Effectiveness of Non-Contact Dietary Coaching in Adults with Diabetes or Prediabetes Using a Continuous Glucose Monitoring Device: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
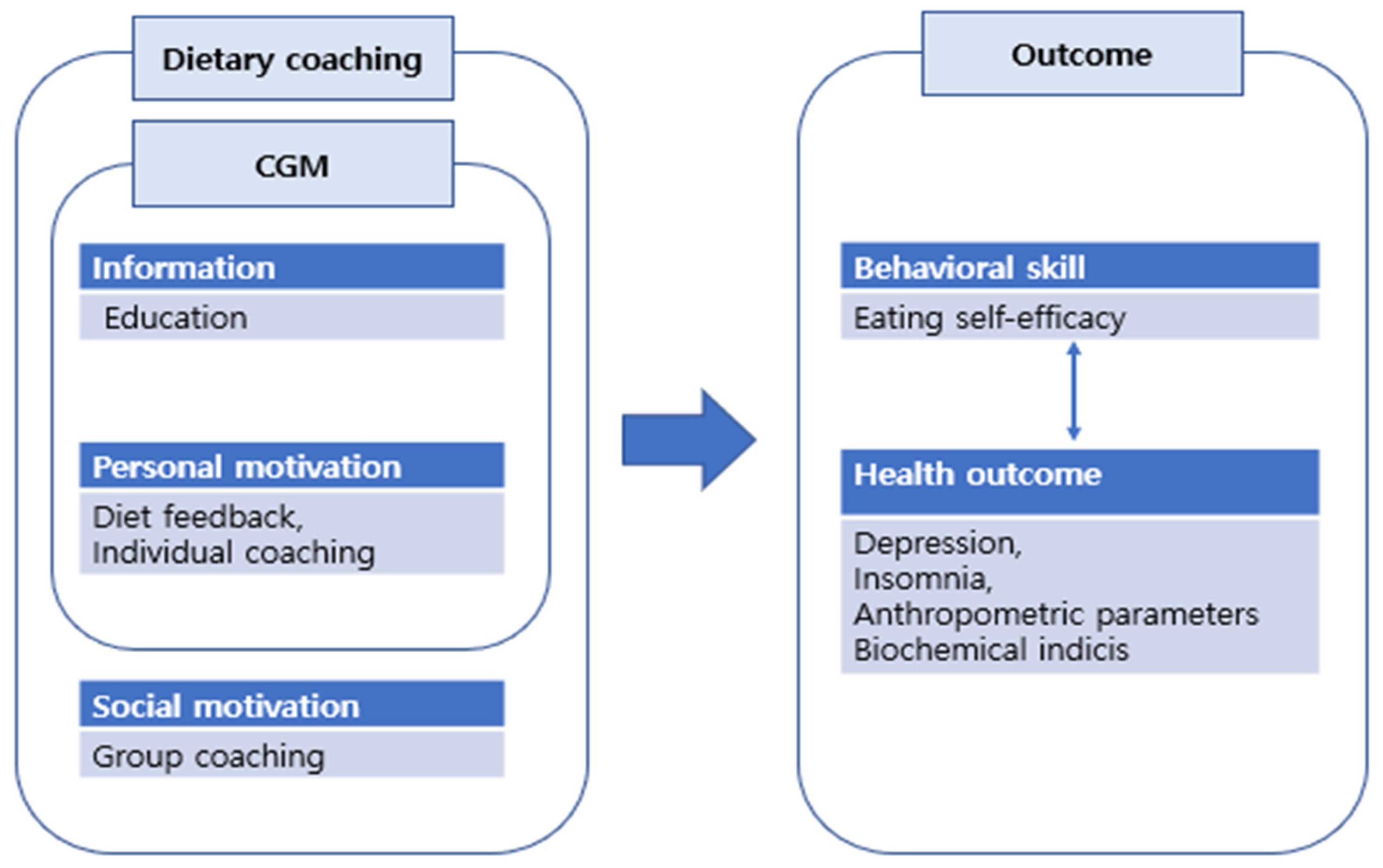
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Participants and Recruitment
2.3. Intervention
2.4. Outcome Measures
2.4.1. Behavioral Skills
2.4.2. Health Outcomes
2.5. Ethical Considerations
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jung, C.H.; Son, J.W.; Kang, S.; Kim, W.J.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, H.S.; Seo, M.; Shin, H.J.; Lee, S.S.; Jeong, S.J.; et al. Diabetes Fact Sheets in Korea, 2020: An Appraisal of Current Status. Diabetes Metab. J. 2021, 45, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeedi, P.; Petersohn, I.; Salpea, P.; Malanda, B.; Karuranga, S.; Unwin, N.; Colagiuri, S.; Guariguata, L.; Motala, A.A.; Ogurtsova, K.; et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9(th) edition. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2019, 157, 107843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yudkin, J.S.; Montori, V.M. The epidemic of pre-diabetes: The medicine and the politics. BMJ 2014, 349, g4485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Uusitupa, M.; Khan, T.A.; Viguiliouk, E.; Kahleova, H.; Rivellese, A.A.; Hermansen, K.; Pfeiffer, A.; Thanopoulou, A.; Salas-Salvado, J.; Schwab, U.; et al. Prevention of type 2 diabetes by lifestyle changes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garcia-Molina, L.; Lewis-Mikhael, A.-M.; Riquelme-Gallego, B.; Cano-Ibanez, N.; Oliveras-Lopez, M.-J.; Bueno-Cavanillas, A. Improving type 2 diabetes mellitus glycaemic control through lifestyle modification implementing diet intervention: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Nutr. 2020, 59, 1313–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenum, A.K.; Brekke, I.; Mdala, I.; Muilwijk, M.; Ramachandran, A.; Kjøllesdal, M.; Andersen, E.; Richardsen, K.R.; Douglas, A.; Cezard, G.; et al. Effects of dietary and physical activity interventions on the risk of type 2 diabetes in South Asians: Meta-analysis of individual participant data from randomised controlled trials. Diabetologia 2019, 62, 1337–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saslow, L.R.; Mason, A.E.; Kim, S.; Goldman, V.; Ploutz-Snyder, R.; Bayandorian, H.; Daubenmier, J.; Hecht, F.M.; Moskowitz, J.T. An Online Intervention Comparing a Very Low-Carbohydrate