Korean Nationwide Exploration of Sarcopenia Prevalence and Risk Factors in Late Middle-Aged Women
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Variables
2.3. Criteria for Sarcopenia
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Prevalence
3.2. Clinical Risk Factors
3.3. Multiple Logistic Regression for Odd Ratio
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rosenberg, I.H. Sarcopenia: Origins and clinical relevance. J. Nutr. 1997, 127, 990S–991S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Bai, L. Sarcopenia in the elderly: Basic and clinical issues. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2012, 12, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulik, C.T.; Ryan, S.; Harper, S.; George, G. Aging populations and management. Acad. Manag. J. 2014, 57, 929–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dam, T.T.; Peters, K.W.; Fragala, M.; Cawthon, P.M.; Harris, T.B.; McLean, R.; Shardell, M.; Alley, D.E.; Kenny, A.; Ferrucci, L.; et al. An evidence-based comparison of operational criteria for the presence of sarcopenia. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2014, 69, 584–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Htun, N.C.; Ishikawa-Takata, K.; Kuroda, A.; Tanaka, T.; Kikutani, T.; Obuchi, S.P.; Hirano, H.; Iijima, K. Screening for Malnutrition in Community Dwelling Older Japanese: Preliminary Development and Evaluation of the Japanese Nutritional Risk Screening Tool (NRST). J. Nutr. Health Aging 2016, 20, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cawthon, P.M.; Blackwell, T.L.; Cauley, J.; Kado, D.M.; Barrett-Connor, E.; Lee, C.G.; Hoffman, A.R.; Nevitt, M.; Stefanick, M.L.; Lane, N.E.; et al. Evaluation of the Usefulness of Consensus Definitions of Sarcopenia in Older Men: Results from the Observational Osteoporotic Fractures in Men Cohort Study. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2015, 63, 2247–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.; Park, Y.M.; Kwon, H.S.; Ko, S.H.; Lee, S.H.; Yim, H.W.; Lee, W.C.; Park, Y.G.; Kim, M.K.; Park, Y.M. Sarcopenia as a determinant of blood pressure in older Koreans: Findings from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (KNHANES) 2008–2010. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent, M.R.; Dedeyne, L.; Dupont, J.; Mellaerts, B.; Dejaeger, M.; Gielen, E. Age-related bone loss and sarcopenia in men. Maturitas 2019, 122, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, F.B.; Leite, A.F.; de Paula, A.P. Relationship between pre-sarcopenia, sarcopenia and bone mineral density in elderly men. Arch. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 59, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reijnierse, E.M.; de van der Schueren, M.A.E.; Trappenburg, M.C.; Doves, M.; Meskers, C.G.M.; Maier, A.B. Lack of knowledge and availability of diagnostic equipment could hinder the diagnosis of sarcopenia and its management. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0185837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehiret, G.; Molla, A.; Tesfaw, A. Knowledge on risk factors and practice of early detection methods of breast cancer among graduating students of Debre Tabor University, Northcentral Ethiopia. BMC Womens Health 2022, 22, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.; Park, S. A Korean Nationwide Cross-Sectional Study Investigating Risk Factors, Prevalence, and Characteristics of Sarcopenia in Men in Early Old Age. Healthcare 2023, 11, 2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.; Park, S. Gender-Specific Prevalence and Risk Factors of Sarcopenic Obesity in the Korean Elderly Population: A Nationwide Cross-Sectional Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2023, 20, 1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.; Park, S. Sex Differences of Sarcopenia in an Elderly Asian Population: The Prevalence and Risk Factors. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2022, 19, 11980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.; Park, S. Gender-Specific Risk Factors and Prevalence for Sarcopenia among Community-Dwelling Young-Old Adults. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2022, 19, 7232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Bahat, G.; Bauer, J.; Boirie, Y.; Bruyere, O.; Cederholm, T.; Cooper, C.; Landi, F.; Rolland, Y.; Sayer, A.A.; et al. Sarcopenia: Revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing 2019, 48, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, I.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Ross, R. Low relative skeletal muscle mass (sarcopenia) in older persons is associated with functional impairment and physical disability. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2002, 50, 889–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kehayias, J.J.; Fiatarone, M.A.; Zhuang, H.; Roubenoff, R. Total body potassium and body fat: Relevance to aging. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1997, 66, 904–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, I.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Wang, Z.M.; Ross, R. Skeletal muscle mass and distribution in 468 men and women aged 18–88 yr. J. Appl. Physiol. 2000, 89, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lexell, J.; Downham, D.; Sjostrom, M. Distribution of different fibre types in human skeletal muscles. Fibre type arrangement in m. vastus lateralis from three groups of healthy men between 15 and 83 years. J. Neurol. Sci. 1986, 72, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Studenski, S.A.; Peters, K.W.; Alley, D.E.; Cawthon, P.M.; McLean, R.R.; Harris, T.B.; Ferrucci, L.; Guralnik, J.M.; Fragala, M.S.; Kenny, A.M.; et al. The FNIH sarcopenia project: Rationale, study description, conference recommendations, and final estimates. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2014, 69, 547–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glickman, S.G.; Marn, C.S.; Supiano, M.A.; Dengel, D.R. Validity and reliability of dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry for the assessment of abdominal adiposity. J. Appl. Physiol. 2004, 97, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kutac, P.; Bunc, V.; Sigmund, M. Whole-body dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry demonstrates better reliability than segmental body composition analysis in college-aged students. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0215599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schubert, M.M.; Seay, R.F.; Spain, K.K.; Clarke, H.E.; Taylor, J.K. Reliability and validity of various laboratory methods of body composition assessment in young adults. Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging 2019, 39, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.C.; Harhay, M.O.; Harhay, M.N. Sarcopenia and mortality among a population-based sample of community-dwelling older adults. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2016, 7, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Confortin, S.C.; Meneghini, V.; Ono, L.M.; Schneider, I.J.C.; Barbosa, A.R.; D’Orsi, E. Anthropometric indicators as a screening tool for sarcopenia in older adults from Florianopolis, Santa Catarina: EpiFloripa Ageing study. Rev. Nutr. Braz. J. Nutr. 2017, 30, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanada, K.; Miyachi, M.; Tanimoto, M.; Yamamoto, K.; Murakami, H.; Okumura, S.; Gando, Y.; Suzuki, K.; Tabata, I.; Higuchi, M. A cross-sectional study of sarcopenia in Japanese men and women: Reference values and association with cardiovascular risk factors. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2010, 110, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamboni, M.; Mazzali, G.; Fantin, F.; Rossi, A.; Di Francesco, V. Sarcopenic obesity: A new category of obesity in the elderly. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2008, 18, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, K.S. Aging muscle. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 81, 953–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesari, M.; Kritchevsky, S.B.; Baumgartner, R.N.; Atkinson, H.H.; Penninx, B.W.; Lenchik, L.; Palla, S.L.; Ambrosius, W.T.; Tracy, R.P.; Pahor, M. Sarcopenia, obesity, and inflammation—Results from the Trial of Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Inhibition and Novel Cardiovascular Risk Factors study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 82, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchmann, N.; Nikolov, J.; Spira, D.; Demuth, I.; Steinhagen-Thiessen, E.; Eckardt, R.; Norman, K. Identifying Sarcopenia in Metabolic Syndrome: Data from the Berlin Aging Study II. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2016, 71, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Wang, X.; Xie, H.; Zheng, S.; Wu, X.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, X.; Xue, S.; Li, H.; Hong, W.; et al. Sex differences in the prevalence and adverse outcomes of sarcopenia and sarcopenic obesity in community dwelling elderly in East China using the AWGS criteria. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2019, 19, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.W.; Yang, K.C.; Chang, H.H.; Lee, L.T.; Chen, C.Y.; Huang, K.C. Sarcopenic obesity is closely associated with metabolic syndrome. Obes. Res. Clin. Pract. 2013, 7, e301–e307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Liu, H.; Yu, J.; He, S.; Li, P.; Ma, C.; Zhang, H.; Xu, L.; Ping, F.; Li, W.; et al. Triglyceride is independently correlated with insulin resistance and islet beta cell function: A study in population with different glucose and lipid metabolism states. Lipids Health Dis. 2020, 19, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundsgaard, A.M.; Kiens, B. Gender differences in skeletal muscle substrate metabolism—Molecular mechanisms and insulin sensitivity. Front. Endocrinol. 2014, 5, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heeren, J.; Scheja, L. Metabolic-associated fatty liver disease and lipoprotein metabolism. Mol. Metab. 2021, 50, 101238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawano, Y.; Cohen, D.E. Mechanisms of hepatic triglyceride accumulation in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 48, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Lee, Y.; Kim, Y.; Seo, Y.; Lee, H.; Ha, J.; Lee, J.; Choi, Y.; Oh, H.; Yoon, Y. Akkermansia muciniphila prevents fatty liver disease, decreases serum triglycerides, and maintains gut homeostasis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e03004–e03019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feingold, K.; Grunfeld, C.; De Groot, L.; Beck-Peccoz, P.; Chrousos, G. The Effect of Inflammation and Infection on Lipids and Lipoproteins; MDText. com. Inc.: South Dartmouth, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Lima, T.; Li, T.Y.; Mottis, A.; Auwerx, J. Pleiotropic effects of mitochondria in aging. Nat. Aging 2022, 2, 199–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawadi, G.; Roman-Roman, S. Mycoplasma membrane lipoproteins induced proinflammatory cytokines by a mechanism distinct from that of lipopolysaccharide. Infect. Immun. 1996, 64, 637–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribas, G.S.; Vargas, C.R. Evidence that oxidative disbalance and mitochondrial dysfunction are involved in the pathophysiology of fatty acid oxidation disorders. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2022, 42, 521–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, S.E.; Pollock, A.C.; Lamon, S. The effect of sex hormones on skeletal muscle adaptation in females. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2022, 22, 1035–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Androga, L.; Sharma, D.; Amodu, A.; Abramowitz, M.K. Sarcopenia, obesity, and mortality in US adults with and without chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. Rep. 2017, 2, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkins, J.L.; Whincup, P.H.; Morris, R.W.; Lennon, L.T.; Papacosta, O.; Wannamethee, S.G. Sarcopenic obesity and risk of cardiovascular disease and mortality: A population-based cohort study of older men. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2014, 62, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashemi, R.; Shafiee, G.; Motlagh, A.D.; Pasalar, P.; Esmailzadeh, A.; Siassi, F.; Larijani, B.; Heshmat, R. Sarcopenia and its associated factors in Iranian older individuals: Results of SARIR study. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2016, 66, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, V.R.d.; Araujo, M.Y.C.; Cardoso, M.R.; Batista, V.C.; Christofaro, D.G.D.; Gobbo, L.A. Association of insufficient physical activity with sarcopenia and sarcopenic obesity in individuals aged 50 years or more. Rev. Nutr. 2017, 30, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huschtscha, Z.; Parr, A.; Porter, J.; Costa, R.J.S. Sarcopenic Characteristics of Active Older Adults: A Cross-Sectional Exploration. Sports Med. Open 2021, 7, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenholm, S.; Harris, T.B.; Rantanen, T.; Visser, M.; Kritchevsky, S.B.; Ferrucci, L. Sarcopenic obesity-definition, etiology and consequences. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2008, 11, 693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
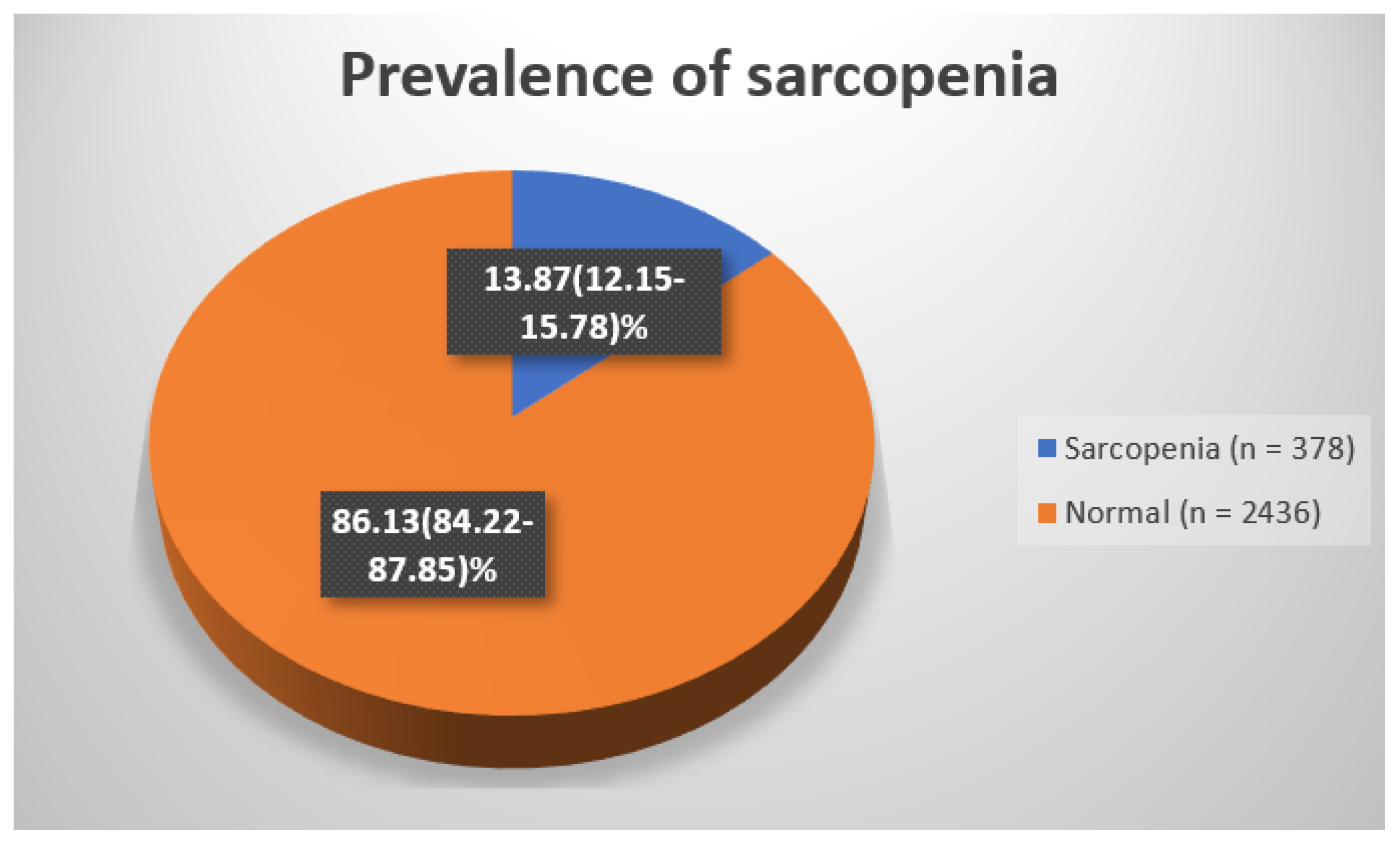
| Sarcopenia | Normal | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 378) | (n = 2436) | (N = 2814) | |
| Un-weighted (%) | 13.43 | 86.57 | 100 |
| Weighted (%) | 13.87 (12.15–15.78) | 86.13 (84.22–87.85) | 100 |
| Sarcopenia | Normal | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 378) | (n = 2436) | ||
| Age (years) | 57.648 ± 4.164 | 56.301 ± 4.366 | 0.000 |
| Height (cm) | 149.69 ± 4.732 | 156.177 ± 4.748 | 0.000 |
| Weight (kg) | 58.954 ± 9.042 | 58.499 ± 7.884 | 0.307 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 26.265 ± 3.537 | 23.961 ± 2.854 | 0.000 |
| WC (cm) | 85.635 ± 9.675 | 81.171 ± 8.575 | 0.000 |
| SMI (kg/m2) | 485.397 ± 29.216 | 617.959 ± 62.806 | 0.000 |
| FG (mg/dL) | 100.85 ± 23.259 | 98.956 ± 22.479 | 0.138 |
| Triglyceride (mg/dL) | 145.047 ± 78.063 | 128.908 ± 85.84 | 0.001 |
| TC (mg/dL) | 207.529 ± 36.083 | 200.999 ± 36.093 | 0.001 |
| SBP (mmHg) | 128.726 ± 17.94 | 123.392 ± 17.574 | 0.000 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 80.242 ± 9.501 | 78.406 ± 10.472 | 0.001 |
| Drinking status (%) (current-/ex-/non-user) | 58.262/19.83/21.908 | 58.724/15.851/25.425 | 0.156 |
| Smoking status (%) (current-/ex-/non-user) | 4.764/2.849/92.387 | 5.943/1.228/92.83 | 0.121 |
| Variables | Odd Ratios (95% of CI) | p |
|---|---|---|
| BMI | 19.178 (4.3080–85.380) | 0.015 |
| WC | 1.362 (1.011–1.836) | 0.042 |
| SMI | 0.115 (0.067–0.193) | 0.000 |
| SBP | 1.349 (1.255–1.451) | 0.000 |
| DBP | 1.845 (1.646–2.067) | 0.000 |
| TC | 1.166 (1.141–1.191) | 0.000 |
| Triglyceride | 1.078 (1.058–1.097) | 0.000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hwang, J.; Park, S. Korean Nationwide Exploration of Sarcopenia Prevalence and Risk Factors in Late Middle-Aged Women. Healthcare 2024, 12, 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12030362
Hwang J, Park S. Korean Nationwide Exploration of Sarcopenia Prevalence and Risk Factors in Late Middle-Aged Women. Healthcare. 2024; 12(3):362. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12030362
Chicago/Turabian StyleHwang, Jongseok, and Soonjee Park. 2024. "Korean Nationwide Exploration of Sarcopenia Prevalence and Risk Factors in Late Middle-Aged Women" Healthcare 12, no. 3: 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12030362
APA StyleHwang, J., & Park, S. (2024). Korean Nationwide Exploration of Sarcopenia Prevalence and Risk Factors in Late Middle-Aged Women. Healthcare, 12(3), 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12030362






