Clinical Application of Droplet Digital PCR for Hepatitis Delta Virus Quantification
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Specimens and Viral RNA Extraction
2.2. Primers and Probe Design
2.3. WHO-HDV International Standard
2.4. RT-qPCR
2.5. Droplet Digital PCR
2.6. Optimization of Annealing Temperature of ddPCR Assay
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Assessment of Optimal Annealing Temperature
3.2. ddPCR Threshold Setting and Internal Control
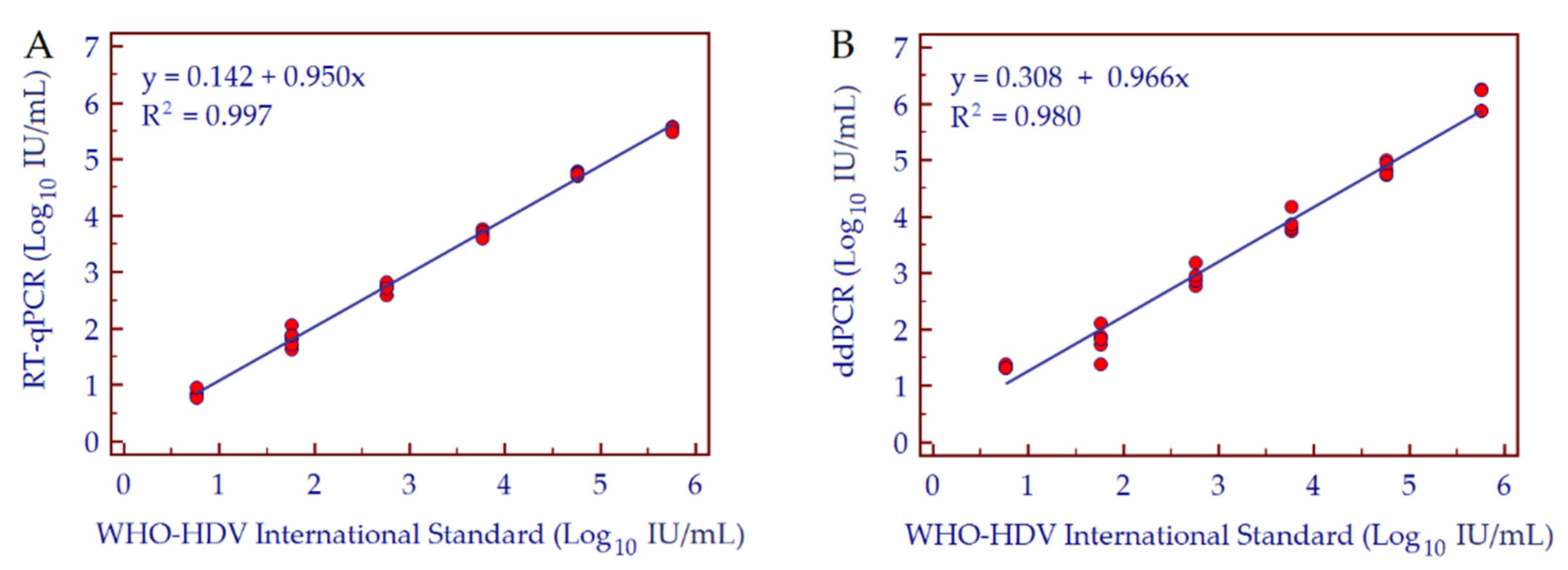
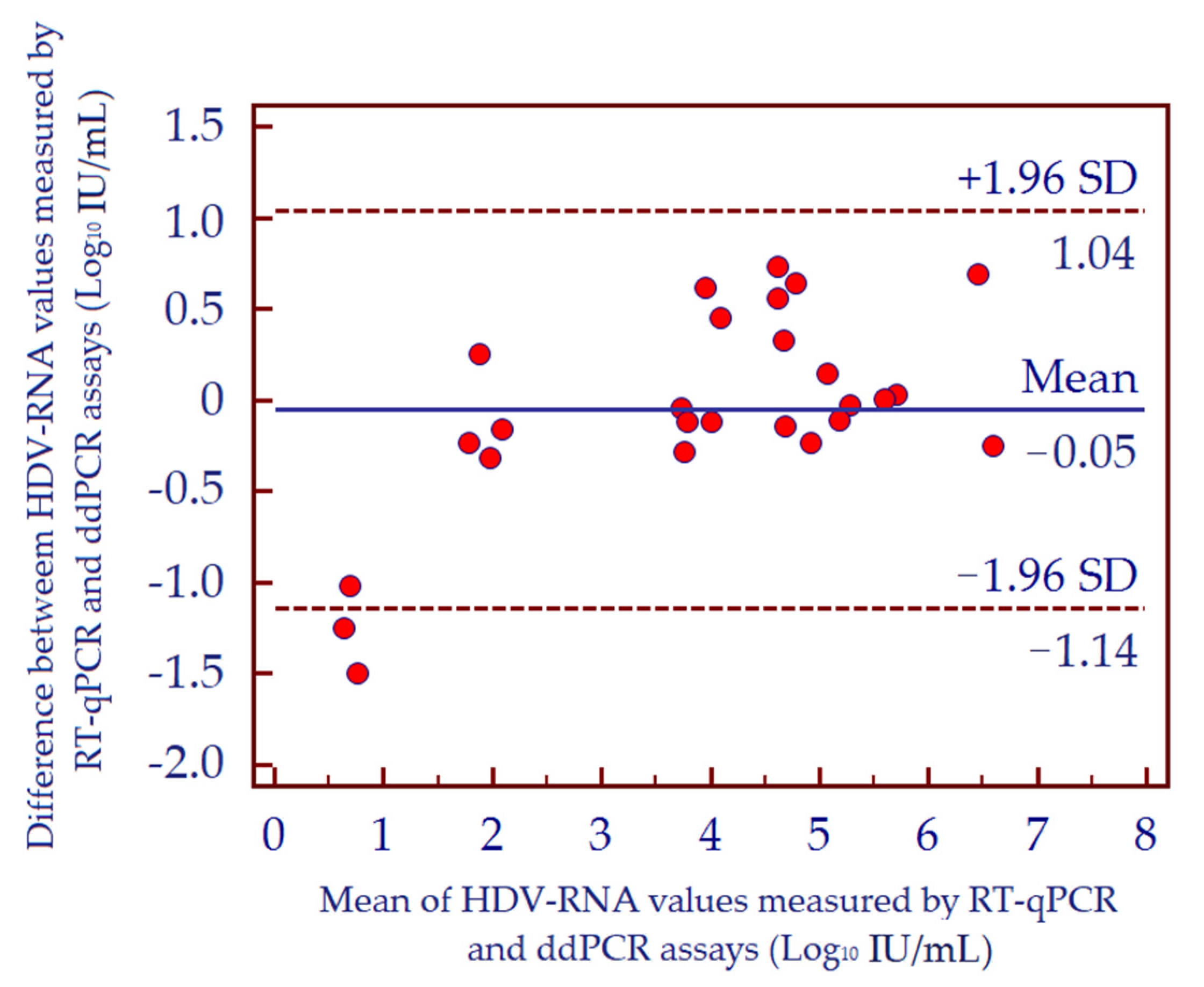
3.3. Conversion Factor Copies/mL to IU/mL, Linearity and Dynamic Range
3.4. Analytical Sensitivity
3.5. Precision and Specificity
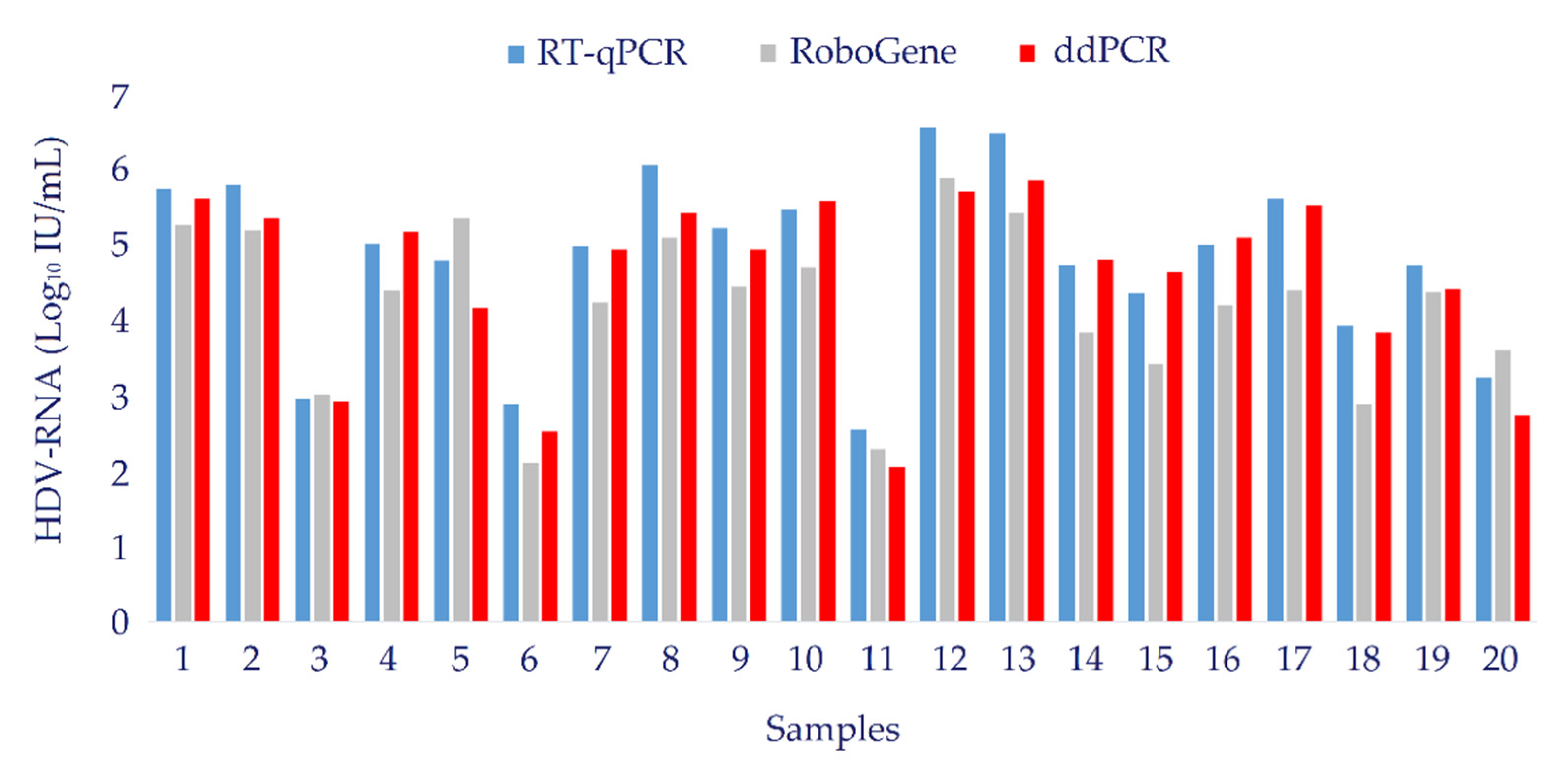
3.6. Clinical Evaluation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rizzetto, M. Hepatitis D: Thirty years after. J. Hepatol. 2009, 50, 1043–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wedemeyer, H. Re-emerging interest in hepatitis delta: New insights into the dynamic interplay between HBV and HDV. J. Hepatol. 2010, 52, 627–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wedemeyer, H.; Manns, M.P. Epidemiology, pathogenesis and management of hepatitis D: Update and challenges ahead. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 7, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivero, A.; Smedile, A. Hepatitis delta virus diagnosis. Semin. Liver Dis. 2012, 32, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Le Gal, F.; Brichler, S.; Sahli, R.; Chevret, S.; Gordien, E. First international external