Economic Burdens of Type 2 Diabetes Hospital Visits with Hypoglycemic Episodes in the Tertiary Care Setting in Thailand
Abstract
1. Introduction
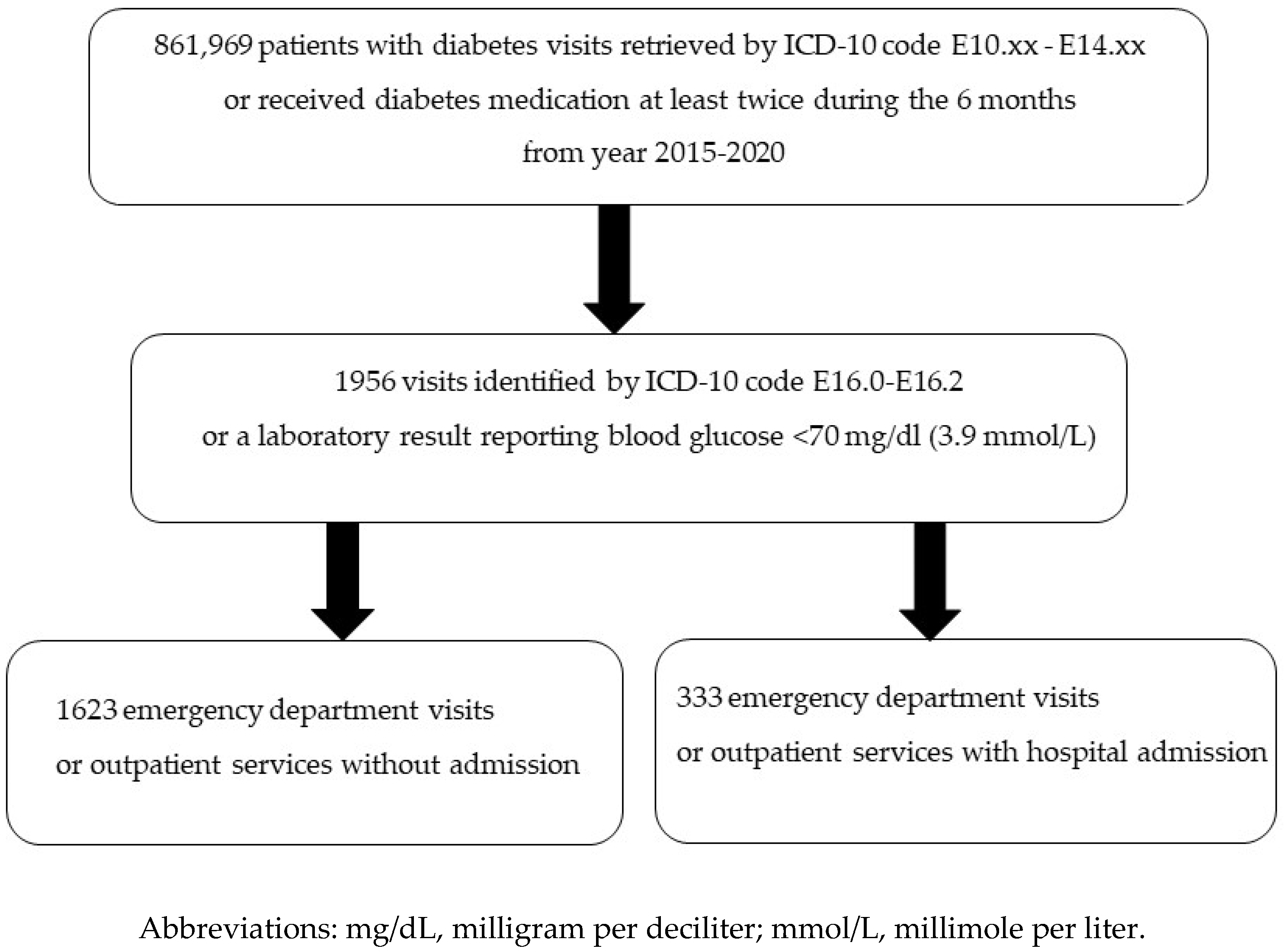
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. Data Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas; International Diabetes Federation: Brussels, Belgium, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Yotsapon, T.; Sirinate, K.; Ekgaluck, W.; Somboon, V.; Tawee, A.; Worawit, K.; Soontaree, N.; Thep, H. Clinical characteristics and outcomes of the oldest old people with type 2 diabetes—Perspective from a tertiary diabetes center in Thailand. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2016, 16, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hypoglycemia in diabetes: An update on pathophysiology, treatment, and prevention. World J. Diabetes 2021, 12, 2036–2049. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aekplakorn, W.; Chariyalertsak, S.; Kessomboon, P.; Assanangkornchai, S.; Taneepanichskul, S.; Putwatana, P. Prevalence of Diabetes and Relationship with Socioeconomic Status in the Thai Population: National Health Examination Survey, 2004–2014. J. Diabetes Res. 2018, 2018, 1654530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okemah, J.; Peng, J.; Quiñones, M. Addressing Clinical Inertia in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Review. Adv. Ther. 2018, 35, 1735–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, S.; Mamdani, M.; Galbo-Jørgensen, C.B.; Bøgelund, M.; Gundgaard, J.; Groleau, D. The Effect of Hypoglycemia on Health-Related Quality of Life: Canadian Results from a Multinational Time Trade-off Survey. Can. J. Diabetes 2014, 38, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, S.A.; Shi, L.; Brenneman, S.K.; Johnson, J.C.; Wegner, J.C.; Fonseca, V. The burden of hypoglycemia on healthcare utilization, costs, and quality of life among type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2012, 26, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Shi, Q.; Wang, Y.; Fonseca, V.; Shi, L. Economic burden of hypoglycemia: Utilization of emergency department and outpatient services in the United States (2005–2009). J. Med. Econ. 2016, 19, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moisan, J.; Breton, M.