Cardiometabolic Disease Risk Factors and Lifestyle Behaviors Among Adolescents: A Latent Class Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants and Procedures
2.2. Cardiometabolic Risk Factor Variables
2.3. Lifestyle Behaviors
2.4. Covariates
2.5. Statistical Analysis
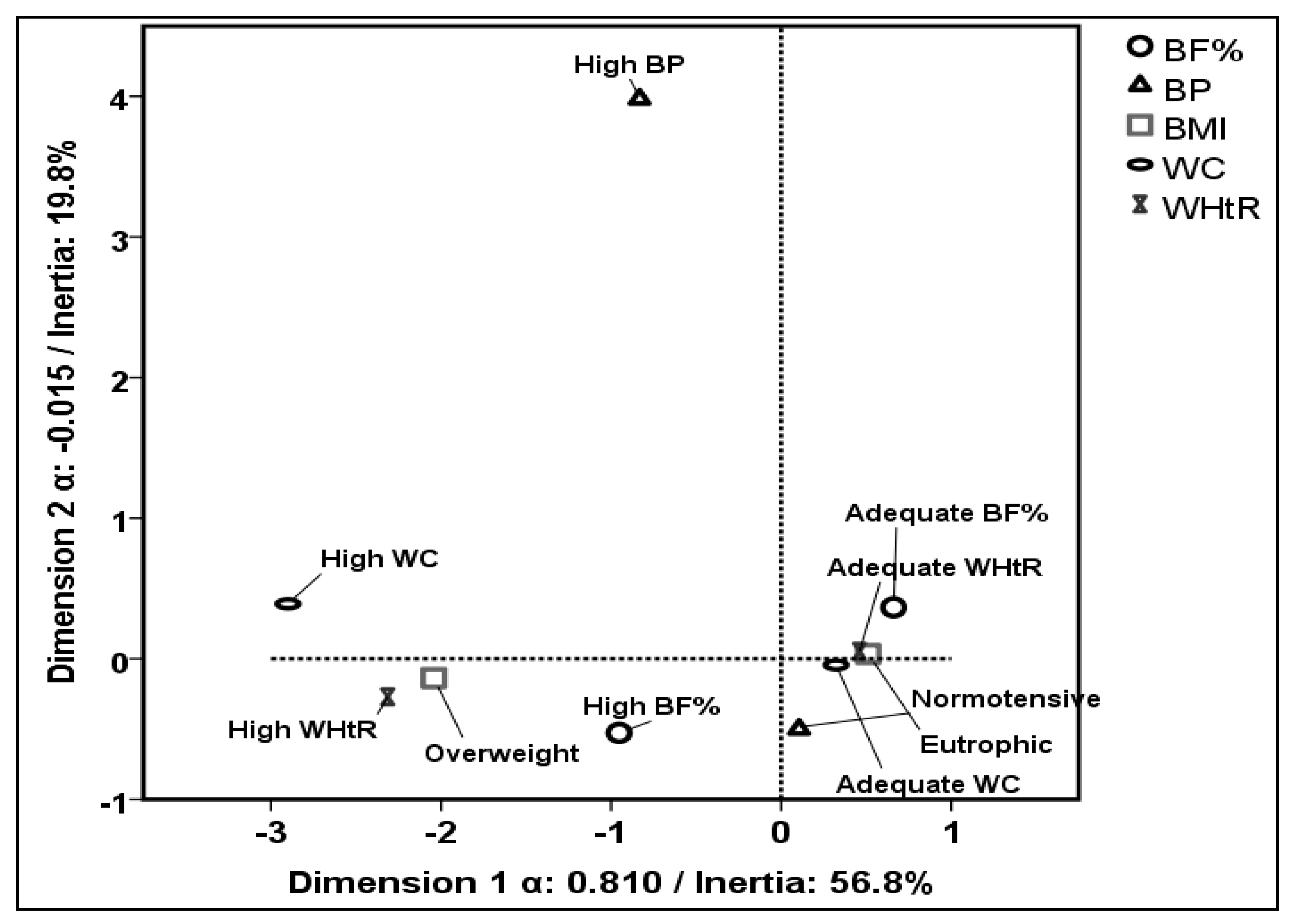
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CD | Cardiometabolic disease |
| WC | Waist circumference |
| BF% | Body fat percentage |
| WtHR | Waist-to-height ratio |
| SB | Sedentary behavior |
| ST | Screen time |
| LCA | Latent class analysis |
| FIESTTM | Federal Institute of Education, Science, and Technology of Triângulo Mineiro |
| BP | Blood pressure |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| MVPA | Moderate-to-vigorous physical activity |
| AIC | Akaike Information Criterion |
| BIC | Bayesian Information Criterion |
| DF | Degree of Freedom |
| χ2 | Pearson’s Goodness-of-Fit |
| G2 | Likelihood Ratio Deviance Statistic |
References
- Chatterjee, A.; Harris, S.B.; Leiter, L.A.; Fitchett, D.H.; Teoh, H.; Bhattacharyya, O.K. Managing cardiometabolic risk in primary care: Summary of the 2011 consensus statement. Can. Fam. Physician Med. Fam. Can. 2012, 58, 389–393, e196–201. [Google Scholar]
- Okosun, I.S.; Seale, J.P.; Boltri, J.M.; Davis-Smith, M. Trends and Clustering of Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in American Adolescents From 1999 to 2008. J. Adolesc. Health 2012, 50, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Précoma, D.B.; Oliveira, G.M.M.; Simão, A.F.; Dutra, O.P.; Coelho-Filho, O.R.; Izar, M.C.d.O.; Póvoa, R.M.d.S.; Giuliano, I.d.C.B.; Filho, A.C.d.A.; Machado, C.A.; et al. Updated Cardiovascular Prevention Guideline of the Brazilian Society of Cardiology—2019. Arq. Bras. Cardiologia 2019, 113, 787–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Melo, E.M.F.S.; Azevedo, G.D.; da Silva, J.B.; Lemos, T.M.A.M.; Maranhão, T.M.O.; Freitas, A.K.M.S.O.; Spyrides, M.H.; Costa, E.C. Clustering of risk factors for cardiometabolic diseases in low-income, female adolescents. Arch. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 60, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristi-Montero, C.; Chillón, P.; Labayen, I.; Casajus, J.A.; Gonzalez-Gross, M.; Vanhelst, J.; Manios, Y.; Moreno, L.A.; Ortega, F.B.; Ruiz, J.R.; et al. Cardiometabolic risk through an integrative classification combining physical activity and sedentary behavior in European adolescents: HELENA study. J. Sport Health Sci. 2019, 8, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloch, K.V.; Klein, C.H.; Szklo, M.; Kuschnir, M.C.C.; Abreu, G.d.A.; Barufaldi, L.A.; da Veiga, G.V.; Schaan, B.; da Silva, T.L.N.; Moraes, A.J.P.; et al. ERICA: Prevalences of hypertension and obesity in Brazilian adolescents. Rev. Saúde Pública 2016, 50 (Suppl. S1), 9s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuschnir, M.C.C.; Bloch, K.V.; Szklo, M.; Klein, C.H.; Barufaldi, L.A.; Abreu, G.d.A.; Schaan, B.; da Veiga, G.V.; da Silva, T.L.N.; de Vasconcellos, M.T.L.; et al. ERICA: Prevalence of metabolic syndrome in Brazilian adolescents. Rev. Saúde Pública 2016, 50 (Suppl. S1), 11s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Pádua Cintra, I.; De Moraes Ferrari, G.L.; De Sousa Vieira Soares, A.C.; Passos, M.A.Z.; Fisberg, M.; De Souza Vitalle, M.S. Body fat percentiles of Brazilian adolescents according to age and sexual maturation: A cross-sectional study. BMC Pediatr. 