quality assessment for hepatitis delta virus RNA quantification in plasma. Hepatology 2016, 64, 1483–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Gal, F.; Brichler, S.; Drugan, T.; Alloui, C.; Roulot, D.; Pawlotsky, J.M.; Dény, P.; Gordien, E. Genetic diversity and worldwide distribution of the deltavirus genus: A study of 2152 clinical strains. Hepatology 2017, 66, 1826–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stelzl, E.; Ciesek, S.; Cornberg, M.; Maasoumy, B.; Heim, A.; Chudy, M.; Olivero, A.; Miklau, F.N.; Nickel, A.; Reinhardt, A.; et al. Reliable quantification of plasma HDV RNA is of paramount importance for treatment monitoring: A European multicenter study. J. Clin. Virol. 2021, 142, 104932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudecova, I. Digital PCR analysis of circulating nucleic acids. Clin. Biochem. 2015, 48, 948–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hindson, C.M.; Chevillet, J.R.; Briggs, H.A.; Gallichotte, E.N.; Ruf, I.K.; Hindson, B.J.; Vessella, R.L.; Tewari, M. Absolute quantification by droplet digital PCR versus analog real-time PCR. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 1003–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogelstein, B.; Kinzler, K.W. Digital PCR. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 9236–9241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morrison, T.; Hurley, J.; Garcia, J.; Yoder, K.; Katz, A.; Roberts, D.; Cho, J.; Kanigan, T.; Ilyin, S.E.; Horowitz, D.; et al. Nanoliter high throughput quantitative PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, e123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huggett, J.F.; Whale, A. Digital PCR as a novel technology and its potential implications for molecular diagnostics. Clin. Chem. 2013, 59, 1691–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cao, L.; Cui, X.; Hu, J.; Li, Z.; Choi, J.R.; Yang, Q.; Lin, M.; Ying Hui, L.; Xu, F. Advances in digital polymerase chain reaction (dPCR) and its emerging biomedical applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 90, 459–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hindson, B.J.; Ness, K.D.; Masquelier, D.A.; Belgrader, P.; Heredia, N.J.; Makarewicz, A.J.; Bright, I.J.; Lucero, M.Y.; Hiddessen, A.L.; Legler, T.C.; et al. High-throughput droplet digital PCR system for absolute quantitation of DNA copy number. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 8604–8610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dressman, D.; Yan, H.; Traverso, G.; Kinzler, K.W.; Vogelstein, B. Transforming single DNA molecules into fluorescent magnetic particles for detection and enumeration of genetic variations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 8817–8822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schwarz, R.F.; Ng, C.K.; Cooke, S.L.; Newman, S.; Temple, J.; Piskorz, A.M.; Gale, D.; Sayal, K.; Murtaza, M.; Baldwin, P.J.; et al. Spatial and temporal heterogeneity in high-grade serous ovarian cancer: A phylogenetic analysis. PLoS Med. 2015, 12, e1001789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferracin, M.; Lupini, L.; Salamon, I.; Saccenti, E.; Zanzi, M.V.; Rocchi, A.; Da Ros, L.; Zagatti, B.; Musa, G.; Bassi, C.; et al. Absolute quantification of cell-free microRNAs in cancer patients. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 14545–14555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Postel, M.; Roosen, A.; Laurent-Puig, P.; Taly, V.; Wang-Renault, S.F. Droplet-based digital PCR and next generation sequencing for monitoring circulating tumor DNA: A cancer diagnostic perspective. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2018, 18, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, M.F.; Gianella, S.; Letendre, S.; Scheffler, K.; Kosakovsky, P.S.L.; Smith, D.M.; Strain, M.; Ellis, R.J. Comparative Analysis of Cell-Associated HIV DNA Levels in Cerebrospinal Fluid and Peripheral Blood by Droplet Digital PCR. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0139510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Cathcart, A.L.; Delaney, W.E., IV; Kitrinos, K.M. Development of a digital droplet PCR assay to measure HBV DNA in patients receiving long-term TDF treatment. J. Virol. Methods 2017, 249, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chudy, M.; Hanschmann, K.M.; Bozsayi, M.; Kress, J.; Nubling, C.M. Collaborative Study to Establish a World Health Organization International Standard for Hepatitis D Virus RNA for Nucleic Acid Amplification Technology (NAT)-Base Assays. WHO Report. 2013. WHO/BS/2013.2227. Available online: http://www.who.int/biologicals/expert_committee/BS_2227_HDV_RNA.pdf (accessed on 29 September 2020).
