Abstract
This study synthesized pristine and aluminum (Al)-doped zinc oxide (Al:ZnO) nanostructures through a simplistic low-temperature ultrasonicated solution immersion method. Al:ZnO nanostructures were synthesized as a sensing material using different immersion times varying from two to five hours. The Al:ZnO nanostructured-based flexible humidity sensor was fabricated by employing cellulose filter paper as a substrate and transparent paper glue as a binder through a simplistic brush printing technique. XRD, FESEM, HRTEM, EDS, XPS, a two-probe I–V measurement system, and a humidity measurement system were employed to investigate the structural, morphological, chemical, electrical, and humidity-sensing properties of the pristine ZnO and Al:ZnO nanostructures. The structural and morphological analysis confirmed that Al cations successfully occupied the Zn lattice or integrated into interstitial sites of the ZnO lattice matrix. Humidity-sensing performance analysis indicated that the resistance of the Al:ZnO nanostructure samples decreased almost linearly as the humidity level increased, leading to better sensitivity and sensing response. The Al:ZnO-4 h nanostructured-based flexible humidity sensor had a maximum sensing response and demonstrated the highest sensitivity towards humidity changes, which was noticeably superior to the other tested samples. Finally, this study explained the Al:ZnO nanostructures-based flexible humidity sensor sensing mechanism in terms of chemical adsorption, physical adsorption, and capillary condensation mechanisms.
1. Introduction
Throughout the past decade, there has been an ever-increasing necessity for efficient environmental humidity surveillance in numerous scientific and industrial sectors including those associated with weather forecasting, medical and semiconductor instruments, agriculture and horticultural cultivation, the aeronautical field, and various commercial manufacturing operations, which has substantially accelerated the pursuit for high-performance and reliable humidity-sensing material [1,2]. Consequently, there has been an upsurge in interest for a humidity sensor with higher responsiveness, swift adsorption/desorption rate of changes, and improved selectivity. Furthermore, the humidity sensor must possess resilience in extreme climatic conditions and more enhanced stability and reproducibility for long-term application than presently offered by the commercial sensors [3]. Resistive-type humidity sensors are frequently manufactured and utilized to fulfill these objectives due to their optimal linearity, high responsiveness, acceptable operational stability and reproducibility over time, relatively uncomplicated architecture, and affordability in terms of manufacturing pricing [4]. A resistive-type humidity sensor is constructed by coating a substrate with a humidity-sensitive sensing material. The effectiveness and performance of a humidity sensor are entirely reliant on the humidity-sensitive sensing material. Therefore, humidity-sensitive sensing materials for resistive-type humidity sensors based on relative humidity (RH) detection are widely used and can be categorized as ceramic, metal oxide semiconductor, and polymer sensing materials [5]. It is worth revealing that compared to ceramic and polymer-type sensing materials, the metal oxide (MO) humidity sensor provides exceptional structural attributes (i.e., large specific surface area and roughness), excellent humidity-sensing performance (i.e., excellent sensitivity, linear responsiveness, swift response and recovery latency, and/or excellent reproducibility), facile fabrication procedure, and offers chemical and physical strength [6,7]. Therefore, MO humidity sensors are recognized as the most reliable for detecting a broad range of humidity levels.
According to the literature, the MOs that are often employed as humidity sensors include zinc oxide (ZnO), copper oxide (CuO and Cu2O), tin oxide (SnO and SnO2), iron oxide (Fe2O3), nickel oxide (NiO), and titanium oxide (TiO2) [8,9,10,11,12]. Given its exceptional chemical, electrical, and physical functionality, ZnO is regarded as one of the acceptable candidates for humidity detection and monitoring instruments compared to the abovementioned Mos. ZnO is established as a multifunctional and beneficial MO semiconductor with a large exciton binding energy (approximately 60 meV) and exhibits a direct energy band gap (3.37 eV at 300 K). Furthermore, due to its morphological heterogeneity, remarkable crystallinity, non-toxic presence, abundant raw material, and exceptional surface porosity, ZnO is an exceedingly effective material for humidity detection and monitoring instruments. There are various techniques for synthesizing ZnO nanostructure materials, including homogeneous precipitation and co-precipitation, solvothermal and hydrothermal, sol–gel processing, and electrochemical methods [13,14,15,16,17]. Recently, it was reported that ZnO was doped with a variety of elements such as lithium (Li) [18], nickel (Ni) [19], iron (Fe) [20], gold (Au) [21], and silver (Ag) [22] for various applications such as an ultraviolet photodetector, photocatalysis, gas sensor, and piezoelectric nanogenerator.
Classical humidity sensors are often constructed on rigid and inflexible substrates [23,24,25], which have some drawbacks including easy electrode cracking, sensitive layer deformation, reduction in stability, and a lack of structural properties, limiting their application comprehensiveness. However, there is a wide range of flexible substrate materials, such as polyethylene terephthalate (PET) [26], polyimide (PI) [27], and cellulose/paper [28]. These materials have attracted attention due to their competitive prices, mechanical flexibility, and biocompatibility. Among the abovementioned flexible substrate materials, paper components have sparked an upsurge in both academic and commercial curiosity in flexible electronics, owing to structural features, desirable mechanical and chemical flexibility, cost-effectiveness, widespread availability, seasoned manufacturing techniques, biocompatibility, recyclability, and chemical inertness [29,30]. For instance, a paper-based humidity-sensing device was fabricated by Niarchos et al. [28]. Their study discovered that plain paper with a porous and rough surface had better sensitivity and a rapid response time, demonstrating the possibility of improving humidity-sensing capability without using auxiliary sensing materials. In another work, Alrammouz et al. constructed a flexible humidity sensor utilizing a simple self-assembly process that embedded a graphene oxide sensing membrane in a porous paper substrate which was reported to increase the sensibility of paper by three times [31].
Humidity sensors manufactured from ZnO nanostructures provide a substantial specific surface area, numerous adsorption active sites, higher electron transport due to an abundance of free carriers, and high porosity. These features improve surface interactions between water molecules and the semiconductor material [32]. For instance, Tsai and Wang reported in the range of 12–96 %RH, and the efficiency of employing laterally oriented ZnO nanosheets as humidity sensors is enhanced with good sensing linearity and improved sensing response [33]. Park et al. utilized electrochemical deposition by chronoamperometry to produce a humidity sensor based on a ZnO nanowire with a sensitivity of 0.89 at a 7.76% humidity level [34]. In addition, Yu et al. demonstrated that a ZnO humidity sensor synthesized in an alkaline environment exhibited acceptable linearity and rapid response/recovery time when tested under diverse humidity conditions [35]. However, a humidity sensor based on pristine ZnO suffers from a multitude of drawbacks, notably low free carriers and a high resistivity of the material, which cause lagging in resistance changes at high relative humidity levels [36]. Apart from that, humidity sensors fabricated from pristine ZnO have some limitations, such as low linearity, a lengthy recovery period, and observably suffering from significant large adsorption and desorption hysteresis [37]. Therefore, to enhance the humidity-sensing performance of pristine ZnO-based humidity sensors, dopant impurities are incorporated into pristine ZnO material. The inclusion of dopant impurities alters fundamental properties, which modifies structural attributes such as lattice parameter and crystallite size, mechanical attributes such as lattice strain and stress, electrical and optical parameters, particularly humidity-sensing performance, and invokes new functionalities. Reports regarding dopant introduction into pristine ZnO nanostructures in premise to improve humidity-sensing-related attributes have been recorded in previous studies. For instance, a relative humidity sensor using tapered plastic optical fiber (POF) coated with seeded Al-doped ZnO nanostructures was suggested and demonstrated by Harith et al. [38]. Employing mechanical etching, the POF was tapered before being coated with seeded Al-doped ZnO nanostructures using a sol–gel immersion route. In the range of 50–75 %RH, the POF with seeded Al-doped ZnO demonstrated a sensitivity of 0.0386 mV/% and slope linearity of 97.84% compared to other samples, with the recorded performance being far superior to those recorded by undoped and unseeded POF sensors. In another study, Ismail et al. analyzed the characteristics of the hierarchical tin-doped ZnO nanorod array (SZO) based on resistive-type humidity sensor applications using the sonicate sol–gel immersion method [39]. The presence of more voids between the nanorods facilitated the capillary condensation at a higher humidity level; thus, the SZO-based humidity sensor’s sensitivity was better compared to the undoped sample. At 40–70 %RH and 70–90 %RH, the sensitivities were 3.41 and 1.41, respectively. Additionally, the response and recovery periods of the SZO-based humidity sensor were also enhanced compared to undoped ZnO due to the easier transmission of charge carriers across the surface. Apart from that, the outcome additionally revealed that the doped device’s humidity-sensing activity was reversible, with rapid response, excellent repeatability, and higher stability. Recently, pure ZnO and Au nanoparticle-modified (ANM) ZnO nanorods-based humidity sensors were fabricated using glass via a two-step procedure that involved sputtering deposition of the ZnO seed layer followed by the hydrothermal method by Young and his colleagues [40]. The photo-to-dark current contrast ratios, response time, and recovery time were 9.82 s, 192.44 s, and 122.42 s, respectively, under 80 %RH. Its performance was better than pure ZnO-based humidity sensors. Moreover, the study suggested that the Au nanoparticles adsorption could have been the cause of the ANM ZnO nanorods-based humidity sensor outperforming the pure ZnO nanorods humidity sensor in terms of humidity-sensing performance. In the most recent work conducted by Li et al., utilizing a hydrothermal synthesis route, the humidity sensors were made from sensitive sensing material silver (Ag) and modified zinc oxide (ZnO) [41]. The result showed that the sensors possessed high sensitivity, improved linearity, less adsorption/desorption hysteresis, minimal lag error, and rapid response/recovery time. This improvement could be attributed to the uniformly dispersed Ag particles on ZnO that induced immense active sites on the surface and more oxygen vacancies, allowing more water molecules to be captured and the decomposition, hence improving humidity sensor performance. In addition, Dubey et al. reported that the humidity sensor based on the aluminum (Al)-doped ZnO thin film sensing membrane prepared via the chemical sol–gel spin-coating method exhibited reduced hysteresis degradation, minimal aging impact, better reproducibility, and excellent sensitivity [42]. The study discovered that the Al-doped ZnO thin film’s sensing membranes were a highly developed nanomaterial for humidity sensing compared to undoped ZnO; hence, by optimizing the Al dopant concentration, the sensor performance can be noticeably improved.
Although several investigations on the morphological and structural characteristics of Al-doped ZnO structures have been conducted, comprehensive studies on the humidity-sensing capabilities of these nanostructures are limited. Moreover, it is critical to optimize the process parameters of synthesizing Al-doped ZnO nanostructures, such as growth time, Al dopant concentration, growth temperature, and annealing temperature. Several studies on the synthesis of Al-doped ZnO have previously been executed. Nevertheless, to the best of authors’ knowledge, the process of synthesizing Al-doped ZnO nanostructured powder using a Schott bottle employing the low-temperature ultrasonicated solution immersion procedure and being utilized notably for flexible humidity-sensor applications has not yet been reported. Moreover, a thorough investigation needs to be performed regarding the effects of synthesis growth time on the crystalline properties (i.e., strain formation), surface morphological characteristics and topology, elemental composition and electronic/chemical state of elements, electrical properties (i.e., conduction mechanism), and humidity-sensing performance of an Al-doped ZnO (Al:ZnO)-based flexible humidity sensor. Herein, in this study, we explored the influence of optimizing the immersion time for Al dopant assimilation on the structural, elemental analysis, electrical, and humidity-sensing performance of an Al-doped ZnO nanostructures (Al:ZnO) flexible resistive-type humidity sensor. The humidity-sensitive sensing material was produced by a simplistic low-temperature ultrasonicated solution immersion method. Utilizing cellulose filter paper as the substrate, a resistive-type humidity sensor based on Al:ZnO nanostructures (Al:ZnO) and humidity-sensitive sensing material with varied immersion time was fabricated using a straightforward, inexpensive, and time-saving brush printing approach. The cellulose filter paper was used as the flexible substrate. The amalgamation Al:ZnO structural properties (i.e., morphology, atomic structure, and crystalline properties), surface chemical (i.e., elemental composition analysis and chemical/electronic state), electrical (i.e., current-voltage measurement and conduction mechanism), and humidity-sensing response were comprehensively explored. In comparison to pristine ZnO nanostructures, the humidity-sensing properties of Al-doped ZnO nanostructure sensors delivered excellent sensitivity, repeatability, and satisfactory long-term stability. The sensor performance can be drastically enhanced by optimizing the Al-doping immersion time in ZnO nanostructures for actual humidity-sensing device applications.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Amalgamation of Humidity-Sensitive Nanostructured Powders
Each of the reagents employed to synthesize the Al-doped ZnO nanostructured powders was of analytical quality and directly employed without additional purification. These consisted of zinc nitrate hexahydrate (Zn(NO3)2·6H2O, 98.5%, Friendemann Schmidt Chemicals, Germany) as starting precursor material, hexamethylenetetramine (HMT) (C6H12N4, 99% purity, Sigma-Aldrich, Germany), and aluminum nitrate nonahydrate (Al(NO3)3·9H2O, 98% purity, Sigma-Aldrich, Germany), which were treated as the stabilizer agent and doping element source, respectively. Implementing the simplistic ultrasonicated solution immersion procedure, the Al-doped ZnO nanostructured powders were synthesized. For the synthesized Al-doped ZnO nanostructured powder, a beaker containing solvent (deionized (DI) water) was used as a dispersion medium for an aqueous solution comprising 0.1 M zinc nitrate hexahydrate, 0.1 M hexamethylenetetramine (HMT), and 1 at.% aluminum nitrate nonahydrate. To promote chemical dispersibility and homogenization, the sonication procedure was utilized via an ultrasonic bath (Hwashin Technology Powersonic 405, South Korea, 40 kHz, 50 °C, 30 min) for the mixture comprising the precursor, stabilizers, dopant, and solvent; further, the mixture was agitated on a magnetized stirrer for 15 min at 200 rpm in ambient condition, culminating a homogeneous mixture. Sequentially, the homogeneity mixture was poured into a Schott bottle (DURAN, Germany, 100 mL). Using widely accessible polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) sealing film, the bottle threads were then sealed to guarantee that the pressure within the bottle was maintained consistently during the immersion stage. Before the immersion procedure, the bottle cap was tightly closed followed by submersion in a water bath (Memmert, Germany, WNB 14, 95 °C, 4 h). These abovementioned procedures were repeated for different immersion times of 2 h, 3 h, and 5 h, respectively. Following the immersion procedure, the temperature of the water bath was supervised to assure that the process’s temperature was maintained uniformly at 95 °C. The precipitates were recovered after the immersion was completed using a pipette and deposited on a crystallization plate. To eliminate excessive water molecules, the nanoparticles were dried in the air at 40 °C for 24 h. The dehydrated nanoparticle powders acquired from the preceding procedure were then annealed utilizing a benchtop chamber furnace (Protherm, Turkey, PLF Series, 500 °C, 1 h, ambient environment) to improve crystallinity. The sample was renamed as Al:ZnO-4 h nanostructured powder. The processes for preparing the undoped ZnO nanostructured powders (referred to as pristine ZnO) were identical to the Al:ZnO-4 h nanostructured powder procedures, except that the solution was prepared in the absence of the aluminum nitrate nonahydrate element.
2.2. Fabrication of the Flexible Humidity Sensor
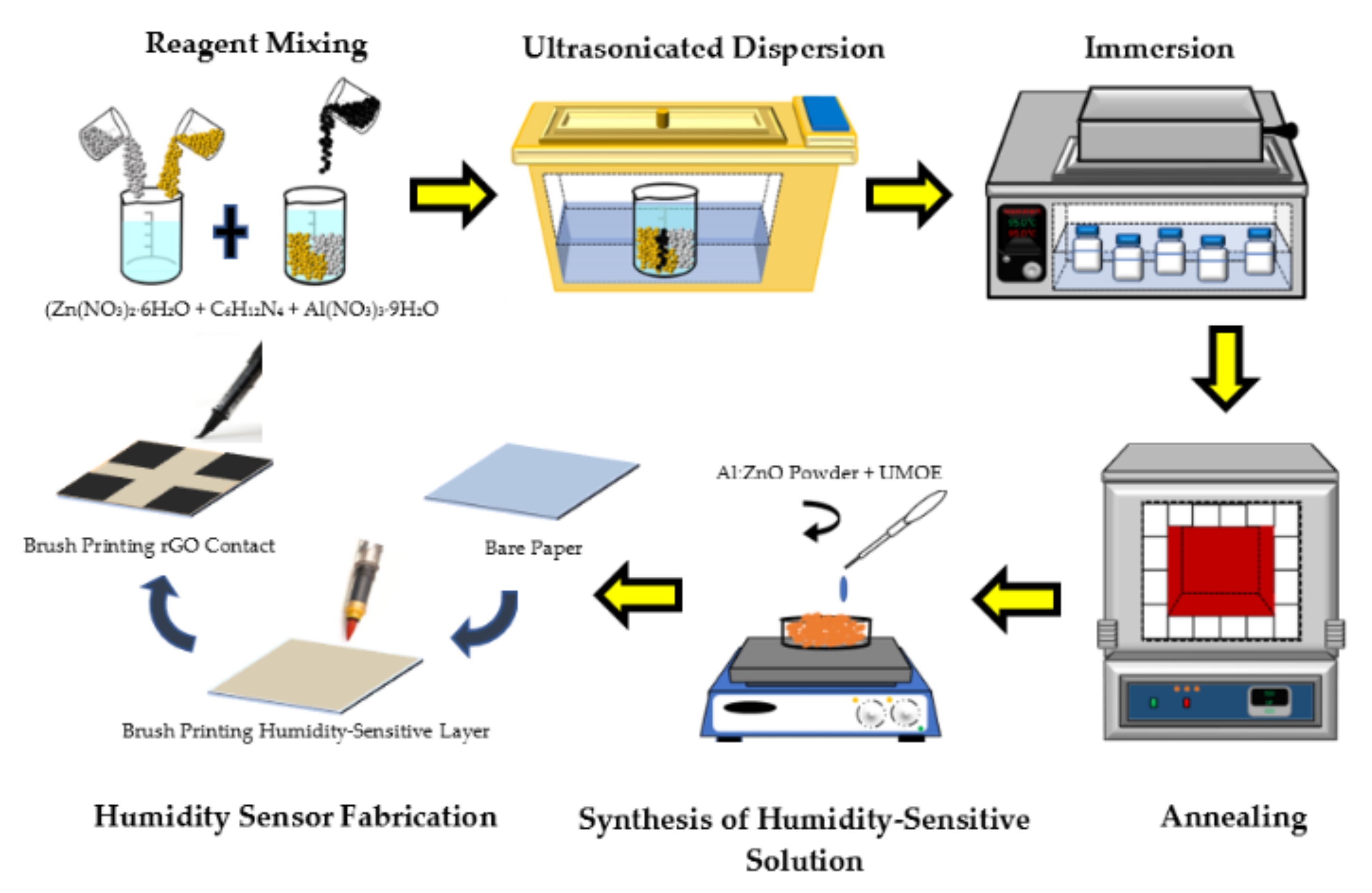
The flexible humidity sensor was fabricated by employing a straightforward and time-saving approach [43]. A 10 mm × 10 mm Whatman Qualitative Grade 1 (thickness: 180 μm, weight: 87 g/m2) cellulose filter paper was utilized as a flexible substrate. A commercial printer was applied to print a 3 mm × 3 mm square pattern which served as a contact, with the distance between the contacts set at 4 mm. The Al:ZnO-4 h nanostructured powder (1 g) was disseminated in 5 mL of transparent paper glue (UMOE, Malaysia) to produce a humidity-sensitive sensing material solution. In this manner, the transparent glue functioned as a binder. The mixture was stirred for 30 min at 300 rpm to achieve a homogenous paste. Consecutively, utilizing the brush printing approach, a layer of the sensing membrane was formed. A paste-like nanocomposite slurry of humidity-sensitive sensing material (Al:ZnO-4 h) was brushed on a cellulose substrate. Before the functional electrode was deposited on the humidity-sensitive sensing film, the freshly smeared humidity-sensitive sensing membrane was cured for 15 min at room temperature. In order to produce the functional electrode, rGO powder (Suzhou Hengqiu Co., Ltd., China, 0.5 g) was incorporated with transparent paper glue (15 mL), and the combination was vigorously whisked until a homogenous paste was created. The resultant paste was uniformly painted on cellulose substrate containing humidity-sensitive sensing material and utilizing the brush printing approach, and then it was air cured for 30 min. Figure 1 depicts the schematic diagram of the preparation procedure of Al:ZnO-based humidity sensor. An identical process was performed to manufacture the remaining humidity sensors, which were labelled as “pristine ZnO”, “Al:ZnO-2 h”, “Al:ZnO-3 h”, and “Al:ZnO:5 h”.
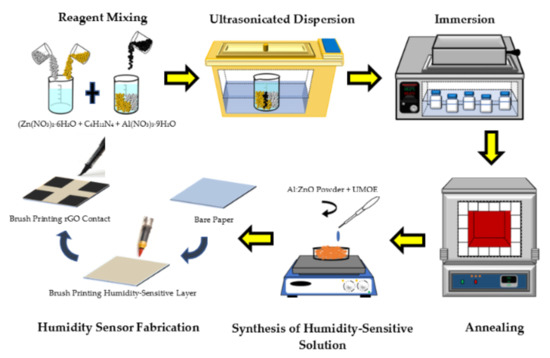
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of Al:ZnO-based humidity sensor preparation procedure.
2.3. Characterization
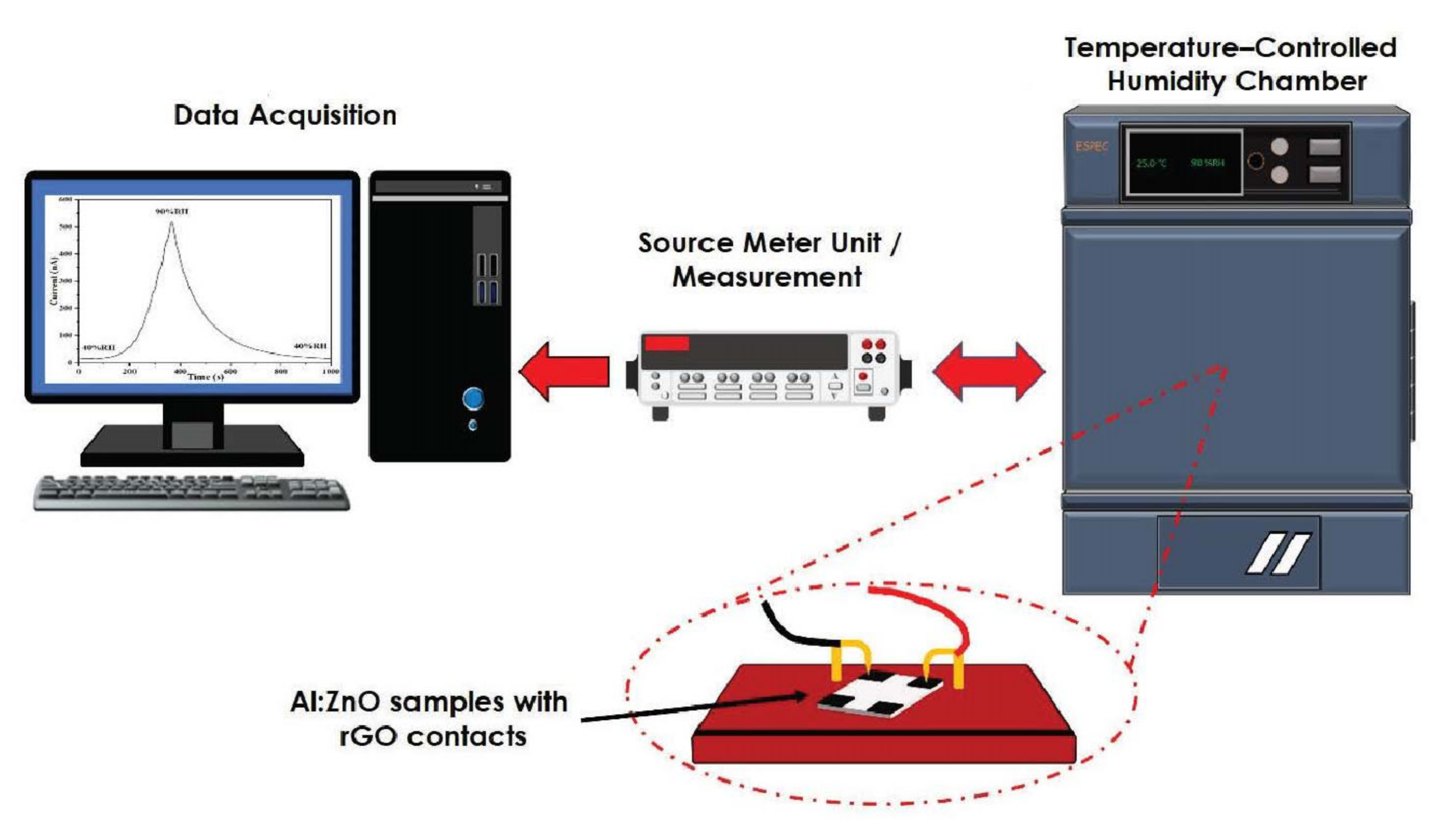
The microstructure morphology studies and elemental composition analysis for the pristine ZnO and Al:ZnO nanostructures were conducted by employing field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM; Hitachi SU-8030, Japan; accelerating voltage: 5 kV) and high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM, Tecnai G2 TF20; accelerating voltage: 200 kV). X-ray diffraction (XRD; PANalytical X’Pert PRO, Netherlands; Cu-Kα1: 1.5406 Å, beam voltage/current: 45-kV/40-mA) was employed to explore the crystallography configuration and phase generation of the nanostructures with the 2θ ranging from 20° to 70° (step size of 0.017°). The elemental composition and mapping of the humidity-sensitive sensing materials were evaluated utilizing high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM, Tecnai G2 20 S-TWIN, Netherlands: accelerating voltage: 200 kV). The chemical composition and element state of the humidity-sensitive sensing materials were investigated through an X-ray photoelectron spectrometer (XPS; PHI Quantera II, Japan; voltage source: 15 kV, beam power/size: 50 W/200 μM). The spectrometer had an excitation source originating from monochromatic radiation of Al-Kα (1486.6 eV). The electricity attributes were evaluated at an ambient temperature through the voltage sweep from −10 V to +10 V, adopting a two-probe, current-voltage measurement tool (I–V; Advantest R6243, Japan). To assess the humidity-sensing capability and functionality of pristine ZnO and Al:ZnO nanostructured-based flexible humidity sensor, the quantification was conducted utilizing a temperature and humidity-controlled benchtop chamber (ESPEC-SH261, Japan) integrated with a measurement device (Keithley 2400, USA), where the chamber temperature was regulated at 25 °C. The changes in electrical current of the humidity sensor were continuously tracked by a Keithley 2400 Source Meter Unit (SMU), which has high-resolution current measuring capacities utilizing a constant voltage source. The humidity-sensing measurement system is depicted in Figure 2.