2013, 13, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kromeyer-Hauschild, K.; Neuhauser, H.; Schaffrath Rosario, A.; Schienkiewitz, A. Abdominal Obesity in German Adolescents Defined by Waist-to-Height Ratio and Its Association to Elevated Blood Pressure: The KiGGS Study. Obes. Facts 2013, 6, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evenson, K.R.; Herring, A.H.; Wen, F. Accelerometry-Assessed Latent Class Patterns of Physical Activity and Sedentary Behavior With Mortality. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2017, 52, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, G.P.; Evenson, K.R.; Herring, A.H.; Hales, D.; Stevens, J. Cardiometabolic Correlates of Physical Activity and Sedentary Patterns in U.S. Youth. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2017, 49, 1826–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Council on Communications and Media; Strasburger, V.C.; Hogan, M.J.; Mulligan, D.A.; Ameenuddin, N.; Christakis, D.A.; Cross, C.; Fagbuyi, D.B.; Hill, D.L.; Levine, A.E.; et al. Children, Adolescents, and the Media. Pediatrics 2013, 132, 958–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, V.P.N.; Dos Santos Amorim, P.R.; Bastos, R.R.; Souza, V.G.B.; De Faria, E.R.; Do Carmo Castro Franceschini, S.; Priore, S.E. Evaluation of lifestyle of female adolescents through latent class analysis approach. BMC Public Health 2019, 19, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biddle, S.J.H.; Pearson, N.; Ross, G.M.; Braithwaite, R. Tracking of sedentary behaviours of young people: A systematic review. Prev. Med. 2010, 51, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallal, P.C.; Victora, C.G.; Azevedo, M.R.; Wells, J.C.K. Adolescent Physical Activity and Health: A Systematic Review. Sports Med. 2006, 36, 1019–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Llamosas-Falcón, L.; Kerr, W.C.; Rehm, J.; Probst, C. Behavioral risk factors and socioeconomic inequalities in ischemic heart disease mortality in the United States: A causal mediation analysis using record linkage data. PLoS Med. 2024, 121, e1004455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, M.; Paganin, S.; Ohn, I.; Lin, L. Bayesian nonparametric latent class analysis with different item types. Psychol Methods 2025. online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, V.P.N.; Coimbra, D.R.; Bastos, R.R.; Miranda Júnior, M.V.; Amorim, P.R.D.S. Use of latent class analysis as a method of assessing the physical activity level, sedentary behavior and nutritional habit in the adolescents’ lifestyle: A scoping review. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0256069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caetano, I.T.; Miranda, V.P.N.; Dos Santos, F.K.; Amorim, P.R.D.S. Ecological correlates related to adolescent movement behaviors: A latent class analysis. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0271111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, V.P.N.; Amorim, P.R.d.S.; Bastos, R.R.; Canabrava, K.L.R.; Júnior, M.V.M.; Faria, F.R.; Franceschini, S.D.C.C.; Peluzio, M.D.C.G.; Priore, S.E. Association of Lifestyle and Body Composition on Risk Factors of Cardiometabolic Diseases and Biomarkers in Female Adolescents. Mediat. Inflamm. 2020, 2020, 9170640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, V.S.D.; Vieira, M.F.S. International Society for the Advancement of Kinanthropometry (ISAK) Global: International accreditation scheme of the competent anthropometrist. Rev. Bras. Cineantropometria Desempenho Hum. 2020, 22, e70517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohman, T.G. Assessing Fat Distribution; Advances in Body Composition Assessment: Current Issues in Exercise Science; Human Kinects: Champaign, IL, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Slaughter, M.H.; Lohman, T.G.; Boileau, R.A.; Horswill, C.A.; Stillman, R.J.; Van Loan, M.D.; Bemben, D.A. Skinfold equations for estimation of body fatness in children and youth. Hum Biol. 1988, 60, 709–723. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.; Wiese, R.; Allen, S.; Nicolay, C. IDF2022-0417 BMI category changes and percent meeting waist circumference goals with tirzepatide for type 2 diabetes from SURPASS 1-4. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2023, 197, 110308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashwell, M.; Hsieh, S.D. Six reasons why the waist-to-height ratio is a rapid and effective global indicator for health risks of obesity and how its use could simplify the international public health message on obesity. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2005, 56, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guedes, D.P.; Lopes, C.C.; Guedes, J.E.R.P. Reprodutibilidade E Validade Do Quest. Int. De Atividade Física Em adolescentes. Rev. Bras. Med. Do Esporte 2005, 11, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, I.; LeBlanc, A.G. Systematic review of the health benefits of physical activity and fitness in school-aged children and youth. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2010, 7, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Global Recommendations on Physical Activity for Health; Recommandations Mondiales Sur L’activité Physique Pour la Santé; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Faria, F.R.D.; Neves Miranda, V.P.; Howe, C.A.; Sasaki, J.E.; Dos Santos Amorim, P.R. Behavioral classes related to physical activity and sedentary behavior on the evaluation of health and mental outcomes among Brazilian adolescents. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0234374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paruthi, S.; Brooks, L.J.; D’Ambrosio, C.; Hall, W.A.; Kotagal, S.; Lloyd, R.M.; Malow, B.A.; Maski, K.; Nichols, C.; Quan, S.F.; et al. Recommended Amount of Sleep for Pediatric Populations: A Consensus Statement of the American Academy of Sleep Medicine. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2016, 12, 785–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ABEP—Associação Brasileira de Empresas de Pesquisa—2003—www.abep.org—abep@abep.org Dados com Base no Levantamento Sócio Econômico—2000—IBOPE. (n.d.). Available online: https://www.abep.org (accessed on 19 November 2024).