- Passing, H.; Bablok, W. A new biochemical procedure for testing the quality of measurements from two different analytical methods. Application of linear regression procedures for method comparison studies in clinical chemistry, Part I. J. Clin. Chem. Clin. Biochem. 1983, 21, 709–720. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bland, J.M.; Altman, D.G. Measuring agreement in method comparison studies. Stat. Methods Med. Res. 1999, 8, 135–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreo, T.; Pirc, M.; Ramšak, Ž.; Pavšič, J.; Milavec, M.; Zel, J.; Gruden, K. Optimising droplet digital PCR analysis approaches for detection and quantification of bacteria: A case study of fire blight and potato brown rot. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 6513–6528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzetto, M.; Hamid, S.; Negro, F. The changing context of hepatitis D. J. Hepatol. 2021, 74, 1200–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamal, H.; Westman, G.; Falconer, K.; Duberg, A.S.; Weiland, O.; Haverinen, S.; Wejstål, R.; Carlsson, T.; Kampmann, C.; Larsson, S.B.; et al. Long-Term Study of Hepatitis Delta Virus Infection at Secondary Care Centers: The Impact of Viremia on Liver-Related Outcomes. Hepatology 2020, 72, 1177–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caviglia, G.P.; Martini, S.; Ciancio, A.; Niro, G.A.; Olivero, A.; Fontana, R.; Tandoi, F.; Rosso, C.; Romagnoli, R.; Saracco, G.M.; et al. The hepatitis D virus in Italy. A vanishing infection, not yet a vanished disease. J. Adv. Res. 2021, 33, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sedlak, R.H.; Kuypers, J.; Jerome, K.R. A multiplexed droplet digital PCR assay performs better than qPCR on inhibition prone samples. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 80, 285–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Hu, T.; Wu, X.; Li, K.; Zhong, Q.; Liu, W. Droplet-digital polymerase chain reaction for detection of clinical hepatitis B virus DNA samples. J. Med. Virol. 2018, 90, 1868–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caviglia, G.P.; Abate, M.L.; Tandoi, F.; Ciancio, A.; Amoroso, A.; Salizzoni, M.; Saracco, G.M.; Rizzetto, M.; Romagnoli, R.; Smedile, A. Quantitation of HBV cccDNA in anti-HBc-positive liver donors by droplet digital PCR: A new tool to detect occult infection. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piermatteo, L.; Scutari, R.; Chirichiello, R.; Alkhatib, M.; Malagnino, V.; Bertoli, A.; Iapadre, N.; Ciotti, M.; Sarmati, L.; Andreoni, M.; et al. Droplet digital PCR assay as an innovative and promising highly sensitive assay to unveil residual and cryptic HBV replication in peripheral compartment. Methods 2021, 5, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicot, F.; Cazabat, M.; Lhomme, S.; Marion, O.; Sauné, K.; Chiabrando, J.; Dubois, M.; Kamar, N.; Abravanel, F.; Izopet, J. Quantification of HEV RNA by Droplet Digital PCR. Viruses 2016, 8, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Frías, M.; Rivero-Juárez, A.; Téllez, F.; Palacios, R.; Jiménez-Arranz, Á.; Pineda, J.A.; Merino, D.; Gómez-Vidal, M.A.; Pérez-Camacho, I.; Camacho, Á.; et al. Evaluation of hepatitis C viral RNA persistence in HIV-infected patients with long-term sustained virological response by droplet digital PCR. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Long, S.; Berkemeier, B. Development and optimization of a simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) droplet digital PCR (ddPCR) assay. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0240447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strain, M.C.; Lada, S.M.; Luong, T.; Rought, S.E.; Gianella, S.; Terry, V.H.; Spina, C.A.; Woelk, C.H.; Richman, D.D. Highly precise measurement of HIV DNA by droplet digital PCR. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.; Williams, J.; Gärtner, K.; Phillips, R.; Hurst, J.; Frater, J. Low copy target detection by Droplet Digital PCR through application of a novel open access bioinformatic pipeline, ‘definetherain’. J. Virol. Methods 2014, 202, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palom, A.; Rodríguez-Tajes, S.; Navascués, C.A.; García-Samaniego, J.; Riveiro-Barciela, M.; Lens, S.; Rodríguez, M.; Esteban, R.; Buti, M. Long-term clinical outcomes in patients with chronic hepatitis delta: The role of persistent viraemia. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 51, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bremer, B.; Anastasiou, O.E.; Hardtke, S.; Caruntu, F.A.; Curescu, M.G.; Yalcin, K.; Akarca, U.S.; Gürel, S.; Zeuzem, S.; Erhardt, A.; et al. Residual low HDV viraemia is associated HDV RNA relapse after PEG-IFNa-based antiviral treatment of hepatitis delta: Results from the HIDIT-II study. Liver Int. 2021, 41, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| HDV WHO (5.76 Log10 IU/mL) | RT-qPCR HDV-RNA (Log10 Copies/mL) | ddPCR HDV-RNA (Log10 Copies/mL) |
|---|---|---|
| 10−1 | 5.71 | 5.86 |
| 10−2 | 5.66 | 5.96 |
| 10−3 | 5.73 | 6.00 |
| Mean | 5.70 | 5.94 |
| Conversion factor (copies/mL to IU/mL) | 1.01 | 0.97 |
| HDV WHO (5.76 Log10 IU/mL) Dilutions | Expected HDV-RNA Concentration (Log10 IU/mL) | Measured HDV-RNA Concentration (Log10 IU/mL) | % Recovery |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10−1 | 4.76 | 4.67 | 98.1 |
| 10−1 | 4.76 | 4.59 | 96.4 |
| 10−1 | 4.76 | 4.83 | 101.5 |
| 10−2 | 3.76 | 3.69 | 98.1 |
| 10−2 | 3.76 | 3.69 | 98.1 |
| 10−2 | 3.76 | 4.05 | 107.7 |
| 10−3 | 2.76 | 2.74 | 99.3 |
| 10−3 | 2.76 | 2.81 | 101.8 |
| 10−3 | 2.76 | 3.10 | 112.3 |
| Dilution Factor | HDV-RNA (IU/mL) | RT-qPCR Replicates (n) | RT-qPCR Positive (n) | ddPCR Replicates (n) | ddPCR Positive (n) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10−4 | 57.5 | 9 | 9 | 7 | 7 |
| 10−4.5 | 18.2 | 9 | 9 | 8 | 8 |
| 10−5 | 5.8 | 20 | 16 | 8 | 7 |
| 10−5.5 | 1.8 | 13 | 7 | 11 | 7 |
| 10−6 | 0.6 | 12 | 0 | 9 | 3 |
| Technical Features | RT-qPCR | ddPCR |
|---|---|---|
| Conversion Factor: Copies/mL to IU/mL | 1.01 | 0.97 |
| Quantification range (IU/mL) | 1 × 10−1 × 108 | 1 × 10−1 × 106 |
| Sensitivity: 95% Limit of Detection (IU/mL) | 9.7 | 9.2 |
| Sensitivity: 50% Limit of Detection (IU/mL) | 2.3 | 1.1 |
| Repeatability: intra-assay (% CV) | 1.42 | 0.80 |
| Reproducibility: inter-assay (% CV) | 1.78 | 1.51 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Olivero, A.; Rosso, C.; Ciancio, A.; Abate, M.L.; Nicolosi, A.; Troshina, G.; Armandi, A.; Ribaldone, D.G.; Saracco, G.M.; Bugianesi, E.; et al. Clinical Application of Droplet Digital PCR for Hepatitis Delta Virus Quantification. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 792. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10040792
Olivero A, Rosso C, Ciancio A, Abate ML, Nicolosi A, Troshina G, Armandi A, Ribaldone DG, Saracco GM, Bugianesi E, et al. Clinical Application of Droplet Digital PCR for Hepatitis Delta Virus Quantification. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(4):792. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10040792
Chicago/Turabian StyleOlivero, Antonella, Chiara Rosso, Alessia Ciancio, Maria Lorena Abate, Aurora Nicolosi, Giulia Troshina, Angelo Armandi, Davide Giuseppe Ribaldone, Giorgio Maria Saracco, Elisabetta Bugianesi, and et al. 2022. "Clinical Application of Droplet Digital PCR for Hepatitis Delta Virus Quantification" Biomedicines 10, no. 4: 792. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10040792
APA StyleOlivero, A., Rosso, C., Ciancio, A., Abate, M. L., Nicolosi, A., Troshina, G., Armandi, A., Ribaldone, D. G., Saracco, G. M., Bugianesi, E., Rizzetto, M., & Caviglia, G. P. (2022). Clinical Application of Droplet Digital PCR for Hepatitis Delta Virus Quantification. Biomedicines, 10(4), 792. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10040792









