Multimodal Characterization of Seizures in Zebrafish Larvae
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Zebrafish Larvae
2.2. Two-Photon Light-Sheet Microscope
2.3. Behavioral Tracking System
2.4. Whole-Brain Functional Imaging
2.5. Behavioral Recordings
2.6. Data Analysis
2.6.1. Whole-Brain Calcium Imaging
2.6.2. Behavioral Recordings
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
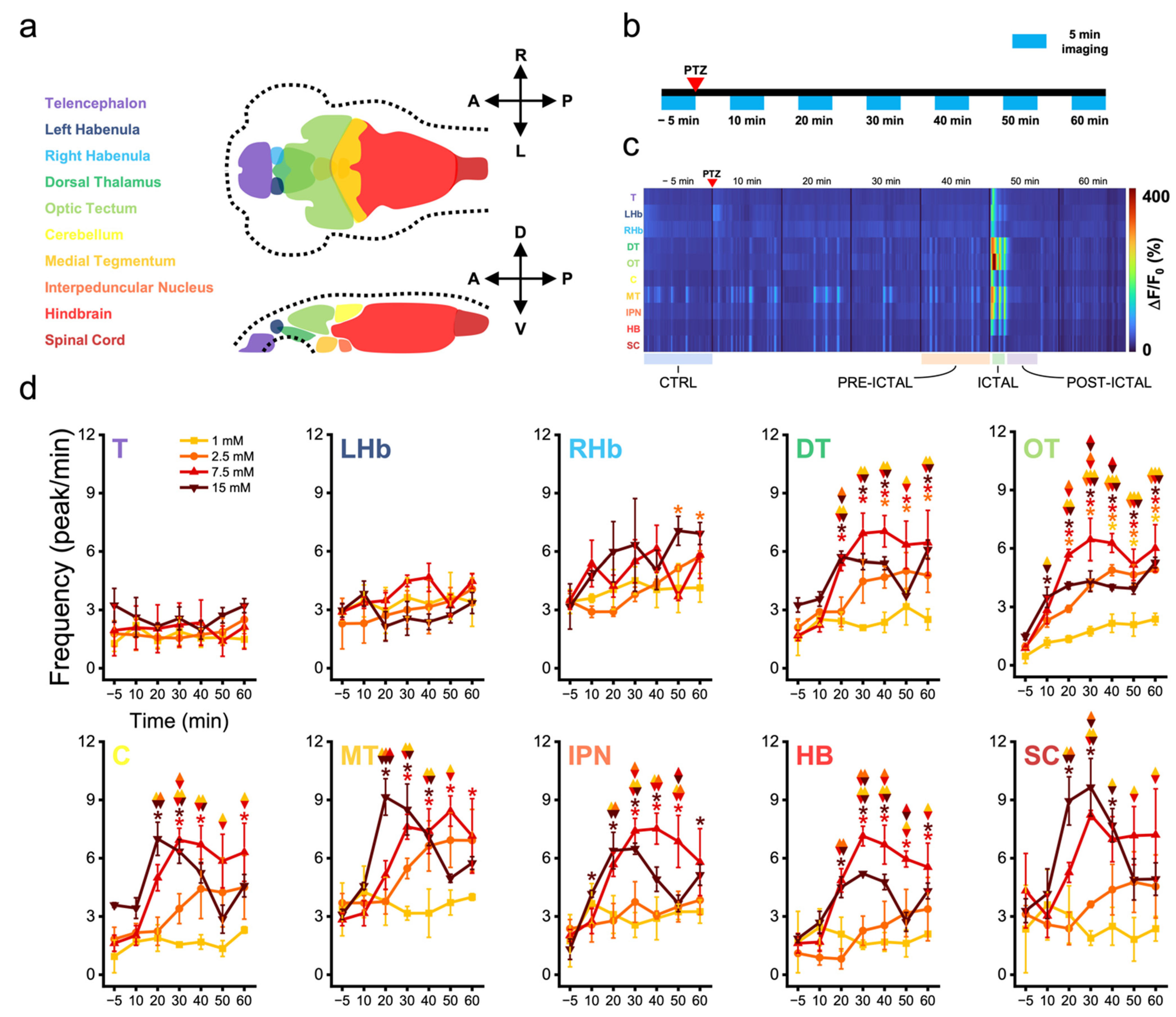
3.1. Zebrafish Brain Regions Present Different Susceptibility to Convulsant Effects
3.2. Zebrafish Brain Undergoes Transition between Different Activity Regimes during Seizures
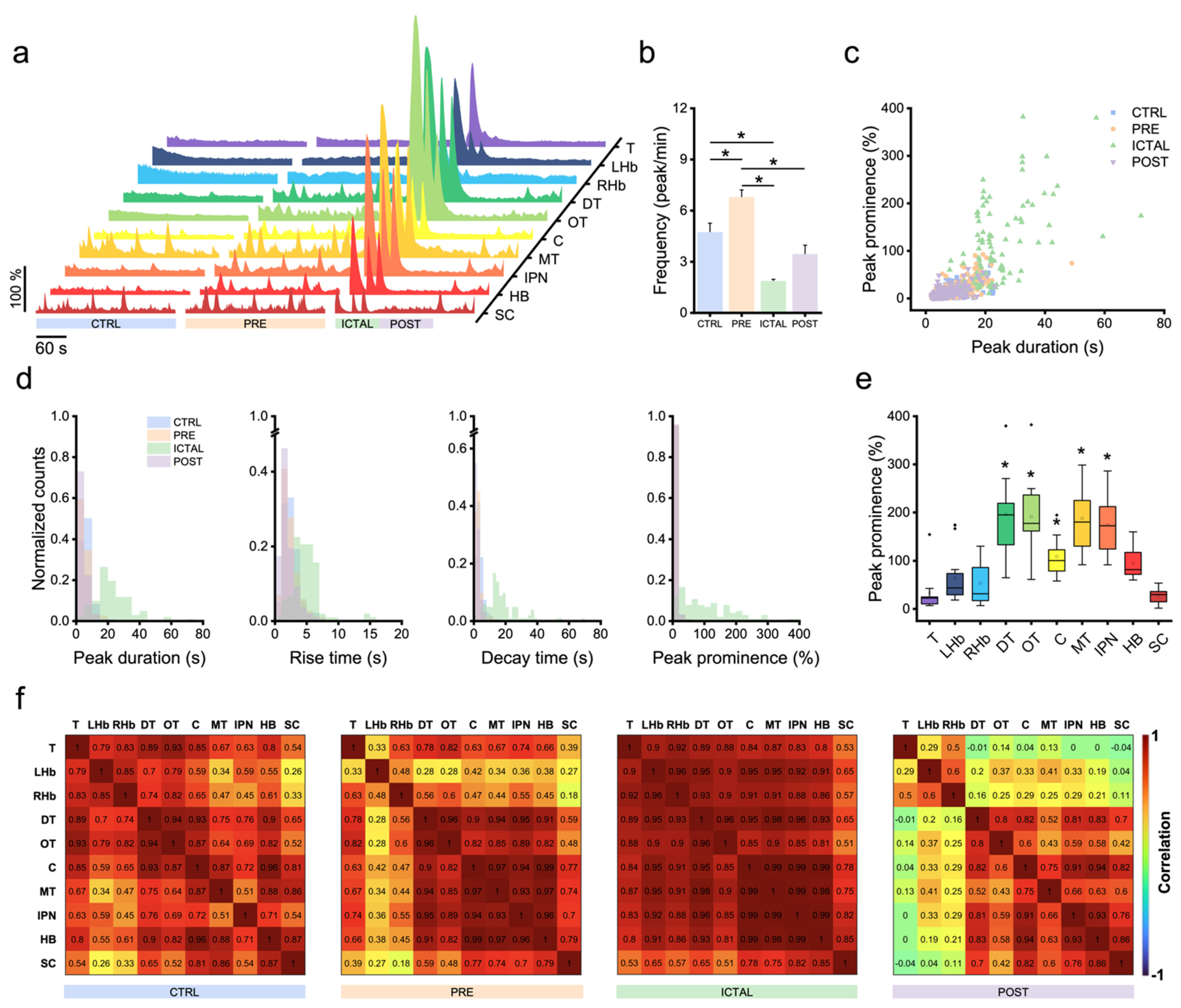
3.3. Zebrafish Larvae Undergoes Alteration of Their Swimming Kinematic during Seizures
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GBD 2016 Epilepsy Collaborators. Global, Regional, and National Burden of Epilepsy, 1990–2016: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 357–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noebels, J.L. The Biology of Epilepsy Genes. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2003, 26, 599–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Olson, H.E.; Poduri, A.; Pearl, P.L. Genetic Forms of Epilepsies and Other Paroxysmal Disorders. Semin. Neurol. 2014, 34, 266–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Myers, K.A.; Johnstone, D.L.; Dyment, D.A. Epilepsy Genetics: Current Knowledge, Applications, and Future Directions. Clin. Genet. 2019, 95, 95–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shamji, M.F.; Fric-Shamji, E.C.; Benoit, B.G. Brain Tumors and Epilepsy: Pathophysiology of Peritumoral Changes. Neurosurg. Rev. 2009, 32, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Politsky, J.M. Brain Tumor-Related Epilepsy: A Current Review of the Etiologic Basis and Diagnostic and Treatment Approaches. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2017, 17, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowenstein, D.H. Epilepsy after Head Injury: An Overview. Epilepsia 2009, 50 (Suppl. S2), 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, K.M.; Sun, M.; Crack, P.; O’Brien, T.J.; Shultz, S.R.; Semple, B.D. Inflammation in Epileptogenesis after Traumatic Brain Injury. J. Neuroinflamm. 2017, 14, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doria, J.W.; Forgacs, P.B. Incidence, Implications, and Management of Seizures Following Ischemic and Hemorrhagic Stroke. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2019, 19, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyou, H.J.; Seo, K.D.; Lee, J.E.; Pak, H.Y.; Lee, J.H. Association of Alzheimer’s Disease with the Risk of Developing Epilepsy: A 10-Year Nationwide Cohort Study. Dement. Neurocogn. Disord. 