Investigating the Temperature-Dependent Kinetics in Humidity-Resilient Tin–Titanium-Based Metal Oxide Gas Sensors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
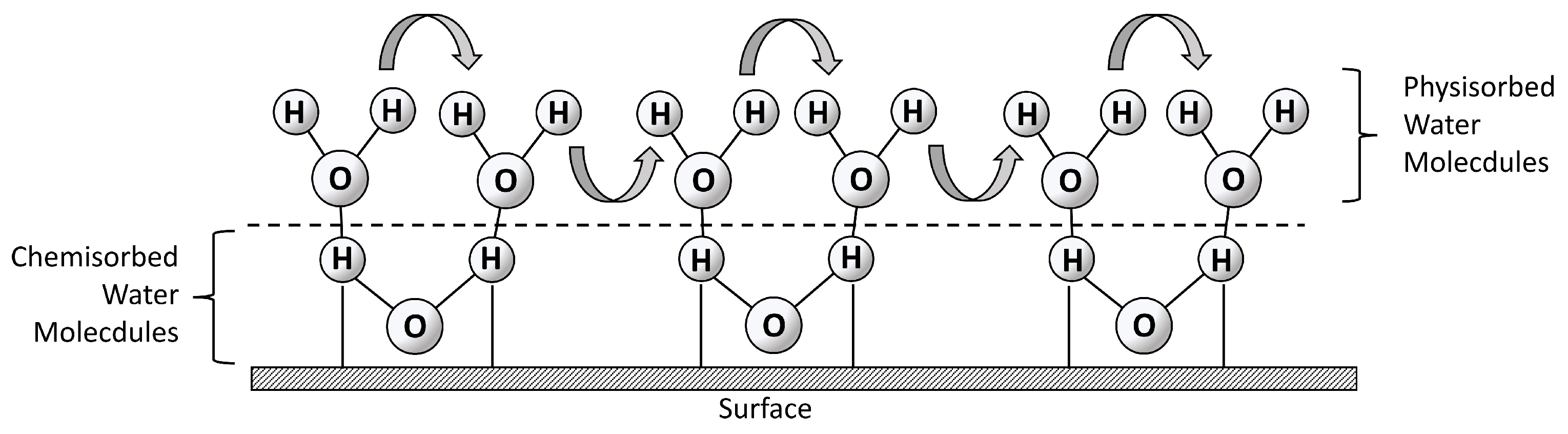
- Unit cell size: The SnO2 larger unit cell reduces the influence of hydrogen bonding between adsorbed water molecules compared to TiO2 [10].
- Bond character: The higher covalent character of Sn–O bonds suggests a stronger Brønsted acidity compared to Ti–O bonds. potentially promoting dissociation on SnO2 [10];
- Water adsorption layers: The structure of the first layer of adsorbed water molecules dictates subsequent layers. TiO2 tends towards associative adsorption (intact molecules), while SnO2 favors dissociation [11].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. SnO2, Sn0.75Ti0.25O2, (SnTi)xO2 Synthesis
2.2. Characterisation and Deposition of Sensing Materials
2.3. Research Questions
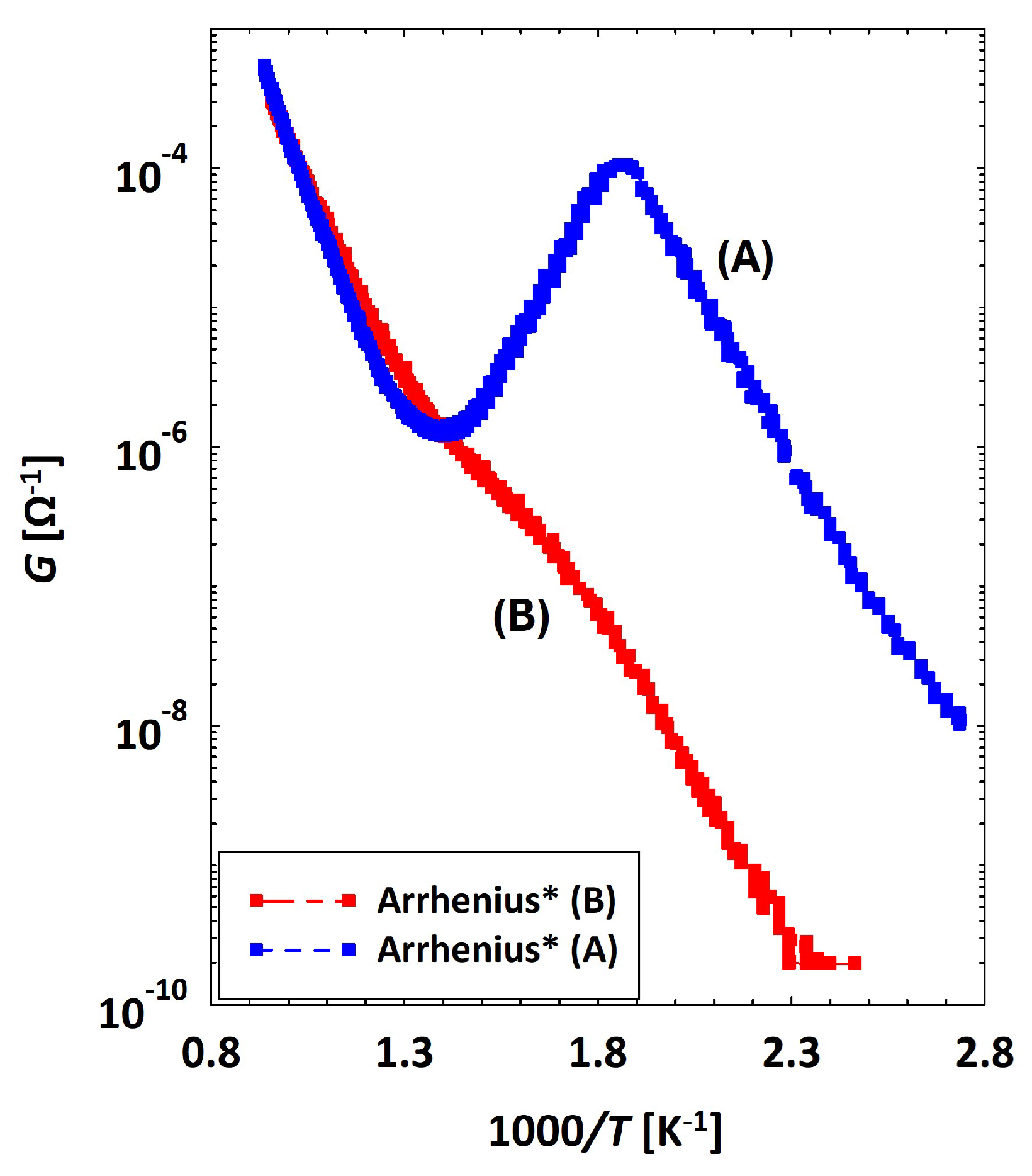
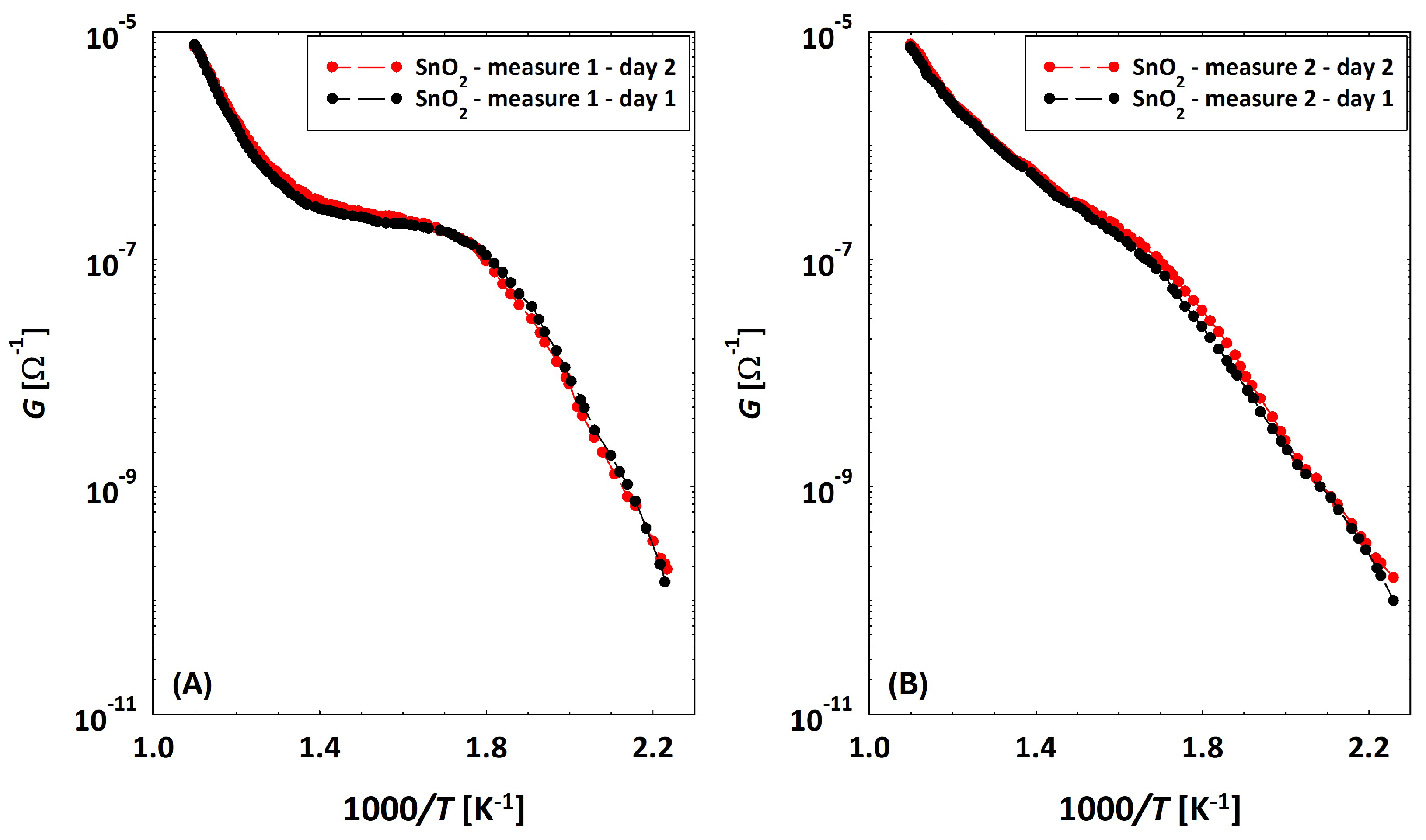
Discrepancy between Conductances of the Same Sensor
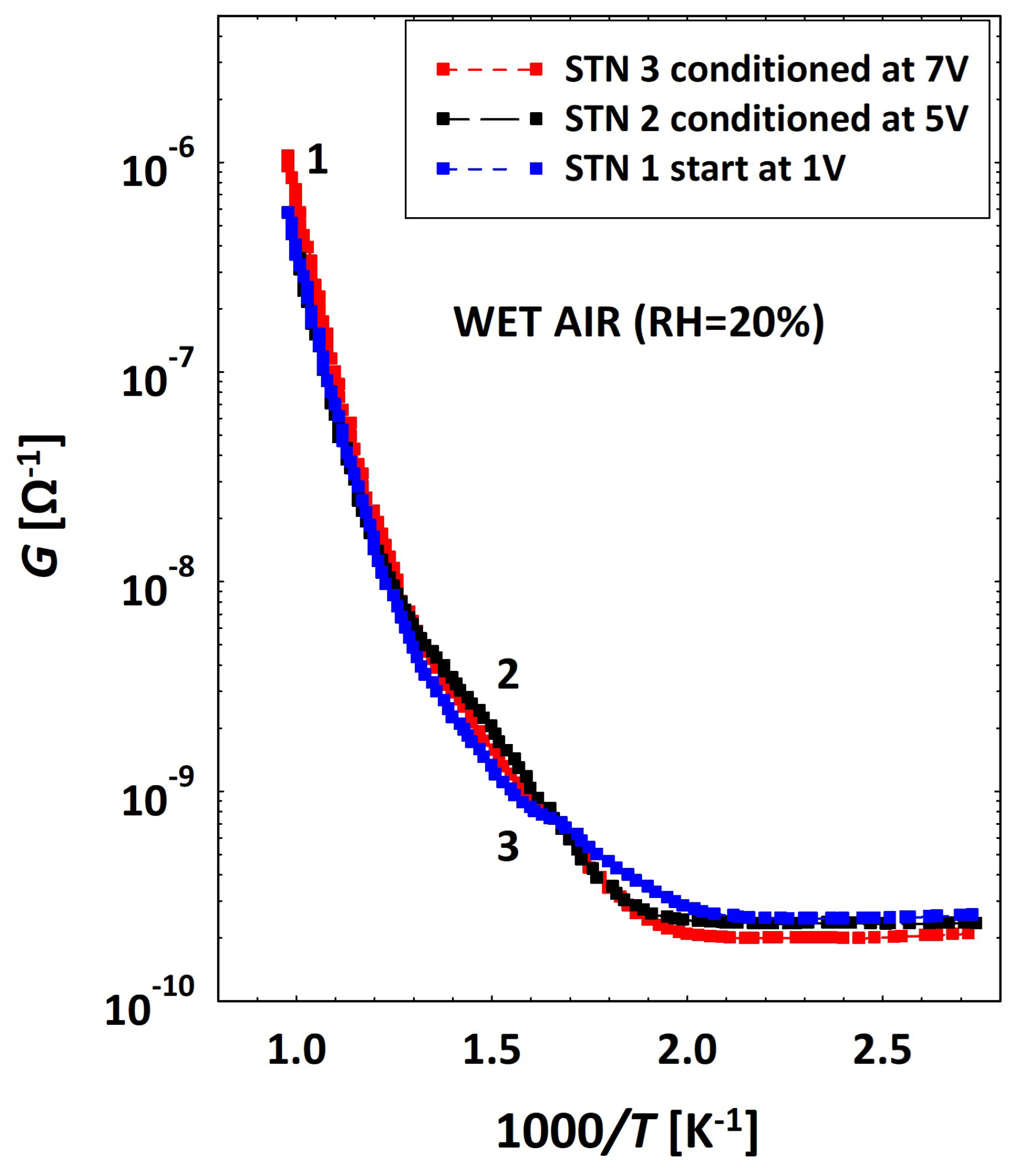
2.4. Humidity Effects on MOX Sensors
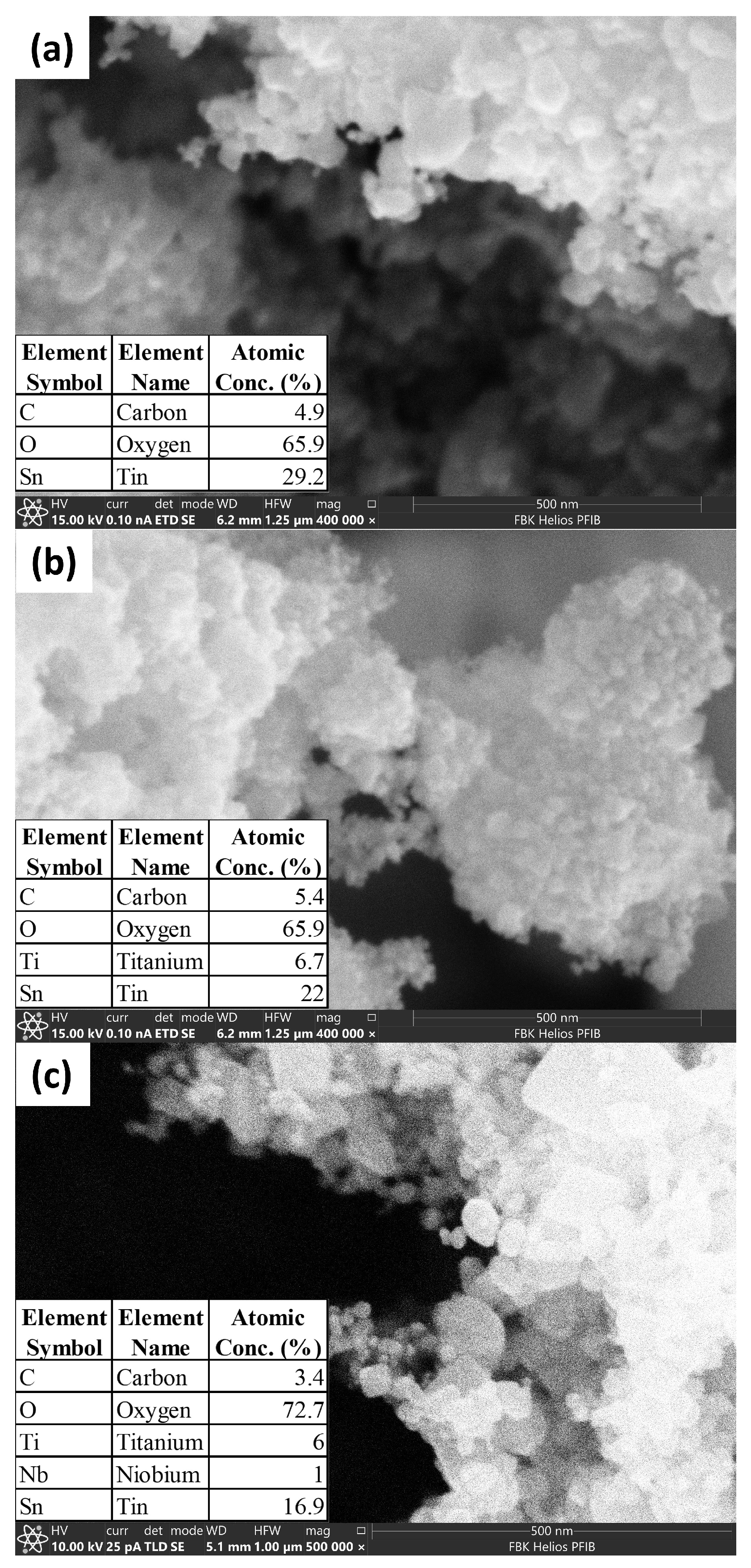
2.5. Morphological and Chemical Characterization of the Nanomaterial Used
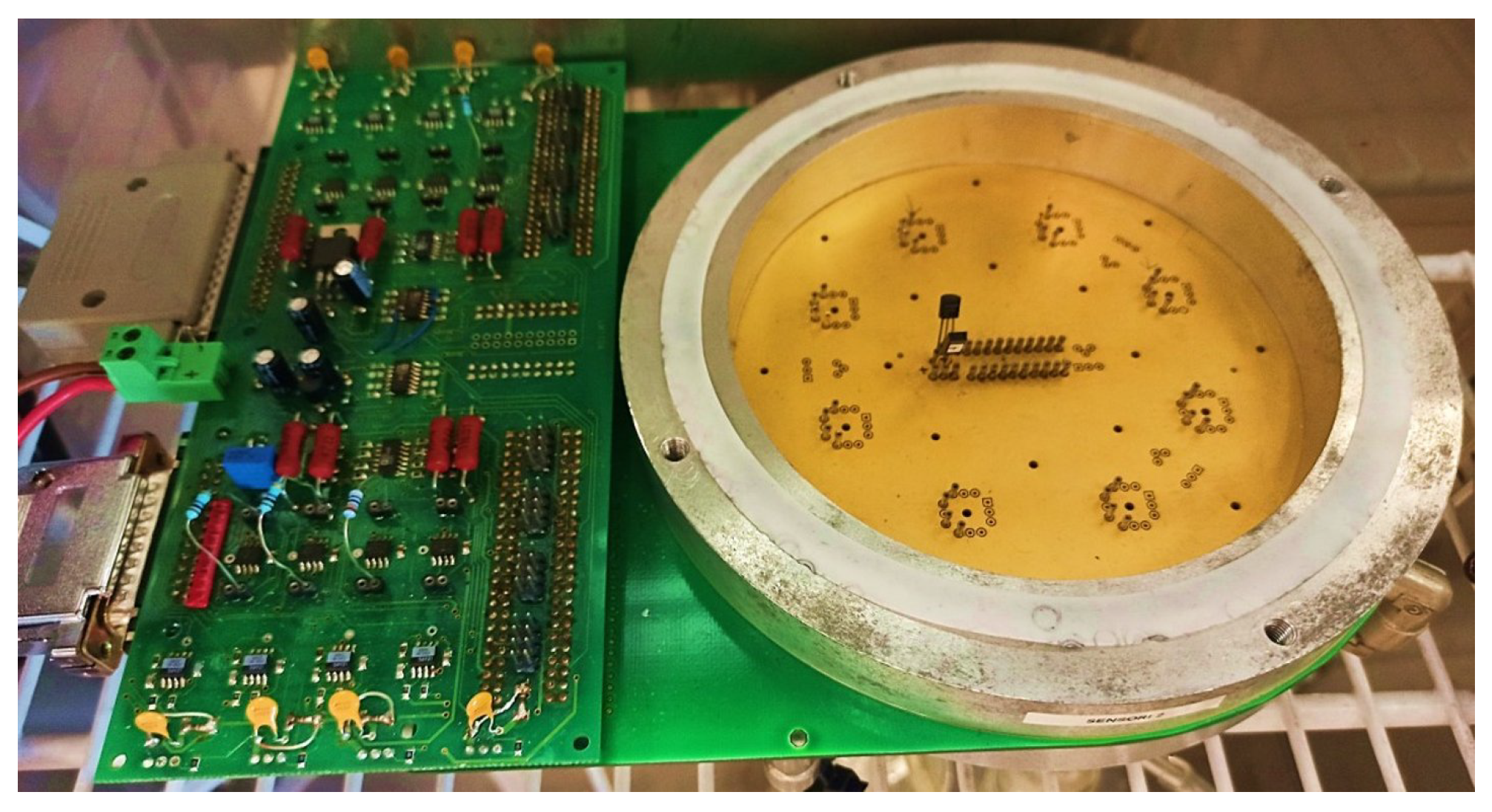
2.6. Gas Test Bench Setup
2.7. SnO2
2.8. SnTiNbO2—(STN)
3. Results and Discussion
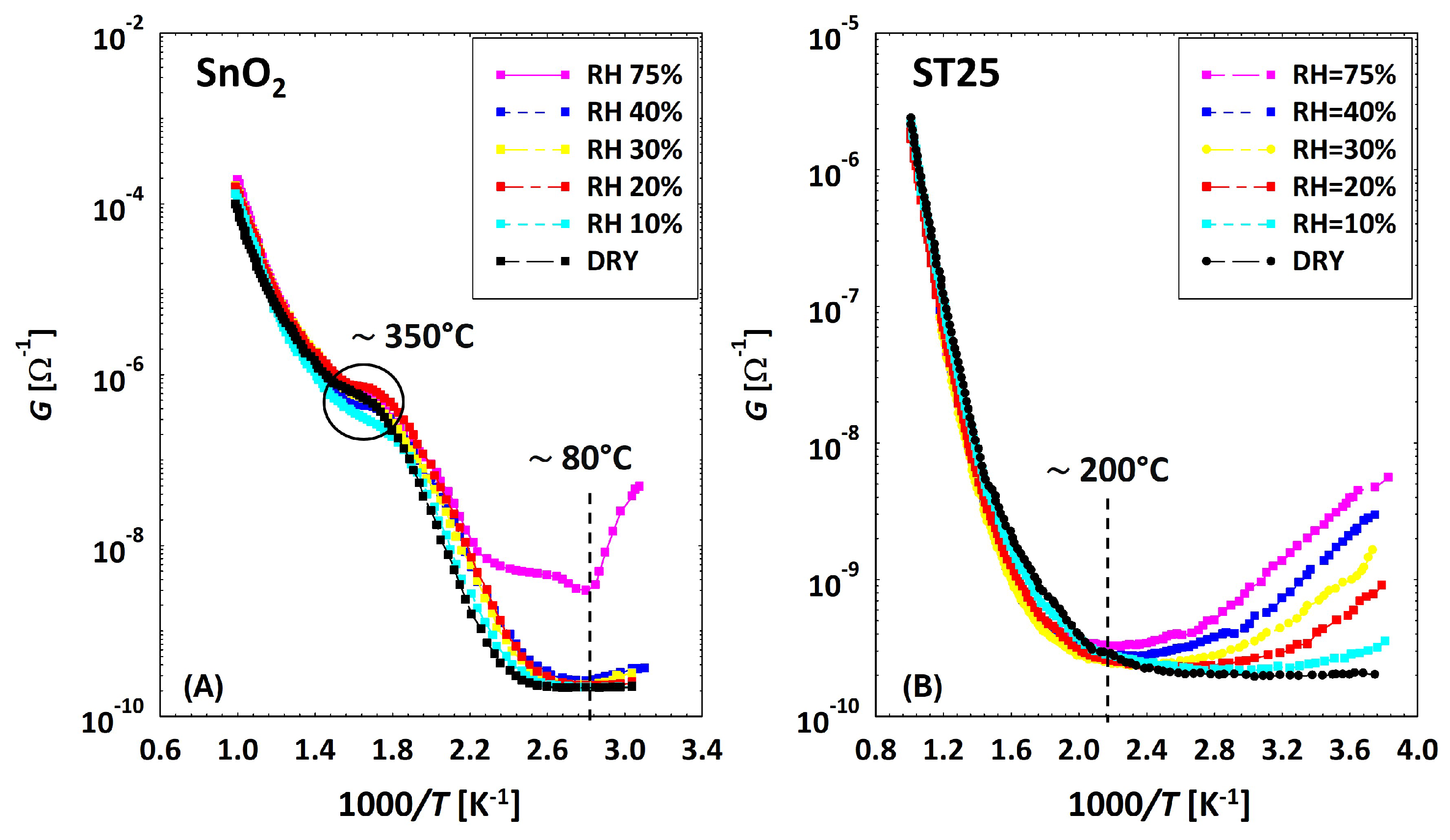
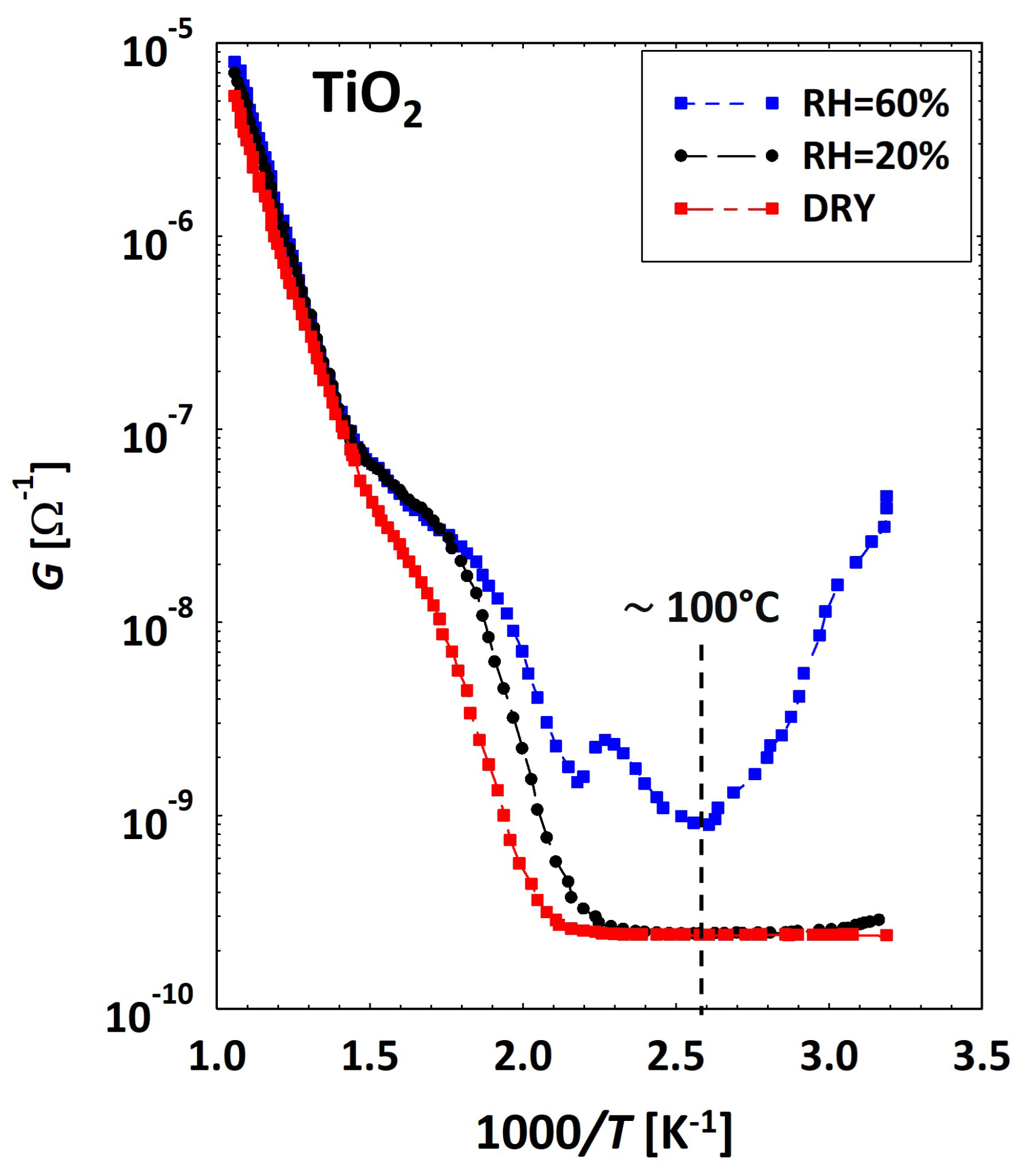
3.1. Theoretical Background for Wet Conductivity in SnO2, TiO2 and (Sn–Ti)O2 Materials
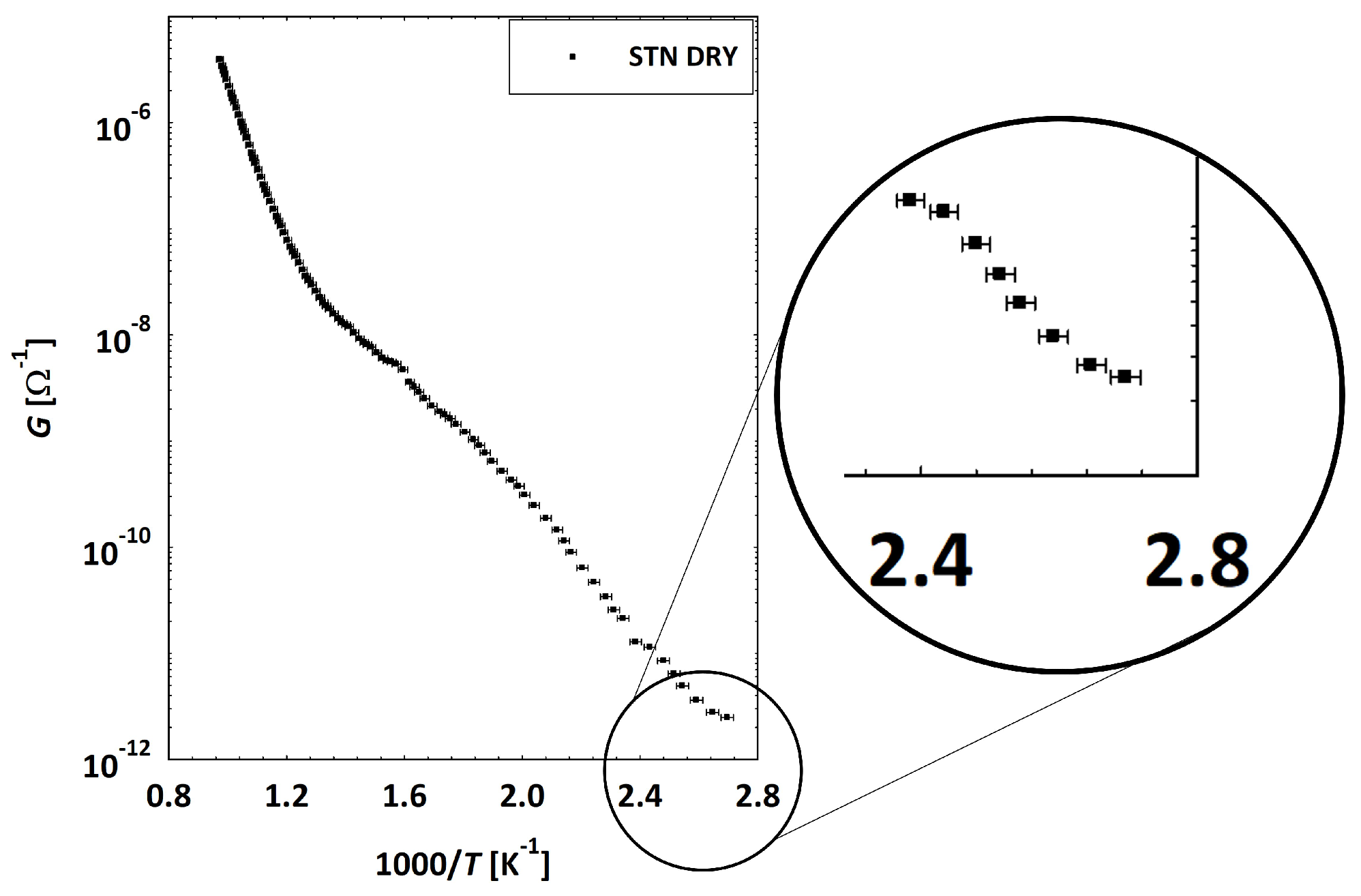
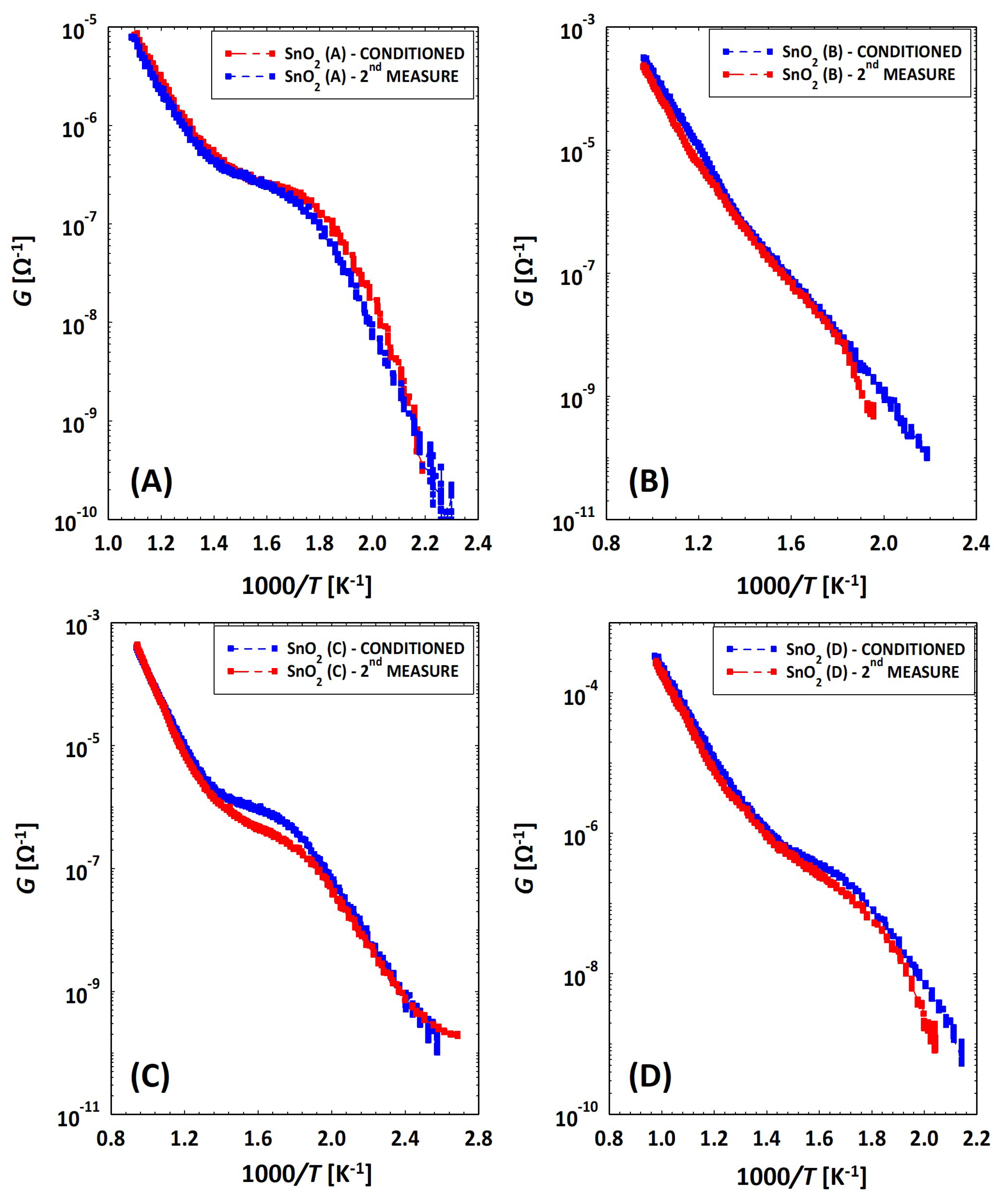
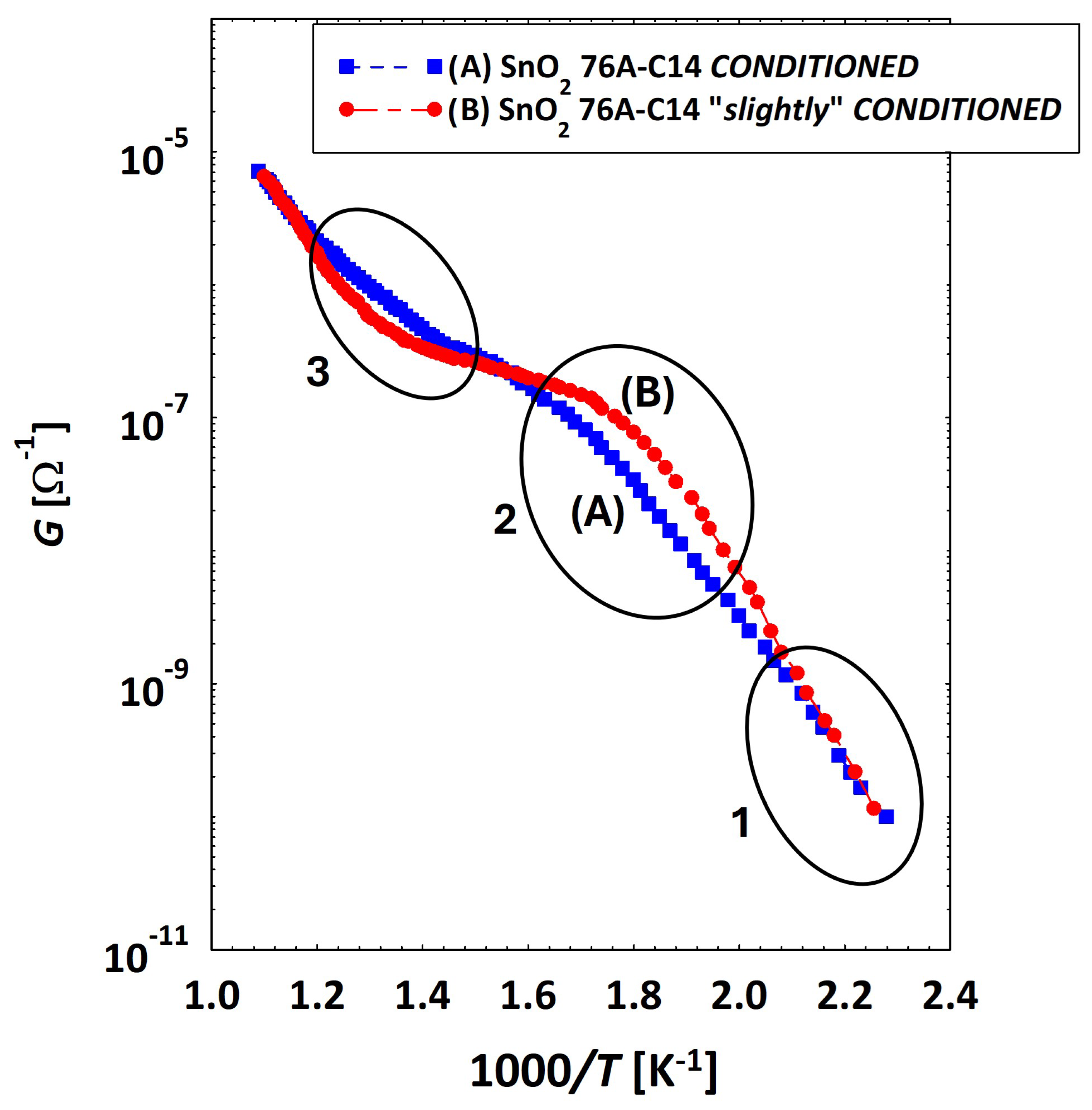
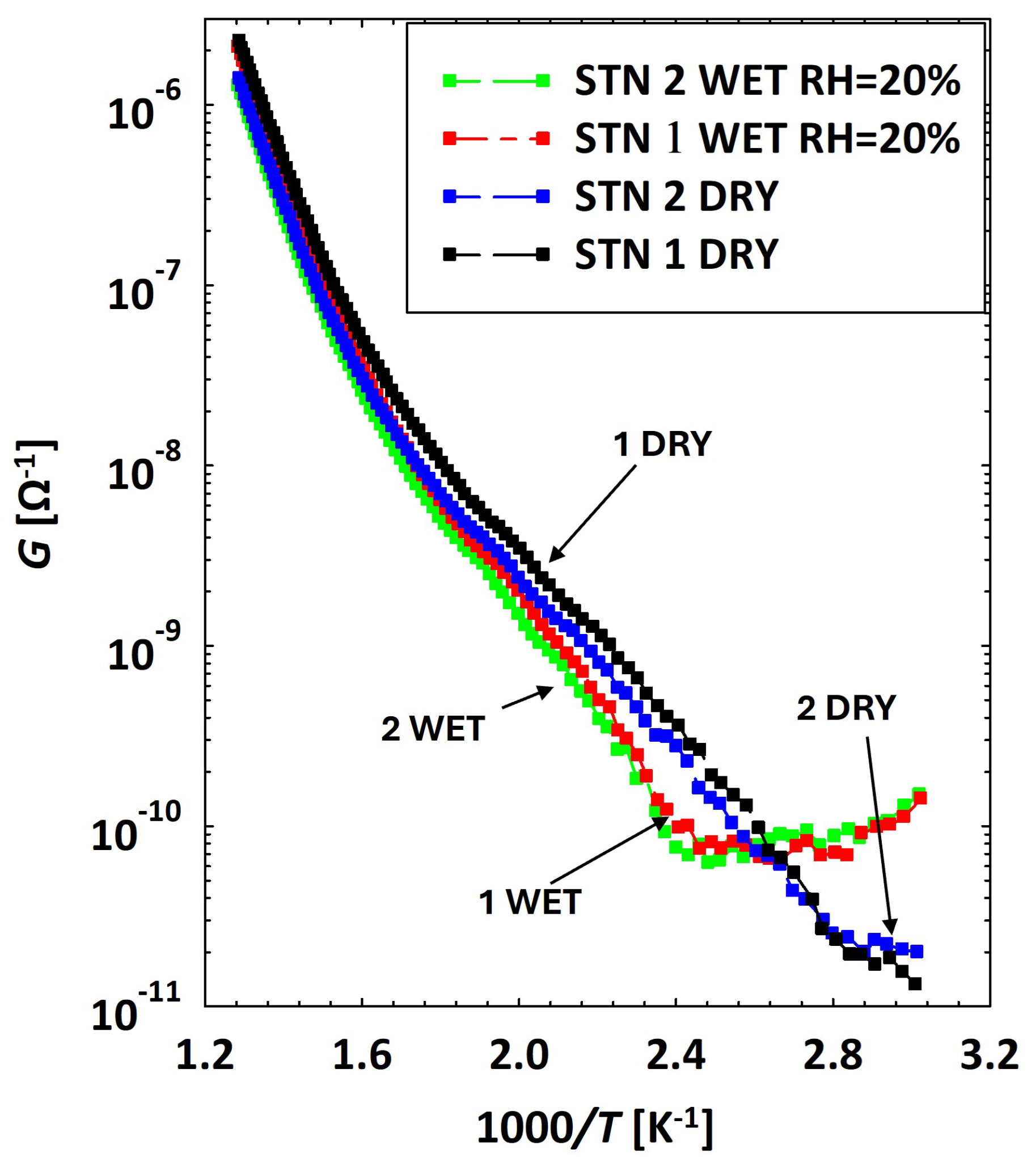
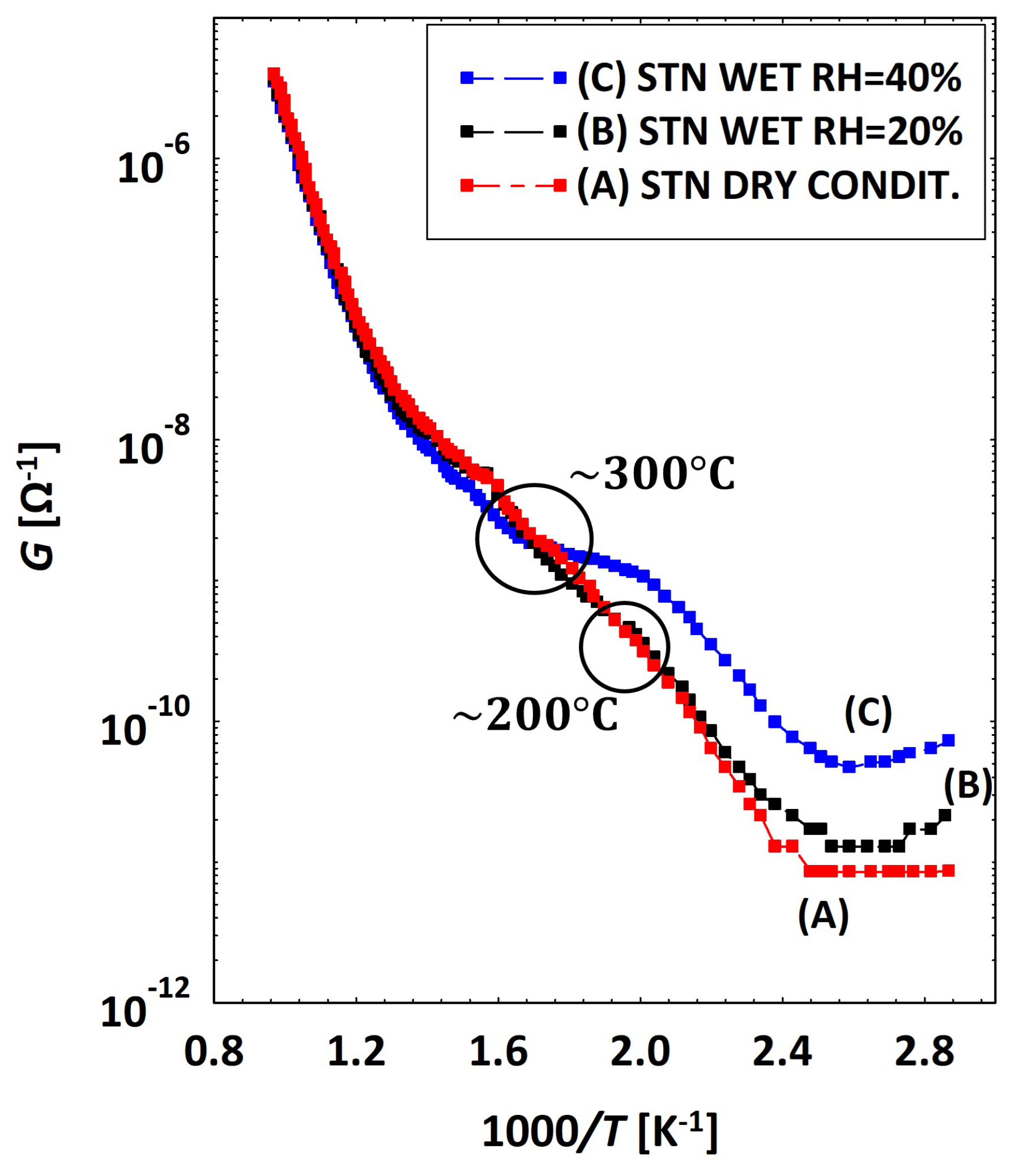
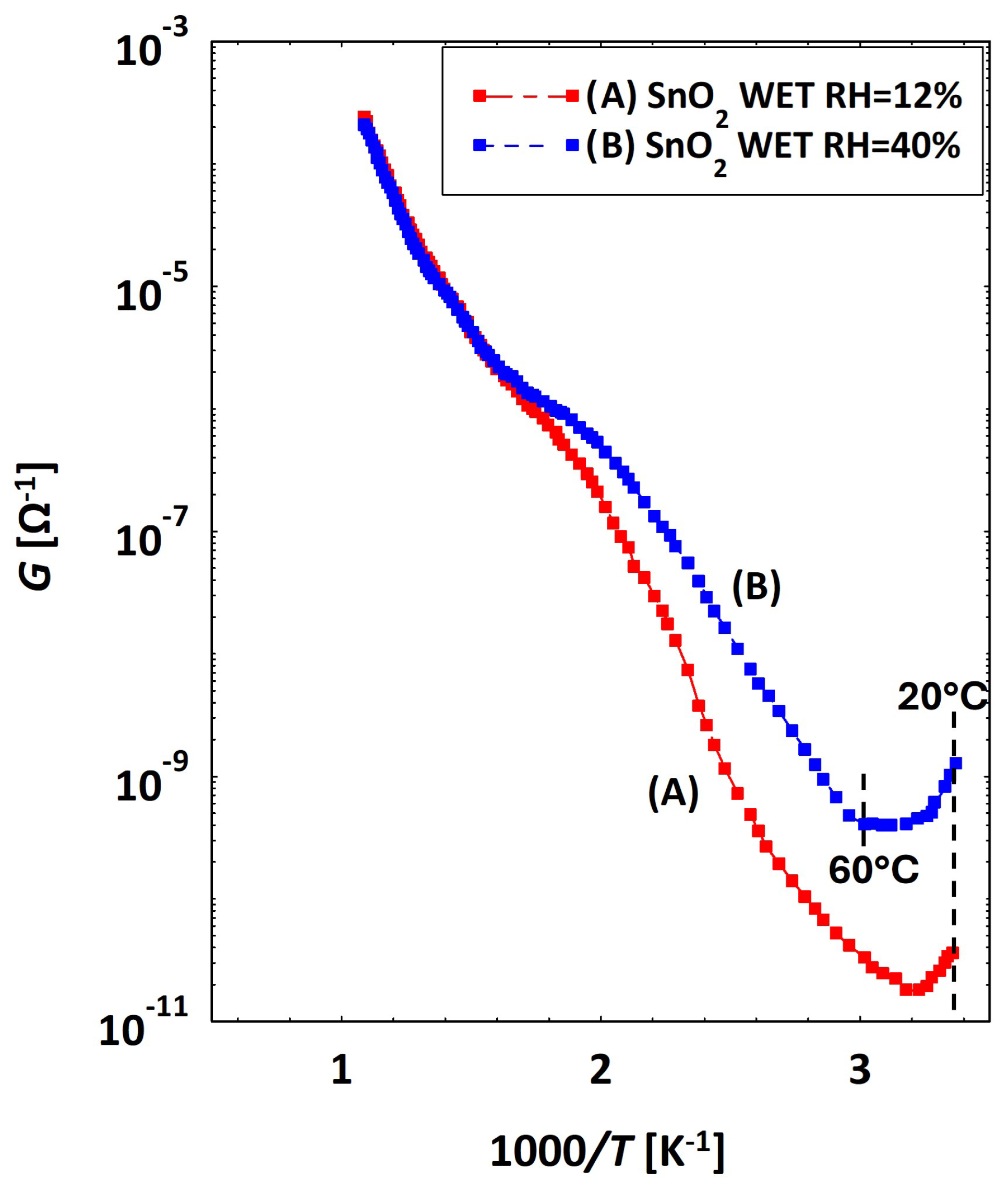
