Variation in Nicotine Metabolization According to Biological Factors and Type of Nicotine Consumer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Determination of Biomarkers in Saliva and Computation of the Rate of Nicotine Metabo-Lism and Nicotine Metabolite Ratio
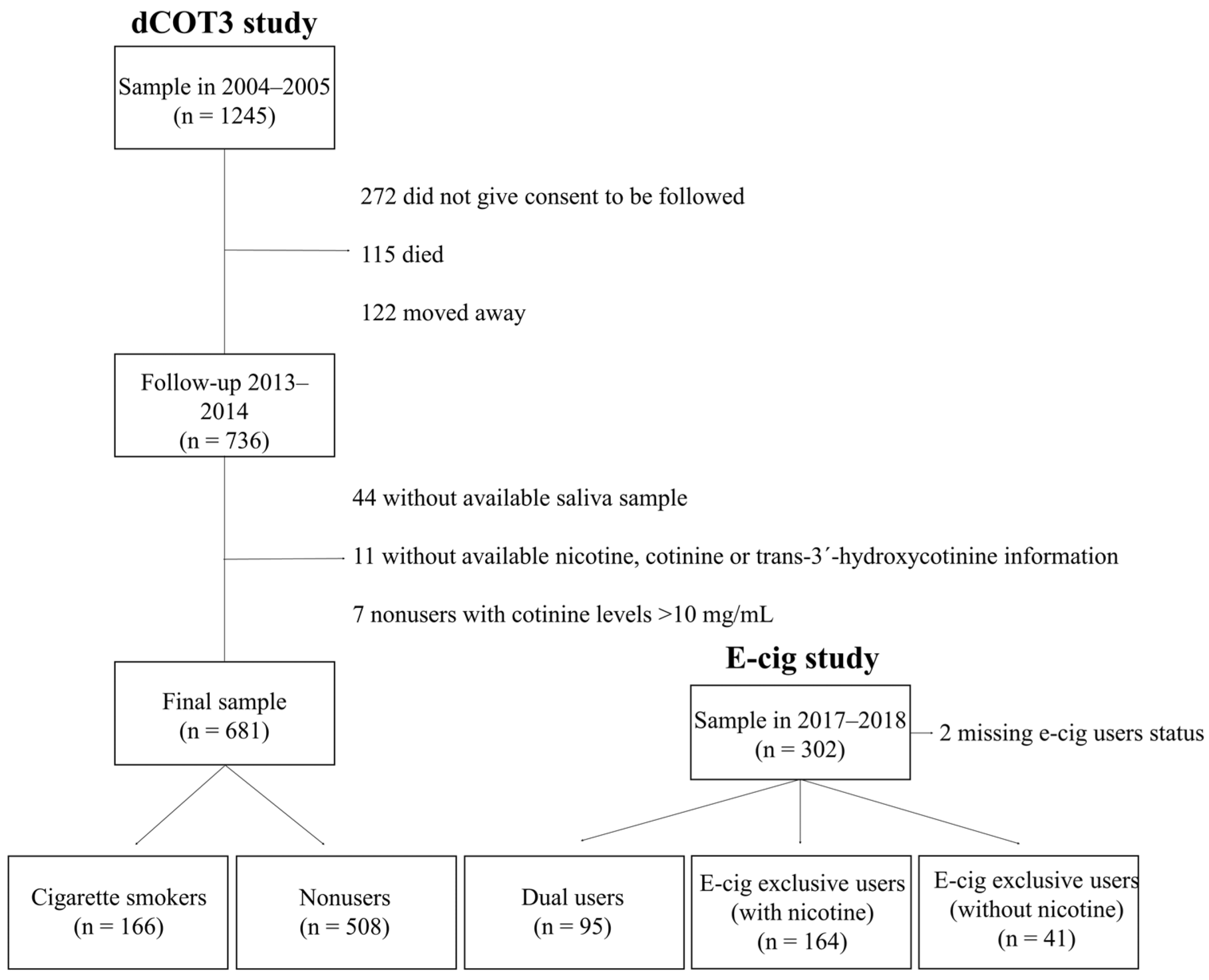
2.2. Smoking Status and Use of E-Cigarettes
2.3. Biological Variables
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Nicotine Metabolite Ratio & Rate of Nicotine Metabolism According to Smoking Status and Use of E-Cigarette
4.2. Nicotine Metabolite Ratio & RNM According to Biological Factors
4.3. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jackler, R.K.; Ramamurthi, D. Nicotine arms race: JUUL and the high-nicotine product market. Tob. Control 2019, 28, 623–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- The International Agency for Research on Cancer. Tobacco Smoke and Involuntary Smoking; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004; ISBN 9283212835. [Google Scholar]
- National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion (US) Office on Smoking and Health. The Health Consequences of Smoking—50 Years of Progress: A Report of the Surgeon General. 2014. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK179276/ (accessed on 28 November 2022).
