Simple Development of Novel Reversible Colorimetric Thermometer Using Urea Organogel Embedded with Thermochromic Hydrazone Chromophore
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Details
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Apparatus and Methods
2.3. Synthetic Methods
2.3.1. Synthesis of Tricyanofuran (TCF)
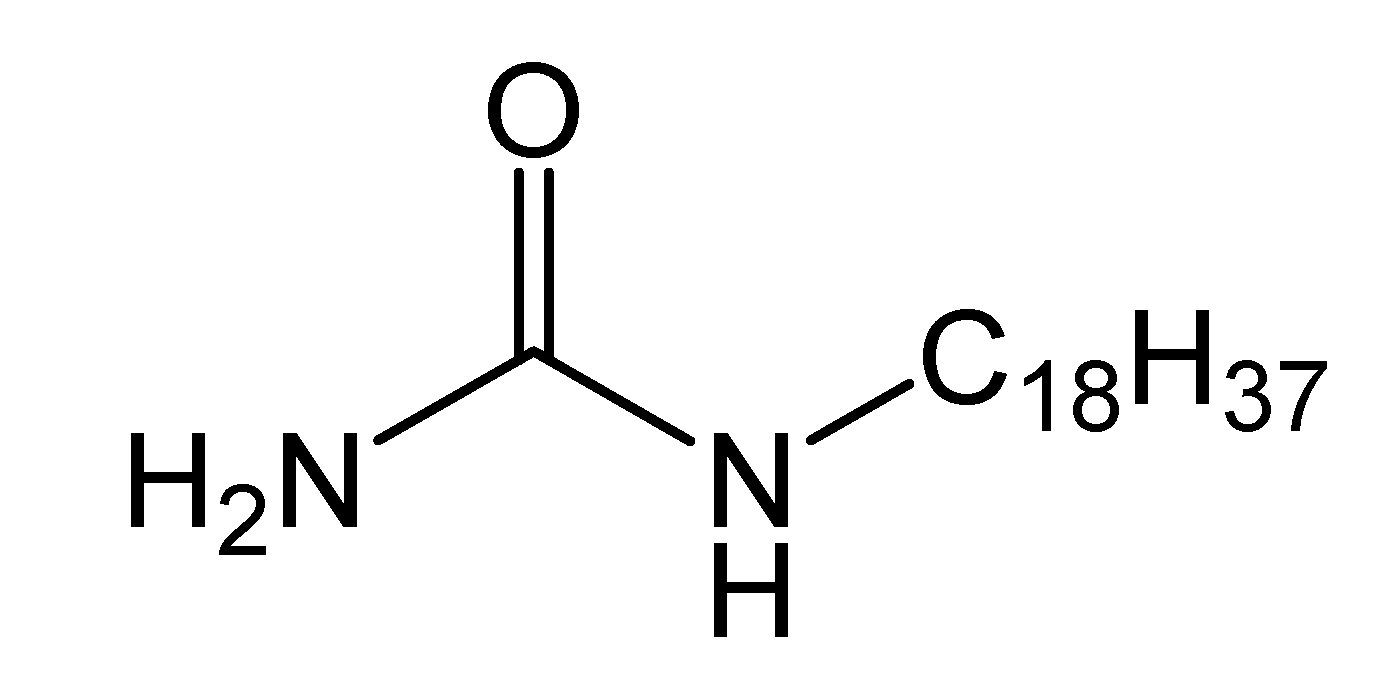
2.3.2. Synthesis of N-n-Octadecylurea
2.3.3. Synthesis of Tricyanofuran Hydrazone Probe (TCFH)
2.4. Preparation and Gelation Procedure of UTCFH
2.5. Thermochromic Measurements
2.6. Reversibility Testing
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization
3.2. Thermal Stability of Tricyanofuran Hydrazone Dye
3.3. Preparation of UTCFH Thermometer
3.4. Thermochromic Activity
3.5. Morphological Properties
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, G.; Guo, Z.; Zeng, G.; Tang, L. Fluorescent and colorimetric sensors for environmental mercury detection. Analyst 2015, 140, 5400–5443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunnlaugsson, T.; Glynn, M.; Tocci, G.M.; Kruger, P.E.; Pfeffer, F.M. Anion recognition and sensing in organic and aqueous media using luminescent and colorimetric sensors. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2006, 250, 3094–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustamante, S.E.; Vallejos, S.; Pascual-Portal, B.S.; Muñoz, A.; Mendia, A.; Rivas, B.L.; García, F.C.; García, J.M. Polymer films containing chemically anchored diazonium salts with long-term stability as colorimetric sensors. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 365, 725–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khattab, T.A.; Kassem, N.F.; Adel, A.M.; Kamel, S. Optical recognition of ammonia and amine vapor using “turn-on” fluorescent chitosan nanoparticles imprinted on cellulose strips. J. Fluoresc. 2019, 29, 693–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khattab, T.A.; Aly, S.A.; Klapötke, T.M. Naked-eye facile colorimetric detection of alkylphenols using Fe (III)-impregnated silica-based strips. Chem. Pap. 2018, 72, 1553–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VS, A.P.; Joseph, P.; SCG, K.D.; Lakshmanan, S.; Kinoshita, T.; Muthusamy, S. Colorimetric sensors for rapid detection of various analytes. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 78, 1231–1245. [Google Scholar]
- Saini, A.; Christenson, C.W.; Khattab, T.A.; Wang, R.; Twieg, R.J.; Singer, K.D. Threshold response using modulated continuous wave illumination for multilayer 3D optical data storage. J. Appl. Phys. 2017, 121, 43101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khattab, T.A.; Fouda, M.M.G.; Allam, A.A.; Othman, S.I.; Bin-Jumah, M.; Al-Harbi, H.M.; Rehan, M. Selective Colorimetric Detection of Fe (III) Using Metallochromic Tannin-Impregnated Silica Strips. ChemistrySelect 2018, 3, 12065–12071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahman, M.S.; Fouda, M.M.G.; Ajarem, J.S.; Maodaa, S.N.; Allam, A.A.; Khattab, T.A. Development of colorimetric cotton swab using molecular switching hydrazone probe in calcium alginate. J. Mol. Struct. 2020, 1216, 128301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.N.; Ren, W.X.; Kim, J.S.; Yoon, J. Fluorescent and colorimetric sensors for detection of lead, cadmium, and mercury ions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 3210–3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, H.; Khattab, T.A.; Mashaly, H.M.; El-Halwagy, A.A.; Rehan, M. Plasma activation toward multi-stimuli responsive cotton fabric via in situ development of polyaniline derivatives and silver nanoparticles. Cellulose 2020, 27, 2913–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.; Chae, S.K.; Kim, J.