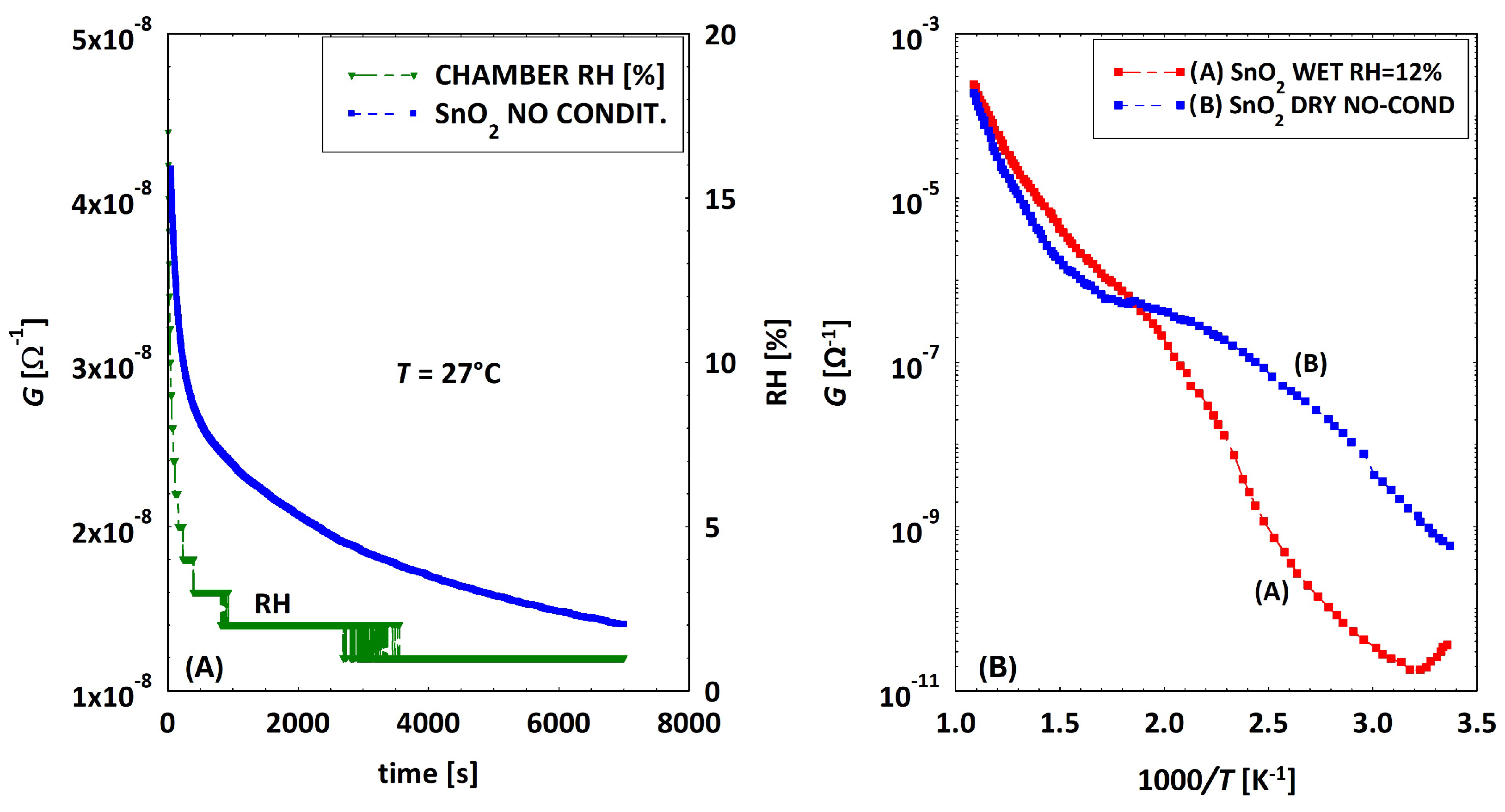
3.2. Low Temperatures’ Experimental Behavior
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| OPAMP | Operational Amplifier |
| STN | SnTiNbO2 tin–titanium–niobium-based metal oxide solid solution |
| ST25 | Sn75Ti25O2 tin–titanium-based solid solution |
| MOX | Metal Oxides |
| PW DFT | Plane-Wave Density Functional Theory |
Appendix A. General Overview on Arrhenius Plots
Appendix B. Signal Reading: The Operational Amplifier (OPAMP)

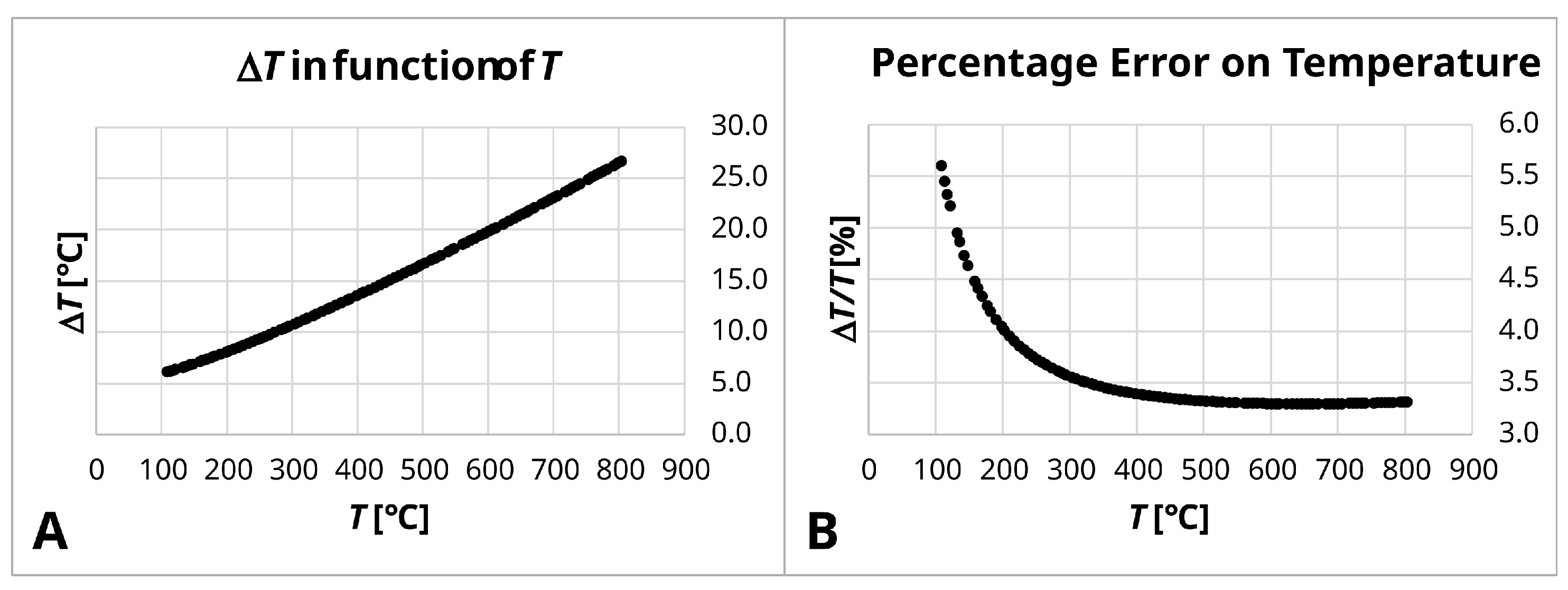
Appendix B.1. Uncertainties on Film Conductance Measurements

Appendix C. Sensor Temperature Regulation

The Callendar–Van Dusen Relation
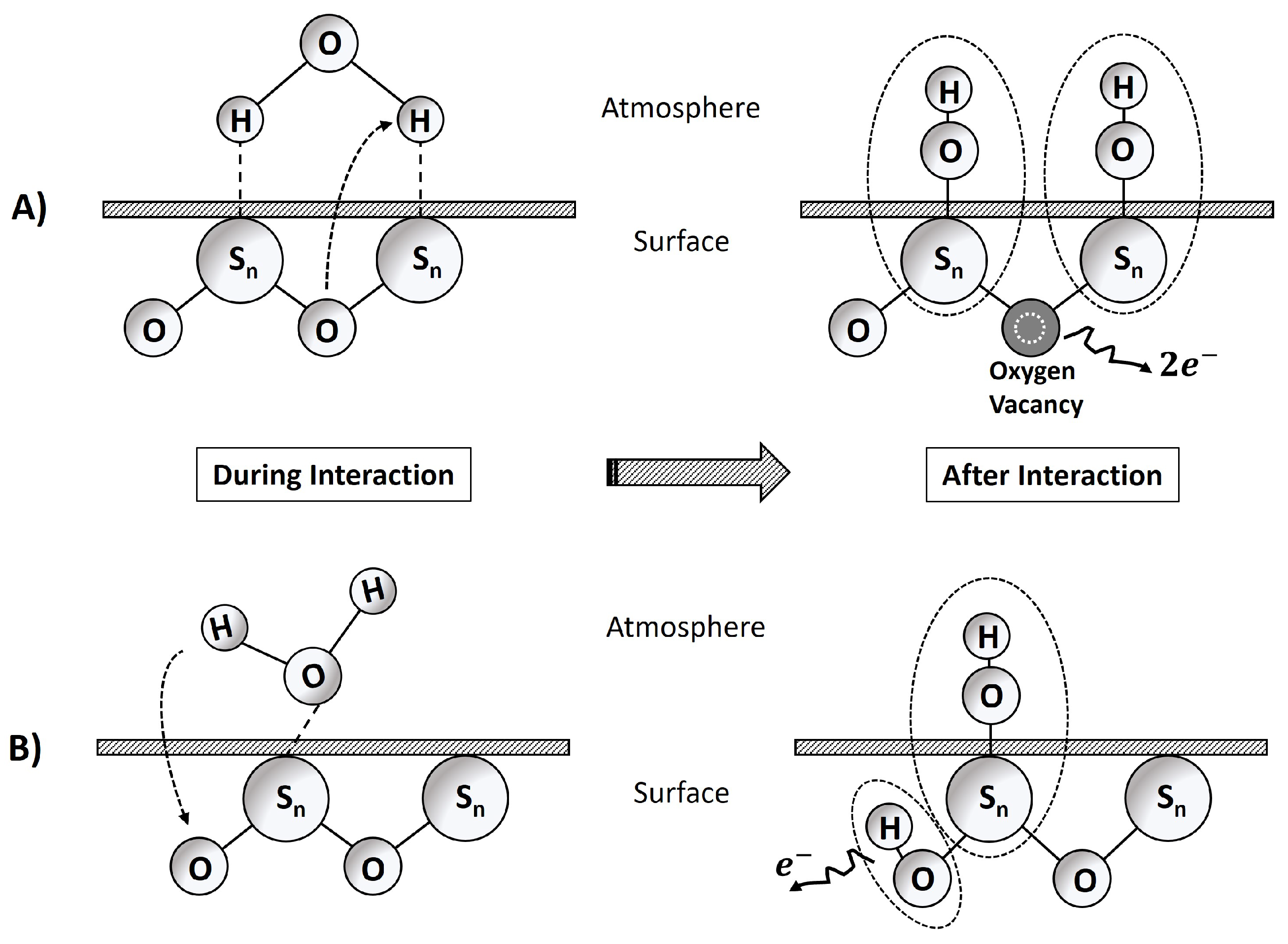
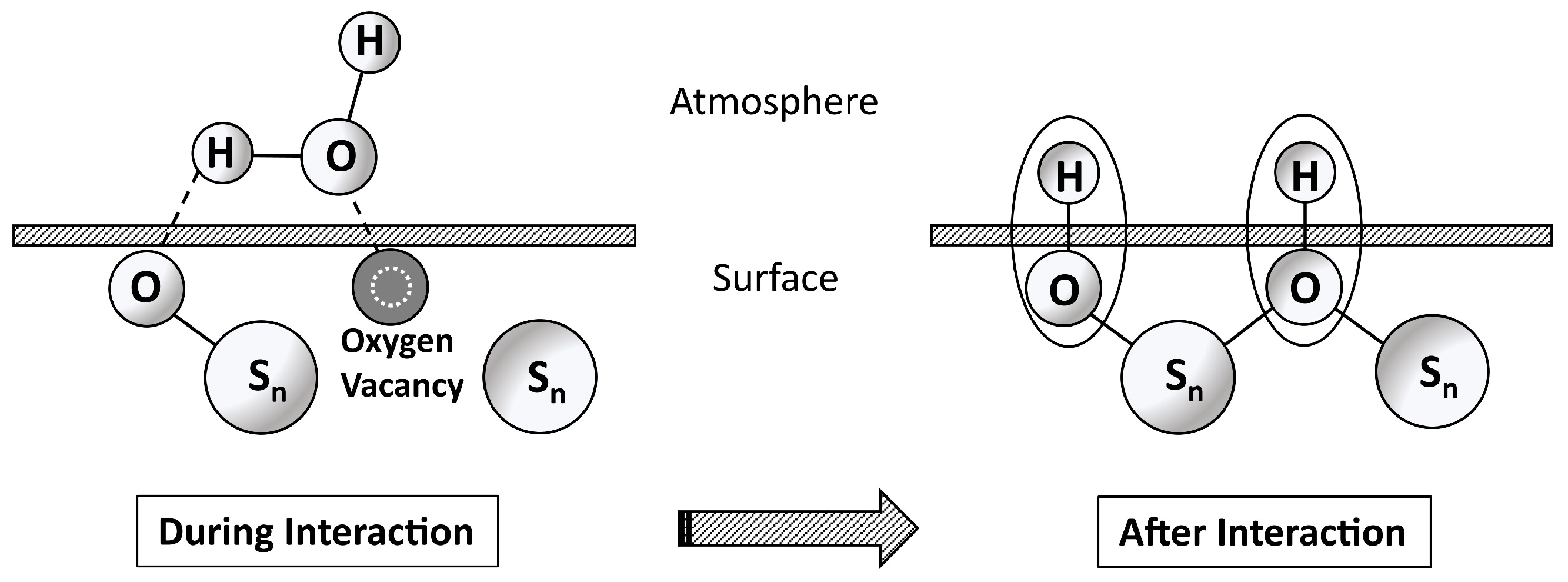
Appendix D. Water–Surface Interactions

References
- Amu-Darko, J.N.O.; Hussain, S.; Issaka, E.; Wang, M.; Alothman, A.A.; Lei, S.; Qiao, G.; Liu, G. Nanosheet assembled NiO−doped-ZnO flower-like sensors for highly sensitive hydrogen sulfide gas detection. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 17681–17690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, A.N.; Kamarudin, K.; Kamarudin, L.M.; Adom, A.H.; Mamduh, S.M.; Mohd Juffry, Z.H.; Bennetts, V.H. Correction Model for Metal Oxide Sensor Drift Caused by Ambient Temperature and Humidity. Sensors 2022, 22, 3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Astolfi, M.; Rispoli, G.; Anania, G.; Zonta, G.; Malagù, C. Chemoresistive Nanosensors Employed to Detect Blood Tumor Markers in Patients Affected by Colorectal Cancer in a One-Year Follow Up. Cancers 2023, 15, 1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zonta, G.; Rispoli, G.; Malagù, C.; Astolfi, M. Overview of Gas Sensors Focusing on Chemoresistive Ones for Cancer Detection. Chemosensors 2023, 11, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astolfi, M.; Rispoli, G.; Benedusi, M.; Zonta, G.; Landini, N.; Valacchi, G.; Malagù, C. Chemoresistive Sensors for Cellular Type Discrimination Based on Their Exhalations. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astolfi, M.; Rispoli, G.; Anania, G.; Artioli, E.; Nevoso, V.; Zonta, G.; Malagù, C. Tin, Titanium, Tantalum, Vanadium and Niobium Oxide Based Sensors to Detect Colorectal Cancer Exhalations in Blood Samples. Molecules 2021, 26, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbri, B.; Valt, M.; Gherardi, S.; Gaiardo, A.; Malagù, C.; Guidi, V. Water Stress Assessment through Gaseous Emissions Monitoring: A Case of Study in Tomato Fields. In Proceedings of the 239th ECS Electrochemical Society Meeting, Virtual, 30 May–3 June 2021; p. 1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yin, L.; Zhang, L.; Xiang, D.; Gao, R. Metal Oxide Gas Sensors: Sensitivity and Influencing Factors. Sensors 2010, 10, 2088–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madou, M.J.; Morrison, S.R. Chemical Sensing with Solid State Devices; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindan, P.J. Water chemistry at the SnO2(110) surface: The role of inter-molecular interactions and surface geometry. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2000, 328, 325–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandura, A.V.; Kubicki, J.D.; Sofo, J.O. Comparisons of Multilayer H2O Adsorption onto the (110) Surfaces of ff-TiO2 and SnO2 as Calculated with Density Functional Theory. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 11616–11624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagolini, A.; Gaiardo, A.; Crivellari, M.; Demenev, E.; Bartali, R.; Picciotto, A.; Valt, M.; Ficorella, F.; Guidi, V.; Bellutti, P. Development of MEMS MOS gas sensors with CMOS compatible PECVD inter-metal passivation. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 292, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonini, M.; Gaiardo, A.; Vecchio, M. MetaNChemo: A meta-heuristic neural-based framework for chemometric analysis. Appl. Soft Comput. 2020, 97, 106712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spagnoli, E.; Gaiardo, A.; Fabbri, B.; Valt, M.; Krik, S.; Ardit, M.; Cruciani, G.; Della Ciana, M.; Vanzetti, L.; Vola, G.; et al. Design of a Metal-Oxide Solid Solution for Sub-ppm H2 Detection. ACS Sens. 2022, 7, 573–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spagnoli, E.; Fabbri, B.; Gaiardo, A.; Valt, M.; Ardit, M.; Krik, S.; Cruciani, G.; Della Ciana, M.; Vanzetti, L.; Vola, G.; et al. Design of a metal-oxide solid solution for selective detection of ethanol with marginal influence by humidity. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 370, 132426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spagnoli, E.; Valt, M.; Gaiardo, A.; Fabbri, B.; Guidi, V. Insights into the Sensing Mechanism of a Metal-Oxide Solid Solution via Operando Diffuse Reflectance Infrared Fourier Transform Spectroscopy. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guidi, V.; Butturi, M.; Carotta, M.; Cavicchi, B.; Ferroni, M.; Malagù, C.; Martinelli, G.; Vincenzi, D.; Sacerdoti, M.; Zen, M. Gas sensing through thick film technology. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2002, 84, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carotta, M.C.; Benetti, M.; Ferrari, E.; Giberti, A.; Malagù, C.; Nagliati, M.; Vendemiati, B.; Martinelli, G. Basic interpretation of thick film gas sensors for atmospheric application. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2007, 126, 672–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidi, V.; Malagù, C.; Carotta, M.; Vendemiati, B. 11—Printed semiconducting gas sensors. In Printed Films; Prudenziati, M., Hormadaly, J., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing Series in Electronic and Optical Materials; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2012; pp. 278–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaiardo, A.; Fabbri, B.; Guidi, V.; Bellutti, P.; Giberti, A.; Gherardi, S.; Vanzetti, L.; Malagù, C.; Zonta, G. Metal Sulfides as Sensing Materials for Chemoresistive Gas Sensors. Sensors 2016, 16, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Astolfi, M.; Rispoli, G.; Gherardi, S.; Zonta, G.; Malagù, C. Reproducibility and Repeatability Tests on (SnTiNb)O2 Sensors in Detecting ppm-Concentrations of CO and Up to 40% of Humidity: A Statistical Approach. Sensors 2023, 23, 1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcaleer, J.F.; Moseley, P.T.; Norris, J.O.W.; Williams, D.E. Tin dioxide gas sensors. Part 1—Aspects of the surface chemistry revealed by electrical conductance variations. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1987, 83, 1323–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astolfi, M.; Zonta, G.; Gherardi, S.; Malagù, C.; Vincenzi, D.; Rispoli, G. A Portable Device for I–V and Arrhenius Plots to Characterize Chemoresistive Gas Sensors: Test on SnO2-Based Sensors. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gherardi, S.; Zonta, G.; Astolfi, M.; Malagù, C. Humidity effects on SnO2 and (SnTiNb)O2 sensors response to CO and two-dimensional calibration treatment. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2021, 265, 115013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marc Madou, S.M. Chemical Sensing with Solid State Devices; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Miyoshi, S.; Akao, Y.; Kuwata, N.; Kawamura, J.; Oyama, Y.; Yagi, T.; Yamaguchi, S. Water uptake and conduction property of nano-grained yttria-doped zirconia fabricated by ultra-high pressure compaction at room temperature. Solid State Ionics 2012, 207, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Jiang, L.; Ismail, S.A.; Guo, H.; Han, D. Surface Protonic Conduction on Oxide Ceramics: Mechanism, Materials, and Method for Characterization. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 10, 2201764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, K.R.; Tricoli, A.; Santarossa, G.; Vargas, A.; Baiker, A. First Principles Analysis of H2O Adsorption on the (110) Surfaces of SnO2, TiO2 and Their Solid Solutions. Langmuir 2012, 28, 1646–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diebold, U. The surface science of titanium dioxide. Surf. Sci. Rep. 2003, 48, 53–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bârsan, N.; Ionescu, R. The mechanism of the interaction between CO and an SnO2 surface: The role of water vapour. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1993, 12, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bârsan, N.; Weimar, U. Understanding the fundamental principles of metal oxide based gas sensors; the example of CO sensing with SnO2 sensors in the presence of humidity. J. Physics Condens. Matter 2003, 15, R813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, M.A. The interaction of water with solid surfaces: Fundamental aspects revisited. Surf. Sci. Rep. 2002, 46, 