A Review on the Advances in Nanomaterials for Electrochemical Non-Enzymatic Glucose Sensors Working in Physiological Conditions
Abstract
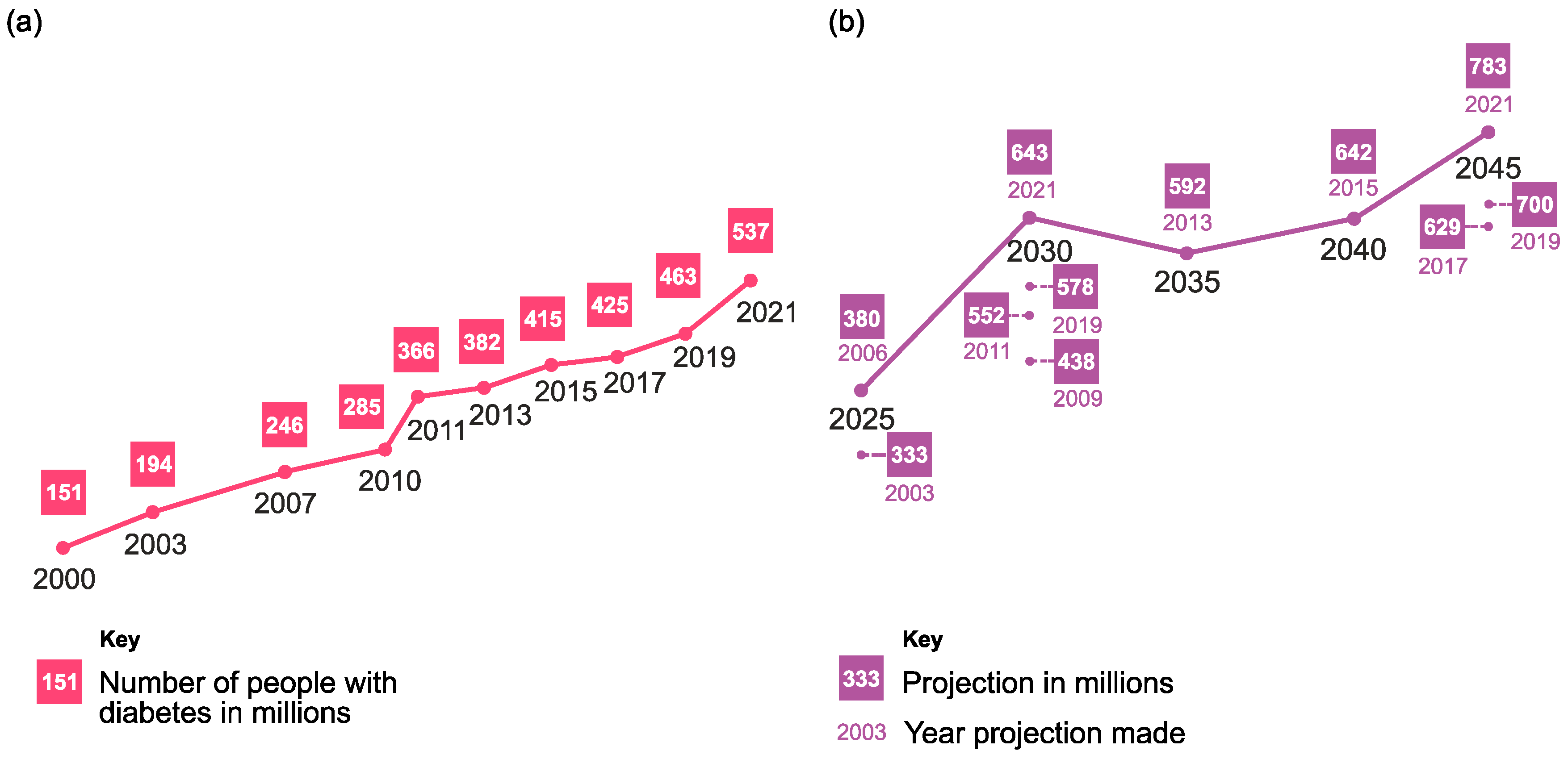
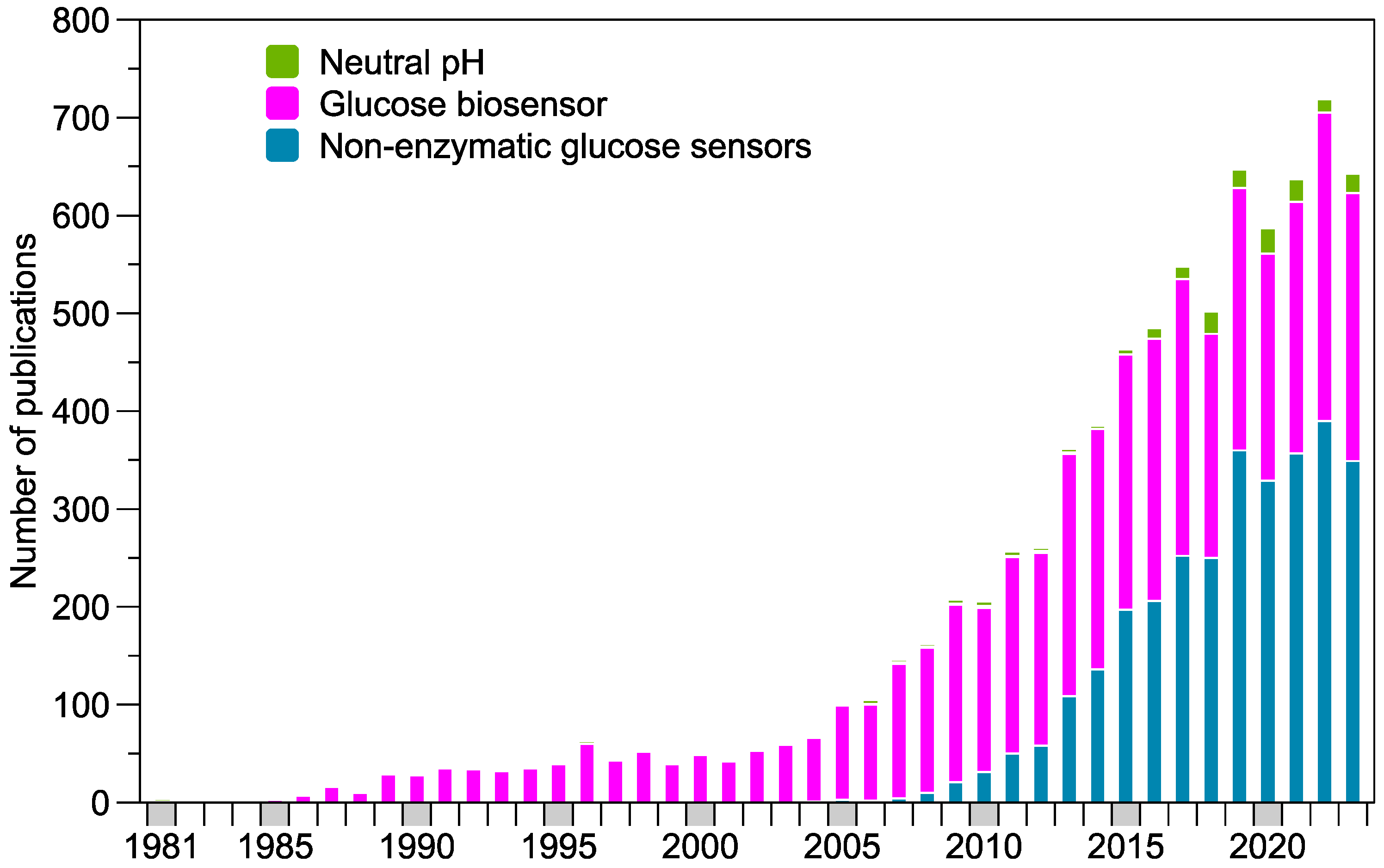
:1. Introduction
2. Electrochemical Glucose Detection Background
2.1. Current Formats for Commercial Glucose Detection
2.2. Accuracy and Precision
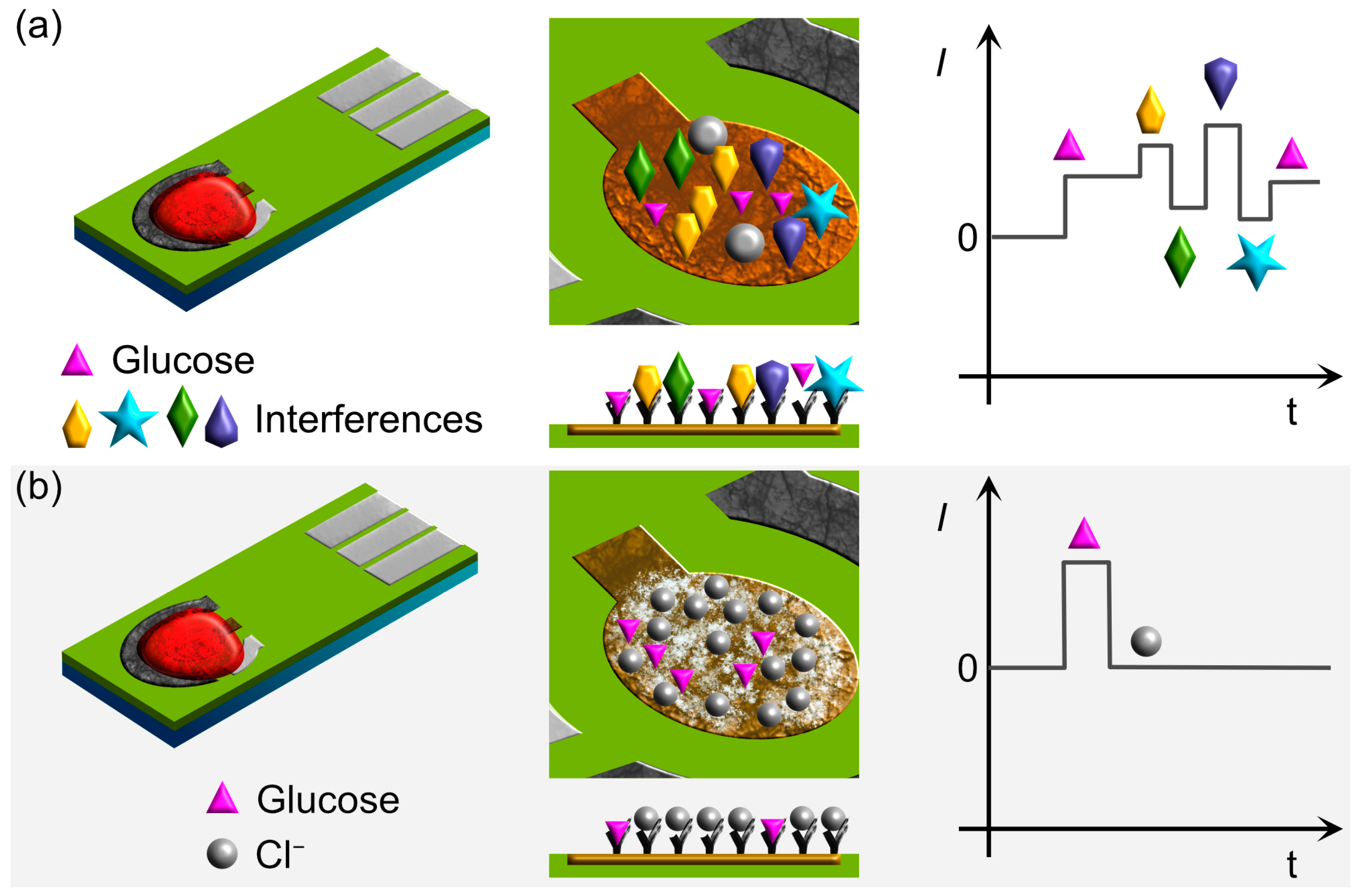
2.3. Selectivity, Interferences, and Poisoning
3. Sensing Mechanisms for Materials Applied for Non-Enzymatic Detection at Neutral pH
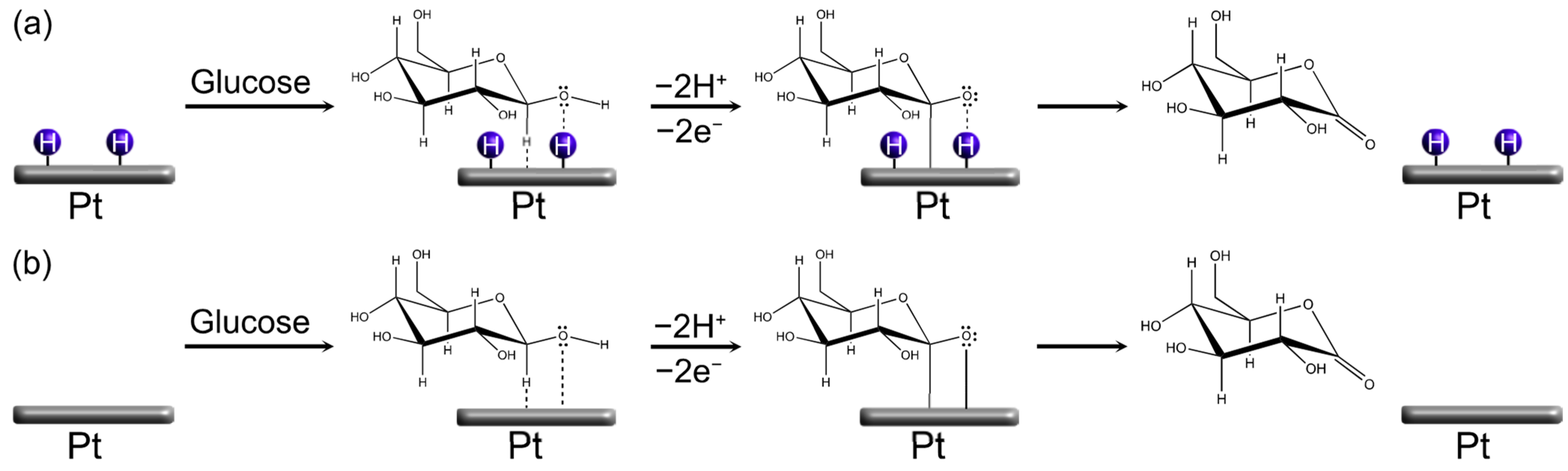
3.1. Platinum
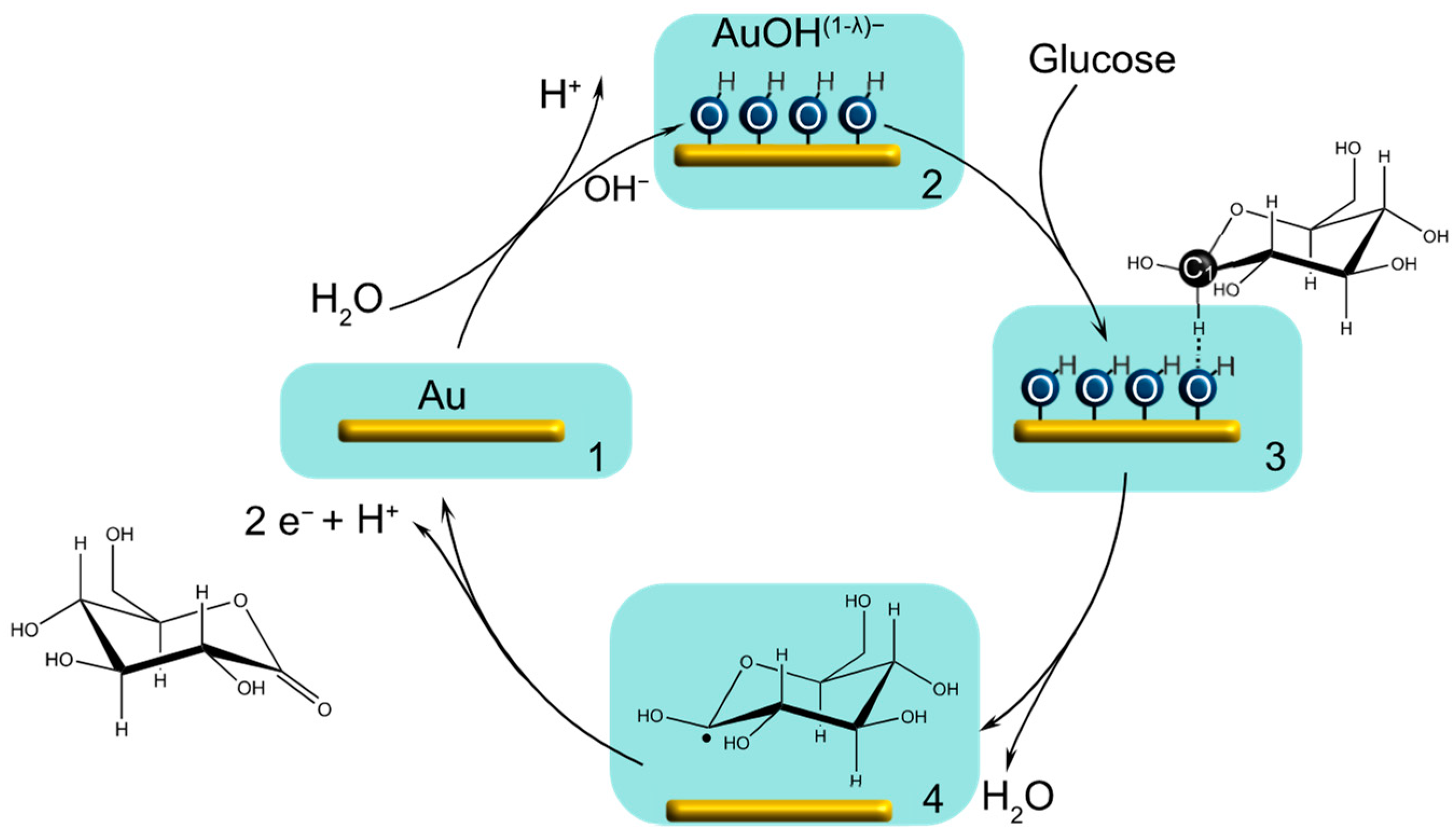
3.2. Gold
3.3. Metallic Ions
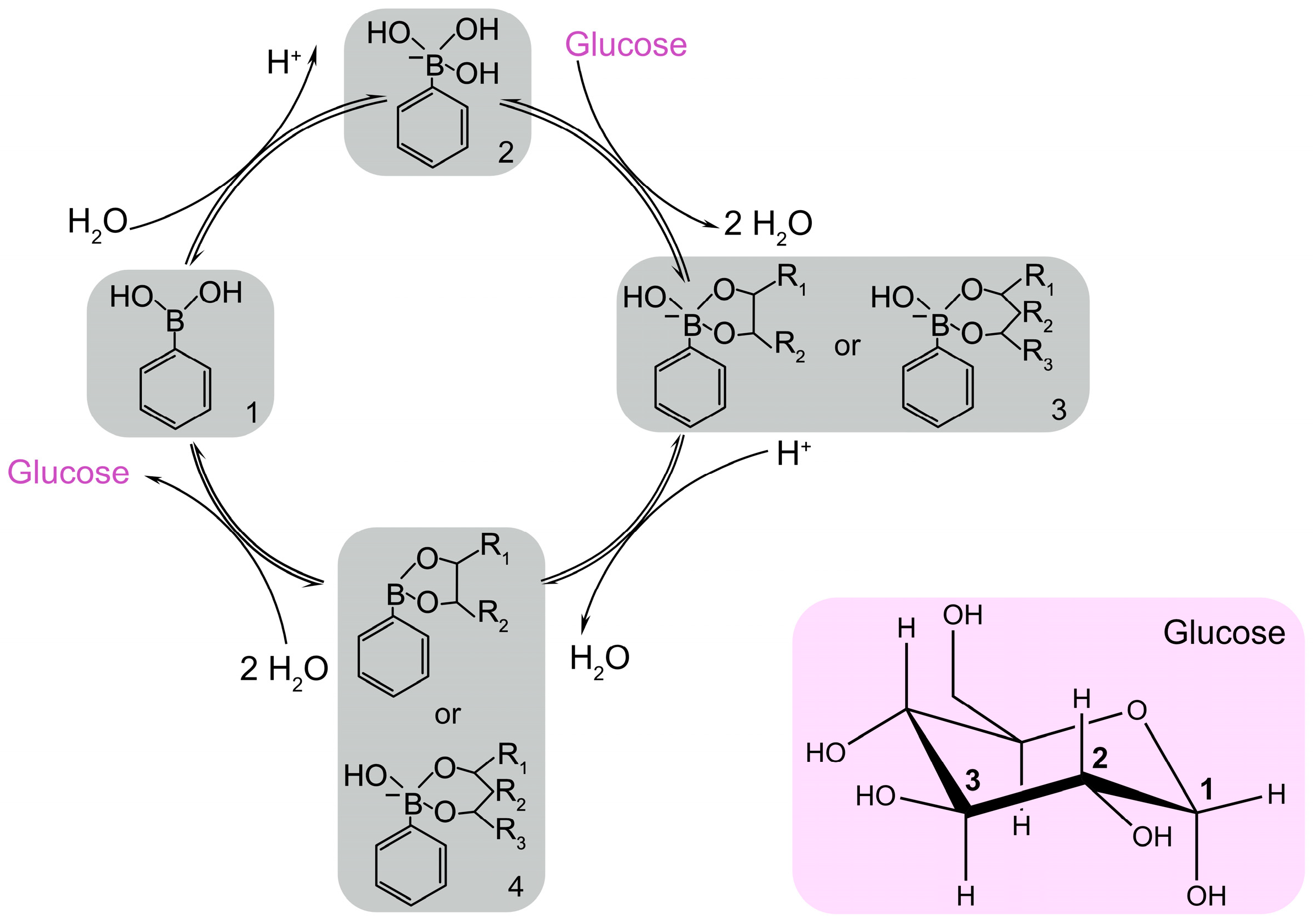
3.4. Phenylboronic Acid and Derivates for Glucose Detection
3.5. New Strategies to Improve the Efficiency of the Sensing Mechanism
4. Nanomaterials for Enzyme-Free Glucose Sensors Working at Neutral pH for Single Measurements
4.1. Platinum and Their Hybrid Nanocomposites
4.2. Gold and Their Hybrid Nanocomposites
4.3. Additional Transition Metals (Ag, Co, Cu, Ni, Ru, and Pd) and Their Nanocomposites
4.4. Phenylboronic Acid and Its Derivates
5. Materials for Non-Enzymatic Glucose Detection at Physiological pH in Wearable and Flexible Systems
6. Prevailing Drawbacks and Challenges Associated with Non-Enzymatic Detection at Neutral pH and Further Perspectives
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, R.; Shen, M.; Yang, Q.; Fairley, C.K.; Chai, Z.; McIntyre, R.; Ong, J.J.; Liu, H.; Lu, P.; Hu, W.; et al. Global Diabetes Prevalence in COVID-19 Patients and Contribution to COVID-19–Related Severity and Mortality: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diabetes Care 2023, 46, 890–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas, 10th ed.; IDF: Brussels, Belgium, 2021; p. 7. [Google Scholar]
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas, 3rd ed.; IDF: Brussels, Belgium, 2006; pp. 192–193. [Google Scholar]
- Freckmann, G.; Pleus, S.; Grady, M.; Setford, S.; Levy, B. Measures of Accuracy for Continuous Glucose Monitoring and Blood Glucose Monitoring Devices. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2019, 13, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pullano, S.A.; Greco, M.; Bianco, M.G.; Foti, D.; Brunetti, A.; Fiorillo, A.S. Glucose Biosensors in Clinical Practice: Principles, Limits and Perspectives of Currently Used Devices. Theranostics 2022, 12, 493–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mian, Z.; Hermayer, K.L.; Jenkins, A. Continuous Glucose Monitoring: Review of an Innovation in Diabetes Management. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 358, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erbach, M.; Freckmann, G.; Hinzmann, R.; Kulzer, B.; Ziegler, R.; Heinemann, L.; Schnell, O. Interferences and Limitations in Blood Glucose Self-Testing: An Overview of the Current Knowledge. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2016, 10, 1161–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reghunath, R.; Devi, K.; Singh, K.K. Recent Advances in Graphene Based Electrochemical Glucose Sensor. Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects 2021, 26, 100750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehit, E.; Altintas, Z. Significance of Nanomaterials in Electrochemical Glucose Sensors: An Updated Review (2016–2020). Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 159, 112165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Qiao, Y.; Zhao, H.; Liang, J.; Li, T.; Luo, Y.; Lu, S.; Shi, X.; Lu, W.; Sun, X. Electrochemical Non-Enzymatic Glucose Sensors: Recent Progress and Perspectives. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 14553–14569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osuna, V.; Vega-Rios, A.; Zaragoza-Contreras, E.A.; Estrada-Moreno, I.A.; Dominguez, R.B. Progress of Polyaniline Glucose Sensors for Diabetes Mellitus Management Utilizing Enzymatic and Non-Enzymatic Detection. Biosensors 2022, 12, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.H.; Shi, L.B.; Zhao, H.L.; Lan, M.B. Advanced Strategies for Improving the Analytical Performance of Pt-Based Nonenzymatic Electrochemical Glucose Sensors: A Minireview. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 1755–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschini, F.; Taurino, I. Nickel-Based Catalysts for Non-Enzymatic Electrochemical Sensing of Glucose: A Review. Phys. Med. 2022, 14, 100054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Li, L.; Zhou, W.; Shao, Z.; Chen, X. Advances in Non-Enzymatic Glucose Sensors Based on Metal Oxides. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 7333–7349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marioli, J.M.; Kuwana, T. Electrochemical Characterization of Carbohydrate Oxidation at Copper Electrodes. Electrochem. Acta 1992, 37, 1187–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, W.L.; Nicoll, W.D.; Strouse, G.C.; Waring, C.E. The Mechanism of Carbohydrate Oxidation. IX. The Action of Copper Acetate Solutions on Glucose, Fructose and Galactose. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1928, 50, 2267–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witkowska Nery, E.; Kundys, M.; Jeleń, P.S.; Jönsson-Niedziółka, M.; Nery, E.W.; Kundys, M.; Jeleń, P.S.; Jönsson-Niedziólka, M. Electrochemical Glucose Sensing: Is There Still Room for Improvement? Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 11271–11282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adeel, M.; Rahman, M.M.; Caligiuri, I.; Canzonieri, V.; Rizzolio, F.; Daniele, S. Recent Advances of Electrochemical and Optical Enzyme-Free Glucose Sensors Operating at Physiological Conditions. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 165, 112331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vassilyev, Y.B.; Khazova, O.A.; Nikolaeva, N.N. Kinetics and Mechanism of Glucose Electrooxidation on Different Electrode-Catalysts. Part I. Adsorption and Oxidation on Platinum. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1985, 196, 105–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassilyev, Y.B.; Khazova, O.A.; Nikolaeva, N.N. Kinetics and Mechanism of Glucose Electrooxidation on Different Electrode-Catalysts. Part II. Effect of the Nature of the Electrode and the Electrooxidation Mechanism. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1985, 196, 127–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorski, W.; Kennedy, R.T. Electrocatalyst for Non-Enzymatic Oxidation of Glucose in Neutral Saline Solutions. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1997, 424, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro Luna, A.M.; de Mele, M.F.L.; Arvia, A.J. The Electro-Oxidation of Glucose on Microcolumnar Gold Electrodes in Different Neutral Solutions. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1992, 323, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, T.; Del Caño, R.; Mahato, K.; De la Paz, E.; Chen, C.; Ding, S.; Yin, L.; Wang, J. Wearable Electrochemical Glucose Sensors in Diabetes Management: A Comprehensive Review. Chem. Rev. 2023, 123, 7854–7889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- North East London Pharmacy and Medicines Optimisation Team. North East London Blood Glucose Test Strips Guideline; North East London Pharmacy and Medicines Optimisation Team: London, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, V.N.; Laffel, L.M.; Wadwa, R.P.; Garg, S.K. Performance of a Factory-Calibrated Real-Time Continuos Glucose Monitoring System Utilizing an Automated Sensor Aplicator. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2018, 20, 428–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonyushkina, K.; Nichols, J.H. Glucose Meters: A Review of Technical Challenges to Obtaining Accurate Results. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2009, 3, 971–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkes, J.L.; Slatin, S.L.; Pardo, S.; Ginsberg, B.H. A New Consensus Error Grid to Evaluate the Clinical Significance of Inaccuracies in the Measurement of Blood Glucose. Diabetes Care 2000, 23, 1143–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 15197:2015; In Vitro Diagnostic Test Systems-Requirements for Blood-Glucose Monitoring Systems for Self-Testing in Managing Diabetes Mellitus. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015.
- FDA-2013-D-1445; Blood Glucose Monitoring Test Systems for Prescription Point-of-Care Use—Guidance for Industry and Food and Drug Administration Staff. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Food and Drug Administration, Center for Devices and Radiological Health: Rockville, MD, USA, 2020.
- FDA-2013-D-1446; Self-Monitoring Blood Glucose Test Systems for Over-the-Counter Use Guidance for Industry and Food and Drug Administration Staff. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Food and Drug Administration, Center for Devices and Radiological Health: Rockville, MD, USA, 2016.
- CLSI POCT12-A3; Point-of-Care Blood Glucose Testing in Acute and Chronic Care Facilities; Approved Guideline—Third Edition. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2013.
