Molecular Understanding of the Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Salivary Fingerprint in People after Sars-COV-2 Infection and in Vaccinated Subjects
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
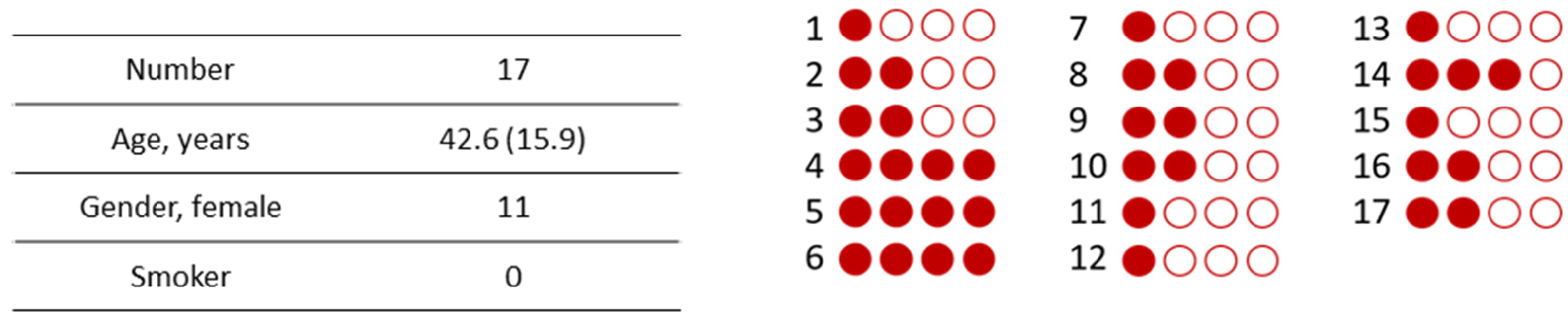
2.1. Saliva and Serum Sample Collection
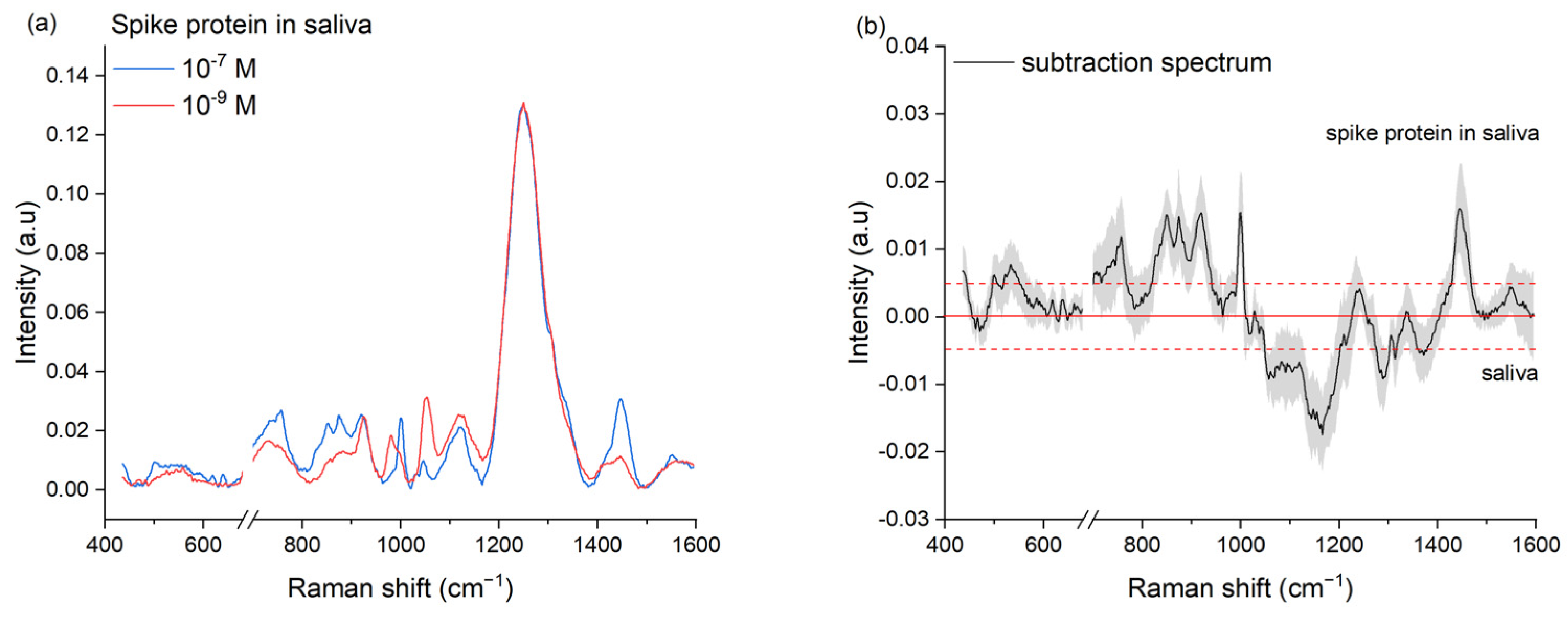
2.2. Preparation of Spike Protein Sample
2.3. Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Analysis
2.4. SERS Data Processing
2.5. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.6. Salivary and Serum IgA Quantification
2.7. Serum IgG Quantification
3. Results and Discussion
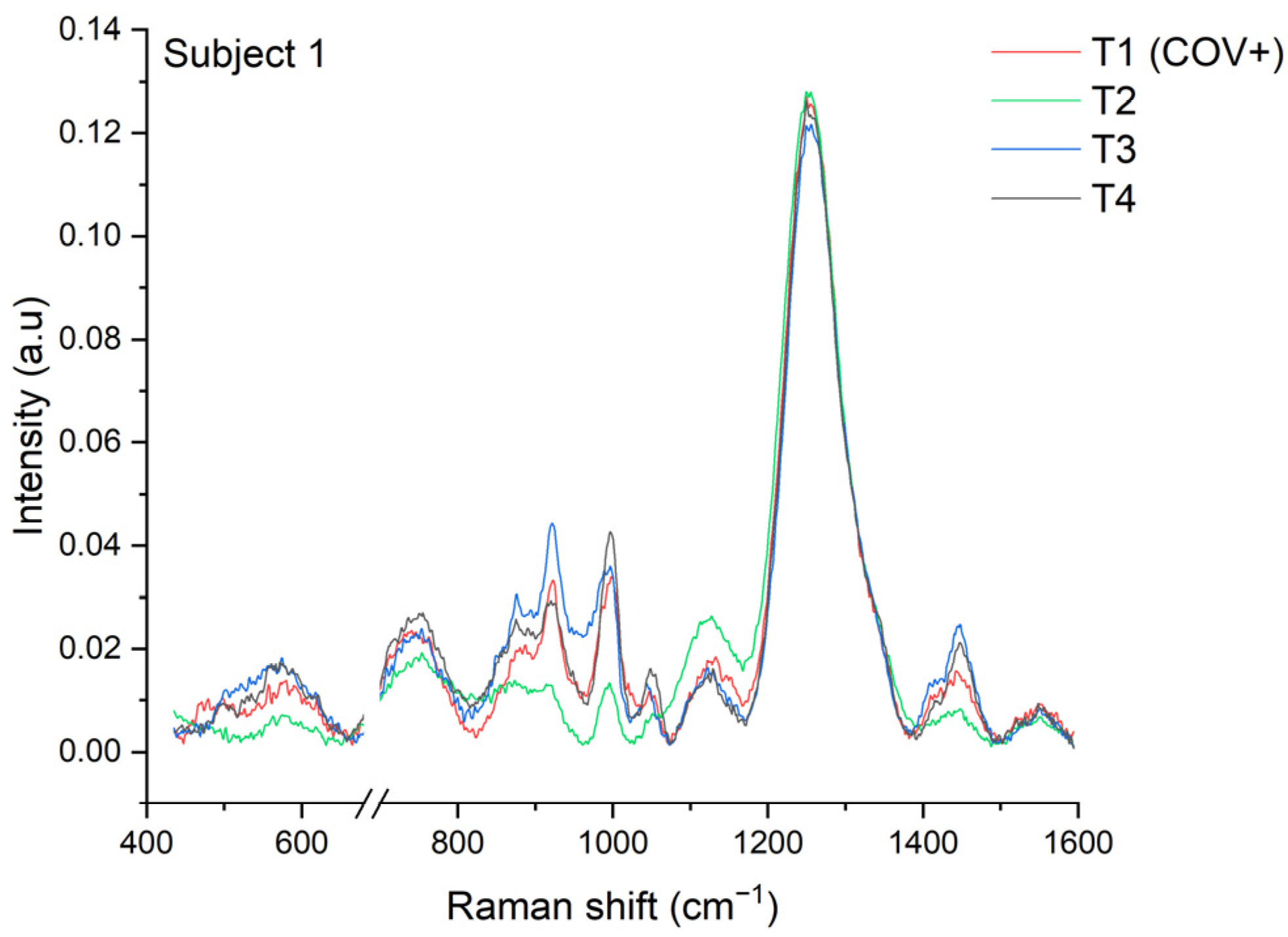
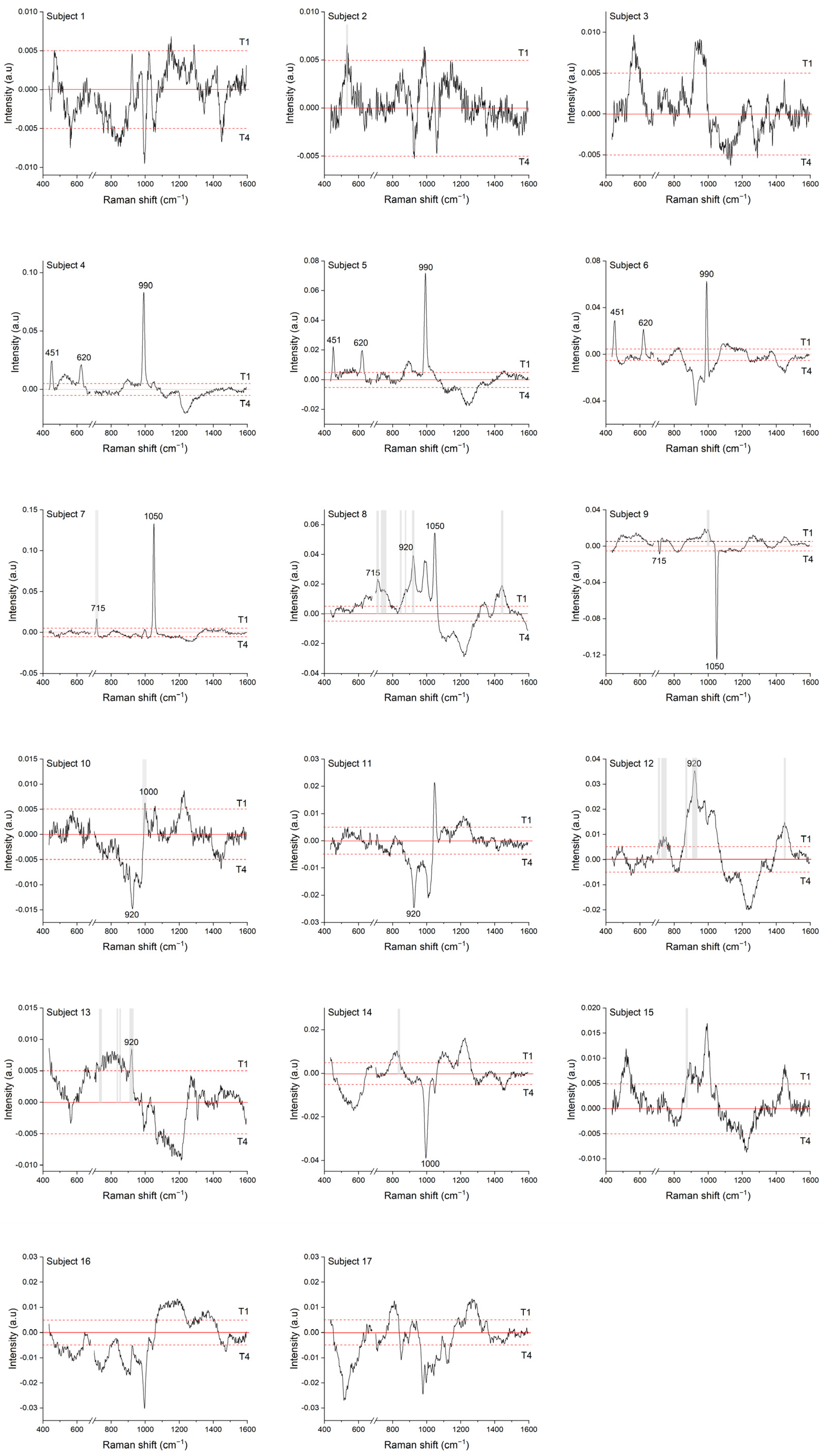
3.1. Longitudinal COVID-19 Fingerprint
3.2. Multivariate Analysis
3.3. Salivary Cortisol Quantification
3.4. SERS Data Interpretation
3.4.1. Nucleocapsid Protein
3.4.2. Spike Protein
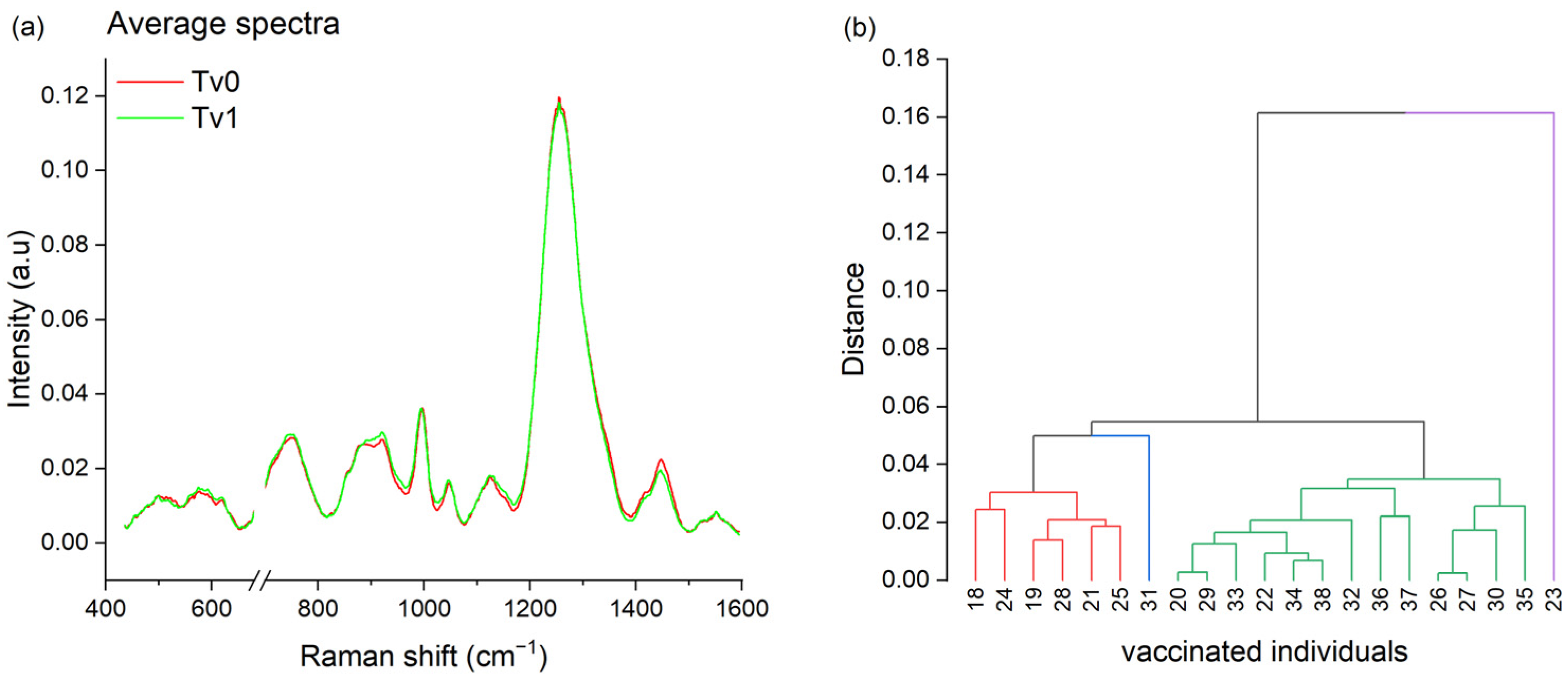
3.5. Vaccination Fingerprint
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, Y.; Yang, C.; Xu, X.; Xu, W.; Liu, S. Structural and Functional Properties of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein: Potential Antivirus Drug Development for COVID-19. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2020, 41, 1141–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magazine, N.; Zhang, T.; Wu, Y.; McGee, M.C.; Veggiani, G.; Huang, W. Mutations and Evolution of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein. Viruses 2022, 14, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern as of 1 March 2024. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/covid-19/variants-concern (accessed on 12 March 2024).
- COVID-19 Medicines|European Medicines Agency. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/human-regulatory-overview/public-health-threats/coronavirus-disease-covid-19/covid-19-medicines (accessed on 12 March 2024).