- Linzer, D.A.; Lewis, J.B. poLCA: An R Package for Polytomous Variable Latent Class Analysis. J. Stat. Softw. 2011, 42, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenhard, W.; Lenhard, A. Calculation of Effect Sizes; Psychometrica: Dettelbach, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Menon, S.; Philipneri, A.; Ratnasingham, S.; Manson, H. The integrated role of multiple healthy weight behaviours on overweight and obesity among adolescents: A cross-sectional study. BMC Public Health 2019, 19, 1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramires, V.V.; Dumith, S.C.; Gonçalves, H. Longitudinal Association Between Physical Activity and Body Fat During Adolescence: A Systematic Review. J. Phys. Act. Health 2015, 12, 1344–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu, S.; Santos, R.; Moreira, C.; Santos, P.C.; Mota, J.; Moreira, P. Food consumption, physical activity and socio-economic status related to BMI, waist circumference and waist-to-height ratio in adolescents. Public Health Nutr. 2014, 17, 1834–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jodar, E.; Dib, A.; Bray, R.; Zeytinoglu, M.; Rodriguez, A.; Brown, K. IDF2022-0540 Impact of weight on Time in Range, Time in Tight Range, and Glycemic Variability as measured using CGM (SURPASS-3 CGM). Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2023, 197, 110312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okunogbe, A.; Nugent, R.; Spencer, G.; Powis, J.; Ralston, J.; Wilding, J. Economic impacts of overweight and obesity: Current and future estimates for 161 countries. BMJ Glob. Health 2022, 7, e009773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, S.D.; Ashwell, M.; Muto, T.; Tsuji, H.; Arase, Y.; Murase, T. Urgency of reassessment of role of obesity indices for metabolic risks. Metabolism 2010, 59, 834–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strasburger, V.C.; Council on Communications and Media. Children, Adolescents, Obesity, and the Media. Pediatrics 2011, 128, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey-López, J.P.; Ruiz, J.R.; Vicente-Rodríguez, G.; Gracia-Marco, L.; Manios, Y.; Sjöström, M.; De Bourdeaudhuij, I.; Moreno, L.A.; HELENA Study Group. Physical activity does not attenuate the obesity risk of TV viewing in youth. Pediatr. Obes. 2012, 7, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, J.S.; Barufaldi, L.A.; Abreu, G.d.A.; Leal, V.S.; Brunken, G.S.; Vasconcelos, S.M.L.; dos Santos, M.M.; Bloch, K.V. ERICA: Use of screens and consumption of meals and snacks by Brazilian adolescents. Rev. Saúde Pública 2016, 50 (Suppl. S1), 7s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, M.; Todd, C.; Scott, S.; Stratton, G.; McCoubrey, S.; Christian, D.; Halcox, J.; Audrey, S.; Ellins, E.; Anderson, S.; et al. Teenage recommendations to improve physical activity for their age group: A qualitative study. BMC Public Health 2018, 18, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, D.; Kim, Y.; Jang, H.; Oh, H. Screen time and obesity prevalence in adolescents: An isotemporal substitution analysis. BMC Public Health 2024, 24, 3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brazil. Law No. 15,100, of 13 January 2025. Regulates the Use of Personal Portable Electronic Devices by Students in Public and Private Basic Education Institutions. Official Gazette of the Union. 14 January 2025. Available online: https://www2.camara.leg.br/legin/fed/lei/2025/lei-15100-13-janeiro-2025-796892-publicacaooriginal-174094-pl.html (accessed on 3 April 2025).


