Targeting Systemic Sclerosis from Pathogenic Mechanisms to Clinical Manifestations: Why IL-6?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
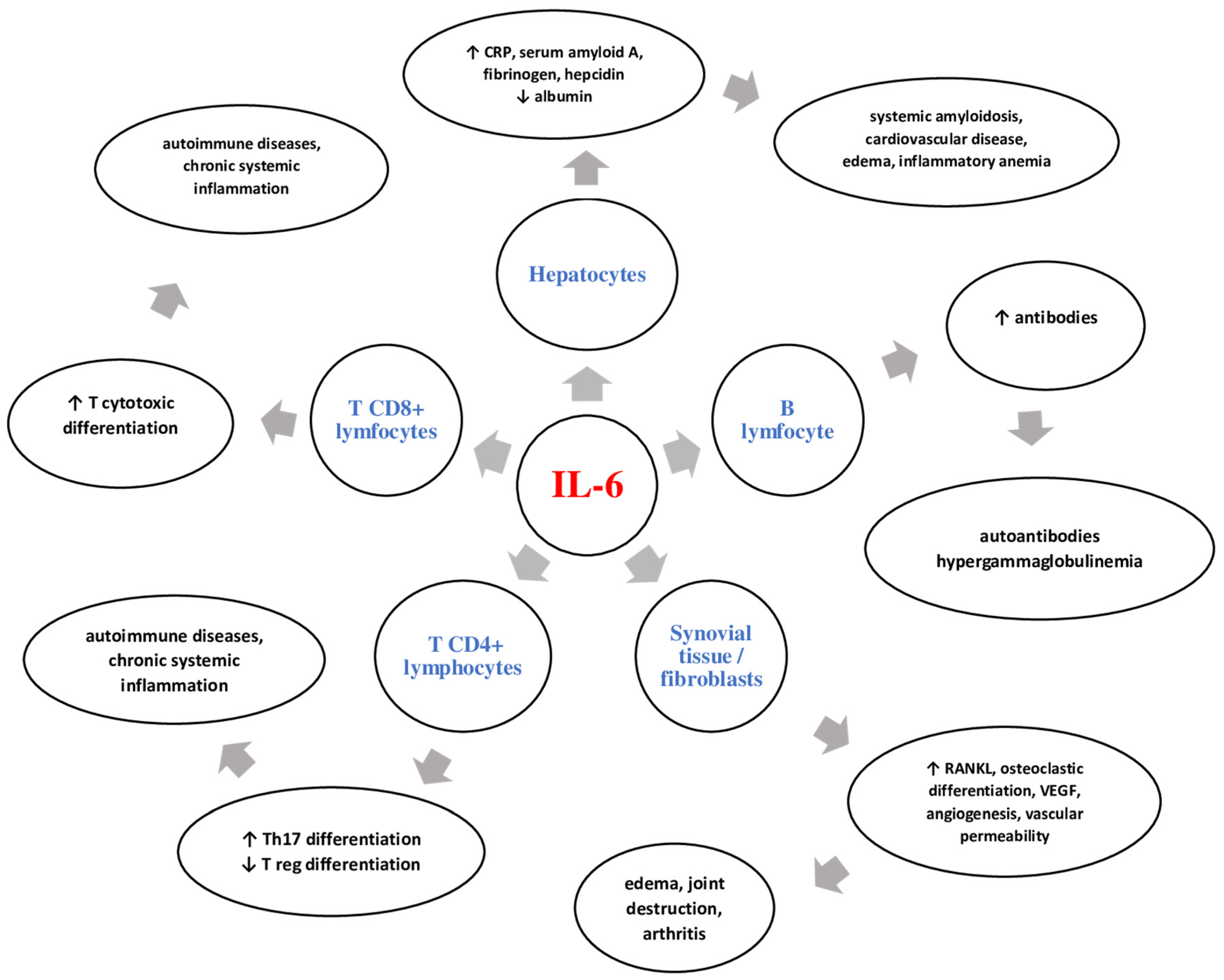
2. IL-6: General Data
3. IL-6 in Systemic Sclerosis
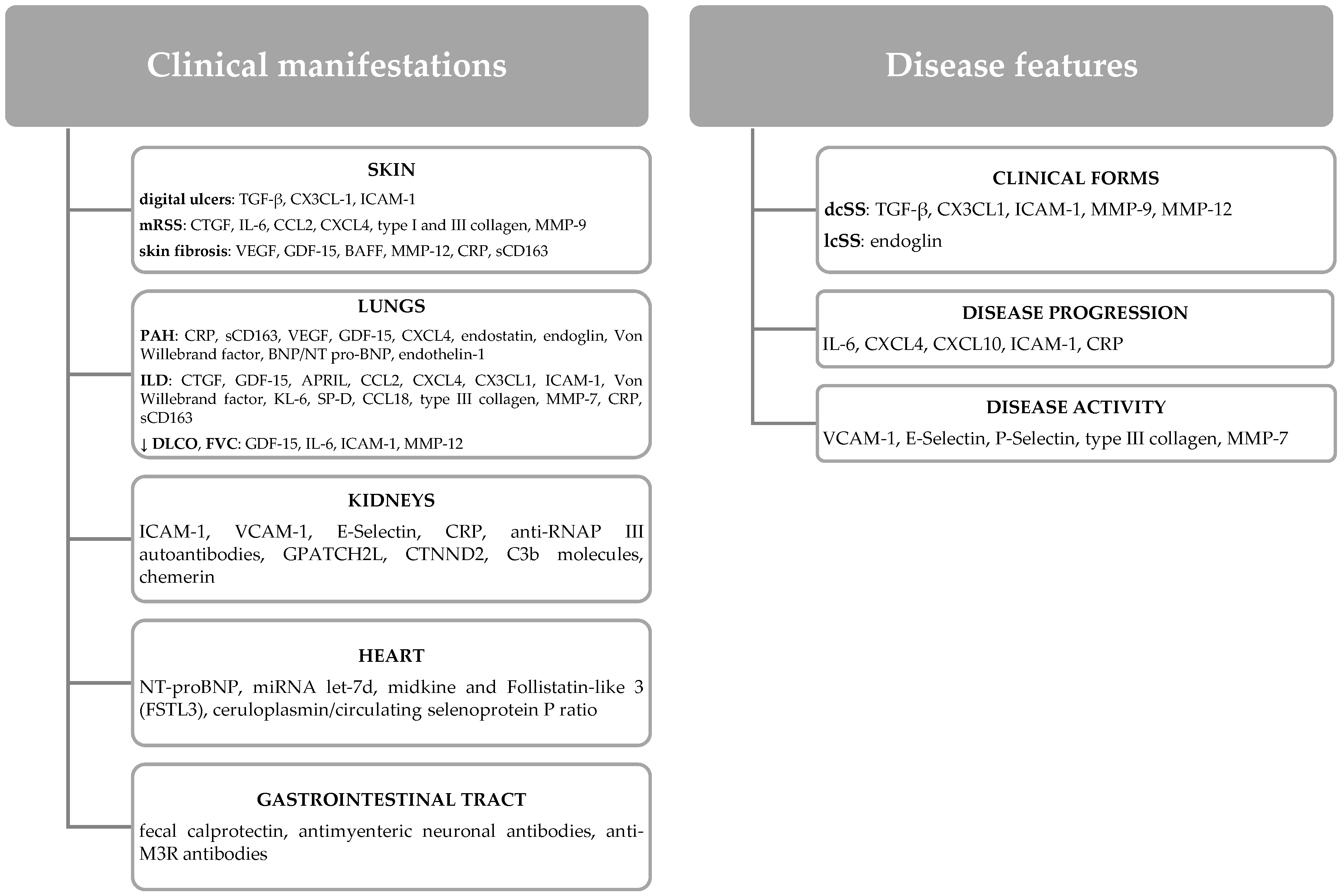
3.1. IL-6 and SS Features
3.2. IL-6 and Skin Manifestations
3.3. IL-6 and Lung Manifestations
3.4. IL-6 and Cardiovascular Manifestations
3.5. IL-6 and Gastrointestinal Manifestations
3.6. IL-6 and Kidney Manifestations
4. Targeting IL-6 in Systemic Sclerosis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Allanore, Y.; Simms, R.; Distler, O.; Trojanowska, M.; Pope, J.; Denton, C.P.; Varga, J. Systemic sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2015, 1, 15002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denton, C.P.; Khanna, D. Systemic sclerosis. Lancet 2017, 390, 1685–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.; O’Reilly, S. The immunopathogenesis of fibrosis in systemic sclerosis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2019, 195, 310–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Asano, Y.; Sato, S. Vasculopathy in scleroderma. Semin. Immunopathol. 2015, 37, 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brembilla, N.C.; Chizzolini, C. T cell abnormalities in systemic sclerosis with a focus on Th17 cells. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 2012, 23, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cossu, M.; van Bon, L.; Nierkens, S.; Bellocchi, C.; Santaniello, A.; Dolstra, H.; Beretta, L.; Radstake, T.R. The magnitude of cytokine production by stimulated CD56+ cells is associated with early stages of systemic sclerosis. Clin. Immunol. 2016, 173, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Utsunomiya, A.; Oyama, N.; Hasegawa, M. Potential Biomarkers in Systemic Sclerosis: A Literature Review and Update. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishimoto, T. Factors Affecting B-Cell Growth and Differentiation. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1985, 3, 133–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishimoto, T. The biology of interleukin-6. Blood 1989, 74, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hunter, C.A.; Jones, S.A. IL-6 as a keystone cytokine in health and disease. Nat. Immunol. 2015, 16, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalaris, A.; Garbers, C.; Rabe, B.; Rose-John, S.; Scheller, J. The soluble Interleukin 6 receptor: Generation and role in inflammation and cancer. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2011, 90, 484–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihara, M.; Hashizume, M.; Yoshida, H.; Suzuki, M.; Shiina, M. IL-6/IL-6 receptor system and its role in physiological and pathological conditions. Clin. Sci. 2012, 122, 143–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saito, M.; Yoshida, K.; Hibi, M.; Taga, T.; Kishimoto, T. Molecular cloning of a murine IL-6 receptor-associated signal trans-ducer, gp130, and its regulated expression in vivo. J. Immunol. 1992, 148, 4066–4071. [Google Scholar]
- Demyanets, S.; Huber, K.; Wojta, J. Vascular effects of glycoprotein130 ligands—Part II: Biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2012, 57, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klouche, M.; Bhakdi, S.; Hemmes, M.; Rose-John, S. Novel path to activation of vascular smooth muscle cells: Up-regulation of gp130 creates an autocrine activation loop by IL-6 and its soluble receptor. J. Immunol. 1999, 163, 4583–4589. [Google Scholar]
- Ernst, M.; Jenkins, B.J. Acquiring signalling specificity from the cytokine receptor gp130. Trends Genet. 2004, 20, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schöbitz, B.; Pezeshki, G.; Pohl, T.; Hemmann, U.; Heinrich, P.C.; Holsboer, F.; Reul, J.M. Soluble interleukin-6 (IL-6) receptor augments central effects of IL-6 in vivo. FASEB J. 1995, 9, 659–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbers, C.; Aparicio-Siegmund, S.; Rose-John, S. The IL-6/gp130/STAT3 signaling axis: Recent advances towards specific inhibition. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2015, 34, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacroix, M.; Rousseau, F.; Guilhot, F.; Malinge, P.; Magistrelli, G.; Herren, S.; Jones, S.A.; Jones, G.W.; Scheller, J.; Lissilaa, R.; et al. Novel Insights into Interleukin 6 (IL-6) Cis- and Trans-signaling Pathways by Differentially Manipulating the Assembly of the IL-6 Signaling Complex. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 26943–26953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garbers, C.; Jänner, N.; Chalaris, A.; Moss, M.L.; Floss, D.M.; Meyer, D.; Koch-Nolte, F.; Rose-John, S.; Scheller, J. Species specificity of ADAM10 and ADAM17 proteins in interleukin-6 (IL-6) trans-signaling and novel role of ADAM10 in inducible IL-6 receptor shedding. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 14804–14811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schumacher, N.; Meyer, D.; Mauermann, A.; Von Der Heyde, J.; Wolf, J.; Schwarz, J.; Knittler, K.; Murphy, G.; Michalek, M.; Garbers, C.; et al. Shedding of Endogenous Interleukin-6 Receptor (IL-6R) Is Governed by A Disintegrin and Metalloproteinase (ADAM) Proteases while a Full-length IL-6R Isoform Localizes to Circulating Microvesicles. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 26059–26071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peters, M.; Jacobs, S.; Ehlers, M.; Vollmer, P.; Müllberg, J.; Wolf, E.; Brem, G.; Büschenfelde, K.H.M.Z.; Rose-John, S. The function of the soluble interleukin 6 (IL-6) receptor in vivo: Sensitization of human soluble IL-6 receptor transgenic mice towards IL-6 and prolongation of the plasma half-life of IL-6. J. Exp. Med. 1996, 183, 1399–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marin, V.; Montero-Julian, F.A.; Grès, S.; Boulay, V.; Bongrand, P.; Farnarier, C.; Kaplanski, G. The IL-6-Soluble IL-6Rα Autocrine Loop of Endothelial Activation as an Intermediate Between Acute and Chronic Inflammation: An Experimental Model Involving Thrombin. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 3435–3442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Croker, B.A.; Krebs, D.L.; Zhang, J.-G.; Wormald, S.; Willson, T.A.; Stanley, E.G.; Robb, L.; Greenhalgh, C.J.; Förster, I.; Clausen, B.E.; et al. SOCS3 negatively regulates IL-6 signaling in vivo. Nat. Immunol. 2003, 4, 540–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babon, J.J.; Varghese, L.N.; Nicola, N.A. Inhibition of IL-6 family cytokines by SOCS3. Semin. Immunol. 2014, 26, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmitz, J.; Weissenbach, M.; Haan, S.; Heinrich, P.C.; Schaper, F. SOCS3 Exerts Its Inhibitory Function on Interleukin-6 Signal Transduction through the SHP2 Recruitment Site of gp130. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 12848–12856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Badgwell, D.B.; Bevers, J.J., III; Schlessinger, K.; Murray, P.J.; Levy, D.E.; Watowich, S.S. IL-6 signaling via the STAT3/SOCS3 pathway: Functional Analysis of the Conserved STAT3 N-domain. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2006, 288, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Narazaki, M.; Yasukawa, K.; Saito, T.; Ohsugi, Y.; Fukui, H.; Koishihara, Y.; Yancopoulos, G.D.; Taga, T.; Kishimoto, T. Soluble forms of the interleukin-6 signal-transducing receptor component gp130 in human serum possessing a potential to inhibit signals through membrane-anchored gp130. Blood 1993, 82, 1120–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yasukawa, K.; Futatsugi, K.; Saito, T.; Yawata, H.; Narazaki, M.; Suzuki, H.; Taga, T.; Kishimoto, T. Association of recombinant soluble IL-6-signal transducer, gp130, with a complex of IL 6 and soluble IL-6 receptor, and establishment of an ELISA for soluble gp130. Immunol. Lett. 1992, 31, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, J.; Waetzig, G.H.; Chalaris, A.; Reinheimer, T.M.; Wege, H.; Rose-John, S.; Garbers, C. Different Soluble Forms of the Interleukin-6 Family Signal Transducer gp130 Fine-tune the Blockade of Interleukin-6 Trans-signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 16186–16196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heinrich, P.C.; Behrmann, I.; Haan, S.; Hermanns, H.M.; Müller-Newen, G.; Schaper, F. Principles of interleukin (IL)-6-type cytokine signalling and its regulation. Biochem. J. 2003, 374, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tanaka, T.; Narazaki, M.; Kishimoto, T. IL-6 in inflammation, immunity, and disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a016295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinrich, P.C.; Castell, J.V.; Andus, T. Interleukin-6 and the acute phase response. Biochem. J. 1990, 265, 621–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemeth, E.; Rivera, S.; Gabayan, V.; Keller, C.; Taudorf, S.; Pedersen, B.K.; Ganz, T. IL-6 mediates hypoferremia of in-flammation by inducing the synthesis of the iron regulatory hormone hepcidin. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 113, 1271–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liuzzi, J.P.; Lichten, L.A.; Rivera, S.; Blanchard, R.K.; Aydemir, T.B.; Knutson, M.D.; Ganz, T.; Cousins, R.J. Interleukin-6 regulates the zinc transporter Zip14 in liver and contributes to the hypozincemia of the acute-phase response. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 6843–6848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Korn, T.; Bettelli, E.; Oukka, M.; Kuchroo, V.K. IL-17 and Th17 Cells. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 27, 485–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettelli, E.; Carrier, Y.; Gao, W.; Korn, T.; Strom, T.B.; Oukka, M.; Weiner, H.L.; Kuchroo, V.K. Reciprocal developmental pathways for the generation of pathogenic effector TH17 and regulatory T cells. Nature 2006, 441, 235–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, A.; Kishimoto, T. IL-6: Regulator of Treg/Th17 balance. Eur. J. Immunol. 2010, 40, 1830–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.S.; Deenick, E.K.; Batten, M.; Tangye, S.G. The origins, function, and regulation of T follicular helper cells. J. Exp. Med. 2012, 209, 1241–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okada, M.; Kitahara, M.; Kishimoto, S.; Matsuda, T.; Hirano, T.; Kishimoto, T. IL-6/BSF-2 functions as a killer helper factor in the in vitro induction of cytotoxic T cells. J. Immunol. 1988, 141, 1543–1549. [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko, Y.; Takeuchi, T. An update on the pathogenic role of IL-6 in rheumatic diseases. Cytokine 2021, 146, 155645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bondeson, J.; Wainwright, S.D.; Lauder, S.; Amos, N.; Hughes, C.E. The role of synovial macrophages and macrophage-produced cytokines in driving aggrecanases, matrix metalloproteinases, and other destructive and inflammatory responses in osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2006, 8, R187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yoshitake, F.; Itoh, S.; Narita, H.; Ishihara, K.; Ebisu, S. Interleukin-6 Directly Inhibits Osteoclast Differentiation by Suppressing Receptor Activator of NF-κB Signaling Pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 11535–11540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Muangchan, C.; Pope, J.E. Interleukin 6 in Systemic Sclerosis and Potential Implications for Targeted Therapy. J. Rheumatol. 2012, 39, 1120–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuschiotti, P.; Medsger, T.A., Jr.; Morel, P.A. Effector CD8+ T cells in systemic sclerosis patients produce abnormally high levels of interleukin-13 associated with increased skin fibrosis. Arthritis Care Res. 2009, 60, 1119–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshizaki, K. Pathogenic Role of IL-6 Combined with TNF-α or IL-1 in the Induction of Acute Phase Proteins SAA and CRP in Chronic Inflammatory Diseases. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2010, 691, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, F.; Tasaka, S.; Inoue, K.-I.; Miyamoto, K.; Nakano, Y.; Ogawa, Y.; Yamada, W.; Shiraishi, Y.; Hasegawa, N.; Fujishima, S.; et al. Role of Interleukin-6 in Bleomycin-Induced Lung Inflammatory Changes in Mice. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2008, 38, 566–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishman, D.; Faulds, G.; Jeffery, R.; Mohamed-Ali, V.; Yudkin, J.S.; Humphries, S.; Woo, P. The effect of novel polymorphisms in the interleukin-6 (IL-6) gene on IL-6 transcription and plasma IL-6 levels, and an association with systemic-onset juvenile chronic arthritis. J. Clin. Investig. 1998, 102, 1369–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steen, V.D.; Medsger, T.A., Jr. Severe organ involvement in systemic sclerosis with diffuse scleroderma. Arthritis Rheum. 2000, 43, 2437–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, D.; Hays, R.D.; Maranian, P.; Seibold, J.R.; Impens, A.; Mayes, M.D.; Clements, P.J.; Getzug, T.; Fathi, N.; Bechtel, A.; et al. Reliability and validity of the university of california, los angeles scleroderma clinical trial consortium gastrointestinal tract instrument. Arthritis Care Res. 2009, 61, 1257–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sfrent-Cornateanu, R.; Mihai, C.; Balan, S.; Ionescu, R.; Moldoveanu, E. The IL—6 promoter polymorphism is associated with disease activity and disability in systemic sclerosis. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2006, 10, 890–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Needleman, B.W.; Wigley, F.M.; Stair, R.W. Interleukin-1, Interleukin-2, Interleukin-4, Interleukin-6, Tumor Necrosis Factor α, and Interferon-γ Levels in Sera from Patients with Scleroderma. Arthritis Care Res. 1992, 35, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, A.E.; Kronfeld-Harrington, L.B.; Szekanecz, Z.; Cho, M.M.; Haines, K.; Harlow, L.A.; Strieter, R.M.; Kunkel, S.L.; Massa, M.C.; Barr, W.G.; et al. In situ Expression of Cytokines and Cellular Adhesion Molecules in the Skin of Patients with Systemic Sclerosis. Their role in early and late disease. Pathobiology 1993, 61, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, T.C.; Spiller, D.G.; Anderson, M.E.; Edwards, S.W.; Moots, R.J. Endothelial activation and apoptosis mediated by neutrophil-dependent interleukin 6 trans-signalling: A novel target for systemic sclerosis? Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2011, 70, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Henderson, J.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Varga, J.; O’Reilly, S. Targeting TLRs and the inflammasome in systemic sclerosis. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 192, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feghali, C.A.; Bost, K.L.; Boulware, D.W.; Levy, L.S. Mechanisms of pathogenesis in scleroderma. I. Overproduction of in-terleukin 6 by fibroblasts cultured from affected skin sites of patients with scleroderma. J. Rheumatol. 1992, 19, 1207–1211. [Google Scholar]
- Gurram, M.; Pahwa, S.; Frieri, M. Augmented interleukin-6 secretion in collagen-stimulated peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with systemic sclerosis. Ann. Allergy 1994, 73, 493–496. [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa, M.; Fujimoto, M.; Matsushita, T.; Hamaguchi, Y.; Takehara, K.; Sato, S. Serum chemokine and cytokine levels as indicators of disease activity in patients with systemic sclerosis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2011, 30, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacomelli, R.; Cipriani, P.; Danese, C.; Pizzuto, F.; Lattanzio, R.; Parzanese, I.; Passacantando, A.; Perego, M.A.; Tonietti, G. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with systemic sclerosis produce increased amounts of interleukin 6, but not transforming growth factor beta 1. J. Rheumatol. 1996, 23, 291–296. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, S.; Hasegawa, M.; Takehara, K. Serum levels of interleukin-6 and interleukin-10 correlate with total skin thickness score in patients with systemic sclerosis. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2001, 27, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, M.; Sato, S.; Fujimoto, M.; Ihn, H.; Kikuchi, K.; Takehara, K. Serum levels of interleukin 6 (IL-6), oncostatin M, soluble IL-6 receptor, and soluble gp130 in patients with systemic sclerosis. J. Rheumatol. 1998, 25, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Matsushita, T.; Hasegawa, M.; Hamaguchi, Y.; Takehara, K.; Sato, S. Longitudinal analysis of serum cytokine concentrations in systemic sclerosis: Association of interleukin 12 elevation with spontaneous regression of skin sclerosis. J. Rheumatol. 2006, 33, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shima, Y.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Kuwana, M. Add-on tocilizumab versus conventional treatment for systemic sclerosis, and cytokine analysis to identify an endotype to tocilizumab therapy. Mod. Rheumatol. 2019, 29, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yamauchi-Takihara, K.; Kishimoto, T. Cytokines and their receptors in cardiovascular diseases—Role of gp130 signalling pathway in cardiac myocyte growth and maintenance. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2000, 81, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkumar, V.S.; Howell, K.; Csiszar, K.; Denton, C.P.; Black, C.M.; Abraham, D.J. Shared expression of phenotypic markers in systemic sclerosis indicates a convergence of pericytes and fibroblasts to a myofibroblast lineage in fibrosis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2005, 7, R1113–R1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kitaba, S.; Murota, H.; Terao, M.; Azukizawa, H.; Terabe, F.; Shima, Y.; Fujimoto, M.; Tanaka, T.; Naka, T.; Kishimoto, T.; et al. Blockade of Interleukin-6 Receptor Alleviates Disease in Mouse Model of Scleroderma. Am. J. Pathol. 2012, 180, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawaguchi, Y.; Hara, M.; Wright, T.M. Endogenous IL-1α from systemic sclerosis fibroblasts induces IL-6 and PDGF-A. J. Clin. Investig. 1999, 103, 1253–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beon, M.; Harley, R.A.; Wessels, A.; Silver, R.M.; Ludwicka-Bradley, A. Myofibroblast induction and microvascular alteration in scleroderma lung fibrosis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2004, 22, 733–742. [Google Scholar]