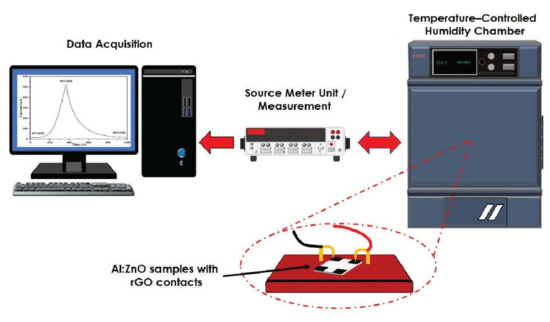
Figure 2.
Schematic diagram of the humidity-sensing measurement system analysis.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Structural and Morphological Characterization—XRD, FESEM, and TEM
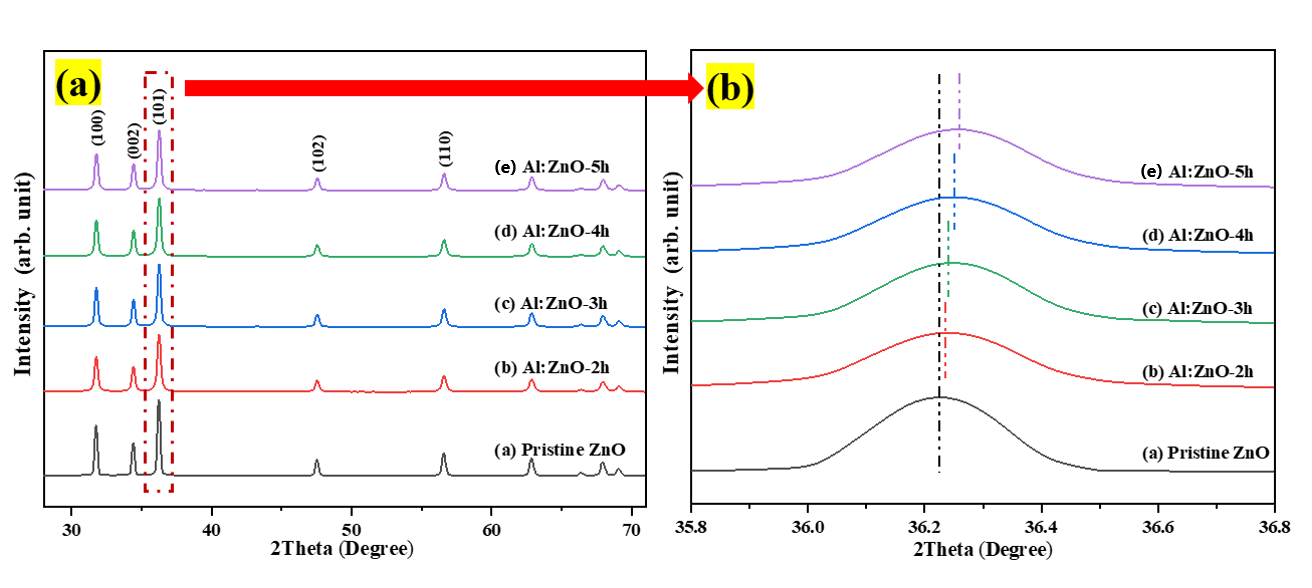
The crystal structure and various attributes related to the structure were determined using the XRD patterns of pristine ZnO and Al:ZnO nanostructured powders. Figure 3 depicts the XRD patterns of pristine ZnO and Al:ZnO nanostructured powders with different immersion times and produced using a low-temperature ultrasonicated solution immersion procedure. The XRD spectrum of pristine ZnO nanostructures exhibited diffraction angles for three primary peaks at 31.77°, 34.42°, and 36.25°, consistent with the lattice planes of (100), (002), and (101), respectively. Additionally, five weak peaks were identified at 47.51°, 56.57°, 62.87°, 67.95°, and 69.08°, implying the presence of the planes (102), (110), (103), (112), and (201) [44]. According to the JCPDS database: no. 36-1451, the wurtzite hexagonal structure of ZnO (space group P63mc), was associated with these diffraction peaks [45]. The existence of numerous distinctive peaks with strong intensities indicated that the polycrystalline structure of as-synthesized pure ZnO was preserved and existed in substantially high crystalline structures. The peak intensity diminished slightly with Al doping, indicating that the crystallinity of Al:ZnO nanostructured powder had been degraded, attributable to the inclusion of defects in the lattice site. Within the XRD examining conditions, no other secondary crystalline phases linked to Al, aluminum oxide (Al2O3), or other impurities were identified in any of the Al:ZnO samples, inferring that Al3+ successfully occupied Zn2+ sites or assimilated into interstitial sites in the ZnO lattice. Moreover, the absence of the secondary zinc aluminum oxide (ZnAl2O4) phase indicated that the Al solubility limit was not excessive [46].
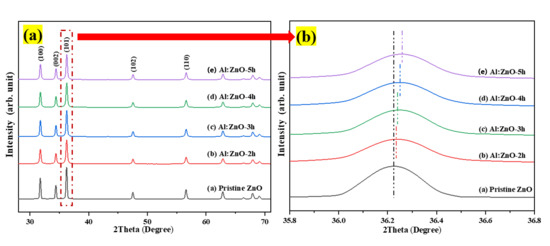
Figure 3.
(a) X-ray diffraction pattern of the pristine ZnO and Al:ZnO nanostructures with varying immersion time; (b) magnification of peak (101).
From the Debye–Scherrer equation, the average crystallite size (D) was assessed as shown in Equation (1) [47]:
where K is the dimensionless shape factor for the crystal (0.94), λ is the X-ray wavelength of CuKα radiation (equal to 1.5406 Å), θ is the assessed Bragg angle of the diffraction peak in degrees, and βDS is the full width at half maximum in radians that was obtained by Lorentz fitting. The calculated average crystallite size through the Debye–Scherrer expression is tabulated in Table 1.

Table 1.
Lattice parameters, average crystallite size, cell volume, and micro-strain for the pristine ZnO and Al:ZnO nanostructures calculated using the Debye–Scherrer method and Williamson–Hall uniform deformation model (WH-UDM).
The results demonstrated that doping Al into pristine ZnO decreased the crystalline size of the nanoparticles due to the substitution of Al for the Zn element. Noticeably, the full width at half maximum (FWHM) of all peaks for all Al:ZnO samples is greater than pristine ZnO. This observation indicated that Al:ZnO nanoparticles were smaller than observed in pristine ZnO. Furthermore, grain size variations can be associated with the FWHM; a smaller FWHM signified a larger grain size and better crystalline quality. The reduced crystallite size of the Al:ZnO samples indicated that the dopant ions restrained the growth of the host lattice. The crystallite size decreased monotonically with the presence of the Al element and hence further decrease with extending immersion time. The integration of Al reduced the amount of Zn in the nanostructures, lowering the diffusivity of ZnO and preventing the nucleation and grain growth in the nanostructures. Furthermore, the Al3+ ion served as an impeding factor at the grain boundary, impeding ZnO growth and decreasing crystallite size. These observations have also been reported in other literature [48,49]. The reduction in crystallite size culminates in an increase in surface area, which can significantly enhance the water molecules’ absorption activity [7]. According to Figure 3b, the XRD peaks shift towards a higher angle with the incorporation of the Al doping element. The diffracting angle of the (101) peak shifted slightly upwards with the increased immersion time, confirming the replacement of Al atoms into the Zn framework and reduction of the lattice parameter of Al:ZnO nanostructures. With reference to pristine ZnO, the displacement in peak positions, Δ(2θ) was determined to be approximately 0.013°, 0.027°, 0.031°, and 0.037° for Al:ZnO-2 h, Al:ZnO-3 h, Al:ZnO-4 h, and Al:ZnO-5 h, respectively. These angle shifts demonstrated that interactions occurred between the dopant and Zn in the lattice due to electronegativity differences (Zn: 1.65 Pauling, Al: 1.61 Pauling), which validated the dopant integration into the ZnO lattice framework. This positive shift in diffraction peaks for Al:ZnO samples also indicated a decrease in lattice parameters, indicating significant integration of dopant ions into the ZnO lattice framework. Similarly, this shifting was also highlighted by Kolhe et al. when a hydrogen sulphide gas sensor was constructed utilizing Al-doped ZnO as a sensing membrane through a simple chemical spray pyrolysis technique [50]. Similar findings were also reported by Yoo et al. as they synthesized Al-doped ZnO as a sensing material for an acetone-sensing chemo-resistive gas sensor using the flame spray pyrolysis method [51]. Consequently, the introduction of Al ions into the ZnO lattice may have induced crystal lattice distortion. The lattice parameters (a and c) of hexagonally structured ZnO nanostructures were calculated using Equations (2) and (3):
where dhkl is the interplanar spacing between the neighboring lattice planes for indices (hkl), and a and c are the lattice parameters whose values were calculated using Equation (3):
where λ is the X-ray wavelength, and θ is the diffracting angle correlated with the (100) and (002) plane orientations, respectively. The analytical approach mentioned above was employed to compute the lattice parameters a and c for pristine ZnO and Al:ZnO nanostructures. All Al:ZnO nanostructure samples had smaller lattice parameters than pristine ZnO nanostructures. Their values reduced as the immersion time increased from 2 h to 5 h.
However, the lesser lattice distortion observed for Al:ZnO-2 h implied that less Al was incorporated into the ZnO lattice. The plausible explanation for this phenomenon was the solid solubility of Al atoms in ZnO increased as the synthesis immersion time increased, and more Al3+ ions dissolved into the ZnO matrix, resulting in decreased lattice parameters [52]. Observably, as the immersion time increased, the lattice parameters a and c of the Al:ZnO nanostructures contracted. This result can be attributed to the differences in the crystallographic characteristics of the nanostructures. The difference in the ionic radii of the Al3+ and Zn2+ ions induced these alterations. The ionic radius of Al3+ was smaller than that of Zn2+ (rAl3+ = 0.53 Å, rZn2+ = 0.74 Å) in the tetrahedral coordination, indicating that Al doping did not alter the wurtzite structure of ZnO. As a result, the Al3+ occupied the Zn2+ lattice site in the crystal lattice [53,54]. The hexagonal wurtzite crystal structure of the samples, which were devoid of secondary phases, was corroborated by the XRD patterns. Khuili et al. asserted that the diffraction peaks of ZnO shift toward higher diffraction angles when ZnO was doped with atoms whose ionic radius is lesser than that of Zn2+ [55]. This finding was consistent with the findings of the current study as well as those reported by other researchers [56]. Moreover, the unit cell volumes for the Al-doped samples shrunk noticeably, indicating a more successful substitution of Zn2+ of the lattice framework by a smaller ionic radius of Al3+ as the immersion duration rose. Similar observations were reported by Das et al. as they attempted to integrate the group III element, Al, as a representative n-type dopant in ZnO rods prepared by sonochemical synthesis for dye-sensitized solar cell application [57]. Table 1 summarizes the retrieved and computed values of average crystallite size, lattice parameters, and cell volume for the pristine ZnO and Al:ZnO nanostructures employing XRD information and the preceding equations for hexagonal wurtzite structures.
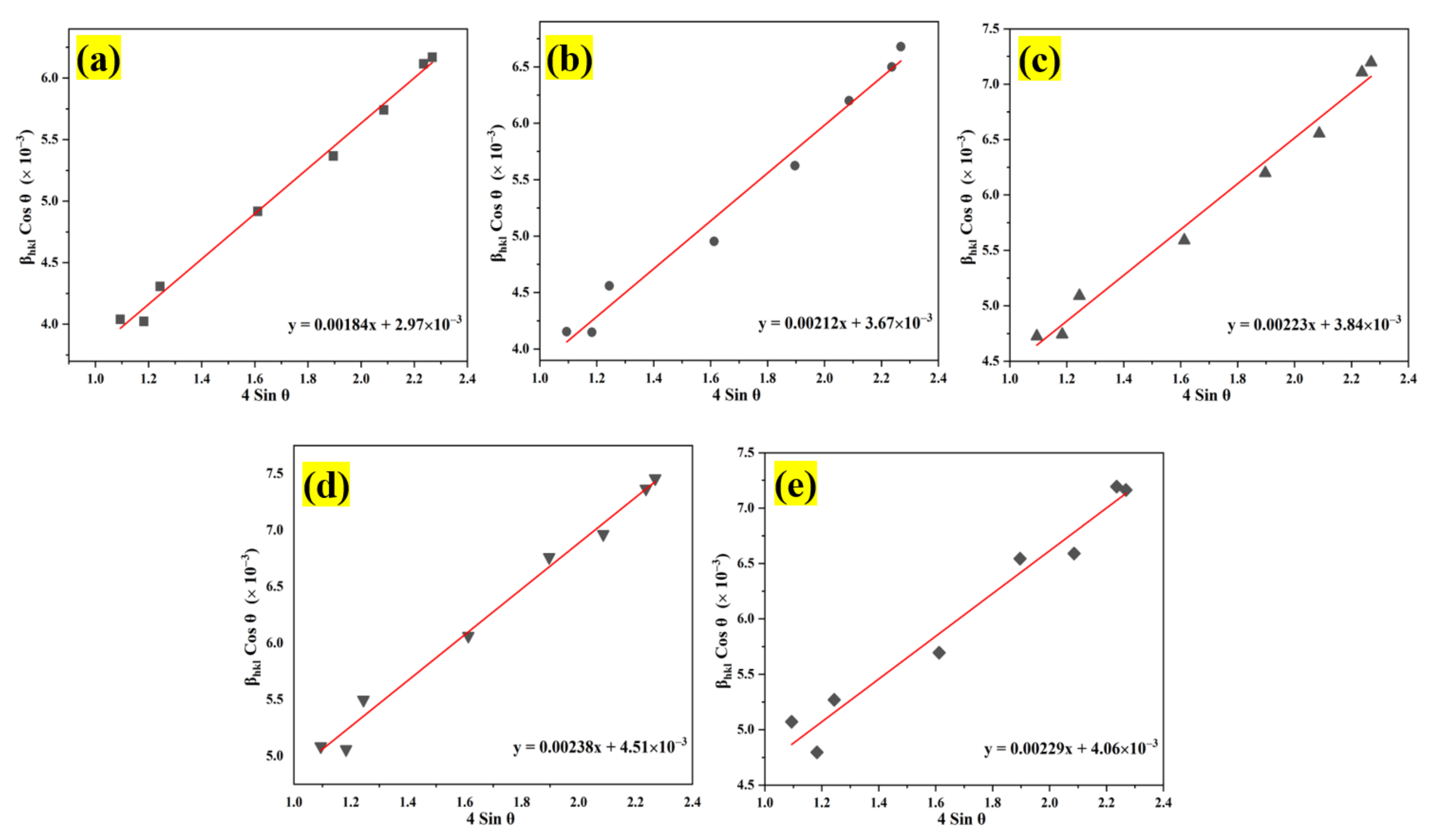
The Williamson–Hall approach is an adjusted integral breadth strategy that differentiates between crystallite size- and strain-induced modification by considering peak width expansion [58]; hence, the size of the crystallites and the micro-strain generated within nanocrystals can be quantitatively analyzed. Assuming that the contributions of the crystallite size and micro-strain to the line broadening are distinctive, Williamson–Hall can be expressed as [59]:
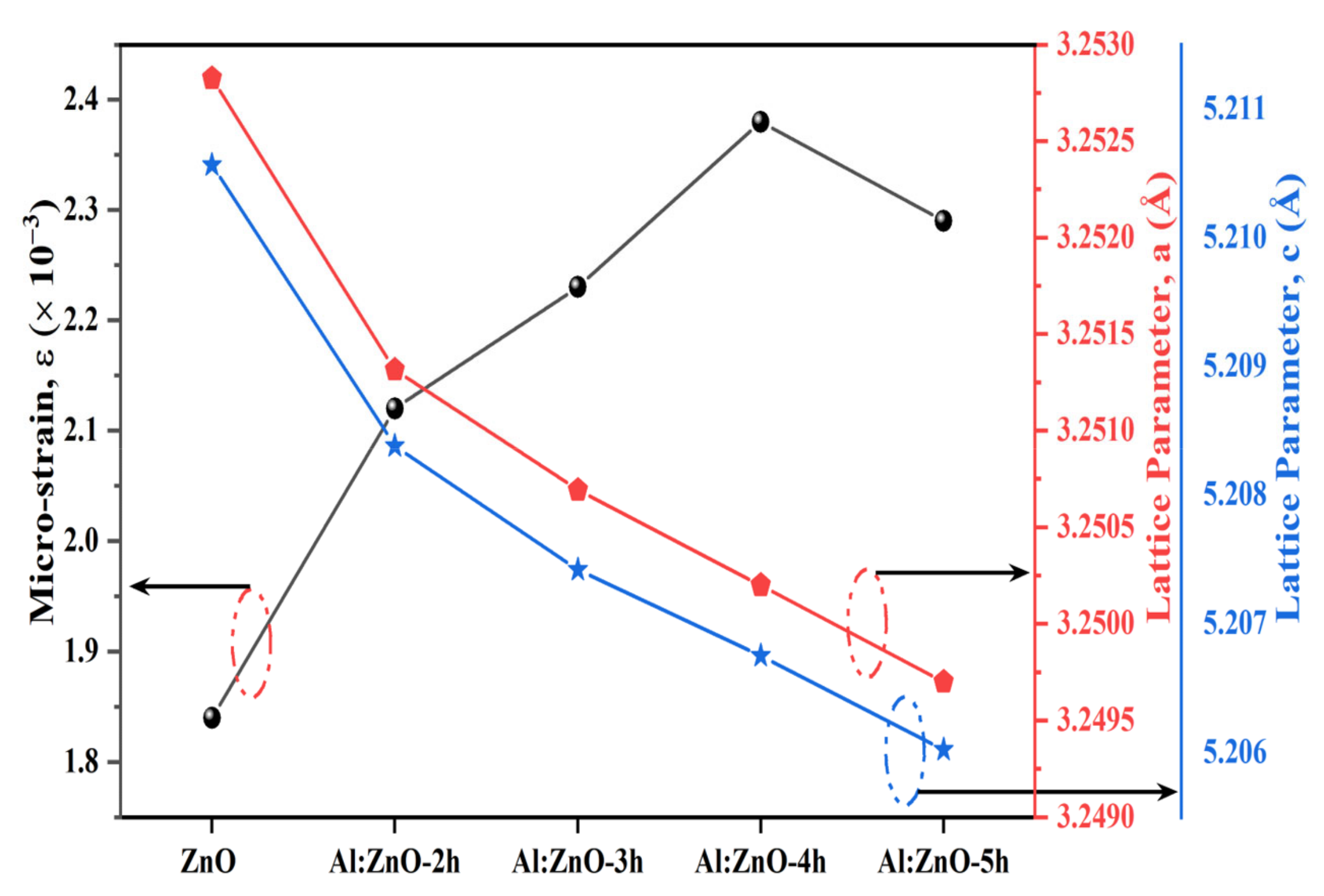
where βhkl is the instrument adjusted to the full-width half-maximum of the XRD peak, λ is the X-ray wavelength, D corresponds to the crystalline size, θ is the Bragg’s angle, and ε is the lattice micro-strain. Broadening of the peak width indicated that modification of the crystallite size was related to strain induced by crystal deficiencies and displacements. The preceding equation was applied to the uniform deformation model (UDM), where the micro-strain in all crystallography orientations was considered unchanged and the crystal retains an isotropic property [58]. Figure 4 depicts the correlation between the lattice parameter and the micro-strain of the nanostructured powders. The incorporation of the Al element in the ZnO nanostructures matrix increases the value of lattice micro-strain due to induced lattice deficiency (rAl3+ < rZn2+), hence further validating the inclusion of Al doping in the ZnO lattice framework. Tensile strain yielded a positive value, whereas compressive strain yields a negative value. According to the Williamson–Hall analysis, all Al:ZnO nanostructured powders had a positive lattice micro-strain, as illustrated in Figure 5.
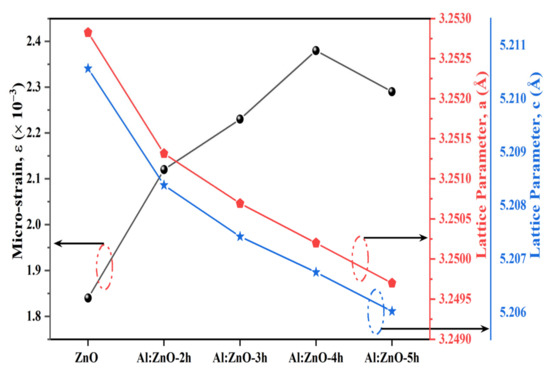
Figure 4.
Correlation of micro-strain and lattice parameter of a and c for pristine ZnO and Al:ZnO nanostructures.
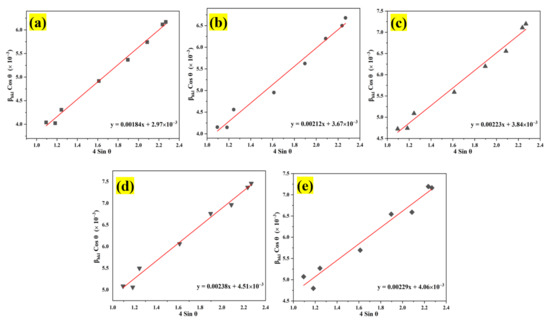
Figure 5.
Analysis of the Williamson–Hall uniform deformation model (WH-UDM) for the pristine ZnO and Al:ZnO nanostructures with different immersion times: (a) WH-UDM of pristine ZnO; (b–e) WH-UDM of Al:ZnO-2 h; Al:ZnO-3 h; Al:ZnO-4 h; and Al:ZnO-5 h, respectively.
The average crystallite size and micro-strain were evaluated according to the plot, and the results are disclosed in Table 1. This positive result of lattice strain for all Al:ZnO samples indicated the presence of tensile strain in the nanostructures when the nanoparticles were stretched, and it was discovered that the tensile strain depended on the grain boundary density [60]. As the Al doping immersion time increased, the number of grain boundaries per unit volume increased (due to the reduction of grain size), leading to an increase in tensile strain [16]. Meanwhile, the average crystallite size of the pristine ZnO and Al:ZnO nanostructures determined by the WHUDM analysis contrasts with that estimated by the Debye–Scherrer equation. This is due to the peak width broadening owing to the micro-strain being recognized in the WHUDM approach. As a result, increased crystallite size measurements were observed.
It is worth mentioning that via the Debye–Scherrer method the calculated average crystallite size for the pristine ZnO and Al:ZnO nanostructures neglected the strain-induced broadening effect. Based on the results, it is obvious that Al-doping has an influence on the structural characteristics of pristine ZnO, particularly crystallite size, lattice parameters, unit cell volume, and micro-strain, implying the incorporation of Al3+ ions into the ZnO host lattice matrix.
