Healthy Lifestyle Score and Glycemic Control in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients: A City-Wide Survey in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Source and Study Population
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Definition of Healthy Lifestyle Score
2.4. Definition of Glycemic Control
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participant Characteristics
3.2. Association between Risk of Poor Glycemic Control and Healthy Lifestyle Factors
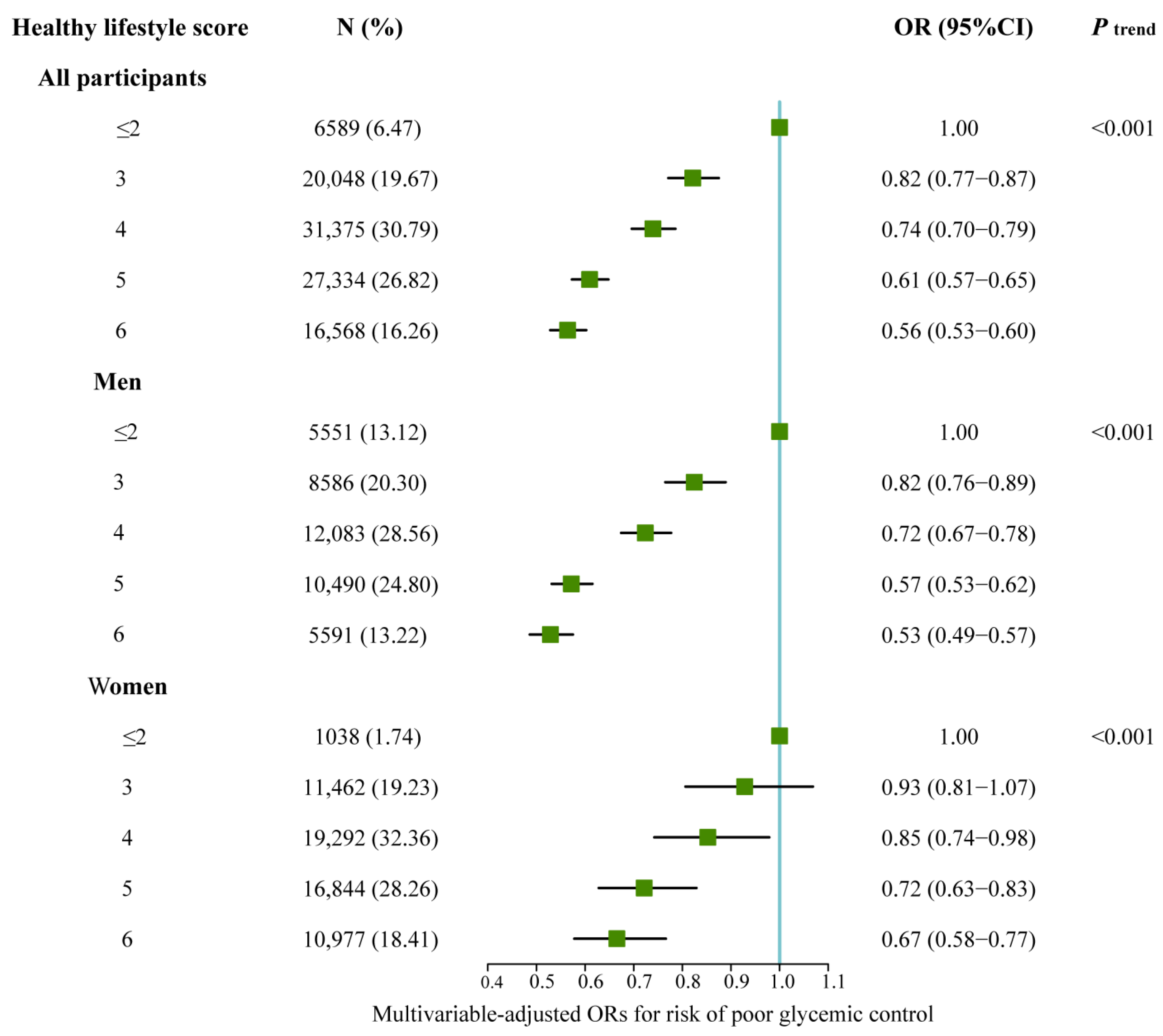
3.3. Association between Risk of Poor Glycemic Control and Healthy Lifestyle Score
3.4. Sensitivity Analysis
3.5. Interactions between Lifestyle Factors and Glycemic Control
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, H.; Saeedi, P.; Karuranga, S.; Pinkepank, M.; Ogurtsova, K.; Duncan, B.B.; Stein, C.; Basit, A.; Chan, J.C.; Mbanya, J.C.; et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 183, 109119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tancredi, M.; Rosengren, A.; Svensson, A.-M.; Kosiborod, M.; Pivodic, A.; Gudbjörnsdottir, S.; Wedel, H.; Clements, M.; Dahlqvist, S.; Lind, M. Excess Mortality among Persons with Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1720–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Emerging Risk Factors Collaboration. Diabetes mellitus, fasting glucose, and risk of cause-specific death. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 829–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoungas, S.; Chalmers, J.; Ninomiya, T.; Li, Q.; Cooper, M.E.; Colagiuri, S.; Fulcher, G.; De Galan, B.E.; Harrap, S.; Hamet, P.; et al. Association of HbA1c levels with vascular complications and death in patients with type 2 diabetes: Evidence of glycaemic thresholds. Diabetologia 2012, 55, 636–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratton, I.M.; Adler, A.I.; Neil, H.A.; Matthews, D.R.; Manley, S.E.; Cull, C.A.; Hadden, D.; Turner, R.C.; Holman, R.R. Association of glycaemia with macrovascular and microvascular complications of type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 35): Prospective observational study. BMJ 2000, 321, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, S.E.; Cooper, M.E.; Del Prato, S. Pathophysiology and treatment of type 2 diabetes: Perspectives on the past, present, and future. Lancet 2014, 383, 1068–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruissen, M.M.; Regeer, H.; Landstra, C.P.; Schroijen, M.; Jazet, I.; Nijhoff, M.F.; Pijl, H.; Ballieux, B.E.P.B.; Dekkers, O.; Huisman, S.D.; et al. Increased stress, weight gain and less exercise in relation to glycemic control in people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes during the COVID-19 pandemic. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2021, 9, e002035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuy, L.Q.; Nam, H.T.P.; An, T.T.H.; Van San, B.; Ngoc, T.N.; Trung, L.H.; Tan, P.H.; Thanh, N.H. Factors Associated with Glycaemic Control among Diabetic Patients Managed at an Urban Hospital in Hanoi, Vietnam. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 8886904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyberg, S.T.; Singh-Manoux, A.; Pentti, J.; Madsen, I.E.H.; Sabia, S.; Alfredsson, L.; Bjorner, J.B.; Borritz, M.; Burr, H.; Goldberg, M.; et al. Association of Healthy Lifestyle with Years Lived without Major Chronic Diseases. JAMA Intern. Med. 2020, 180, 760–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, P.R.; Weigl, K.; Jansen, L.; Walter, V.; Erben, V.; Chang-Claude, J.; Brenner, H.; Hoffmeister, M. Healthy Lifestyle Factors Associated with Lower Risk of Colorectal Cancer Irrespective of Genetic Risk. Gastroenterology 2018, 155, 1805–1815.