- Brissett, M.; Veraldi, K.L.; Pilewski, J.M.; Medsger, T.A., Jr.; Feghali-Bostwick, C.A. Localized expression of tenascin in systemic sclerosis-associated pulmonary fibrosis and its regulation by insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3. Arthritis Care Res. 2012, 64, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crestani, B.; Seta, N.; De Bandt, M.; Soler, P.; Rolland, C.; Dehoux, M.; Boutten, A.; Dombret, M.C.; Palazzo, E.; Kahn, M.F. Interleukin 6 secretion by monocytes and alveolar macrophages in systemic sclerosis with lung involvement. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1994, 149, 1260–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renaud, L.; da Silveira, W.A.; Takamura, N.; Hardiman, G.; Feghali-Bostwick, C. Prominence of IL6, IGF, TLR, and Bioenergetics Pathway Perturbation in Lung Tissues of Scleroderma Patients with Pulmonary Fibrosis. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.-T.T.; Karmouty-Quintana, H.; Melicoff, E.; Le, T.-T.T.; Weng, T.; Chen, N.-Y.; Pedroza, M.; Zhou, Y.; Davies, J.; Philip, K.; et al. Blockade of IL-6 Trans Signaling Attenuates Pulmonary Fibrosis. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 3755–3768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Lauretis, A.; Sestini, P.; Pantelidis, P.; Hoyles, R.; Hansell, D.M.; Goh, N.S.; Zappala, C.J.; Visca, D.; Maher, T.M.; Denton, C.P.; et al. Serum Interleukin 6 Is Predictive of Early Functional Decline and Mortality in Interstitial Lung Disease Associated with Systemic Sclerosis. J. Rheumatol. 2013, 40, 435–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, K.; Xu, S.; Nihtyanova, S.; Derrett-Smith, E.; Abraham, D.; Denton, C.P.; Ong, V.H. Clinical and pathological significance of interleukin 6 overexpression in systemic sclerosis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2012, 71, 1235–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuggioli, D.; Lumetti, F.; Colaci, M.; Fallahi, P.; Antonelli, A.; Ferri, C. Rituximab in the treatment of patients with systemic sclerosis. Our experience and review of the literature. Autoimmun. Rev. 2015, 14, 1072–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosello, S.; De Santis, M.; Lama, G.; Spanò, C.; Angelucci, C.; Tolusso, B.; Sica, G.; Ferraccioli, G. B cell depletion in diffuse progressive systemic sclerosis: Safety, skin score modification and IL-6 modulation in an up to thirty-six months follow-up open-label trial. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2010, 12, R54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abignano, G.; Del Galdo, F. Biomarkers as an opportunity to stratify for outcome in systemic sclerosis. Eur. J. Rheumatol. 2020, 7, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Magied, R.A.; Kamel, S.; Said, A.F.; Ali, H.M.; Gawad, E.A.A.; Moussa, M.M. WITHDRAWN: Serum interleukin-6 in systemic sclerosis and its correlation with disease parameters and cardiopulmonary involvement. Egypt. J. Chest Dis. Tuberc. 2016, 33, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pendergrass, S.A.; Hayes, E.; Farina, G.; Lemaire, R.; Farber, H.W.; Whitfield, M.L.; Lafyatis, R. Limited Systemic Sclerosis Patients with Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Show Biomarkers of Inflammation and Vascular Injury. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steen, V.; Medsger, T.A., Jr. Predictors of isolated pulmonary hypertension in patients with systemic sclerosis and limited cutaneous involvement. Arthritis Care Res. 2003, 48, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorfmüller, P.; Humbert, M.; Perros, F.; Sanchez, O.; Simonneau, G.; Müller, K.-M.; Capron, F. Fibrous remodeling of the pulmonary venous system in pulmonary arterial hypertension associated with connective tissue diseases. Hum. Pathol. 2007, 38, 893–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawut, S.M.; Taichman, D.B.; Archer-Chicko, C.L.; Palevsky, H.I.; Kimmel, S.E. Hemodynamics and Survival in Patients with Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Related to Systemic Sclerosis. Chest 2003, 123, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fisher, M.R.; Mathai, S.C.; Champion, H.C.; Girgis, R.E.; Housten-Harris, T.; Hummers, L.; Krishnan, J.A.; Wigley, F.; Hassoun, P.M. Clinical differences between idiopathic and scleroderma-related pulmonary hypertension. Arthritis Care Res. 2006, 54, 3043–3050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cool, C.D.; Kennedy, D.; Voelkel, N.F.; Tuder, R.M. Pathogenesis and evolution of plexiform lesions in pulmonary hypertension associated with scleroderma and human immunodeficiency virus infection. Hum. Pathol. 1997, 28, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjogren, R.W. Gastrointestinal motility disorders in scleroderma. Arthritis Care Res. 1994, 37, 1265–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cénit, M.C.; Simeón, C.P.; Vonk, M.C.; Callejas-Rubio, J.L.; Espinosa, G.; Carreira, P.; Blanco, F.J.; Narvaez, J.; Tolosa, C.; Román-Ivorra, J.A.; et al. Influence of the IL6 Gene in Susceptibility to Systemic Sclerosis. J. Rheumatol. 