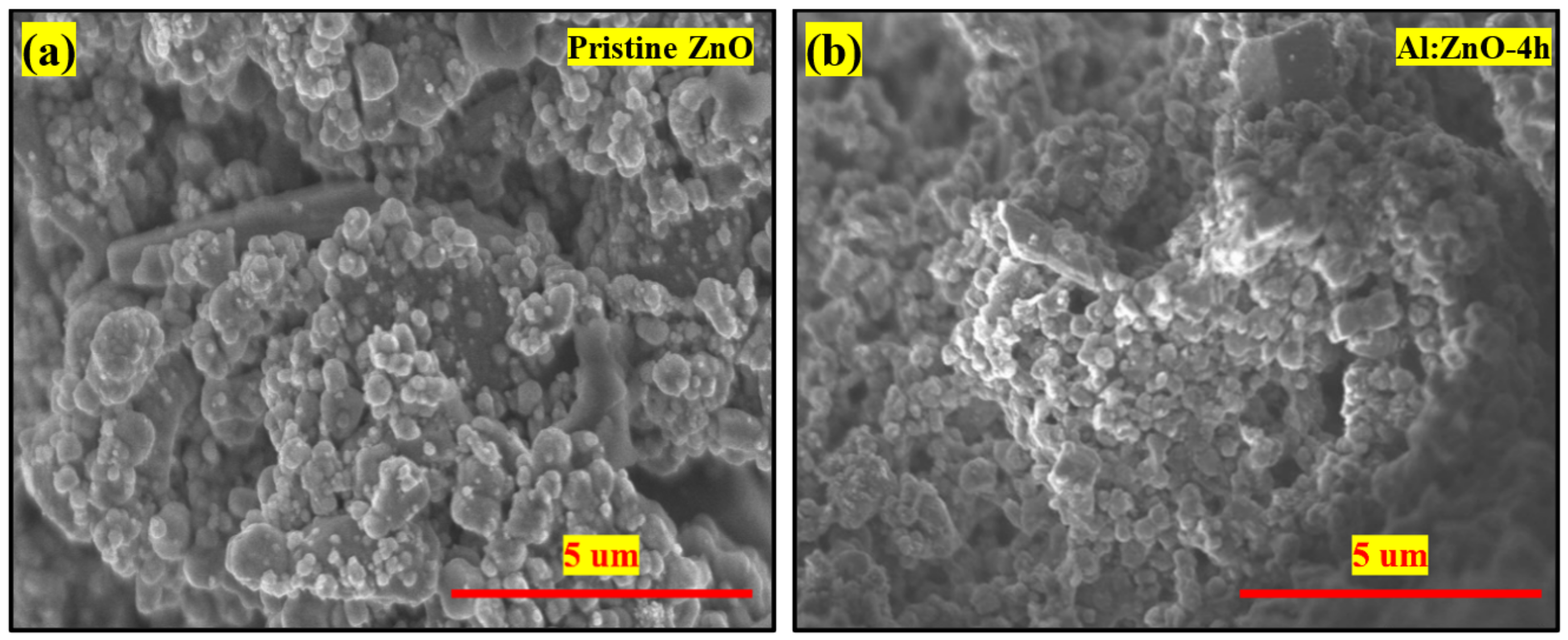
Figure 6 illustrates the deposited microstructures of pristine ZnO and Al:ZnO-4 h on cellulose substrate at ×10,000 magnification (5 kV applied voltage). It appears that pristine ZnO comprised irregular particle shapes dispersed in various sizes, as shown in Figure 6a. Comparably, the Al:ZnO-4 h sample as depicted in Figure 6b has smaller particles with nearly similar shapes and morphology to pristine ZnO. The particle was attached to cellulose fibers to construct a well-linked network structure with decent adhesiveness between the substrate and the deposited sensing material. Furthermore, the polycrystalline Al:ZnO-4 h sample appears porous, and with the incorporation of the Al doping element, the porosity of the surface increased due to the reduction in particle size. The nanoporous surface structure morphology played a substantial role in the accumulation and adhesion of water molecules on the sensing surface of a material which accelerated the rate of reaction between water molecules and the sensor surface, resulting in increased sensor sensitivity [61]. Therefore, the fabrication of a flexible humidity sensor utilizing the synthesized Al:ZnO-4 h nanostructures is appropriate for humidity-sensing applications.
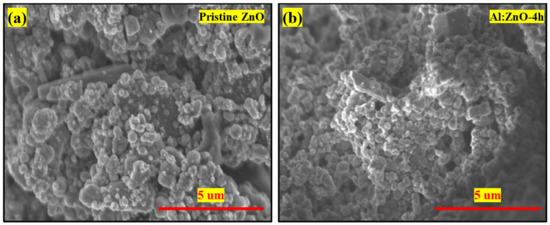
Figure 6.
FESEM morphology (×10,000 magnification; 5 kV applied voltage) of the (a) pristine ZnO and (b) Al:ZnO-4 h nanostructured-based flexible humidity sensor deposited on cellulose filter paper.
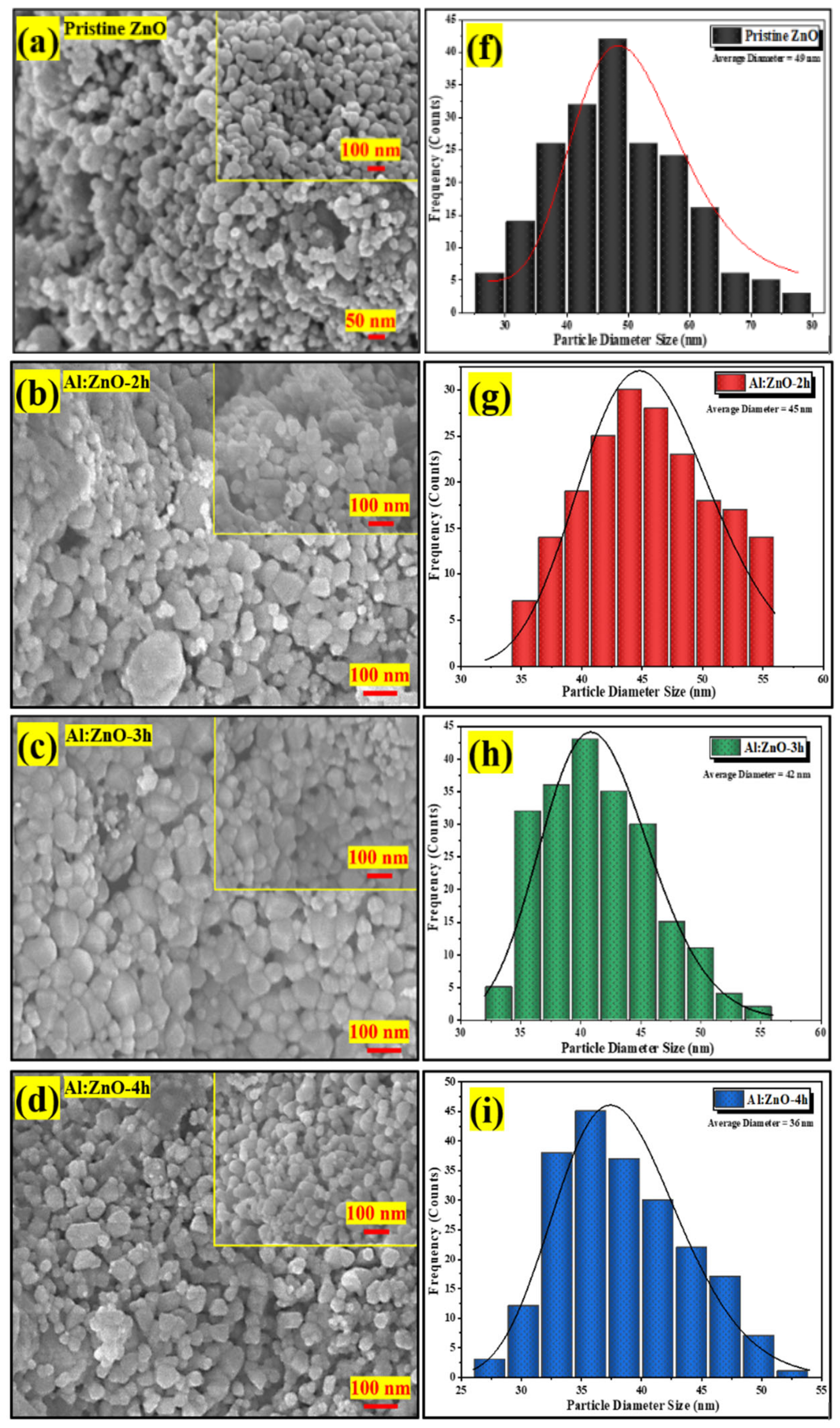
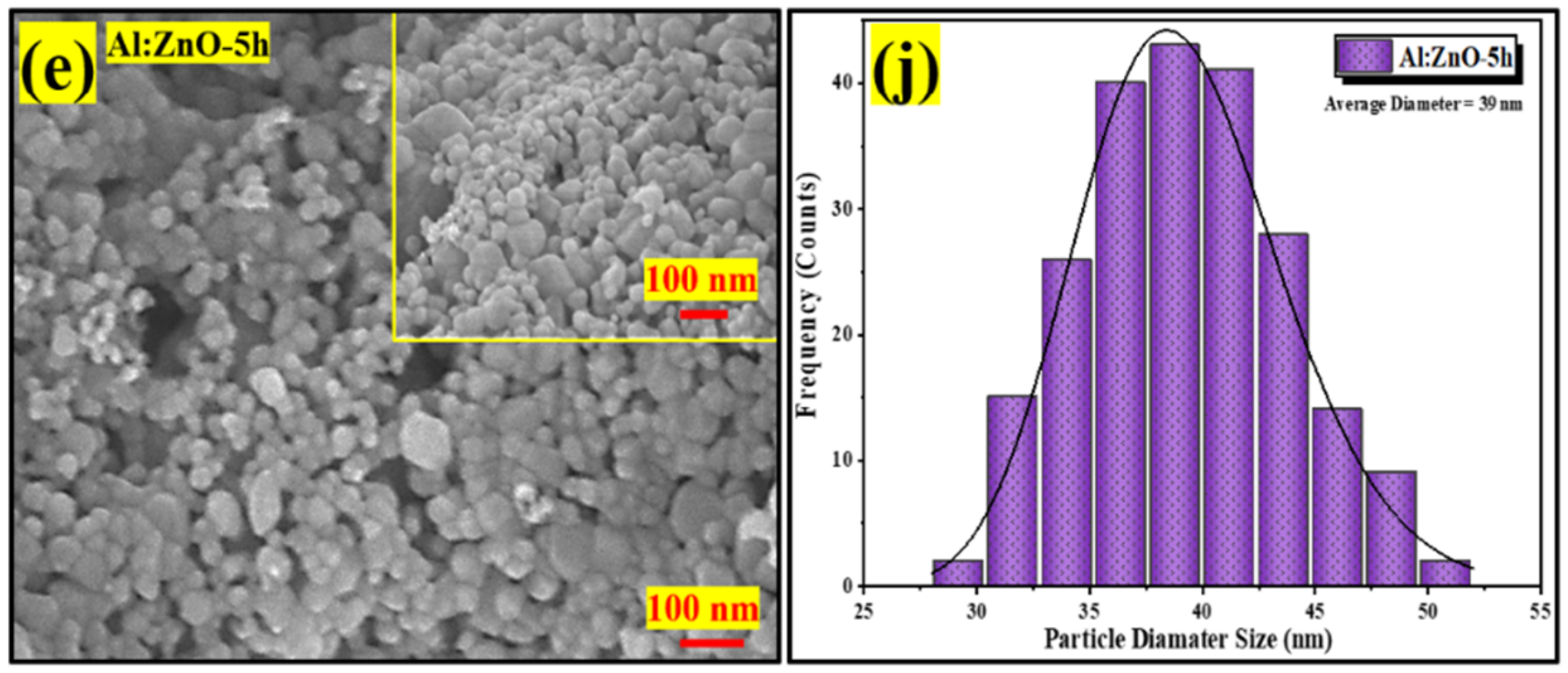
Figure 7a–e display high-magnification FESEM micrographs of pristine ZnO, Al:ZnO-2 h, Al:ZnO-3 h, Al:ZnO-4 h, and Al:ZnO-5 h nanostructured powder at a magnification of ×100,000 (5 kV applied voltage). These micrograph images show that the specific agglomerated granules were discovered to be made up of interlinked nanoparticles with asymmetrical quasi-spherical morphologies. According to the XRD analysis, all Al:ZnO nanoparticles had facets, edges, and vertices suggesting a polycrystalline hexagonal structure. The inset images in Figure 7a–e illustrate the higher magnification micrograph (×150,000) with a similar accelerating voltage. The majority of nanoparticles were engaged with one another, which causes them to resemble clusters with obvious voids. This cluster formation was caused by attraction forces that occur between the nanoparticles as a result of an upsurge in surface-area-to-volume ratio and high surface energy [62]. By estimating the individual nanoparticles having an asymmetrical quasi-spherical or oval shape, the average grain diameter histograms were generated for each sample by choosing a sample section of 200 nanoparticles. Figure 7f–j illustrated the histograms of the grain diameter distribution for pristine ZnO, Al:ZnO-2 h, Al:ZnO-3 h, Al:ZnO-4 h, and Al:ZnO-5 h with the average diameter of the nanoparticles being 49 nm, 45 nm, 42 nm, 36 nm, and 39 nm, respectively, estimated through ImageJ software. The average diameter of the nanoparticles decreased noticeably as the immersion time increased from 2 h to 4 h, and the diameter was observed to increase at higher immersion time. The observed change in nanoparticle size with Al doping was mediated by either compression or expansion of the lattice framework [16]. The particle diameter decreased (in range between 25 and 55 nm), and the size distribution became more homogeneous after the Al element was incorporated, compared to the nanoparticle diameter of the pristine ZnO nanostructured powder, which ranged between 30 and 80 nm. The Al:ZnO nanostructured powders were aggregated by nanoparticles of uniform size. This structure unquestionably enhanced surface roughness and specific surface area [63]. These findings demonstrated that Al3+ doping induced significant alterations in the ZnO nanostructure. Thus, through the Al doping strategy, a large roughness surface area, the homogeneous size distribution of nanoparticles, and a significant abundance of water molecule adsorption sites were obtained.
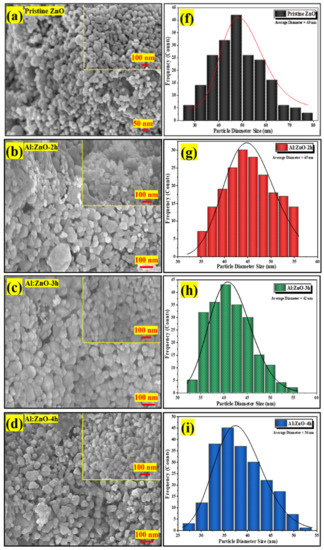
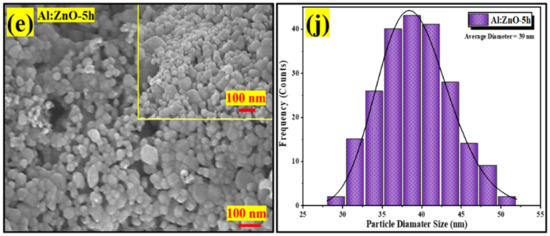
Figure 7.
FESEM micrographs of the nanostructured powders and the corresponding histogram of the nanoparticle diameter size at different immersion times: (a,f) pristine ZnO; (b,g) Al:ZnO-2 h; (c,h) Al:ZnO-3 h; (d,i) Al:ZnO-4 h; and (e,j) Al:ZnO-5 h at 95 °C.
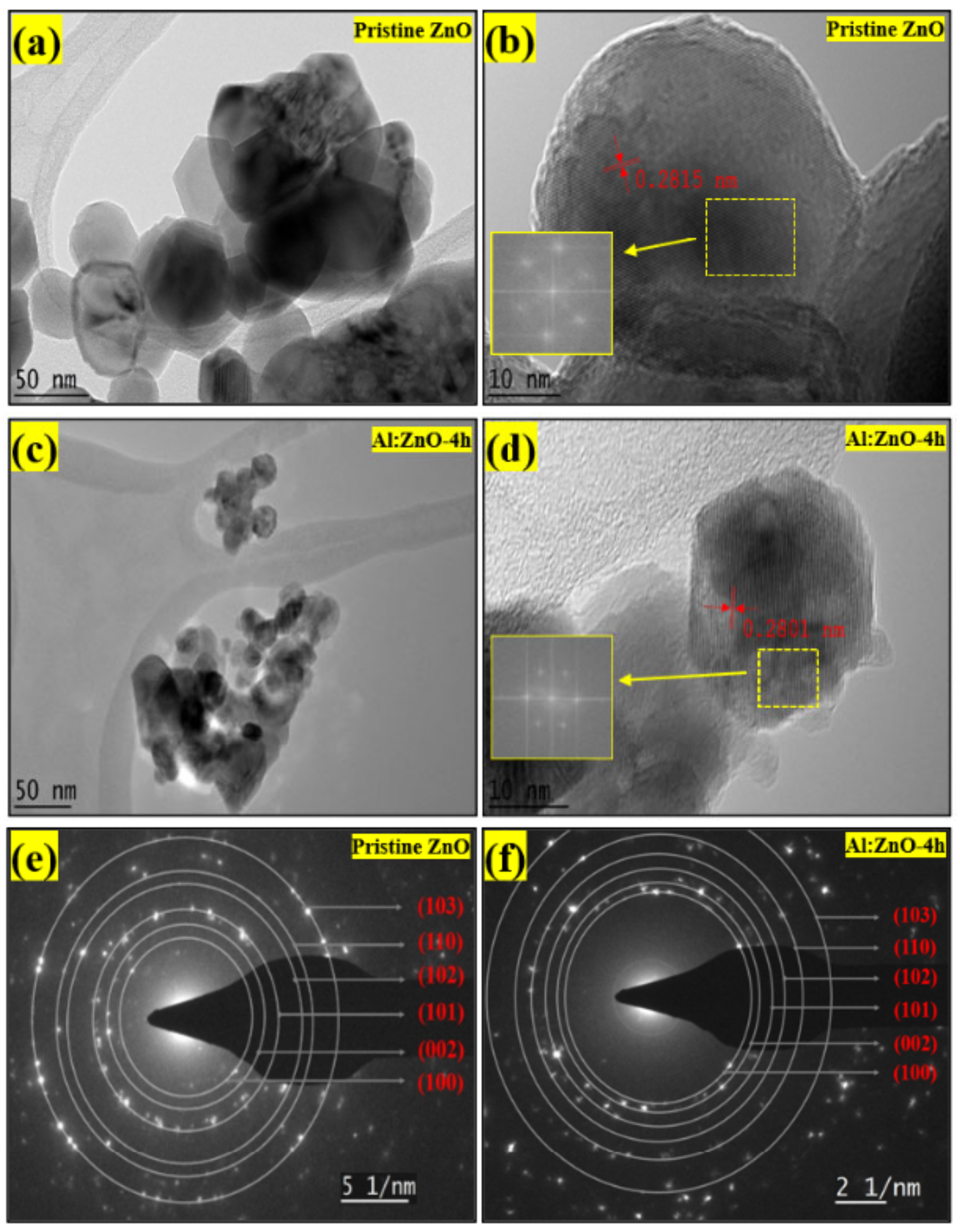
The morphological features of pristine ZnO and Al:ZnO-4 h nanostructured powders were characterized by HRTEM, as exhibited in Figure 8. According to the low-magnification HRTEM micrograph (Figure 8a), the pristine ZnO comprised a multi-layer aggregated structure with prominent boundaries and irregularly shaped quasi-spherical nanoparticles. The nanoparticles had an average diameter of 50 nm, which was congruent with the findings of the Williamson–Hall analysis and the Scherrer equation. A high-magnification micrograph of more fringe lines revealed a decent crystallographic characteristic, as well as the nanoparticles, which were relatively homogeneous in morphology, arrangement, and size. In the high-magnification HRTEM micrograph of pristine ZnO, the lattice fringes of 0.2815 nm were ascribed with interplanar spacing that coincided with the (100) plane, as exhibited in Figure 8b. Therefore, it was confirmed that the pristine ZnO nanostructures possessed a crystalline hexagonal wurtzite structure without a dislocation defect [64]. The d-spacing values in the (100) plane were also congruent with JCPDS no. 36-1451, confirming crystal formation in that orientation. As demonstrated in Figure 8c, the low-magnification HRTEM micrograph of Al:ZnO-4 h possessed a similar irregularly shaped quasi-spherical nanoparticles structure as pristine ZnO, with the hierarchical multi-layer aggregated structure having been preserved. Al:ZnO-4 h nanoparticles had smaller diameters than pristine ZnO nanoparticles. The Al:ZnO-4 h nanoparticles appeared particulate, with a homogenous size distribution with an average diameter of approximately 35 nm. This was justified by Al atoms infiltrating the Zn lattice framework and restricting the evolution of Zn grains, resulting in decreased sizes of the Al:ZnO nanoparticles. The interplanar distance is reduced to 0.2801 nm, which is compatible with the ZnO crystal plane (100) presented in the high-magnification HRTEM micrograph as depicted in Figure 8d. These alterations arose due to lattice shrinkage as Al cations substituted the Zn cation sites. The fast Fourier transformation (FFT) on an HRTEM micrograph provides information on the lattice fringes and could be employed to index the observed spots. The distinct lattice fringes that can be seen in Figure 8b,d suggested that the pristine ZnO and Al:ZnO-4 h nanoparticles had a single crystal structure. Furthermore, the FFT pattern (inset of Figure 8b,d) further validated that the observed region of the nanoparticles was close to the single crystallinity of quantum-sized nanoparticles. Moreover, a micrograph of a selected area electron diffraction (SAED) configuration was utilized to evaluate the crystallographic attributes of the samples. The SAED traces of the pristine ZnO and Al:ZnO-4 h nanoparticles, as demonstrated in Figure 8e,f in agreement with crystallographic orientations with the symmetrical alignment, revealed that both samples had a hexagonal wurtzite structure. Similar to the XRD assessment, the presence of substantial spots distributed in six concentric rings illustrated the polycrystalline nature of pristine ZnO and Al:ZnO-4 h nanoparticles. It confirmed the high level of crystallinity and phase purity. The absence of diffraction spots or lattice fringes pertaining to Al and its oxides could be ascribed to the minimal content and high dispersion of Al species. This absence was consistent with XRD and EDS mapping analyses. Moreover, the rough surface of the Al:ZnO-4 h nanoparticles, as depicted in Figure 8d, might be beneficial as water molecule adsorption sites for humidity-sensing applications.
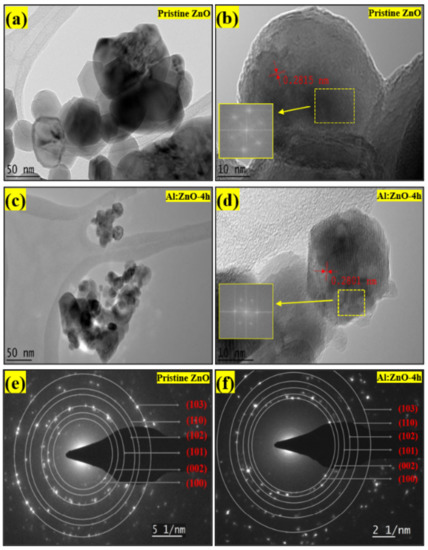
Figure 8.
TEM micrograph at low magnification of: (a) pristine ZnO and (c) Al:ZnO-4 h. HRTEM micrograph with FFT analysis of: (b) pristine ZnO and (d) Al:ZnO-4 h. SAED pattern with indexing annotations of: (e) pristine ZnO and (f) Al:ZnO:4 h.
3.2. Surface Chemistry, Elemental Characterization, and Composition Analysis—EDS and XPS
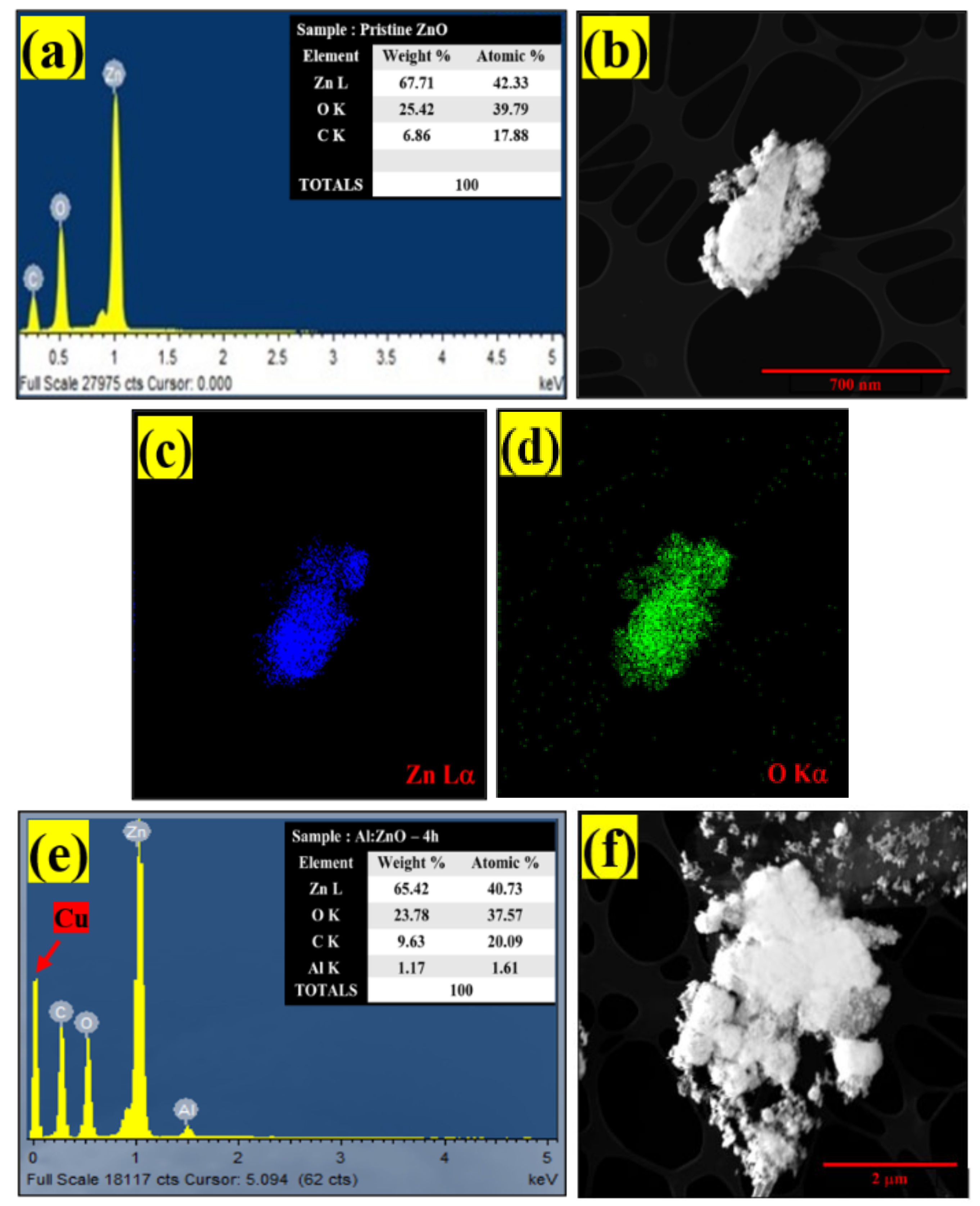
The elemental composition of pristine ZnO and Al:ZnO-4 h was assessed by EDS (Figure 9). Initial observation suggested that the sensing membrane was formed from the desired elements. The EDS spectra as in Figure 9a confirmed the occurrence and indicated that pristine ZnO was composed of two elements: zinc (Zn) and oxygen (O). Moreover, the EDS spectra validated the occurrence of three major components of zinc (Zn), oxygen (O), and aluminum (Al) for Al:ZnO-4 h at 1 at.% Al doping, as depicted in Figure 9e.
