Sustainability, Big Data and Mathematical Techniques: A Bibliometric Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Q1: What are the main trends in scientific production on sustainability based on big data?
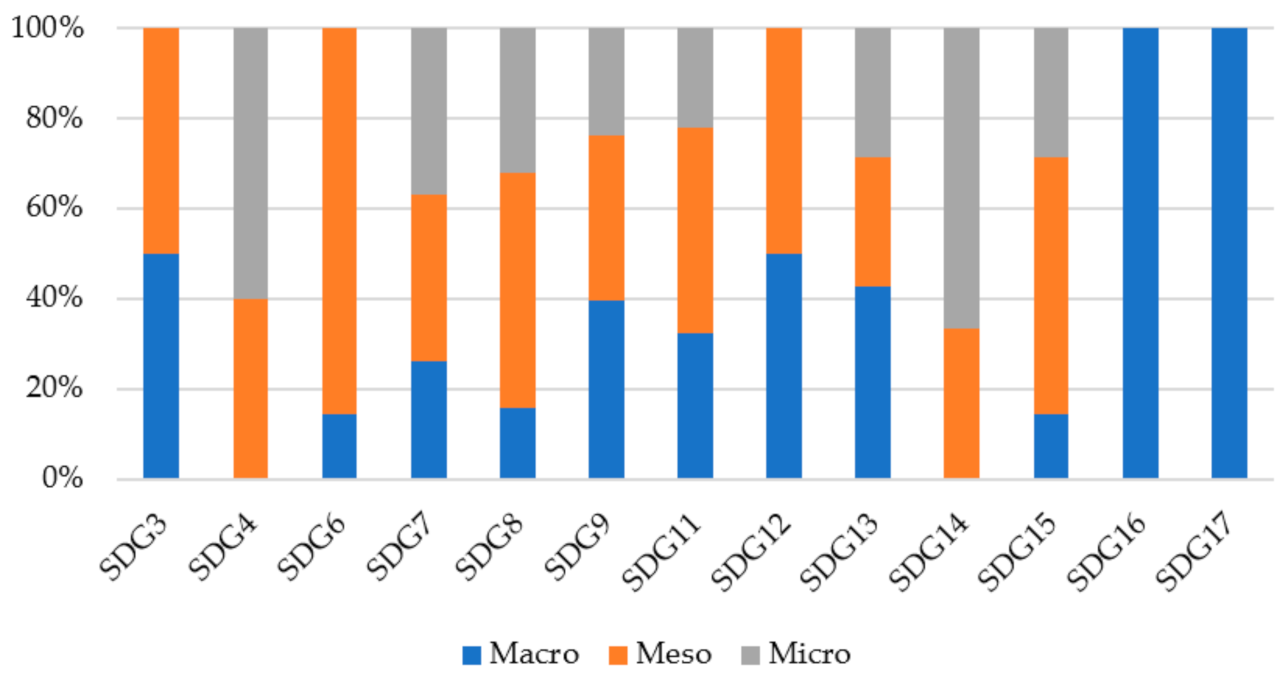
- Q2: Which SDGs do the papers relate to?
- Q3: At what spatial level were the empirical papers conducted?
- Q4: What kind of mathematical techniques are applied?
2. Materials and Methods
- Time scale: as the importance afforded to sustainability has mainly occurred in the last decades, it was decided not to include time restrictions, obtaining all the documents up to 30 June 2021.
- In the search of the existing literature in the WoS database, three words were always used, taking as a basis: “sustainab* and big data” to which were added: “indicator”, “index”, “assessment”, “evaluation”, “measurement”. Finally, the results found in each of them were joined according to the following sentence: “sustainab* and big data and indicator” OR “sustainab* and big data and index” OR “sustainab* and big data and assessment” OR “sustainab* and big data and evaluation” OR “sustainab* and big data and measuring”.
- The required document type was article, also including review article. The result was n = 507 documents.
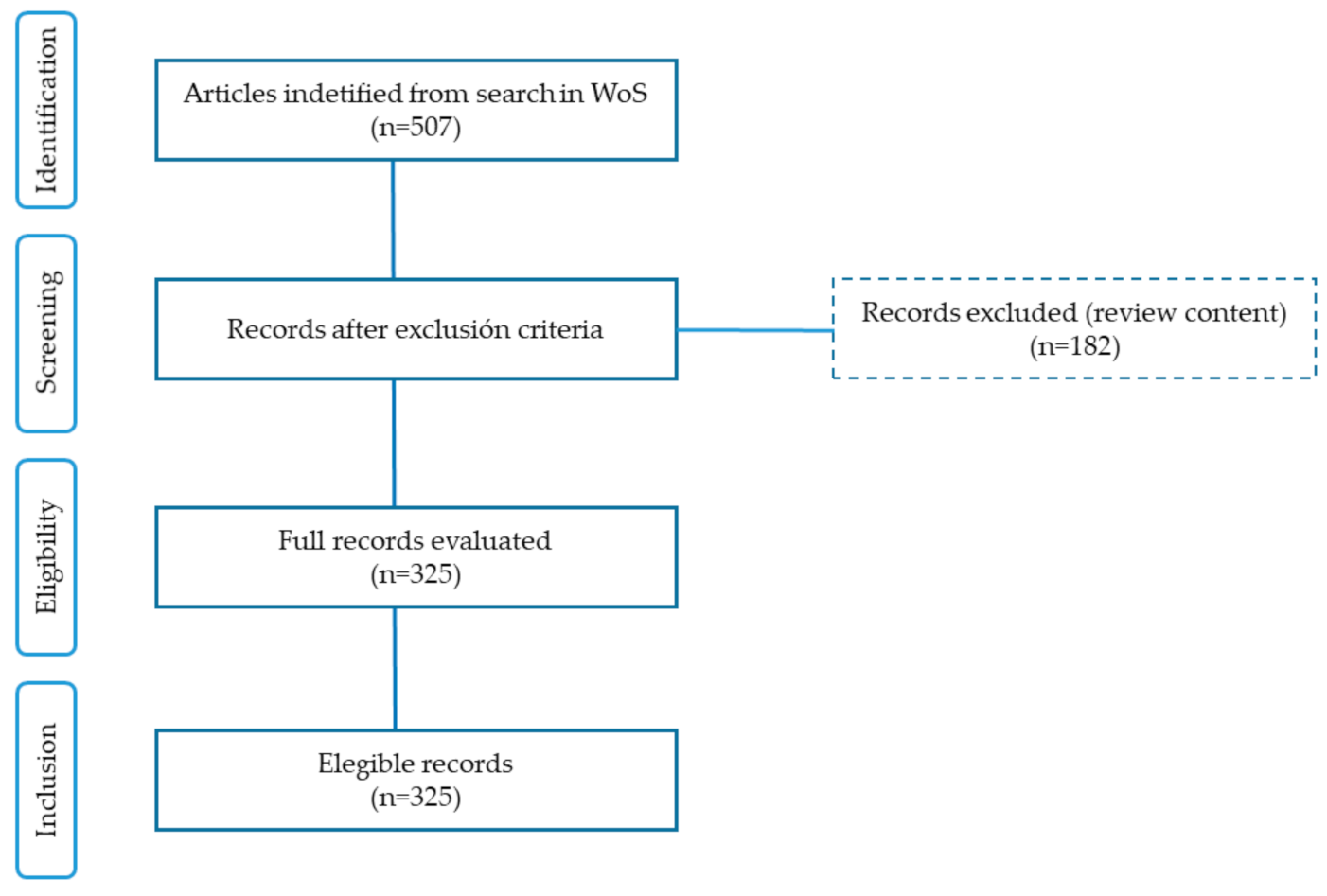
- A preliminary reading of the abstract was initially carried out, followed by a more exhaustive reading of each article to verify that it met the established inclusion criteria. From the search carried out, we have eliminated those works (182 publications) that use some combination of the key words in a tangential way, without giving them the strict sense that our research pursues. For example, papers that include the word sustainability, but have nothing to do with mathematical techniques for sustainability, have been discarded. After this filtering, n = 325 documents were obtained, of which 34 are bibliometric studies (Figure 1).