-C.; Villeneuve, J.; Grégoire, J.-P. Hypoglycemia-Related Emergency Department Visits and Hypoglycemia-Related Hospitalizations among New Users of Antidiabetes Treatments. Can. J. Diabetes 2013, 37, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amiel, S.A.; Dixon, T.; Mann, R.; Jameson, K. Hypoglycaemia in Type 2 diabetes. Diabet. Med. 2008, 25, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, G.; Lee, Y.-H.; Han, M.H.; Lee, E.-K.; Kim, C.H.; Kwon, H.S.; Jeong, I.K.; Kang, E.S.; Kim, D.J. Economic Burden of Hypoglycemia in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus from Korea. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aljunid, S.M.; Aung, Y.N.; Ismail, A.; Rashid, S.A.Z.A.; Nur, A.M.; Cheah, J.; Matzen, P. Economic burden of hypoglycemia for type II diabetes mellitus patients in Malaysia. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0211248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strizek, A.; Chang, C.-J.; Furnback, W.; Wang, B.; Lebrec, J.; Lew, T. The Cost of Hypoglycemia Associated With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Taiwan. Value Health Reg. Issues 2019, 18, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riewpaiboon, A.; Pornlertwadee, P.; Pongsawat, K. Diabetes Cost Model of a Hospital in Thailand. Value Health 2007, 10, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riewpaiboon, A.; Chatterjee, S.; Piyauthakit, P. Cost analysis for efficient management: Diabetes treatment at a public district hospital in Thailand. Int. J. Pharm. Pr. 2011, 19, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Permsuwan, U.; Chaiyakunapruk, N.; Dilokthornsakul, P.; Thavorn, K.; Saokaew, S. Long-Term Cost-Effectiveness of Insulin Glargine Versus Neutral Protamine Hagedorn Insulin for Type 2 Diabetes in Thailand. Appl. Health Econ. Health Policy 2016, 14, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bank of Thailand. Foreign Exchange Rates. Available online: https://www.bot.or.th/App/BTWS_STAT/statistics/ReportPage.aspx?reportID=123&language=th (accessed on 14 September 2022).
