Abstract
Abdominal obesity (AO) and dynapenia (DP) are associated with cognitive decline, and the relationship between dynapenic abdominal obesity (DAO), a combination of DP and AO, and mild cognitive impairment (MCI) has been confirmed. This study aims to determine whether this relationship exhibits potential sex differences. The relationship between MCI and DAO was confirmed in 1309 community elderly individuals aged 65 years or older who were not diagnosed with dementia. The MCI was defined as a Korean mini-mental state examination (K-MMSE) score of 18–23 points. Multiple logistic regression analyses were conducted, categorizing participants into groups: a control group without AO or DP, an AO group, a DP group, and a DAO group. The study results showed that in women, both DP and DAO were significantly associated with MCI not only in the unadjusted Model 1 but also in Model 2, which adjusted for general characteristics and health behaviors, and Model 3, which additionally adjusted for chronic diseases and disease-related characteristics. In men, DP was associated with MCI in the unadjusted Model 1. The findings highlight sex differences in the impact of the DAO on MCI. These differences should be considered when studying the factors related to MCI in old age.
1. Introduction
Cognitive function is an important indicator of mental health and successful aging in later years [1]. Aging is characterized by a decline in muscle mass and an increase in fat mass—essentially, the muscle becomes converted to fat [2]. Alterations in body composition are inherent to the aging process, with shifts in fat and muscle mass holding paramount significance [3]. Recent studies investigating factors associated with cognitive decline in the elderly suggest that obesity increases the risk of cognitive decline (MCI) [4,5], while regular physical activity reduces the risk of cognitive decline and dementia [6,7]. Longitudinal studies on aging suggest that maintaining or increasing muscle mass does not prevent age-related decline in strength [8,9]. Furthermore, dynapenia (DP) is defined as the age-related decline in muscle strength [10]. In previous studies, research has linked DP to a decline in cognitive function [11], and abdominal obesity (AO) in the elderly has been associated with an elevated risk of cognitive impairment and dementia, irrespective of body mass index (BMI) [12,13]. Dynapenic AO (DAO), a combination of DP and AO, has been shown to exert an additional deteriorating impact on cognitive function compared to either sarcopenia or obesity alone [14].
Meanwhile, older women engage in far less physical activity than men in the same age group, and older women have higher body fat and relatively lower muscle strength than men [15]. When elderly women become obese, even a small decrease in muscle strength can lead to difficulties with mobility or weight-bearing, and the resulting consequences become more serious [16]. In a previous study, it was demonstrated that DAO was related to MCI. However, sex differences were not confirmed because the analysis was not categorized by sex in that study [14]. Considering these characteristics in women, this study aims to determine the relationship between AO, DP, DAO, and MCI by considering differences in sex and analyzing how these relationships differ.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
This study analyzed the epidemiological survey data from the 6th follow-up (7th period) of a community-based cohort. These data are part of the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study (KoGES), a large prospective cohort study conducted by the National Institute of Health (NIH), the Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency, and the Republic of Korea [17]. These cohort data were established in 2001 and are being tracked until 2020. The data utilized in this analysis were the 6th follow-up data, encompassing 5906 individuals who were surveyed between 2013 and 2014. To access data for analysis, the researcher applied for data use at NIH after receiving a research ethics review of the research plan at the affiliated institution, Gachon University (IRB number: 1044396-202203-HR-066-02). After passing NIH’s review, the researcher went to the data analysis room of the National Biobank of Korea and conducted data analysis. Among these subjects, those who were aged 65 years, had not been diagnosed with dementia or received treatment for depression, and had handgrip strength and BMI data were included. The analysis excluded patients with dementia with a Korean mini-mental state examination (K-MMSE) score of 17 or less. The final analysis utilized data from 1309 participants (597 men and 801 women) (Figure 1).
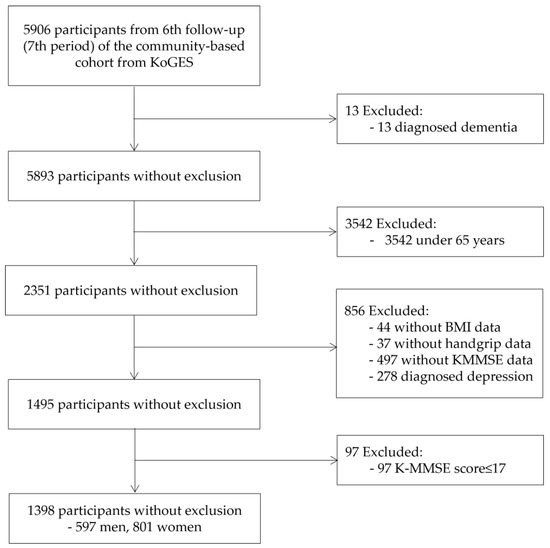
Figure 1.