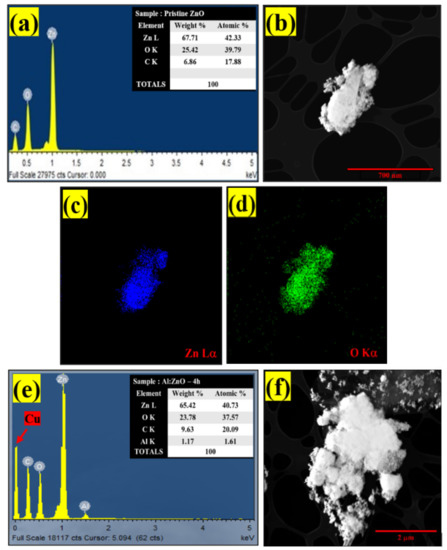
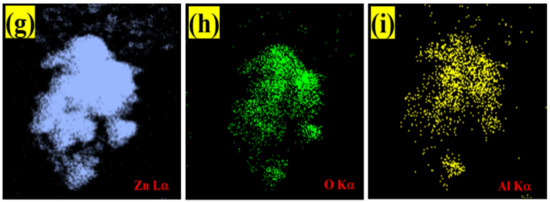
Figure 9.
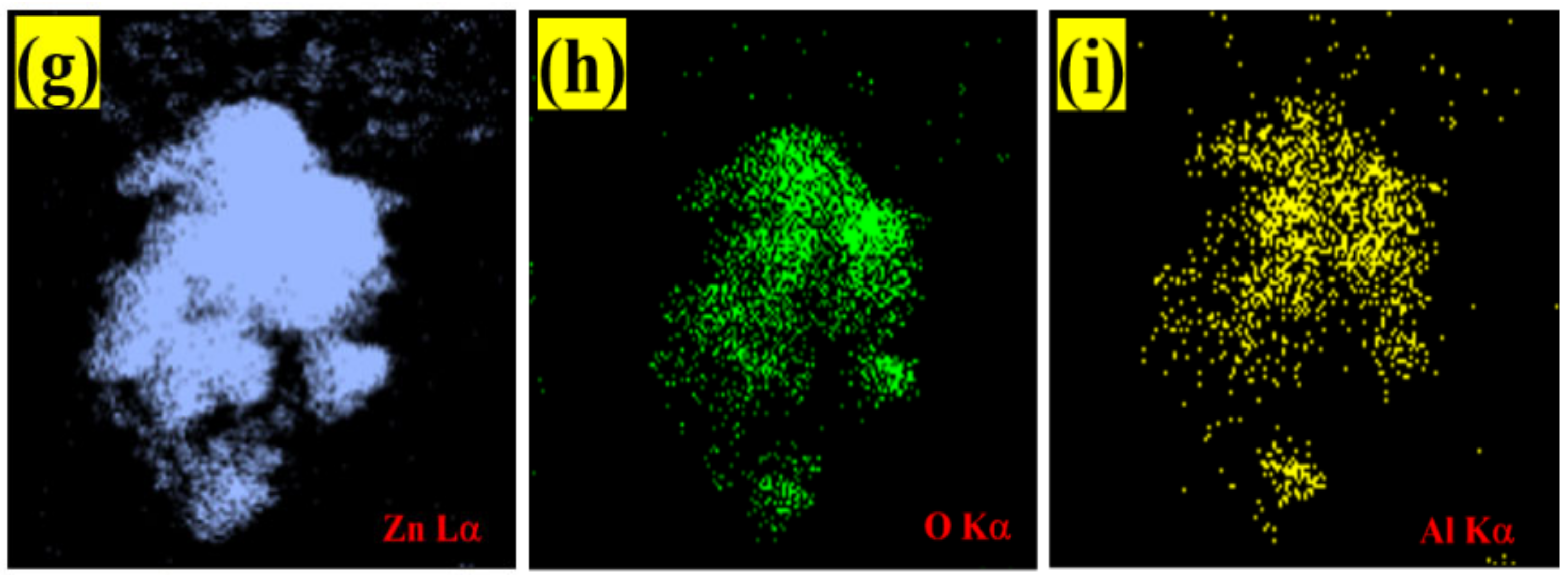
EDS spectra of: (a) pristine ZnO and (e) Al:ZnO-4 h. EDS elemental mapping of (b–d) pristine ZnO and (f–i) Al:ZnO-4 h.
The copper grid was responsible for the Cu, while the C peaks were attributed to the adhesive carbon tape. Additionally, there was an absence of foreign elemental peaks in the spectra of pristine ZnO and Al:ZnO-4 h, validating the purity of the synthesized nanostructured material. For pristine ZnO, the peaks of O (Kα) and Zn (Lα) elements were observed at energies 0.53 keV and 1.01 keV, respectively. For Al:ZnO-4 h, the Zn element is recognized by the Lα, Kα1, and Kβ peaks, which were positioned at energies of 1.02 keV, 8.58 keV, and 9.52 keV, respectively. The Kα peak of O and Al were detected at energies of 0.52 keV and 1.49 keV, respectively. The atomic ratios of all elements are displayed in the enclosure table of Figure 8a–e, and the findings validated the predicted Al/Zn percentage of ~1%. According to the evidence gathered, EDS confirmed the presence of Al, verifying the integration of Al into the ZnO lattice framework. The EDS micrograph images of Zn and O elemental mapping in pristine ZnO were investigated using HRTEM (EDS) analysis as portrayed in Figure 8b–d. Corresponding to the EDS elemental study, the Zn element was uniformly distributed across the pristine ZnO TEM morphology. The elemental distributions of the Al dopant, Zn, and O elements together with the TEM morphology of the Al:ZnO nanostructured sensing membrane are shown in Figure 9f–i. The elemental mapping images of Al:ZnO-4 h showed homogenous distributions of Zn (blue), O (green), and Al (yellow) elements over the TEM nanostructures’ morphology, indicating the presence of Al and Zn elements in the doped sample. The dispersion of Zn, O, and Al atoms across the ZnO matrix verified that Al3+ ions substituted Zn2+ ions in the ZnO lattice framework. Due to doping being uncontrollable, the arrangement of Al ions and their placement of the Zn site in the host matrix might be randomized. Although EDS analysis confirmed the presence of Al, characterizing the Al oxidation state necessitated extensive XPS characterization.
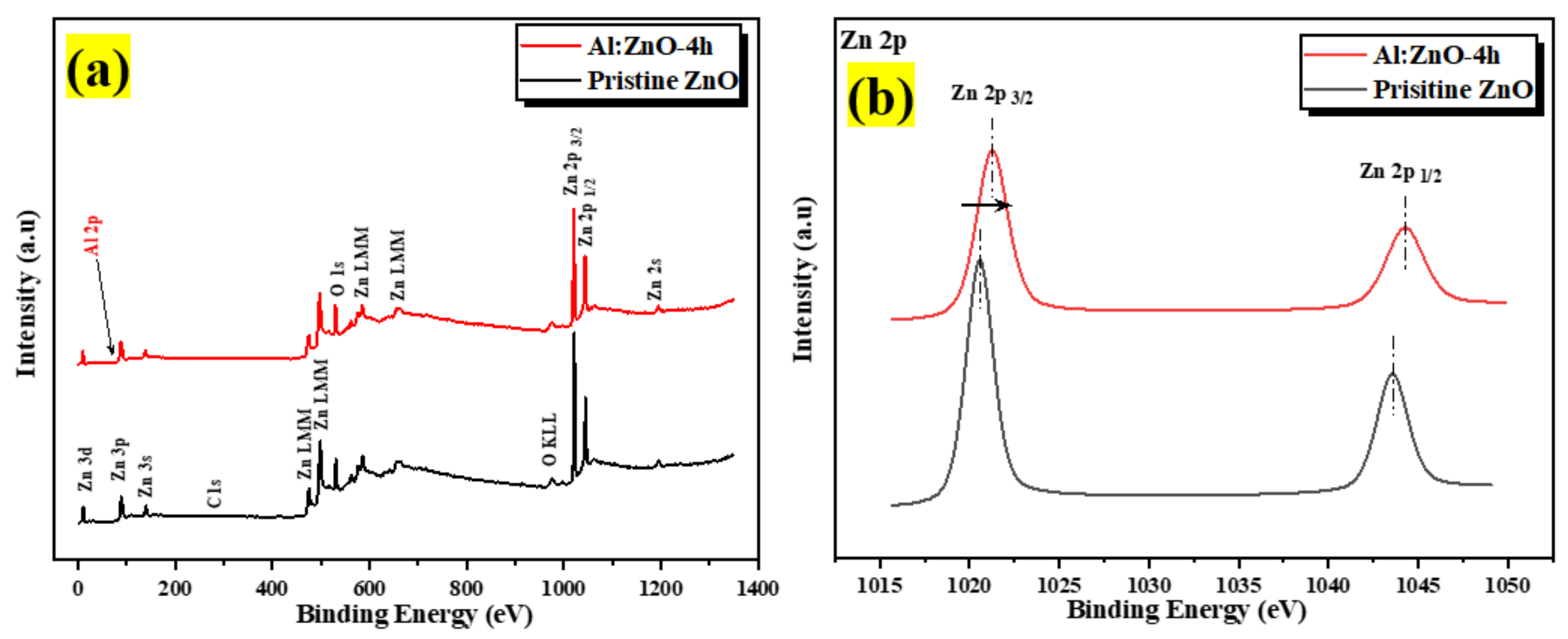
The chemical states of the compositional elements contained in pristine ZnO and Al:ZnO-4 h nanostructured powder were analyzed using XPS, as illustrated in the survey scan spectrum in Figure 10a. All elements’ core- and valence-level peaks, as well as peaks of Auger transition, were detected. The charges-corrected procedure was applied to all XPS spectra by modifying the adventitious carbon element, C 1s binding peak energy situated at 284.6 eV. The occurrence of binding energies of zinc (Zn), aluminum (Al), and oxygen (O) elements was discovered during an XPS survey scan of Al:ZnO-4 h nanostructured powder. The detected peaks of the Zn component in Al:ZnO-4 h nanostructured powder were comparable with that observed in pristine ZnO nanostructured powder, whereas the peaks of the Al element indicated that Al elements had been incorporated into ZnO nanostructured powder. The XPS spectra of pristine ZnO and Al:ZnO-4 h nanostructured powder indicated the common peaks of Zn 2p1/2, Zn 2p3/2, O 1s, C 1s, Zn 3s, Zn 3p, and Zn 3d. No auxiliary peak was found, reflecting the high purity of the pristine and Al-doped ZnO nanostructured powder produced. Figure 10b displays a high-resolution XPS spectrum of Zn 2p core energy level spectra for pristine ZnO and Al:ZnO-4 h nanostructured powder. The doublet binding energy peaks at 1020.56 eV and 1043.58 eV were associated with Zn 2p3/2 and Zn 2p1/2, respectively, with the spin-orbit splitting of 23.02 eV and well-matched with the standard ZnO values [65]. In Al:ZnO-4 h nanostructured powder, the Zn 2p3/2 and Zn 2p1/2 peaks were relocated to higher binding energies of 1021.28 eV and 1044.28 eV, respectively, with the splitting of the Zn 2p doublet at approximately 23 eV. The analysis verified that the Zn in Al-doped ZnO was Zn2+ [66]. The blue-shifted peak positions in the Al:ZnO nanostructured powder could be ascribed to the synergetic electronic engagement involving the ZnO and Al dopant, which implies that Al3+ cations had infiltrated the ZnO lattice (either in Zn2+ sites or interstitial sites) and replaced the Zn2+ cations. Furthermore, the insertion of the Al element reduced the intensity of the Zn 2p core energy level spectra peak. This observation also implied that Zn2+ sites were replaced with Al3+ in Al:ZnO nanostructured powder [67].
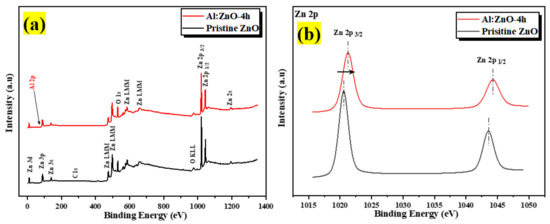
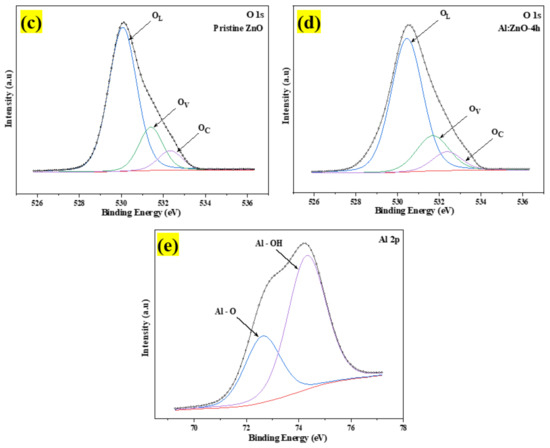
Figure 10.
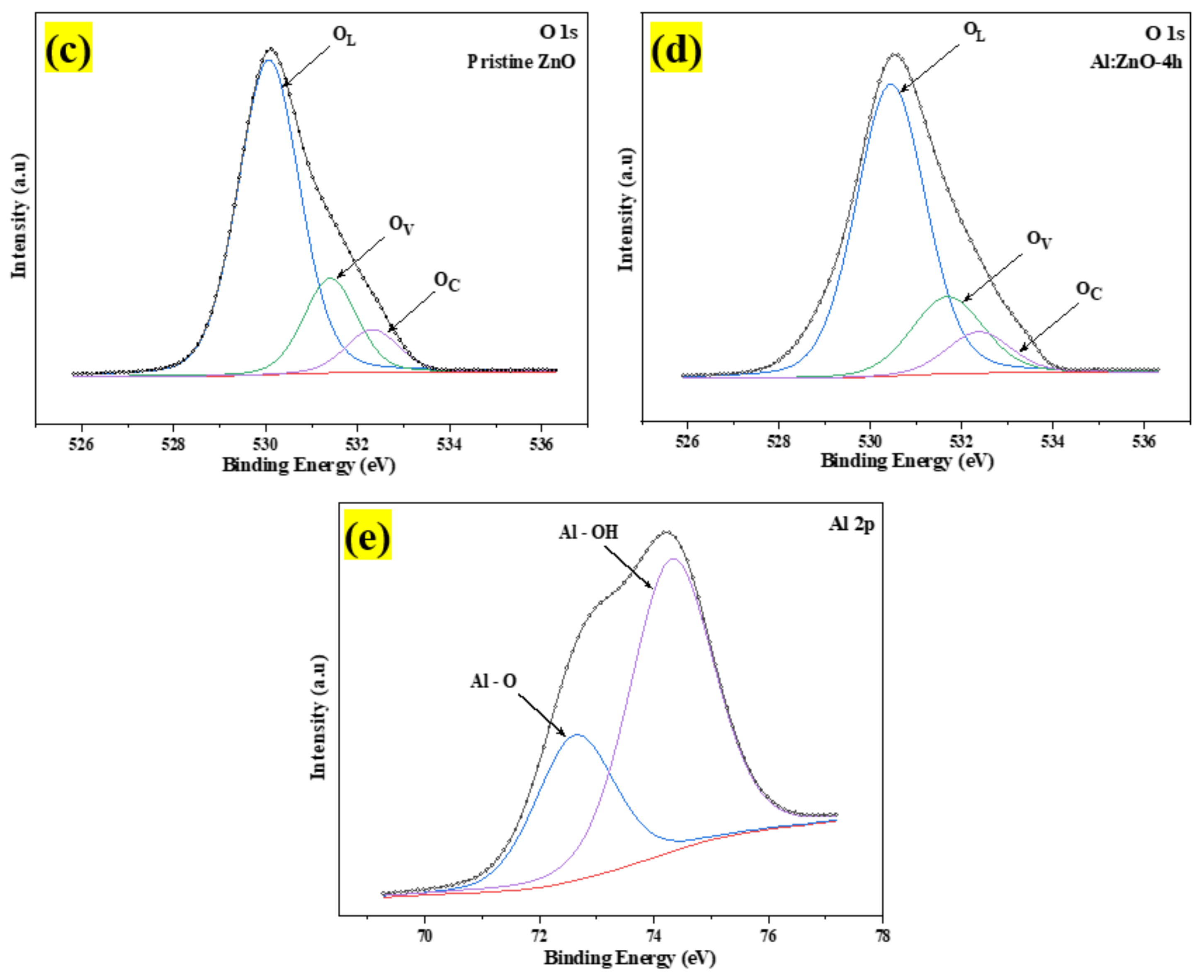
The XPS spectra of the pristine ZnO and Al:ZnO-4 h nanostructured powder: (a) Full survey scan spectra. High-resolution spectra of (b) Zn 2p region; (c) O 1s region for pristine ZnO; (d) O 1s region for Al:ZnO-4 h; and (e) Al 2p region of Al:ZnO-4 h.
The high-resolution O 1s core energy-level spectrum for pristine ZnO and Al:ZnO-4 h nanostructured powder primarily arises at binding energies of 530.12 eV and 530.49 eV, respectively, as presented in Figure 10c,d. The peak was deconvolved into three Gaussian peaks utilizing peak deconvolution processing tools (PHI MultiPak). These peaks were categorized as lattice oxygen (OL), oxygen vacancy (OV), and chemisorbed oxygen (OC) species. As portrayed in Figure 10d, the OL, OV, and OC peaks that were attributed to the O2− anions bonded to the Zn2+ cations (surrounded by the substitution of Al elements) in the wurtzite structure of the hexagon array of the ZnO, oxygen vacancy in the oxygen-deficient regions within the ZnO matrix, and weakly bound chemisorbed oxygen (O2− or O−) peaks, existing at approximately 530.51 eV, 531.71 eV, and 532.39 eV, respectively [66,68]. As previously stated, the OV peak was related to oxygen vacancy, in which the area of the OV peak was proportional to the oxygen vacancy concentration [69]. The area of OV rose slightly after Al doping, and the amount of OV improved from 18.2% to 21.1% of pristine ZnO contrasted to Al:ZnO-4 h nanostructured powder. This was due to the replacement of Zn2+ cations in the zinc oxide lattice by Al3+ cations [70]. The composition of each O 1s species sub-peak in detail for each sample is provided in Table 2. The OV/OL ratio was applied to assess the existence of oxygen vacancy and oxygen lattice in materials [69]. As confirmed in Table 2, the OV/OL ratio was particularly high in Al:ZnO-4 h nanostructured powder, which indicated that oxygen vacancy was more intensively formed in Al:ZnO-4 h than in pristine ZnO nanostructured powder. The prominent peak in the high-resolution XPS spectrum of Al 2p core energy level at the binding energy of 74.37 eV, as exhibited in Figure 10e, confirmed the integration of Al elements in Zn2+ locations of the ZnO crystal framework. The XPS spectrum of the Al 2p core energy level was segmented into two components, which were ascribed to the Al–O bonds (centered at 72.9 eV) and Al-OH bonds (centered at 74.37 eV) formed in the crystal structure of ZnO [71]. The deconvoluted peak of the Al 2p core energy level was higher than the metallic energy level and lower than the stoichiometric Al2O3 peak. This observation corresponded to Al ions existing with the oxidation state of +3 and proved that Al3+ cations are substituted for Zn2+ cations in the ZnO lattice [66,72]. In comparison, due to the low aluminum concentration in the materials, the intensity of the Al 2p peak was less intense than that of the Zn 2p peak.

Table 2.
The atomic percentage of fitted high-resolution spectra of the O 1s of Al:ZnO-4 h and pristine ZnO nanostructures.
3.3. Electrical Properties—I–V Measurement
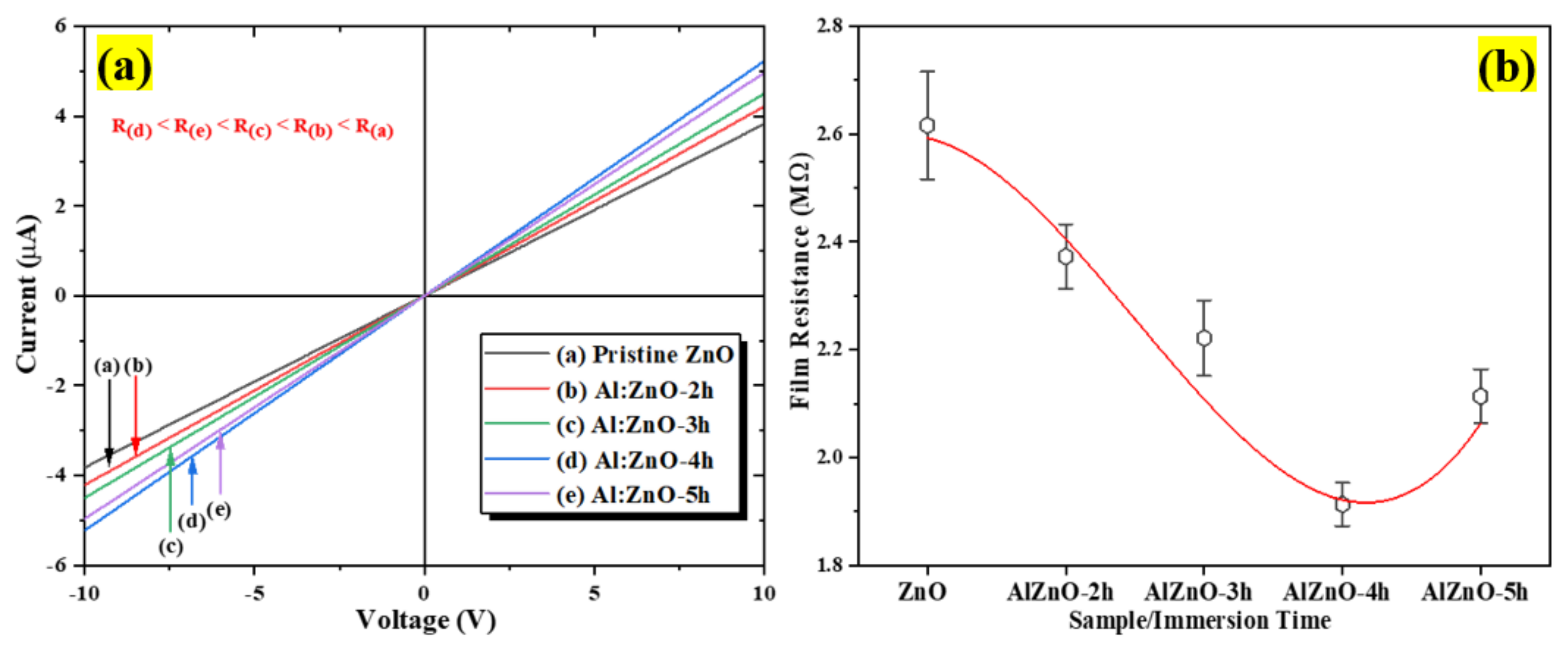
The I–V measurement characteristic profile at room temperature for the pristine ZnO to Al:ZnO-5 h nanostructured-based flexible humidity sensor is depicted in Figure 11a. The samples were examined with two-probe measuring equipment under room illumination. According to the acquired I–V characteristic results, the functional rGO contact displayed ohmic behavior with pristine ZnO to Al:ZnO-5 h samples and satisfied Ohm’s law, which asserts that the flow of the current flowing through elements from one site to another is perfectly proportional to the voltage between the two sites. The I–V plots (Figure 11a) show that the current increased for all samples with 1 at. % Al doping concentration in the voltage range of −10 V to +10 V. Therefore, the effects of Al-doping immersion time on the resistance of the sensing materials were examined further. The findings demonstrated that the current value for the doped samples increased in the following sequence with respect to the applied voltage: Al:ZnO-4 h > Al:ZnO-5 h > Al:ZnO-3 h > Al:ZnO-2 h > ZnO. The current intensity of the ZnO nanostructured sample doped at 1 at. % Al and immersed for 4 h (Al:ZnO-4 h) was the highest, denoting the ideal electrical properties of the sensing membrane. On the other hand, the current intensity of pristine ZnO sensing film was the lowest, inferring poor electrical conductance behavior compared to the doped nanostructures sample. For all samples, the reciprocated value of the slope was exploited to assess the sensing material resistance. The resistances of the sensing material as the function of Al doping immersion time are illustrated in Figure 11b. The sensing material resistances with 2 h, 3 h, 4 h, and 5 h Al doping immersion times were 2.37 MΩ, 2.22 MΩ, 1.91 MΩ, and 2.11 MΩ, respectively. The maximum film resistance of 2.62 MΩ was attained by the pristine ZnO nanostructures.