- Argyle, M.D.; Bartholomew, C.H. Heterogeneous Catalyst Deactivation and Regeneration: A Review. Catalysts 2015, 5, 145–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayed, D.; Laubender, E.; Souiri, M.; Yurchenko, O.; Marmouch, H.; Urban, G.; Othmane, A. Carbon Nanotubes Supported Ru-Au Nanoparticles with Core-Shell Structure for Glucose Detection with High Resistance against Chloride Poisoning. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2017, 164, B767–B775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mello, G.A.B.; Cheuquepán, W.; Briega-Martos, V.; Feliu, J.M. Glucose Electro-Oxidation on Pt(100) in Phosphate Buffer Solution (PH 7): A Mechanistic Study. Electrochim. Acta 2020, 354, 136765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naikoo, G.A.; Arshad, F.; Hassan, I.U.; Omar, F.B.; Tambuwala, M.M.; Mustaqeem, M.; Saleh, T.A. Trends in Bimetallic Nanomaterials and Methods for Fourth-Generation Glucose Sensors. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 162, 117042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.N.; Kim, S.I.; Yoon, J.C.; Kim, J.; Cahoon, C.; Jang, J.H. Bi-Functional 3D-NiCu-Double Hydroxide@Partially Etched 3D-NiCu Catalysts for Non-Enzymatic Glucose Detection and the Hydrogen Evolution Reaction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 33013–33023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanam, A.; Haddour, N.; Mohammadi, H.; Amine, A.; Sabac, A.; Buret, F. A Membrane-Less Glucose/O2 Non-Enzymatic Fuel Cell Based on Bimetallic Pd–Au Nanostructure Anode and Air-Breathing Cathode: Towards Micro-Power Applications at Neutral PH. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 210, 114335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ataei Kachouei, M.; Shahrokhian, S.; Ezzati, M. Bimetallic CoZn-MOFs Easily Derived from CoZn-LDHs, as a Suitable Platform in Fabrication of a Non-Enzymatic Electrochemical Sensor for Detecting Glucose in Human Fluids. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 344, 130254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pletcher, D. Electrocatalysis: Present and Future. J. Appl. Electrochem. 1984, 14, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, L.D. Premonolayer Oxidation and Its Role in Electrocatalysis. Pergamoa Electrochim. Acta 1994, 39, 1841–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernst, S.; Heitbaum, J.; Hamann, C.H. The Electrooxidation of Glucose in Phosphate Buffer Solutions Part I. Reactivity and Kinetics below 350 MV/RHE. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1979, 100, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernst, S.; Heitbaum, J.; Hamann, C.H. The Electrooxidation of Glucose in Phosphate Buffer Solutions: Kinetics and Reaction Mechanism. Phys. Chem. 1980, 84, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Laffir, F.; MxCormac, T.; Dempsey, E. PtAu/C Based Bimetallic Nanocomposites for Non-Enzymatic Electrochemical Glucose Detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 150, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.S.; Wu, Z.W.; Lee, C.L. Concave Pd Core/Island Pt Shell Nanoparticles: Synthesis and Their Promising Activities toward Neutral Glucose Oxidation. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 281, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adžic, R.R.; Hsiao, M.W.; Yeager, E.B. Electrochemical Oxidation of Glucose on Single Crystal Gold Surfaces. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1989, 260, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.N.H.; Jin, X.; Nolan, J.K.; Xu, J.; Le, K.V.H.; Lam, S.; Wang, Y.; Alam, M.A.; Lee, H. Printable Nonenzymatic Glucose Biosensors Using Carbon Nanotube-PtNP Nanocomposites Modified with AuRu for Improved Selectivity. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 6, 5315–5325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, M.W.; Adžic, R.R.; Yeager, E.B. Electrochemical Oxidation of Glucose on Single Crystal and Polycrystalline Gold Surfaces in Phosphate Buffer. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1996, 143, 759–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
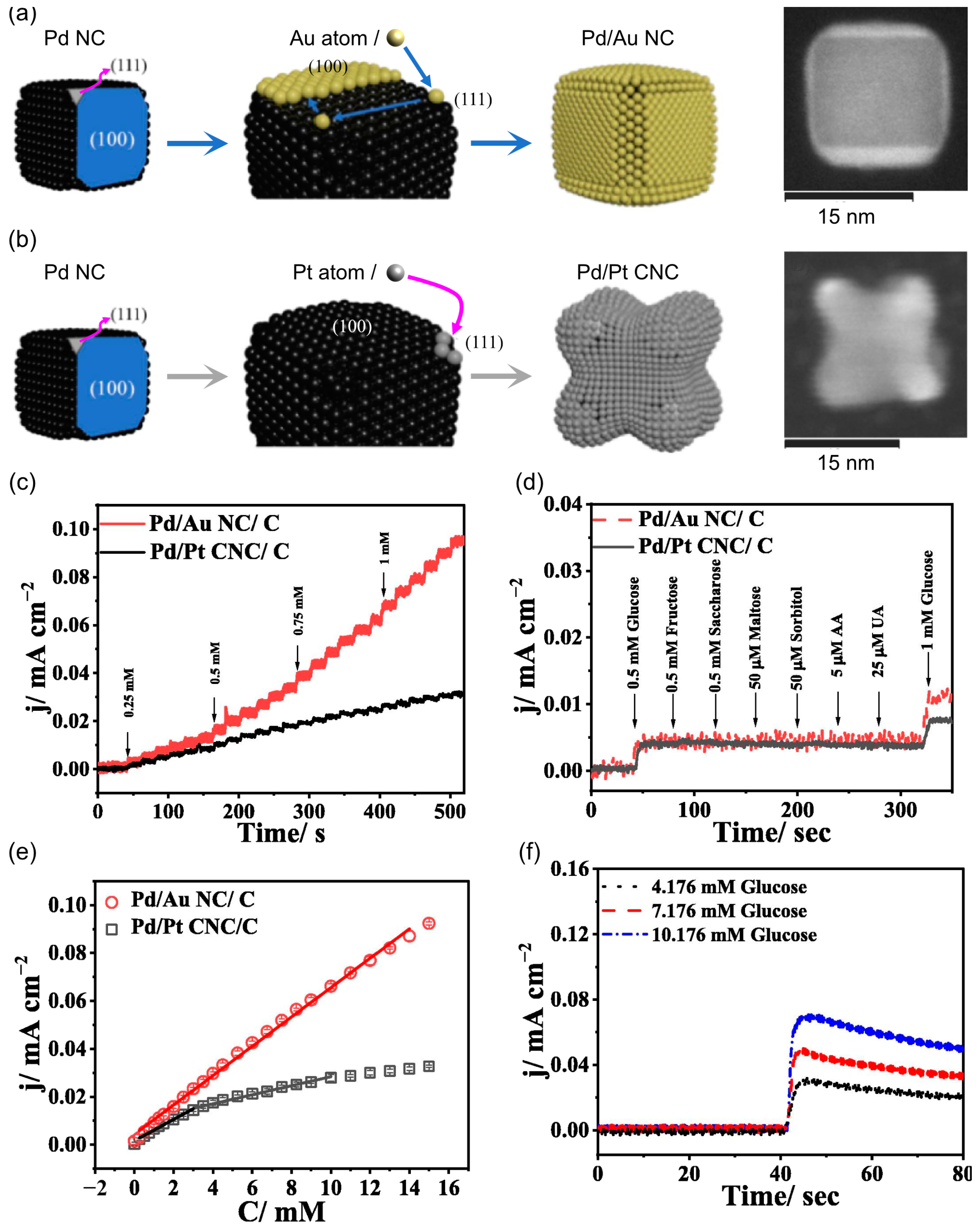
- Wang, S.S.; Wu, C.W.; Chen, P.Y.; Lee, C.L. Preferential Deposition of Gold and Platinum Atom on Palladium Nanocube as Catalysts for Oxidizing Glucose in the Phosphate-Buffered Solution. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2023, 930, 117142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karra, S.; Wooten, M.; Griffith, W.; Gorski, W. Morphology of Gold Nanoparticles and Electrocatalysis of Glucose Oxidation. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 218, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, K.C.; Wong, W.L.; Ma, D.L.; Lai, T.S.; Wong, K.Y. Transition Metal Complexes as Electrocatalysts-Development and Applications in Electro-Oxidation Reactions. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2007, 251, 2367–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, D.G. Strucuture, Properties, and Preparation of Boronic Acid Derivatives. Overview of Their Reactions and Applications. In Boronic Acids: Preparation and Applications in Organic Synthesis and Medicine, 1st ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2005; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Egawa, Y.; Seki, T.; Takahashi, S.; Anzai, J.I. Electrochemical and Optical Sugar Sensors Based on Phenylboronic Acid and Its Derivatives. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2011, 31, 1257–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anzai, J. Recent Progress in Electrochemical Biosensors Based on Phenylboronic Acid and Derivatives. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 67, 737–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Kong, L.; Zhu, J.; Tan, L. One-Pot Preparation of Conductive Composite Containing Boronic Acid Derivative for Non-Enzymatic Glucose Detection. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 498, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cambre, J.N.; Sumerlin, B.S. Biomedical Aplications of Boronic Acid Polymers. Polymer 2011, 52, 4361–4643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Ju, Y.; Chen, J.; Liu, D.; Liu, H. Nonenzymatic Wearable Sensor for Electrochemical Analysis of Perspiration Glucose. ACS Sens. 2018, 3, 1135–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berni, A.; Amine, A.; García-Guzmán, J.J.; Cubillana-Aguilera, L.; Palacios-Santander, J.M. Feather-like Gold Nanostructures Anchored onto 3D Mesoporous Laser-Scribed Graphene: A Highly Sensitive Platform for Enzymeless Glucose Electrochemical Detection in Neutral Media. Biosensors 2023, 13, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Yuan, S.; Ju, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhao, C.; Liu, H. Water Splitting-Assisted Electrocatalytic Oxidation of Glucose with a Metal-Organic Framework for Wearable Nonenzymatic Perspiration Sensing. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 10764–10771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Chinnadayyala, S.R.; Le, H.T.N.; Cho, S. Sensitive Electrochemical Non-Enzymatic Detection of Glucose Based on Wireless Data Transmission. Sensors 2022, 22, 2787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Wang, T.; Li, K.; Long, D.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, F.; Gong, W. A Flexible Nonenzymatic Sweat Glucose Sensor Based on Au Nanoflowers Coated Carbon Cloth. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 388, 133798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, S.; Yuwen, T.; Liu, Y.; Fan, J.; Zang, G. Glucose Determination Behaviour of Gold Microspheres-Electrodeposited Carbon Cloth Flexible Electrodes in Neutral Media. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1159, 338442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toi, P.T.; Trung, T.Q.; Dang, T.M.L.; Bae, C.W.; Lee, N.E. Highly Electrocatalytic, Durable, and Stretchable Nanohybrid Fiber for On-Body Sweat Glucose Detection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 10707–10717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Chung, T.D.; Kim, H.C. Nonenzymatic Glucose Detection Using Mesoporous Platinum. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 3046–3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.; Wang, K.; Xia, X. Highly Ordered Platinum-Nanotubule Arrays for Amperometric Glucose Sensing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2005, 15, 803–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.-Y.; Zhang, D.; Gao, W.; Xia, X.-H. Nonenzymatic Glucose Detection by Using a Three-Dimensionally Ordered, Macroporous Platinum Template. Chem. Eur. J. 2005, 11, 2177–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.S.; Wang, T.P.; Chen, P.Y.; Lee, C.L. Vacant Graphene Nanosheet-Supported Platinum Nanoparticles as Catalysts for Neutral Glucose Oxidation Reaction. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 578, 152060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Dempsey, E.; Dickinson, C.; Laffir, F. Inside/Outside Pt Nanoparticles Decoration of Functionalised Carbon Nanofibers (Pt19.2/f-CNF80.8) for Sensitive Non-Enzymatic Electrochemical Glucose Detection. Analyst 2012, 137, 1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
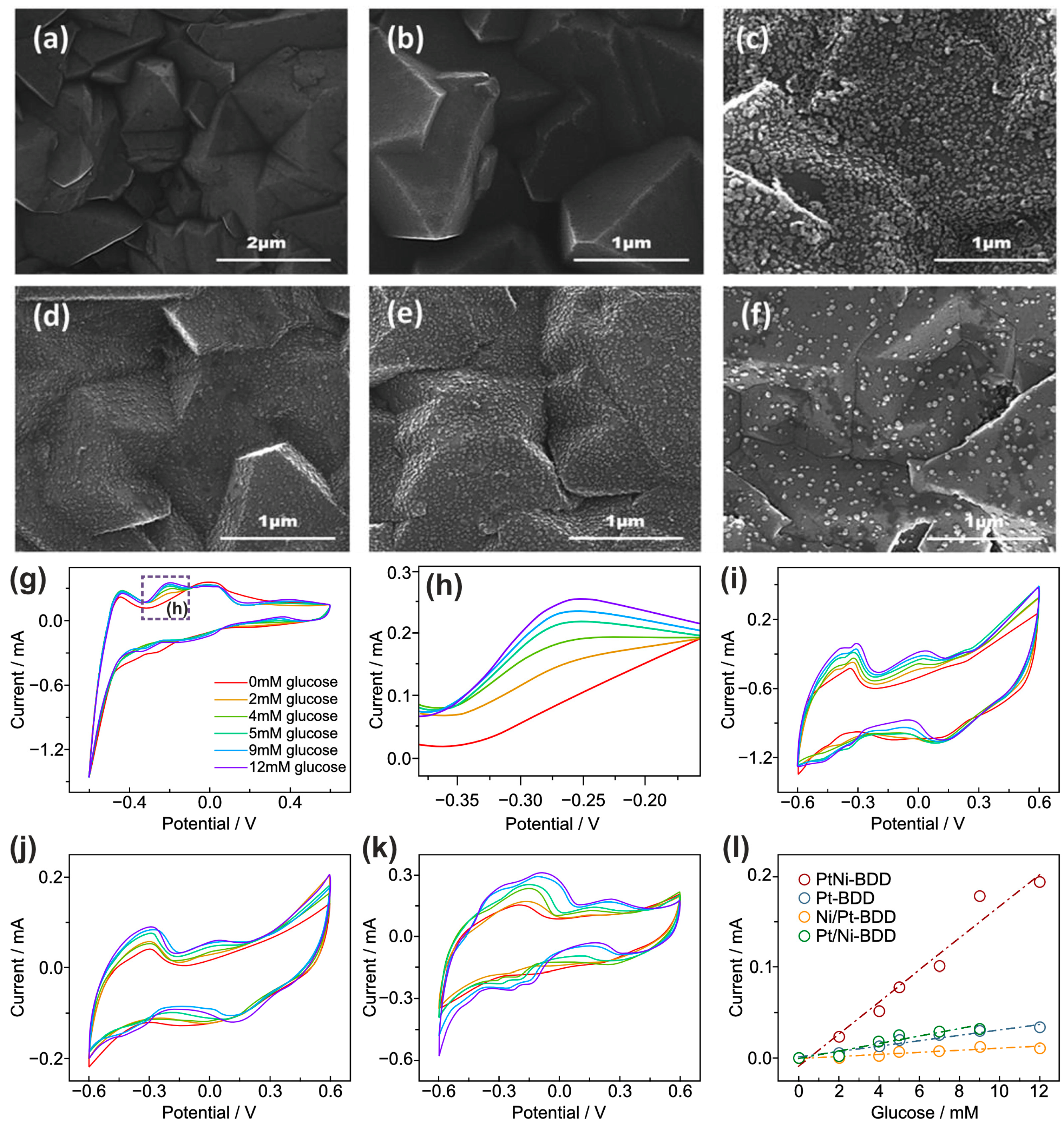
- Zhu, R.; Zhao, Z.; Cao, J.; Li, H.; Ma, L.; Zhou, K.; Yu, Z.; Wei, Q. Effect of Pt-Ni Deposition Sequence on the Bimetal-Modified Boron-Doped Diamond on Catalytic Performance for Glucose Oxidation in Neutral Media. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2022, 907, 116084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.; Lan, M.; Zhao, H.; Chen, C. Well-Dispersed Pt Cubes on Porous Cu Foam: High-Performance Catalysts for the Electrochemical Oxidation of Glucose in Neutral Media. Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 9534–9541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, B.; Hong, L.; Lu, J.; Hu, J.; Yang, Y.; Yuan, J.; Niu, L. A Novel Amperometric Glucose Sensor Based on PtIr Nanoparticles Uniformly Dispersed on Carbon Nanotubes. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 91, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, C.H.; Chen, J.C.; Tai, C.C.; Sun, I.W.; Zen, J.M. A Nonenzymatic Glucose Sensor Using Nanoporous Platinum Electrodes Prepared by Electrochemical Alloying/Dealloying in a Water-Insessitive Zinc Chloride-1-Ethyl-3-Methylimidazolium Chloride Ionic Liquid. Electroanalysis 2008, 20, 771–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.F.; Ye, J.S.; Liu, X.; Zhang, W.D.; Sheu, F.S. Pt-Pb Alloy Nanoparticle/Carbon Nanotube Nanocomposite: A Strong Electrocatalyst for Glucose Oxidation. Nanotechnology 2006, 17, 2334–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Baig, M.; Milligan, B.; Jiang, G.; Tam, K.C.; Amiri, A. Highly Dispersed Pt Supported by N-Doped Mesoporous Carbon for Ultrasensitive Non-Enzymatic. J. Bionanosci. 2017, 11, 522–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnadayyala, S.R.; Cho, S. Porous Platinum Black-Coated Minimally Invasive Microneedles for Non-Enzymatic Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Interstitial Fluid. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Liang, X.; Liu, H.; Cui, L.; Zhang, X.; Liu, C. Non-Enzymatic Electrochemical Glucose Sensor Based on Monodispersed Stone-like PtNi Alloy Nanoparticles. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Liang, X.; Cui, L.; Liu, H.; Xie, J.; Liu, W. A Novel Non-Enzymatic Glucose Sensor Based on Pt3Ru1 Alloy Nanoparticles with High Density of Surface Defects. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 80, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Niu, X.; Zhao, H.; Tang, J.; Lan, M. Enzyme-Free Amperometric Detection of Glucose on Platinum-Replaced Porous Copper Frameworks. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 165, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, G.; Shu, H.; Huang, Q.; Oyama, M.; Ji, K.; Liu, X.; He, Y. Synthesis of Highly Dispersed Pt Nanoclusters Anchored Graphene Composites and Their Application for Non-Enzymatic Glucose Sensing. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 157, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Dempsey, E.; Laffir, F. Carbon Nanochips and Nanotubes Decorated PtAuPd-Based Nanocomposites for GlucoseSensing: Role of Support Material and Efficient Pt Utilization. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 205, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badhulika, S.; Paul, R.K.; Rajesh; Terse, T.; Mulchandani, A. Nonenzymatic Glucose Sensor Based on Platinum Nanoflowers Decorated Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes-Graphene Hybrid Electrode. Electroanalysis 2014, 26, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Wu, G.; Cai, Z.; Zhao, T.; Yao, Q.; Chen, X. Ultrasensitive Non-Enzymatic Glucose Sensing at near-Neutral PH Values via Anodic Stripping Voltammetry Using a Glassy Carbon Electrode Modified with Pt3Pd Nanoparticles and Reduced Graphene Oxide. Microchim. Acta 2015, 182, 2055–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, X.; Yin, Y.; Wu, P.; Cai, C. Nonenzymatic Electrochemical Detection of Glucose Based on Pd1Pt3–Graphene Nanomaterials. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2013, 690, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathod, D.; Dickinson, C.; Egan, D.; Dempsey, E. Platinum Nanoparticle Decoration of Carbon Materials with Applications in Non-Enzymatic Glucose Sensing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 143, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.; Huang, X. Effects of Pt Decoration on the Electrocatalytic Activity of Nanoporous Gold Electrode toward Glucose and Its Potential Application for Constructing a Nonenzymatic Glucose Sensor. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2010, 643, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Zhao, F.; Mei, D.; Mo, Z.; Zeng, B. Nonenzymatic Glucose Sensor Based on Ultrasonic-Electrodeposition of Bimetallic PtM (M = Ru, Pd and Au) Nanoparticles on Carbon Nanotubes-Ionic Liquid Composite Film. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 24, 3481–3486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Thomas, D.F.; Chen, A. Nonenzymatic Electrochemical Glucose Sensor Based on Nanoporous PtPb Networks. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 997–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasta, M.; La Mantia, F.; Cui, Y. Mechanism of Glucose Electrochemical Oxidation on Gold Surface. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 5561–5568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocón, P.; Alonso, C.; Celdrán, R.; González-Velasco, J. Study of the Electrooxidation of N-Propanol on an Au Electrode in Basic Medium. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1986, 206, 179–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Huang, W.; Zheng, J.; Niu, Z.; Li, Z. Nonenzymatic Amperometric Response of Glucose on a Nanoporous Gold Film Electrode Fabricated by a Rapid and Simple Electrochemical Method. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 3555–3561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, H.; Cao, L.; Chang, G.; He, H.; Zhang, Y.; He, Y. Direct Electrodeposition of Gold Nanostructures onto Glassy Carbon Electrodes for Non-Enzymatic Detection of Glucose. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 132, 524–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, N.S.; Le, Q.H.; Yoshikawa, H.; Saito, M.; Tamiya, E. Development of Non-Enzymatic Electrochemical Glucose Sensor Based on Graphene Oxide Nanoribbon—Gold Nanoparticle Hybrid. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 146, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branagan, D.; Breslin, C.B. Electrochemical Detection of Glucose at Physiological PH Using Gold Nanoparticles Deposited on Carbon Nanotubes. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 282, 490–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prehn, R.; Cortina-Puig, M.; Muñoz, F.X. A Non-Enzymatic Glucose Sensor Based on the Use of Gold Micropillar Array Electrodes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2012, 159, F134–F139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, T.; Dong, J.; Xu, J. Direct Electrodeposition of Highly Ordered Gold Nanotube Arrays for Use in Non-Enzymatic Amperometric Sensing of Glucose. Microchim. Acta 2016, 183, 1925–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolaev, K.G.; Ermakov, S.S.; Offenhäusser, A.; Mourzina, Y. Nonenzymatic Determination of Glucose on Electrodes Prepared by Directed Electrochemical Nanowire Assembly (DENA). J. Anal. Chem. 2017, 72, 371–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajeev, R.; Datta, R.; Varghese, A.; Sudhakar, Y.N.; George, L. Recent Advances in Bimetallic Based Nanostructures: Synthesis and Electrochemical Sensing Applications. Microchem. J. 2021, 163, 105910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.; Kumar, A.; Sharma, S.; Naushad, M.; Prakash Dwivedi, R.; ALOthman, Z.A.; Mola, G.T. Novel Development of Nanoparticles to Bimetallic Nanoparticles and Their Composites: A Review. J. King Saud. Univ. Sci. 2019, 31, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lei, Y. Pt-Au Nanocorals, Pt Nanofibers and Au Microparticles Prepared by Electrospinning and Calcination for Nonenzymatic Glucose Sensing in Neutral and Alkaline Environment. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 171–172, 954–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, P.; Huang, Y.; Wang, T.; Ma, J. Nanomaterials for Electrochemical Non-Enzymatic Glucose Biosensors. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 3487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, K.; Lee, W.C.; Park, M.S.; Shahabuddin, M.; Yamauchi, Y.; Hossain, M.S.A.; Shim, Y.B.; Kim, J.H. Au Decorated Core-Shell Structured Au@Pt for the Glucose Oxidation Reaction. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 278, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.; Kang, C. Nonenzymatic Glucose Detection with Good Selectivity against Ascorbic Acid on a Highly Porous Gold Electrode Subjected to Amalgamation Treatment. Electroanalysis 2007, 19, 2315–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomanin, P.P.; Cherepanov, P.V.; Besford, Q.A.; Christofferson, A.J.; Amodio, A.; McConville, C.F.; Yarovsky, I.; Caruso, F.; Cavalieri, F. Cobalt Phosphate Nanostructures for Non-Enzymatic Glucose Sensing at Physiological PH. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 42786–42795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batool, R.; Akhtar, M.A.; Hayat, A.; Han, D.; Niu, L.; Ahmad, M.A.; Nawaz, M.H. A Nanocomposite Prepared from Magnetite Nanoparticles, Polyaniline and Carboxy-Modified Graphene Oxide for Non-Enzymatic Sensing of Glucose. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, L.; Jin, J.; Yang, G.; Lu, T.; Zhang, H.; Cai, C. Nonenzymatic Electrochemical Detection of Glucose Based on Palladium−Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube Hybrid Nanostructures. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 7271–7280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zang, G.; Hao, W.; Li, X.; Huang, S.; Gan, J.; Luo, Z.; Zhang, Y. Copper Nanowires-MOFs-Graphene Oxide Hybrid Nanocomposite Targeting Glucose Electro-Oxidation in Neutral Medium. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 277, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, J.S.; Anjalidevi, C.; Dharuman, V. Nonenzymatic Glucose Sensing at Ruthenium Dioxide-Poly(Vinyl Chloride)-Nafion Composite Electrode. J. Solid. State Electrochem. 2013, 17, 937–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, L.; Wang, M.; Wang, C.; Hu, X.; Wang, G. Self-Made Non-Enzymatic Silver Electrode from Recordable CDs for Fast Detection of Glucose in Blood. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 177, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barman, K.; Jasimuddin, S. Non-Enzymatic Electrochemical Sensing of Glucose and Hydrogen Peroxide Using a Bis(Acetylacetonato)Oxovanadium(iv) Complex Modified Gold Electrode. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 20800–20806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodnight, L.; Butler, D.; Xia, T.; Ebrahimi, A. Non-Enzymatic Detection of Glucose in Neutral Solution Using PBS-Treated Electrodeposited Copper-Nickel Electrodes. Biosensors 2021, 11, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatema, K.N.; Zhu, L.; Cho, K.Y.; Jung, C.H.; Ullah, K.; Oh, W.C. Non-Enzymatic Sensing of Glucose with High Specificity and Sensitivity Based on High Surface Area Mesoporous BiZnSbV-G-SiO2. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2021, 32, 8330–8346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalil Oglou, R.; Ulusoy Ghobadi, T.G.; Ozbay, E.; Karadas, F. Electrodeposited Cobalt Hexacyanoferrate Electrode as a Non-Enzymatic Glucose Sensor under Neutral Conditions. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1188, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashemi, S.A.; Mousavi, S.M.; Bahrani, S.; Omidifar, N.; Arjmand, M.; Ramakrishna, S.; Hagfeldt, A.; Lankarani, K.B.; Chiang, W.H. Decorated Graphene Oxide Flakes with Integrated Complex of 8-Hydroxyquinoline/NiO toward Accurate Detection of Glucose at Physiological Conditions. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2021, 893, 115303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajisa, T.; Hosoyamada, S. Mesoporous Silica-Based Metal Oxide Electrode for a Nonenzymatic Glucose Sensor at a Physiological PH. Langmuir 2021, 37, 13559–13566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, P.; Zong, N.; Li, F. A Sensitive Non-Enzyme Sensing Platform for Glucose Based on Boronic Acid-Diol Binding. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 161, 832–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthuchamy, N.; Gopalan, A.; Lee, K.P. Highly Selective Non-Enzymatic Electrochemical Sensor Based on a Titanium Dioxide Nanowire-Poly(3-Aminophenyl Boronic Acid)-Gold Nanoparticle Ternary Nanocomposite. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 2138–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uner-Bahar, D.; Isildak, A.I. Determination of Glucose Using Flow Injection Analysis and Borate Selective Electrode. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2020, 15, 12724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, C.; Jha, S.S.; Kumar, R.; Chhabra, M.; Malhotra, B.D.; Dixit, A. Exfoliated Graphite Carbon Paper-Based Flexible Nonenzymatic Glucose Sensor. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2022, 285, 115931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalil Oglou, R.; Ulusoy Ghobadi, T.G.; Ozbay, E.; Karadas, F. Selective Glucose Sensing under Physiological PH with Flexible and Binder-Free Prussian Blue Coated Carbon Cloth Electrodes. Chem. Electr. Chem. 2022, 9, 1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

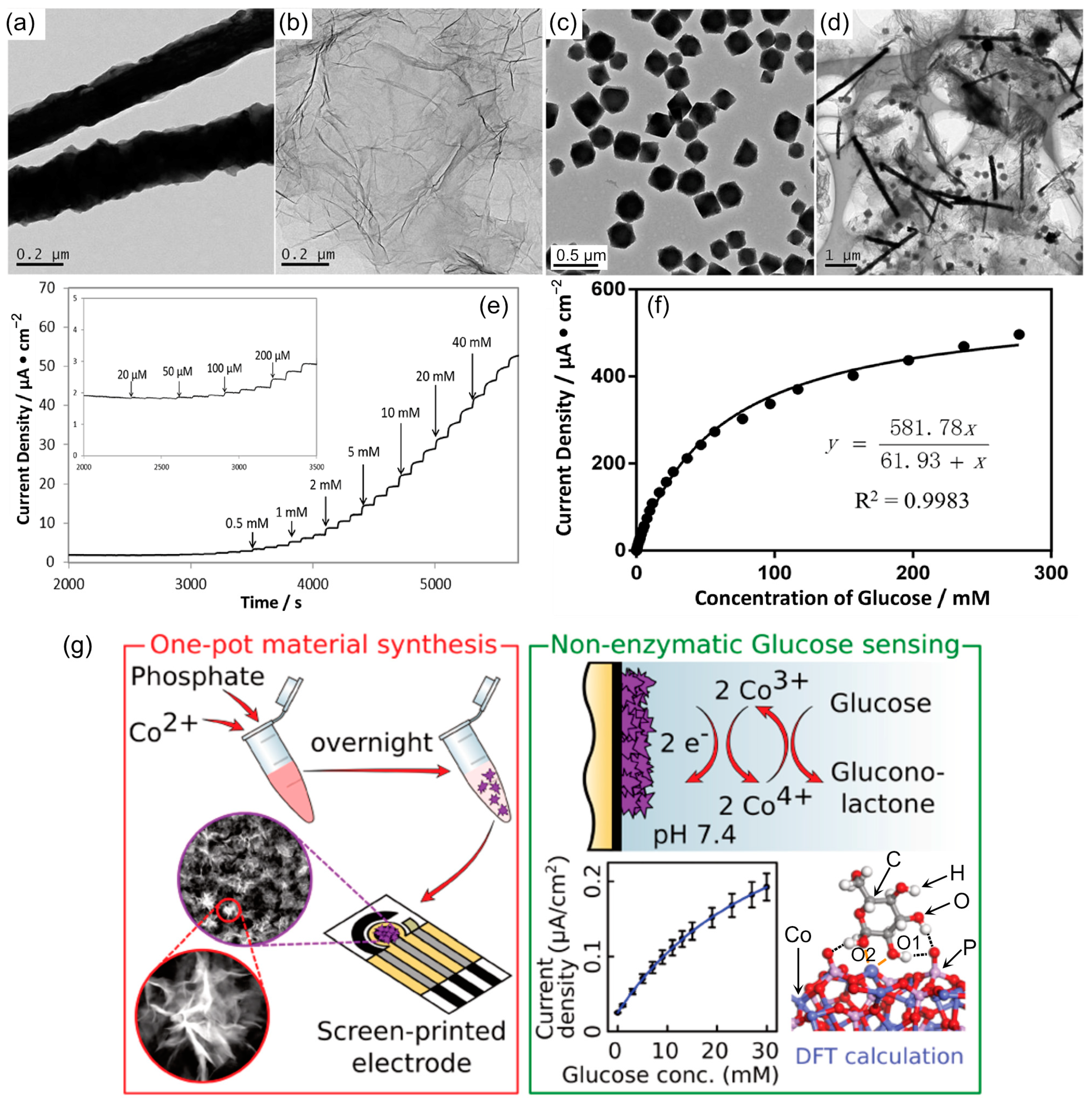

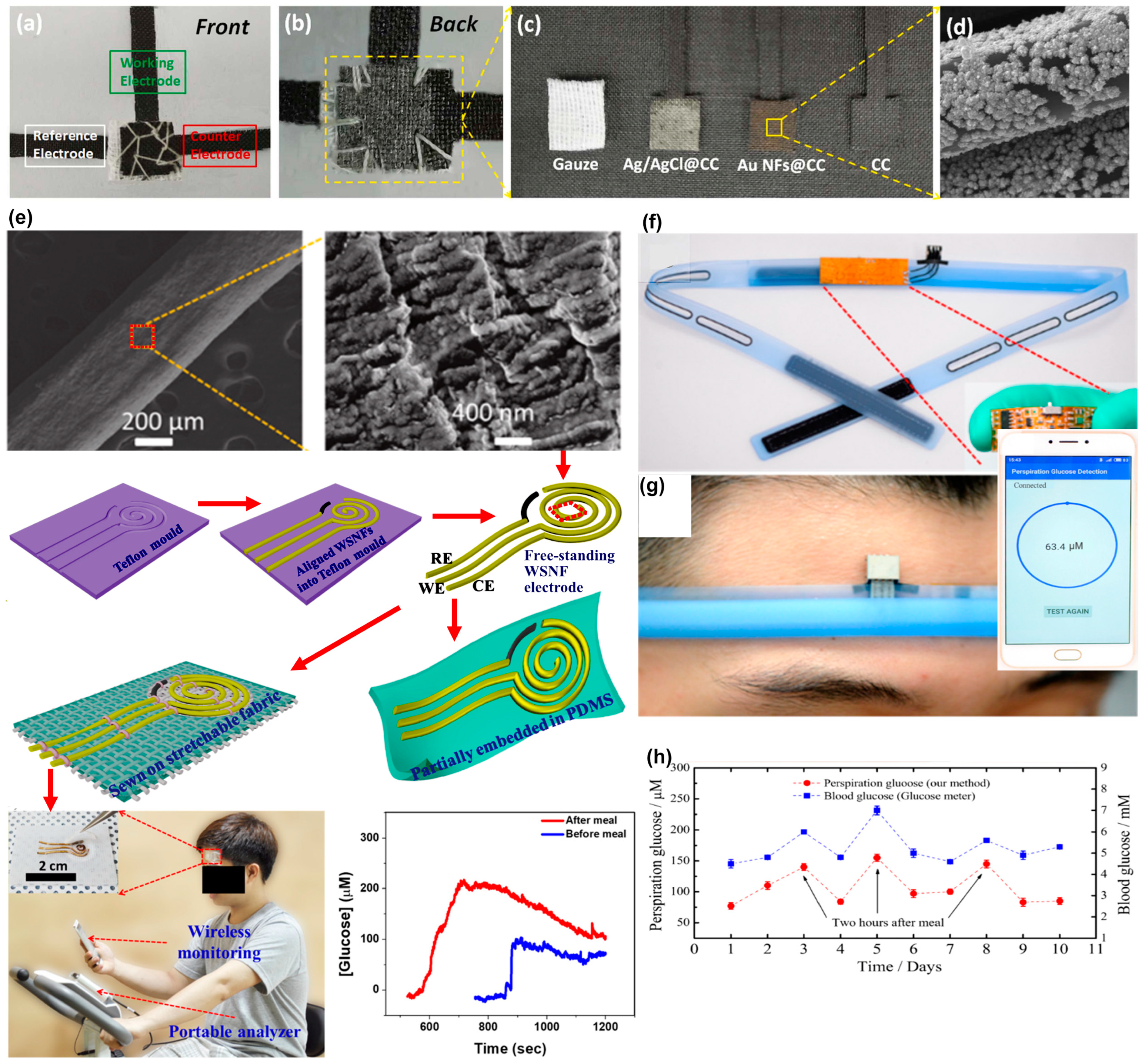
| Format | Detection | Analyzed Sample | Sample [µL] | Linear Range [mM] | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BGMT | Invasive | Capillary blood | 0.3 to 0.7 | 1.1–33.3 | [24] |
| CGM | Minimally invasive | Interstitial fluid | -- | 2.2–22.2 | [25] |
| Device | Sample | Concentration [mg/dL] | Standard | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Point of Care test | Venous whole blood | 5 intervals between 30 and 400 | FDA-2013-D-1445 (2020) | [29] |
| Over the counter, Blood glucose monitoring test systems | Venous whole blood | 5 intervals between 30 and 400 | FDA-2013-D-1446 (2016) | [30] |
| Blood glucose monitoring test systems | Venous whole blood | 5 intervals between 30 and 400 | ISO 15197 (2015) | [28] |
| Point of Care test | CLSI POCT12-A3 (2013) | [31] |
| Interference | Recommended Test Concentration (mg/dL) | Interference | Recommended Test Concentration (mg/dL) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acetaminophen (AC) | 20 | Ibuprofen (IBU) | 50 |
| Ascorbic acid (AA) | 6 | L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (L-Dopa) | 0.75 |
| Conjugated Bilirubin (CB) | 50 | Maltose (Mlt) | 480 |
| Unconjugated Bilirubin (UB) | 40 | Mannitol (Man) | 1800 |
| Cholesterol (CH) | 500 | Methyldopa (Mdp) | 2 |
| Creatinine (CR) | 15 | Salicylic acid (SA) | 60 |
| Dopamine (DA) | 0.09 | Sodium (Na) | 180 (mmol/L) |
| Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) * | 0.1 | Tolbutamide (TA) | 72 |
| Galactose (Gal) | 60 | Tolazamide (Tol) | 9 |
| Gentisic acid (GA) | 1.8 | Triglycerides (TG) | 1500 |
| Reduced glutathione (GSH) | 4.6 | Uric acid (UA) | 23.5 |
| Hemoglobin (Hb) | 1000 | Xylose (Xyl) | 600 |
| Heparin * (Hep) | 300 (IU/dL) | Sugar Alcohols (sorbitol, xylitol, lactitol, isomalt, maltitol) | 0.09 |
| Strategy | Ref. |
|---|---|
| Electrochemical pretreatment with high anodic or cathodic potential | [56,57] |
| Water-splitting electrocatalytic reaction | [58,59] |
| Chemical pretreatment of Au in an alkaline solution | [60] |
| Chemical pretreatment of carbon in an acidic solution | [61] |
| Surface functionalization | [62] |
| Electrode | Material | Electrolyte | pH | Technique | E [V] | LR (mM) | S μM mM−1 cm−2 | LOD [μM] | Interference | Real Sample | Stability [Days] | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Au | Pt/dGN600 | PB 0.1 M | 7.4 | AMP | 0.05 1 | 0.5–9 | 27.28 | 0.06 | Fru, Suc, Mlt, Sor, AA, UA | Human serum | [66] | |
| Pt/dGN400 | 0.5–9.5 | 23.14 | 0.08 | - | - | 25 cycles | ||||||
| Pt/dGN200 | 1.5–9 | 8.06 | 0.07 | - | - | |||||||
| Pt/dGNech | 1.5–8.5 | 6.21 | 0.12 | - | - | |||||||
| GCE | Pt5Ni1 | PBS [1 × 10−5] + NaCl 0.9% | 7.4 | AMP | +0.1 2 | 0.5–40 | 40.17 | 0.35 | AA, UA, Fru | Human serum | 30 | [75] |
| GCE | Pd@Pt CINPs | PBS [0.1 M] | AMP | −0.1 1 | 1–8.5 | 15.14 | 0.82 | Fru, Suc, Mlt, Sor | Human serum | 25 cycles | [44] | |
| GCE | PtNPs/pDA-NCNR | PBS 1X [10 mM] | CAMP | +0.28 3 | 0.01–2 | 7.65 | 0.01 | AA, UA | - | [73] | ||
| PBS 1X [10 mM] | +0.28 3 | 2–30 | 81.24 | 0.01 | ||||||||
| GCE | Pt3Ru1 | PBS [0.01 M] | 7.4 | AMP | +0.05 2 | 0–4 | 31.3 | 0.3 | UA, AA, Fru | 30 | [76] | |
| SPCE | Pt-replaced Cu foams | PBS [0.1 M] | 7.4 | AMP | +0.4 1 | 1–11 | 9.62 | 385 | AA, UA, Fru, AP | -- | [77] | |
| GCE | PtNCs/graphene (PVP) | PBS [0.1 M] | 7.4 | AMP | 0.05 4 | 1–25 | 1.21 | 30 | AA, UA, AP | 20 | [78] | |
| GCE | PtAuPd/f-CaNC | PBS [0.01 M] | 7.4 | AMP | 0.43 | 0–10 | 11.24 | 2.9 | - | - | - | [79] |
| GCE | PtNFs/MWCNTs/graphene | PBS [0.1 M] | 7.4 | AMP | +0.4 1 | 1–7 | 11.06 | 387 | AA, UA | - | [80] | |
| GCD | Pt2Ir1/MWCNT | PBS [0.2 M] | 7.4 | AMP | 0.1 4 | 0.1–1 | 206 | 0.5 | AA, UA, AP, CR, CH | - | [70] | |
| GCD | Pt3Pt1/graphene | PBS [0.05 M] + NaCl [0.1 M] | 7.4 | AMP | −0.45 2 | (30 μM–3 mM) | (1.52 μM mM−1) | --- | AA, UA, AP | >14 | [81] | |
| GCD | Pd1Pt3/graphene | PBS [0.1 M] | 7.4 | AMP | +0.1 2 | 1–23 | --- | 5 | AA, UA, DOPAC | - | [82] | |
| SPCE | Pt/Cu | PBS [0.1 M] + KCl [0.15 M] | 7.4 | CAMP | 0.5 1 | 7.7 | AA, UA, DA, AP | [69] | ||||
| CAMP | 0 1 | 5.9 | - | |||||||||
| CAMP | −0.4 1 | 6.7 | ||||||||||
| GCE | Pt/Au/C | PBS [0.01 M] | 7.4 | AMP | 0.3 3 | 0–10 | 47 | 20 | UA, AA, AC, DA, Xyl, Mlt, Gal, Fru | - | [43] | |
| GCE | Pt-MWCNT | PBS [0.1 M] | AMP | 0.55 3 | 2–20 | 1.10 | AA, UA, Fru, Suc, Xyl, Gal | [83] | ||||
| Pt-AC | 1.07 | 20 cycles | ||||||||||
| Pt-CNF | 0.52 | |||||||||||
| Gold disk | Nanoporous Au-Pt (24%) | PBS [0.1 M] | 7.4 | AMP | +0.35 2 | 0.5–10 | 145.7 | 0.6 | AA, UA, AP | 30 | [84] | |
| GCE | PtRu(1:1)-MWNT-IL/GCE | PBS | 7.4 | AMP | −0.1 2 | 15 | 10.6 | 0.05 | AA, UA, Fru, AP | >50 | [85] | |
| Pt wire (1 cm, r = 0.1 cm) | PtZn alloy | PBS [0.1 M] | 7.4 | 0.4 1 | 0–10 | 291 | AA, AP | - | [71] | |||
| Ti plates | PtPb Networks | PBS [0.1 M] + NaCl [0.15 M] | 7.4 | AMP | 0.4 4 | 0–16 | 10.8 | AA, UA, AP | - | [86] | ||
| Au (111) | Pt-NTAEs (ca. 40 nm thickness and length ca. 3 μm) | PBS [0.05 M] + KCl (0.1 M) | 7.4 | AMP | 0.4 2 | 2–14 | 0.1 | 1.0 | AA, UA, AP | - | [64] | |
| Pt rod | Pt mesoporous electrodeposition | PBS 0.1 M + NaCl 0.15 M | 7.4 | AMP | 0.4 3 | 0–10 | 9.6 | AA, AP | - | [63] |