Ketogenic Diet and Lifestyle Recommendations Versus a Plate Method Diet in Overweight Individuals With Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Med. Internet Res. 2017, 19, e36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rhoon, L.V.; Byrne, M.; Morrissey, E.; Murphy, J.; McSharry, J. A systematic review of the behaviour change techniques and digital features in technology-driven type 2 diabetes prevention interventions. Digit. Health 2020, 6, 2055207620914427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmingsen, B.; Gimenez-Perez, G.; Mauricio, D.; Roqué, I.F.M.; Metzendorf, M.I.; Richter, B. Diet, physical activity or both for prevention or delay of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its associated complications in people at increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes mellitus. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 12, Cd003054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.; Hur, M.H. The Effects of Dietary Education Interventions on Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toi, P.L.; Anothaisintawee, T.; Chaikledkaew, U.; Briones, J.R.; Reutrakul, S.; Thakkinstian, A. Preventive Role of Diet Interventions and Dietary Factors in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: An Umbrella Review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrhardt, N.; Al Zaghal, E. Behavior Modification in Prediabetes and Diabetes: Potential Use of Real-Time Continuous Glucose Monitoring. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2019, 13, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yost, O.; DeJonckheere, M.; Stonebraker, S.; Ling, G.; Buis, L.; Pop-Busui, R.; Kim, N.; Mizokami-Stout, K.; Richardson, C. Continuous glucose monitoring with low-carbohydrate diet coaching in adults with prediabetes: Mixed methods pilot study. JMIR Diabetes 2020, 5, e21551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mian, Z.; Hermayer, K.L.; Jenkins, A. Continuous Glucose Monitoring: Review of an Innovation in Diabetes Management. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 358, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blum, A. Freestyle Libre glucose monitoring system. Clin Diabetes. 2018, 36, 203–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- FreeStyle Libre Flash glucose monitoring system. User Manual. May 2022. Available online: https://www.diabetescare.abbott/support/manuals/uk.html (accessed on 20 November 2020).