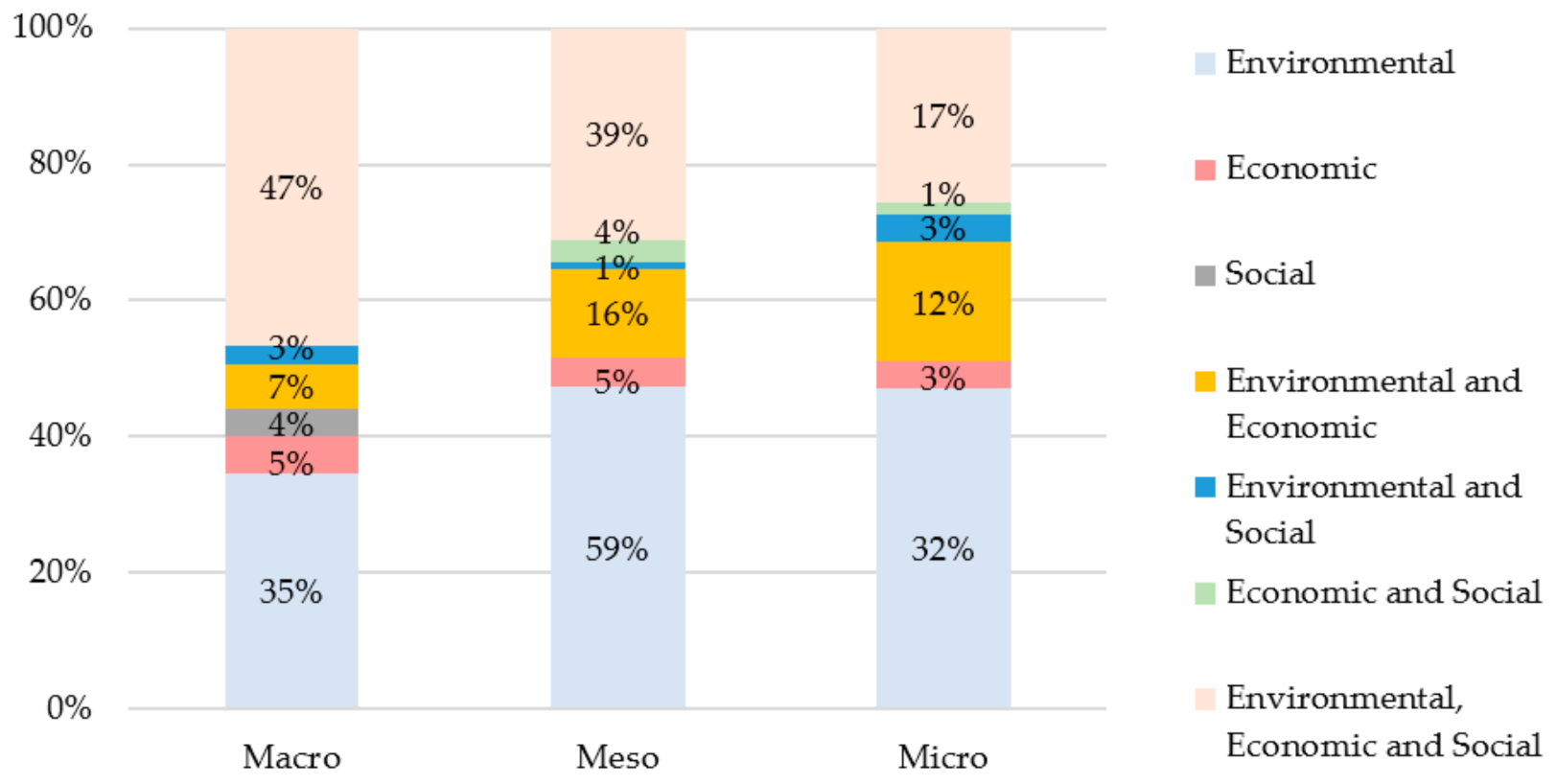
- The denomination “micro-level” refers to the fact that the analysed document performs its empirical application in companies or places located in a small territory.
- The term “meso-level” has been used when the work has been carried out in several places at the same time or in industrial parks.
- The term “macro” refers to the fact that the document has a global or country-wide application.
