Unmutated IGHV1-69 CLL Clone Displays a Distinct Gene Expression Profile by a Comparative qRT-PCR Assay
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Samples Collection
2.2. Validation of p1 Binding on CLL Cells
2.3. NF-κB and Apoptosis Related Genes
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kipps, T.J.; Stevenson, F.K.; Wu, C.J.; Croce, C.M.; Packham, G.; Wierda, W.G.; O’Brien, S.; Gribben, J.; Rai, K. Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 16096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visentin, A.; Facco, M.; Gurrieri, C.; Pagnin, E.; Martini, V.; Imbergamo, S.; Frezzato, F.; Trimarco, V.; Severin, F.; Raggi, F.; et al. Prognostic and Predictive Effect of IGHV Mutational Status and Load in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Focus on FCR and BR Treatments. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2019, 19, 678–685.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagnara, D.; Tang, C.; Brown, J.R.; Kasar, S.; Fernandes, S.; Colombo, M.; Vergani, S.; Mazzarello, A.N.; Ghiotto, F.; Bruno, S.; et al. Post-Transformation IGHV-IGHD-IGHJ Mutations in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia B Cells: Implications for Mutational Mechanisms and Impact on Clinical Course. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 640731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frost, S.D.W.; Murrell, B.; Hossain, A.S.M.M.; Silverman, G.J.; Pond, S.L.K. Assigning and visualizing germline genes in antibody repertoires. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2015, 370, 20140240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, P.; Nogueras González, G.M.; Kanagal-Shamanna, R.; Rozovski, U.; Sarwari, N.; Tam, C.; Wierda, W.G.; Thompson, P.A.; Jain, N.; Luthra, R.; et al. The absolute percent deviation of IGHV mutation rather than a 98% cut-off predicts survival of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia patients treated with fludarabine, cyclophosphamide and rituximab. Br. J. Haematol. 2018, 180, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaramillo, S.; Agathangelidis, A.; Schneider, C.; Bahlo, J.; Robrecht, S.; Tausch, E.; Bloehdorn, J.; Hoechstetter, M.; Fischer, K.; Eichhorst, B.; et al. Prognostic impact of prevalent chronic lymphocytic leukemia stereotyped subsets: Analysis within prospective clinical trials of the German CLL Study Group (GCLLSG). Haematologica 2019, 105, 2598–2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallek, M. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia: 2020 update on diagnosis, risk stratification and treatment. Am. J. Hematol. 2019, 94, 1266–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albano, F.; Chiurazzi, F.; Mimmi, S.; Vecchio, E.; Pastore, A.; Cimmino, C.; Frieri, C.; Iaccino, E.; Pisano, A.; Golino, G.; et al. The expression of inhibitor of bruton’s tyrosine kinase gene is progressively up regulated in the clinical course of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia conferring resistance to apoptosis. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koehrer, S.; Burger, J.A. B-cell receptor signaling in chronic lymphocytic leukemia and other B-cell malignancies. Clin. Adv. Hematol. Oncol. 2016, 14, 55–65. [Google Scholar]
- Burger, J.A.; Chiorazzi, N. B cell receptor signaling in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Trends Immunol. 2013, 34, 592–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fais, F.; Ghiotto, F.; Hashimoto, S.; Sellars, B.; Valetto, A.; Allen, S.L.; Schulman, P.; Vinciguerra, V.P.; Rai, K.; Rassenti, L.Z.; et al. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells express restricted sets of mutated and unmutated antigen receptors. J. Clin. Investig. 1998, 102, 1515–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agathangelidis, A.; Chatzidimitriou, A.; Gemenetzi, K.; Giudicelli, V.; Karypidou, M.; Plevova, K.; Davis, Z.; Yan, X.-J.; Jeromin, S.; Schneider, C.; et al. Higher-order connections between stereotyped subsets: Implications for improved patient classification in CLL. Blood 2021, 137, 1365–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messmer, B.T.; Albesiano, E.; Efremov, D.; Ghiotto, F.; Allen, S.; Kolitz, J.; Foa, R.; Damle, R.N.; Fais, F.; Messmer, D.; et al. Multiple Distinct Sets of Stereotyped Antigen Receptors Indicate a Role for Antigen in Promoting Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 200, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dühren-Von Minden, M.; Übelhart, R.; Schneider, D.; Wossning, T.; Bach, M.P.; Buchner, M.; Hofmann, D.; Surova, E.; Follo, M.; Köhler, F.; et al. Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia is driven by antigen-independent cell-autonomous signalling. Nature 2012, 489, 309–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, S.; Li, Z.; Zou, D.; An, G.; Cui, R.; Zhong, S.; Li, H.; Xiong, W.; Li, C.; Chen, W.; et al. Intratumoral genetic heterogeneity and number of cytogenetic aberrations provide additional prognostic significance in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Genet. Med. 2017, 19, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mimmi, S.; Maisano, D.; Nisticò, N.; Vecchio, E.; Chiurazzi, F.; Ferrara, K.; Iannalfo, M.; D’Ambrosio, A.; Fiume, G.; Iaccino, E.; et al. Detection of chronic lymphocytic leukemia subpopulations in peripheral blood by phage ligands of tumor immunoglobulin B cell receptors. Leukemia 2020, 35, 610–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, L.-A.; Hadzidimitriou, A.; Baliakas, P.; Agathangelidis, A.; Langerak, A.W.; Stilgenbauer, S.; Pospisilova, S.; Davis, Z.; Forconi, F.; Davi, F.; et al. Immunoglobulin genes in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Key to understanding the disease and improving risk stratification. Haematologica 2017, 102, 968–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangini, M.; Iaccino, E.; Mosca, M.G.; Mimmi, S.; D’Angelo, R.; Quinto, I.; Scala, G.; Mariggiò, S. Peptide-guided targeting of GPR55 for anti-cancer therapy. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 5179–5195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupia, A.; Mimmi, S.; Iaccino, E.; Maisano, D.; Moraca, F.; Talarico, C.; Vecchio, E.; Fiume, G.; Ortuso, F.; Scala, G.; et al. Molecular modelling of epitopes recognized by neoplastic B lymphocytes in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 185, 111838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maisano, D.; Iaccino, E.; D’Ambrosio, A.; Chiurazzi, F.; Dattilo, V.; Scalise, M.; Gentile, M.; Vecchio, E.; Nisticò, N.; Aloisio, A.; et al. Predominant VH1-69 IgBCR Clones Show Higher Expression of CD5 in Heterogeneous Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Populations. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 703254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, C.; Wu, C.J. Clonal dynamics in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 3759–3769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montserrat, E.; Sanchez-Bisono, J.; Viñolas, N.; Rozman, C. Lymphocyte doubling time in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: Analysis of its prognostic significance. Br. J. Haematol. 1986, 62, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Sinha, S.; Wellik, L.E.; Secreto, C.R.; Rech, K.L.; Call, T.G.; Parikh, S.A.; Kenderian, S.S.; Muchtar, E.; Hayman, S.R.; et al. Distinct immune signatures in chronic lymphocytic leukemia and Richter syndrome. Blood Cancer J. 2021, 11, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ten Hacken, E.; Gounari, M.; Ghia, P.; Burger, J.A. The importance of B cell receptor isotypes and stereotypes in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia 2018, 33, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leeksma, A.C.; Taylor, J.; Wu, B.; Gardner, J.R.; He, J.; Nahas, M.; Gonen, M.; Alemayehu, W.G.; Te Raa, D.; Walther, T.; et al. Clonal diversity predicts adverse outcome in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia 2019, 33, 390–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaiti, F.; Chaligne, R.; Gu, H.; Brand, R.M.; Kothen-Hill, S.; Schulman, R.C.; Grigorev, K.; Risso, D.; Kim, K.-T.; Pastore, A.; et al. Epigenetic evolution and lineage histories of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Nature 2019, 569, 576–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landau, D.A.; Carter, S.L.; Stojanov, P.; McKenna, A.; Stevenson, K.; Lawrence, M.S.; Sougnez, C.; Stewart, C.; Sivachenko, A.; Wang, L.; et al. Evolution and Impact of Subclonal Mutations in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Cell 2013, 152, 714–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landau, D.A.; Tausch, E.; Taylor-Weiner, A.N.; Stewart, C.; Reiter, J.G.; Bahlo, J.; Kluth, S.; Bozic, I.; Lawrence, M.S.; Böttcher, S.; et al. Mutations driving CLL and their evolution in progression and relapse. Nature 2015, 526, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, J.; Nadeu, F.; Colomer, D.; Campo, E. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia: From molecular pathogenesis to novel therapeutic strategies. Haematologica 2020, 105, 2205–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damle, R.N.; Wasil, T.; Fais, F.; Ghiotto, F.; Valetto, A.; Allen, S.L.; Buchbinder, A.; Budman, D.; Dittmar, K.; Kolitz, J.; et al. Ig V gene mutation status and CD38 expression as novel prognostic indicators in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 1999, 94, 1840–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamblin, T.J.; Davis, Z.; Gardiner, A.; Oscier, D.G.; Stevenson, F.K. Unmutated Ig V(H) genes are associated with a more aggressive form of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 1999, 94, 1848–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kikushige, Y. Pathogenesis of chronic lymphocytic leukemia and the development of novel therapeutic strategies. J. Clin. Exp. Hematop. 2020, 60, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guarini, A.; Chiaretti, S.; Tavolaro, S.; Maggio, R.; Peragine, N.; Citarella, F.; Ricciardi, M.R.; Santangelo, S.; Marinelli, M.; De Propris, M.S.; et al. BCR ligation induced by IgM stimulation results in gene expression and functional changes only in IgV H unmutated chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) cells. Blood 2008, 112, 782–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Packham, G.; Krysov, S.; Allen, A.; Savelyeva, N.; Steele, A.J.; Forconi, F.; Stevenson, F.K. The outcome of B-cell receptor signaling in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Proliferation or anergy. Haematologica 2014, 99, 1138–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svanberg, R.; Janum, S.; Patten, P.E.M.; Ramsay, A.G.; Niemann, C.U. Targeting the tumor microenvironment in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Haematologica 2021, 106, 2312–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Attekum, M.H.; Eldering, E.; Kater, A.P. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells are active participants in microenvironmental cross-talk. Haematologica 2017, 102, 1469–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallek, M.; Shanafelt, T.D.; Eichhorst, B. Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Lancet 2018, 14, 1524–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallek, M.; Fischer, K.; Fingerle-Rowson, G.; Fink, A.; Busch, R.; Mayer, J.; Hensel, M.; Hopfinger, G.; Hess, G.; von Grünhagen, U.; et al. Addition of rituximab to fludarabine and cyclophosphamide in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: A randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2010, 376, 1164–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cramer, P.; von Tresckow, J.; Eichhorst, B.; Hallek, M. Aktuelle Standards in der Diagnostik und Therapie der chronischen lymphatischen Leukämie [Current diagnosis and treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia]. Dtsch. Med. Wochenschr. 2020, 145, 1139–1144. [Google Scholar]
- Stilgenbauer, S.; Eichhorst, B.; Schetelig, J.; Coutre, S.; Seymour, J.F.; Munir, T.; Puvvada, S.D.; Wendtner, C.-M.; Roberts, A.W.; Jurczak, W.; et al. Venetoclax in relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukaemia with 17p deletion: A multicentre, open-label, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 768–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stilgenbauer, S.; Eichhorst, B.; Schetelig, J.; Hillmen, P.; Seymour, J.F.; Coutre, S.; Jurczak, W.; Mulligan, S.P.; Schuh, A.; Assouline, S.; et al. Venetoclax for Patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia with 17p Deletion: Results From the Full Population of a Phase II Pivotal Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 1973–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cramer, P.; Isfort, S.; Bahlo, J.; Stilgenbauer, S.; Döhner, H.; Bergmann, M.; Stauch, M.; Kneba, M.; Lange, E.; Langerbeins, P.; et al. Outcome of advanced chronic lymphocytic leukemia following different first-line and relapse therapies: A meta-analysis of five prospective trials by the German CLL Study Group (GCLLSG). Haematologica 2015, 100, 1451–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fink, A.M.; Böttcher, S.; Ritgen, M.; Fischer, K.; Pflug, N.; Eichhorst, B.; Wendtner, C.-M.; Winkler, D.; Bühler, A.; Zenz, T.; et al. Prediction of poor outcome in CLL patients following first-line treatment with fludarabine, cyclophosphamide and rituximab. Leukemia 2013, 27, 1949–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kienle, D.; Benner, A.; Kröber, A.; Winkler, D.; Mertens, D.; Bühler, A.; Seiler, T.; Jäger, U.; Lichter, P.; Döhner, H.; et al. Distinct gene expression patterns in chronic lymphocytic leukemia defined by usage of specific VH genes. Blood 2006, 107, 2090–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
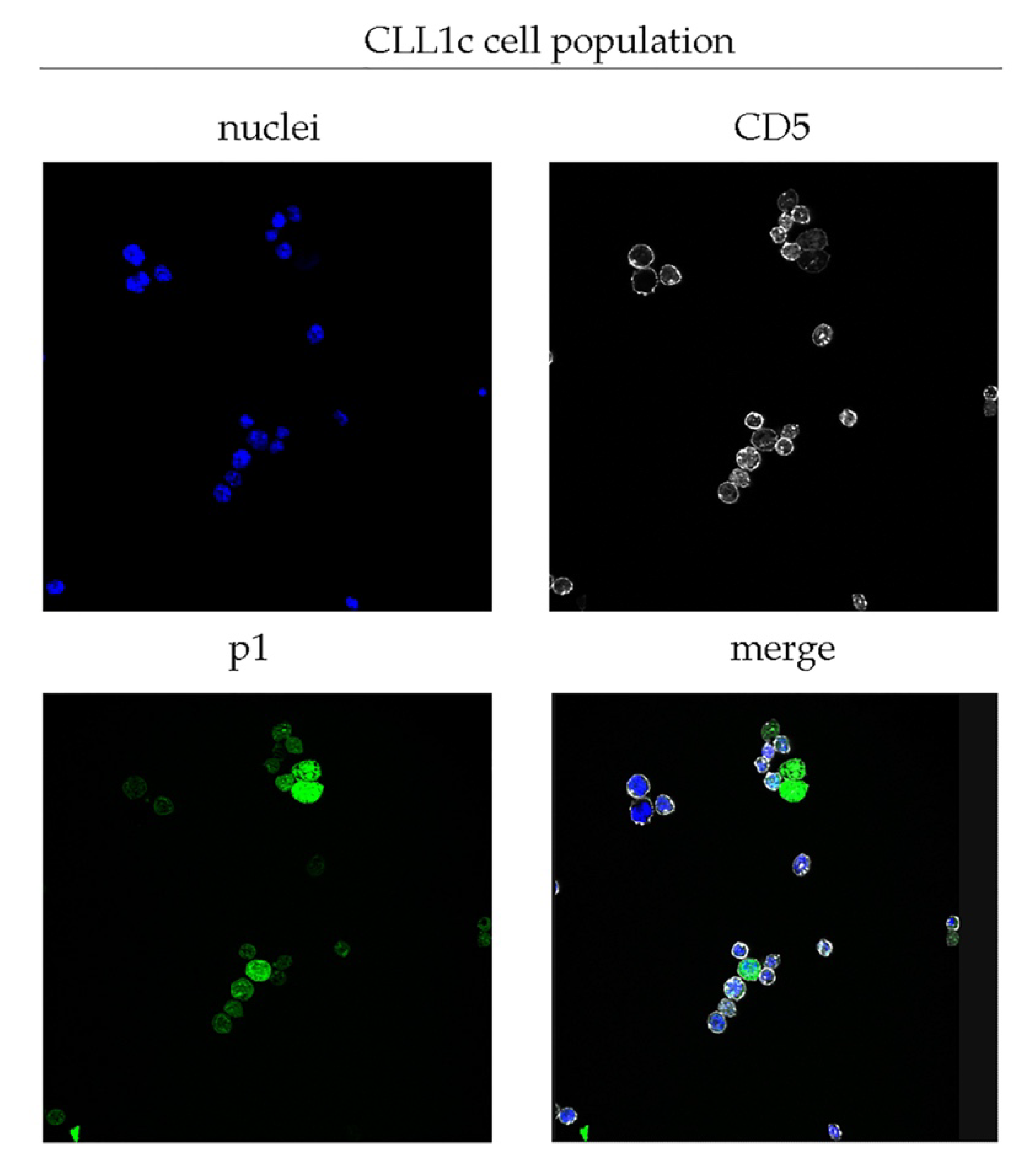