- Benkhadra, K.; Alahdab, F.; Tamhane, S.; Wang, Z.; Prokop, L.J.; Hirsch, I.B.; Raccah, D.; Riveline, J.P.; Kordonouri, O.; Murad, M.H. Real-time continuous glucose monitoring in type 1 diabetes: A systematic review and individual patient data meta-analysis. Clin. Endocrinol. 2017, 86, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokutsu, A.; Okada, Y.; Torimoto, K.; Tanaka, Y. Relationship between glycemic intraday variations evaluated in continuous glucose monitoring and HbA1c variability in type 2 diabetes: Pilot study. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2021, 13, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiorne, M.I.; Signoriello, S.; Maio, A.; Chiodini, P.; Bellastella, G.; Scappaticcio, L.; Longo, M.; Giugliano, D.; Esposito, K. Effects of continuous glucose monitoring on metrics of glycemic control in diabetes: A systematic review with meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, 1146–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Rocha, R.B.; Silva, C.S.; Cardoso, V.S. Self-care in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2020, 16, 598–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, M.A.; Ahmann, A.; Shah, V.N. Type 2 diabetes and the use of real-time continuous glucose monitoring. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2021, 23, S27–S34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oser, T.K.; Litchman, M.L.; Allen, N.A.; Kwan, B.M.; Fisher, L.; Jortberg, B.T.; Polonsky, W.H.; Oser, S.M. Personal continuous glucose monitoring use among adults with type 2 diabetes: Linical efficacy and economic impacts. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2021, 21, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayin Kasar, K.; Duru Asiret, G.; Kutmec Yilmaz, C.; Canlar, Ş. The effect of model-based telephone counseling on HbA1c and self-management for individuals with type 2 diabetes: A randomized controlled trial. Prim. Care Diabetes 2022, 16, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, E.; Park, H.A. Experiences of Patients With a Diabetes Self-Care App Developed Based on the Information-Motivation-Behavioral Skills Model: Before-and-After Study. JMIR Diabetes 2019, 4, e11590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, J.D.; Fisher, W.A.; Amico, K.R.; Harman, J.J. An information-motivation-behavioral skills model of adherence to antiretroviral therapy. Health Psychol. Off. J. Div. Health Psychol. Am. Psychol. Assoc. 2006, 25, 462–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodbard, D. Continuous glucose monitoring: A review of successes, chanllenges, and opportunities. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2016, 18 (Suppl. S2), S3–S13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lawton, J.; Blackburn, M.; Allen, J.; Campbell, F.; Elleri, D.; Leelarathna, L.; Rankin, D.; Tauschmann, M.; Thabit, H.; Hovorka, R. Patients’ and caregivers’ experiences of using continuous glucose monitoring to support diabetes self-management: Qualitative study. BMC Endocrinol. Disord. 2018, 18, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bakır, E.; Çavuşoğlu, H.; Mengen, E. Effects of the Information-Motivation-Behavioral Skills Model on Metabolic Control of Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes in Turkey: Randomized Controlled Study. J. Pediatr. Nurs. 2021, 58, e19–e27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morowatisharifabad, M.A.; Movahed, E.; Farokhzadian, J.; Nikooie, R.; Hosseinzadeh, M.; Askarishahi, M.; Bidaki, R. Antiretroviral therapy adherence and its determinant factors among people living with HIV/AIDS: A case study in Iran. BMC Res. Notes 2019, 12, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Wang, J.; Yang, S.; Gao, M.; Cao, L.; Li, X.; Hong, D.; Tian, S.; Sun, C. Effect of the ketogenic diet on glycemic control, insulin resistance, and lipid metabolism in patients with T2DM: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutr. Diabetes 2020, 10, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldenberg, J.Z.; Day, A.; Brinkworth, G.D.; Sato, J.; Yamada, S.; Jönsson, T.; Beardsley, J.; Johnson, J.A.; Thabane, L.; Johnston, B.C. Efficacy and safety of low and very low carbohydrate diets for type 2 diabetes remission: Systematic review and meta-analysis of published and unpublished randomized trial data. BMJ 2021, 372, m4743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Nan, F.; Wang, L.Y.; Jiang, H.; Chen, W.; Jiang, Y. Effects of high-protein diet on glycemic control, insulin resistance and blood pressure in type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 39, 1724–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janapala, R.N.; Jayaraj, J.S.; Fathima, N.; Kashif, T.; Usman, N.; Dasari, A.; Jahan, N.; Sachmechi, I. Continuous glucose monitoring versus self-monitoring of blood glucose in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Cureus 2019, 11, e5634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Whitmore, J. Business Coaching International: Unlocking the Secrets and the Power; Taylor & Francis: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ames, G.E.; Heckman, M.G.; Grothe, K.B.; Clark, M.M. Eating self-efficacy: Development of a short-form WEL. Eat. Behav. 2012, 13, 375–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.-H.; Kim, H.-C.; Jung, C.-H.; Kim, J.-B.; Jung, S.-W.; Cho, H.-J.; Jung, S.-h. The standardization of the Korean version of the Patient Health Questionnaire-2. J. Korean Neuropsychiatr. Assoc. 2013, 52, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.J. Validation of the Korean Version of the Mini-Sleep Questionnaire-Insomnia in Korean College Students. Asian Nurs. Res. (Korean Soc. Nurs. Sci.) 2017, 11, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yen, T.S.; Htet, M.K.; Lukito, W.; Bardosono, S.; Setiabudy, R.; Basuki, E.S.; Wibudi, A.; Martianto, D.; Subekti, I.; Fahmida, U. Increased vegetable intake improves glycaemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A clustered randomised clinical trial among Indonesian white-collar workers. J. Nutr. Sci. 2022, 11, e49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansel, B.; Giral, P.; Gambotti, L.; Lafourcade, A.; Peres, G.; Filipecki, C.; Kadouch, D.; Hartemann, A.; Oppert, J.-M.; Bruckert, E.; et al. A fully automated web-based program improves lifestyle habits and HbA1c in patients with type 2 diabetes and abdominal obesity: Randomized trial patient e-coaching nutritional support (The ANODE Study). J. Med. Internet Res. 2017, 19, e360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Strombotne, K.L.; Lum, J.; Ndugga, N.J.; Utech, A.E.; Pizer, S.D.; Frakt, A.B.; Conlin, P.R. Effectiveness of a ketogenic diet and virtual coaching intervention for patients with diabetes: A difference- in-differences analysis. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2021, 23, 2643–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Khawaldeh, O.A.; Al-Hassan, M.A.; Froelicher, E.S. Self-efficacy, self-management, and glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2012, 26, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilcharan Singh, H.K.; Chee, W.S.S.; Hamdy, O.; Mechanick, J.I.; Lee, V.K.M.; Barua, A.; Mohd Ali, S.Z.; Hussein, Z.J.P.O. Eating self-efficacy changes in individuals with type 2 diabetes following a structured lifestyle intervention based on the transcultural Diabetes Nutrition Algorithm (tDNA): A secondary analysis of a randomized controlled trial. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0242487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rollo, M.E.; Baldwin, J.N.; Hutchesson, M.; Aguiar, E.J.; Wynne, K.; Young, A.; Callister, R.; Haslam, R.; Collins, C.E. The Feasibility and Preliminary Efficacy of an eHealth Lifestyle Program in Women with Recent Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: A Pilot Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandura, A. Self-efficacy: Toward a unifying theory of behavioral change. Psychol. Rev. 1977, 84, 191–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, M.; Patel, A.; Khoja, A.; Luo, Y.; Lin, W.; He, Q.; Zhao, X.; Wang, J.; Yang, S.; Hu, P. Barriers and facilitators of diabetes management by continuous glucose monitoring systems among adults with type 2 diabetes: A protocol of qualitative systematic review. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e046050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azhar, A.; Gillani, S.W.; Mohiuddin, G.; Majeed, R.A. A systematic review on clinical implication of continuous glucose monitoring in diabetes management. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2020, 12, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cowart, K.; Updike, W.; Bullers, K. Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials Evaluating Glycemic Efficacy and Patient Satisfaction of Intermittent-Scanned Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Patients with Diabetes. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2020, 22, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumlin, L.L.; Garcia, T.J.; Brown, S.A.; Winter, M.A.; García, A.A.; Brown, A.; Cuevas, H.E. Depression and adherence to lifestyle changes in type 2 diabetes: A systematic review. Diabetes Educ. 2014, 40, 731–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naguib, M.N.; Hegedus, E.; Raymond, J.K.; Goran, M.I.; Salvy, S.J.; Wee, C.P.; Durazo-Arvizu, R.; Moss, L.; Vidmar, A.P. Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Adolescents With Obesity: Monitoring of Glucose Profiles, Glycemic Excursions, and Adherence to Time Restricted Eating Programs. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 841838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Q.; Aris, I.M.; Tan, K.H.; Li, L.J. Application and Utility of Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Pregnancy: A Systematic Review. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallieni, M.; De Salvo, C.; Lunati, M.E.; Rossi, A.; D’Addio, F.; Pastore, I.; Sabiu, G.; Miglio, R.; Zuccotti, G.V.; Fiorina, P. Continuous glucose monitoring in patients with type 2 diabetes on hemodialysis. Acta Diabetol. 2021, 58, 975–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franceschi, R.; Micheli, F.; Mozzillo, E.; Cauvin, V.; Liguori, A.; Soffiati, M.; Giani, E. Intermittently Scanned and Continuous Glucose Monitor Systems: A Systematic Review on Psychological Outcomes in Pediatric Patients. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 660173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilliard, M.E.; Levy, W.; Anderson, B.J.; Whitehouse, A.L.; Commissariat, P.V.; Harrington, K.R.; Laffel, L.M.; Miller, K.M.; Van Name, M.; Tamborlane, W.V.; et al. Benefits and Barriers of Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Young Children with Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2019, 21, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kline, C.E.; Chasens, E.R.; Bizhanova, Z.; Sereika, S.M.; Buysse, D.J.; Imes, C.C.; Kariuki, J.K.; Mendez, D.D.; Cajita, M.I.; Rathbun, S.L.; et al. The association between sleep health and weight change during a 12-month behavioral weight loss intervention. Int. J. Obes. 2021, 45, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Q.R.; Wu, M.; Pan, L.; Lyu, J.; Guo, Y.; Pei, P.; Du, H.D.; Chen, J.S.; Yu, C.Q.; Chen, L.M.; et al. The correlation of sleep duration and insomnia with low muscle mass, strength and quality in Chinese adults. Zhonhua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi 2022, 43, 175–182. [Google Scholar]