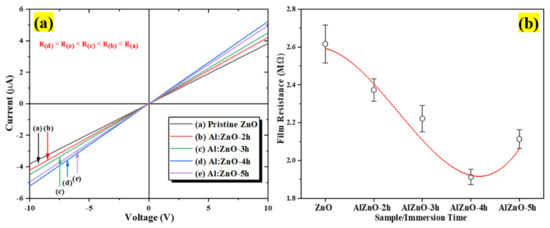
Figure 11.
(a) Current-voltage (I–V) characteristics of the pristine ZnO and Al:ZnO sensing material at different immersion times and (b) sensing film resistance variations.
Compared to the pristine ZnO sensing material, the resistance was observed to be diminished in all samples with Al dopant. Therefore, suggesting the inclusion of the Al element with pristine ZnO caused the resistivity of the sensing material to decrease substantially, thereby successively increasing the conductivity of the sensing material. Nevertheless, as the immersion time was beyond 4 h, the resistance increased, signifying that at an Al doping concentration of 1.0 at.%, the optimum immersion period was 4 h, yielding the sensing material with the lowest resistance (maximum conductivity). If the Al doping immersion time was increased further (5 h), the exorbitant replacement of Al atoms in the ZnO lattice structure deteriorated the ZnO lattice framework instead of yielding an additional carrier concentration. Furthermore, if a dopant impurity was introduced to the pristine material, the electrical resistivity initially declined due to an enhancement of carrier concentration. Conversely, as the dopant dosage or immersion time increased beyond nominal limits, the electrical resistance of doped materials increased, owing to a decrease in carrier mobility triggered by scattering on the grain boundary [73].
The impacts of intrinsic defects, for instance, zinc interstitials and oxygen vacancies, were presumably accountable for the enhanced conductivity in Al:ZnO samples induced by the growth circumstances and occurrence of impurity cations. Therefore, the existence of Al impurity in the humidity-sensitive sensing material composition was a conceivable factor in enhancing the pristine ZnO conductivity, which might be ascribed predominantly to the electronic correlation between Al atoms and ZnO. A plausible argument for this phenomenon was the Al doping in ZnO, which was fulfilled through the effective Al3+ cations’ substitution in the Zn2+ matrix of the ZnO structure and Al3+ cations being positioned in the interstitial region. It facilitated the movement of electrons and increased the free carrier concentration (extra electron in doped ZnO) [16].
The replacement of Al3+ at a Zn2+ site in the ZnO lattice was described by the subsequent possible mechanisms (Equations (5) and (6)). The electrons were produced through electron and/or ionic compensation mechanisms [74,75]:
where is an Al ion with a positive charge on the zinc lattice site, is an oxygen ion with a neutral charge on the oxygen lattice site, and is the negatively charged zinc vacancy. The electron compensation mechanism (Equation (5)) stated that the electron concentration in n-type ZnO increases due to electron generation; hence, the resistance (resistivity) of the doped sample declined substantially due to enhanced carrier concentration. Therefore, Al doping stimulated the creation of either electrons or Zn vacancies. Ajala et al. proposed that the substitution of Al3+ ions for Zn2+ ions released the oxygen and left its electron in the lattice; hence, in contrast to pristine ZnO, the system had a higher electron concentration and elevated its n-type character [76]. Nevertheless, the ionic compensation mechanism, represented by Equation (6), did not influence the electron concentration in n-type ZnO. To conclude, with Al doping insertion, Equation (5) implies a decrease in resistance, whereas Equation (6) suggests an increase in resistance. As portrayed in Figure 11b, the sensing material resistance for Al:ZnO-5 h is rising compared to Al:ZnO-4 h. In their study, Algun and Alkay discovered that AFZO nanostructured thin film electrical resistivity begins to increase owing to lattice disturbances that reduce carrier mobility attributable to scattering on the grain boundary [77]. Considering another standpoint, owing to carriers scattered by disorganized atomic layers at the grain boundary, the electrical characteristics of polycrystalline materials are affected by the grain size. When the grain size was at an optimum level, more atoms were orderly arranged, and the grain boundary was reduced. This mechanism allowed carrier electrons to convey from grain to grain easily, reducing electrical resistance. Hence, this study proposes that for immersion times less and equal to 4 h, Equation (5) may predominate, resulting in a decrease in resistance, whereas Equation (6) was more favorable for longer immersion times. Based on the justifications presented above, it was genuinely presumed that the electron compensation mechanism was highly plausible in this report. As confirmed by the XPS and I–V results earlier, the predominant effects were oxygen vacancies and electron compensation results in the formation of oxygen vacancies and free electrons. In turn, the oxygen vacancy served as a doubly charged donor and provided free electrons, as shown in Equation (7) [78].
Subsequently, Al functioned as a cationic dopant (Al3+) in the ZnO lattice framework and provided available electrons and oxygen vacancies. These oxygen vacancies and other associated imperfections in the ZnO lattice framework served as advantageous prospective water molecule adsorption sites for humidity-sensing applications.
3.4. Flexible Humidity Sensor Sensing Characteristics
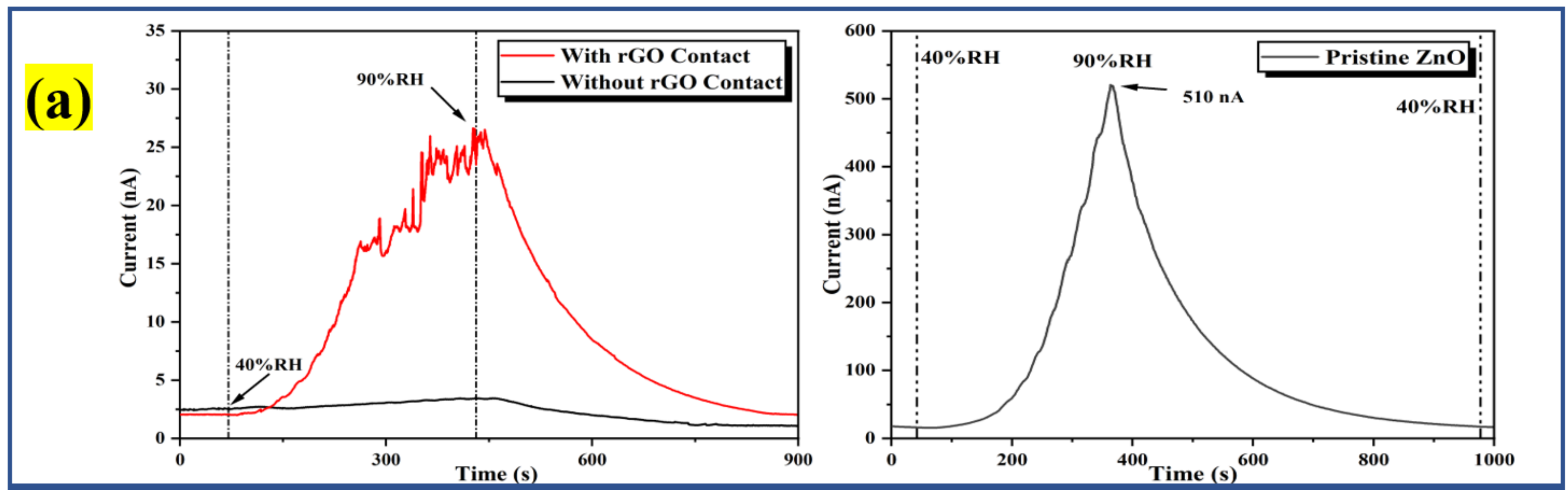
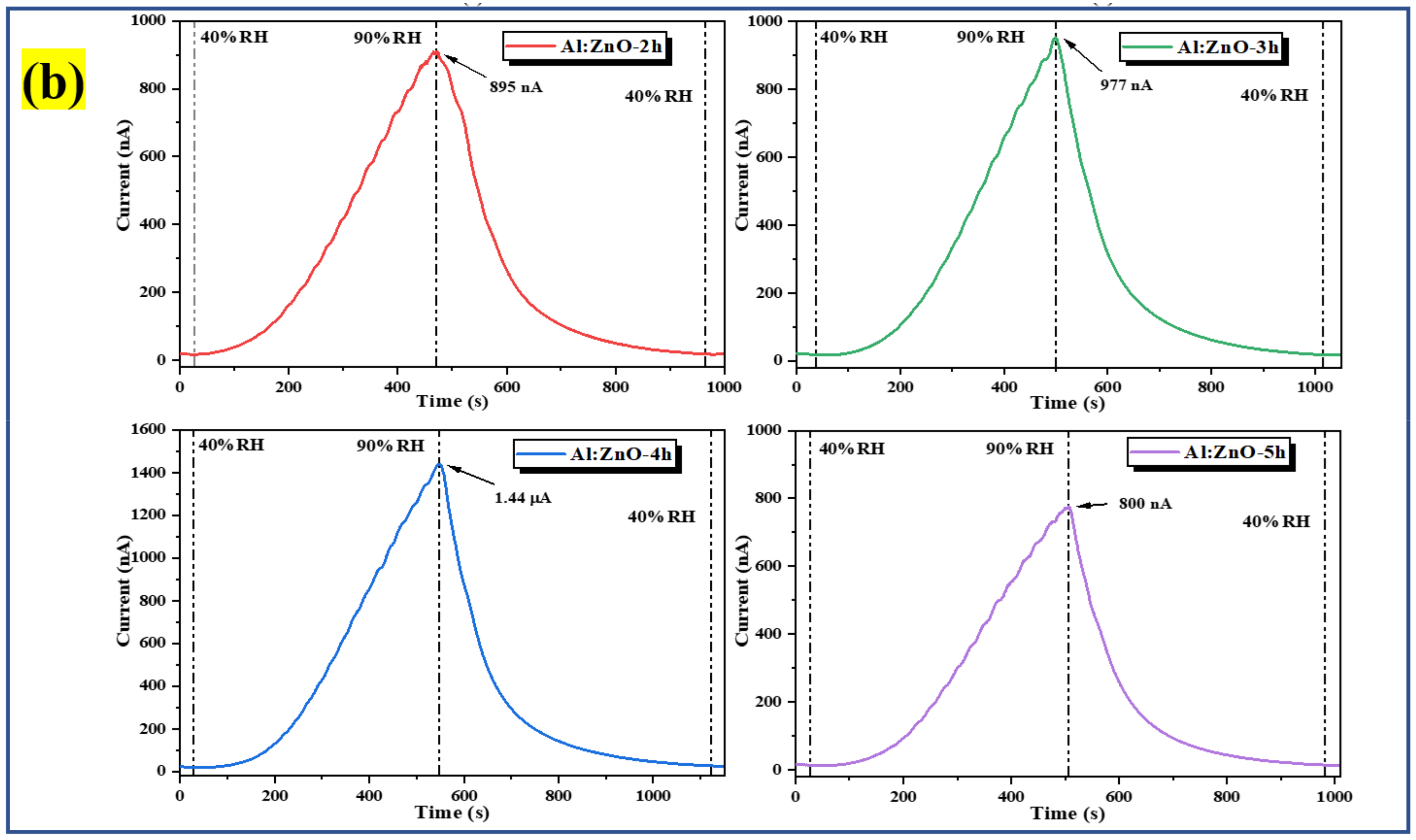
The humidity-sensing characteristics of the pristine ZnO and Al:ZnO nanostructures-based flexible humidity sensors were investigated by employing a temperature and humidity-controlled benchtop chamber with a bias voltage regulated at 5 V. During the measurement process, the temperature inside the chamber was regulated at 25 °C to replicate the surrounding temperature [79]. To investigate the sensor response toward humidity adsorption, the measurement was executed employing dynamic switching behavior by stepping the RH from a baseline humidity level (40 %RH) to a maximum humidity level (90 %RH). Subsequently, to assess the sensor response to humidity desorption, the RH was reduced from the maximum to the baseline humidity level. The response of the pristine ZnO and Al:ZnO nanostructured-based flexible humidity sensors towards humidity variations is illustrated in the current versus time plane at varying humidity levels, as seen in Figure 12. In addition, the bare substrate (without a sensitive layer) response curve is depicted in Figure 12a. At a baseline humidity level of 40 %RH, all samples demonstrated a consistent amplitude before the ramp-up in humidity. Notably, the current signal gradually increased until it reached a maximum value when the humidity level ascended, approaching 90 %RH. Contrasted to pristine ZnO nanostructured-based flexible humidity sensors, all the Al:ZnO-based flexible humidity sensors demonstrated exceptional responses toward humidity variations in the adsorption and desorption process. The current value increased gradually in all samples as the humidity level increased and then progressively diminished as the humidity level declined. Compared to the Al:ZnO nanostructured-based flexible humidity sensor, the pristine ZnO nanostructured-based flexible humidity sensor generated slight output current variations throughout one completed cycle of the adsorption/desorption process. This infers that the doping strategy significantly enhanced humidity-sensing competencies. The flexible humidity sensor based on Al-ZnO-4 h nanostructures showed the largest oscillations in current, indicating an excellent sensitivity toward humidity adjustments. Adsorption and desorption take place through dissimilar mechanisms. The water vapor molecule absorbed to the sensing material surface necessitates external energy to be released, creating an endothermic operation. Disintegrated bonds usually required a longer time than anticipated; thus, recovery time usually requires longer than response time, as reflected in Figure 12. The water molecules’ adsorption releases energy, hence making the process an exothermic process. The splitting of the hydrogen bond between the oxide anion and the hydroxyl functional group required activation energy; thus, desorption kinematics was slower than adsorption kinematics.
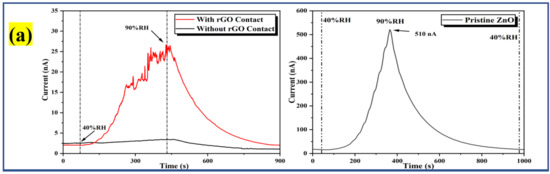
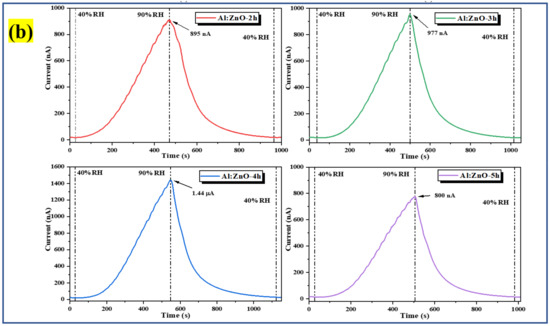
Figure 12.
Humidity response of the (a) bare substrate with and without rGO contact and pristine ZnO; and (b) Al:ZnO-based flexible humidity sensors with varying doping immersion time at humidity levels from 40% to 90 %RH with 5 V bias.
The sensitivity, S, of the pristine ZnO and Al:ZnO nanostructured-based flexible humidity sensor was computed assuming the following relationships, concentrating on the proportion of the current variations as normally used for gas/chemical sensor sensitivity calculation [80,81,82]:
where Ro is denoted as the baseline humidity level resistance, and Rx is the fluctuating humidity levels resistance. The resistance values were obtained by interpreting the current measurements from response curves and applying Ohm’s law. Furthermore, the sensitivity (S) of the samples, particularly for the humidity sensor, could be estimated by computing the relationship between a difference in resistance (RO − RX) and changes in relative humidity (Δ%RH), as shown in Equation (8) [83,84]. Table 3 presents the average value of Ro, Rx, and sensitivity of the pristine ZnO and Al:ZnO nanostructured-based flexible humidity sensors at baseline and maximum humidity levels. The sensitivity for bare substrate with and without rGO was 9.52 and 1.75, respectively. The presence of rGO contacts potentially behaved as a gateway to facilitate the transportation of electrons due to the graphitization and formation of sp2 carbon.

Table 3.
Average resistance, sensitivity, and sensing response of the pristine ZnO and Al:ZnO nanostructured-based flexible humidity sensors.
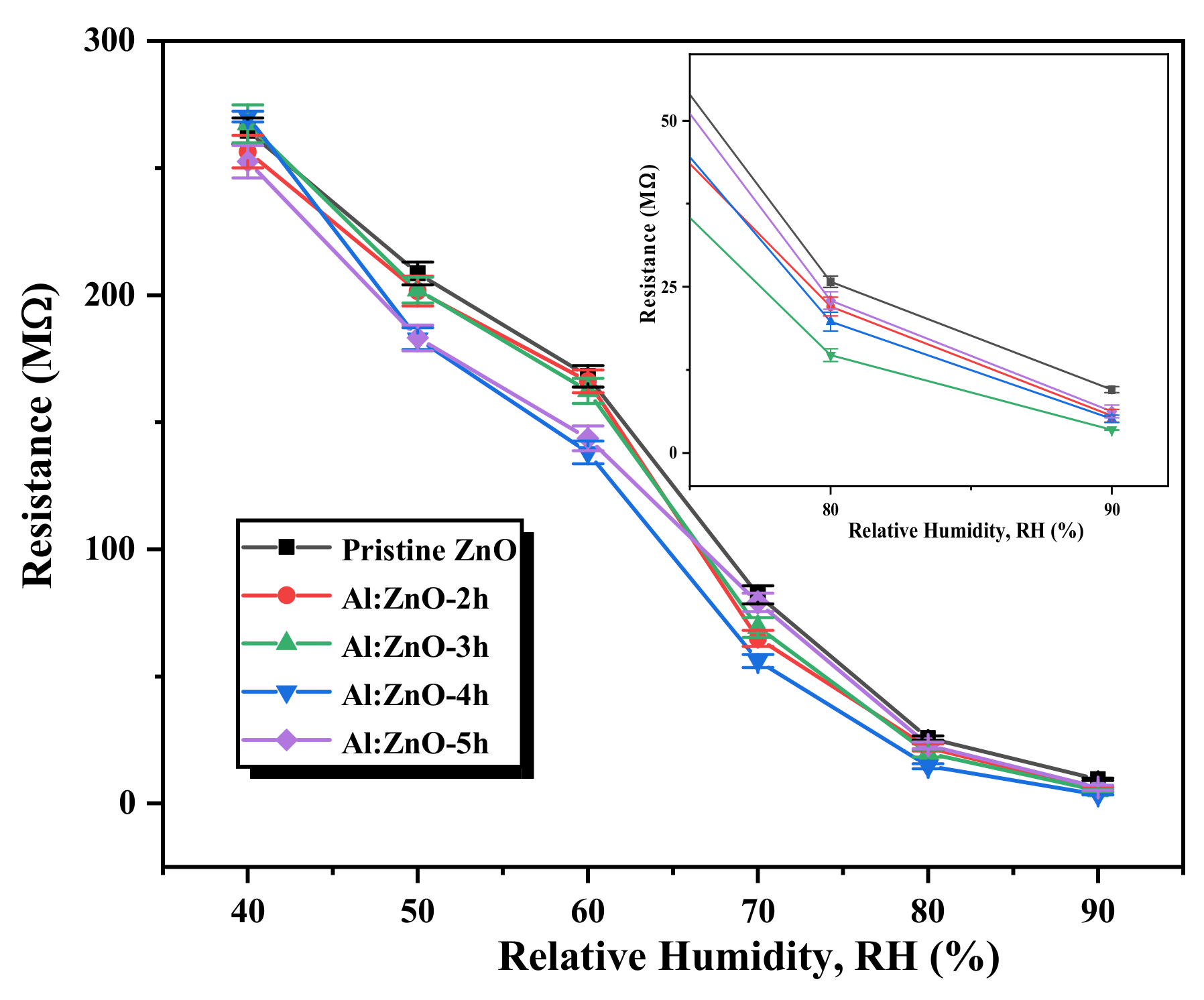
The differences in the resistance of the pristine ZnO and Al:ZnO nanostructured-based flexible humidity sensors are portrayed in Figure 13. It vividly elucidates that the resistance of the Al:ZnO nanostructure samples diminished approximately linearly when the humidity level increased in the operational range of the RH. This observation infers that, compared to pristine ZnO, Al:ZnO nanostructured-based flexible humidity sensors are highly sensitive to humidity variations. The adsorption of water molecules on the surface of sensing materials can be credited to various factors, including morphological, structural, chemical composition, and electrical properties induced by Al doping. These factors are widely accepted as a cause of resistance decreasing with increasing relative humidity. Consequently, this behavior verified the feasibility and efficacy of Al:ZnO nanostructures for humidity-sensing intentions. Furthermore, the fundamental intention of this research is for enhancing the humidity sensitivity and sensing response of pristine Zn by optimizing Al doping assimilation immersion time.
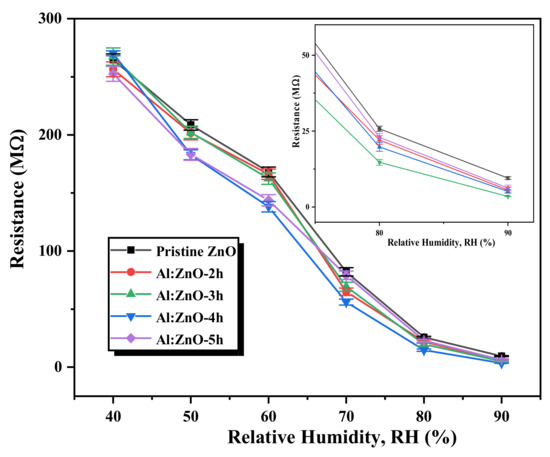
Figure 13.
Variation in the resistance of the pristine ZnO and Al:ZnO nanostructured-based flexible humidity sensors with varying doping immersion time at various humidity levels at 25 °C (inset shows the magnified image at 80 %RH and 90 %RH).
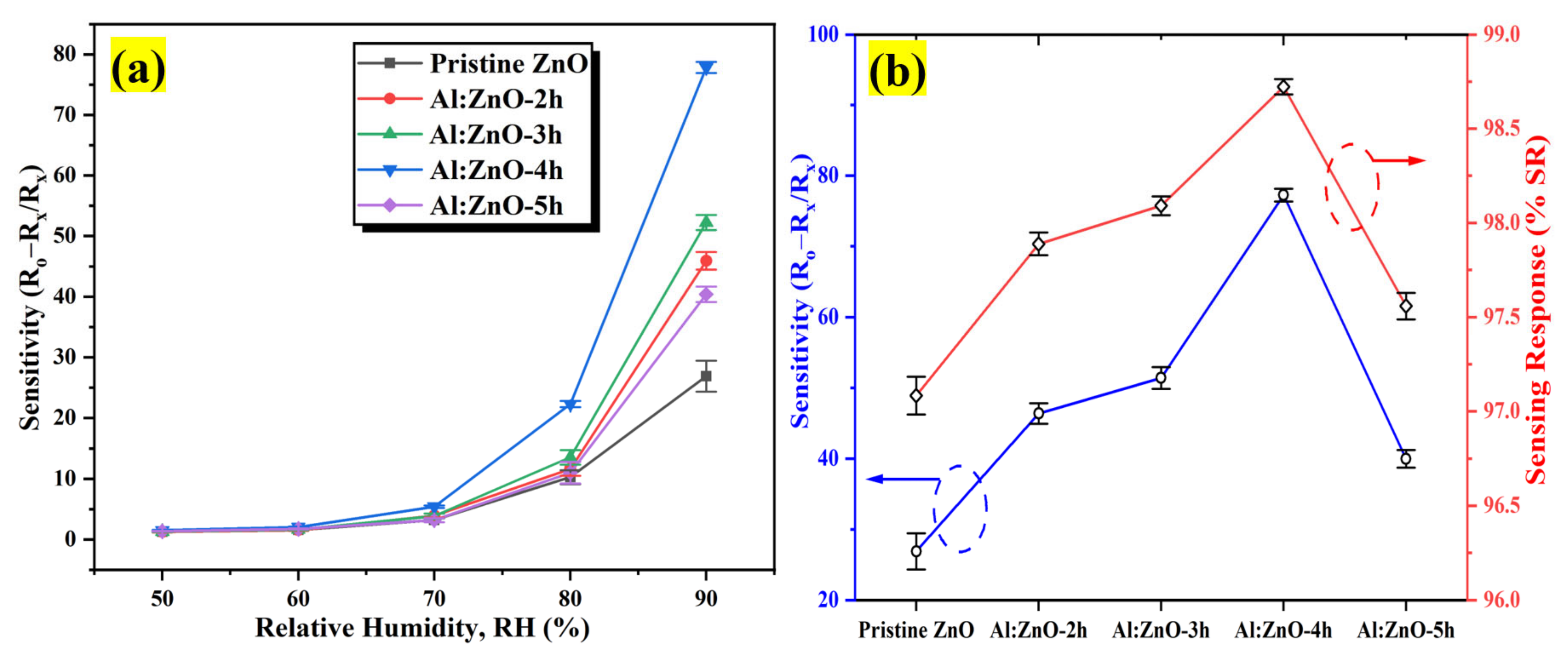
The sensitivity profiles at different humidity levels, as presented in Figure 14a, corroborate the performance of the Al:ZnO-4 h at elevated humidity levels greater than 70 %RH, which performed significantly better than other samples. A substantial enhancement in sensitivity driven by the optimum immersion time for the Al doping strategy was demonstrated according to the sensitivity profile in Figure 14b. The results revealed that the proposed sensors obtained by introducing the Al dopant element exhibited the highest change in sensor resistance with respect to the change in RH%. This trend was possibly due to the lowest film resistance (maximum conductivity) obtained for the Al:ZnO-4 h sample, as shown in Figure 11b, which improved electron migration and increased free carrier concentration, thus enhancing the number of ionized water molecules on the surface of the Al:ZnO-4 h humidity sensor. Furthermore, the FESEM analysis showed that the Al:ZnO-4 h contained smaller nanoparticles than other samples, promoting the surface porosity of the sample. As the humidity level increased (>70 %RH), the porosity enhanced the water adsorption process due to the higher surface area of the capillary nanopores. The AlZnO-4 h nanostructures-based flexible humidity sensor showed a maximum sensitivity of 77.3 or 5.37 ± 0.04 MΩ/%RH. The AlZnO-2 h, AlZnO-3 h, and AlZnO-5 h nanostructured-based flexible humidity sensors had a sensitivity of 46.4 or 5.13 ± 0.07 MΩ/%RH, 51.3 or 5.27 ± 0.09 MΩ/%RH, and 39.9 or 5.07 ± 0.08 MΩ/%RH, respectively. The flexible humidity sensor based on pristine ZnO had a sensitivity of 26.9 or 4.95 ± 0.09 MΩ/%RH. These results confirmed that the doping approach provides the maximum improvements in sensor sensitivity and suggested that the optimum time for the immersion procedure was 4 h. Furthermore, the sensitivity measured by the proposed Al:ZnO-4 h humidity sensor was higher than that reported by Sahoo et al. (4.49 MΩ/%RH) in the same relative humidity ranges [83]. From five measurements of the same flexible humidity sensor, the calculated error bars represented the standard deviation from the mean readings at the prescribed RH. For Al:ZnO-4 h, the standard deviation was less than 0.5%, signifying that the sensitivity was reproducible from one measurement to another. Figure 15 exhibits the relationship between resistance and sensitivity for Al:ZnO-4 h at distinct RH levels.
