ARDL as an Elixir Approach to Cure for Spurious Regression in Nonstationary Time Series
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data-Generating Process (DGP)
2.2. The Testing and Simulations
2.2.1. The ARDL Model (Ghouse Equation)
2.2.2. The Engle and Granger Cointegration Explanation
- (i)
- , when is small, and so, .
- (ii)
“The components of vector are said to be cointegrated of order (d, b), if (i) all components ofare I (d); (ii) there exists a vector (≠ 0) = , b > 0. The vector is called the cointegrated vector.”
2.2.3. Johansen and Juselius Cointegration Test
2.2.4. The ARDL Bound Testing
3. Results
Size Analysis with Nonstationary Series
4. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yule, G.U. Why do we sometimes get Nonsense-Correlations between Time-Series? A Study in Sampling and the Nature of Time-Series. J. R. Stat. Soc. 1926, 89, 1–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granger, C.W.; Newbold, P. Spurious Regressions in Econometrics. J. Econom. 1974, 2, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nelson, C.R.; Plosser, C.R. Trends and Random Walks in Macroeconmic Time Series: Some Evidence and Implications. J. Monet. Econ. 1982, 10, 139–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, A.U.R.; Zaman, A. Model Specification, Observational Equivalence and Performance of Unit Root Tests; University Library of Munich: München, Germany, 2008; p. 13489. [Google Scholar]
- Simon, H.A. Spurious Correlation: A Causal Interpretation. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1954, 49, 467–479. [Google Scholar]
- Hendry, D.F. Econometrics—Alchemy or Science? Economica 1980, 47, 387–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plosser, C.I.; Schwert, G.W. Money, Income, and Sunspots: Measuring Economic Relationships and the Effects of Differencing. J. Monet. Econ. 1978, 4, 637–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, P.C. Understanding Spurious Regressions in Econometrics. J. Econom. 