Flow chart illustrating the inclusion of participants. KoGES: Korean genome and epidemiology study; BMI: body mass index; K-MMSE: Korea-Mini Mental State Examination.
2.2. Definition of AO, DP, and DAO
Abdominal obesity was categorized based on waist circumference (WC). According to the results of previous studies on the WC of Korean adults, AO was defined as 90 cm or more for men, and AO was defined as 85 cm or more for women [18]. The DP is defined as low muscle strength measured by handgrip strength (HGS). The HGS was measured utilizing a digital hand dynamometer (digital grip strength dynamometer; T. K. K. 5401, Takei Scientific Instruments Co., Ltd., Nigata, Japan). If the subject underwent surgery or was injured in the hand or wrist within three months, only the uninjured hand was measured [19]. The HGS was measured with the subject sitting on a chair, placing his or her arm on a desk, and maintaining the arm angle at 90° [19]. The test was repeated for approximately 15 s. When the measurements of one hand are complete, the other hand is also measured using the same procedure [19]. As in previous studies, the average HGS of the dominant arm was utilized as the HGS value [20]. Low muscle strength was defined as HGS < 28 kg in men and <18 kg in women [21]. Participants were divided into four groups, namely: AO only, DP only, DAO with both, and Control without both [22].
2.3. Definition of Cognitive Impairment
The K-MMSE utilizes the cumulative score of all items, with a total score of 23 generally employed as the evaluation standard (cutoff point) for cognitive dysfunction. Epidemiological research findings suggest that, depending on the total K-MMSE score, scores of 24–30 indicate no cognitive impairment, scores of 18–23 indicate MCI, and scores of 0–17 indicate definite cognitive impairment [23]. Consequently, participants with a score of 17 or less were excluded from the study, and subjects with scores of 18–23 and 24–30 were divided into MCI and normal groups.
2.4. General Characteristics, Health Behavior, and Disease-Related Characteristics
General characteristics, such as age, sex, education level, and marital status, were measured using questionnaires. The BMI is calculated as weight divided by the square of the height. Among the health behaviors, smoking, drinking, and physical activity were also measured. Physical activity was classified into inactive, moderate, and active exercise groups by calculating the total amount of exercise per week as metabolic equivalent (MET) based on the International Physical Activity Questionnaire [24]. The inactive exercise group is less than 600 MET per week, the moderate exercise group is 600 to 3000 MET, and the active group is more than 3000 MET [24]. Weekly exercise is classified into 3.3 MET for walking, 4.0 MET for moderate-intensity exercise, and 8.0 MET for vigorous exercise, depending on the type of daily exercise [24]. The activity intensity was converted to MET by multiplying the number of participation days per week by the average activity time.
Disease-related characteristics included whether patients were diagnosed with hypertension, hyperlipidemia, ischemic heart diseases, or diabetes. Systolic blood pressure was measured, and blood examinations included total cholesterol, high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, triglyceride (TG), serum high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP), hemoglobin, and plasma glycohemoglobin (HbA1c).
2.5. Statistical Analysis
The characteristics of all participants are described, along with the mean and standard deviation (SD) and frequency percentages by sex. The sex differences in characteristics were analyzed with a t-test or chi-square test.
DAO groups such as control, AO, DP, and DAO were compared with the normal group and MCI group by sex with a chi-square test. HGS and WC were compared with the normal group and MCI group by sex with a t-test.