1–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perron, H.; Vandenborre, J.; Domain, C.; Drot, R.; Roques, J.; Simoni, E.; Ehrhardt, J.J.; Catalette, H. Combined investigation of water sorption on TiO2 rutile (110) single crystal face: XPS vs. periodic DFT. Surf. Sci. 2007, 601, 518–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carotta, M.; Fioravanti, A.; Gherardi, S.; Malagù, C.; Sacerdoti, M.; Ghiotti, G.; Morandi, S. (Ti, Sn) solid solutions as functional materials for gas sensing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 194, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lide, D.R. CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 77th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Carotta, M.; Ferrari, E.; Giberti, A.; Malagù, C.; Nagliati, M.; Gherardi, S.; Vendemiati, B.; Martinelli, G. Semiconductor Gas Sensors for Environmental Monitoring. Adv. Sci. Technol. 2006, 45, 1818–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lantto, V.; Rompplainen, P.; Leppävuori, S. A study of the temperature dependence of the barrier energy in porous tin dioxide. Sens. Actuators 1988, 14, 149–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heiland, G.; Kohl, D. Physical and Chemical Aspects of Oxidic Semiconductor Gas Sensors. Chem. Sens. Technol. 1988, 1, 15–38. [Google Scholar]
- Shankar, P.; Rayappan, J.B.B. Gas sensing mechanism of metal oxides: The role of ambient atmosphere, type of semiconductor and gases—A review. Sci. Lett. 2015, 4, 126. [Google Scholar]