1986, 33, 311–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dar, N.A.; Bhat, G.A.; Shah, I.A.; Iqbal, B.; Kakhdoomi, M.A.; Nisar, I.; Rafiq, R.; Iqbal, S.T.; Bhat, A.B.; Nabi, S.; et al. Hookah smoking, nass chewing, and oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma in Kashmir, India. Br. J. Cancer 2012, 107, 1618–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chaouachi, K. False Positive Result in Study on Hookah Smoking and Cancer in Kashmir: Measuring Risk of Poor Hygiene Is Not the Same as Measuring Risk of Inhaling Water Filtered Tobacco Smoke All Over the World. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 108, 1389–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sapsford, R.; Jupp, V. Data Collection and Analysis; Sage: Newbury Park, CA, USA, 2006; ISBN 0-7619-4362-5. [Google Scholar]
- Höfer, T.; Hildegard, P.; Silvia, V. New Evidence for the Theory of the Stork. Paediatr. Perinat. Epidemiol. 2004, 18, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engle, R.F.; Granger, C.W. Co-integration and Error Correction: Representation, Estimation, and Testing. Econom. J. Econom. Soc. 1987, 55, 251–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engle, R.; Yoo, S. Forecasting and Testing in Co-Integrated Systems. In Long Run Economic Relationships: Readings in Cointegration; Engle, R.F., Granger, C.W.J., Eds.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1991; Volume 35, pp. 237–267. [Google Scholar]
- Johansen, S.; Juselius, K. Testing Structural Hypotheses in a Multivariate Cointegration Analysis of the PPP and the UIP for the UKG. J. Econom. 1992, 53, 211–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, P.C.; Ouliaris, S. Asymptotic Properties of Residual Based Tests for Cointegration. Econom. J. Econom. Soc. 1990, 58, 165–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pesaran, M.H. The Role of Economic Theory in Modelling the Long Run. Econ. J. 1997, 107, 178–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesaran, M.H.; Smith, R. Estimating Long-Run Relationships from Dynamic Heterogeneous Panels. J. Econom. 1995, 68, 79–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agunloye, O.K.; Shangodoyin, D.K. Lag Length Specification in Engle-Granger Cointegration Test: A Modified Koyck Mean Lag Approach Based on Partial Correlation. Stat. Transit. New Ser. 2014, 15, 559–572. [Google Scholar]