3. Results
3.1. Bibliometric Analysis
3.1.1. Number of Publications per Year
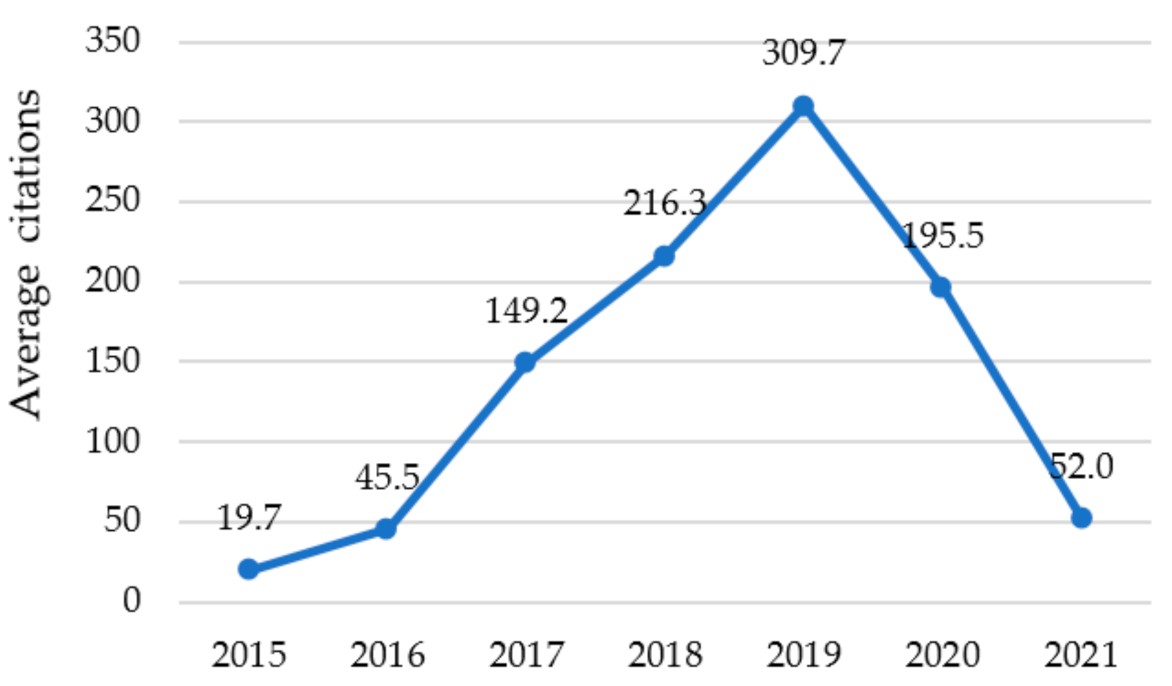
3.1.2. Average Number of Citations per Year per Publication
3.1.3. Distribution of Publications by Knowledge Area
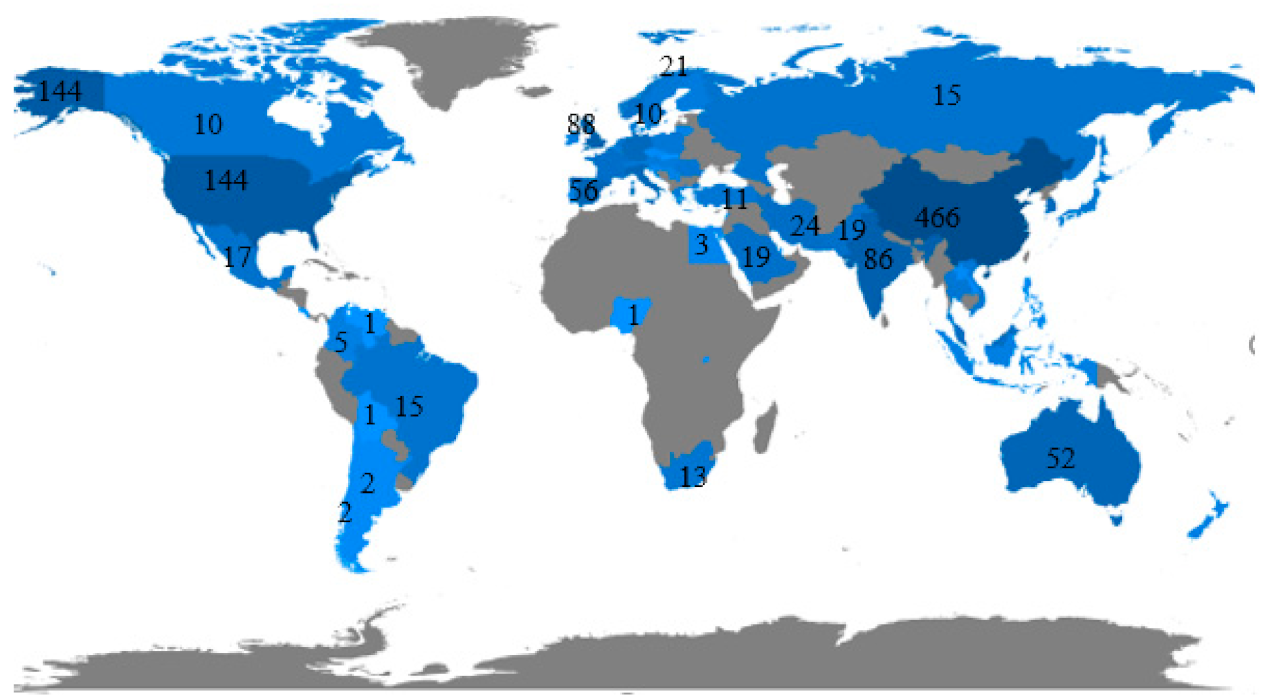
3.1.4. Distribution by Institution
3.1.5. Productivity of Authors
3.1.6. Distribution by Journal
3.2. Aggregation of Documents
3.2.1. According to Sustainability Indicator and SDGs
3.2.2. According to Spatial Level
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Manyika, J.; Chui, M.; Brown, B.; Bughin, J.; Dobbs, R.; Roxburgh, C.; Hung Byers, A. Big Data: The Next Frontier for Innovation, Competition, and Productivity; McKinsey Global Institute: Columbia, WA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Cowls, J.; Schroeder, R. Causation, correlation, and big data in social science research. Policy Internet 2015, 7, 447–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Bhattacharyya, S.S. Micro-foundation strategies of IOT, BDA, Cloud Computing: Do they really matter in bottom of pyramid? Strateg. Dir. 2016, 32, 36–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ylijoki, O.; Porras, J. Perspectives to definition of big data: A mapping study and discussion. J. Innov. Manag. 2016, 4, 69–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amankwah-Amoah, J. An integrative process model of organisational failure. J. Bus. Res. 2016, 69, 3388–3397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McAfee, A.; Brynjolfsson, E.; Davenport, T.H.; Patil, D.J.; Barton, D. Big data: The management revolution. Harv. Bus. Rev. 2012, 90, 60–68. [Google Scholar]
- Khade, A.A. Performing customer behavior analysis using big data analytics. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2016, 79, 986–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Calvard, T.S. Big data, organizational learning, and sensemaking: Theorizing interpretive challenges under conditions of dynamic complexity. Manag. Learn. 2016, 47, 65–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marfo, J.S.; Boateng, R. Big Data and Organizational Learning: Conceptualizing the Link. In Second International Conference on E-Learning, E-Education, and Online Training; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 159–164. [Google Scholar]
- Gamage, P. New development: Leveraging ‘big data’ analytics in the public sector. Public Money Manag. 2016, 36, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desouza, K.C.; Jacob, B. Big data in the public sector: Lessons for practitioners and scholars. Adm. Soc. 2017, 49, 1043–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredriksson, C.; Mubarak, F.; Tuohimaa, M.; Zhan, M. Big data in the public sector: A systematic literature review. Scand. J. Public Adm. 2017, 21, 39–62. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, G.H.; Trimi, S.; Chung, J.H. Big-data applications in the government sector. Commun. ACM 2014, 57, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creutzig, F.; Roy, J.; Lamb, W.F.; Azevedo, I.M.; De Bruin, W.B.; Dalkmann, H.; Edelenbosch, O.Y.; Geels, F.W.; Grubler, A.; Hepburn, C.; et al. Towards demand-side solutions for mitigating climate change. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2018, 8, 260–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Solomon, C.G.; LaRocque, R.C. Climate change—A health emergency. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 209–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmberg, J.; Sandbrook, R. Sustainable development: What is to be done? In Policies for a Small Planet; Routledge: London, UK, 2019; pp. 19–38. [Google Scholar]
- Mauerhofer, V. Sustainable development law in (only) one world: Challenges and perspectives for governance and governments. In Sustainability and Law; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 15–31. [Google Scholar]
- Szopik-Depczyńska, K.; Kędzierska-Szczepaniak, A.; Szczepaniak, K.; Cheba, K.; Gajda, W.; Ioppolo, G. Innovation in sustainable development: An investigation of the EU context using 2030 agenda indicators. Land Use Policy 2018, 79, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G. Development of a general sustainability indicator for renewable energy systems: A review. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2014, 31, 611–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahdari, A.H.; Rostamy, A.A.A. Designing a general set of sustainability indicators at the corporate level. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 108, 757–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Guo, X. Spatial quantification and pattern analysis of urban sustainability based on a subjectively weighted indicator model: A case study in the city of Saskatoon, SK, Canada. Appl. Geogr. 2014, 53, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutaia, F. The Use of Landscape Indicators in Environmental Assessment. In Strategic Environmental Assessment: Integrating Landscape and Urban Planning; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 29–43. [Google Scholar]