- Pan, B.; Jin, X.; Jun, L.; Qiu, S.; Zheng, Q.; Pan, M. The relationship between smoking and stroke: A meta-analysis. Medicine 2019, 98, e14872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, O.; Hajek, P.; McRobbie, H. Systematic review of the relationship between the 3-hydroxycotinine/cotinine ratio and cigarette dependence. Psychopharmacology 2011, 218, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheidweiler, K.B.; Marrone, G.F.; Shakleya, D.M.; Singleton, E.G.; Heishman, S.J.; Huestis, M.A. Oral fluid nicotine markers to assess smoking status and recency of use. Ther. Drug Monit. 2011, 33, 609–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Verplaetse, T.L.; Peltier, M.R.; Roberts, W.; Moore, K.E.; Pittman, B.P.; McKee, S.A. Associations Between Nicotine Metabolite Ratio and Gender With Transitions in Cigarette Smoking Status and E-Cigarette Use: Findings Across Waves 1 and 2 of the Population Assessment of Tobacco and Health (PATH) Study. Nicotine Tob. Res. 2020, 22, 1316–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaiyandi, V.; Goodz, S.D.; Sellers, E.M.; Tyndale, R.F. CYP2A6 genotype, phenotype, and the use of nicotine metabolites as biomarkers during Ad libitum smoking. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2006, 15, 1812–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, M.; Fernandez, E.; Martínez-Snchez, J.M.; Pascual, J.A.; Schiaffino, A.; Agudo, A.; Ariza, C.; Borrs, J.M.; Samet, J.M.; Martínez-Sánchez, J.M.; et al. Salivary cotinine concentrations in daily smokers in Barcelona, Spain: A cross-sectional study. BMC Public Health 2009, 9, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Torres, S.; Merino, C.; Paton, B.; Correig, X.; Ramírez, N. Biomarkers of exposure to secondhand and thirdhand Tobacco smoke: Recent advances and future perspectives. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raja, M.; Garg, A.; Yadav, P.; Jha, K.; Handa, S. Diagnostic Methods for Detection of Cotinine Level in Tobacco Users: A Review. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2016, 10, ZE04–ZE06. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benowitz, N.L.; Lessov-Schlaggar, C.N.; Swan, G.E.; Jacob, P. 3rd Female sex and oral contraceptive use accelerate nicotine metabolism. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2006, 79, 480–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnstone, E.; Benowitz, N.; Cargill, A.; Jacob, R.; Hinks, L.; Day, I.; Murphy, M.; Walton, R. Determinants of the rate of nicotine metabolism and effects on smoking behavior. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2006, 80, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, A.E.; Richmond, R.C.; Palviainen, T.; Loukola, A.; Wootton, R.E.; Kaprio, J.; Relton, C.L.; Davey Smith, G.; Munafò, M.R. The effect of body mass index on smoking behaviour and nicotine metabolism: A Mendelian randomization study. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2019, 28, 1322–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dempsey, D.; Tutka, P.; Jacob III, P.; Allen, F.; Schoedel, K.; Tyndale, R.F.; Benowitz, N.L. Nicotine metabolite ratio as an index of cytochrome P450 2A6 metabolic activity. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2004, 76, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghazi, A.M.; Salhab, A.S.; Arafat, T.A.; Irshaid, Y.M. Effect of mint drink on metabolism of nicotine as measured by nicotine to cotinine ratio in urine of Jordanian smoking volunteers. Nicotine Tob. Res. 2011, 13, 661–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allenby, C.E.; Boylan, K.A.; Lerman, C.; Falcone, M. Precision Medicine for Tobacco Dependence: Development and Validation of the Nicotine Metabolite Ratio. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2016, 11, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sifat, A.E.; Vaidya, B.; Kaisar, M.A.; Cucullo, L.; Abbruscato, T.J. Nicotine and electronic cigarette (E-Cig) exposure decreases brain glucose utilization in ischemic stroke. J. Neurochem. 2018, 147, 204–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tanner, J.-A.; Novalen, M.; Jatlow, P.; Huestis, M.A.; Murphy, S.E.; Kaprio, J.; Kankaanpää, A.; Galanti, L.; Stefan, C.; George, T.P.; et al. Nicotine metabolite ratio (3-hydroxycotinine/cotinine) in plasma and urine by different analytical methods and laboratories: Implications for clinical implementation. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2015, 24, 1239–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siegel, S.D.; Lerman, C.; Flitter, A.; Schnoll, R.A. The Use of the Nicotine Metabolite Ratio as a Biomarker to Personalize Smoking Cessation Treatment: Current Evidence and Future Directions. Cancer Prev. Res. 2020, 13, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DeVito, E.E.; Krishnan-Sarin, S. E-cigarettes: Impact of E-Liquid Components and Device Characteristics on Nicotine Exposure. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2018, 16, 438–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim MPH, J.P.; Lee, S. Daily Cigarette Consumption and Urine Cotinine Level between Dual Users of Electronic and Conventional Cigarettes, and Cigarette-Only Users. J. Psychoact. Drugs 2020, 52, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comiford, A.L.; Rhoades, D.A.; Spicer, P.; Ding, K.; Dvorak, J.D.; Driskill, L.; Wagener, T.L.; Doescher, M.P. E-cigarettes and Tobacco Exposure Biomarkers among American Indian Smokers. Am. J. Health Behav. 2018, 42, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lidón-Moyano, C.; Fu, M.; Ballbè, M.; Martín-Sánchez, J.C.; Matilla-Santander, N.; Martínez, C.; Fernández, E.; Martínez-Sánchez, J.M. Impact of the Spanish smoking laws on tobacco consumption and secondhand smoke exposure: A longitudinal population study. Addict. Behav. 2017, 75, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lidón-Moyano, C.; Fu, M.; Perez-Ortuño, R.; Ballbè, M.; Sampedro-Vida, M.; Martín-Sánchez, J.C.; Pascual, J.A.; Fernández, E.; Martínez-Sánchez, J.M. Assessment of salivary cotinine concentration among general non-smokers population: Before and after Spanish smoking legislations. Cancer Epidemiol. 2017, 51, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matilla-Santander, N.; Fu, M.; Ballbè, M.; Lidón-Moyano, C.; Martín-Sánchez, J.C.; Fernández, E.; Martínez-Sánchez, J.M. Uso de paneles de consumidores en estudios observacionales de salud pública. Gac. Sanit. 2017, 31, 436–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Sánchez, J.M.; Fu, M.; Ariza, C.; López, M.J.; Saltó, E.; Pascual, J.A.; Schiaffino, A.; Borràs, J.M.; Peris, M.; Agudo, A.; et al. Punto de corte óptimo de la concentración de cotinina en saliva para discriminar entre fumadores y no fumadores en la población adulta de Barcelona. Gac. Sanit. 