- Rahman, M.M.; Masum, M.H.U.; Wajed, S.; Talukder, A. A Comprehensive Review on COVID-19 Vaccines: Development, Effectiveness, Adverse Effects, Distribution and Challenges. Virusdisease 2022, 33, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afzal, A. Molecular Diagnostic Technologies for COVID-19: Limitations and Challenges. J. Adv. Res. 2020, 26, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-López, B.; Mir, M. Commercialized Diagnostic Technologies to Combat SARS-CoV2: Advantages and Disadvantages. Talanta 2021, 225, 121898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khurshid, Z.; Zafar, M.; Khan, E.; Mali, M.; Latif, M. Human Saliva Can Be a Diagnostic Tool for Zika Virus Detection. J. Infect. Public Health 2019, 12, 601–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.-Z.; Cheng, X.-Q.; Li, J.-Y.; Zhang, P.; Yi, P.; Xu, X.; Zhou, X.-D. Saliva in the Diagnosis of Diseases. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2016, 8, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chojnowska, S.; Ptaszyńska-Sarosiek, I.; Kępka, A.; Knaś, M.; Waszkiewicz, N. Salivary Biomarkers of Stress, Anxiety and Depression. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saheb Sharif-Askari, N.; Soares, N.C.; Mohamed, H.A.; Saheb Sharif-Askari, F.; Alsayed, H.A.H.; Al-Hroub, H.; Salameh, L.; Osman, R.S.; Mahboub, B.; Hamid, Q.; et al. Saliva Metabolomic Profile of COVID-19 Patients Associates with Disease Severity. Metabolomics 2022, 18, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Prieto, A.; Rubić, I.; Gonzalez-Sanchez, J.C.; Kuleš, J.; Martínez-Subiela, S.; Cerón, J.J.; Bernal, E.; Torres-Cantero, A.; Vicente-Romero, M.R.; Mrljak, V.; et al. Saliva Changes in Composition Associated to COVID-19: A Preliminary Study. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 10879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardo, R.A.; Roque, J.V.; de Oliveira Júnior, C.I.; Lima, N.M.; Machado, L.S.; Duarte, G.R.M.; Costa, N.L.; Sorgi, C.A.; Soares, F.F.L.; Vaz, B.G.; et al. Exploring Salivary Lipid Profile Changes in COVID-19 Patients: Insights from Mass Spectrometry Analysis. Talanta 2024, 269, 125522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sapkota, D.; Søland, T.M.; Galtung, H.K.; Sand, L.P.; Giannecchini, S.; To, K.K.W.; Mendes-Correa, M.C.; Giglio, D.; Hasséus, B.; Braz-Silva, P.H. COVID-19 Salivary Signature: Diagnostic and Research Opportunities. J. Clin. Pathol. 2020, 74, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azzi, L.; Maurino, V.; Baj, A.; Dani, M.; d’Aiuto, A.; Fasano, M.; Lualdi, M.; Sessa, F.; Alberio, T. Diagnostic Salivary Tests for SARS-CoV-2. J. Dent. Res. 2021, 100, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, S.H.; Allicock, O.; Armstrong-Hough, M.; Wyllie, A.L. Saliva as a Gold-Standard Sample for SARS-CoV-2 Detection. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, 562–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlomagno, C.; Gualerzi, A.; Picciolini, S.; Rodà, F.; Banfi, P.I.; Lax, A.; Bedoni, M. Characterization of the COPD Salivary Fingerprint through Surface Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy: A Pilot Study. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlomagno, C.; Bertazioli, D.; Gualerzi, A.; Picciolini, S.; Andrico, M.; Rodà, F.; Meloni, M.; Banfi, P.I.; Verde, F.; Ticozzi, N.; et al. Identification of the Raman Salivary Fingerprint of Parkinson’s Disease through the Spectroscopic—Computational Combinatory Approach. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 704963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardy, M.; Kelleher, L.; de Carvalho Gomes, P.; Buchan, E.; Chu, H.O.M.; Goldberg Oppenheimer, P. Methods in Raman Spectroscopy for Saliva Studies—A Review. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2022, 57, 177–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chisanga, M.; Muhamadali, H.; Ellis, D.I.; Goodacre, R. Enhancing Disease Diagnosis: Biomedical Applications of Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchan, E.; Hardy, M.; Gomes, P.d.C.; Kelleher, L.; Chu, H.O.M.; Oppenheimer, P.G. Emerging Raman Spectroscopy and Saliva-Based Diagnostics: From Challenges to Applications. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2022, 59, 277–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Li, X.; Pan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, C.; Yan, X.; Liu, X.; Lu, G. Ultrasensitive Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein in Untreated Saliva Using SERS-Based Biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 190, 113421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuckmantel Bido, A.; Brolo, A.G. Digital SERS Protocol Using Au Nanoparticle-Based Extrinsic Raman Labels for the Determination of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein in Saliva Samples. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2023, 6, 15426–15436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, M.; Antoine, D.; Vitt, M.; Dickie, J.M.; Sultana Jyoti, S.; Wall, J.G.; Johnson, P.A.; Wawrousek, K.E. A Fast, Ultrasensitive SERS Immunoassay to Detect SARS-CoV-2 in Saliva. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1229, 340290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, S.; Liu, Y.; Fang, S.; Wu, Q.; Fan, M.; Lin, D.; Lin, J.; Feng, S. Ultrasensitive Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Antigen Using Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy-Based Lateral Flow Immunosensor. J. Biophotonics 2023, 16, e202300004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Yuan, X.; Zhuang, K.; Li, Y.; Luo, X. Simultaneous and Sensitive Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Proteins Spike and Nucleocapsid Based on Long-Range SERS Biosensor. Anal. Chim. Acta 2024, 1287, 342070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlomagno, C.; Bertazioli, D.; Gualerzi, A.; Picciolini, S.; Banfi, P.I.; Lax, A.; Messina, E.; Navarro, J.; Bianchi, L.; Caronni, A.; et al. COVID-19 Salivary Raman Fingerprint: Innovative Approach for the Detection of Current and Past SARS-CoV-2 Infections. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ember, K.; Daoust, F.; Mahfoud, M.; Dallaire, F.; Ahmad, E.Z.; Tran, T.; Plante, A.; Diop, M.-K.; Nguyen, T.; St-Georges-Robillard, A.; et al. Saliva-Based Detection of COVID-19 Infection in a Real-World Setting Using Reagent-Free Raman Spectroscopy and Machine Learning. J. Biomed. Opt. 2022, 27, 025002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berus, S.M.; Nowicka, A.B.; Wieruszewska, J.; Niciński, K.; Kowalska, A.A.; Szymborski, T.R.; Dróżdż, I.; Borowiec, M.; Waluk, J.; Kamińska, A. SERS Signature of SARS-CoV-2 in Saliva and Nasopharyngeal Swabs: Towards Perspective COVID-19 Point-of-Care Diagnostics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, Y.-J.; Le, T.-N.; Hsiao, W.W.-W.; Tung, K.-L.; Ostrikov, K.; Chiang, W.-H. Plasmonic Nanostructure-Enhanced Raman Scattering for Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein and Spike Protein Variants. Anal. Chim. Acta 2023, 1239, 340651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancuso, R.; Agostini, S.; Citterio, L.A.; Chiarini, D.; Santangelo, M.A.; Clerici, M. Systemic and Mucosal Humoral Immune Response Induced by Three Doses of the BNT162b2 SARS-CoV-2 mRNA Vaccines. Vaccines 2022, 10, 1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Movasaghi, Z.; Rehman, S.; Rehman, I.U. Raman Spectroscopy of Biological Tissues. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2007, 42, 493–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymborski, T.R.; Berus, S.M.; Nowicka, A.B.; Słowiński, G.; Kamińska, A. Machine Learning for COVID-19 Determination Using Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Guo, J.; Xu, Y.; Chen, X. Viral Dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 in Saliva from Infected Patients. J. Infect. 