Odds ratios for MCI in the group of DAO categories (control, AO, DP, and DAO) in multiple regression analyses according to sex were calculated. Multiple logistic regression analyses were performed with Models 1, 2, and 3. Model 1 was the unadjusted model, while Model 2 was adjusted to the characteristics of the study subjects, including health behavior. Additionally, Model 3 was adjusted by including variables reflecting diseases that are frequent in the elderly. Furthermore, Model 2 was adjusted with age, education, marital status, smoking status, drinking status, BMI, and physical activity. Model 3 was adjusted with the variables in Model 2 and further adjusted in Model 2 for hypertension, dyslipidemia, ischemic heart disease, diabetes mellitus, SBP, total cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, TG, hsCRP, hemoglobin, and HbA1c. Multiple logistic regressions with the dependent variable HGS (low handgrip as HGS < 28 kg in men and <18 kg in women) and WC (high WC as 90 cm or more for men and as 85 cm or more for women) were carried out for Models 1, 2, and 3. All analyses were conducted using SAS version 9.4 (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA). The statistical significance of all comparison values was based on p < 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of All Participants According to Sex
Participants characteristics by sex are presented in Table 1. Men were 72.3 years old, and women were 72.5 years old. Regarding the level of education, the proportion of women with no education was higher than that of men, and the proportion of middle school graduates or higher was higher among men than women. Marital status, smoking status, drinking status, BMI, and physical activity all differed between men and women. Specifically, the proportion of married people was higher in men, and the BMI was higher in women. There were more men than women who smoked and drank, and the rate of inactivity was higher among women than men. In terms of health-related characteristics, there were differences in SBP, total cholesterol, hsCRP, and hemoglobin between men and women. The average SBP and total cholesterol values were higher in women than in men, and the hsCRP and hemoglobin values were lower in women than in men.

Table 1.
Characteristics of all participants according to sex (N = 1398).
3.2. DAO Parameters of the Normal Group and MCI Group According to Sex
The results of analyzing whether there were differences in the DAO category, HGS, and WC between the normal cognitive group and MCI according to sex are presented in Table 2.

Table 2.
DAO parameters of the normal group and the MCI group according to sex (N = 1398).
There was no difference in frequency between the normal cognitive group and MCI according to the DAO category (control, AO, DP, and DAO) in men, but there was a difference in women. There was a difference in handgrip strength values between the normal cognitive group and MCI in men and women. There was no difference in WC values between the normal cognitive group and MCI in men and women.
3.3. Odds Ratios for MCI in the Group of DAO Category in Multiple Logistic Regression Analysis According to Sex
Multiple logistic regression results obtained by calculating the odds ratio according to sex, using control as a reference among DAO categories, are presented in Table 3. In Model 1, an unadjusted model, DP was significantly associated with MCI in men (OR = 1.79, 95% CI = 1.01–3.16). In women, the odds for DP compared to control were 3.00 (95% CI = 1.71–5.26), and for DAO, the odds were 2.21 (95% CI = 1.36–3.59). In Models 2 and 3, no significant odds values were calculated for each man in the DAO category. In Model 2, for women, both DP and DAO were significantly associated with MCI (OR = 2.29, 95% CI = 1.22–4.34, OR = 2.15, 95% CI = 1.18–3.96, respectively). Similarly, in Model 3, for women, both DP and DAO were significantly associated with MCI (OR = 2.42, 95% CI = 1.28–4.64, OR = 2.37, 95% CI = 1.28–4.45, respectively).

Table 3.
Odds ratios for MCI in the group of DAO category in multiple logistic regression analysis according to sex.
3.4. Association between Handgrip Strength and High Waist Circumference in the Logistic Analysis According to Sex
Table 4 shows the results of a multiple logistic regression analysis that categorized HGS and WC and calculated the odds ratio by sex. The odds ratio for the likelihood of developing MCI for low HGS was calculated to be significant only in Model 1 for men. (odds ratio = 1.70, 95% CI = 1.12–2.59). For low HGS, significant odds ratios were calculated in Models 1, 2, and 3 for women. No significant odds ratios were calculated for both men and women when WC was high compared to when WC was low.

Table 4.
Association between handgrip strength or high waist circumference in the logistic analysis according to sex.
4. Discussion
This study aimed to determine the relationship between the DAO category (control, AO, DP, and DAO) and MCI according to sex in community-dwelling elderly individuals. The results of the study exhibited that DP and DAO were related to MCI in women, not only in the unadjusted Model 1 but also in Model 2, which adjusted for general characteristics and health behaviors. Additionally, Model 3 adjusted for chronic disease and disease-related characteristics. In men, DP was associated with MCI in the unadjusted Model 1. Previous studies have exhibited that elderly women with low muscle strength (<20.4 kg) have a 3.04 times higher risk of being exposed to MCI than participants with high physical function [25]. It was confirmed that there is an independent relationship with the risk of sarcopenic MCI in elderly women [25]. In cross-sectional studies, MCI has been shown to be associated with lower HGS [26].