- Silbert, R.; Salcido-Montenegro, A.; Rodriguez-Gutierrez, R.; Katabi, A.; McCoy, R.G. Hypoglycemia Among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: Epidemiology, Risk Factors, and Prevention Strategies. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2018, 18, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chirakup, S.; Chaiyakunapruk, N.; Chaikledkeaw, U.; Pongcharoensuk, P.; Ongphiphadhanakul, B.; Roze, S.; Valentine, W.J.; Palmer, A.J. Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Thiazolidinediones in Uncontrolled Type 2 Diabetic Patients Receiving Sulfonylureas and Metformin in Thailand. Value Health 2008, 11, S43–S51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldhaber-Fiebert, J.D.; Li, H.; Ratanawijitrasin, S.; Vidyasagar, S.; Wang, X.Y.; Aljunid, S.M.; Shah, N.; Wang, Z.; Hirunrassamee, S.; Bairy, K.L.; et al. Inpatient treatment of diabetic patients in Asia: Evidence from India, China, Thailand and Malaysia. Diabet. Med. 2009, 27, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, S.; Riewpaiboon, A.; Piyauthakit, P.; Riewpaiboon, W.; Boupaijit, K.; Panpuwong, N.; Archavanuntagul, V. Cost of diabetes and its complications in Thailand: A complete picture of economic burden. Health Soc. Care Community 2011, 19, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Diabetes Association. 9. Pharmacologic Approaches to Glycemic Treatment: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2020. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, S98–S110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Year | Total | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | ||
| Total visits with type 2 diabetes | 93,860 | 99,363 | 106,506 | 175,925 | 189,385 | 196,930 | 861,969 |
| Number of visits with blood glucose <70 mg/dL | 259 | 285 | 337 | 363 | 431 | 281 | 1956 |
| Incidence rate of visits with hypoglycemia 1 (per 1000 visits per year) | 2.8 | 2.9 | 3.2 | 2.1 | 2.3 | 1.4 | 2.3 |
| Number of inpatients | 32 | 34 | 35 | 46 | 66 | 72 | 285 2 |
| Number of admissions | 35 | 37 | 40 | 52 | 78 | 91 | 333 |
| Admissions 3 (percent) | 13.5 | 13.0 | 11.9 | 14.3 | 18.1 | 32.4 | 17.0 |
| Admission rate 4 (per 10,000 visits per year) | 3.7 | 3.7 | 3.8 | 3.0 | 4.1 | 4.6 | 3.9 |
| Total of 333 Admissions (%) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Number of antidiabetic drugs patients received | ||
| 5 | 1 | (0.3) |
| 4 | 8 | (2.4) |
| 3 | 69 | (20.7) |
| 2 | 130 | (39.0) |
| 1 | 123 | (36.9) |
| Diet control | 2 | (0.6) |
| Classes of antidiabetic drugs | ||
| Insulin -1 insulin preparation -2 insulin preparations | 204 194 10 | (61.3) (58.3) (3.0) |
| Biguanides | 127 | (38.1) |
| Sulfonylureas | 119 | (35.7) |
| Thiazolidinedione | 81 | (24.3) |
| Dipeptidyl peptidase inhibitors | 60 | (18.0) |
| Sodium glucose cotransporter inhibitors | 4 | (1.2) |
| Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists | 1 | (0.3) |
| Combined drugs | 17 | (5.1) |
| Other classes | 4 | (1.2) |
| Insulin | ||
| First insulin preparation | 204 | (61.3) |
| -Premixed insulin | 174 | (52.3) |
| -Long-acting insulin | 20 | (6.0) |
| -Intermediate-acting insulin | 10 | (3.0) |
| Second insulin preparation | 10 | (3.0) |
| -Rapid-acting insulin | 6 | (1.8) |
| -Intermediate-acting insulin | 3 | (0.9) |
| -Premixed insulin | 1 | (0.3) |
| Cost Item | Year 2015 | Year 2016 | Year 2017 | Year 2018 | Year 2019 | Year 2020 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | % | Value | % | Value | % | Value | % | Value | % | Value | % | |
| Cost of outpatient visit THB (USD) | ||||||||||||