2020, 81, e48–e50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- To, K.K.-W.; Tsang, O.T.-Y.; Leung, W.-S.; Tam, A.R.; Wu, T.-C.; Lung, D.C.; Yip, C.C.-Y.; Cai, J.-P.; Chan, J.M.-C.; Chik, T.S.-H.; et al. Temporal Profiles of Viral Load in Posterior Oropharyngeal Saliva Samples and Serum Antibody Responses during Infection by SARS-CoV-2: An Observational Cohort Study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pannala, A.S.; Mani, A.R.; Spencer, J.P.E.; Skinner, V.; Bruckdorfer, K.R.; Moore, K.P.; Rice-Evans, C.A. The Effect of Dietary Nitrate on Salivary, Plasma, and Urinary Nitrate Metabolism in Humans. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2003, 34, 576–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, A.M.; Garde, A.H.; Persson, R. Sources of Biological and Methodological Variation in Salivary Cortisol and Their Impact on Measurement among Healthy Adults: A Review. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 2008, 68, 448–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nater, U.M.; Hoppmann, C.A.; Scott, S.B. Diurnal Profiles of Salivary Cortisol and Alpha-Amylase Change across the Adult Lifespan: Evidence from Repeated Daily Life Assessments. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2013, 38, 3167–3171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umeda, T.; Hiramatsu, R.; Iwaoka, T.; Shimada, T.; Miura, F.; Sato, T. Use of Saliva for Monitoring Unbound Free Cortisol Levels in Serum. Clin. Chim. Acta 1981, 110, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heaney, J.L.J.; Phillips, A.C.; Carroll, D. Aging, Health Behaviors, and the Diurnal Rhythm and Awakening Response of Salivary Cortisol. Exp. Aging Res. 2012, 38, 295–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, T.J.; Sharma, B. Direct Surface Enhanced Raman Spectroscopic Detection of Cortisol at Physiological Concentrations. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 2052–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, J.E.; Jaramillo, S.A.; Settles, E.; Salazar, J.J.V.; Lehr, A.; Gonzalez, J.; Aranda, C.R.; Navarro-Contreras, H.R.; Raniere, M.O.; Harvey, M.; et al. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 and Its S and N Proteins Using Surface Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 25788–25794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, D.; Johnson, J.M.; Fernandes, S.C.; Suib, H.; Hwang, S.; Wuelfing, D.; Mendes, M.; Holdridge, M.; Burke, E.M.; Beauregard, K.; et al. N-Protein Presents Early in Blood, Dried Blood and Saliva during Asymptomatic and Symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batoulis, H.; Schmidt, T.H.; Weber, P.; Schloetel, J.-G.; Kandt, C.; Lang, T. Concentration Dependent Ion-Protein Interaction Patterns Underlying Protein Oligomerization Behaviours. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quevedo, M.; Karbstein, H.P.; Emin, M.A. Concentration-Dependent Changes in the Reaction Behavior of Whey Proteins: Diffusion-Controlled or Transition State-Controlled Reactions? Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 118, 106745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Song, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wu, N.; Xu, J.; Sun, C.; Zhang, J.; Weng, T.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, Z.; et al. Molecular Architecture of the SARS-CoV-2 Virus. Cell 2020, 183, 730–738.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| 500 | 702 | 738 | 835 | 999 |
| 521 | 707 | 741 | 849 | 1445 |
| 533 | 712 | 749 | 874 | |
| 538 | 728 | 758 | 884 | |
| 542 | 733 | 828 | 919 |
| Subject | T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 918 (+) | 919 (+) | 919 (+) | 924 (+) |
| 5 | 918 (+) | 920 (+) | 920 (+) | 921 (+) |
