Kegel Exercise Training Program among Women with Urinary Incontinence
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Design
2.2. Setting
2.3. Subjects
2.4. Instruments
2.5. Pilot Study
2.6. Fieldwork
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Strengths and Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Milsom, I.; Gyhagen, M. The prevalence of urinary incontinence. Climacteric J. Int. Menopause Soc. 2019, 22, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Batmani, S.; Jalali, R.; Mohammadi, M.; Bokaee, S. Prevalence and factors related to urinary incontinence in older adults women worldwide: A comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. BMC Geriatr. 2021, 21, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bo, K.; Frawley, H.C.; Haylen, B.T.; Abramov, Y.; Almeida, F.G.; Berghmans, B.; Bortolini, M.; Dumoulin, C.; Gomes, M.; McClurg, D.; et al. An International Urogynecological Association (IUGA)/International Continence Society (ICS) joint report on the terminology for the conservative and nonpharmacological management of female pelvic floor dysfunction. Int. Urogynecol. J. 2017, 28, 191–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aoki, Y.; Brown, H.W.; Brubaker, L.; Cornu, J.N.; Daly, J.O.; Cartwright, R. Urinary incontinence in women. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2017, 3, 17042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Milsom, I.; Altman, D.; Cartwright, R.; Lapitan, M.C.; Nelson, R.; Sillén, U.; Tikkinen, K. Epidemiology of urinary incontinence (UI) and other lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS), pelvic organ prolapse (POP) and anal incontinence (AI). In Incontinence: 6th International Consultation on Incontinence; International Continence Society: Tokyo, Japan, 2017; pp. 1–141. [Google Scholar]
- Gram, M.C.D.; Bø, K. High level rhythmic gymnasts and urinary incontinence: Prevalence, risk factors, and influence on performance. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sport. 2020, 30, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mota, R.L. Female urinary incontinence and sexuality. Int. Braz. J. Urol. 2017, 43, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hay-Smith, E.J.; Herderschee, R.; Dumoulin, C.; Herbison, G.P. Comparisons of approaches to pelvic floor muscle training for urinary incontinence in women. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2011, 12, CD009508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frigerio, M.; Barba, M.; Cola, A.; Braga, A.; Celardo, A.; Munno, G.M.; Schettino, M.T.; Vagnetti, P.; Simone, F.D.; Lucia, A.D.; et al. Quality of Life, Psychological Wellbeing, and Sexuality in Women with Urinary Incontinence-Where Are We Now: A Narrative Review. Medicina 2022, 58, 525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrés-Godayol, P.; Jerez-Roig, J.; Minobes-Molina, E.; Yildirim, M.; Tuneu, M.M.; Salvans, A.E.; Fochs, S.R.; Mas, M.R.; Moreno, M.T.; Planas, L.C.; et al. Urinary Incontinence and Its Association with Physical and Psycho-Cognitive Factors: A Cross-Sectional Study in Older People Living in Nursing Homes. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.S.; Kim, E.G.; Shin, K.Y.; Choo, H.J.; Kim, M.J. Combined pelvic muscle exercise and yoga program for urinary incontinence in middle-aged women. Jpn. J. Nurs. Sci. 2015, 12, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.-H.; Kang, C.-B. Effect of Kegel Exercises on the Management of Female Stress Urinary Incontinence: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials. Adv. Nurs. 2014, 2014, 640262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cho, S.T.; Kim, K.H. Pelvic floor muscle exercise and training for coping with urinary incontinence. J. Exerc. Rehabil. 2021, 17, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roongsirisangrat, S.; Rangkla, S.; Manchana, T.; Tantisiriwat, N. Rectal balloon training as an adjunctive method for pelvic floor muscle training in conservative management of stress urinary incontinence: A pilot study. J. Med. Assoc. Thail. 2012, 95, 1149–1155. [Google Scholar]
- Sawaqed, F.; Al Kharabsheh, A.; Tout, M.; Zaidan, M.; Khashram, H.; AlShunaigat, N. Prevalence of stress urinary incontinence and its impact on quality of life among women in Jordan: A correlational study. J. Int. Med. Res. 2020, 48, 300060520925651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, D.W.; Weir, M.; Cahill, J.J.; Rizk, D.E.E. The self-reported prevalence and knowledge of urinary incontinence and barriers to health care-seeking in a community sample of Canadian women. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2013, 3, 97–102. [Google Scholar]