- Gutierrez, C.E.; Souza, R.C.; de Carvalho Guillén, O.T. Selection of Optimal Lag Length in Cointegrated VAR Models with Weak form of Common Cyclical Features. Braz. Rev. Econom. 2009, 29, 59–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahking, F.W. Model Mis-Specification and Johansen’s Co-integration Analysis: An Application to the US Money Demand. J. Macroecon. 2002, 24, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leybourne, S.J.; Newbold, P. Spurious Rejections by Cointegration Tests Induced by Structural Breaks. Appl. Econ. 2003, 35, 1117–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, C.Y.; Hu, L.; Ogaki, M. A Spurious Regression Approach to Estimating Structural Parameters. In Proceedings of the North American Winter Meetings, San Diego, CA, USA, 3–5 January 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Diebold, F.X.; Senhadji, A.S. The Uncertain Unit Root in Real GNP: Comment. Am. Econ. Rev. 1996, 86, 1291–1298. [Google Scholar]
- Papell, D.H.; Prodan, R. Restricted Structural Change and the Unit Root Hypothesis. Econ. Inq. 2007, 45, 834–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perron, P. Testing for a Unit Root in a Time Series with a Changing Mean. J. Bus. Econ. Stat. 1990, 8, 153–162. [Google Scholar]
- Zivot, E.; Andrews, D.W.K. Further Evidence on the Great Crash, the Oil-Price Shock, and the Unit-Root Hypothesis. J. Bus. Econ. Stat. 1992, 10, 251–270. [Google Scholar]
- Kilian, L.; Ohanian, L.E. Unit Roots, Trend Breaks, And Transitory Dynamics: A Macroeconomic Perspective. Macroecon. Dyn. 2002, 6, 614–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, C.J.; Nelson, C.R. The Great Depression and Output Persistance. J. Money Credit. Bank. 2002, 34, 1090–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudebusch, G.D. The Uncertain Unit Root in Real GNP. Am. Econ. Rev. 1993, 83, 264–272. [Google Scholar]
- Charemza, W.W.; Deadman, D.F. New Directions in Econometric Practice; Edward Elgar Publishing: Cheltenham, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Hendry, D.F.; Pagan, A.R.; Sargan, J.D. Dynamic Specification. Handb. Econom. 1984, 2, 1023–1100. [Google Scholar]