2018, 17, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruntz, K.; Bloechliger, M.; Becker, C.; Jick, S.S.; Fuhr, P.; Meier, C.R.; Ruegg, S. Parkinson Disease and the Risk of Epileptic Seizures. Ann. Neurol. 2018, 83, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cloud, L.J.; Rosenblatt, A.; Margolis, R.L.; Ross, C.A.; Pillai, J.A.; Corey-Bloom, J.; Tully, H.M.; Bird, T.; Panegyres, P.K.; Nichter, C.A.; et al. Seizures in Juvenile Huntington’s Disease: Frequency and Characterization in a Multicenter Cohort. Mov. Disord. 2012, 27, 1797–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giorgi, F.S.; Saccaro, L.F.; Busceti, C.L.; Biagioni, F.; Fornai, F. Epilepsy and Alzheimer’s Disease: Potential Mechanisms for an Association. Brain Res. Bull. 2020, 160, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casillas-Espinosa, P.M.; Ali, I.; O’Brien, T.J. Neurodegenerative Pathways as Targets for Acquired Epilepsy Therapy Development. Epilepsia Open 2020, 5, 138–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano, A.; Fonseca, E.; Ettcheto, M.; Sanchez-Lopez, E.; de Rojas, I.; Alonso-Lana, S.; Morato, X.; Souto, E.B.; Toledo, M.; Boada, M.; et al. Epilepsy in Neurodegenerative Diseases: Related Drugs and Molecular Pathways. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stafstorm, C.E. Mechanisms of Action of Antiepileptic Drugs: The Search for Synergy. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2010, 23, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan, P.; Schachter, S.C.; Brodie, M.J. Drug-Resistant Epilepsy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 919–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rossi, L.F.; Wykes, R.C.; Kullmann, D.M.; Carandini, M. Focal Cortical Seizures Start as Standing Waves and Propagate Respecting Homotopic Connectivity. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wenzel, M.; Hamm, J.P.; Peterka, D.S.; Yuste, R. Reliable and Elastic Propagation of Cortical Seizures In Vivo. Cell. Rep. 2017, 19, 2681–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aeed, F.; Shnitzer, T.; Talmon, R.; Schiller, Y. Layer- and Cell-Specific Recruitment Dynamics During Epileptic Seizures In Vivo. Ann. Neurol. 2020, 87, 97–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaksi, E.; Jamali, A.; Verdugo, C.D.; Jurisch-Yaksi, N. Past, Present and Future of Zebrafish in Epilepsy Research. FEBS J. 2021, 288, 7243–7255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turrini, L.; Fornetto, C.; Marchetto, G.; Mullenbroich, M.C.; Tiso, N.; Vettori, A.; Resta, F.; Masi, A.; Mannaioni, G.; Pavone, F.S.; et al. Optical Mapping of Neuronal Activity During Seizures in Zebrafish. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baraban, S.C.; Dinday, M.T.; Hortopan, G.A. Drug Screening in Scn1a Zebrafish Mutant Identifies Clemizole as a Potential Dravet Syndrome Treatment. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dinday, M.T.; Baraban, S.C. Large-Scale Phenotype-Based Antiepileptic Drug Screening in a Zebrafish Model of Dravet Syndrome. eNeuro 2015, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hortopan, G.A.; Dinday, M.T.; Baraban, S.C. Zebrafish as a Model for Studying Genetic Aspects of Epilepsy. Dis. Model Mech. 2010, 3, 144–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Samarut, E.; Swaminathan, A.; Riche, R.; Liao, M.; Hassan-Abdi, R.; Renault, S.; Allard, M.; Dufour, L.; Cossette, P.; Soussi-Yanicostas, N.; et al. Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid Receptor Alpha 1 Subunit Loss of Function Causes Genetic Generalized Epilepsy by Impairing Inhibitory Network Neurodevelopment. Epilepsia 2018, 59, 2061–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liao, M.; Kundap, U.; Rosch, R.E.; Burrows, D.R.W.; Meyer, M.P.; Bencheikh, B.O.A.; Cossette, P.; Samarut, E. Targeted Knockout of Gaba-a Receptor Gamma 2 Subunit Provokes Transient Light-Induced Reflex Seizures in Zebrafish Larvae. Dis. Model Mech. 2019, 12, dmm040782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brenet, A.; Hassan-Abdi, R.; Somkhit, J.; Yanicostas, C.; Soussi-Yanicostas, N. Defective Excitatory/Inhibitory Synaptic Balance and Increased Neuron Apoptosis in a Zebrafish Model of Dravet Syndrome. Cells 2019, 8, 1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baraban, S.C.; Taylor, M.R.; Castro, P.A.; Baier, H. Pentylenetetrazole Induced Changes in Zebrafish Behavior, Neural Activity and C-Fos Expression. Neuroscience 2005, 131, 759–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, A.M.; Desmond, D.; Kyzar, E.; Gaikwad, S.; Roth, A.; Riehl, R.; Collins, C.; Monnig, L.; Green, J.; Kalueff, A.V. Perspectives of Zebrafish Models of Epilepsy: What, How and Where Next? Brain Res. Bull. 2012, 87, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afrikanova, T.; Serruys, A.S.; Buenafe, O.E.; Clinckers, R.; Smolders, I.; de Witte, P.A.; Crawford, A.D.; Esguerra, C.V. Validation of the Zebrafish Pentylenetetrazol Seizure Model: Locomotor Versus Electrographic Responses to Antiepileptic Drugs. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hong, S.; Lee, P.; Baraban, S.C.; Lee, L.P. A Novel Long-Term, Multi-Channel and Non-Invasive Electrophysiology Platform for Zebrafish. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cho, S.J.; Byun, D.; Nam, T.S.; Choi, S.Y.; Lee, B.G.; Kim, M.K.; Kim, S. Zebrafish as an Animal Model in Epilepsy Studies with Multichannel Eeg Recordings. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawakami, K. Tol2: A Versatile Gene Transfer Vector in Vertebrates. Genome Biol. 2007, 8 (Suppl. S1), S7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kawakami, K.; Asakawa, K.; Hibi, M.; Itoh, M.; Muto, A.; Wada, H. Gal4 Driver Transgenic Zebrafish: Powerful Tools to Study Developmental Biology, Organogenesis, and Neuroscience. Adv. Genet. 2016, 95, 65–87. [Google Scholar]