- Sobhgol, S.S.; Priddis, H.; Smith, C.A.; Dahlen, H.G. The Effect of Pelvic Floor Muscle Exercise on Female Sexual Function During Pregnancy and Postpartum: A Systematic Review. Sex. Med. Rev. 2019, 7, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Wang, K.; Sun, T.; Xu, D.; Palmer, M.H. Predicting help-seeking intention of women with urinary incontinence in Jinan, China: A theory of planned behaviour model. J. Clin. Nurs. 2015, 24, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gjerde, J.L.; Rortveit, G.; Muleta, M.; Blystad, A. Silently waiting to heal: Experiences among women living with urinary incontinence in northwest Ethiopia. Int. Urogynecol. J. 2013, 24, 953–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bani-Issa, W.; Almomani, F.; Eldeirawi, K. Urinary incontinence among adult women with diabetes in Jordan: Epidemiology, correlates and perceived impact on emotional and social well-being. J. Clin. Nurs. 2014, 23, 2451–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Azab, A.S.; Mohamed, E.M.; Sabra, H.I. The prevalence and risk factors of urinary incontinence and its influence on the quality of life among Egyptian women. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2007, 26, 783–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayachandran, C. Prevalence of Stress, Urge, and Mixed Urinary Incontinence in Women. Master’s Thesis, Eastern Michigan University, Ypsilanti, MI, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Joshi, C.; Mohsin, Z.; Joshi, A.K. Role of postpartum Kegel exercises in the prevention and cure of stress incontinence. Int. J. Reprod. Contracept. Obstet. Gynecol. 2016, 5, 669–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elbana, H.M.; Salama, A.M.; Barakat, M.M. Effect of urinary incontinence on quality of life and self esteem of postmenopausal women. Am. J. Nurs. Sci. 2018, 7, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, H.G.; Hafez, S.K.; Basyouni, N.R. Effect of Pelvic Floor Muscle Strengthening-Kegel’s Exercise-on Severity of Stress Urinary Incontinence and Quality of Life among Women. Int. J. Nov. Res. Healthc. Nurs. 2018, 5, 421–438. [Google Scholar]
- Abd El-Aty, E.M.; Hassan, M.E.-G. Effect of Kegel Exercise Training Program On Improving Quality Of Life Among Women With Urinary Incontinence. Egypt. J. Health Care 2021, 12, 946–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Brazález, B.; Prieto-Gómez, V.; Prieto-Merino, D.; Sánchez-Sánchez, B.; McLean, L.; Torres-Lacomba, M. Effectiveness of Hypopressive Exercises in Women with Pelvic Floor Dysfunction: A Randomised Controlled Trial. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Özlü, A.; Yıldız, N.; Öztekin, Ö. Comparison of the efficacy of perineal and intravaginal biofeedback assisted pelvic floor muscle exercises in women with urodynamic stress urinary incontinence. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2017, 36, 2132–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitz, F.F.; Stüpp, L.; da Costa, T.F.; Bortolini, M.A.T.; Castello Girão, M.J.B.; Castr, R.A. Outpatient biofeedback in addition to home pelvic floor muscle training for stress urinary incontinence: A randomized controlled trial. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2017, 36, 2034–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radzimińska, A.; Strączyńska, A.; Weber-Rajek, M.; Styczyńska, H.; Strojek, K.; Piekorz, Z. The impact of pelvic floor muscle training on the quality of life of women with urinary incontinence: A systematic literature review. Clin. Interv. Aging 2018, 13, 957–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Soliman, S.; Omar, H.H.; Zarzour, A.H.; ElAzab, A.S. Urinary Incontinence Among Women at in an Egyptian Primary Health Center. Egypt. Fam. Med. J. 2020, 4, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaderi, F.; Oskouei, A.E. Physiotherapy for women with stress urinary incontinence: A review article. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2014, 26, 1493–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kulaksizoğlu, H.; Akand, M.; Cakmakci, E.; Gül, M.; Seçkin, B. Effectiveness of pelvic floor muscle training on symptoms and uroflowmetry parameters in female patients with overactive bladder. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2015, 45, 449–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Concepcion, K.; Cheng, Y.; McGeechan, K.; Robertson, S.; Stewart, M.; Bateson, D.; Estoesta, J.; Chiarelli, P. Prevalence and associated factors of urinary leakage among women participating in the 45 and Up Study. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2018, 37, 2782–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro Brazález, B.; Torres Lacomba, M.; de la Villa, P.; Sanchez Sanchez, B.; Prieto Gómez, V.; Asúnsolo del Barco, Á.; McLean, L. The evaluation of pelvic floor muscle strength in women with pelvic floor dysfunction: A reliability and correlation study. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2018, 37, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
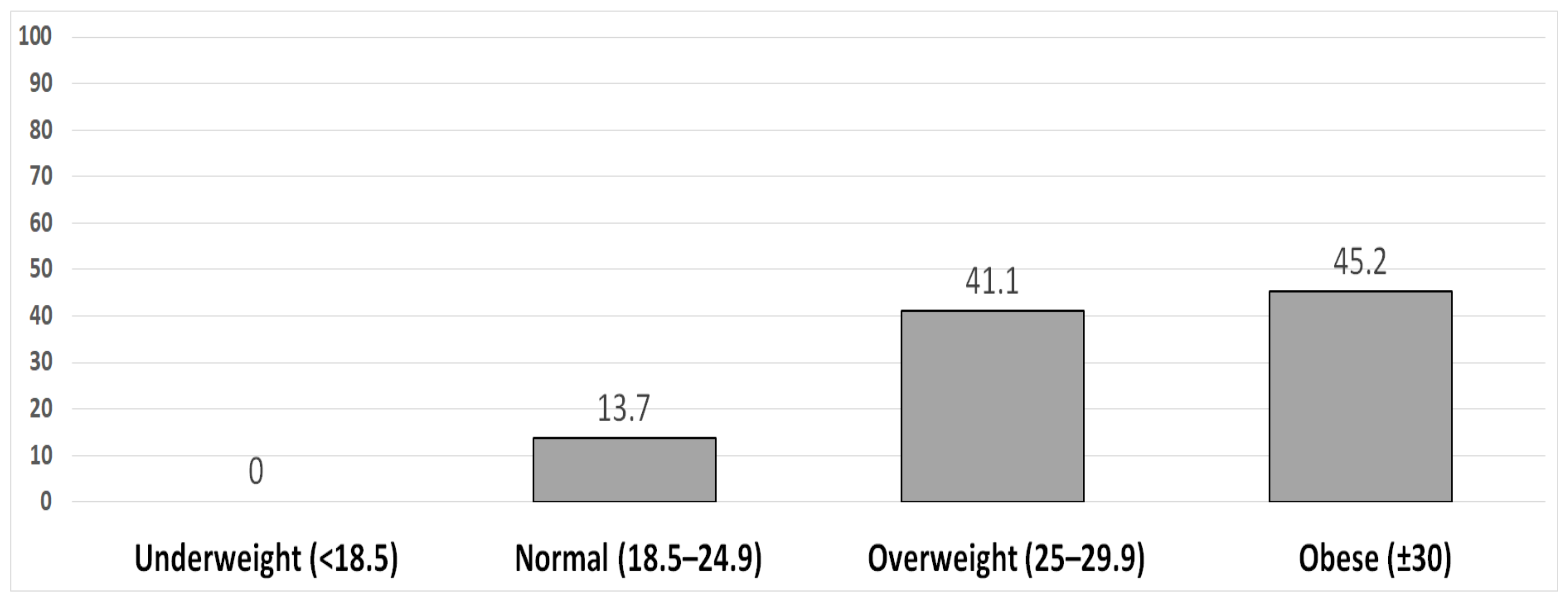
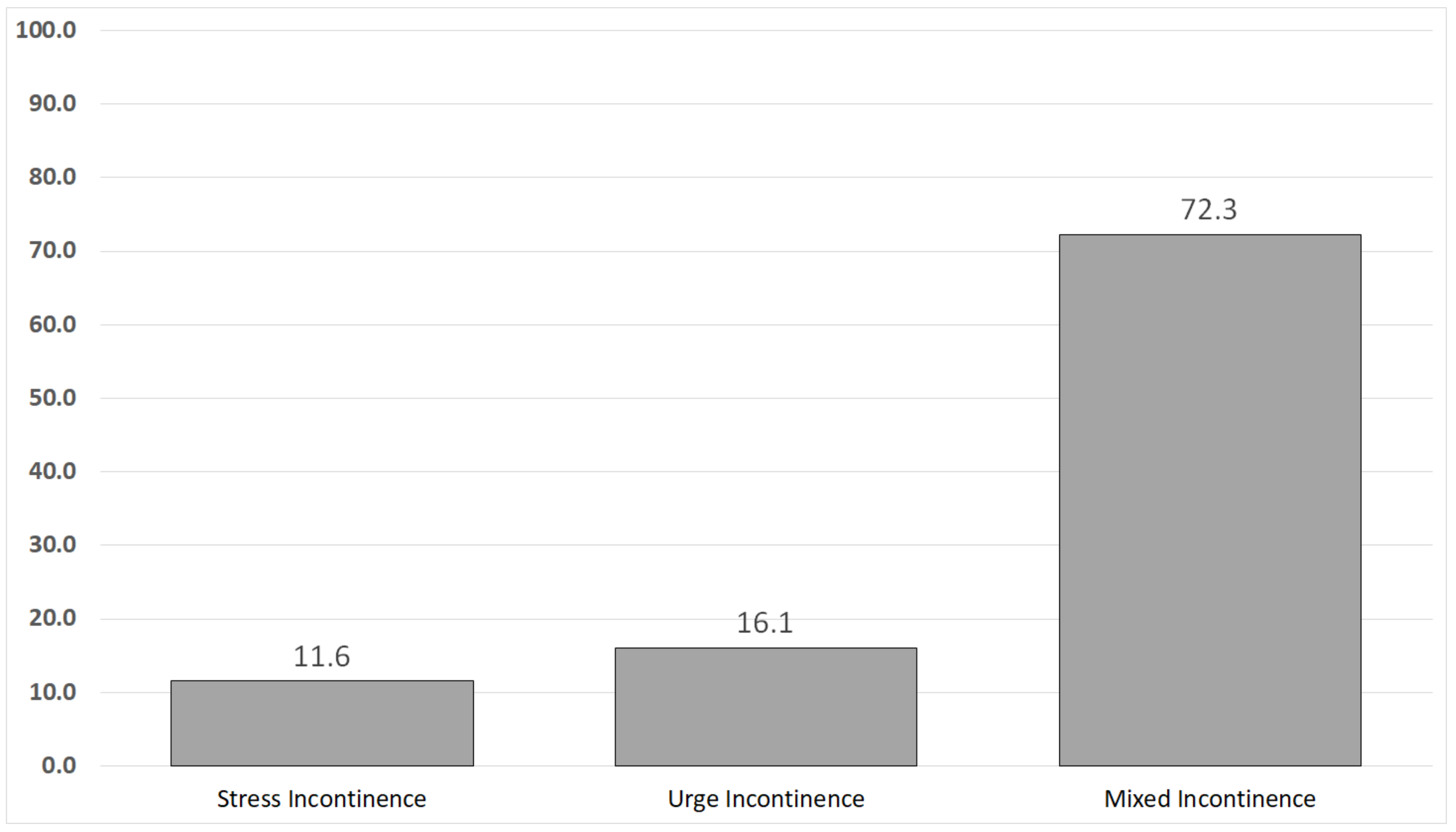
| No. | % | Min | Max | Mean | SD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (Years) | 17 | 45 | 33.38 | 6.9 | ||
| 17–25 | 42 | 14.4% | ||||
| >25–35 | 142 | 48.6% | ||||
| >35–45 | 108 | 37.0% | ||||
| Level of Education | ||||||
| Illiterate | 74 | 25.3% | ||||