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, Z.; Zhu, C.; Yuan, H.; Chen, Y. Combined impact of lifestyle-related factors on total mortality among the elder Chinese: A prospective cohort study. BMC Geriatr. 2022, 22, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chudasama, Y.V.; Khunti, K.; Gillies, C.L.; Dhalwani, N.N.; Davies, M.J.; Yates, T.; Zaccardi, F. Healthy lifestyle and life expectancy in people with multimorbidity in the UK Biobank: A longitudinal cohort study. PLoS Med. 2020, 17, e1003332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burke, G.L.; Hunter, S.M.; Croft, J.B.; Cresanta, J.L.; Berenson, G.S. The interaction of alcohol and tobacco use in adolescents and young adults: Bogalusa Heart Study. Addict. Behav. 1988, 13, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvaavik, E.; Lund, I.; Nygård, M.; Hansen, B.T. Lifestyle Correlates of Female Snus Use and Smoking: A Large Population-Based Survey of Women in Norway. Nicotine Tob. Res. Off. J. Soc. Res. Nicotine Tob. 2016, 18, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Guo, Z.; Wu, M.; Hao, C.; Zhou, Z.; Yao, X. Interaction of smoking and obesity on type 2 diabetes risk in a Chinese cohort. Physiol. Behav. 2015, 139, 240–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franz, M.J.; Boucher, J.L.; Rutten-Ramos, S.; VanWormer, J.J. Lifestyle weight-loss intervention outcomes in overweight and obese adults with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2015, 115, 1447–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansen, M.Y.; Macdonald, C.S.; Hansen, K.B.; Karstoft, K.; Christensen, R.; Pedersen, M.; Hansen, L.S.; Zacho, M.; Wedell-Neergaard, A.-S.; Nielsen, S.T.; et al. Effect of an Intensive Lifestyle Intervention on Glycemic Control in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2017, 318, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dirmaier, J.; Watzke, B.; Koch, U.; Schulz, H.; Lehnert, H.; Pieper, L.; Wittchen, H.-U. Diabetes in primary care: Prospective associations between depression, nonadherence and glycemic control. Psychother. Psychosom. 2010, 79, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.W.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Lei, L.; Peng, J.; Shi, W.H.; Wang, J.L.; Yang, Y.B.; Ma, J.X. The behavior and lifestyles and association with disease control among hypertensive or diabetic patients in Shenzhen. Chin. J. Prev. Control Chronic Dis. 2021, 29, 735–740. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Khor, C.-C.; Fan, J.; Lv, J.; Yu, C.; Guo, Y.; Bian, Z.; Yang, L.; Millwood, I.Y.; Walters, R.G.; et al. Genetic risk, adherence to a healthy lifestyle, and type 2 diabetes risk among 550,000 Chinese adults: Results from 2 independent Asian cohorts. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 111, 698–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Health and Family Planning Committee of the People’s Republic of China. Health Industry Standard: Criteria of Weight for Adults; China NHaFPCotPsRo, Ed.; Chinese Standards Press: Beijing, China, 2013; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Chinese Diabetes Society. Guideline for the prevention and treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus in China (2020 edition). Chin. J. Diabetes Mellit. 2021, 13, 315–409. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, J.; Yu, C.; Guo, Y.; Bian, Z.; Yang, L.; Chen, Y.; Hu, X.; Hou, W.; Chen, J.; Chen, Z.; et al. Adherence to a healthy lifestyle and the risk of type 2 diabetes in Chinese adults. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 46, 1410–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Laguna, N.; Martínez-González, M.A.; Toledo, E.; Babio, N.; Sorlí, J.V.; Ros, E.; Muñoz, M.Á.; Estruch, R.; Lapetra, J.; Muñoz-Bravo, C.; et al. Risk of peripheral artery disease according to a healthy lifestyle score: The PREDIMED study. Atherosclerosis 2018, 275, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, F.B.; Manson, J.E.; Stampfer, M.J.; Colditz, G.; Liu, S.; Solomon, C.G.; Willett, W.C. Diet, lifestyle, and the risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus in women. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 345, 790–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Xu, Y.; Wan, Q.; Shen, F.; Xu, M.; Zhao, Z.; Lu, J.; Gao, Z.; Chen, G.; Wang, T.; et al. Individual and Combined Associations of Modifiable Lifestyle and Metabolic Health Status with New-Onset Diabetes and Major Cardiovascular Events: The China Cardiometabolic Disease and Cancer Cohort (4C) Study. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, 1929–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.; Yang, Y. Factors Associated with Poor Glycemic Control Amongst Rural Residents with Diabetes in Korea. Healthcare 2021, 9, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munekawa, C.; Hosomi, Y.; Hashimoto, Y.; Okamura, T.; Takahashi, F.; Kawano, R.; Nakajima, H.; Osaka, T.; Okada, H.; Majima, S.; et al. Effect of coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic on the lifestyle and glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes: A cross-section and retrospective cohort study. Endocr. J. 2021, 68, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.M.; Kim, J.D.; Jung, H. A Cross-Sectional Study of the Effects of Physical Activity and Nutrient Intakes on Blood Glucose Control Rates in Middle-Aged and Elderly Diabetes Patients: Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2015–2017. Inq. J. Med. Care Organ. Provis. Financ. 2021, 58, 469580211035727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrieks, I.C.; Heil, A.L.; Hendriks, H.F.; Mukamal, K.J.; Beulens, J.W. The effect of alcohol consumption on insulin sensitivity and glycemic status: A systematic review and meta-analysis of intervention studies. Diabetes Care 2015, 38, 723–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, A.A.; Arnsten, J.H.; Gourevitch, M.N. Effect of alcohol consumption on diabetes mellitus: A systematic review. Ann. Intern. Med. 2004, 140, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiva-Blanch, G.; Badimon, L. Benefits and Risks of Moderate Alcohol Consumption on Cardiovascular Disease: Current Findings and Controversies. Nutrients 2019, 12, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van de Wiel, A. Diabetes mellitus and alcohol. Diabetes/Metab. Res. Rev. 2004, 20, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smyth, A.; Teo, K.K.; Rangarajan, S.; O’Donnell, M.; Zhang, X.; Rana, P.; Leong, D.P.; Dagenais, G.; Seron, P.; Rosengren, A.; et al. Alcohol consumption and cardiovascular disease, cancer, injury, admission to hospital, and mortality: A prospective cohort study. Lancet 2015, 386, 1945–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagnardi, V.; Rota, M.; Botteri, E.; Tramacere, I.; Islami, F.; Fedirko, V.; Scotti, L.; Jenab, M.; Turati, F.; Pasquali, E.; et al. Light alcohol drinking and cancer: A meta-analysis. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2013, 24, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Thani, M.; Al Thani, A.A.; Al-Chetachi, W.; Al Malki, B.; Khalifa, S.A.H.; Bakri, A.H.; Hwalla, N.; Nasreddine, L.; Naja, F. A ‘High Risk’ Lifestyle Pattern Is Associated with Metabolic Syndrome among Qatari Women of Reproductive Age: A Cross-Sectional National Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paramastri, R.; Hsu, C.-Y.; Chuang, Y.-K.; Lee, H.-A.; Wiratama, B.S.; Chao, J.C.-J. Synergistic Interaction of Dietary Pattern and Concordance Lifestyle with Abnormal Liver Function among Young Adults in Taiwan: A Population-Based Longitudinal Study. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Pan, X.-F.; Chen, J.; Xia, L.; Cao, A.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, H.; Yang, K.; Guo, K.; et al. Combined lifestyle factors and risk of incident type 2 diabetes and prognosis among individuals with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Diabetologia 2020, 63, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.-F.; Song, X.-Y.; Pan, X.-F.; Feng, L.; Luo, N.; Yuan, J.-M.; Pan, A.; Koh, W.-P. Association between Combined Lifestyle Factors and Healthy Ageing in Chinese Adults: The Singapore Chinese Health Study. J. Gerontol. Ser. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2021, 76, 1796–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Liu, X.; Xue, H.; Wang, Y.; Shi, Z. Comparisons of Visceral Adiposity Index, Body Shape Index, Body Mass Index and Waist Circumference and Their Associations with Diabetes Mellitus in Adults. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Feng, T.; Wang, L.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, P.; Pan, P.; Wang, M.; Binnay, I.T.S.; Wang, Y.; Chai, R.; et al. Causal associations of waist circumference and waist-to-hip ratio with type II diabetes mellitus: New evidence from Mendelian randomization. Mol. Genet. Genom. MGG 2021, 296, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, L.; Yang, X.; Wang, R.; Ku, C.; Wu, B.; Dai, M.; Liu, L.; Ping, Z. Waist Circumference-Years Construct Analysis and the Incidence of Type 2 Diabetes: China Health and Nutrition Survey, 1997–2015. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Ma, X.; Tang, T.; Jin, L.; Peng, D.; Zhang, R.; Chen, M.; Yan, J.; Wang, S.; Yan, D.; et al. Overall and central obesity with insulin sensitivity and secretion in a Han Chinese population: A Mendelian randomization analysis. Int. J. Obes. 2016, 40, 1736–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashim, S.A.; Barakatun-Nisak, M.Y.; Abu Saad, H.; Ismail, S.; Hamdy, O.; Mansour, A.A. Association of Health Literacy and Nutritional Status Assessment with Glycemic Control in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derr, R.; Garrett, E.; Stacy, G.A.; Saudek, C.D. Is HbA(1c) affected by glycemic instability? Diabetes Care 2003, 26, 2728–2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilpatrick, E.S.; Rigby, A.S.; Atkin, S.L. Variability in the relationship between mean plasma glucose and HbA1c: Implications for the assessment of glycemic control. Clin. Chem. 2007, 53, 897–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohlfing, C.L.; Wiedmeyer, H.-M.; Little, R.R.; England, J.D.; Tennill, A.; Goldstein, D.E. Defining the relationship between plasma glucose and HbA(1c): Analysis of glucose profiles and HbA(1c) in the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial. Diabetes Care 2002, 25, 275–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Lifestyle | Category | Healthy/Unhealthy | Score |