-M. Colorimetric sensors for volatile organic compounds (VOCs) based on conjugated polymer-embedded electrospun fibers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 3038–3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, H.; Xue, X.; Wang, H.; Xue, Z. Gold nanorod etching-based multicolorimetric sensors: Strategies and applications. J. Mater. Chem. C 2019, 7, 4610–4621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Xu, Y.; Ferhan, A.R.; Chen, G.; Kim, D.-H. Oriented gold nanoparticle aggregation for colorimetric sensors with surprisingly high analytical figures of merit. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 12338–12345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, X.; Aprahamian, I. Hydrazone-based switches, metallo-assemblies and sensors. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 1963–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ryabchun, A.; Li, Q.; Lancia, F.; Aprahamian, I.; Katsonis, N. Shape-persistent actuators from hydrazone photoswitches. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 1196–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kamel, S.; A Khattab, T. Recent Advances in Cellulose-Based Biosensors for Medical Diagnosis. Biosensors 2020, 10, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahman, M.S.; Khattab, T.A.; Aldalbahi, A.; Hatshan, M.R.; El-Naggar, M.E. Facile development of microporous cellulose acetate xerogel immobilized with hydrazone probe for real time vapochromic detection of toxic ammonia. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 104573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Font-Sanchis, E.; Galian, R.E.; Céspedes-Guirao, F.J.; Sastre-Santos, Á.; Domingo, L.R.; Fernández-Lázaro, F.; Pérez-Prieto, J. Alkoxy-styryl DCDHF fluorophores. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2010, 12, 7768–7771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kim, H.; Choi, Y.; Kim, Y. A ratiometric fluorescent probe based on a BODIPY–DCDHF conjugate for the detection of hypochlorous acid in living cells. Analyst 2013, 138, 3368–3371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khattab, T.A.; Dacrory, S.; Abou-Yousef, H.; Kamel, S. Smart microfibrillated cellulose as swab sponge-like aerogel for real-time colorimetric naked-eye sweat monitoring. Talanta 2019, 205, 120166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khattab, T.A. Novel solvatochromic and halochromic sulfahydrazone molecular switch. J. Mol. Struct. 2018, 1169, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khattab, T.A. From chromic switchable hydrazones to smart materials. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 254, 123456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khattab, T.A.; Fouda, M.M.G.; Rehan, M.; Okla, M.K.; Alamri, S.A.; Alaraidh, I.A.; Al-Ghamdi, A.A.; Soufan, W.H.; Abdelsalam, E.M.; Allam, A.A. Novel halochromic cellulose nanowhiskers from rice straw: Visual detection of urea. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 231, 115740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montaser, A.S.; Rehan, M.; El-Naggar, M.E. pH-Thermosensitive hydrogel based on polyvinyl alcohol/sodium alginate/N-isopropyl acrylamide composite for treating re-infected wounds. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 124, 1016–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, A.M.; El-Naggar, M.E.; Malhat, F.M.; El Sharkawi, H.M. Efficient removal of pesticides and heavy metals from wastewater and the antimicrobial activity of f-MWCNTs/PVA nanocomposite film. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 206, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshaarawy, R.F.M.; Seif, G.A.; El-Naggar, M.E.; Mostafa, T.B.; El-Sawi, E.A. In-situ and ex-situ synthesis of poly-(imidazolium vanillyl)-grafted chitosan/silver nanobiocomposites for safe antibacterial finishing of cotton fabrics. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 116, 210–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sponchioni, M.; Palmiero, U.C.; Moscatelli, D. Thermo-responsive polymers: Applications of smart materials in drug delivery and tissue engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 102, 589–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Hsu, P.-C.; Lopez, J.; Li, Y.; To, J.W.F.; Liu, N.; Wang, C.; Andrews, S.C.; Liu, J.; Cui, Y. Fast and reversible thermoresponsive polymer switching materials for safer batteries. Nat. Energy 2016, 1, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aroua, S.; Tiu, E.G.V.; Ishikawa, T.; Yamakoshi, Y. Well-Defined Amphiphilic C60-PEG Conjugates: Water-Soluble and Thermoresponsive Materials. Helv. Chim. Acta 2016, 99, 805–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelgawad, A.M.; El-Naggar, M.E.; Hudson, S.M.; Rojas, O.J. Fabrication and characterization of bactericidal thiol-chitosan and chitosan iodoacetamide nanofibres. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 94, 96–105. [Google Scholar]
- El-Newehy, M.H.; El-Naggar, M.E.; Alotaiby, S.; El-Hamshary, H.; Moydeen, M.; Al-Deyab, S. Preparation of Biocompatible System Based on Electrospun CMC/PVA Nanofibres as Controlled Release Carrier of Diclofenac Sodium. J. Macromol. Sci. Part A Pure Appl. Chem. 2016, 53, 566–573. [Google Scholar]
- El-Newehy, M.H.; El-Naggar, M.E.; Alotaiby, S.; El-Hamshary, H.; Moydeen, M.; Al-Deyab, S. Green Electrospining of Hydroxypropyl Cellulose Nanofibres for Drug Delivery Applications. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2018, 18, 805–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Naggar, M.E.; Abdelgawad, A.M.; Salas, C.; Rojas, O.J. Curdlan in fibers as carriers of tetracycline hydrochloride: Controlled release and antibacterial activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radwan, E.K.; Kafafy, H.; El-Wakeel, S.T.; Shaheen, T.I.; Gad-Allah, T.A.; El-Kalliny, A.S.; El-Naggar, M.E. Remediation of Cd(II) and reactive red 195 dye in wastewater by nanosized gels of grafted carboxymethyl cellulose. Cellulose 2018, 25, 6645–6660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Naggar, M.E.; Radwan, E.K.; El-Wakeel, S.T.; Kafafy, H.; Gad-Allah, T.A.; El-Kalliny, A.S.; Shaheen, T.I. Synthesis, characterization and adsorption properties of microcrystalline cellulose based nanogel for dyes and heavy metals removal. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 113, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khattab, T.A. Synthesis and Self-assembly of Novel s-Tetrazine-based Gelator. Helv. Chim. Acta 2018, 101, e1800009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-M.; Lin, Q.; Wei, T.-B.; Qin, X.-P.; Li, Y. A novel smart organogel which could allow a two channel anion response by proton controlled reversible sol–gel transition and color changes. Chem. Commun. 2009, 6074–6076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, S.; Das, A.K.; Banerjee, A. Smart oligopeptide gels: In situ formation and stabilization of gold and silver nanoparticles within supramolecular organogel networks. Chem. Commun. 2006, 2816–2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Jiang, X.-M.; Liu, L.; Chen, J.-F.; Zhang, Y.-M.; Yao, H.; Wei, T.-B. A novel supramolecular organogel based on acylhydrazone functionalized pillar [5] arene acts as an I− responsive smart material. Soft Matter 2017, 13, 7222–7226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.; Li, X.; Hu, J.; Huang, S.; Yu, H. Supramolecular liquid-crystalline polymer organogel: Fabrication, multiresponsiveness, and holographic switching properties. Chem. Mater. 