- Hendry, D.F.; Richard, J.F. The Econometric Analysis of Economic Time Series. Int. Stat. Rev. 1983, 51, 111–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granger, C.W. Some Properties of Time Series Data and Their Use in Econometric Model Specification. J. Econom. 1981, 16, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perron, P.; Campbell, J.Y. A note on Johansen’s cointegration procedure when trends are present. In New Developments in Time Series Econometrics; Physica HD: Heidelberg, Germany, 1994; pp. 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podivinsky, J.M. Testing Misspecified Cointegrating Relationships. Econ. Lett. 1998, 60, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, D. Principal Components Analysis of Cointegrated Time Series. Econom. Theory 1997, 13, 529–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, J.H.; Watson, M.W. Testing for Common Trends. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1988, 83, 1097–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| OLS | G.E (1, 1) | G.E (2, 2) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xt | Xt | xt−1 | yt−1 | F-stat | Xt | xt−1 | xt−2 | yt−1 | yt−2 | F-stat | |
| N | = 0 | ||||||||||
| 50 | 66.6 | 6.6 | 6.6 | 100.0 | 6.4 | 7.3 | 6.2 | 7.0 | 100.0 | 7.0 | 6.7 |
| 100 | 78.2 | 6.1 | 6.5 | 99.7 | 6.5 | 7.2 | 6.1 | 7.0 | 100.0 | 7.3 | 6.7 |
| 200 | 86.3 | 6.0 | 6.6 | 95.8 | 6.5 | 7.3 | 6.1 | 6.9 | 100.0 | 6.9 | 6.8 |
| N | = 0 | ||||||||||
| 50 | 100.0 | 94.9 | 81.8 | 100.0 | 80.4 | 75.4 | 7.8 | 36.2 | 100.0 | 56.0 | 55.3 |
| 100 | 100.0 | 93.0 | 80.0 | 100.0 | 81.5 | 75.2 | 8.1 | 35.1 | 100.0 | 58.3 | 56.6 |
| 200 | 100.0 | 93.1 | 81.1 | 100.0 | 81.0 | 76.8 | 7.9 | 35.6 | 100.0 | 60.2 | 56.4 |
| N | = 0 | ||||||||||
| 50 | 100.0 | 6.1 | 8.0 | 100.0 | 7.0 | 8.3 | 6.3 | 8.2 | 100.0 | 6.4 | 7.5 |
| 100 | 100.0 | 6.1 | 6.4 | 100.0 | 6.2 | 7.5 | 6.5 | 8.6 | 100.0 | 6.6 | 7.4 |
| 200 | 100.0 | 6.3 | 7.2 | 100.0 | 6.4 | 7.6 | 6.6 | 8.4 | 100.0 | 6.5 | 6.6 |
| N | 0 | ||||||||||
| 50 | 100.0 | 95.9 | 83.1 | 100.0 | 81.7 | 76.8 | 7.6 | 36.7 | 100.0 | 55.9 | 56.6 |
| 100 | 100.0 | 93.5 | 83.4 | 100.0 | 80.9 | 76.3 | 7.4 | 33.2 | 100.0 | 56.1 | 56.3 |
| 200 | 100.0 | 94.1 | 83.5 | 100.0 | 82.3 | 77.1 | 8.3 | 35.8 | 100.0 | 55.6 | 57.2 |
