A Simple Method to Fabricate the Highly Sensitive SERS Substrate by Femtosecond Laser-Based 3D Printer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemical Agents
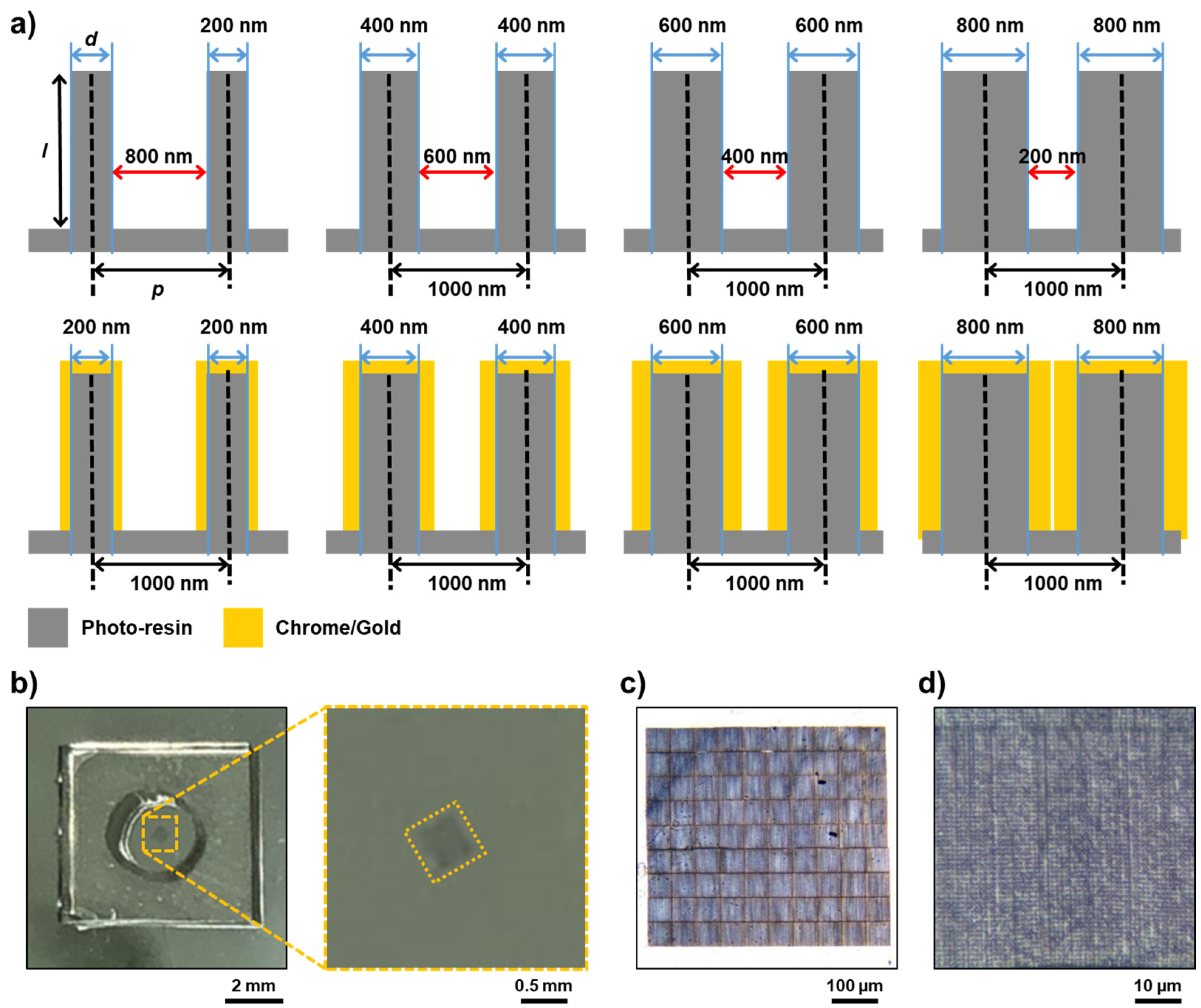
2.2. Fabrication of Three-Dimensional Nanostructure by Femtosecond Laser 3D Printer
2.3. SEM Analysis of 3D-Printed Nanostructure by Femtosecond Laser 3D Printer
2.4. SERS Analysis of 3D-Printed Nanostructure by Femtosecond Laser 3D Printer
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Fabrication of 3D Nanostructure via Femtosecond Laser 3D Printer
3.2. Optimization of 3D Nanostructure via Femtosecond Laser 3D Printer
3.3. SEM Analysis of 3D Nanostructure via Femtosecond Laser 3D Printer
3.4. SERS Analysis of Au-Coated 3D Nanostructure
3.5. SERS Analysis of Ag-Coated 3D Nanostructure
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, W.; Park, J.; Kim, W.; Jo, S.; Kim, M.; Kim, C.; Park, H.; Bang, D.; Lee, W.; Park, J. Bio-Inspired Ag Nanovilli-Based Sandwich-Type SERS Aptasensor for Ultrasensitive and Selective Detection of 25-Hydroxy Vitamin D3. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 188, 113341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.; Lee, W.; Park, H.; Park, J.; Kim, W.; Kang, B.; Choi, E.; Kim, C.-S.; Park, J.-O.; Lee, G.; et al. Biomimetic Nano-Pine-Pollen Structure-Based Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Sensing Platform for the Hypersensitive Detection of Toxicants: Cadmium and Amyloid. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 3180–3190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuen, C.; Zheng, W.; Huang, Z. Principles of Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy: And Related Plasmonic Effects. J. Innov. Opt. Health Sci. 2008, 1, 267–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kneipp, K.; Wang, Y.; Kneipp, H.; Perelman, L.T.; Itzkan, I.; Dasari, R.R.; Feld, M.S. Single Molecule Detection Using Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS). Phys. Rev. Lett. 1997, 78, 1667–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Futamata, M.; Maruyama, Y.; Ishikawa, M. Local Electric Field and Scattering Cross Section of Ag Nanoparticles under Surface Plasmon Resonance by Finite Difference Time Domain Method. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 7607–7617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amendola, V.; Pilot, R.; Frasconi, M.; Maragò, O.M.; Iatì, M.A. Surface Plasmon Resonance in Gold Nanoparticles: A Review. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2017, 29, 203002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, P.K.; Huang, X.; El-Sayed, I.H.; El-Sayed, M.A. Review of Some Interesting Surface Plasmon Resonance-Enhanced Properties of Noble Metal Nanoparticles and Their Applications to Biosystems. Plasmonics 2007, 2, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, V.; Zougagh, M.; Ríos, Á. Analytical Nanometrological Approach for Screening and Confirmation of Titanium Dioxide Nano/Micro-Particles in Sugary Samples Based on Raman Spectroscopy—Capillary Electrophoresis. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1050, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, P.; Bonyár, A.; Veres, M.; Himics, L.; Balázs, L.; Juhász, L.; Csarnovics, I. A Generalized Exponential Relationship between the Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS) Efficiency of Gold/Silver Nanoisland Arrangements and Their Non-Dimensional Interparticle Distance/Particle Diameter Ratio. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2020, 314, 112225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.Q. Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy: Advancements and Applications. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2005, 36, 466–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campion, A.; Kambhampati, P. Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering. Chem. Soc. Rev. 1998, 27, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.W.; Zhai, W.L.; Li, Y.T.; Long, Y.T. Recent Progress in Surface Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy for the Detection of Environmental Pollutants. Microchim. Acta 2014, 181, 23–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Gong, L.; Wang, W.; Gong, Z.; Wang, D.; Fan, M. Surface-enhanced Raman Spectroscopy for On-site Analysis: A Review of Recent Developments. Luminescence 2020, 35, 808–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritzler, K.B.; Prinz, V.Y. 3D Printing Methods for Micro- and Nanostructures. Physics-Uspekhi 2019, 62, 54–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaitpal, S.; Chavva, S.R.; Mabbott, S. 3D Printed SERS-Active Thin-Film Substrates Used to Quantify Levels of the Genotoxic Isothiazolinone. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 2850–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, J.; Li, J.; Li, W.; Luo, Q.; Gu, C. Hollow Metallic Pyramid Plasmonic Structures Fabricated by Direct Laser Writing and Electron Beam Evaporation. Microelectron. Eng. 2013, 110, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, A.; Maier, S.A. Versatile Direct Laser Writing Lithography Technique for Surface Enhanced Infrared Spectroscopy Sensors. ACS Sens. 2016, 1, 1155–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, H.; Hironou, A.; Shen, Z.; Tamiya, E. Versatile Micropatterning of Plasmonic Nanostructures by Visible Light Induced Electroless Silver Plating on Gold Nanoseeds. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 23932–23940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.; Serien, D.; Hu, A.; Sugioka, K. 3D Microfluidic Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy (SERS) Chips Fabricated by All-Femtosecond-Laser-Processing for Real-Time Sensing of Toxic Substances. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1706262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yuan, G.; Yu, W.; Xing, J.; Zou, Y.; Zhao, C.; Kong, W.; Yu, Z.; Guo, C. A Self-Driven Microfluidic Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Device for Hg2+ Detection Fabricated by Femtosecond Laser. Lab Chip 2020, 20, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugioka, K. Hybrid Femtosecond Laser Three-Dimensional Micro-and Nanoprocessing: A Review. Int. J. Extrem. Manuf. 