| Reading and Writing | 16 | 5.5% | ||||
| Primary Education | 22 | 7.5% | ||||
| Secondary Education | 145 | 49.7% | ||||
| High Education and Above | 35 | 12.0% | ||||
| Marital Status | ||||||
| Single | 10 | 3.4% | ||||
| Married | 273 | 93.5% | ||||
| Widowed | 4 | 1.4% | ||||
| Divorced | 5 | 1.7% | ||||
| Employment Status | ||||||
| Housewives | 246 | 84.2% | ||||
| Working | 46 | 15.8% |
| No. | % | Min | Max | Mean | SD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Medical History | ||||||
| None | 195 | 66.7% | ||||
| Hypertension | 75 | 25.7% | ||||
| Cardiac Disease | 2 | 0.7% | ||||
| Arthritis/Rheumatism | 12 | 4.1% | ||||
| Anemia | 6 | 2.1% | ||||
| Hepatitis C | 2 | 0.7% | ||||
| Surgical History | ||||||
| None | 218 | 74.7% | ||||
| Hysterectomy | 8 | 2.7% | ||||
| Appendectomy | 32 | 10.9% | ||||
| Cholecystectomy | 18 | 6.1% | ||||
| Thyroidectomy | 4 | 1.4% | ||||
| Oophorectomy | 2 | 0.7% | ||||
| Ovarian Cyst Removal | 6 | 2.1% | ||||
| Uterine Fibroid Removal | 2 | 0.7% | ||||
| Back Cartilage Discectomy | 2 | 0.7% | ||||
| No. of Gravida | 0 | 9 | 3.22 | 1.67 | ||
| None | 21 | 7.2% | ||||
| 1–2 | 72 | 24.7% | ||||
| 3–4 | 143 | 49.0% | ||||
| ≥5 | 56 | 19.1% | ||||
| No. of Parity | 0 | 9 | 2.61 | 1.4 | ||
| None | 25 | 8.6% | ||||
| 1–2 | 112 | 38.4% | ||||
| 3–4 | 135 | 46.2% | ||||
| ≥5 | 20 | 6.8% | ||||
| No. of Abortions | 0 | 4 | 0.62 | 0.93 | ||
| 0 | 174 | 59.6% | ||||
| 1 | 78 | 26.7% | ||||
| 2 | 24 | 8.2% | ||||
| 3 | 10 | 3.4% | ||||
| 4 | 6 | 2.1% | ||||
| No. of Living Children | 0 | 11 | 2.72 | 1.58 | ||
| 1–2 | 135 | 46.2% | ||||
| 3–4 | 131 | 44.9% | ||||
| 5–6 | 20 | 6.8% | ||||
| ≥6 | 6 | 2.1% | ||||
| Mode of Delivery | ||||||
| None | 25 | 8.6% | ||||
| Cesarean | 180 | 61.6% | ||||
| Vaginal | 87 | 29.8% |
| No. | % | Min | Max | Mean | SD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pulse | ||||||
| <60 | 8 | 2.7% | ||||
| 60–100 | 282 | 96.6% | ||||
| >100 | 2 | 0.7% | ||||
| Blood Pressure | ||||||
| Below Normal | 19 | 6.5% | ||||
| Normal | 227 | 77.7% | ||||
| Above Normal | 46 | 15.8% | ||||
| Respiration Rate | ||||||
| <12 | ||||||
| 12–20 | 265 | 90.8% | ||||
| >20 | 27 | 9.2% | ||||
| Temperature | ||||||
| <36.5 | 2 | 0.7% | ||||
| 36.5–37.5 | 290 | 99.3% | ||||
| >37.5 | 0 | 0.0% | ||||
| Weight | 55 | 138 | 84.77 | 14.54 | ||
| <60 kg | 4 | 1.4% | ||||
| 60–90 kg | 201 | 68.8% | ||||
| >90 kg | 87 | 29.8% | ||||
| Height | 150 | 192 | 164.97 | 8.94 | ||
| <160 | 81 | 27.7% | ||||
| 160–170 | 142 | 48.6% | ||||
| >170 | 69 | 23.6% |