| 6 | 920 (+) | 923 (+) | - | - |
| 9 | 920 (+) | 920 (+) | 924 | 924 |
| Number | 21 |
|---|---|
| Age, years | 42.8 (14.2) |
| Gender, female | 13 |
| Previous COVID-19 | 3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodà, F.; Gualerzi, A.; Picciolini, S.; Forleo, L.; Mangolini, V.; Mancuso, R.; Agostini, S.; Rossetto, R.A.; Pierucci, P.; Banfi, P.I.; et al. Molecular Understanding of the Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Salivary Fingerprint in People after Sars-COV-2 Infection and in Vaccinated Subjects. Chemosensors 2024, 12, 136. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12070136
Rodà F, Gualerzi A, Picciolini S, Forleo L, Mangolini V, Mancuso R, Agostini S, Rossetto RA, Pierucci P, Banfi PI, et al. Molecular Understanding of the Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Salivary Fingerprint in People after Sars-COV-2 Infection and in Vaccinated Subjects. Chemosensors. 2024; 12(7):136. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12070136
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodà, Francesca, Alice Gualerzi, Silvia Picciolini, Luana Forleo, Valentina Mangolini, Roberta Mancuso, Simone Agostini, Rudy Alexander Rossetto, Paola Pierucci, Paolo Innocente Banfi, and et al. 2024. "Molecular Understanding of the Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Salivary Fingerprint in People after Sars-COV-2 Infection and in Vaccinated Subjects" Chemosensors 12, no. 7: 136. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12070136
APA StyleRodà, F., Gualerzi, A., Picciolini, S., Forleo, L., Mangolini, V., Mancuso, R., Agostini, S., Rossetto, R. A., Pierucci, P., Banfi, P. I., & Bedoni, M. (2024). Molecular Understanding of the Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Salivary Fingerprint in People after Sars-COV-2 Infection and in Vaccinated Subjects. Chemosensors, 12(7), 136. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12070136