- Henrich, V.E.; Cox, P.A. The Surface Science of Metal Oxides; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Kannan, P.K.; Saraswathi, R.; Rayappan, J.B.B. A highly sensitive humidity sensor based on DC reactive magnetron sputtered zinc oxide thin film. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2010, 164, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahani, H.; Wagiran, R.H.M. Humidity sensors principle, mechanism, and fabrication technologies: A comprehensive review. Sensors 2014, 14, 7881–7939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stub, S.; Vøllestad, E.; Norby, T. Mechanisms of Protonic Surface Transport in Porous Oxides: Example of YSZ. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 12817–12825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gherardi, S.; Astolfi, M.; Gaiardo, A.; Malagù, C.; Rispoli, G.; Vincenzi, D.; Zonta, G. Investigating the Temperature-Dependent Kinetics in Humidity-Resilient Tin–Titanium-Based Metal Oxide Gas Sensors. Chemosensors 2024, 12, 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12080151
Gherardi S, Astolfi M, Gaiardo A, Malagù C, Rispoli G, Vincenzi D, Zonta G. Investigating the Temperature-Dependent Kinetics in Humidity-Resilient Tin–Titanium-Based Metal Oxide Gas Sensors. Chemosensors. 2024; 12(8):151. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12080151
Chicago/Turabian StyleGherardi, Sandro, Michele Astolfi, Andrea Gaiardo, Cesare Malagù, Giorgio Rispoli, Donato Vincenzi, and Giulia Zonta. 2024. "Investigating the Temperature-Dependent Kinetics in Humidity-Resilient Tin–Titanium-Based Metal Oxide Gas Sensors" Chemosensors 12, no. 8: 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12080151
APA StyleGherardi, S., Astolfi, M., Gaiardo, A., Malagù, C., Rispoli, G., Vincenzi, D., & Zonta, G. (2024). Investigating the Temperature-Dependent Kinetics in Humidity-Resilient Tin–Titanium-Based Metal Oxide Gas Sensors. Chemosensors, 12(8), 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12080151