- Auyeung, T.W.; Kwok, T.; Leung, J.; Lee, J.S.W.; Ohlsson, C.; Vandenput, L.; Wing, Y.K.; Woo, J. Sleep duration and disturbances were associated with testosterone level, muscle mass, and muscle strength: A cross sectional study in 1274 older men. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2015, 16, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, F.; Al-Habori, M.; Al-Zabedi, E.; Saif-Ali, R. Impact of triglycerides and waist circumference on insulin resistance and β-cell function in non-diabetic first-degree relatives of type 2 diabetes. BMC Endocrinol. Disord. 2021, 21, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jun, J.E.; Choi, Y.J.; Lee, Y.H.; Kim, D.J.; Park, S.W.; Huh, B.W.; Lee, E.J.; Jee, S.H.; Hur, K.Y.; Choi, S.H.; et al. ApoB/ApoA-I ratio is independently associated with carotid atherosclerosis in type 2 diabetes mellitus with well-controlled LDL cholesterol levels. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2018, 33, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, T.; Zhao, B.; Pei, D. Relationship between the ApoB/ApoA-I ratio trajectory and risk of type 2 diabetes in China: A retrospective cohort study. Endocrine 2022, 76, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Han, T.; Xu, H.; Zhou, H.; Ren, X.; Wu, P.; Zheng, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, M.; Jiang, Y.; et al. Associations of apolipoprotein B/apolipoprotein A-I ratio with pre-diabetes and diabetes risks: A cross-sectional study in Chinese adults. BMJ Open 2017, 7, e014038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Munan, M.; Oliveira, C.L.P.; Marcotte-Chénard, A.; Rees, J.L.; Prado, C.M.; Riesco, E.; Boulé, N.G. Acute and Chronic Effects of Exercise on Continuous Glucose Monitoring Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes: A Meta-Analysis. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cranney, L.; O’Hara, B.; Gale, J.; Rissel, C.; Bauman, A.; Phongsavan, P. Telephone based coaching for adults at risk of diabetes: Impact of Australia’s Get Healthy Service. Transl. Behav. Med. 2019, 9, 1178–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratley, R.E.; Kanapka, L.G.; Rickels, M.R.; Ahmann, A.; Aleppo, G.; Beck, R.; Bhargava, A.; Bode, B.W.; Carlson, A.; Chaytor, N.S.; et al. Effect of Continuous Glucose Monitoring on Hypoglycemia in Older Adults With Type 1 Diabetes: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2020, 323, 2397–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, G.; Bolter, L.-M.; Sluka, R.; Holler, Y.; Bathke, A.C.; Thomschewski, A.; Leis, S.; Lattanzi, S.; Brigo, F.; Trinka, E. Sample sizes and statistical methods in interventional studies on individuals with spinal cord injury: A systematic review. J. Evid. -Based Med. 2019, 12, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nanayakkara, N.; Curtis, A.J.; Heritier, S.; Gadowski, A.M.; Pavkov, M.E.; Kenealy, T.; Owens, D.R.; Thomas, R.L.; Song, S.; Wong, J.; et al. Impact of age at type 2 diabetes mellitus diagnosis on mortality and vascular complications: Systematic review and meta-analyses. Diabetologia 2021, 64, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Characteristic | Categories | Con. (n = 22) | Exp. (n = 23) | t (p) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M ± SD or n (%) | ||||
| Age (Year) | 49.80 ± 10.42 | 47.16 ± 10.60 | 0.89 (0.379) | |
| Sex | Male | 11 (50.0) | 6 (26.1) | 4.16 (0.79) |
| Female | 11 (50.0) | 17 (73.9) | ||
| Height (cm) | 167.52 ± 8.36 | 164.90 ± 8.43 | 1.10 (0.275) | |
| Weight (Kg) | 77.07 ± 14.96 | 78.09 ± 15.47 | 0.24 (0.407) | |
| Behavioral skills | Eating self-efficacy | 6.88 ± 1.76 | 6.17 ± 2.18 | 0.11 (0.240) |
| Health outcome | Depression | 0.66 ± 0.71 | 0.43 ± 0.55 | 1.18 (0.243) |
| Insomnia | 2.07 ± 1.06 | 1.95 ± 0.75 | 0.45 (0.657) | |
| BMI | 26.82 ± 3.47 | 29.01 ± 5.09 | −1.68 (0.100) | |
| Waist circumference | 95.80 ± 9.80 | 96.20 ± 9.26 | −0.14 (0.886) | |
| Thigh circumference | 50.52 ± 6.22 | 51.87 ± 6.00 | −0.74 (0.464) | |
| HbA1c | 6.97 ± 1.04 | 6.78 ± 1.09 | 0.58 (0.562) | |
| ApoB/ApoA | 2.44 ± 8.39 | 0.56 ± 0.21 | 0.41 (0.687) | |
| HOMAIR | 6.68 ± 8.04 | 4.65 ± 4.73 | 1.07 (0.289) | |
| Characteristics | Categories | Con. (n = 11) | Exp. (n = 6) | Z (p) | Effect Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Differences between Pre-Post Test | |||||
| M ± SD | |||||
| Behavioral skills | Eating self-efficacy | 0.20 ± 1.29 | 0.29 ± 1.01 | −0.30 (0.763) | 0.006 |
| Health outcome | Depression | −0.14 ± 0.50 | −0.08 ± 0.20 | −0.20 (0.839) | 0.003 |
| Insomnia | 0.41 ± 0.62 | −0.04 ± 0.37 | −1.34 (0.180) | 0.112 | |
| BMI | −0.60 ± 0.76 | −1.72 ± 1.46 | −1.56 (0.118) | 0.152 | |