- Guru, A.; Post, R.J.; Ho, Y.Y.; Warden, M.R. Making Sense of Optogenetics. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2015, 18, pyv079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.Z.; Schnitzer, M.J. Genetically Encoded Indicators of Neuronal Activity. Nat. Neurosci. 2016, 19, 1142–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wyatt, C.; Bartoszek, E.M.; Yaksi, E. Methods for Studying the Zebrafish Brain: Past, Present and Future. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2015, 42, 1746–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Randlett, O.; Wee, C.L.; Naumann, E.A.; Nnaemeka, O.; Schoppik, D.; Fitzgerald, J.E.; Portugues, R.; Lacoste, A.M.; Riegler, C.; Engert, F.; et al. Whole-Brain Activity Mapping onto a Zebrafish Brain Atlas. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 1039–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kunst, M.; Laurell, E.; Mokayes, N.; Kramer, A.; Kubo, F.; Fernandes, A.M.; Forster, D.; Maschio, M.D.; Baier, H. A Cellular-Resolution Atlas of the Larval Zebrafish Brain. Neuron 2019, 103, 21–38.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Power, R.M.; Huisken, J. A Guide to Light-Sheet Fluorescence Microscopy for Multiscale Imaging. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 360–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahrens, M.B.; Orger, M.B.; Robson, D.N.; Li, J.M.; Keller, P.J. Whole-Brain Functional Imaging at Cellular Resolution Using Light-Sheet Microscopy. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vito, G.; Turrini, L.; Müllenbroich, C.; Ricci, P.; Sancataldo, G.; Mazzamuto, G.; Tiso, N.; Sacconi, L.; Fanelli, D.; Silvestri, L.; et al. Fast Whole-Brain Imaging of Seizures in Zebrafish Larvae by Two-Photon Light-Sheet Microscopy. Biomed. Opt. Express 2022, 13, 1516–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullenbroich, M.C.; Turrini, L.; Silvestri, L.; Alterini, T.; Gheisari, A.; Tiso, N.; Vanzi, F.; Sacconi, L.; Pavone, F.S. Bessel Beam Illumination Reduces Random and Systematic Errors in Quantitative Functional Studies Using Light-Sheet Microscopy. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zfin Feature: B4. Available online: https://zfin.org/ZDB-ALT-980203-365 (accessed on 16 April 2022).