| Drugs | 711,019 | 53 | 798,829 | 59 | 1,820,045 | 72 | 2,213,188 | 81 | 2,558,889 | 84 | 1,714,570 | 84 |
| (19,426.7) | (21,825.9) | (49,728.0) | (60,469.6) | (69,915.0) | (46,846.2) | |||||||
| Laboratory work | 518,897 | 39 | 414,204 | 31 | 579,777 | 23 | 423,183 | 15 | 371,504 | 12 | 254,837 | 12 |
| (14,177.5) | (11,317.0) | (15,840.9) | (11,562.4) | (10,150.4) | (6962.8) | |||||||
| Chest X-ray | 33,457 | 3 | 40,424 | 3 | 42,020 | 2 | 15,51 | 1 | 15,996 | 1 | 16,059 | 1 |
| (914.1) | (1104.5) | (1148.1) | (427.6) | (437.0) | (438.8) | |||||||
| Others | 67,942 | 5 | 97,357 | 7 | 100,166 | 4 | 93,131 | 3 | 89,856 | 3 | 54,345 | 3 |
| (1856.3) | (2660.0) | (2736.8) | (2544.6) | (2455.1) | (1484.8) | |||||||
| Total cost | 1,331,314 | 100 | 1,350,813 | 100 | 2,542,008 | 100 | 2,745,153 | 100 | 3,036,245 | 100 | 2,039,811 | 100 |
| (36,374.7) | (36,907.5) | (69,453.8) | (75,004.2) | (82,957.5) | (55,732.5) | |||||||
| Average | 2,174,224 (59,405.03) | |||||||||||
| Cost of inpatient visit THB (USD) | ||||||||||||
| Drugs | 122,709 | 19 | 335,696 | 23 | 357,327 | 19 | 209,412 | 25 | 381,314 | 19 | 689,552 | 21 |
| (3352.7) | (9172.0) | (9763.0) | (5721.6) | (10,418.4) | (18,840.2) | |||||||
| Laboratory work | 161,620 | 24 | 249,388 | 17 | 238,712 | 13 | 168,576 | 20 | 424,729 | 21 | 569,549 | 17 |
| (4415.9) | (6813.9) | (6522.2) | (4605.9) | (11,604.6) | (15,561.4) | |||||||
| Chest X-ray | 39,732 | 6 | 70,149 | 5 | 135,383 | 7 | 27,069 | 3 | 95,238 | 5 | 202,207 | 6 |
| (1085.6) | (1916.6) | (3699.0) | (739.6) | (2602.1) | (5524.8) | |||||||
| Surgeries/ | 11,132 | 2 | 61,948 | 4 | 104,717 | 6 | 570 | 0.1 | 78,067 | 4 | 47,276 | 1 |
| operations | (304.1) | (1692.6) | (2861.1) | (15.6) | (2133.0) | (1291.7) | ||||||
| Services | 246,341 | 37 | 544,423 | 37 | 677,734 | 36 | 311,282 | 37 | 693,182 | 34 | 1,181,732 | 36 |
| (6730.6) | (14,874.9) | (18,517.3) | (8505.0) | (18,939.4) | (32,287.8) | |||||||
| Instruments | 14,061 | 2 | 96,166 | 7 | 109,252 | 6 | 38,041 | 5 | 100,122 | 5 | 353,712 | 11 |
| (384.2) | (2627.5) | (2985.0) | (1039.4) | (2735.6) | (9664.2) | |||||||
| Food/room | 65,736 | 10 | 119,951 | 8 | 260,846 | 14 | 86,031 | 10 | 237,090 | 12 | 211,525 | 6 |
| (1796.1) | (3277.3) | (7126.9) | (2350.6) | (6477.9) | (5779.4) | |||||||
| Total cost | 661,331 | 100 | 1,477,719 | 100 | 1,883,971 | 100 | 840,980 | 100 | 2,009,741 | 100 | 3,255,553 | 100 |
| (18,069.1) | (40,374.8) | (51,474.6) | (22,977.6) | (54,911.0) | (88,949.5) | |||||||
| Average | 1,688,216 (46,126.11) | |||||||||||
| Costs | Year 2015 | Year 2016 | Year 2017 | Year 2018 | Year 2019 | Year 2020 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | |
| Average outpatient cost per visit THB (USD) | ||||||||||||
| Drugs | 2745 (75.0) | 8397 (229.4) | 2803 (76.6) | 9504 (259.7) | 5401 (147.6) | 15,138 (413.6) | 6097 (166.6) | 17,307 (472.9) | 5937 (162.2) | 20,546 (561.4) | 6102 (166.7) | 20,859 (569.9) |
| Laboratory Work | 2003 (54.7) | 5847 (159.8) | 1453 (39.7) | 3360 (91.8) | 1720 (47.0) | 5257 (143.6) | 1166 (31.9) | 2317 (63.3) | 862 (23.6) | 887 (24.2) | 907 (24.8) | 997 (27.2) |
| Chest X-ray | 129 (3.5) | 1075 (29.4) | 142 (3.9) | 970 (26.5) | 125 (3.4) | 671 (18.3) | 43 (1.2) | 222 (6.1) | 37 (1.0) | 188 (5.1) | 57 (1.6) | 364 (9.9) |
| Others | 262 (7.2) | 606 (16.6) | 342 (9.3) | 925 (25.3) | 297 (8.1) | 927 (25.3) | 257 (7.0) | 649 (17.7) | 208 (5.7) | 529 (14.4) | 193 (5.3) | 317 (8.7) |
| Total cost | 5140 (140.4) | 9997 (273.1) | 4740 (129.5) | 10,127 (276.7) | 7543 (206.1) | 16,19 (442.5) | 7562 (206.6) | 17,684 (483.2) | 7045 (192.5) | 20,667 (564.7) | 7259 (198.3) | 20,964 (572.8) |