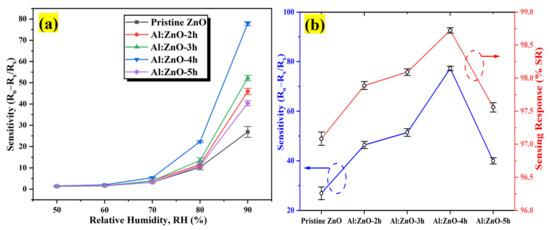
Figure 14.
(a) Sensitivity plot of the pristine ZnO and Al:ZnO nanostructured-based flexible humidity sensors with a different immersion time of Al doping process at different humidity levels at 25 °C and (b) sensitivity and sensing response variation of the pristine ZnO and Al:ZnO nanostructured-based flexible humidity sensors.
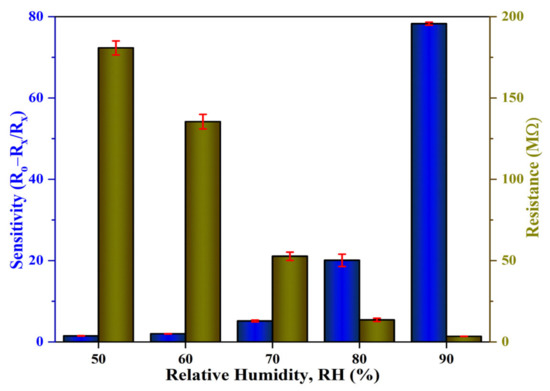
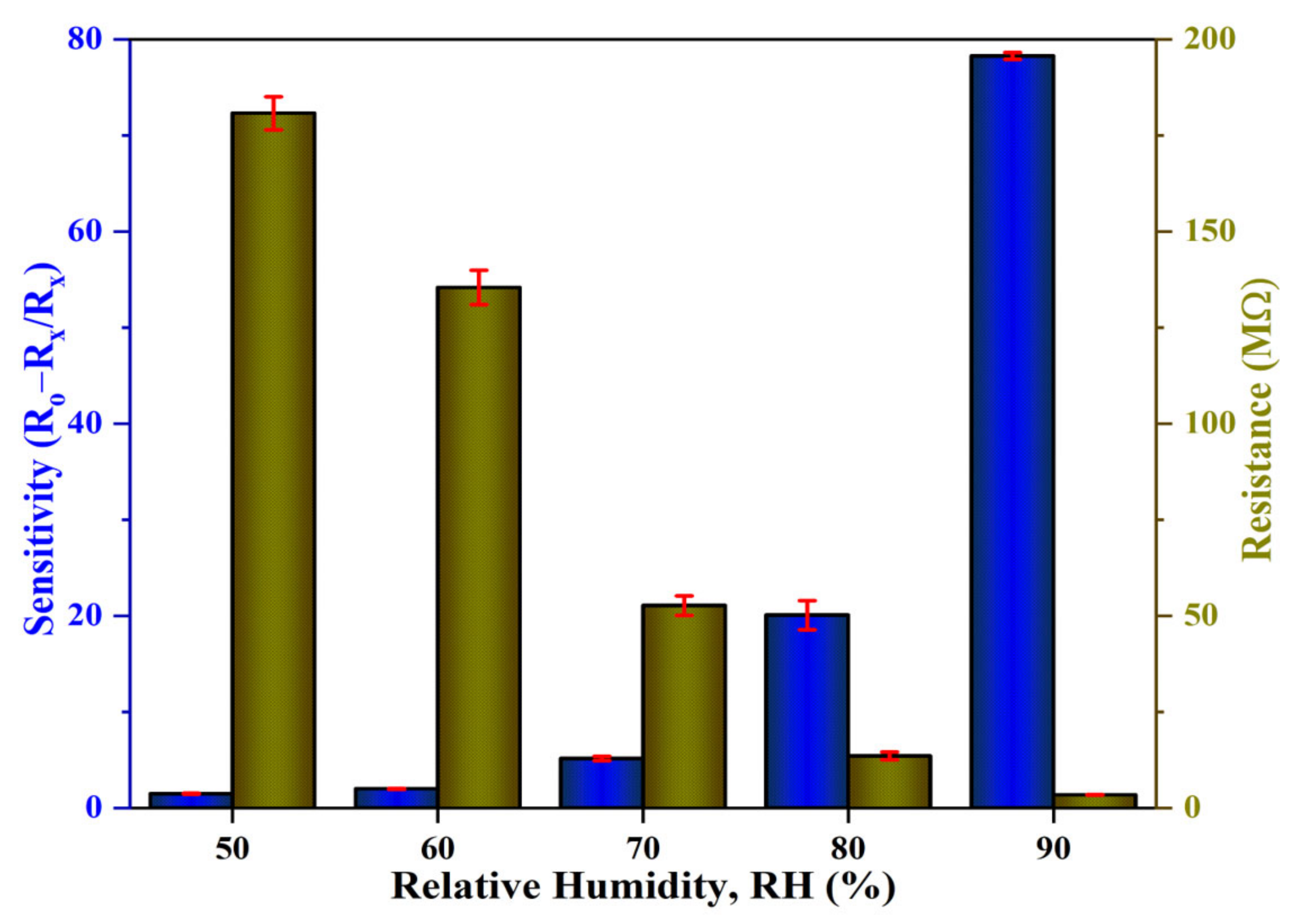
Figure 15.
Correlation of the resistance and sensitivity of the Al:ZnO-4 h nanostructured-based flexible humidity sensor.
The factor that contributed to increased sensitivity was the existence of a high surface area, which accelerated water vapor diffusion and expedited the adsorption of water molecules throughout sensing activities [9]. The increased sensitivity demonstrated in the Al:ZnO-4 h nanostructured-based flexible humidity sensor was ascribed to the decreased crystallite size due to appropriate Al impurity integration in the ZnO lattice framework. According to the HRTEM and FESEM analyses, Al:ZnO-4 h nanostructures had a higher surface area due to the reduction in crystallite size, implying improved water-vapor adsorption. The reduction in crystallite size enhanced the humidity mechanism by providing extensive grain boundaries and increasing porosity for the capillary condensation mechanism.
According to Arularasu et al., the hybrid nanocomposites’ greater spherical surface area was induced by the formation of the pores owing to the intergranular particle interaction, promoting the sensitivity and improved performance of the humidity sensor due to the improved electrical conductivity through continuous water layers within the pores [85]. Furthermore, the smaller crystallite size enabled better crystallinity, validated by XRD data. Algun et al. reported that the structure with a highly crystalline nature was much inclined to combine with water molecules, maximizing the absorbed water molecules quantity [77]. If a structure possessed a low crystallinity, the lattice atoms were less prone to engaging with water molecules, resulting in a lower sensitivity to humidity variation. All Al:ZnO nanostructured-based flexible humidity sensors outperformed their pure counterparts in term of sensitivity and sensing response. The other plausible justification is due to the formation of a greater number of oxygen defect (oxygen vacancy) sites in Al:ZnO nanostructures. The XPS results of this work showed that incorporating Al3+ cations into the zinc oxide lattice matrix increased the rich surface oxygen vacancies on the surface of ZnO nanostructures, hence facilitating the absorption of immense water molecules on the surface of Al-doped ZnO nanostructures [63]. Furthermore, incorporating doping impurity into the pristine material considerably elevated its conductivity due to an increase in carrier concentration [86]. According to Ismail et al., the highest sensitivity of the evaluated humidity sensor may be connected with the material’s highest conductivity behavior [87]. This argument was corroborated by the I–V measurement analysis obtained, which confirmed that the Al:ZnO-4 h nanostructured-based flexible humidity sensor exhibited a decreased film resistance, leading to enhanced electron transport capacities and an increase in the number of free charge carriers. The flexible humidity sensor’s sensing performance was marginally diminished when immersion time increased for 5 h. As mentioned earlier, the exorbitant replacement of dopant impurity atoms in the ZnO lattice structure weakened the structure instead of increasing the amount of carrier concentration. This argument is corroborated by the I–V measurement profile, which reveals that a humidity-sensitive sensing material immersed for 5 h possesses an increased film resistance, resulting in the decreased number of free charge carriers and inadequate electron transport competencies because of the carrier-scattering effect that occurs at grain boundaries. The humidity sensor’s sensing response was defined as the relative difference in sensor resistance compared to the resistance associated with the baseline humidity level, in percentage value as realized in Equation (9) below [88]:
where, Ro represents the baseline humidity level resistance, while Rx denotes the fluctuating humidity-level resistance. The calculated %SR values for the pristine ZnO and Al:ZnO nanostructured-based flexible humidity sensors are tabulated in Table 3. The Al:ZnO-4 h nanostructured-based flexible humidity sensor logged the maximum %SR with a standard deviation that was less than 0.1%. Several studies have been carried out to assess the potential dopant element that can be integrated into the ZnO lattice framework and its potential as a humidity-sensitive sensing material for humidity sensors application. Table 4 summarizes the fabricated humidity sensor’s sensing characteristics (sensitivity calculation) in contrast to previous research. The humidity-sensing assessment presented in this study was comparable and showed an improvement compared to previous works. The proposed Al:ZnO nanostructured-based flexible humidity sensor (Al:ZnO-4 h) possessed good sensitivity toward humidity changes. This study discovered that employing cellulose paper as flexible substrates with enhanced surface functionalization exhibits a high sensitivity in the humidity range of 40 %RH to 90 %RH. This implied that our Al:ZnO samples had a higher sensitivity to humidity fluctuations when compared to previously reported ZnO-based humidity sensors.

Table 4.
Comparison of the humidity-sensing performance of the Al:ZnO nanostructured-based flexible humidity sensor with other reported dopant-induced ZnO-based humidity sensor devices.
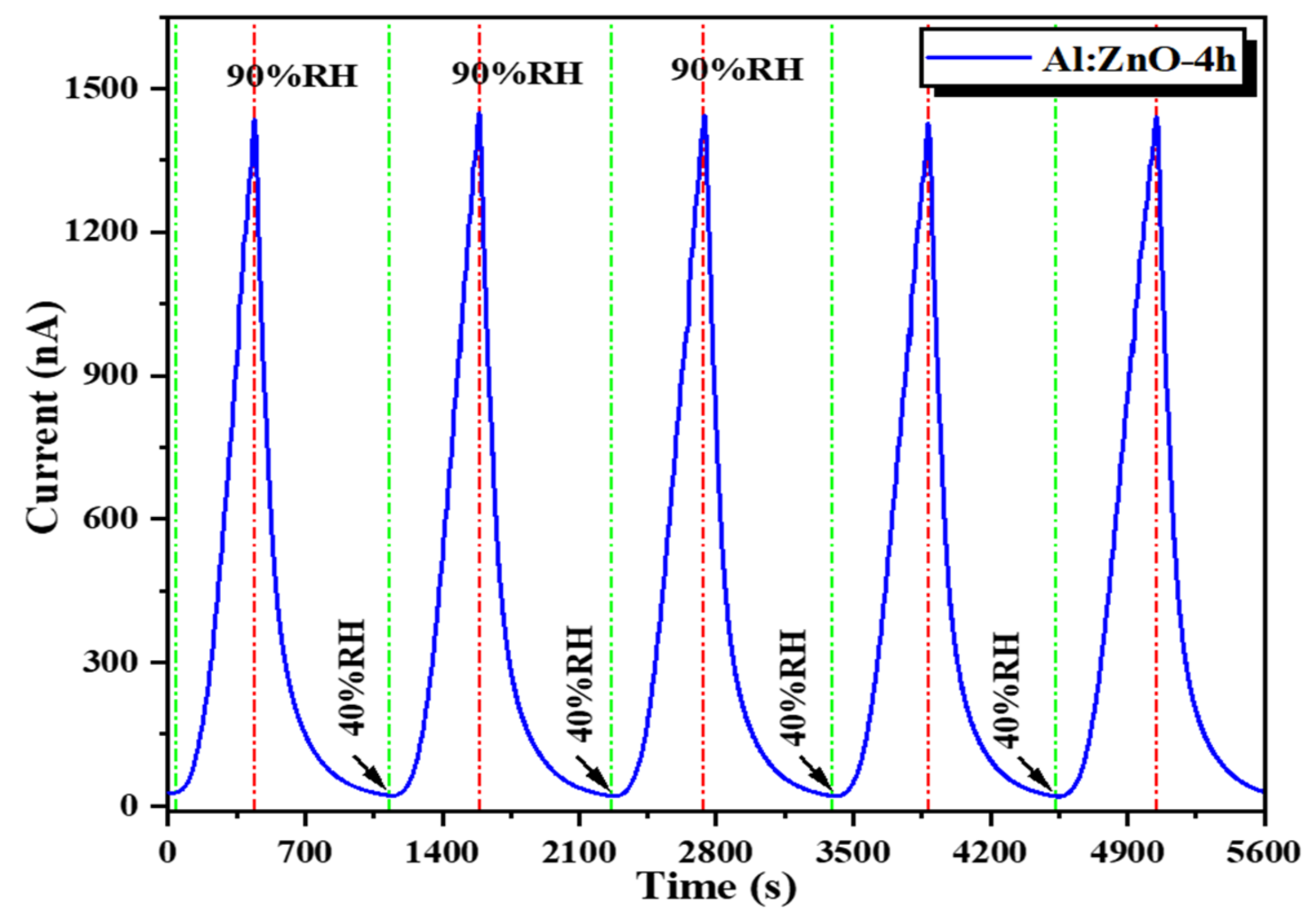
Furthermore, due to the highest evaluated sensitivity and sensing response towards humidity variation, the Al:ZnO-4 h nanostructured-based flexible humidity sensor was submitted to various performance assessments. For five cycles, the responsiveness of the Al:ZnO-4 h flexible humidity sensor was assessed to accurately evaluate its repeatability and reproducibility performance. As depicted in Figure 16, the Al:ZnO-4 h sensors demonstrated a coherent response/recovery feature with sufficient repeatability and reproducibility characteristics for the humidity-sensing instrument. The Al:ZnO-4 h nanostructured-based flexible humidity sensor was exceptionally stable throughout five cycles, with nearly comparable profiles and consistent current values. No substantial reduction was observed in the current amplitude in any cycle. This outcome was congruent with the previous research outcome by Musa et al. [89].
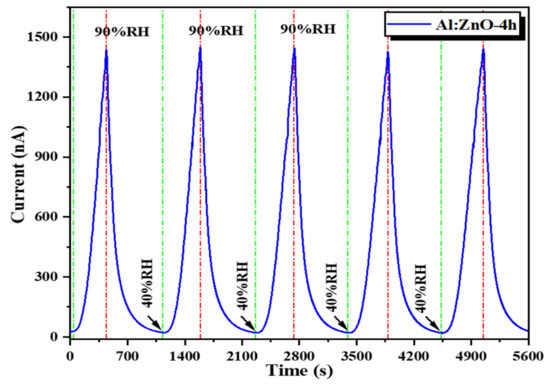
Figure 16.
Repeatability behavior (response/recovery characteristic) of the Al:ZnO-4 h nanostructured-based flexible humidity sensor.
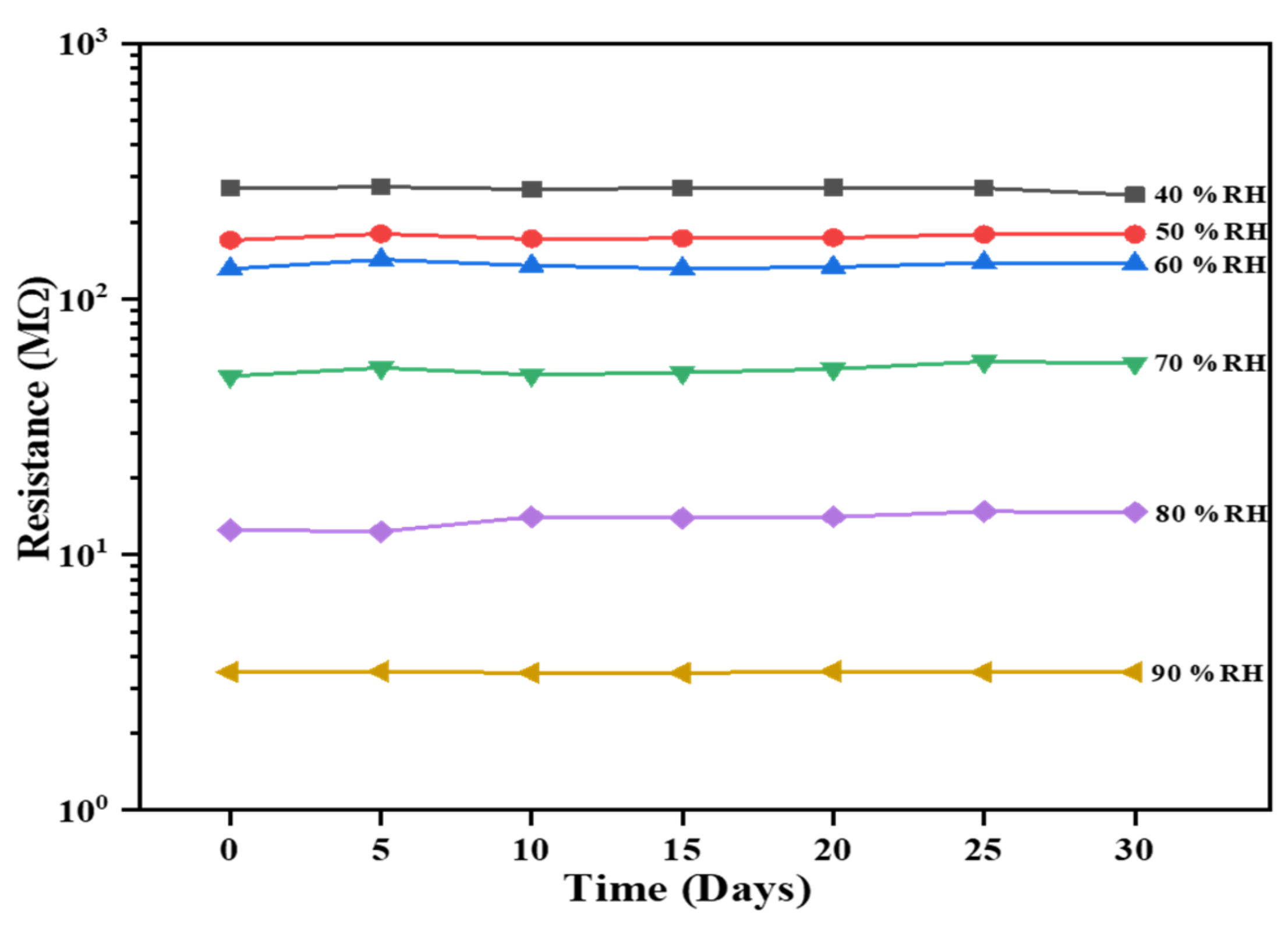
Another crucial and indispensable criterion in assessing the sensing performance of the Al:ZnO-4 h sensor is through sensing stability over time. The sensor’s excellent efficiency is accomplished by long-term stability. The sensing response of the Al:ZnO-4 h flexible humidity sensor was evaluated every 5 days for over a month, and the resultant stability at 40%, 50%, 60%, 70%, 80%, and 90 %RH is exhibited in Figure 17. The resistance values of the humidity-sensitive sensing nanostructures material showed negligible fluctuation in resistances for each cycle throughout the 30-day time frame. Therefore, the long-term stability for humidity detection of the Al:ZnO-4 h nanostructures-based flexible humidity sensor demonstrated a coherent and adequate result with acceptable reliability.
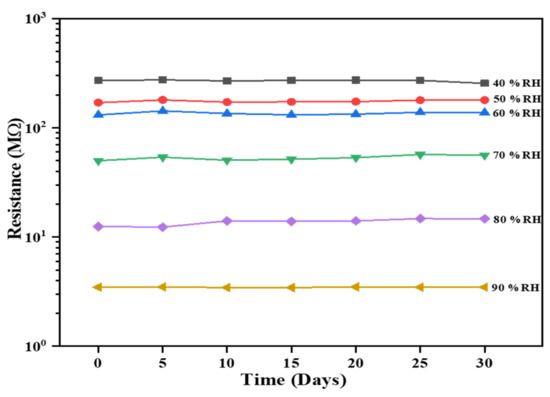
Figure 17.
Stability over time of the Al:ZnO-4 h nanostructured-based flexible humidity sensor exposed to 40%, 50%, 60%, 70%, 80%, and 90 %RH.