| Pretest | Posttest | t | Sig. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | % | No. | % | |||
| Rate of Urine Leakage | 1.000 | 0.000 | ||||
| Never | 0 | 0.0% | 0 | 0.0% | ||
| About once a week or less often | 46 | 15.8% | 53 | 18% | ||
| Two or three times a week | 62 | 21.2% | 86 | 30% | ||
| About once a day | 24 | 8.2% | 36 | 12% | ||
| Several times a day | 145 | 49.7% | 104 | 36% | ||
| All the time | 15 | 5.1% | 13 | 4% | ||
| Amount of Urine Leakage | 1.000 | 0.000 | ||||
| None | 0 | 0.0% | 0 | 0.0% | ||
| A small amount | 218 | 74.7% | 224 | 77% | ||
| A moderate amount | 50 | 17.1% | 46 | 16% | ||
| A large amount | 24 | 8.2% | 22 | 7% | ||
| Quality of Life | 1.000 | 0.000 | ||||
| <4 | 18 | 6% | 11 | 3.8% | ||
| 4–6 | 58 | 20% | 52 | 17.8% | ||
| >6 | 216 | 74% | 229 | 78.4% | ||
| Min–Max | 0–10 | 0–10 | ||||
| Mean ± SD | 6.67 ± 1.72 | 8.20 ± 2.16 | ||||
| Unstandardized Coefficients | Standardized Coefficients | t | Sig. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | Std. Error | Beta | |||
| (Constant) | −6.134 | 6.078 | |||
| Age | 0.008 | 0.007 | 0.081 | 1.169 | 0.026 * |
| Education | −0.042 | 0.030 | −0.087 | −1.407 | 0.161 |
| Marital status | −0.171 | 0.079 | −0.133 | −2.163 | 0.031 * |
| Employment Status | −0.138 | 0.115 | −0.073 | −1.205 | 0.229 |
| No. of Para | −0.107 | 0.057 | −0.218 | −1.867 | 0.063 |
| No. of Abortion | −0.033 | 0.044 | −0.044 | −0.741 | 0.459 |
| No. of Children | 0.017 | 0.048 | 0.039 | 0.351 | 0.726 |
| Mode of Delivery | −0.017 | 0.076 | −0.014 | −0.217 | 0.828 |
| Pulse | −0.019 | 0.008 | −0.264 | −2.344 | 0.020 * |
| BP | 0.093 | 0.080 | 0.079 | 1.165 | 0.245 |
| Respiratory | 0.090 | 0.033 | 0.269 | 2.733 | 0.007 * |
| Temperature | 0.236 | 0.174 | 0.119 | 1.357 | 0.176 |
| BMI | 0.202 | 0.090 | 0.193 | 2.243 | 0.026 * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abu Raddaha, A.H.; Nasr, E.H. Kegel Exercise Training Program among Women with Urinary Incontinence. Healthcare 2022, 10, 2359. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare10122359
Abu Raddaha AH, Nasr EH. Kegel Exercise Training Program among Women with Urinary Incontinence. Healthcare. 2022; 10(12):2359. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare10122359
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbu Raddaha, Ahmad H., and Elsayeda H. Nasr. 2022. "Kegel Exercise Training Program among Women with Urinary Incontinence" Healthcare 10, no. 12: 2359. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare10122359