| Average outpatient cost per visit ± SD 6669 ± 17,005 (182.2 ± 464.6) | ||||||||||||
| Average inpatient cost per admission THB (USD) | ||||||||||||
| Drugs | 3506 (95.8) | 6079 (166.1) | 9073 (247.9) | 21,956 (599.9) | 8933 (244.1) | 31,385 (857.5) | 4027 (110.0) | 13,394 (366.0) | 4889 (133.6) | 10,954 (299.3) | 7578 (207.0) | 50,300 (1374.3) |
| Laboratory Work | 4618 (126.2) | 5752 (157.2) | 6740 (184.2) | 8979 (245.3) | 5968 (163.1) | 14,214 (388.4) | 3242 (88.6) | 5505 (150.4) | 5445 (148.8) | 11,182 (305.5) | 6259 (171.0) | 20,874 (570.3) |
| Chest X-ray | 1135 (31.0) | 2472 (67.5) | 1896 (51.8) | 4241 (115.9) | 3385 (92.5) | 11,513 (314.6) | 521 (14.2) | 1277 (34.9) | 1221 (33.4) | 3535 (96.6) | 2222 (60.7) | 9294 (253.9) |
| Surgeries/ operations | 318 (8.7) | 872 (23.8) | 1674 (45.7) | 7441 (203.3) | 2618 (71.5) | 14,286 (390.3) | 11 (0.3) | 79 (2.2) | 1001 (27.3) | 3942 (107.7) | 520 (14.2) | 3286 (89.8) |
| Services | 7038 (192.3) | 9757 (266.6) | 14,714 (402.0) | 23,151 (632.5) | 16,943 (462.9) | 57,129 (1560.9) | 5986 (163.6) | 16,243 (443.8) | 8887 (242.8) | 25,302 (691.3) | 12,986 (354.8) | 57,756 (1578.0) |
| Instruments | 402 (11.0) | 645 (17.6) | 2599 (71.0) | 4980 (136.1) | 2731 (74.6) | 10,042 (274.4) | 732 (20.0) | 2202 (60.2) | 1284 (35.1) | 2878 (78.6) | 3887 (106.2) | 27,781 (759.0) |
| Food/room | 1878 (51.3) | 3232 (88.3) | 3242 (88.6) | 5948 (162.5) | 6521 (178.2) | 28,608 (781.6) | 1654 (45.2) | 3848 (105.1) | 3040 (83.0) | 7524 (205.6) | 2324 (63.5) | 8706 (237.9) |
| Total cost | 18,895 (516.3) | 25,413 (694.4) | 39,938 (1091.2) | 63,738 (17,415) | 47,099 (1286.9) | 153,035 (4181.3) | 16,173 (441.9) | 40,907 (1117.7) | 25,766 (704.0) | 54,365 (1485.4) | 35,775 (977.5) | 172,517 (4713.6) |
| Average inpatient costs per admission ± SD 30,418 ± 111,224 (831.1 ± 3038.9) | ||||||||||||
| Variables | Coefficient | Standard Error | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 9.3337 | 0.5514 | <0.001 |
| Age | −0.0033 | 0.0048 | 0.489 |
| Female | −0.0278 | 0.1442 | 0.847 |
| Length of stay | 0.1586 | 0.0319 | <0.001 |
| Insulin use | −0.2285 | 0.2074 | 0.271 |
| Metformin use | −0.2126 | 0.1657 | 0.199 |
| Sulfonylurea use | 0.0702 | 0.2088 | 0.737 |
| Thiazolidinedione use | −0.1109 | 0.1387 | 0.424 |
| DPP-4 inhibitor use | −0.2449 | 0.1914 | 0.201 |
| GLP-1 agonist use | −0.3255 | 0.1833 | 0.076 |
| SGLT-2 inhibitor use | −0.0240 | 0.2833 | 0.933 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kosachunhanun, N.; Wongsa, D.; Permsuwan, U. Economic Burdens of Type 2 Diabetes Hospital Visits with Hypoglycemic Episodes in the Tertiary Care Setting in Thailand. Healthcare 2023, 11, 949. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11070949
Kosachunhanun N, Wongsa D, Permsuwan U. Economic Burdens of Type 2 Diabetes Hospital Visits with Hypoglycemic Episodes in the Tertiary Care Setting in Thailand. Healthcare. 2023; 11(7):949. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11070949
Chicago/Turabian StyleKosachunhanun, Natapong, Danil Wongsa, and Unchalee Permsuwan. 2023. "Economic Burdens of Type 2 Diabetes Hospital Visits with Hypoglycemic Episodes in the Tertiary Care Setting in Thailand" Healthcare 11, no. 7: 949. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11070949
APA StyleKosachunhanun, N., Wongsa, D., & Permsuwan, U. (2023). Economic Burdens of Type 2 Diabetes Hospital Visits with Hypoglycemic Episodes in the Tertiary Care Setting in Thailand. Healthcare, 11(7), 949. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11070949