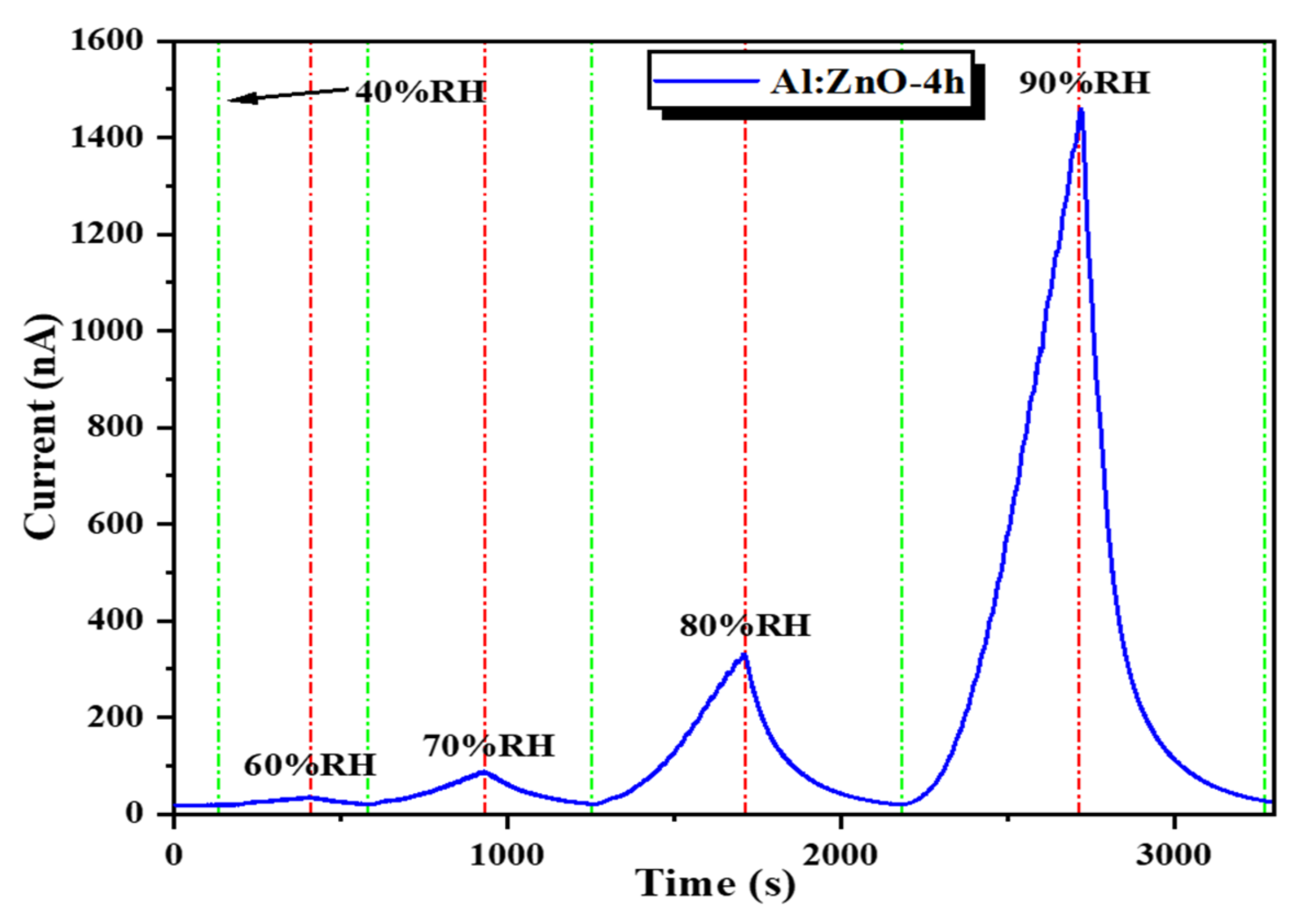
The Al:ZnO-4 h flexible humidity sensor, subjected to distinct RH levels of sensing response, was measured in a stacking manner (Figure 18). The cycle switching RH testing was performed by assessing the response/recovery behavior of the sensor under various RH cycles known as C1: 40 %RH → 60 %RH → 40 %RH, C2: 40 %RH → 70 %RH → 40 %RH, C3: 40 %RH → 80 %RH → 40 %RH, and C4: 40 %RH → 90 %RH → 40 %RH. The Al:ZnO-4 h sensor generated good detectability and response/recovery behavior towards each level of humidity adjustment. The calculated sensitivities were 2.01 (C1), 5.17 (C2), 20.08 (C3), and 77.3 (C4). According to this observation, the Al:ZnO-4 h flexible humidity sensor was sensitive to distinct RH levels, and its sensitivity improved as RH levels increased.
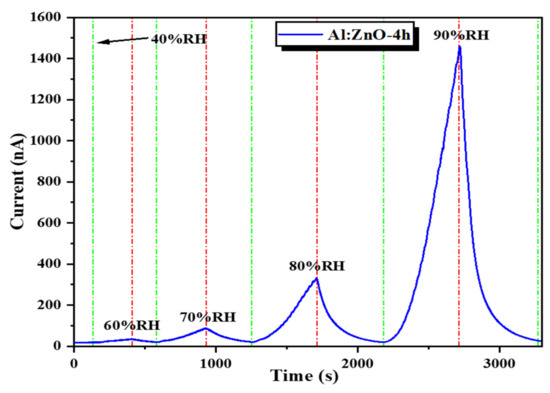
Figure 18.
Humidity-sensing response of the Al:ZnO-4 h nanostructured-based flexible humidity sensor at various relative humidity levels.
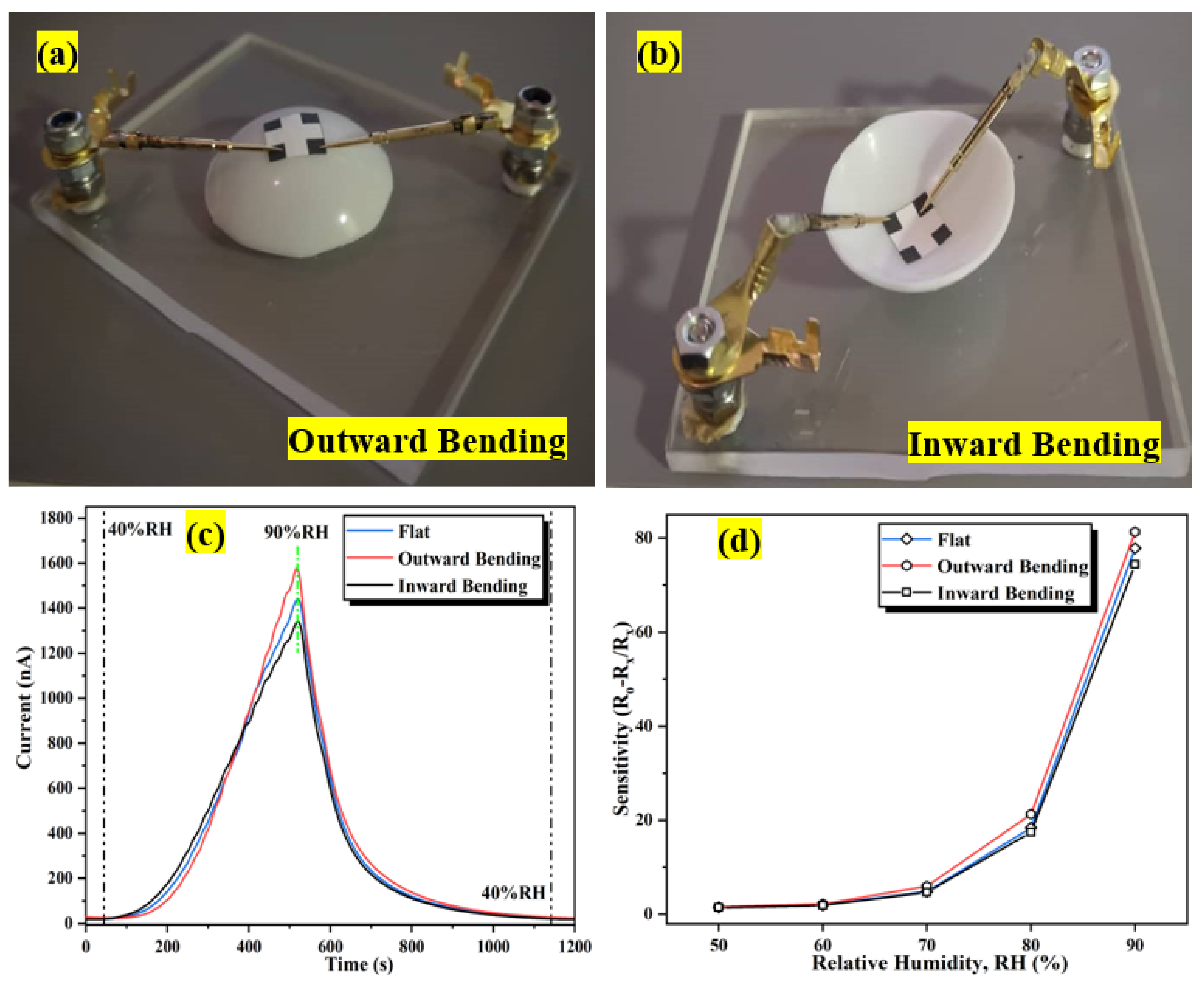
Flexible humidity sensors must have decent conformal properties to efficiently prevent humidity-sensitive materials from cracking and deforming, hence degrading the sensing structure. The bending assessment of a flexible humidity sensor is essential towards its functional application. Therefore, the flexibility of the humidity sensor was investigated by comparing the performance of the sensor with and without bending under different bending conditions. Figure 19a,b shows the configuration of the sensor bent outward and inward at an 8 mm radius, followed by exposure to a dynamic humidity sweeping from 40 %RH to 90 %RH. Although there is a slight variation in the sensor’s initial current (I40) and fluctuating current (I90) values under different bending conditions, there is no discernible difference in the sensor response curve under outward or inward bending compared to the flat condition as portrayed in Figure 19c, which signifies that this flexible sensor is resistant to substantial bending deformation with an 8 mm bending radius. Similar observations have been reported by Wu and his co-worker [93]. Under bending conditions, the output current signal of the sensor remains stable in one complete cycle, with only a minimal variation in current response observed while the response/recovery time is unaffected. Figure 19d indicates the sensitivity profiles of the sensor at different humidity levels (%RH) at flat and two configurations of bending conditions (outward and inward). The maximum sensitivity for flat, outward, and inward bending configurations are 77.8, 81.3, and 74.4, respectively, denoting that, compared to flat configuration, the sensitivity increases (outward bending) and decreases (inward bending) within 5% depending on the bending conditions. The results portray that during the outward bending condition, the Al:ZnO sensitive layer’s contact region increases and enlarges the pores, hence allowing water molecules to penetrate deeper into the sensitive material, increasing the sensitivity of the sensor [7]. Generally, the stress within the sensitive layer induces signal drift in flexible devices during bending. As the bending magnitude is high, a stress mismatch between the sensitive layer and the substrate or detachment of the sensitive layer and the substrate may occur [30].
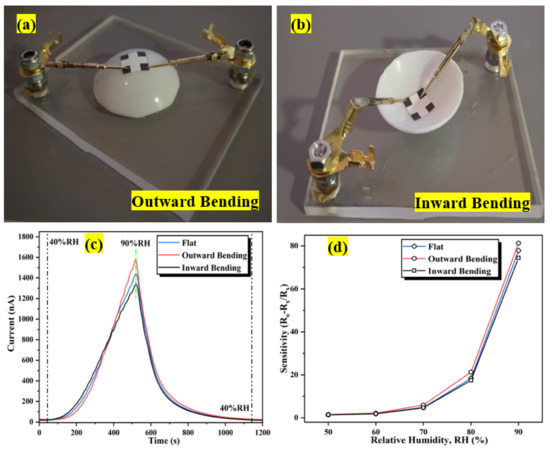
Figure 19.
Configuration of the bending assessment: (a) outward bending; (b) inward bending. (c) Dynamic humidity-sensing response variation after distinct bending conditions. (d) Sensitivity profiles at different humidity levels (%RH) under flat and bending conditions.
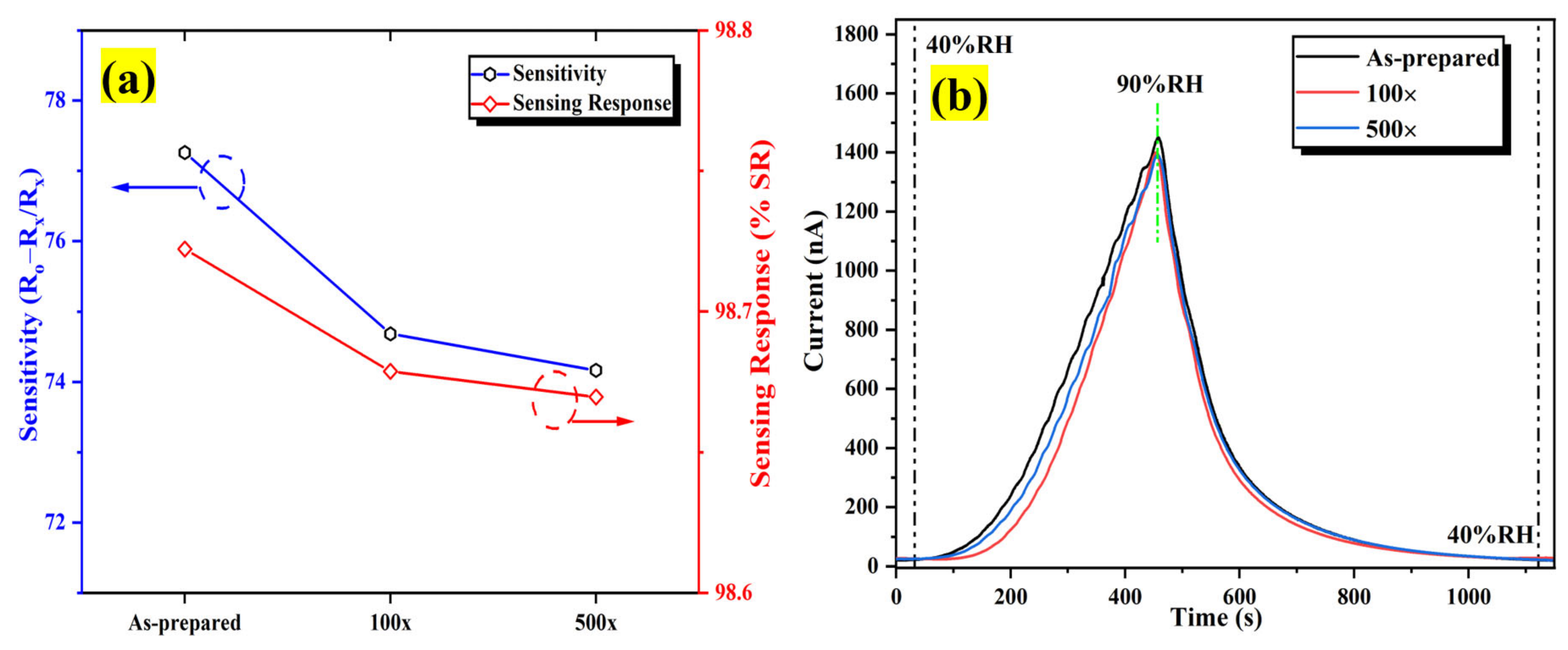
The repeatability assessment was conducted utilizing a bending radius of 8 mm. Figure 20a clearly illustrates that the sensitivity after bend deformation 500 times is marginally lesser compared to the as-prepared humidity sensor but approximately identical to the humidity sensor that has been bent 100 times. As depicted in Figure 20b, there is a less significant change in the dynamic response/recovery humidity sweeping characteristic after bending 100 and 500 times, inferring that the Al:ZnO flexible humidity sensor possesses decent bending properties. Resultantly, the fluctuation in sensitivity was less than 5%, implying that the proposed Al:ZnO flexible humidity sensors have decent stability and reversibility under bending cycles, which is comparable with findings reported by Romero et al. [94].
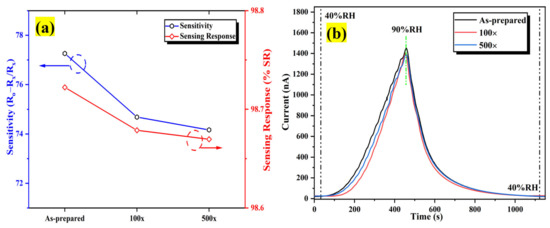
Figure 20.
The influence of bending assessment on the performance of the humidity sensor (a) sensitivity and (b) dynamic sensing response variation after distinct bending times.
From this investigation, this study discovered that the existence of a high surface area, reduction in particle size, decent crystallinity structure, formation of oxygen defect sites in Al:ZnO nanostructures, and intensification in carrier concentration were related to the incorporation of Al doping impurity. Furthermore, these factors were beneficial for the electrical and humidity-sensing capabilities of a humidity sensor. The electrical and humidity-sensing performance assessment outcomes for the Al:ZnO nanostructures determined in this investigation were equivalent and better than those achieved in our colleagues’ prior studies [79,87]. These findings implied that the fabrication of a flexible humidity sensor utilizing cellulose filter paper as a flexible substrate with the integration of Al-doped ZnO nanostructures synthesized with an optimal immersion time of 4 h as the sensing material yielded a positive effect in terms of sensitivity, repeatability, detectability, and stability of the sensor. Therefore, it possessed potential as a humidity-sensing material.
From the literature, one plausible sensing mechanism is based on the changes in resistance of the sensing material’s surface induced by water molecule adsorption and desorption process on the metal oxide (MO) grains covering the whole surface of the humidity sensor [95]. For a relatively lower humidity level (40 %RH), the small amount of water molecule becomes chemisorbed to the MO surface, where the water molecules self-ionize and decompose at the surface sites to form a hydroxyl anion (OH−), hydrogen cation (H+), and produce oxygen vacancies. This formation culminates in a high resistance condition for the sensor. The existence of Zn2+ and Al3+ cations in the sensing material surface with oxygen vacancies creates a dense local charge density and a substantial electrostatic field, facilitating the water molecule chemisorption mechanism and stimulating the decomposition of water molecules [24]. At this stage, because of the scarce concentration of protons and the increased energy required for proton transportation, conduction is predominantly regulated by the H+ cation; thus, conduction does not occur continuously. The concentration of the carrier is lowered by the occurrence of chemisorbed water molecules, leading to higher resistance in the sensing material. This observation aligned with our observations, as illustrated in Figure 12. The chemisorption procedure was irreversible at ambient temperature, resulting in a perpetual formation of a chemisorbed hydroxyl layer on the Al:ZnO-4 h surface. Water molecules adhered to the surface oxygen vacancies of the sensing material. Due to the generation of doubled hydrogen bonds, transportation of charge carriers was restricted to transmit efficiently in the chemisorbed layer, resulting in increased electrical resistance. As for the Al:ZnO-4 h nanostructured-based flexible humidity sensor, additional free electrons were generated in the ZnO lattice due to an oxygen vacancies deficiency, which improved the overall humidity-sensing performance, as represented in the subsequent reaction [96]:
where, the lattice oxygen at the oxygen matrix is denoted as Oo, and the vacancy formed at the oxygen matrix is marked as Voo. XPS studies showed that substituting a Zn cation with an Al cation triggered lattice distortion, contributing to significantly more oxygen deficiencies. The oxygen vacancies enhanced the assimilation of additional water vapor molecules on the surface of Al:ZnO nanostructures and accelerated the decomposition process. As indicated in reaction Equation (10), the resistance was expected to reduce with increasing relative humidity due to the presence of free electrons (an increase in carrier concentration) [97].
As the humidity slightly increased (>40 %RH), the adsorbed water molecules gradually formed a continuous monolayer on the sensing surface. Because of the strong electrostatic interaction in the chemisorbed layer, the hydroxyl radical anions (OH−) establish indefinite bonds with the humidity sensor’s positively charged metal ions (Zn2+ and Al3+ cations), hence producing and releasing highly dense hydrogen cations for electrical conduction. At this stage, on top of a chemisorbed aqueous layer, a considerable quantity of water molecules was bound and intensified the connection with a hydroxyl group. These molecules assisted in the establishment of an aqueous physical adsorption layer on the humidity-sensitive sensing surface. The persistent adsorption of water molecules dismantled the single hydrogen bonding, permitting protons to migrate relatively freely and establishing the second layer of physisorption water molecules. The resistance in sensing material was minimized by the existence of physisorbed multilayers, which encourage carriers to commence transportation efficiently, as depicted in Figure 13. Auxiliary protons disconnected and engaged with the disintegrated water molecules from the physisorbed component as the water molecule adsorption increased. The water molecules ionized as an outcome of the existence of a significant electrostatic field on the interface of the Al:ZnO nanostructures as well as persistent hydration. This resulted in the formation of hydronium cations and hydroxyl anions. The hydronium cations, H3O+, functioning as charge carriers, and ionic conduction modulated the detection methodology and facilitated the enhancement of sensor responsiveness towards humidity changes. Electrostatic interaction gradually adsorbed the water molecules due to the availability of hydroxyl groups, forming a perpetual aqueous layer. The humidity-sensitive membrane became blanketed with a continuous water layer, constructing a network film that resembled a liquid-like network as the relative humidity further elevated. Therefore, protonic transportation (ionic conductivity) was the predominant electrical conductivity, which emerges as H+ ions were discharged from H3O+ ions and hopped to the next adjacent H+ ions. As a product of the hydration of H3O+, protons (H+ ions) were generated and employed as the principal source of charge carriers for hopping transportation. During this phase, the protonic conduction was extremely effortless. The electrical reaction is triggered by drastically lowering the sensor resistance (contributes towards enhanced conductivity). The H+ ions became liberated to transport smoothly in the continuing physical adsorption of multi-layer water due to their exceptional maneuverability in water vapor, enhancing the proton hopping mechanism. The above process is described as the Grotthuss chain mechanism, expressed in the Equations (11) and (12) below [97,98].
The Al:ZnO-4 h nanostructures’ sensing membrane comprised nanosized asymmetrical quasi-spherical nanoparticles in stacking formation. This formation contributed to a porous channel structure that permitted water molecules to permeate and populate the capillary pathways. Therefore, as a possible consequence, at exceptionally elevated humidity levels, an extensive quantity of water molecules might have effectively occupied the crevices, causing capillary condensation to occur (electrolytic conduction) [99]. At this stage, the protons are fluidly migrating between the boundaries of the nanostructures attributable to the co-existence of the conduction mechanism (protonic and electrolytic), which was mediated by the abundance quantity of H3O+; henceforth, the intensity of charge transportation was significantly enhanced, increasing electrical conductivity of the sensor. The Al:ZnO-4 h sensor’s resistance significantly decreased as the humidity levels increased, enhancing the conductivity and producing a sensitive, flexible humidity sensor. The findings indicated that the Al:ZnO-4 h nanostructures-based flexible humidity sensor outperformed the pristine ZnO in terms of sensing performance. This is primarily attributed to the higher cationic charge, high specific surface area, enhanced crystallinity due to nanoparticle size reduction, and improved surface oxygen vacancy deficiency related to the Al-doping strategy.