2019, 31, 3388–3394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, P.; Yao, B.; Wang, P.; Gong, P.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, R. Strong fluorescent smart organogel as a dual sensing material for volatile acid and organic amine vapors. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 17508–17515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Liang, H.; Sun, P.; Gao, Y.; Zheng, L. A tri-responsive and fast self-healing organogel with stretchability based on multiple dynamic covalent bonds. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 1609–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Ju, J.; Yang, S.; Wang, J.; Jiang, L. Temperature-Driven Switching of Water Adhesion on Organogel Surface. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 1895–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, G.; Shan, X.; Chen, W.; Lv, Z.; Xiong, P.; Sun, T. Solvent-driven chiral-interaction reversion for organogel formation. Angew. Chemie Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 2124–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, M.; Tan, G.; John, V.T.; Weiss, R.G. Urea and Thiourea Derivatives as Low Molecular-Mass Organogelators. Chem. Eur. J. 2005, 11, 3243–3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, J.G. Reactions of Long-chain Amines. II. Reactions with Urea1. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1954, 76, 3977–3978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khattab, T.A.; Tiu, B.D.B.; Adas, S.; Bunge, S.D.; Advincula, R.C. pH triggered smart organogel from DCDHF-Hydrazone molecular switch. Dye. Pigment. 2016, 130, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khattab, T.A.; Tiu, B.D.B.; Adas, S.; Bunge, S.D.; Advincula, R.C. Solvatochromic, thermochromic and pH-sensory DCDHF-hydrazone molecular switch: Response to alkaline analytes. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 102296–102305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Ayyagari, M.; Tata, M.; John, V.T.; McPherson, G.L. Formation of novel organogels by the addition of phenols to AOT micelles in isooctane. J. Phys. Chem. 1993, 97, 11350–11353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tata, M.; John, V.T.; Waguespack, Y.Y.; McPherson, G.L. Intercalation in Novel Organogels with a" Stacked" Phenol Microstructure. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1994, 116, 9464–9470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khattab, T.A.; El-Naggar, M.E.; Abdelrahman, M.S.; Aldalbahi, A.; Hatshan, M.R. Simple Development of Novel Reversible Colorimetric Thermometer Using Urea Organogel Embedded with Thermochromic Hydrazone Chromophore. Chemosensors 2020, 8, 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors8040132
Khattab TA, El-Naggar ME, Abdelrahman MS, Aldalbahi A, Hatshan MR. Simple Development of Novel Reversible Colorimetric Thermometer Using Urea Organogel Embedded with Thermochromic Hydrazone Chromophore. Chemosensors. 2020; 8(4):132. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors8040132
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhattab, Tawfik A., Mehrez E. El-Naggar, Meram S. Abdelrahman, Ali Aldalbahi, and Mohammad Rafe Hatshan. 2020. "Simple Development of Novel Reversible Colorimetric Thermometer Using Urea Organogel Embedded with Thermochromic Hydrazone Chromophore" Chemosensors 8, no. 4: 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors8040132
APA StyleKhattab, T. A., El-Naggar, M. E., Abdelrahman, M. S., Aldalbahi, A., & Hatshan, M. R. (2020). Simple Development of Novel Reversible Colorimetric Thermometer Using Urea Organogel Embedded with Thermochromic Hydrazone Chromophore. Chemosensors, 8(4), 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors8040132