2019, 1, 012003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugioka, K.; Cheng, Y. Femtosecond Laser Three-Dimensional Micro-and Nanofabrication. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2014, 1, 041303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sima, F.; Sugioka, K.; Vázquez, R.M.; Osellame, R.; Kelemen, L.; Ormos, P. Three-Dimensional Femtosecond Laser Processing for Lab-on-a-Chip Applications. Nanophotonics 2018, 7, 613–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.; Sugioka, K. Recent Advances in the Fabrication of Highly Sensitive Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Substrates: Nanomolar to Attomolar Level Sensing. Light Adv. Manuf. 2021, 2, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharati, M.S.S.; Byram, C.; Soma, V.R. Femtosecond Laser Fabricated Ag@Au and Cu@Au Alloy Nanoparticles for Surface Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Based Trace Explosives Detection. Front. Phys. 2018, 6, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Long, L.; Ju, W.; Yang, H.Y.; Li, Z. Dimensional Design for Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. ACS Mater. Au 2022, 2, 552–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.Y.; Tsai, M.S. Tunable Silver Nanoparticle Arrays by Hot Embossing and Sputter Deposition for Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Todeschini, M.; Bastos Da, A.; Fanta, S.; Jensen, F.; Wagner, J.B.; Han, A. Influence of Ti and Cr Adhesion Layers on Ultrathin Au Films. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, W.; Lee, W.; Choi, H.; Lee, G.; Son, J.; Lee, S.W.; Park, J.; Kim, W.; Kim, M.; Yoon, D.S.; et al. Bioinspired Micro Glue Threads Fabricated by Liquid Bridge-to-Solidification as an Effective Sensing Platform. ACS Sens. 2020, 5, 1977–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, W.; Kim, W.; Bang, D.; Park, J.; Lee, W. A Simple Method to Fabricate the Highly Sensitive SERS Substrate by Femtosecond Laser-Based 3D Printer. Chemosensors 2023, 11, 340. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11060340
Kim W, Kim W, Bang D, Park J, Lee W. A Simple Method to Fabricate the Highly Sensitive SERS Substrate by Femtosecond Laser-Based 3D Printer. Chemosensors. 2023; 11(6):340. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11060340
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Woong, Woochang Kim, Doyeon Bang, Jinsung Park, and Wonseok Lee. 2023. "A Simple Method to Fabricate the Highly Sensitive SERS Substrate by Femtosecond Laser-Based 3D Printer" Chemosensors 11, no. 6: 340. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11060340
APA StyleKim, W., Kim, W., Bang, D., Park, J., & Lee, W. (2023). A Simple Method to Fabricate the Highly Sensitive SERS Substrate by Femtosecond Laser-Based 3D Printer. Chemosensors, 11(6), 340. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11060340