| Number of Classes | AIC | BIC | DF | χ2 | G2 | p-G2 | Entropy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 Classes | 1194.32 | 1236.73 | 11 | 29.01 | 32.24 | 0.04 | 0.91 |
| 3 Classes * | 1186.06 | 1251.59 | 14 | 17.10 | 11.97 | 0.61 | 0.88 |
| 4 Classes | 1191.25 | 1279.91 | 8 | 9.86 | 5.17 | 0.74 | 0.93 |
| 5 Classes | 1198.22 | 1310.02 | 2 | 0.08 | 0.15 | 0.93 | 0.78 |
| α (Intercept) | Moderate Risk/Low Risk | |||||
| β(Coefficient) | SE | Odds Ratio | CI (95%) | p-Value | ||
| Female † | 2.33 | 0.67 | 10.28 | 2.77 | 38.09 | 0.004 ** |
| High ST (25th P) ‡ | 0.07 | 0.27 | 1.07 | 0.63 | 1.82 | 0.790 |
| High SB ¥ | −1.06 | 1.32 | 0.34 | 0.02 | 4.61 | 0.439 |
| High Risk/Low Risk | ||||||
| β (Coefficient) | SE | Odds Ratio | CI (95%) | p-Value | ||
| Female † | 0.55 | 0.37 | 1.74 | 0.84 | 3.59 | 0.186 |
| High ST (25th P) ‡ | 1.48 | 0.50 | 4.39 | 1.64 | 11.07 | 0.013 * |
| High SB ¥ | 0.79 | 0.38 | 2.20 | 1.05 | 4.61 | 0.062 |
| Variables | “Low Risk” Class | “Moderate Risk” Class | “High Risk” Class | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median | P25–P75 | Median | P25–P75 | Median | P25–P75 | ||
| Age (years) | 16 | 15–17 | 16 | 15–17 | 16 | 15–17 | 0.886 |
| MVPA (h/week) | 3 †† | 1–6 | 1.5 †† | 0.17–3.7 | 2 | 0.2–4.5 | 0.014 * |
| SB—Week days (h/day) | 11 | 9.5–13 | 10.5 | 9–12.5 | 12 | 9.3–14.5 | 0.402 |
| SB—Weekend days (h/day) | 9 † | 6–12 | 8 ‡ | 5.13–10.75 | 12 †‡ | 9.2–14.5 | 0.002 ** |
| SB 7 days (h) | 10.4 | 8.6–12.6 | 10 | 7.8–12.1 | 11.4 | 9.4–15.1 | 0.067 £ |
| Sleep Duration (h/day) | 7 | 6–7.5 | 6.5 | 5.12–7 | 6.5 | 6–7 | 0.060 ¥ |
| ST (h/day) | 6 | 4–9 | 6 | 4.6–11.5 | 6 | 5–10.12 | 0.112 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Faria, F.R.; Miranda, V.P.N.; Howe, C.; Sasaki, J.E.; Amato, A.; Musumeci, G.; Amorim, P.R.d.S. Cardiometabolic Disease Risk Factors and Lifestyle Behaviors Among Adolescents: A Latent Class Analysis. Healthcare 2025, 13, 925. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13080925
de Faria FR, Miranda VPN, Howe C, Sasaki JE, Amato A, Musumeci G, Amorim PRdS. Cardiometabolic Disease Risk Factors and Lifestyle Behaviors Among Adolescents: A Latent Class Analysis. Healthcare. 2025; 13(8):925. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13080925
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Faria, Fernanda Rocha, Valter Paulo Neves Miranda, Cheryl Howe, Jeffer Eidi Sasaki, Alessandra Amato, Giuseppe Musumeci, and Paulo Roberto dos Santos Amorim. 2025. "Cardiometabolic Disease Risk Factors and Lifestyle Behaviors Among Adolescents: A Latent Class Analysis" Healthcare 13, no. 8: 925. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13080925
APA Stylede Faria, F. R., Miranda, V. P. N., Howe, C., Sasaki, J. E., Amato, A., Musumeci, G., & Amorim, P. R. d. S. (2025). Cardiometabolic Disease Risk Factors and Lifestyle Behaviors Among Adolescents: A Latent Class Analysis. Healthcare, 13(8), 925. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13080925