| Specification Cases | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Data-Generating Process | |||
| Drift | Drift and Trend | ||
| Test Equation | Drift | Exactly Specified | Under Specified |
| Drift and Trend | Over Specified | Exactly Specified | |
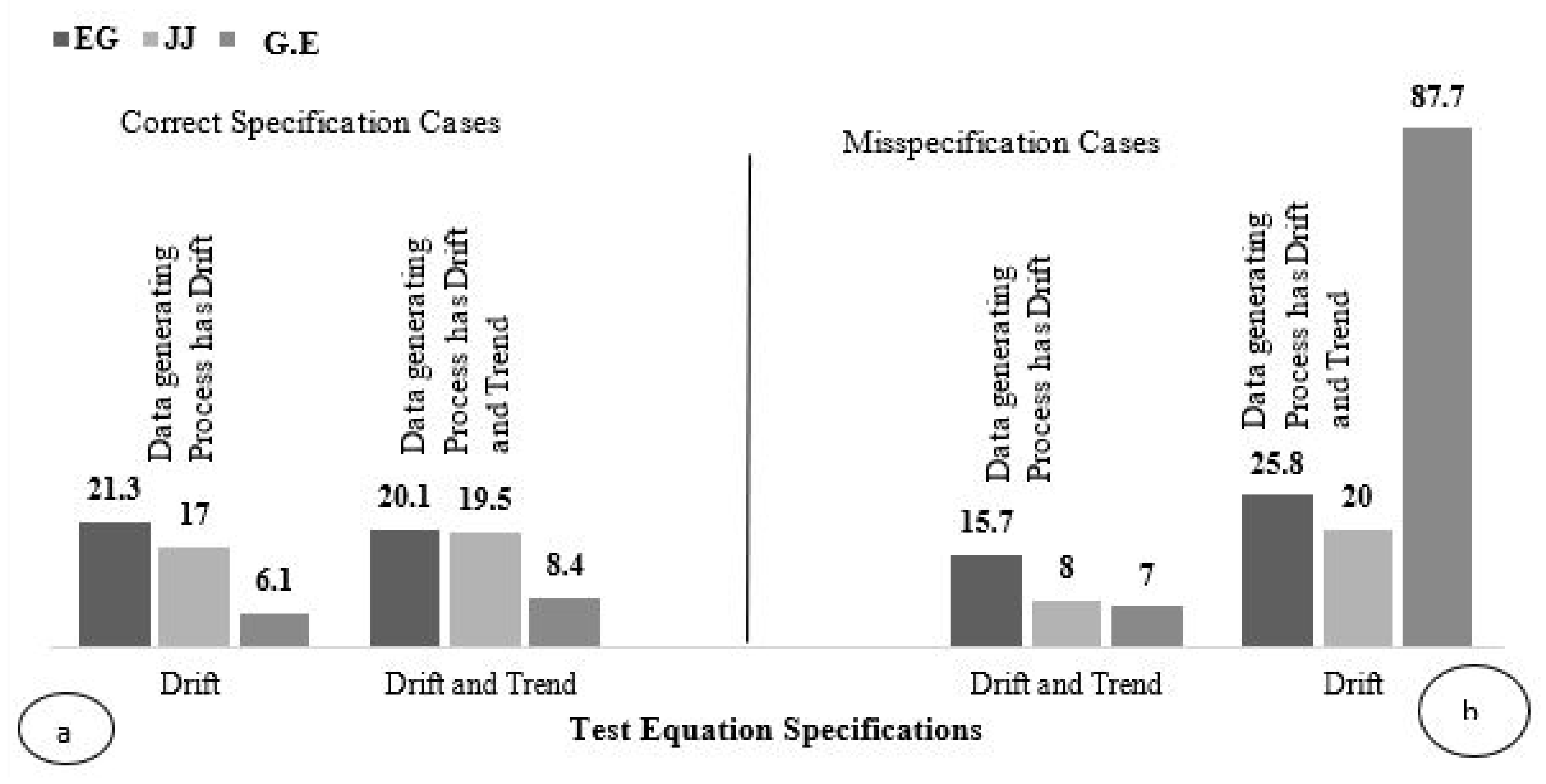
| Engle Granger (EG) Cointegration Test | |||
| Data Generating Process | |||
| Drift | Drift and Trend | ||
| Test Equation | Drift | 21.3 | 25.8 |
| Drift and Trend | 15.7 | 20.1 | |
| Johansen and Juselius (JJ) Cointegration Test | |||
| Data Generating Process | |||
| Drift | Drift and Trend | ||
| Test Equation | Drift | 17 | 20 |
| Drift and Trend | 8 | 19.5 | |
| ARDL Model | |||
| Data Generating Process | |||
| Drift | Drift and Trend | ||
| Test Equation | Drift | 6.1 | 87.7 |
| Drift and Trend | 7 | 8.4 | |
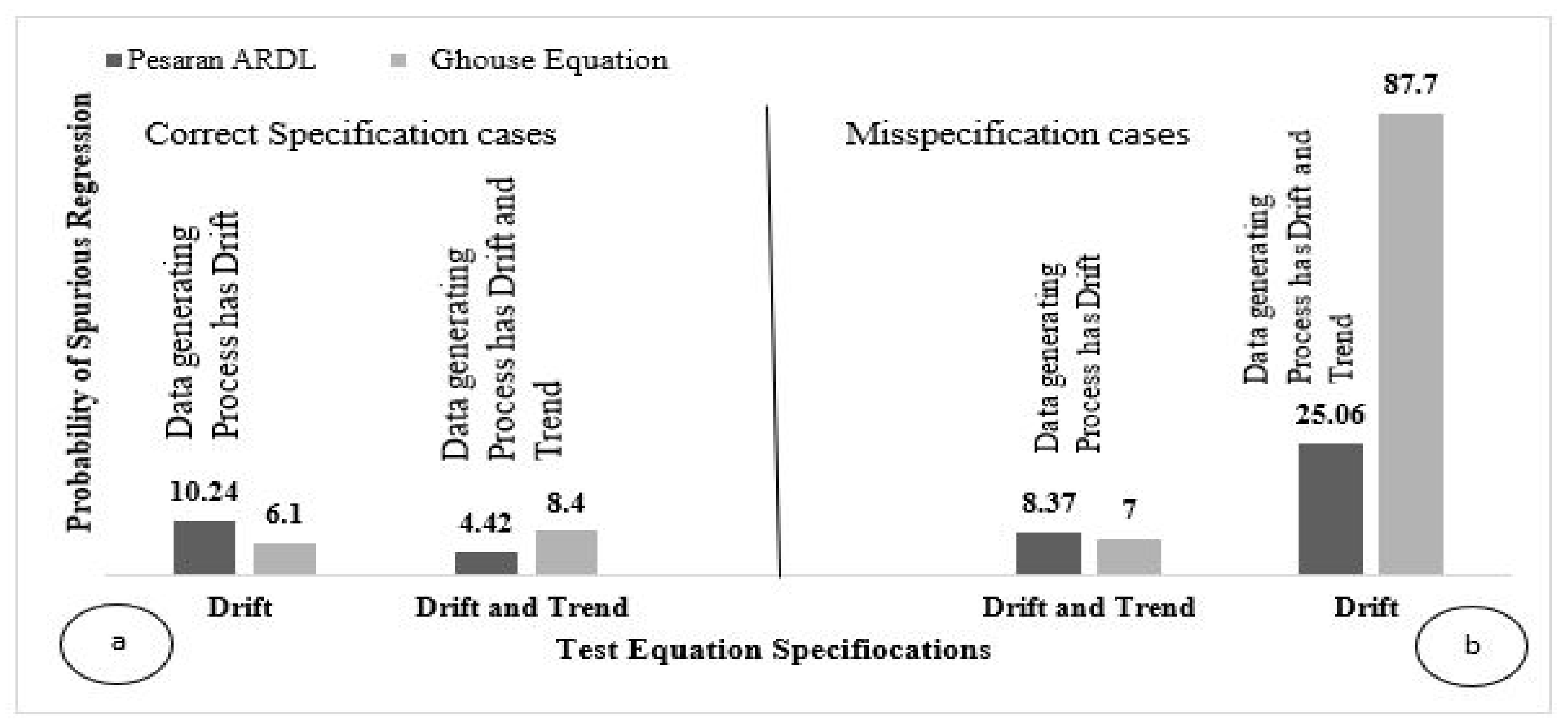
| Pesaran ARDL Model Test | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Data-Generating Process | |||
| Drift | Drift and Trend | ||
| Test Equation | Drift | 10.24 | 25.06 |
| Drift and Trend | 8.37 | 4.42 | |
| Ghouse Equation | |||
| Data-Generating Process | |||
| Drift | Drift and Trend | ||
| Test Equation | Drift | 6.1 | 87.7 |
| Drift and Trend | 7 | 8.4 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ghouse, G.; Khan, S.A.; Rehman, A.U.; Bhatti, M.I. ARDL as an Elixir Approach to Cure for Spurious Regression in Nonstationary Time Series. Mathematics 2021, 9, 2839. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9222839
Ghouse G, Khan SA, Rehman AU, Bhatti MI. ARDL as an Elixir Approach to Cure for Spurious Regression in Nonstationary Time Series. Mathematics. 2021; 9(22):2839. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9222839
Chicago/Turabian StyleGhouse, Ghulam, Saud Ahmad Khan, Atiq Ur Rehman, and Muhammad Ishaq Bhatti. 2021. "ARDL as an Elixir Approach to Cure for Spurious Regression in Nonstationary Time Series" Mathematics 9, no. 22: 2839. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9222839
APA StyleGhouse, G., Khan, S. A., Rehman, A. U., & Bhatti, M. I. (2021). ARDL as an Elixir Approach to Cure for Spurious Regression in Nonstationary Time Series. Mathematics, 9(22), 2839. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9222839