2012, 39, 2294–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zekovic, A.; Vreća, M.; Spasovski, V.; Andjelković, M.; Pavlovic, S.; Damjanov, N. Association between the -174 C/G polymorphism in the interleukin-6 (IL-6) gene and gastrointestinal involvement in patients with systemic sclerosis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2018, 37, 2447–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, P.M.; LeRoy, E.C. Pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis: A vascular hypothesis. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 1975, 4, 351–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steen, V.D.; Medsger, T.A., Jr. The value of the health assessment questionnaire and special patient-generated scales to demonstrate change in systemic sclerosis patients over time. Arthritis Care Res. 1997, 40, 1984–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taroni, J.N.; Martyanov, V.; Huang, C.-C.; Mahoney, J.M.; Hirano, I.; Shetuni, B.; Yang, G.-Y.; Brenner, D.; Jung, B.; Wood, T.A.; et al. Molecular characterization of systemic sclerosis esophageal pathology identifies inflammatory and proliferative signatures. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2015, 17, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thoua, N.M.; Abdel-Halim, M.; Forbes, A.; Denton, C.P.; Emmanuel, A.V. Fecal Incontinence in Systemic Sclerosis Is Secondary to Neuropathy. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 107, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Mehendiratta, V.; Del Galdo, F.; Jimenez, S.; Cohen, S.; Dimarino, A.J.; Rattan, S. Immunoglobulins from scleroderma patients inhibit the muscarinic receptor activation in internal anal sphincter smooth muscle cells. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 2009, 297, G1206–G1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, B.Y.; Giang, R.; Mbuagbaw, L.; Larche, M.; Thabane, L. Factors associated with development of gastrointestinal problems in patients with scleroderma: A systematic review. Syst. Rev. 2015, 4, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fertig, N.; Domsic, R.T.; Rodriguez-Reyna, T.; Kuwana, M.; Lucas, M.; Medsger, T.A., Jr.; Feghali-Bostwick, C.A. Anti-U11/U12 RNP antibodies in systemic sclerosis: A new serologic marker associated with pulmonary fibrosis. Arthritis Care Res. 2009, 61, 958–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kawaguchi, Y.; Nakamura, Y.; Matsumoto, I.; Nishimagi, E.; Satoh, T.; Kuwana, M.; Sumida, T.; Hara, M. Muscarinic-3 acetylcholine receptor autoantibody in patients with systemic sclerosis: Contribution to severe gastrointestinal tract dysmotility. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2009, 68, 710–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marie, I.; Leroi, A.-M.; Menard, J.-F.; Levesque, H.; Quillard, M.; Ducrotte, P. Fecal calprotectin in systemic sclerosis and review of the literature. Autoimmun. Rev. 2015, 14, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.B.; Gandhi, N.; Clarke, J.; Mcmahan, Z. Gastrointestinal Involvement in Systemic Sclerosis. JCR J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2018, 24, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denton, C.P.; Black, C.M. Scleroderma—Clinical and pathological advances. Best Pr. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2004, 18, 271–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penn, H.; Howie, A.J.; Kingdon, E.J.; Bunn, C.; Stratton, R.; Black, C.; Burns, A.; Denton, C. Scleroderma renal crisis: Patient characteristics and long-term outcomes. QJM Int. J. Med. 2007, 100, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, E.P.; Guerra, S.G.; Chinque, H.; Acquaah, V.; González-Serna, D.; Ponticos, M.; Martin, J.; Ong, V.H.; Khan, K.; Nihtyanova, S.I.; et al. Analysis of Anti-RNA Polymerase III Antibody-positive Systemic Sclerosis and Altered GPATCH2L and CTNND2 Expression in Scleroderma Renal Crisis. J. Rheumatol. 2020, 47, 1668–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Hou, Y.; Xu, D.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, L.; Yan, S.; Zhang, F.; Li, Y. Analysis of anti-RNA polymerase III antibodies in Chinese Han systemic sclerosis patients. Clin. Rheumatol. 2020, 39, 1191–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scala, E.; Pallotta, S.; Frezzolini, A.; Abeni, D.; Barbieri, C.; Sampogna, F.; DE Pità, O.; Puddu, P.; Paganelli, R.; Russo, G. Cytokine and chemokine levels in systemic sclerosis: Relationship with cutaneous and internal organ involvement. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2004, 138, 540–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doran, J.P.; Veale, D.J. Biomarkers in systemic sclerosis. Rheumatology 2008, 47, v36–v38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.; Lee, S.; Sharma, K. The pathogenesis of fibrosis and renal disease in scleroderma: Recent insights from glomerulosclerosis. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2004, 6, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, C.; Clements, P.; Furst, D.F. Systemic sclerosis: Hypothesis-driven treatment strategies. Lancet 2006, 367, 1683–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steen, V.D. Scleroderma renal crisis. Rheum. Dis. Clin. North Am. 2003, 29, 315–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steen, V.D.; Medsger, T.A., Jr. Long-Term Outcomes of Scleroderma Renal Crisis. Ann. Intern. Med. 2000, 133, 600–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihara, M.; Kasutani, K.; Okazaki, M.; Nakamura, A.; Kawai, S.; Sugimoto, M.; Matsumoto, Y.; Ohsugi, Y. Tocilizumab inhibits signal transduction mediated by both mIL-6R and sIL-6R, but not by the receptors of other members of IL-6 cytokine family. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2005, 5, 1731–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burmester, G.R.; Feist, E.; Kellner, H.; Braun, J.; Iking-Konert, C.; Rubbert-Roth, A. Effectiveness and safety of the interleukin 6-receptor antagonist tocilizumab after 4 and 24 weeks in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis: The first phase IIIb real-life study (TAMARA). Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2011, 70, 755–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohsugi, Y. The immunobiology of humanized Anti-IL6 receptor antibody: From basic research to breakthrough medicine. J. Transl. Autoimmun. 2020, 3, 100030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castañeda, S.; Martínez-Quintanilla, D.; Martín-Varillas, J.L.; García-Castañeda, N.; Atienza-Mateo, B.; González-Gay, M.A. Tocilizumab for the treatment of adult-onset Still’s disease. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2019, 19, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, J.H.; Tuckwell, K.; Dimonaco, S.; Klearman, M.; Aringer, M.; Blockmans, D.E.; Brouwer, E.; Cid, M.C.; Dasgupta, B.; Rech, J.; et al. Trial of Tocilizumab in Giant-Cell Arteritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid, M.B.; Peck, R.; Abid, M.A.; Al-Sakkaf, W.; Zhang, Y.; Dunnill, G.S.; Staines, K.; Sequeiros, I.-M.; Lowry, L. Is tocilizumab a potential therapeutic option for refractory unicentric Castleman disease? Hematol. Oncol. 2017, 36, 320–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khanna, D.; Denton, C.P.; Jahreis, A.; van Laar, J.M.; Frech, T.M.; Anderson, M.E.; Baron, M.; Chung, L.; Fierlbeck, G.; Lakshminarayanan, S.; et al. Safety and efficacy of subcutaneous tocilizumab in adults with systemic sclerosis (faSScinate): A phase 2, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet 2016, 387, 2630–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, D.; Lin, C.J.F.; Kuwana, M.; Allanore, Y.; Batalov, A.; Butrimiene, I.; Carreira, P.; Matucci Cerinic, M.; Distler, O.; Kaliterna, D.M.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Tocilizumab for the Treatment of Systemic Sclerosis: Results from a Phase 3 Randomized Controlled Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018, 70, 1000–1002. [Google Scholar]
- Denton, C.P.; Ong, V.H.; Xu, S.; Chen-Harris, H.; Modrusan, Z.; Lafyatis, R.; Khanna, D.; Jahreis, A.; Siegel, J.; Sornasse, T. Therapeutic interleukin-6 blockade reverses transforming growth factor-beta pathway activation in dermal fibroblasts: Insights from the faSScinate clinical trial in systemic sclerosis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 77, 1362–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shima, Y.; Kuwahara, Y.; Murota, H.; Kitaba, S.; Kawai, M.; Hirano, T.; Arimitsu, J.; Narazaki, M.; Hagihara, K.; Ogata, A.; et al. The skin of patients with systemic sclerosis softened during the treatment with anti-IL-6 receptor antibody tocilizumab. Rheumatology 2010, 49, 2408–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zacay, G.; Levy, Y. Outcomes of patients with systemic sclerosis treated with tocilizumab: Case series and review of the literature. Best Pr. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2018, 32, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhai, M.; Meunier, M.; Matucci-Cerinic, M.; Maurer, B.; Riemekasten, G.; Leturcq, T.; Pellerito, R.; Von Mühlen, C.A.; Vacca, A.; Airo, P.; et al. Outcomes of patients with systemic sclerosis-associated polyarthritis and myopathy treated with tocilizumab or abatacept: A EUSTAR observational study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 72, 1217–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Codina, A.; Walker, K.M.; Pope, J.E. Treatment Algorithms for Systemic Sclerosis According to Experts. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018, 70, 1820–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khanna, D.; Lin, C.J.F.; Furst, D.E.; Goldin, J.; Kim, G.; Kuwana, M.; Allanore, Y.; Matucci-Cerinic, M.; Distler, O.; Shima, Y.; et al. Tocilizumab in systemic sclerosis: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 963–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, D.; Jahreis, A.; Furst, D.E. Tocilizumab Treatment of Patients with Systemic Sclerosis: Clinical Data. J. Scleroderma Relat. Disord. 2017, 2, S29–S35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roofeh, D.; Lin, C.J.F.; Goldin, J.; Kim, G.H.; Furst, D.E.; Denton, C.P.; Huang, S.; Khanna, D. Tocilizumab Prevents Progression of Early Systemic Sclerosis–Associated Interstitial Lung Disease. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021, 73, 1301–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narváez, J.; Lluch, J.; Alegre Sancho, J.J.A.; Molina-Molina, M.; Nolla, J.M.; Castellvi, I. Effectiveness and safety of tocilizumab for the treatment of refractory systemic sclerosis associated interstitial lung disease: A case series. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, e123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khanna, D.; Lin, C.J.F.; Furst, D.E.; Wagner, B.; Zucchetto, M.; Raghu, G.; Martinez, F.J.; Goldin, J.; Siegel, J.; Denton, C.P.; et al. Long-Term Safety and Efficacy of Tocilizumab in Early Systemic Sclerosis–Interstitial Lung Disease: Open Label Extension of a Phase 3 Randomized Controlled Trial. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 204, 1245–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panopoulos, S.T.; Tektonidou, M.G.; Bournia, V.-K.; Arida, A.; Sfikakis, P.P. Anti-interleukin 6 Therapy Effect for Refractory Joint and Skin Involvement in Systemic Sclerosis: A Real-world, Single-center Experience. J. Rheumatol. 2022, 49, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahan, A.; Allanore, Y. Primary myocardial involvement in systemic sclerosis. Rheumatology 2006, 45, iv14–iv17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meléndez, G.C.; McLarty, J.L.; Levick, S.P.; Du, Y.; Janicki, J.S.; Brower, G.L. Interleukin 6 Mediates Myocardial Fibrosis, Concentric Hypertrophy, and Diastolic Dysfunction in Rats. Hypertension 2010, 56, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ishizaki, Y.; Ooka, S.; Doi, S.; Kawasaki, T.; Sakurai, K.; Mizushima, M.; Kiyokawa, T.; Takakuwa, Y.; Tonooka, K.; Kawahata, K. Treatment of myocardial fibrosis in systemic sclerosis with tocilizumab. Rheumatology 2020, 60, e205–e206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrovic, A.; Yildiz, M.; Haslak, F.; Koker, O.; Aliyeva, A.; Sahin, S.; Barut, K.; Kasapcopur, O. Tocilizumab therapy in juvenile systemic sclerosis: A retrospective single centre pilot study. Rheumatol. Int. 2021, 41, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Author | Number of Patients | Clinical and Paraclinical Parameters | Follow-Up Period | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shima et al., 2010 [117] | 2 | mRSS | 6 months |
|
| Elhai et al., 2013 [119] | 27 | Polyarthritis Myopathy mRSS | 5 months |
|
| Khanna et al., 2016 [114] | 87 | mRSS FVC | 6 months |
|
| Khanna et al., 2017 [122] | 78 | mRSS FVC | 24 months |
|
| Khanna et al., 2018 [115] | 210 | mRSS FVC | 12 months |
|
| Denton et al., 2018 [116] | 12 | mRSS | 6 months |
|
| Zacay et al., 2018 [118] | 16 | Arthritis/arthralgia Myalgia/myositis FVC mRSS | 8 months |
|
| Shima et al., 2019 [63] | 7 | mRSS | 6 months |
|
| Narvaez et al., 2019 [124] | 9 | FVC DLCO 6 min walking test | 12 months |
|
| Khanna et al. 2020 [121] | 78 | FVC | 24 months |
|
| Roofeh et al., 2021 [123] | 136 | FVC | 12 months |
|
| Khanna et al., 2021 [125] | 82 | mRSS FVC | 24 months |
|
| Adrovic et al., 2021 [130] | 9 | Juvenile SS mRSS DLCO | 24 months |
|
| Panopoulos et al., 2022 [126] | 21 | mRSS Polyarthritis FVC PROs | 12 months |
|
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cardoneanu, A.; Burlui, A.M.; Macovei, L.A.; Bratoiu, I.; Richter, P.; Rezus, E. Targeting Systemic Sclerosis from Pathogenic Mechanisms to Clinical Manifestations: Why IL-6? Biomedicines 2022, 10, 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10020318
Cardoneanu A, Burlui AM, Macovei LA, Bratoiu I, Richter P, Rezus E. Targeting Systemic Sclerosis from Pathogenic Mechanisms to Clinical Manifestations: Why IL-6? Biomedicines. 2022; 10(2):318. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10020318
Chicago/Turabian StyleCardoneanu, Anca, Alexandra Maria Burlui, Luana Andreea Macovei, Ioana Bratoiu, Patricia Richter, and Elena Rezus. 2022. "Targeting Systemic Sclerosis from Pathogenic Mechanisms to Clinical Manifestations: Why IL-6?" Biomedicines 10, no. 2: 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10020318