|---|---|---|---|
| Physical activities | Total physical activity hours per week > 150 min | Healthy | 1 |
| Total physical activity hours per week ≤ 150 min | Unhealthy | 0 | |
| Waist circumference | Men: <90 cm; Women: <85 cm | Healthy | 1 |
| Men: ≥90 cm; Women: ≥85 cm | Unhealthy | 0 | |
| Body Mass Index | 18.5–23.9 kg/m2 | Healthy | 1 |
| <18.5 kg/m2/≥24.0 kg/m2 | Unhealthy | 0 | |
| Dietary habits | Balanced consumption of meat and vegetarian diet, moderate salt consumption, moderate oil consumption, and moderate added sugar consumption | Healthy | 1 |
| Prefer meat/prefer vegetarian diet/high salt consumption/high oil consumption/high added sugar consumption | Unhealthy | 0 | |
| Smoking | Never | Healthy | 1 |
| Current/former | Unhealthy | 0 | |
| Alcohol consumption | Never | Healthy | 1 |
| Current/former | Unhealthy | 0 |
| Overall (n = 101,914) | Glycemic Control a | p Value b | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Good (n = 52,381) | Poor (n = 49,533) | |||
| Sex, n (%) | 0.002 | |||
| Men | 42,301 (41.51) | 21,494 (41.03) | 20,807 (42.01) | |
| Women | 59,613 (58.49) | 30,887 (58.97) | 28,726 (57.99) | |
| Age, years, mean ± SD | 65.86 ± 10.19 | 66.13 ± 10.38 | 65.58 ± 9.99 | <0.001 |
| Duration of diabetes, years, mean ± SD | 5.93 ± 5.64 | 5.57 ± 5.40 | 6.30 ± 5.86 | <0.001 |
| Ethnicity (Han), n (%) | 101,744 (99.83) | 52,297 (99.84) | 49,447 (99.83) | 0.659 |
| Education, n (%) | <0.001 | |||
| Illiteracy | 27,866 (27.34) | 14,081 (26.88) | 13,785 (27.83) | |
| Primary and high school education | 41,439 (40.66) | 21,493 (41.03) | 19,946 (40.27) | |
| College education and above | 32,064 (31.46) | 16,483 (31.47) | 15,581 (31.46) | |
| Marriage (Married), n (%) | 90,505 (88.81) | 46,448 (88.67) | 44,057 (88.94) | 0.241 |
| Family history of diabetes, n (%) | 7141 (7.01) | 3407 (6.50) | 3734 (7.54) | <0.001 |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 57,804 (56.72) | 30,791 (58.78) | 27,013 (54.54) | <0.001 |
| Waist circumference, cm, mean ± SD | 85.98 ± 25.83 | 85.36 ± 34.48 | 86.64 ± 10.71 | <0.001 |
| Body mass index, kg/m2, mean ± SD | 24.68 ± 3.98 | 24.52 ± 3.71 | 24.84 ± 4.24 | <0.001 |
| Sufficient physical activity | 59,003 (57.89) | 30,470 (58.17) | 28,533 (57.60) | 0.068 |
| Smoking, n (%) | <0.001 | |||
| Never | 84,568 (82.98) | 44,164 (84.31) | 40,404 (81.57) | |
| Former | 4142 (4.06) | 2003 (3.82) | 2139 (4.32) | |
| Current | 13,204 (12.94) | 6214 (11.87) | 6990 (14.11) | |
| Alcohol consumption, n (%) | <0.001 | |||
| Never | 91,368 (89.65) | 47,636 (90.94) | 43,732 (88.29) | |
| Former | 1686 (1.65) | 807 (1.54) | 879 (1.77) | |
| Current | 8860 (8.69) | 3938 (7.52) | 4922 (9.94) | |
| Dietary habits, n (%) | 0.022 | |||
| Balanced meat and vegetarian diet | 98,431 (96.58) | 50,618 (96.63) | 47,813 (96.53) | |
| Prefer meat | 973 (0.95) | 458 (0.87) | 515 (1.04) | |
| Prefer vegetarian diet | 2510 (2.46) | 1305 (2.49) | 1205 (2.43) | |
| High salt consumption, n (%) | 1084 (1.06) | 537 (1.03) | 547 (1.10) | 0.230 |
| High oil consumption, n (%) | 392 (0.38) | 184 (0.35) | 208 (0.42) | 0.086 |
| High sugar consumption, n (%) | 240 (0.24) | 125 (0.24) | 115 (0.23) | 0.882 |
| Diabetes treatment | 0.018 | |||
| None | 26,922 (26.42) | 13,868 (26.48) | 13,054 (26.35) | |
| Oral hypoglycemic drugs | 69,074 (67.78) | 35,577 (67.92) | 33,497 (67.63) | |
| Insulin or insulin + oral hypoglycemic drugs | 5918 (5.81) | 2936 (5.61) | 2982 (6.02) | |