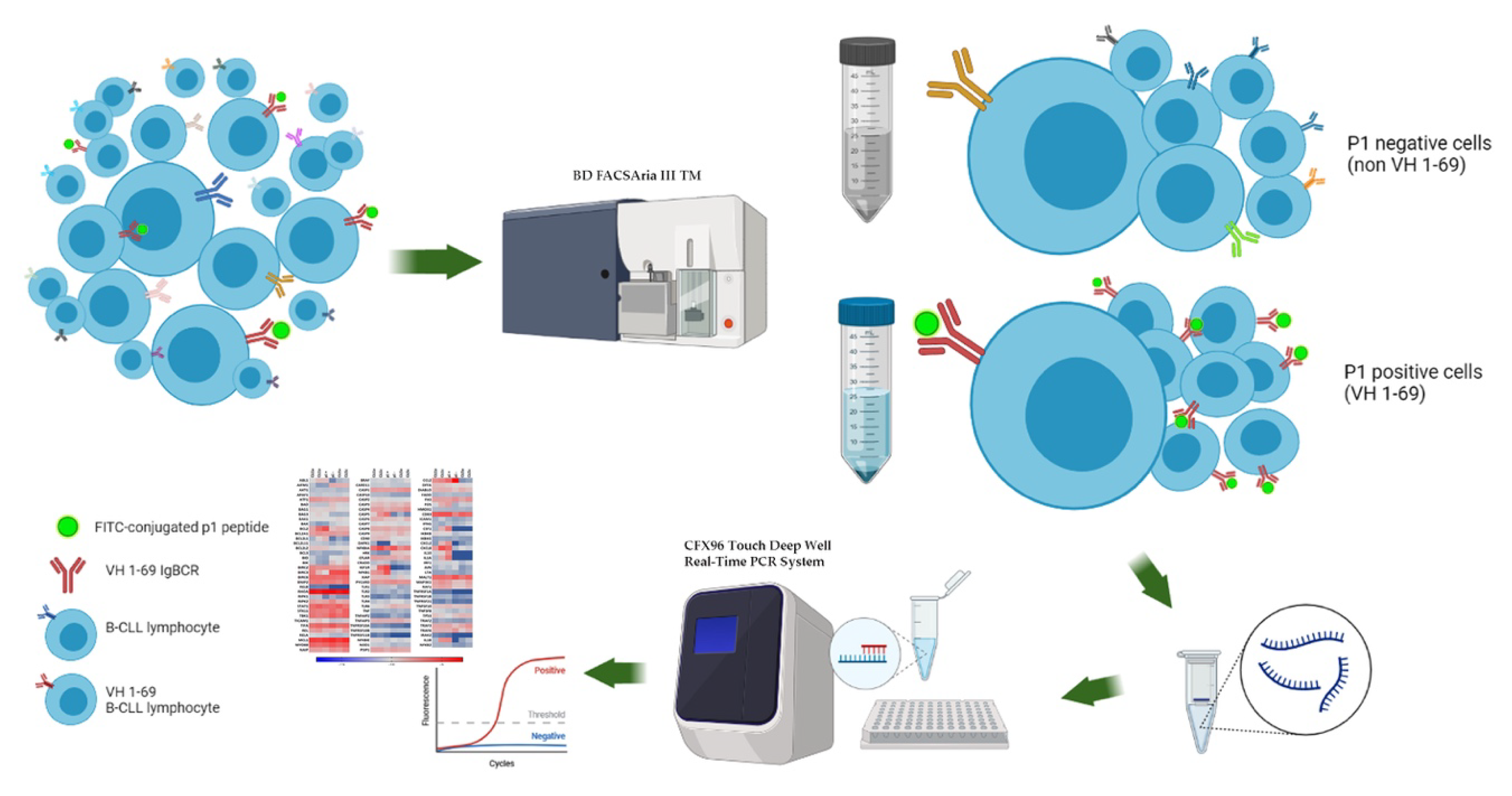
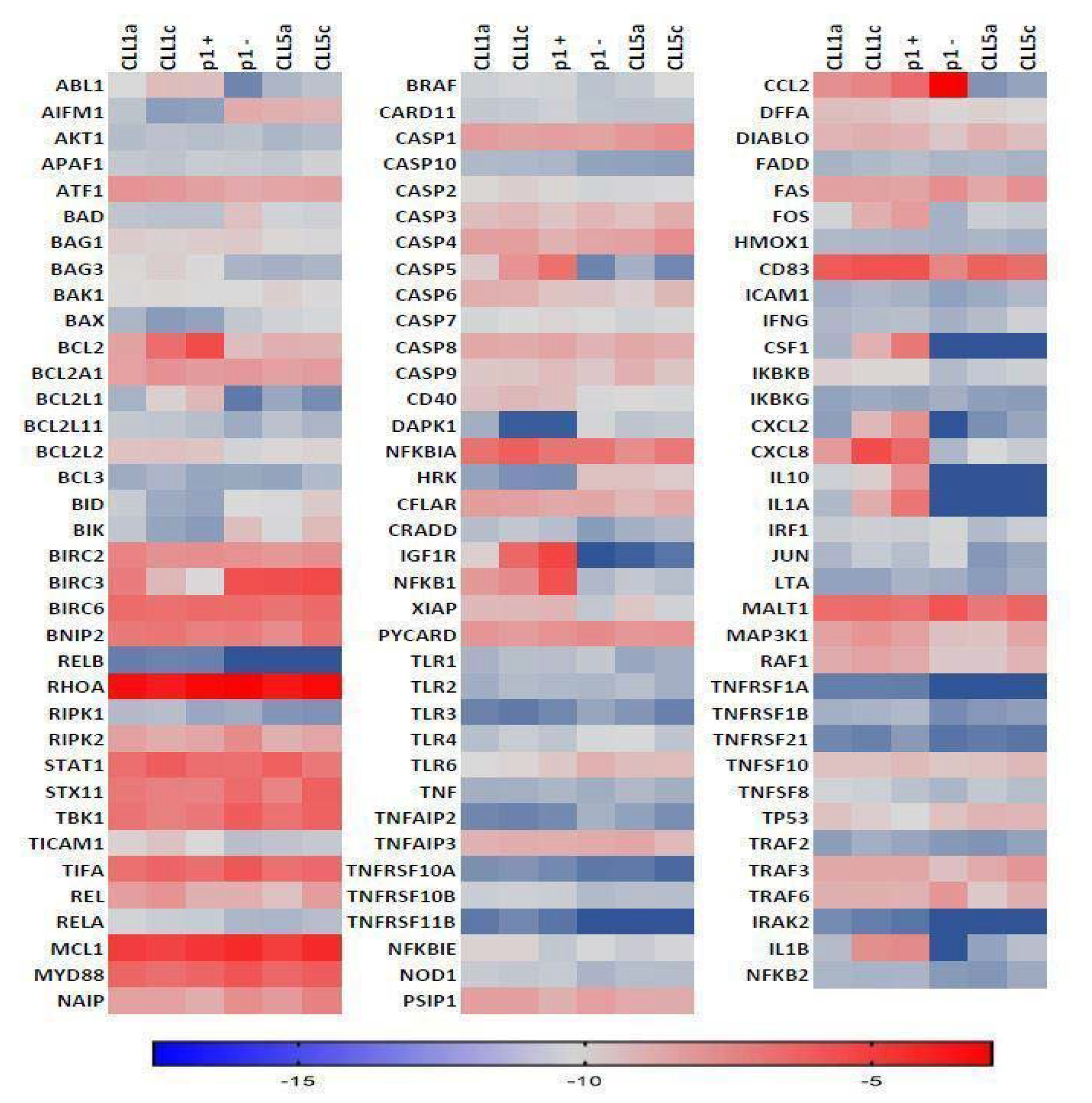

| Patient | Sample (Collection Time) | WBC (% of CD19+/CD5+) | Binet Stage | IGHV Rearrangement (Mutational Status) | (%)/Total CLL Population | Cytogenetic Alteration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CLL1 65-years old male | CLL1a (month 1) | 40,410/mmc (90%) | A | V1-69 (U-CLL) V4-4 (U-CLL) | 60 40 | del13q14 |
| CLL1c (month 8) | 92,970/mmc (99%) | C | V1-69 (U-CLL) V4-59*08 (U-CLL) V5-10*03 (U-CLL) | 80 10 10 | ||
| CLL5 80-years old woman | CLL5a (month 1) | 57,210/mmc (95%) | A | V1-69 (U-CLL) V3-7*03 (M-CLL) | 75 25 | del13q14 |
| CLL5c (month 24) | 86,500/mmc (96%) | A | V1-69 (U-CLL) V3-49 (U-CLL) V4-4*02 (U-CLL) V3-7*03 (M-CLL) | 35 25 25 15 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mimmi, S.; Maisano, D.; Dattilo, V.; Gentile, M.; Chiurazzi, F.; D’Ambrosio, A.; Zimbo, A.; Nisticò, N.; Aloisio, A.; Vecchio, E.; et al. Unmutated IGHV1-69 CLL Clone Displays a Distinct Gene Expression Profile by a Comparative qRT-PCR Assay. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 604. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10030604
Mimmi S, Maisano D, Dattilo V, Gentile M, Chiurazzi F, D’Ambrosio A, Zimbo A, Nisticò N, Aloisio A, Vecchio E, et al. Unmutated IGHV1-69 CLL Clone Displays a Distinct Gene Expression Profile by a Comparative qRT-PCR Assay. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(3):604. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10030604
Chicago/Turabian StyleMimmi, Selena, Domenico Maisano, Vincenzo Dattilo, Massimo Gentile, Federico Chiurazzi, Alessandro D’Ambrosio, Annamaria Zimbo, Nancy Nisticò, Annamaria Aloisio, Eleonora Vecchio, and et al. 2022. "Unmutated IGHV1-69 CLL Clone Displays a Distinct Gene Expression Profile by a Comparative qRT-PCR Assay" Biomedicines 10, no. 3: 604. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10030604
APA StyleMimmi, S., Maisano, D., Dattilo, V., Gentile, M., Chiurazzi, F., D’Ambrosio, A., Zimbo, A., Nisticò, N., Aloisio, A., Vecchio, E., Fiume, G., Iaccino, E., & Quinto, I. (2022). Unmutated IGHV1-69 CLL Clone Displays a Distinct Gene Expression Profile by a Comparative qRT-PCR Assay. Biomedicines, 10(3), 604. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10030604