- King, L.O. Functional sustainability indicators. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 66, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhringer, C.; Jochem, P.E. Measuring the immeasurable—A survey of sustainability indices. Ecol. Econ. 2007, 63, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pupphachai, U.; Zuidema, C. Sustainability indicators: A tool to generate learning and adaptation in sustainable urban development. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 72, 784–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Wu, J.; Yan, L. Defining and measuring urban sustainability: A review of indicators. Landsc. Ecol. 2015, 30, 1175–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dizdaroglu, D. Developing micro-level urban ecosystem indicators for sustainability assessment. Env. Impact Assess Rev. 2015, 54, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huovila, A.; Bosch, P.; Airaksinen, M. Comparative analysis of standardized indicators for Smart sustainable cities: What indicators and standards to use and when? Cities 2019, 89, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavadskas, E.K.; Govindan, K.; Antucheviciene, J.; Turskis, Z. Hybrid multiple criteria decision-making methods: A review of applications for sustainability issues. Econ. Res.-Ekon. Istraz. 2016, 29, 857–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farsi, M.; Hosseinian-Far, A.; Daneshkhah, A.; Sedighi, T. Mathematical and computational modelling frameworks for integrated sustainability assessment (ISA). In Strategic Engineering for Cloud Computing and Big Data Analytics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 3–27. [Google Scholar]
- Rossberg, A.G. On the mathematics of sustainability. Nat. Sustain. 2018, 1, 615–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammad, A.W.; Rey, D.; Bu-Qammaz, A.; Grzybowska, H.; Akbarnezhad, A. Mathematical optimization in enhancing the sustainability of aircraft trajectory: A review. Int. J. Sustain. Transp. 2020, 14, 413–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holden, G.; Rosenberg, G.; Barker, K. Bibliometrics: A potential decision making aid in hiring, reappointment, tenure and promotion decisions. Soc. Work Health Care 2005, 41, 67–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ball, R. Handbook Bibliometrics; De Gruyter Saur, ETH-Library: Zürich, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ghisellini, P.; Cialani, C.; Ulgiati, S. A review on circular economy: The expected transition to a balanced interplay of environmental and economic systems. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 114, 11–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Pascale, A.; Arbolino, R.; Szopik-Depczyńska, K.; Limosani, M.; Ioppolo, G. A systematic review for measuring circular economy: The 61 indicators. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 281, 124942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahlschmidt, S.; Stephen, D. Comparison of Web of Science, Scopus and Dimensions databases. In KB Forschungspoolprojekt; DZHW: Hannover, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Persson, O.; Danell, R.; Schneider, J.W. How to use Bibexcel for various types of bibliometric analysis. In Celebrating Scholarly Communication Studies: A Festschrift for Olle Persson at His 60th Birthday; Sweden, 2009; pp. 9–24. Available online: https://portal.research.lu.se/ws/files/5902071/1458992.pdf (accessed on 10 October 2021).
- Chen, C. CiteSpace II: Detecting and visualizing emerging trends and transient patterns in scientific literature. J. Assoc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2006, 57, 359–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. CitNetExplorer: A new software tool for analyzing and visualizing citation networks. J. Informetr. 2014, 8, 802–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics 2010, 84, 523–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bailón Moreno, R. Ingeniería del Conocimiento y Vigilancia Tecnológica Aplicada a la Investigación en el Campo de los Tensioactivos. Desarrollo de un Modelo Ciencimétrico Unificado; Universidad de Granada: Granada, Spain, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Aria, M.; Cuccurullo, C. Bibliometrix: An R-tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis. J. Inf. 2017, 11, 959–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobo, M.J.; López-Herrera, A.G.; Herrera-Viedma, E.; Herrera, F. SciMAT: A new science mapping analysis software tool. J. Assoc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2012, 63, 1609–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sci2 Team. Science of Science (Sci2) Tool. Indiana University and SciTech Strategies. 2009. Available online: https://sci2.cns.iu.edu (accessed on 15 August 2021).
- Uddin, A. ScientoText: Text & Scientometric Analytics. R Package Version 0.1. 2016. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/scientoText/index.html (accessed on 10 October 2021).