| Electrode | Material | Electrolyte | pH | Technique | E [V] | LR (mM) | S μM mM−1 cm−2 | LOD [μM] | Interferents | Real Sample | Stability [Days] | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Au | Au amalgamation | PB [0.1 M] | 7.0 | AMP | 0.25 4 | 0–10 | 32 | 2 | UA, AP, AA | [101] | ||
| Au | NPGF | PBS [0.1 M] | 7.4 | AMP | 0.2 2 | 0.001–11 | 66 | 8.7 | AA, UA | 20 cycles | [89] | |
| Au | AuNPs/GONR/CS | PBS [0.1 M] | 7.4 | AMP | 0.2 4 | 0.0005–10 | 57.1 | 0.5 | UA, AP, AA | [91] | ||
| Au | DGN | PBS [0.1 M] | 7.4 | AMP | 0.15 3 | 0.1–25 | 190.7 | 50 | UA, AP, AA | [90] | ||
| Au | Au Nanowire | PBS [0.1 M] | 7.2 | AMP | 0.35 1 | 0.0004–0.005 | 0.00037 | 33 | -- | [95] | ||
| Au | AuNTAs/Au NWAs | PBS [0.1 M] | 7.2 | AMP | 0.25 2 | 0.005–16.4 | 44.2 | 2.1 | AA, DA, UA, Fru, Suc | [94] | ||
| GCE | Irregular AuNPs | PBS [0.1 M] | 7.4 | AMP | 0.3 4 | 0.2–110 | 66 | 100 | - | - | - | [49] |
| Au | AuNPs/MWCNTs | PBS [0.1 M] | 7.4 | AMP | 0.2 3 | 0.1–25 | 2.77 | 4.1 | AA, Gal, Fru, UA | 14 | [92] | |
| Au | Pt-Au nanocoral | PB | 7 | AMP | 0.4 1 | 22 | 2.1 | 28 | AA, UA | [98] | ||
| Au | Au@Pt NPs Au@PtNPs | PBS | 7.4 | AMP | +0.35 3 | 0.0005–0.01, 0.01–10.0 | 445.7 | AA, AP, UA, DA | Blood | [100] | ||
| Au | Pd/AuNC | PBS [0.1 M] | 7.4 | AMP | 0.25 2 | 0.25–14 | 13.56 | Fru, Suc, Mlt, Sor, UA, AA | Serum | [48] | ||
| Au | AuRu/CNT -PtNP | PBS [0.01 M] | 7.4 | AMP | 0.2 3 | 1–10 | 0.2347 | 68 | UA, AP, AA | 21 | [46] |
| Electrode | Material | Electrolyte | pH | Technique | E [V] | LR [mM] | S μM mM−1 cm−2 | LOD [μM] | Interferences | Real Sample | Stability [Days] | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GCE | Pd/SWCNT | 0.1 M PBS/ 0.15 M NaCl | 7.4 | AMP | −0.35 2 | 0.5–17 | 160 | 0.2 | AA, UA, AP, DOPAC | Human blood (diluted) | 30 | [104] |
| Pt | RuO2/PVC/ Nafion | 0.01 M PBS/ 10 mM NaCl/ 2.7 mM KCl | 7.4 | AMP | 0.45 3 | 0.1–107, 0.1–61.8 | -- | -- | AA, DA, UA, Cat, Fru, Suc, Man, Lac, Gal | serum | -- | [106] |
| -- | Ag from CD | 0.1 M PBS | 6.5 | AMP | −0.5 3 | 0.5–13 | -- | 35 | UA, AA | Human blood | 120 | [107] |
| Au/PATP | [VO(acac)2] | 0.1 M PBS | 7.0 | AMP | 0.65 1 | 0.001–0.5 | -- | 0.1 | AA, UA, L-dopa, L-cys, Na+, K+, Cl | blood | 20 | [108] |
| GCE | CuNWs/MOF/GO/Nafion | 0.1 M PBS | 7.4 | AMP | 0.3 1 | 0.02–26.6 | 7.72 | 7 | Lac, Fru, Suc, Mlt, Xyl, and satisfactory anti-interference performance to AP, AA, UA | serum | 30 | [105] |
| SPCE | Co3(PO4)2 CPN | 0.01 M PBS | 7.4 | AMP | 0.65 3 | 1–30 | 7.90 nA/mM | 300 | Lac, Gal, AA, DA | serum | -- | [102] |
| SPCE | Functionalized GO/Fe3O4)/PANI | PBS | 7.0 | CV | -- | 5 × 10−5–5 | -- | 0.01 | CH, UA, AA, DA, Fru, Mlt, Suc, CGN | serum | 16 days | [103] |
| -- | PBS pretreated Ni-Cu NPs | 0.1 M Na2SO4 | 6.4 | CV | 0.2 3 | 5 × 10−6–20 | 5.47 | 4.2 × 10−3 | AA, UA | artificial saliva | 7 days | [109] |
| Ni foam | BiZnSbV-G- SiO2 (BZSVGS) | 0.1 M PBS | 7.4 | CV | 0.2 3 | 6 × 10−5–0.001 | -- | 0.06 | Lac, Gal, AA, Starch, Fru, NaCl, KCl, and Urea | urine | -- | [110] |
| FTO | CoFe Prussian Blue composite | 0.1 M PBS/ 0.1 M KCl | 7.4 | AMP | 1.15 1 | 0.1–8.2 mM | 18.69 | 67 | Suc, Fru, AA, UA | -- | -- | [111] |
| GCE | GO-NiO-8H-NHS | PBS | 7.4 | AMP | 0.55 3 | 2 × 10−3–0.08/0.08–5 | 712.5 | 0.041 | Urea, AA, Mlt, Lac, Suc, Fru | plasma | 30 days | [112] |
| Electrode | Material | Electrolyte | pH | Technique | E [V] | LR [mM] | S μM mM−1 cm−2 | LOD [μM] | Interferences | Real Sample | Stability [Days] | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Au | Au-PB/ pDA/AuNPs/ MPBA | 0.1 M KNO3 | 7.0 | DPV | −0.1–0.4 1 | 1 × 10−4–1.35 × 10−2 | -- | 0.05 | Fru, Gal, Man, UA, AA, Pro, Ala, MA | serum | 30 | [114] |
| GCE | PAA-AuNPs/MPBA | 0.1 M PBS | 6.5 | CV | −0.1–0.5 1 | 1 × 10−5–0.01 | -- | 4 × 10−3 | DA, AA, UA | serum | 30 | [54] |
| GCE | TiO2NW/ PAPBA/ AuNPs | 0.1 M PBS | 7.0 | DPV | 0–0.7 2 | 0.5–11 | 66.8 | 9.3 | AA, UA, DA, Fru, Lac, Suc, Man, | serum | -- | [115] |
| -- | CNT--SB | PBS | 7.4 | POT | 0.1–100 | -- | 100 | -- | -- | -- | [116] | |
| Ta2O5 | PBA-MPSi | PBS | 7.4 | POT | 0–20 | -- | -- | -- | serum | -- | [113] |
| Electrode | Material | Type | Electrolyte | pH | Technique | E [V] | LR [mM] | S μM mM−1 cm−2 | LOD [μM] | Interference | Real Sample | Stability [Days] | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| -- | Au/Nafion | wristband | 0.1 M PBS | 5.0 | MPS | 0.2 1 | 0.3–1.1 | 114 µA/mM/cm2 | 15 | AA, UA, LA, Glu | human sweat | -- | [56] |
| SPCE | Pd NPs encapsulated in a Co-ZIF- 67 | sweatband | 0.1 M PBS | 7.4 | PAD | 0.6 2 | 0.01–1 | -- | 2.0 | AA, UA, LA, Glu, AP | human sweat | 60 (closed) | [58] |
| -- | rGO-PU/Au nanowrinkles | patch | 0.1 M PBS | 7.4 | CV | 0.2 3 | 0.001–1 | 140 µA/mM/cm2 | 0.5 | AA, UA, LA, NaCl | human sweat | -- | [62] |
| CC | cotton-like Au microspheres | flexible electrode | 0.1 M PBS/ 0.1 M NaCl | 7.4 | AMP | 0.3 4 | 0.001–0.114 0.114–21.6 | 25.39/20.609 µA/mM/cm2 | 0.78 | Urea, AcOH, LA, Xyl, Mlt, Suc, Fru, NaCl | human sweat, human blood | 35 | [61] |
| MNEA | Au/ porous Pt black/ Nafion | patch | 10X PBS | 7.4 | AMP | 0.12 3 | 1–30 | 1.792 µA/mM/cm2 | 7.2 | AA, LA, Gal, Man, AP, Fru, NaCl, UA, Urea | ISF | 16 | [74] |
| CC | PB/ CoFe-NO NPs | flexible electrode | 0.1 M PBS/ 0.5 M KCl | 7.0 | AMP | 1.15 5 | 0.1–6.5 | 145.43 µA/mM/cm2 | 28 | Suc, Lac, NaCl, AA, UA | -- | 15 | [118] |
| MNEA | Au/porous Pt black/ Nafion | patch | 10X PBS | 7.4 | AMP | 0.12 6 | 1–10/ 15–30 | 445.75/165.83 µA/mM/cm2 | 268 | AA, UA, LA, Urea, AP, DA, Man, Fru, Gal, NaCl | ISF | 16 | [59] |
| ExGCP | -- | flexible electrode | 0.01 M PBS | -- | CV | −0.8 to 0.8 3 | 2–8 | 5.93 μA/mMcm−2 | 812 | -- | -- | 7 | [117] |
| carbon cloth | Au NF | patch | PBS | 7.4 | AMP | 0.35 2 | 0.008–4 | 63.9 μA/mMcm−2 | 5.18 | LA, Urea, AA, NaCl, UA | human sweat | -- | [60] |
| LIG | Au dendrite/ Nafion | flexible electrode | 0.1 M PBS | 7.4 | AMP | 0.2 2 | 0.5–20 | 1.06 μA/mM | 210 | AA, UA, AP, Suc, Lac, Fru | human serum | 20 | [57] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Osuna, V.; Aparicio Martínez, E.P.; Dominguez, R.B.; Vega Rios, A. A Review on the Advances in Nanomaterials for Electrochemical Non-Enzymatic Glucose Sensors Working in Physiological Conditions. Chemosensors 2024, 12, 159. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12080159
Osuna V, Aparicio Martínez EP, Dominguez RB, Vega Rios A. A Review on the Advances in Nanomaterials for Electrochemical Non-Enzymatic Glucose Sensors Working in Physiological Conditions. Chemosensors. 2024; 12(8):159. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12080159
Chicago/Turabian StyleOsuna, Velia, Eider Pedro Aparicio Martínez, Rocio B. Dominguez, and Alejandro Vega Rios. 2024. "A Review on the Advances in Nanomaterials for Electrochemical Non-Enzymatic Glucose Sensors Working in Physiological Conditions" Chemosensors 12, no. 8: 159. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12080159
APA StyleOsuna, V., Aparicio Martínez, E. P., Dominguez, R. B., & Vega Rios, A. (2024). A Review on the Advances in Nanomaterials for Electrochemical Non-Enzymatic Glucose Sensors Working in Physiological Conditions. Chemosensors, 12(8), 159. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12080159