When DAO was divided into groups, the relationship with MCI was significantly greater when DP and DAO were utilized than when AO was utilized alone, suggesting that muscle strength or muscle strength and obesity at the same time are simultaneously more related to MCI than simple obesity. These results are consistent with those of previous research exhibiting that cognitive function and muscle strength are related [11,12,27].
As age increases, physical function and muscle function decrease [28], which is related to a decline in cognitive function, and strength as opposed to muscle mass is related to cognitive decline [11,25]. High skeletal muscle power reduces the risk of frailty, cardiovascular disease, cardiovascular disease-related factors, and mortality [29]. The relationship between cognitive function and low muscle strength can be inferred from changes in nervous system activity and white matter integrity, such as weakened muscle strength or decreased frontal lobe function, which requires neuromuscular coordination [30]. In a cohort study examining the relationship between HGS and neuroimaging, brain white matter hyperactivity was significantly greater when HGS was low [31]. These findings reflect the research results demonstrating that vascular endothelial dysfunction causes cognitive aging [32]. Additionally, this is related to muscle weakness [33].
Muscle strength was measured using the HGS, which can be easily measured in community and clinical settings [34]. Additionally, it is employed as a diagnostic criterion for sarcopenia and exhibits a high correlation with overall cognitive functions such as executive function, attention, and language [3]. The decrease in HGS exhibits a significant inverse correlation with an individual’s cognitive function; therefore, it is a functional marker that can infer the degree of cognitive decline and is a crucial indicator primarily utilized in muscle strength evaluation in sarcopenia [3].
In a previous study, a relationship between men’s handgrip power and MCI was confirmed [26]. However, in this study, a weak relationship was confirmed solely in the univariate analysis. In a cohort study that followed a large population over a relatively long period of time, the relationship between HGS and dementia risk, cognition, and neuroimaging was confirmed, and similar results were found in men and women [31]. Conversely, there is a previous study that found differences in the relationship between sarcopenia and MCI depending on sex [35]. In this study, the relationship between sarcopenia and MCI according to sex was due to sex hormones such as androgen and estrogen [35]. In other words, there is a difference in the distribution of sex hormone receptors that affect muscle mass in the hippocampus between men and women [36]. Since differences between men and women in the relationship between muscle propensity and MCI are not consistently shown, there is a need to conduct long-term studies targeting both male and female populations. In addition, it is necessary to assess other muscle strength parameters that can predict cognitive decline, such as gait speed, step length, and timed chair stand test results [37].
Considering the changes in body composition during old age, caution is required when interpreting the relationship between obesity in old age and cognitive function. BMI is one of the most commonly employed obesity indices; however, it has limitations in reflecting the amount of fat in the body and does not effectively reflect body types with several muscles or body types with little muscle or fat [13]. Even if body weight is maintained in old age, body composition changes. Age-related changes in body composition, particularly decreased muscle mass and increased body fat, strongly interact with each other from an etiological perspective [38]. Visceral fat is positively correlated with CRP; therefore, low-intensity inflammation is believed to be an important cause of sarcopenic obesity [38]. In addition to inflammatory factors, insulin resistance also plays a major role in the development of sarcopenic obesity. Insulin resistance is independently related to muscle weakness, whereas resistance exercise improves muscle insulin resistance [39], and low physical activity is an important risk factor considered for weight gain. Obese individuals have reduced physical activity, which increases the likelihood that it will lead to decreased muscle strength [40].
This process generates DAO in the elderly, which is an important health problem, acting as a mediating factor that changes brain structure and function and affects cognitive function [5,14]. In this study, no significant relationship was found between abdominal circumference alone and MCI. Adiposity is a well-known risk factor for dementia. A recent study exhibited that the normal-weight group with abdominal obesity had a significantly increased risk of dementia compared to the group without abdominal obesity [13]. However, in previous studies, general obesity was not associated with dementia, but central obesity was positively correlated [41]. In a previous study that confirmed the degree of prediction of late-onset Alzheimer’s disease (LOAD) by measuring WC and waist-to-hip ratio (WHR) as indicators of central obesity in the elderly, the highest WC quartile was compared between LOAD and LOAD in a model adjusted for age and sex [41]. There was a relationship; however, in the model adjusted for other covariates, this relationship was significantly reduced [41]. The highest WHR quartile was most strongly associated with LOAD, and this association was robust in all models, leading researchers to suggest the utilization of WHR as a measure of central obesity [41].