- Westerfield, M. The Zebrafish Book. A Guide for the Laboratory Use of Zebrafish (Danio Rerio), 4th ed.; University of Oregon Press: Eugene, OR, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- de Vito, G.; Ricci, P.; Turrini, L.; Gavryusev, V.; Mullenbroich, M.C.; Tiso, N.; Vanzi, F.; Silvestri, L.; Pavone, F. Effects of Excitation Light Polarization on Fluorescence Emission in Two-Photon Light-Sheet Microscopy. Biomed. Opt. Express 2020, 11, 4651–4665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stih, V.; Petrucco, L.; Kist, A.M.; Portugues, R. Stytra: An Open-Source, Integrated System for Stimulation, Tracking and Closed-Loop Behavioral Experiments. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2019, 15, e1006699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Emran, F.; Rihel, J.; Adolph, A.R.; Dowling, J.E. Zebrafish Larvae Lose Vision at Night. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 6034–6039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fisher, R.S.; Scharfman, H.E.; deCurtis, M. How Can We Identify Ictal and Interictal Abnormal Activity? Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2014, 813, 3–23. [Google Scholar]
- de Vito, G.; Turrini, L.; Fornetto, C.; Ricci, P.; Müllenbroich, C.; Sancataldo, G.; Trabalzini, E.; Mazzamuto, G.; Tiso, N.; Sacconi, L.; et al. Two-Photon Light-Sheet Microscopy for High-Speed Whole-Brain Functional Imaging of Zebrafish Physiology and Pathology. Neurophotonics 2020, 11360, 1136004. [Google Scholar]
- de Vito, G.; Fornetto, C.; Ricci, P.; Müllenbroich, C.; Sancataldo, G.; Turrini, L.; Mazzamuto, G.; Tiso, N.; Sacconi, L.; Fanelli, D.; et al. Two-Photon High-Speed Light-Sheet Volumetric Imaging of Brain Activity During Sleep in Zebrafish Larvae. Neural Imaging Sens. 2020, 2020, 11226. [Google Scholar]
- Ricci, P.; Gavryusev, V.; Mullenbroich, C.; Turrini, L.; de Vito, G.; Silvestri, L.; Sancataldo, G.; Pavone, F.S. Removing Striping Artifacts in Light-Sheet Fluorescence Microscopy: A Review. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2022, 168, 52–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.Q.; Bell-Horner, C.L.; Dibas, M.I.; Covey, D.F.; Drewe, J.A.; Dillon, G.H. Pentylenetetrazole-Induced Inhibition of Recombinant Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid Type a (Gaba(a)) Receptors: Mechanism and Site of Action. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2001, 298, 986–995. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Diaz Verdugo, C.; Myren-Svelstad, S.; Aydin, E.; van Hoeymissen, E.; Deneubourg, C.; Vanderhaeghe, S.; Vancraeynest, J.; Pelgrims, R.; Cosacak, M.I.; Muto, A.; et al. Glia-Neuron Interactions Underlie State Transitions to Generalized Seizures. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Betzel, R.F. Organizing Principles of Whole-Brain Functional Connectivity in Zebrafish Larvae. Netw. Neurosci. 