- Porter, A.L.; Cunningham, S.W. Tech Mining: Exploiting New Technologies for Competitive Advantage; Wiley-Interscience: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Sangam, S.; Mogali, M.S.S. Mapping and visualization software tools: A review. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Content Management in Networked, Tumkur University, Tumkur, India, 3–4 December 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Alhuay-Quispe, J. Evaluación de Software Aplicados a Estudios Métricos. IV Jornadas Académicas Bibliotecológicas yArchivísticas. Medellín-Colombia, 10 y 11 de Setiembre del 2015. Available online: http://eprints.rclis.org/27963/ (accessed on 10 August 2021).
- Moral-Muñoz, J.A.; Herrera-Viedma, E.; Santisteban-Espejo, A.; Cobo, M.J. Software tools for conducting bibliometric analysis in science: An up-to-date review. Prof. Inf. 2020, 29, e290103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pinto, A.L.; de Aquino Silva, R.; Dyck, A.F.; de Araújo, G.M.; Dutra, M.L. Expert Bibliometrics: An Application Service for Metric Studies of Information. In International Conference on Data and Information in Online; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 54–63. [Google Scholar]
- Wuni, I.Y.; Shen, G.Q.; Osei-Kyei, R. Scientometric Review of Global Research Trends on Green Buildings in Construction Journals from 1992 to 2018. Energy Build. 2019, 190, 69–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Gu, Z.; Zhong, H.; Zha, Q.; Yang, L.; Zhu, C.; Chen, E. A bibliometric analysis using VOSviewer of publications on COVID-19. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.; Wu, H.; Yang, S.; Su, B.; Tang, K.; Quan, Z.; Zhong, W.; Luo, X. Global trends of researches on sacral fracture surgery: A bibliometric study based on VOSviewer. Spine 2020, 45, E721–E728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Chen, Z.; Wang, H.; Zheng, C.; Jiang, J. Bibliometric and visualized analysis of scientific publications on atlantoaxial spine surgery based on Web of Science and VOSviewer. World Neurosurg. 2020, 137, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dervis, H. Bibliometric analysis using Bibliometrix an R Package. J. Scientometr. Res. 2019, 8, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalal, S.K. Co-authorship and co-occurrences analysis using Bibliometrix R-package: A case study of India and Bangladesh. Ann. Libr. Inf. Stud. 2019, 66, 57–64. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Soler, R.; Uribe-Toril, J.; Valenciano, J.D.P. Worldwide trends in the scientific production on rural depopulation, a bibliometric analysis using bibliometrix R-tool. Land Use Policy 2020, 97, 104787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K. Author productivity of covid-19 research output globally: Testing lotka’s law in Kumar, K Dr, “Author Productivity of COVID-19 Research Output Globally: Testing Lotka’s Law”, 2020. Libr. Philos. Pract. E-J. 2020, 4372, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, C.Y.; Aytac, S. Scientific Productivity, Lotka’s Law, and STEM Librarianship. Sci. Technol. Libr. 2021, 40, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, S.; Perlin, M.; Matsushita, R.; Santos, A.A.; Imasato, T.; Borenstein, D. Lotka’s law for the Brazilian scientific output published in journals. J. Inf. Sci. 2019, 45, 705–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueredo-Gaspari, E. Valoración curricular de las publicaciones científicas. Med. Clin 2005, 125, 661–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanclay, J.K. On the robustness of the h-index. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2007, 58, 1547–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harzing, A.-W. Reflections on the h-Index. Research in International Management. 2007. Available online: https://harzing.com/publications/white-papers/reflections-on-the-h-index (accessed on 10 August 2021).
- El-Kassar, A.N.; Singh, S.K. Green innovation and organizational performance: The influence of big data and the moderating role of management commitment and HR practices. Technol. Soc. Chang. 2019, 144, 483–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yigitcanla, T.; Kamruzzaman, M.; Foth, M.; Sabatini-Marques, J.; da Costa, E.; Ioppolo, G. Can cities become smart without being sustainable? A systematic review of the literature. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 45, 348–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.J.; Liao, C.J.; Tseng, M.L.; Lim, M.K.; Hu, J.; Tan, K. Toward sustainability: Using big data to explore the decisive attributes of supply chain risks and uncertainties. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 142, 663–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kissling, W.D.; Ahumada, J.A.; Bowser, A.; Fernandez, M.; Fernández, N.; García, E.A.; Guralnick, R.P.; Isaac, N.J.B.; Kelling, S.; Los, W.; et al. Building essential biodiversity variables (EBV s) of species distribution and abundance at a global scale. Biol. Rev. 2018, 93, 600–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hazen, B.T.; Skipper, J.B.; Ezell, J.D.; Boone, C.A. Big data and predictive analytics for supply chain sustainability: A theory-driven research agenda. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2016, 101, 592–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Cen, L.; Zheng, Z.; Fisher, R.; Liang, X.; Wang, Y.; Huisingh, D. How would big data support societal development and environmental sustainability? Insights and practices. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 142, 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsai, S.B.; Xue, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Dong, W. Models for forecasting growth trends in renewable energy. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 77, 1169–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cao, Z.; Long, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, W. Dynamic analysis of ecological environment combined with land cover and NDVI changes and implications for sustainable urban–rural development: The case of Mu Us Sandy Land, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 142, 697–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamble, S.S.; Gunasekaran, A.; Gawankar, S.A. Achieving sustainable performance in a data-driven agriculture supply chain: A review for research and applications. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2019, 219, 179–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosavi, A.; Salimi, M.; Faizollahzadeh Ardabili, S.; Rabczuk, T.; Shamshirband, S.; Varkonyi-Koczy, A.R. State of the art of machine learning models in energy systems, a systematic review. Energies 2020, 12, 1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dehdarirad, T.; Villarroya, A.; Barrios, M. Research on women in science and higher education: A bibliometric analysis. Scientometrics 2015, 103, 795–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Su, Y.S.; Lin, C.L.; Chen, S.Y.; Lai, C.F. Bibliometric Study of Social Network Analysis Literature. Libr. Hi Tech 2019, 38, 420–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

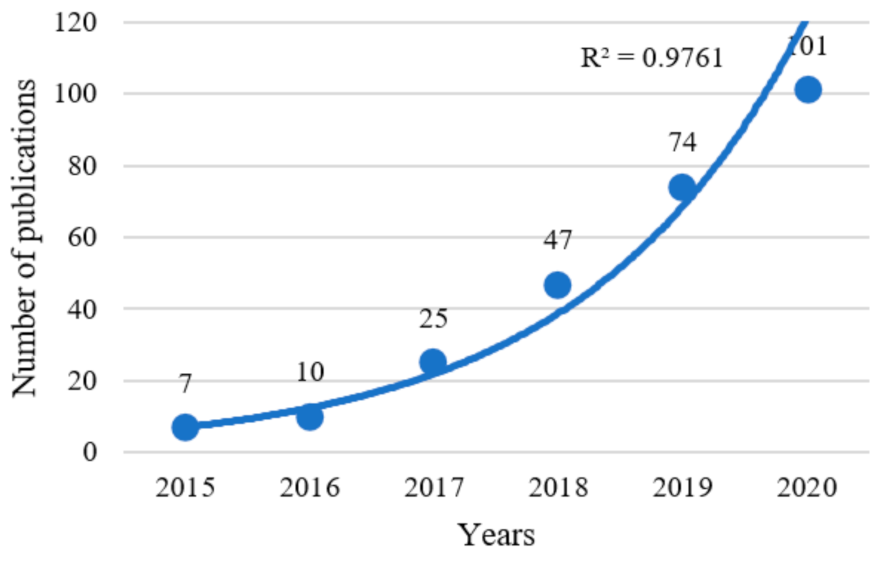


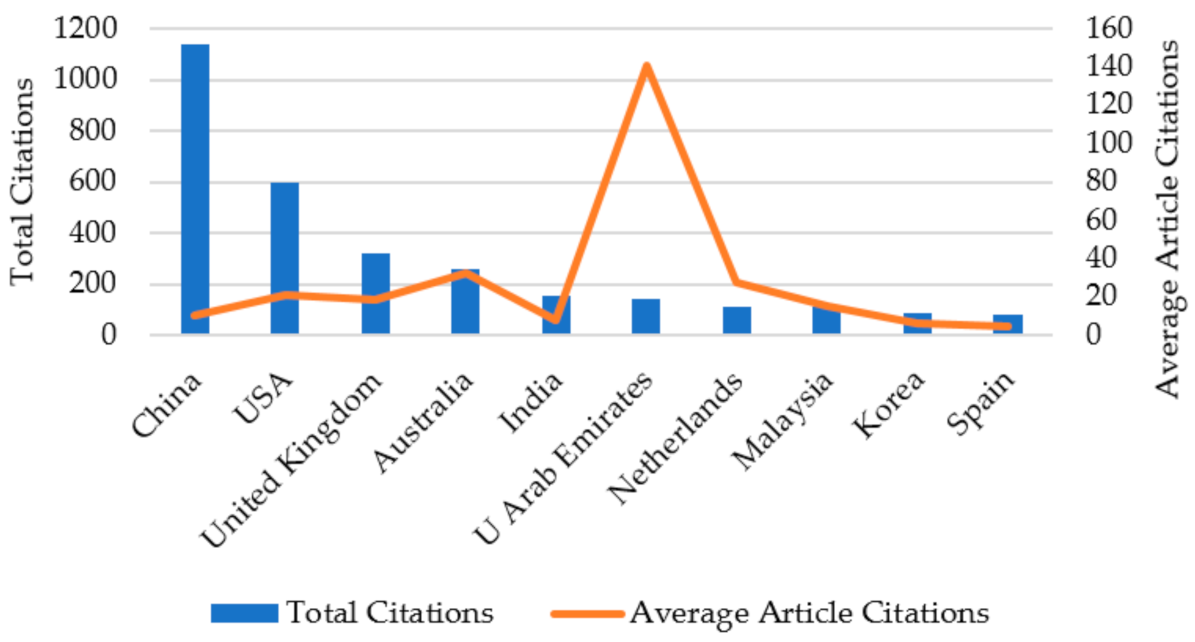


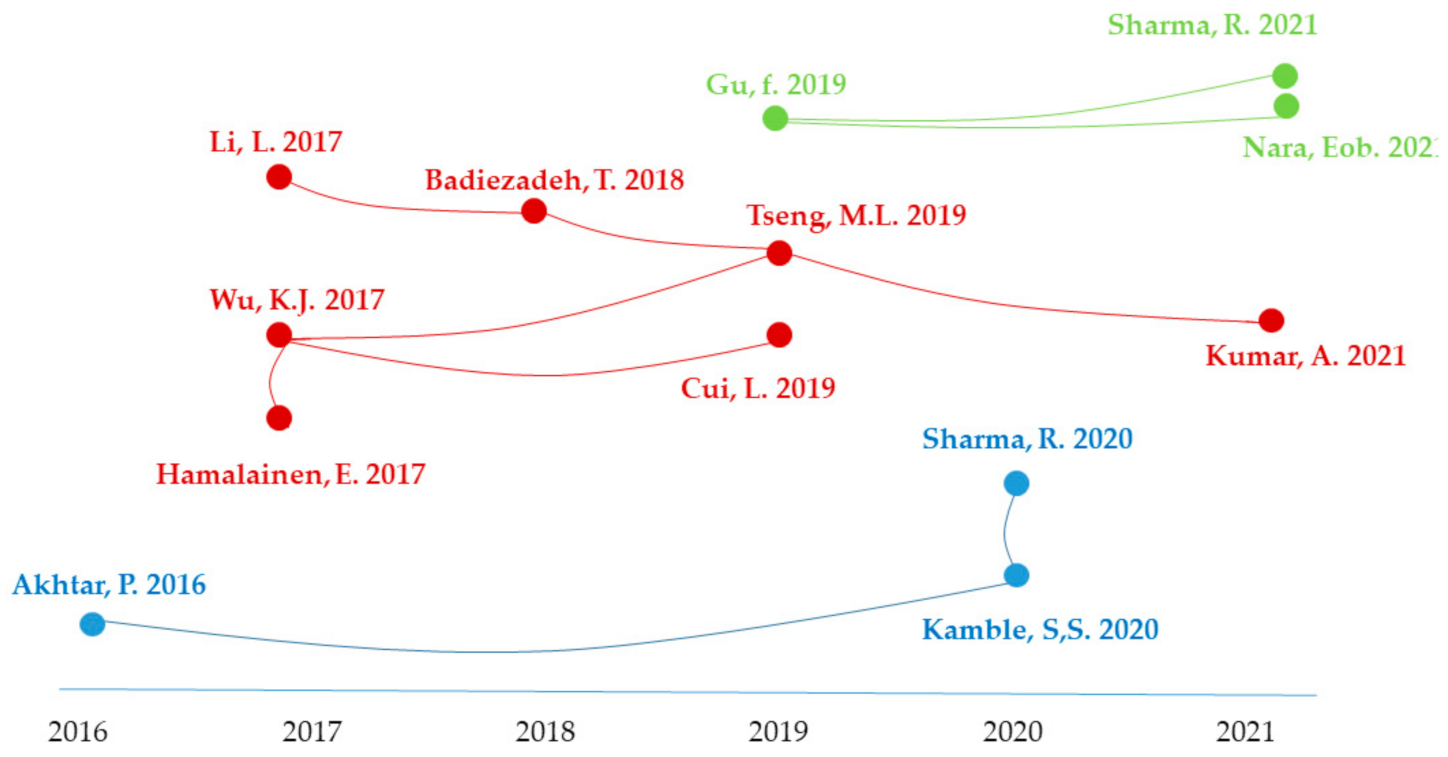

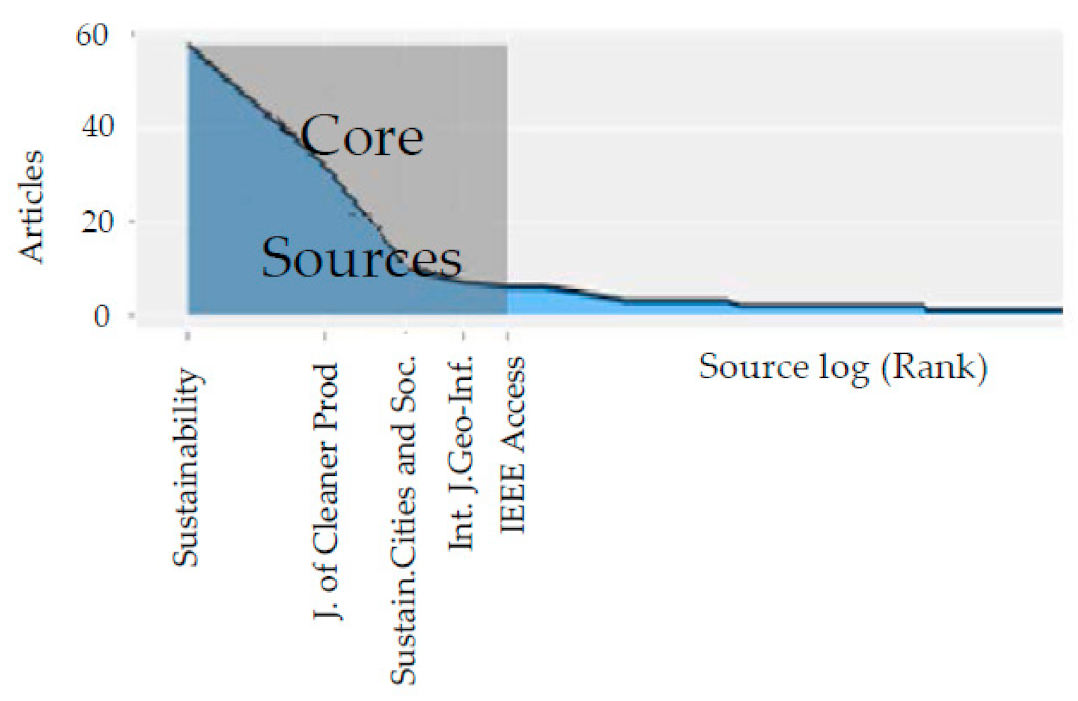


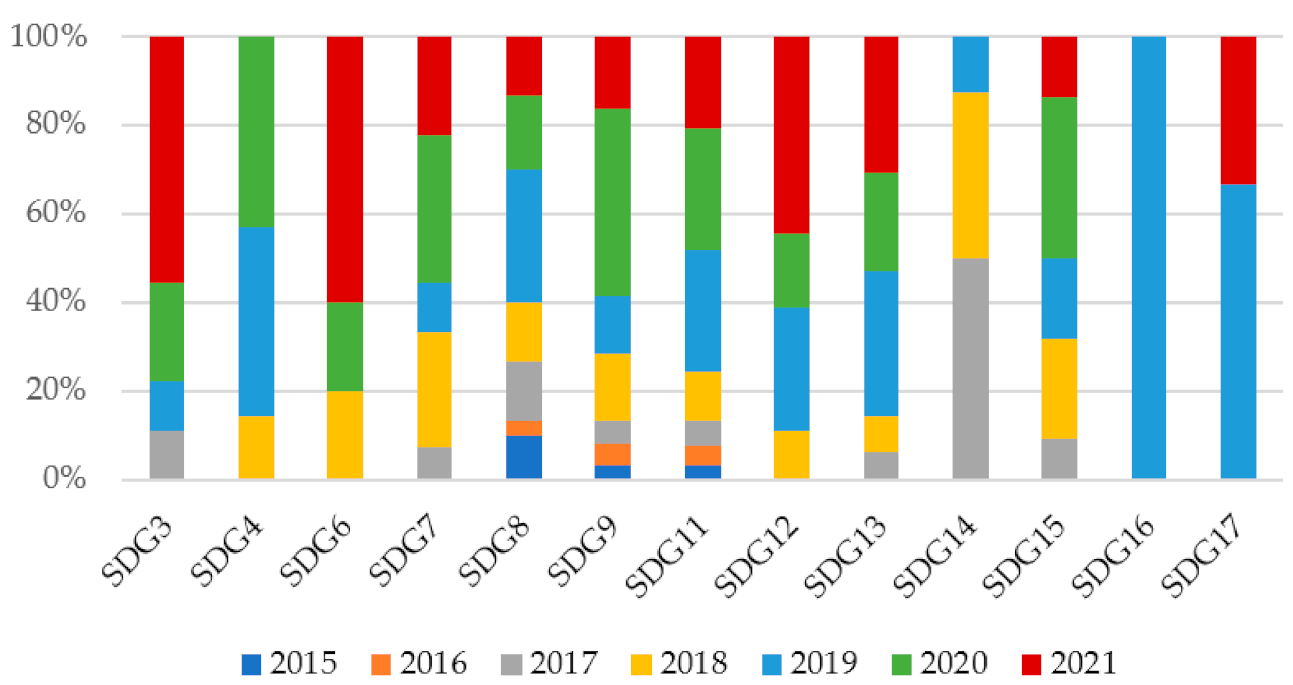

| Year | Number of Publications |
|---|---|
| 2015 | 7 |
| 2016 | 10 |
| 2017 | 25 |
| 2018 | 47 |
| 2019 | 74 |
| 2020 | 101 |
| 2021 | 61 |
| Total | 325 |
| Knowledge Area | |
|---|---|
| 1. Environmental Sciences Ecology | 142 |
| 2. Science Technology Other Topics | 121 |
| 3. Engineering | 90 |
| 4. Computer Science | 46 |
| 5. Business Economics | 34 |
| 6. Energy Fuels | 21 |
| 7. Remote Sensing | 15 |
| 8. Operations Research Management Science | 13 |
| 9. Construction Building Technology | 12 |
| 10. Physical Geography | 9 |
| Author | Articles | Fractional Index | Total Cites | Total Cites/Articles | Total Citas/Year | h-Index | g-Index | m-Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tseng, Ming-Lang | 7 | 1.4 | 141 | 20.1 | 28.2 | 6 | 7 | 1.20 |
| Cui, Li | 4 | 0.9 | 45 | 11.3 | 11.3 | 4 | 4 | 0.80 |
| Mosavi, Amir | 4 | 0.7 | 66 | 16.5 | 22.0 | 3 | 4 | 1.00 |
| Song, Malin | 4 | 0.9 | 109 | 27.3 | 21.8 | 3 | 4 | 0.60 |
| Wu, Kuo-Jui | 4 | 0.9 | 134 | 33.5 | 44.7 | 4 | 4 | 0.80 |
| Lim, Ming K. | 4 | 0.8 | 122 | 30.5 | 24.4 | 3 | 4 | 0.60 |
| Kamble, Sachin S. | 3 | 0.9 | 91 | 30.3 | 91.0 | 3 | 3 | 1.50 |
| Dai, Jing | 3 | 0.7 | 40 | 13.3 | 20.0 | 3 | 3 | 1.00 |
| Huisingh, Donald | 3 | 1.1 | 190 | 63.3 | 95.0 | 3 | 3 | 0.60 |
| Liu, Yang | 3 | 0.6 | 3 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1 | 3 | 0.33 |
| Luthra, Sunil | 3 | 0.8 | 31 | 10.3 | 10.3 | 2 | 3 | 0.67 |
| Artículo | Citations | Average |
|---|---|---|
| Green innovation and organizational performance: The influence of big data and the moderating role of management commitment and HR practices [65] | 127 | 42.33 |
| Can cities become smart without being sustainable? A systematic review of the literature [66] | 114 | 38 |
| Toward sustainability: using big data to explore the decisive attributes of supply chain risks and uncertainties [67] | 97 | 19.4 |
| Building essential biodiversity variables (EBVs) of species distribution and abundance at a global scale [68] | 94 | 23.5 |
| Big data and predictive analytics for supply chain sustainability: A theory-driven research agenda [69] | 89 | 14.83 |
| How would big data support societal development and environmental sustainability? Insights and practices [70] | 80 | 16 |
| Models for forecasting growth trends in renewable energy [71] | 73 | 14.6 |