As sarcopenic obesity not only affects physical activity, metabolism, and cardiovascular function but also cognitive function, research on it is of significant interest not only in medicine, nutrition, and geriatrics but also in public health. The treatment of sarcopenic obesity should focus not only on reducing body fat but also on maintaining and increasing strength, muscle function, and muscle mass [38]. There are also research results exhibiting that combined exercise with a variety of aerobic and resistance training exercises can be effective in reducing visceral fat and increasing muscle mass and strength to prevent the progression to dementia [42]. It is essential to develop exercise programs for the elderly population in the future.
This study has some limitations. A cross-sectional analysis was performed to determine the relationship between the DAO and MCI. Therefore, care must be taken to check the relationship between the DAO and MCI. In the future, a cohort data analysis is required to confirm the relationship between the DAO status and MCI occurrence. As this study utilized Koreans as the standard for AO to define DAO, and in defining MCI, the K-MMSE score was classified, caution should be exercised when comparing populations in other countries. In addition, the subjects of this study were elderly individuals in certain regions of Korea; therefore, it is difficult to regard them as representative of the Korean elderly. Nevertheless, this study confirmed that when considering the characteristics of obesity related to MCI in elderly women, muscle strength or muscle strength and obesity should be considered simultaneously, as opposed to AO alone.
5. Conclusions
Sex differences in the influence of the DAO on MCI were observed, and these distinctions should be considered when formulating strategies for preventing cognitive decline. Future research is warranted to elucidate sex-specific differences in the incidence of MCI, encompassing forms of obesity, muscle strength, muscle function, and muscle mass.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.K. and Y.P.; methodology, J.K.; validation, J.K. and Y.P.; formal analysis, J.K.; investigation, J.K. and Y.P.; data curation, J.K.; writing—original draft preparation, J.K. and Y.P.; writing—review and editing, J.K. and Y.P.; supervision, J.K.; project administration, J.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Gachon University Research Fund of 2023 (GCU-202303690001).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical approval for the KoGES was obtained from the institutional review boards (IRBs) of the National Institute of Health and collaborators of the KoGES groups. This study was approved by the IRB of Gachon University (IRB number: 1044396-202203-HR-066-02, 21 July 2023).
Informed Consent Statement
When the KoGES data were collected, all participants provided informed consent for the baseline data and biospecimens and underwent an interview and physical examination.
Data Availability Statement
The data analyzed in this study are de-identified data from the KoGES research and are publicly available upon request under the request policy available online.
Acknowledgments
Data in this study were from the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study (KoGES; 6635-302), National Institute of Health, Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency, Republic of Korea.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- WHO. Risk Reduction of Cognitive Decline and Dementia: WHO Guidelines. 2019. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241550543 (accessed on 4 January 2024).
- Ding, J.; Kritchevsky, S.B.; Newman, A.B.; Taaffe, D.R.; Nicklas, B.J.; Visser, M.; Lee, J.S.; Nevitt, M.; A Tylavsky, F.; Rubin, S.M.; et al. Effects of birth cohort and age on body composition in a sample of community-based elderly. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 85, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchman, A.S.; Boyle, P.A.; Wilson, R.S.; Tang, Y.; Bennett, D.A. Frailty is Associated with Incident Alzheimer’s Disease and Cognitive Decline in the Elderly. Psychosom. Med. 2007, 69, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tou, N.X.; Wee, S.-L.; Pang, B.W.J.; Lau, L.K.; Jabbar, K.A.; Seah, W.T.; Chen, K.K.; Ng, T.P. Associations of fat mass and muscle function but not lean mass with cognitive impairment: The Yishun Study. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0256702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Hai, S.; Liu, Y.X.; Cao, L.; Liu, P.; Yang, Y.; Dong, B. Associations between Sarcopenic Obesity and Cognitive Impairment in Elderly Chinese Community-Dwelling Individuals. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2019, 23, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livingston, G.; Huntley, J.; Sommerlad, A.; Ames, D.; Ballard, C.; Banerjee, S.; Brayne, C.; Burns, A.; Cohen-Mansfield, J.; Cooper, C.; et al. Dementia prevention, intervention, and care: 2020 report of the Lancet Commission. Lancet Comm. 2020, 396, 413–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandler, M.J.; Parks, A.C.; Marsiske, M.; Rotblatt, L.J.; Smith, G.E. Everyday Impact of Cognitive Interventions in Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Neuropsychol. Rev. 2016, 26, 225–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodpaster, B.H.; Park, S.W.; Harris, T.B.; Kritchevsky, S.B.; Nevitt, M.; Schwartz, A.V.; Simonsick, E.M.; Tylavsky, F.A.; Visser, M.; Newman, A.B.; et al. The Loss of Skeletal Muscle Strength, Mass, and Quality in Older Adults: The Health, Aging and Body Composition Study. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2006, 61, 1059–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, V.A.; Frontera, W.R.; Wood, M.; Evans, W.J.; Dallal, G.E.; Roubenoff, R.; Singh, M.A.F. Longitudinal Muscle Strength Changes in Older Adults: Influence of Muscle Mass, Physical Activity, and Health. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2001, 56, B209–B217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manini, T.M.; Clark, B.C. Dynapenia and Aging: An Update. J. Gerontol. Ser. A 2012, 67, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beeri, M.S.; Leugrans, S.E.; Delbono, O.; Bennett, D.A.; Buchman, A.S. Sarcopenia is associated with incident Alzheimer’s dementia, mild cognitive impairment, and cognitive decline. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2021, 69, 1826–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerwin, D.R.; Gaussoin, S.A.; Chlebowski, R.T.; Kuller, L.H.; Vitolins, M.; Coker, L.H.; Kotchen, J.M.; Nicklas, B.J.; Wassertheil-Smoller, S.; Hoffmann, R.G.; et al. Interaction between body mass index and central adiposity and risk of incident cognitive impairment and dementia: Results from the Women’s Health Initiative Memory Study. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2011, 59, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, G.J.; Hwang, S.Y.; Lee, K.; Choi, K.M.; Baik, S.H.; Kim, T.; Han, S.W.; Yoo, H.J. Association Between Waist Circumference and Dementia in Older Persons: A Nationwide Population-Based Study. Obesity 2019, 27, 1883–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oba, K.; Tamura, Y.; Ishikawa, J.; Suzuki, H.; Fujiwara, Y.; Tachibana, A.; Kodera, R.; Toyoshima, K.; Chiba, Y.; Araki, A. Dynapenic abdominal obesity is associated with mild cognitive impairment in patients with cardiometabolic disease: A cross-sectional study. BMC Geriatr. 2022, 22, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visser, M.; Kritchevsky, S.B.; Goodpaster, B.H.; Newman, A.B.; Nevitt, M.; Stamm, E.; Harris, T.B. Leg Muscle Mass and Composition in Relation to Lower Extremity Performance in Men and Women Aged 70 to 79: The Health, Aging and Body Composition Study. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2002, 50, 897–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenholm, S.; Sainio, P.; Rantanen, T.; Alanen, E.; Koskinen, S. Effect of co-morbidity on the association of high body mass index with walking limitation among men and women aged 55 years and older. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2007, 19, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Han, B.G. Cohort Profile: The Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study (KoGES) Consortium. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 46, e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.-Y.; Kang, S.M.; Kang, J.-H.; Kang, S.Y.; Kim, K.K.; Kim, B.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, Y.-H.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, J.H.; et al. 2020 Korean society for the study of obesity guidelines for the management of obesity in Korea. J. Obes. Metab. Syndr. 2021, 30, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, B.Y.; Kim, S.S. Manual of Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study: Survey and Health Examination; Osong: Cheongju-si, Republic of Korea, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, E.; Soh, H.S.; Lee, J.R.; Yun, J.; Bae, W.K.; Lee, H. Association between smoking status and handgrip strength in Korean male adults: Based on Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2016–2019. Front. Med. 2023, 27, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.-K.; Woo, J.; Assantachai, P.; Auyeung, T.-W.; Chou, M.-Y.; Iijima, K.; Jang, H.C.; Kang, L.; Kim, M.; Kim, S.; et al. Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia: 2019 Consensus Update on Sarcopenia Diagnosis and Treatment. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2020, 21, 300–307.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, R.; Srivastava, S.; Muhammad, T.; Rashmi, R. Determinants of acquired disability and recovery from disability in Indian older adults: Longitudinal influence of socio-economic and health-related factors. BMC Geriatr. 2021, 21, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kim, H.C. An Overview of the Mini-Mental State Examination. Korean J. Psychopharmacol. 1996, 7, 13–32. [Google Scholar]