2020, 4, 234–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chicchi, L.; Cecchini, G.; Adam, I.; de Vito, G.; Livi, R.; Pavone, F.S.; Silvestri, L.; Turrini, L.; Vanzi, F.; Fanelli, D. Reconstruction Scheme for Excitatory and Inhibitory Dynamics with Quenched Disorder: Application to Zebrafish Imaging. J. Comput. Neurosci. 2021, 49, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosch, R.E.; Hunter, P.R.; Baldeweg, T.; Friston, K.J.; Meyer, M.P. Calcium Imaging and Dynamic Causal Modelling Reveal Brain-Wide Changes in Effective Connectivity and Synaptic Dynamics During Epileptic Seizures. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2018, 14, e1006375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, F.; Kwan, A.C. Interpreting in Vivo Calcium Signals from Neuronal Cell Bodies, Axons, and Dendrites: A Review. Neurophotonics 2020, 7, 011402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Baraban, S.C. Network Properties Revealed During Multi-Scale Calcium Imaging of Seizure Activity in Zebrafish. eNeuro 2019, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ricci, P.; Marchetti, M.; Sorelli, M.; Turrini, L.; Resta, F.; Gavryusev, V.; de Vito, G.; Sancataldo, G.; Vanzi, F.; Silvestri, L.; et al. Power-Effective Scanning with Aods for 3d Optogenic Applications. J. Biophotonics 2022, 15, e202100256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz, J.T.; Davidson, T.J.; Frechette, E.S.; Delord, B.; Parada, I.; Peng, K.; Deisseroth, K.; Huguenard, J.R. Closed-Loop Optogenetic Control of Thalamus as a Tool for Interrupting Seizures after Cortical Injury. Nat. Neurosci. 2013, 16, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Turrini, L.; Sorelli, M.; de Vito, G.; Credi, C.; Tiso, N.; Vanzi, F.; Pavone, F.S. Multimodal Characterization of Seizures in Zebrafish Larvae. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 951. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10050951
Turrini L, Sorelli M, de Vito G, Credi C, Tiso N, Vanzi F, Pavone FS. Multimodal Characterization of Seizures in Zebrafish Larvae. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(5):951. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10050951
Chicago/Turabian StyleTurrini, Lapo, Michele Sorelli, Giuseppe de Vito, Caterina Credi, Natascia Tiso, Francesco Vanzi, and Francesco Saverio Pavone. 2022. "Multimodal Characterization of Seizures in Zebrafish Larvae" Biomedicines 10, no. 5: 951. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10050951
APA StyleTurrini, L., Sorelli, M., de Vito, G., Credi, C., Tiso, N., Vanzi, F., & Pavone, F. S. (2022). Multimodal Characterization of Seizures in Zebrafish Larvae. Biomedicines, 10(5), 951. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10050951