2009, 23, 501–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pérez-Ortuño, R.; Martínez-Sánchez, J.M.; Fu, M.; Ballbè, M.; Quirós, N.; Fernández, E.; Pascual, J.A. Assessment of tobacco specific nitrosamines (TSNAs) in oral fluid as biomarkers of cancer risk: A population-based study. Environ. Res. 2016, 151, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lidón-Moyano, C.; Martínez-Sánchez, J.M.; Fu, M.; Ballbè, M.; Martín-Sánchez, J.C.; Martínez, C.; Saltó, E.; Fernández, E. Impact of the Spanish smoking legislations in the adoption of smoke-free rules at home: A longitudinal study in Barcelona (Spain). Tob. Control 2017, 26, 557–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Obesity: Preventing and Managing the Global Epidemic: Report of a WHO Consultation; WHO technical report series; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Chenoweth, M.J.; Novalen, M.; Hawk, L.W.J.; Schnoll, R.A.; George, T.P.; Cinciripini, P.M.; Lerman, C.; Tyndale, R.F. Known and novel sources of variability in the nicotine metabolite ratio in a large sample of treatment-seeking smokers. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2014, 23, 1773–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, A.; Krebs, N.M.; Zhu, J.; Muscat, J.E. Nicotine metabolite ratio predicts smoking topography: The Pennsylvania Adult Smoking Study. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2018, 190, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, R.B. Nicotine metabolite ratios in serum and urine among US adults: Variations across smoking status, gender and race/ethnicity. Biomarkers 2020, 25, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St Helen, G.; Benowitz, N.L.; Ahluwalia, J.S.; Tyndale, R.F.; Addo, N.; Gregorich, S.E.; Pérez-Stable, E.J.; Cox, L.S. Black Light Smokers: How Nicotine Intake and Carcinogen Exposure Differ Across Various Biobehavioral Factors. J. Natl. Med. Assoc. 2019, 111, 509–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, R.B. Revised and extended serum cotinine cut-offs to classify smokers and non-smokers. Biomarkers 2018, 23, 502–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.O.; Nonnemaker, J.M.; Bradfield, B.; Hensel, E.C.; Robinson, R.J. Examining Daily Electronic Cigarette Puff Topography Among Established and Nonestablished Cigarette Smokers in their Natural Environment. Nicotine Tob. Res. 2018, 20, 1283–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grando, S.A. Connections of nicotine to cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molander, L.; Hansson, A.; Lunell, E. Pharmacokinetics of nicotine in healthy elderly people. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2001, 69, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mooney, M.E.; Li, Z.-Z.; Murphy, S.E.; Pentel, P.R.; Le, C.; Hatsukami, D.K. Stability of the nicotine metabolite ratio in ad libitum and reducing smokers. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2008, 17, 1396–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lea, R.A.; Dickson, S.; Benowitz, N.L. Within-Subject Variation of the Salivary 3HC/COT Ratio in Regular Daily Smokers: Prospects for Estimating CYP2A6 Enzyme Activity in Large-Scale Surveys of Nicotine Metabolic Rate. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2006, 30, 386–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| n (%) | RNM GM (GSD) | NMR GM (GSD) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Overall | 974 | 0.43 (4.27) | 0.22 (2.09) |
| Smoking and e-cigarette status a | |||
| Nonusers of any product a5 | 508 (52.16) | 0.27 (2.30) (a1, a2, a3, a4) *** | 0.23 (1.99) a2 * |
| E-cigarette exclusive users without nicotine a4 | 41 (4.21) | 0.08 (8.12) (a1, a2, a3, a5) *** | 0.23 (1.80) |