- Craig, C.L.; Marshall, A.L.; Sjöström, M.; Bauman, A.E.; Booth, M.L.; Ainsworth, B.E.; Pratt, M.; Ekelund, U.L.; Yngve, A.; Sallis, J.F.; et al. International Physical Activity Questionnaire: 12-Country Reliability and Validity. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2003, 35, 1381–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.G.; Kim, G.M.; Bae, S.; Park, H. Nonlinear Association between Physical Function and Risk of Mild Cognitive Impairment in Older Women with Low Muscle Mass. Exerc. Sci. 2022, 31, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.Y.; Kim, J. Association between handgrip strength and cognitive impairment in elderly Koreans: A population-based cross-sectional study. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2015, 27, 3911–3915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.-Y.; Hwang, A.-C.; Liu, L.-K.; Lee, W.-J.; Peng, L.-N.; Lin, M.-H.; Chen, L.-K. Association of dynapenia, sarcopenia, and cognitive impairment among community-dwelling older Taiwanese. Rejuvenation Res. 2016, 19, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, H.; Yu, M.; Xue, H.; Lu, X.; Chang, Y.; Li, Z. Association between sarcopenia and cognitive function in older Chinese adults: Evidence from the China health and retirement longitudinal study. Front. Public. Health. 2023, 10, 1078304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamiya, K.; Masuda, T.; Tanaka, S.; Hamazaki, N.; Matsue, Y.; Mezzani, A.; Matsuzawa, R.; Nozaki, K.; Maekawa, E.; Noda, C.; et al. Quadriceps Strength as a Predictor of Mortality in Coronary Artery Disease. Am. J. Med. 2015, 128, 1212–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhary, A.K.; Jiwane, R.; Alam, T.; Kishanrao, S.S. Grip Strength, and Impact on Cognitive Function in Healthy Kitchen Workers. Achiev. Life Sci. 2016, 10, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchowny, K.A.; Ackley, S.F.; Brenowitz, W.D.; Wang, J.; Zimmerman, S.C.; Caunca, M.R.; Glymour, M.M. Associations between handgrip strength and dementia risk, cognition, and neuroimaging outcomes in the UK Biobank Cohort Study. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2218314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins-Filho, R.K.; Zotin, M.C.; Rodrigues, G.; Pontes-Neto, O. Biomarkers related to endothelial dysfunction and vascular cognitive impairment: A systematic review. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2020, 49, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarasekera, A.T.; Chang, D.; Schwarz, P.; Tan, T.C. Does vascular endothelial dysfunction play a role in physical frailty and sarcopenia? A systematic review. Age Ageing 2021, 50, 725–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaishya, R.; Misra, A.; Vaish, A.; Ursino, N.; D’Ambrosi, R. Hand grip strength as a proposed new vital sign of health: A narrative review of evidences. J. Health Popul. Nutr. 2024, 43, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.-J.; Choi, J.-Y.; Hong, D.; Kim, D.; Min, J.-Y.; Min, K.-B. Sex differences in the association between sarcopenia and mild cognitive impairment in the older Korean population. BMC Geriatr. 2023, 23, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yagi, S.; Galea, L.A.M. Sex differences in hippocampal cognition and neurogenesis. Neuropsychopharmacology 2019, 44, 200–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auyeung, T.W.; Lee, J.S.W.; Kwok, T.; Woo, J. Physical frailty predicts future cognitive decline—A four-year prospective study in 2737 cognitively normal older adults. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2011, 15, 690–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.N.; Choi, K.M. Sarcopenic Obesity. J. Korean Diabetes 2013, 14, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Goodpaster, F.H.; Brown, F.F. Skeletal Muscle Lipid and Its Association with Insulin Resistance: What Is the Role for Exercise? Exerc. Sport. Sci. Rev. 2005, 33, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaMonte, M.J.; Blair, S.N. Physical activity, cardiorespiratory fitness, and adiposity: Contributions to disease risk. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2006, 9, 540–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luchsinger, J.A.; Cheng, D.; Tang, M.X.; Schupf, N.; Mayeux, R. Central Obesity in the Elderly is Related to Late-onset Alzheimer Disease. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 2012, 26, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadore, E. Strength and Endurance Training Prescription in Healthy and Frail Elderly. Aging Dis. 2014, 5, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).