| Waist circumference | −2.09 ± 5.52 | −4.50 ± 4.68 | −1.01 (0.314) | 0.064 | |
| Thigh circumference | −1.37 ± 3.73 | 2.37 ± 2.68 | −2.02 (0.044) | 0.255 | |
| HbA1c | −0.13 ± 0.31 | −0.07 ± 0.29 | −0.31 (0.754) | 0.006 | |
| ApoB/ApoA | −0.06 ± 0.18 | 0.00 ± 0.10 | −0.30 (0.763) | 0.006 | |
| HOMAIR | 11.08 ± 108.05 | 8.66 ± 13.45 | −0.10 (0.920) | 0.001 | |
| Characteristics | Categories | Con. (n = 11) | Exp. (n = 17) | Z (p) | Effect Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Differences between Pre-Post Test | |||||
| M ± SD or n (%) | |||||
| Behavioral skills | Eating self-efficacy | −0.75 ± 1.46 | 0.79 ± 1.29 | −2.66 (0.008) | 0.262 |
| Health outcome | Depression | 0.05 ± 0.47 | 0.09 ± 0.44 | −0.44 (0.660) | 0.007 |
| Insomnia | 0.20 ± 0.66 | 0.07 ± 0.53 | −0.41 (0.685) | 0.006 | |
| BMI | −0.22 ± 0.68 | −0.30 ± 1.10 | −0.14 (0.887) | 0.001 | |
| Waist circumference | −0.06 ± 4.45 | −3.08 ± 5.12 | −1.28 (0.200) | 0.013 | |
| Thigh circumference | 0.45 ± 1.27 | −0.05 ± 2.41 | −1.63 (0.104) | 0.098 | |
| HbA1c | −0.18 ± 0.25 | −0.09 ± 0.43 | −1.02 (0.308) | 0.039 | |
| ApoB/ApoA | −3.64 ± 11.87 | 0.03 ± 0.17 | −1.53 (0.126) | 0.087 | |
| HOMAIR | −5.41 ± 37.90 | 8.18 ± 49.41 | −0.23 (0.815) | 0.002 | |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r (p) | ||||||||||
| 1. Group | 1.00 | |||||||||
| 2. Sex | 0.25 (0.103) | 1.00 | ||||||||
| 3. Change of eating self-efficacy | 0.34 (0.023) | −0.02 (0.913) | 1.00 | |||||||
| 4. Change of depression | 0.10 (0.504 | 0.21 (0.164) | −0.25 (0.098) | 1.00 | ||||||
| 5. Change of insomnia | −0.23 (0.123) | −0.11 (0.483) | −0.35 (0.018) | 0.23 (0.135) | 1.00 | |||||
| 6. Change of BMI | −0.12 (0.423) | 0.33 (0.026) | −0.04 (0.801) | −0.18 (0.249) | 0.02 (0.908) | 1.00 | ||||
| 7. Change of waist circumference | −0.24 (0.117) | 0.10 (0.508) | −0.26 (0.086) | 0.05 (0.764) | 0.14 (0.361) | 0.25 (0.092) | 1.00 | |||
| 8. Change of thigh circumference | 0.05 (0.750) | 0.17 (0.267) | 0.09 (0.539) | −0.10 (0.509) | −0.35 (0.017) | 0.10 (0.514) | 0.30 (0.048) | 1.00 | ||
| 9. Change of HbA1c | 0.11 (0.483) | −0.03 (0.857) | 0.11 (0.492) | −0.28 (0.068) | 0.15 (0.312) | 0.12 (0.436) | 0.27 (0.077) | 0.22 (0.147) | 1.00 | |
| 10. Change of ApoB/ApoA | 0.16 (0.290) | −0.12 (0.453) | 0.06 (0.686) | −0.00 (0.996) | 0.11 (0.472) | −0.21 (0.160) | −10 (0.527) | −0.06 (0.720) | 0.22 (0.148) | 1.00 |
| 11. Change of HOMAIR | 0.04 (0.774) | −0.06 (0.706) | 0.02 (0.896) | −0.16 (0.297) | −0.12 (0.440) | 0.19 (0.203) | 0.35 (0.020) | 0.12 (0.440) | 0.17 (0.255) | 0.05 (0.760) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahn, Y.-C.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, B.; Ryu, J.M.; Kim, M.S.; Kang, M.; Park, J. Effectiveness of Non-Contact Dietary Coaching in Adults with Diabetes or Prediabetes Using a Continuous Glucose Monitoring Device: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Healthcare 2023, 11, 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11020252
Ahn Y-C, Kim YS, Kim B, Ryu JM, Kim MS, Kang M, Park J. Effectiveness of Non-Contact Dietary Coaching in Adults with Diabetes or Prediabetes Using a Continuous Glucose Monitoring Device: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Healthcare. 2023; 11(2):252. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11020252
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhn, Yeh-Chan, Yang Seok Kim, Bukyung Kim, Jung Mi Ryu, Myoung Soo Kim, Minkyeong Kang, and Jiwon Park. 2023. "Effectiveness of Non-Contact Dietary Coaching in Adults with Diabetes or Prediabetes Using a Continuous Glucose Monitoring Device: A Randomized Controlled Trial" Healthcare 11, no. 2: 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11020252
APA StyleAhn, Y.-C., Kim, Y. S., Kim, B., Ryu, J. M., Kim, M. S., Kang, M., & Park, J. (2023). Effectiveness of Non-Contact Dietary Coaching in Adults with Diabetes or Prediabetes Using a Continuous Glucose Monitoring Device: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Healthcare, 11(2), 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11020252