| Fasting blood glucose, mmol/L, mean ± SD | 7.86 ± 5.05 | 5.87 ± 0.77 | 9.96 ± 6.58 | <0.001 |
| Cases, n (%) | OR (95% CI) a | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Model 1 | Model 2 | ||
| Physical activity b | |||
| Unhealthy | 42,911 (42.11) | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Healthy | 59,003 (57.89) | 0.98 (0.96–1.01) | 0.96 (0.93–0.99) |
| Waist circumference c | |||
| Unhealthy | 44,523 (43.69) | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Healthy | 57,391 (56.31) | 0.77 (0.74–0.79) | 0.74 (0.72–0.77) |
| BMI d | |||
| Unhealthy | 58,146 (57.05) | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Healthy | 43,768 (42.95) | 0.99 (0.96–1.02) | 0.97 (0.94–1.00) |
| Dietary habit e | |||
| Unhealthy | 4636 (4.55) | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Healthy | 97,278 (95.45) | 0.96 (0.90–1.02) | 0.95 (0.89–1.01) |
| Smoking f | |||
| Unhealthy | 17,346 (17.02) | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Healthy | 84,568 (82.98) | 0.88 (0.84–0.91) | 0.89 (0.85–0.93) |
| Alcohol consumption g | |||
| Unhealthy | 10,546 (10.35) | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Healthy | 91,368 (89.65) | 0.81 (0.78–0.85) | 0.81 (0.77–0.85) |
| 5-Score HLS a | Pinteraction | ORs (95% CIs) for Interaction | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low (0–2) | High (3–5) | |||
| Physical activity b | 0.001 | 1.10 (1.04–1.16) | ||
| Unhealthy | 1.00 | 0.70 (0.67–0.73) | ||
| Healthy | 0.92 (0.88–0.95) | 0.70 (0.67–0.73) | ||
| Waist circumference c | <0.001 | 0.90 (0.85–0.95) | ||
| Unhealthy | 1.00 | 0.94 (0.91–0.99) | ||
| Healthy | 0.79 (0.75–0.83) | 0.67 (0.65–0.70) | ||
| BMI d | 0.001 | 0.90 (0.84–0.96) | ||
| Unhealthy | 1.00 | 0.80 (0.77–0.83) | ||
| Healthy | 0.95 (0.90–1.01) | 0.69 (0.66–0.71) | ||
| Dietary habit e | 0.435 | 0.95 (0.83–1.08) | ||
| Unhealthy | 1.00 | 0.79 (0.69–0.90) | ||
| Healthy | 0.97 (0.89–1.06) | 0.72 (0.66–0.79) | ||
| Smoking f | 0.703 | 0.99 (0.92–1.06) | ||
| Unhealthy | 1.00 | 0.78 (0.72–0.83) | ||
| Healthy | 0.85 (0.81–0.90) | 0.65 (0.62–0.68) | ||
| Alcohol consumption g | 0.011 | 0.88 (0.80–0.97) | ||
| Unhealthy | 1.00 | 0.87 (0.79–0.96) | ||
| Healthy | 0.81 (0.77–0.86) | 0.62 (0.59–0.66) | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Che, M.; Zhou, Q.; Lin, W.; Yang, Y.; Sun, M.; Liu, X.; Liu, H.; Zhang, C. Healthy Lifestyle Score and Glycemic Control in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients: A City-Wide Survey in China. Healthcare 2023, 11, 2037. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11142037
Che M, Zhou Q, Lin W, Yang Y, Sun M, Liu X, Liu H, Zhang C. Healthy Lifestyle Score and Glycemic Control in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients: A City-Wide Survey in China. Healthcare. 2023; 11(14):2037. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11142037
Chicago/Turabian StyleChe, Mengmeng, Qin Zhou, Weiquan Lin, Yunou Yang, Minying Sun, Xiangyi Liu, Hui Liu, and Caixia Zhang. 2023. "Healthy Lifestyle Score and Glycemic Control in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients: A City-Wide Survey in China" Healthcare 11, no. 14: 2037. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11142037
APA StyleChe, M., Zhou, Q., Lin, W., Yang, Y., Sun, M., Liu, X., Liu, H., & Zhang, C. (2023). Healthy Lifestyle Score and Glycemic Control in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients: A City-Wide Survey in China. Healthcare, 11(14), 2037. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11142037