| E-cigarette exclusive users with nicotine a3 | 164 (16.84) | 0.49 (3.45) (a2, a4, a5) *** | 0.22 (1.90) |
| Dual users a1 | 95 (9.75) | 0.48 (4.70) (a2, a4, a5) *** | 0.24 (1.80) |
| Cigarette smokers a2 | 166 (17.04) | 2.08 (4.90) (a1, a3, a4, a5) *** | 0.18 (2.61) a5 * |
| Sex b | |||
| Female b1 | 442 (45.38) | 0.43 (3.98) | 0.24 (2.11) b2 *** |
| Male b2 | 532 (54.62) | 0.43 (4.52) | 0.21 (2.06) b1 *** |
| Age (years) c | |||
| 18–44 c1 | 371 (38.09) | 0.53 (4.97) c3 *** | 0.21 (1.96) c3 *** |
| 45–64 c2 | 363 (37.27) | 0.42 (4.17) c3 ** | 0.22 (2.13) |
| 65–89 c3 | 240 (24.64) | 0.31 (3.18) c1 ***, c2 ** | 0.25 (2.20) c1 *** |
| BMI (kg/m2) d | |||
| 10–20 d1 | 64 (6.57) | 0.54 (4.93) | 0.26 (2.07) |
| 21–25 d2 | 378 (38.81) | 0.52 (4.56) d3 ***, d4 ** | 0.22 (2.12) |
| 26–30 d3 | 336 (34.50) | 0.35 (3.93) d2 *** | 0.22 (2.09) |
| 31–60 d4 | 186 (49.21) | 0.36 (3.86) d2 ** | 0.23 (2.01) |
| Title 1 | RNM | NMR | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Log-linear Models | exp(Estimate) c | CI d | p-Value | exp(Estimate) c | CI d | p-Value |
| Unadjusted model a | ||||||
| Intercept | 0.27 | 0.24; 0.30 | <0.001 | 0.23 | 0.22; 0.25 | <0.001 |
| E-cigarette exclusive users without nicotine | 0.08 | 0.05; 0.14 | <0.001 | 0.23 | 0.17; 0.32 | 0.96 |
| E-cigarette exclusive users with nicotine | 0.49 | 0.36; 0.68 | <0.001 | 0.22 | 0.18; 0.27 | 0.37 |
| Dual users | 0.48 | 0.33; 0.70 | <0.001 | 0.24 | 0.19; 0.30 | 0.71 |
| Cigarette smokers only | 2.08 | 1.51; 2.85 | <0.001 | 0.18 | 0.15; 0.22 | <0.001 |
| Adjusted model b | 0.27 | 0.24; 0.30 | <0.001 | 0.23 | 0.22; 0.25 | <0.001 |
| Users of e-cigarettes without nicotine | 0.09 | 0.05; 0.14 | <0.001 | 0.23 | 0.17; 0.32 | 0.97 |
| Users of e-cigarettes with nicotine | 0.65 | 0.45; 0.95 | <0.001 | 0.21 | 0.16; 0.26 | 0.18 |
| Dual | 0.60 | 0.4; 0.89 | <0.001 | 0.23 | 0.18; 0.29 | 0.91 |
| Cigarette smokers | 2.43 | 1.74; 3.39 | <0.001 | 0.18 | 0.14; 0.22 | <0.001 |
| Daily number of cigarettes smoked | 0.26 | 0.23; 0.29 | <0.001 | 0.23 | 0.22; 0.25 | 0.29 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pérez-Martín, H.; Lidón-Moyano, C.; González-Marrón, A.; Fu, M.; Pérez-Ortuño, R.; Ballbè, M.; Martín-Sánchez, J.C.; Pascual, J.A.; Fernández, E.; Martínez-Sánchez, J.M. Variation in Nicotine Metabolization According to Biological Factors and Type of Nicotine Consumer. Healthcare 2023, 11, 179. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11020179
Pérez-Martín H, Lidón-Moyano C, González-Marrón A, Fu M, Pérez-Ortuño R, Ballbè M, Martín-Sánchez JC, Pascual JA, Fernández E, Martínez-Sánchez JM. Variation in Nicotine Metabolization According to Biological Factors and Type of Nicotine Consumer. Healthcare. 2023; 11(2):179. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11020179
Chicago/Turabian StylePérez-Martín, Hipólito, Cristina Lidón-Moyano, Adrián González-Marrón, Marcela Fu, Raúl Pérez-Ortuño, Montse Ballbè, Juan Carlos Martín-Sánchez, José A. Pascual, Esteve Fernández, and Jose M. Martínez-Sánchez. 2023. "Variation in Nicotine Metabolization According to Biological Factors and Type of Nicotine Consumer" Healthcare 11, no. 2: 179. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11020179
APA StylePérez-Martín, H., Lidón-Moyano, C., González-Marrón, A., Fu, M., Pérez-Ortuño, R., Ballbè, M., Martín-Sánchez, J. C., Pascual, J. A., Fernández, E., & Martínez-Sánchez, J. M. (2023). Variation in Nicotine Metabolization According to Biological Factors and Type of Nicotine Consumer. Healthcare, 11(2), 179. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11020179








