Stratified MHD Flow through an Elastic Surface: A Successive Relaxation Approach. Mathematics, 9(19), 2514. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9192514