4. Conclusions
A sensitive, flexible humidity sensor relying on Al:ZnO nanostructures’ humidity-sensitive sensing material was successfully fabricated in this study. Sensing materials based on the pristine ZnO and Al:ZnO nanostructures were synthesized using a facile and low-temperature ultrasonicated solution immersion procedure. A fine coating of humidity-sensitive sensing material was deposited onto flexible cellulose substrates using an unsophisticated and cost-effective brush printing method. Similarly, a fine coating of humidity-sensitive sensing material paste-like nanocomposite slurry consisting of pristine ZnO and Al:ZnO nanostructures was evenly dispersed across the substrate, enhancing the water molecule absorption’s active sites. Characterization approaches such as XRD, FESEM, TEM with EDS, and XPS were utilized to analyze the structural, morphological, and chemical identification of the synthesized nanostructures. The result confirmed that Al3+ successfully occupied the Zn2+ lattice framework or assimilated into interstitial sites in the ZnO lattice. Consequently, Al impurity doped into pristine ZnO altered different properties of Al:ZnO nanostructures, and the Al doping immersion time strongly influenced this alteration. The XRD analysis revealed that all nanostructures were polycrystalline within the hexagonal wurtzite phase structure, with dominant preferential growth orientation along the (101) peak. The Debye–Scherrer equation and WH-UDM approach were capitalized to estimate the value of average crystallite size and lattice micro-strain. The lattice parameters “a” and “c” were decreased as the Al doping immersion duration increased from 2 h to 5 h, and this change resulted in the diffraction peaks shifting towards a higher angle. Moreover, the crystallinity of nanostructures is marginally deteriorated as the average crystallite size decreased from 48.8 mm to 32.1 nm with the increasing positive lattice tensile strain identified in Al:ZnO nanostructures. According to FESEM analysis, the pristine ZnO and Al:ZnO nanoparticles of various sizes were evenly dispersed, adhered to, and arbitrarily arranged onto the cellulose fibers to form a well-linked network structure with decent adhesiveness. The polycrystalline Al:ZnO-4 h sensing material exhibited porous structures, and the surface porosity improved with Al doping element incorporation due to particle size reduction. Furthermore, according to the HRTEM micrograph, the pristine ZnO and Al:ZnO nanostructures constituted multi-layered aggregated formations with identifiable boundaries and irregularly shaped quasi-spherical nanoparticles. The interplanar distance lowered due to lattice shrinking because Al cations substituted Zn cation sites. The efficiency of doping was verified by quantifying the Al content using EDS and evaluating the Al oxidation states through XPS analysis. EDS detected the Zn, O, and Al elements in the Al:ZnO-4 h nanostructures. Furthermore, the occurrence of Zn, O, and Al is confirmed by a comprehensive XPS survey scan spectrum as the foremost chemical elements of the Al:ZnO-4 h without foreign elemental peaks detected. Moreover, the existence of the oxygen vacancy deficiency and Al ion oxidation state was corroborated by the high-resolution XPS narrow scan spectrum deconvolution. Based on the I–V measurements, the smallest resistance value of 1.93 MΩ was estimated for the Al:ZnO-4 h nanostructure, implying its exceptional electrical properties. Inserting Al3+ into the ZnO lattice decreased the film resistance, increasing conductivity and indicating an increase in the concentration of charge carriers. In terms of the sensitivity and sensing response, all Al:ZnO nanostructured-based flexible humidity sensors outperformed pristine ZnO. Al:ZnO-4 h nanostructures had the highest sensitivity of 77.3 ± 0.9 or 5.37 ± 0.04 MΩ/RH% and a sensing response of 98.72 ± 0.012 in the range of 40 %RH to 90 %RH. The repeatability assessment of the Al:ZnO-4 h nanostructured-based flexible humidity sensor indicated that the sensor was competent to react swiftly to fluctuating humidity levels. As an outcome, the findings indicated that the flexible humidity sensor composed of Al:ZnO-4 h nanostructures exhibited the highest sensitivity towards water molecules adsorption. Furthermore, it showed an improved and decent sensing response, exceptional responsiveness and recovery to humidity differences, outstanding repeatability, and acceptable stability. Furthermore, the fabricated sensor is decently flexible, responded well to humidity variation under different bending conditions (outward and inward), and its performance remained stable after 500 bends. All of these findings revealed that Al:ZnO nanostructures possess a high potential and are a credible sensing material for cost-effective, flexible humidity-sensing applications. Consequently, optimizing the immersion time during doping element integration is crucial.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.S.R.A.S. and M.H.M.; methodology, A.S.R.A.S., M.M.Z., I.B.S.B., N.V. and M.D.B.; validation, M.H.A., M.H.M., M.M.Z., M.K.A. and N.N.; formal analysis, A.S.R.A.S., M.M.Z. and M.H.A.; investigation, A.S.R.A.S., M.D.B., M.K.A. and N.N.; resources, M.H.M., A.M., S.A.B., M.H.A. and M.R.M.; writing—original draft preparation, A.S.R.A.S.; writing—review and editing, A.S.R.A.S., M.H.M., A.M. and S.A.B.; visualization, I.B.S.B., N.V., M.K.A., N.N., A.M., S.A.B. and M.R.M.; supervision, M.H.M., I.B.S.B., N.V., M.R.M. and M.D.B.; funding acquisition, M.H.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Fundamental Research Grant Scheme (FRGS) (FRGS/1/2022/TK07/UITM/02/7). The authors thank the Kementerian Pengajian Tinggi, UiTM’s College of Engineering, Research Management Centre (RMC), and Office of Deputy Vice-Chancellor (Research and Innovation) for their contribution and endless support.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
The authors would wish to articulate their appreciation to the Kementerian Pengajian Tinggi, Pengajian Kejuruteraan Elektrik, Kolej Pengajian Kejuruteraan, UiTM Shah Alam, and Fakulti Teknologi Kejuruteraan Elektrik dan Elektronik (FTKEE), UTeM.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Lei, G.; Lou, C.; Liu, X.; Xie, J.; Li, Z.; Zheng, W.; Zhang, J. Thin films of tungsten oxide materials for advanced gas sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 341, 129996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamat, M.H.; Ismail, A.S.; Parimon, N.; Vasimalai, N.; Abdullah, M.H.; Malek, M.F.; Yaakob, M.K.; Ahmad, M.K.; Nafarizal, N.; Suriani, A.B.; et al. Heterojunction of SnO2 nanosheet/arrayed ZnO nanorods for humidity sensing. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2022, 288, 126436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwiputra, M.A.; Fadhila, F.; Imawan, C.; Fauzia, V. The enhanced performance of capacitive-type humidity sensors based on ZnO nanorods/WS2 nanosheets heterostructure. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 310, 127810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Li, P.; Zhang, H. Preparation and research of a high-performance Zno/SnO2 humidity sensor. Sensors 2022, 22, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahani, H.; Wagiran, R.; Hamidon, M.N. Humidity sensors principle, mechanism, and fabrication technologies: A comprehensive review. Sensors 2014, 14, 7881–7939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakya, V.; Pandey, N.K.; Misra, S.K.; Roy, A. Electrical and optical properties of ZnO-WO3 nanocomposite and its application as a solid-state humidity sensor. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2017, 40, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Chen, Z.; Zeng, L.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, G.; Zhou, R. The effect of rgo-doping on the performance of SnU2/rGO flexible humidity sensor. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 3368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malook, K.; Khan, H.; Ali, M.; Ihsan-Ul-Haque. Investigation of room temperature humidity sensing performance of mesoporous CuO particles. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2020, 113, 105021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parimon, N.; Mamat, M.H.; Banu, I.S.; Vasimalai, N.; Ahmad, M.K.; Suriani, A.B.; Mohamed, A.; Rusop, M. Annealing temperature dependency of structural, optical and electrical characteristics of manganese-doped nickel oxide nanosheet array films for humidity sensing applications. Nanomater. Nanotechnol. 2021, 11, 1847980420982788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed Zahidi, M.; Mamat, M.H.; Malek, M.F.; Yaakob, M.K.; Ahmad, M.K.; Abu Bakar, S.; Mohamed, A.; Subki, A.S.R.A.; Mahmood, M.R. Evaluating Different TiO2 Nanoflower-Based Composites for Humidity Detection. Sensors 2022, 22, 5794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morsy, M.; Mokhtar, M.M.; Ismail, S.H.; Mohamed, G.G.; Ibrahim, M. Humidity Sensing Behaviour of Lyophilized rGO/Fe2O3 Nanocomposite. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2020, 30, 4180–4190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, D.; Pimentel, A.; Gonçalves, A.; Pereira, S.; Branquinho, R.; Barquinha, P.; Fortunato, E.; Martins, R. Metal oxide nanostructures for sensor applications. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2019, 34, 043001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puneetha, J.; Kottam, N.; Nagaraju, G.; Rathna, A. Visible light active ZnO nanostructures prepared by simple co-precipitation method. Photonics Nanostruct. Fundam. Appl. 2020, 39, 100781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Peres, M.L.; de Avila Delucis, R.; Amico, S.C.; Gatto, D.A. Zinc oxide nanoparticles from microwave-assisted solvothermal process: Photocatalytic performance and use for wood protection against xylophagous fungus. Nanomater. Nanotechnol. 2019, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.; Rai, P.; Gatell, E.N.; Llobet, E.; Güell, F.; Kumar, M.; Awasthi, K. Gas sensing properties of ZnO nanostructures (flowers/rods)synthesized by hydrothermal method. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 292, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.R.; Rahman, M.; Farhad, S.F.U.; Podder, J. Structural, optical and photocatalysis properties of sol–gel deposited Al-doped ZnO thin films. Surf. Interfaces 2019, 16, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovchinov, K.; Marinov, G.; Petrov, M.; Tyutyundzhiev, N.; Babeva, T. Influence of ZnCl2 concentration on the structural and optical properties of electrochemically deposited nanostructured ZnO. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 456, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Hao, N.; Xu, Z.; Trase, I.; Nie, Y.; Dong, L.; Closson, A.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, J.X.J. Flexible piezoelectric nanogenerators using metal-doped ZnO-PVDF films. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2020, 305, 111912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.-L.; Ji, L.-W.; Hsiao, Y.-J.; Lu, H.-Y.; Young, S.-J.; Tang, I.-T.; Chu, T.-T.; Chen, X.-J. Fabrication and Characterization of Ni-Doped ZnO Nanorod Arrays for UV Photodetector Application. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 067506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, C.B.; Mohammad, A.W.; Ng, L.Y. Integrated adsorption-solar photocatalytic membrane reactor for degradation of hazardous Congo red using Fe-doped ZnO and Fe-doped ZnO/rGO nanocomposites. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 33856–33869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Garnica, M.; Galdámez-Martínez, A.; Malagón, F.; Ramos, C.D.; Santana, G.; Abolhassani, R.; Kumar Panda, P.; Kaushik, A.; Mishra, Y.K.; Karthik, T.V.K.; et al. One dimensional Au-ZnO hybrid nanostructures based CO2 detection: Growth mechanism and role of the seed layer on sensing performance. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 337, 129765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, W.; Zhang, D.; Mi, Q.; Yu, S. Self-powered ethanol gas sensor based on the piezoelectric Ag/ZnO nanowire arrays at room temperature. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2021, 32, 7739–7750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Chen, X.; Yu, X.; Ding, X.; Yu, X.L.; Chen, X.P. Fast response humidity sensor based on graphene oxide films supported by TiO2 nanorods. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2020, 109, 108031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.; Ye, Z.; Kuang, X.; Liu, W.; Li, G.; Bai, W.; Tang, X. High sensitivity capacitive humidity sensors based on Zn1−xNixO nanostructures and plausible sensing mechanism. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2019, 30, 1724–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chethan, B.; Ravikiran, Y.T.; Vijayakumari, S.C.; Rajprakash, H.G.; Thomas, S. Nickel substituted cadmium ferrite as room temperature operable humidity sensor. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2018, 280, 466–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Zong, X.; Wu, Z. Fabrication of tin disulfide/graphene oxide nanoflower on flexible substrate for ultrasensitive humidity sensing with ultralow hysteresis and good reversibility. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 287, 398–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Zhang, F.; Lin, Q. Flexible relative humidity sensor based on reduced graphene oxide and interdigital electrode for smart home. Micro Nano Lett. 2022, 17, 134–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niarchos, G.; Dubourg, G.; Afroudakis, G.; Georgopoulos, M.; Tsouti, V.; Makarona, E.; Crnojevic-Bengin, V.; Tsamis, C. Humidity sensing properties of paper substrates and their passivation with ZnO nanoparticles for sensor applications. Sensors 2017, 17, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Yan, M.; Wang, S.; Yuan, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Sun, P.; Xie, G.; Du, X.; Tai, H. Facile, Flexible, Cost-Saving, and Environment-Friendly Paper-Based Humidity Sensor for Multifunctional Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 21840–21849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Hou, Z.; Wu, K.; Zhao, H.; Liu, S.; Fei, T.; Zhang, T. Flexible humidity sensor based on modified cellulose paper. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 339, 129879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alrammouz, R.; Podlecki, J.; Vena, A.; Garcia, R.; Abboud, P.; Habchi, R.; Sorli, B. Highly porous and flexible capacitive humidity sensor based on self-assembled graphene oxide sheets on a paper substrate. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 298, 126892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvez Ahmad, M.D.; Venkateswara Rao, A.; Suresh Babu, K.; Narsinga Rao, G. Particle size effect on the dielectric properties of ZnO nanoparticles. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2019, 224, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, F.S.; Wang, S.J. Enhanced sensing performance of relative humidity sensors using laterally grown ZnO nanosheets. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 193, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Lee, D.; Kwak, B.; Lee, H.S.; Lee, S.; Yoo, B. Synthesis of self-bridged ZnO nanowires and their humidity sensing properties. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 268, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z. Effects of pH on High-Performance ZnO Resistive Humidity Sensors Using One-Step Synthesis. Sensors 2019, 19, 5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.C.; Xiao, B.J.; Ji, Z.S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, P. Progress in the development of the EAST timing synchronization system upgrade based on precision time protocol. Fusion Eng. Des. 2018, 129, 236–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Gu, W.; Chen, C. Preparation and mechanism analysis of non-contact respiratory sensor based on ZnO/RGO composites. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 599, 154031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harith, Z.; Batumalay, M.; Irawati, N.; Harun, S.W.; Arof, H.; Ahmad, H. Relative humidity sensor employing tapered plastic optical fiber coated with seeded Al-doped ZnO. Optik 2017, 144, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, A.S.; Mamat, M.H.; Md Sin, N.D.; Malek, M.F.; Zoolfakar, A.S.; Suriani, A.B.; Mohamed, A.; Ahmad, M.K.; Rusop, M. Fabrication of hierarchical Sn-doped ZnO nanorod arrays through sonicated sol-gel immersion for room temperature, resistive-type humidity sensor applications. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 9785–9795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, S.J.; Lai, L.T. Investigation of a Highly Sensitive Au Nanoparticle-Modified ZnO Nanorod Humidity Sensor. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2021, 68, 775–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Yu, S.; Zhang, H. Preparation and performance analysis of Ag/ZnO humidity sensor. Sensors 2021, 21, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, K.C.; Zaidi, A.; Awasthi, R.R. Environmentally Benign Structural, Topographic, and Sensing Properties of Pure and Al-Doped ZnO Thin Films. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 28946–28954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subki, A.S.R.A.; Mamat, M.H.; Musa, M.Z.; Abdullah, M.H.; Banu, I.B.S.; Vasimalai, N.; Ahmad, M.K.; Nafarizal, N.; Suriani, A.B.; Mohamad, A.; et al. Effects of varying the amount of reduced graphene oxide loading on the humidity sensing performance of zinc oxide/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites on cellulose filter paper. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 926, 166728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponnusamy, R.; Venkatesan, R.; Gangan, A.; Samal, R.; Chakraborty, B.; Late, D.J.; Rout, C.S. Experimental and density functional theory investigations of catechol sensing properties of ZnO/RGO nanocomposites. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 495, 143588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, K.; Aadil, M.; Zulfiqar, S.; Ullah, S.; Haider, S.; Agboola, P.O.; Warsi, M.F.; Shakir, I. Graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide supported ZnO nanochips for removal of basic dyes from the industrial effluents. Fuller. Nanotub. Carbon Nanostruct. 2021, 29, 915–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çolak, H.; Karaköse, E. Synthesis and characterization of different dopant (Ge, Nd, W)-doped ZnO nanorods and their CO2 gas sensing applications. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 296, 126629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nageswara Rao, B.; Srinadhu, E.S.; Madhusudhan Rao, V.; Satyanarayana, N. Structural and Optical Studies of ZnO Nanostructures Synthesized by Rapid Microwave Assisted Hydrothermal and Solvothermal Methods. Trans. Indian Ceram. Soc. 2018, 77, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamat, M.H.; Parimon, N.; Ismail, A.S.; Shameem Banu, I.B.; Sathik Basha, S.; Rani, R.A.; Zoolfakar, A.S.; Malek, M.F.; Suriani, A.B.; Ahmad, M.K.; et al. Synthesis, structural and optical properties of mesostructured, X-doped NiO (x = Zn, Sn, Fe) nanoflake network films. Mater. Res. Bull. 2020, 127, 110860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kathwate, L.H.; Umadevi, G.; Kulal, P.M.; Nagaraju, P.; Dubal, D.P.; Nanjundan, A.K.; Mote, V.D. Ammonia gas sensing properties of Al doped ZnO thin films. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2020, 313, 112193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolhe, P.S.; Shinde, A.B.; Kulkarni, S.G.; Maiti, N.; Koinkar, P.M.; Sonawane, K.M. Gas sensing performance of Al doped ZnO thin film for H2S detection. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 748, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, R.; Güntner, A.T.; Park, Y.; Rim, H.J.; Lee, H.S.; Lee, W. Sensing of acetone by Al-doped ZnO. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 283, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Liu, Y.; Si, X.; Shen, Y.; Yu, W.; Wang, W.; Luo, X.; Zhou, T. Temperature-dependence on the structural, optical, and magnetic properties of Al-doped ZnO nanoparticles. Opt. Mater. 2016, 62, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avcı, B.; Caglar, Y.; Caglar, M. Controlling of surface morphology of ZnO nanopowders via precursor material and Al doping. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2019, 99, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varudkar, H.A.; Umadevi, G.; Nagaraju, P.; Dargad, J.S.; Mote, V.D. Fabrication of Al-doped ZnO nanoparticles and their application as a semiconductor-based gas sensor for the detection of ammonia. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2020, 31, 12579–12585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khuili, M.; Fazouan, N.; El Makarim, H.A.; El Halani, G.; Atmani, E.H. Comparative first principles study of ZnO doped with group III elements. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 688, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, D.; Lin, K.; Xue, T.; Cui, C.; Chen, X.; Yao, P.; Li, H. Influence of Al doping on structural and optical properties of Mg-Al co-doped ZnO thin films prepared by sol-gel method. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 589, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.P.; Roy, A.; Devi, P.S.; Lee, Y. Solution processed Al-doped ZnO and its performance in dye sensitized solar cells. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2021, 30, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mote, V.; Purushotham, Y.; Dole, B. Williamson-Hall analysis in estimation of lattice strain in nanometer-sized ZnO particles. J. Theor. Appl. Phys. 2012, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousaf, S.; Zulfiqar, S.; Din, M.I.; Agboola, P.O.; Aly Aboud, M.F.; Warsi, M.F.; Shakir, I. Solar light irradiated photocatalytic activity of ZnO-NiO/rGO nanocatalyst. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 12, 999–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambedkar, A.K.; Singh, M.; Kumar, V.; Kumar, V.; Singh, B.P.; Kumar, A.; Gautam, Y.K. Structural, optical and thermoelectric properties of Al-doped ZnO thin films prepared by spray pyrolysis. Surf. Interfaces 2020, 19, 100504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimbalkar, A.R.; Patil, N.B.; Ganbavle, V.V.; Mohite, S.V.; Madhale, K.V.; Patil, M.G. Sol-gel derived aluminium doped zinc oxide thin films: A view of aluminium doping effect on physicochemical and NO2 sensing properties. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 775, 466–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thambidurai, S.; Gowthaman, P.; Venkatachalam, M.; Suresh, S. Natural sunlight assisted photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue by spherical zinc oxide nanoparticles prepared by facile chemical co-precipitation method. Optik 2020, 207, 163865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.; Chen, C. Enhancement of the humidity sensing performance in Mg-doped hexagonal ZnO microspheres at room temperature. Sensors 2019, 19, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labhane, P.K.; Patle, L.B.; Sonawane, G.H.; Sonawane, S.H. Fabrication of ternary Mn doped ZnO nanoparticles grafted on reduced graphene oxide (RGO) sheet as an efficient solar light driven photocatalyst. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2018, 710, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, M.; Mahapatra, R.; Mondal, M.K.; Krishnamurthy, S.; Ghosh, R. Fast response and low temperature sensing of acetone and ethanol using Al-doped ZnO microrods. Phys. E Low-Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 2020, 118, 113868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sa-nguanprang, S.; Phuruangrat, A.; Thongtem, T.; Thongtem, S. Preparation of Visible-Light-Driven Al-Doped ZnO Nanoparticles Used for Photodegradation of Methylene Blue. J. Electron. Mater. 2020, 49, 1841–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Farsi, B.; Al Marzouqi, F.; Al-Maashani, M.; Souier, M.T.; Tay Zar Myint, M.; Al-Abri, M.Z. Rapid microwave-assisted fabrication of Al-doped zinc oxide nanorods on a glass substrate for photocatalytic degradation of phenol under visible light irradiation. Mater. Sci. Eng. B Solid State Mater. Adv. Technol. 2021, 264, 114977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Chowdhury, A.H.; Bahrami, B.; Khan, M.R.; Qiao, Q.; Kumar, M. Origin of enhanced carrier mobility and electrical conductivity in seed-layer assisted sputtered grown Al doped ZnO thin films. Thin Solid Films 2020, 700, 137916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodwihok, C.; Wongratanaphisan, D.; Ngo, Y.L.T.; Khandelwal, M.; Hur, S.H.; Chung, J.S. Effect of GO additive in ZnO/rGO nanocomposites with enhanced photosensitivity and photocatalytic activity. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Li, Y.L.; Gong, F.L.; Xie, K.F.; Liu, M.; Zhang, H.L.; Fang, S.M. Al doped narcissus-like ZnO for enhanced NO2 sensing performance: An experimental and DFT investigation. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 305, 127489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Tang, Y.; Tian, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Q. Magnetron co-sputtering optimized aluminum-doped zinc oxide (AZO) film for high-response formaldehyde sensing. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 880, 160510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Farsi, B.; Souier, T.M.; Al Marzouqi, F.; Al Maashani, M.; Bououdina, M.; Widatallah, H.M.; Al Abri, M. Structural and optical properties of visible active photocatalytic Al doped ZnO nanostructured thin films prepared by dip coating. Opt. Mater. 2021, 113, 110868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, S.; Majumder, R.; Ghosh, R.; Pal Chowdhury, M. Superior positive relative humidity sensing properties of porous nanostructured Al:ZnO thin films deposited by jet-atomizer spray pyrolysis technique. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2019, 30, 4618–4625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navale, S.C.; Ravi, V.; Mulla, I.S.; Gosavi, S.W.; Kulkarni, S.K. Low temperature synthesis and NOx sensing properties of nanostructured Al-doped ZnO. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2007, 126, 382–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Singh, B.; Yadav, P.; Bhatt, V.; Kumar, M.; Singh, K.; Abhyankar, A.C.; Kumar, A.; Yun, J.H. Effect of structural defects, surface roughness on sensing properties of Al doped ZnO thin films deposited by chemical spray pyrolysis technique. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 3562–3568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajala, F.; Hamrouni, A.; Houas, A.; Lachheb, H.; Megna, B.; Palmisano, L.; Parrino, F. The influence of Al doping on the photocatalytic activity of nanostructured ZnO: The role of adsorbed water. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 445, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algün, G.; Akçay, N. Enhanced sensing characteristics of relative humidity sensors based on Al and F co-doped ZnO nanostructured thin films. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2019, 30, 16124–16134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, R.; Mamat, M.H.; Ismail, A.S.; Malek, M.F.; Zoolfakar, A.S.; Khusaimi, Z.; Suriani, A.B.; Mohamed, A.; Ahmad, M.K.; Rusop, M. Hierarchically assembled tin-doped zinc oxide nanorods using low-temperature immersion route for low temperature ethanol sensing. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2017, 28, 16292–16305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, A.S.; Mamat, M.H.; Shameem Banu, I.B.; Amiruddin, R.; Malek, M.F.; Parimon, N.; Zoolfakar, A.S.; Md Sin, N.D.; Suriani, A.B.; Ahmad, M.K.; et al. Structural modification of ZnO nanorod array through Fe-doping: Ramification on UV and humidity sensing properties. Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects 2019, 18, 100262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, V.; Pandey, N.K.; Gupta, P.; Singh, K.; Singh, P. Humidity sensing enhancement and structural evolution of tungsten doped ZnO nanosensors fabricated through co-precipitation synthesis. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2021, 619, 413224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arote, S.A.; Pathan, A.S.; Hase, Y.V.; Bardapurkar, P.P.; Gapale, D.L.; Palve, B.M. Investigations on synthesis, characterization and humidity sensing properties of ZnO and ZnO-ZrO2 composite nanoparticles prepared by ultrasonic assisted wet chemical method. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 55, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondal, S.; Min, B.K.; Yi, Y.; Choi, C.G. Highly Sensitive and Fast Responsive Humidity Sensor based on 2D PtSe2 with Gamma Radiation Tolerance. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2022, 7, 2100751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, K.; Mohanty, B.; Biswas, A.; Nayak, J. Role of hexamethylenetetramine in ZnO-cellulose nanocomposite enabled UV and humidity sensor. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2020, 105, 104699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Yin, N.; Xia, B.; Sun, Y.; Liao, Y.; He, Z.; Hao, S. Humidity-sensing properties of hierarchical ZnO/MWCNTs/ZnO nanocomposite film sensor based on electrostatic layer-by-layer self-assembly. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2016, 27, 2481–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arularasu, M.V.; Harb, M.; Vignesh, R.; Rajendran, T.V.; Sundaram, R. PVDF/ZnO hybrid nanocomposite applied as a resistive humidity sensor. Surf. Interfaces 2020, 21, 100780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mututu, V.; Sunitha, A.K.; Thomas, R.; Pandey, M.; Manoj, B. An investigation on structural, electrical and optical properties of GO/ZnO nanocomposite. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2019, 14, 3752–3763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, A.S.; Mamat, M.H.; Shameem Banu, I.B.; Malek, M.F.; Yusoff, M.M.; Mohamed, R.; Ahmad, W.R.W.; Abdullah, M.A.R.; Md Sin, N.D.; Suriani, A.B.; et al. Modulation of Sn concentration in ZnO nanorod array: Intensification on the conductivity and humidity sensing properties. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2018, 29, 12076–12088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velumani, M.; Meher, S.R.; Alex, Z.C. Composite metal oxide thin film based impedometric humidity sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 301, 127084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musa, M.Z.; Mamat, M.H.; Vasimalai, N.; Shameem Banu, I.B.; Malek, M.F.; Ahmad, M.K.; Suriani, A.B.; Mohamed, A.; Rusop, M. Fabrication and structural properties of flower-like TiO2 nanorod array films grown on glass substrate without FTO layer. Mater. Lett. 2020, 273, 127902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.P.; Pawbake, A.S.; Sathe, B.R.; Late, D.J.; Walke, P.S. Superior humidity sensor and photodetector of mesoporous ZnO nanosheets at room temperature. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 293, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, W.; Li, P.; Fu, Y.; Xing, L.; Xue, X. Hydrothermal synthesis of Co-ZnO nanowire array and its application as piezo-driven self-powered humidity sensor with high sensitivity and repeatability. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 84343–84349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagtap, S.; Rane, S.; Arbuj, S.; Rane, S.; Gosavi, S. Optical fiber based humidity sensor using Ag decorated ZnO nanorods. Microelectron. Eng. 2018, 187–188, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Sun, Y.M.; Wu, Z.; Li, X.; Wang, N.; Tao, K.; Wang, G.P. Carbon Nanocoil-Based Fast-Response and Flexible Humidity Sensor for Multifunctional Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 4242–4251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero, F.J.; Rivadeneyra, A.; Becherer, M.; Morales, D.P.; Rodríguez, N. Fabrication and characterization of humidity sensors based on graphene Oxide-PEDOT:PSS composites on a flexible substrate. Micromachines 2020, 11, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, H.; Li, L.; Tuokedaerhan, K.; Jia, Z. Er-enhanced humidity sensing performance in black ZnO-based sensor. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 744, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, W.P.; Oh, J.H. Humidity sensing behaviors of nanocrystalline Al-doped ZnO thin films prepared by sol-gel process. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2002, 13, 391–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Ye, Z.; Sun, N.; Kuang, X.; Liu, W.; Song, X.; Zhang, L.; Bai, W.; Tang, X. Preparation and properties of humidity sensor based on K-doped ZnO nanostructure. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2019, 30, 18767–18779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Xu, Z.; Yang, Z.; Song, X. High-performance flexible self-powered tin disulfide nanoflowers/reduced graphene oxide nanohybrid-based humidity sensor driven by triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2020, 67, 104251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parimon, N.; Mamat, M.H.; Shameem Banu, I.B.; Vasimalai, N.; Ahmad, M.K.; Suriani, A.B.; Mohamed, A.; Rusop, M. Fabrication, structural, optical, electrical, and humidity sensing characteristics of hierarchical NiO nanosheet/nanoball-flower-like structure films. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2020, 31, 11673–11687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).