| Dynamic analysis of ecological environment combined with land cover and NDVI changes and implications for sustainable urban-rural development: The case of Mu Us Sandy Land, China [72] | 72 | 14.4 |
| Achieving sustainable performance in a data-driven agriculture supply chain: A review for research and applications [73] | 64 | 32 |
| State-of-the-Art of Machine Learning Models in Energy Systems, a Systematic Review [74] | 64 | 21.33 |
| Sources | No. of Articles | Area | WoS Quartile | Impact Factor (2020) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sustainability | 58 | EVSC, EVST, GST | Q2 | 3.251 |
| Journal of Cleaner Production | 32 | ENG, EVSC, GST | Q1 | 9.297 |
| Sustainable Cities and Society | 10 | CBT, EGF, GST | Q1 | 8.530 |
| ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information | 7 | CS, GEO, RTS | Q2 | 3.390 |
| IEEE Access | 6 | CS, ENG, TEL | Q2 | 4.48 |
| Resources, Conservation & Recycling | 6 | ENG, EVSC | Q1 | 10.204 |
| Remote Sensing | 5 | EVSC, GES, ISP, RTS | Q1 | 4.848 |
| Journal of Enterprise Information Management | 4 | ISL, MNG | Q1 | 5.396 |
| Applied Sciences-Basel | 3 | CHE, PHY, ENG, MSC | Q2 | 2.679 |
| Computers & Operations Research | 3 | CS, ENG, ORM | Q2 | 4.008 |
| Energies | 3 | EF | Q3 | 3.004 |
| Environmental Science and Pollution Research | 3 | EVSC | Q2 | 4.223 |
| International Journal of Production Economics | 3 | ENG | Q1 | 7.885 |
| Technological Forecasting and Social Change | 3 | BUS, RUP | Q1 | 8.593 |
| Source | h-Index | g-Index | m-Index | TC | NP | PY-Start |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sustainability | 8 | 11 | 1.6 | 238 | 58 | 2017 |
| Journal of Cleaner Production | 18 | 27 | 3.6 | 767 | 32 | 2017 |
| Sustainable Cities and Society | 4 | 10 | 0.8 | 194 | 10 | 2017 |
| ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information | 3 | 4 | 0.75 | 20 | 7 | 2018 |
| IEEE Access | 3 | 6 | 0.75 | 70 | 6 | 2018 |
| Resources Conservation and Recycling | 4 | 6 | 1 | 135 | 6 | 2018 |
| Remote Sensing | 2 | 5 | 0.5 | 73 | 5 | 2018 |
| Journal of Enterprise Information Management | 2 | 4 | 16 | 4 | 2021 | |
| Applied Sciences-Basel | 2 | 3 | 0.67 | 25 | 3 | 2019 |
| Computers & Operations Research | 3 | 3 | 0.75 | 87 | 3 | 2018 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lafuente-Lechuga, M.; Cifuentes-Faura, J.; Faura-Martínez, U. Sustainability, Big Data and Mathematical Techniques: A Bibliometric Review. Mathematics 2021, 9, 2557. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9202557
Lafuente-Lechuga M, Cifuentes-Faura J, Faura-Martínez U. Sustainability, Big Data and Mathematical Techniques: A Bibliometric Review. Mathematics. 2021; 9(20):2557. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9202557
Chicago/Turabian StyleLafuente-Lechuga, Matilde, Javier Cifuentes-Faura, and Ursula Faura-Martínez. 2021. "Sustainability, Big Data and Mathematical Techniques: A Bibliometric Review" Mathematics 9, no. 20: 2557. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9202557
APA StyleLafuente-Lechuga, M., Cifuentes-Faura, J., & Faura-Martínez, U. (2021). Sustainability, Big Data and Mathematical Techniques: A Bibliometric Review. Mathematics, 9(20), 2557. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9202557







