Overview of Neural Tube Defects: Gene–Environment Interactions, Preventative Approaches and Future Perspectives
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Neural Tube Formation and Defects
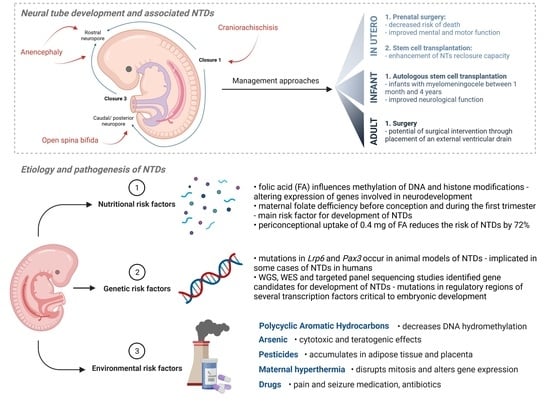
2.1. Neural Tube Development
2.2. Neural Tube Defects (NTDs)
3. Etiology and Pathogenesis of Neural Tube Defects (NTDs)
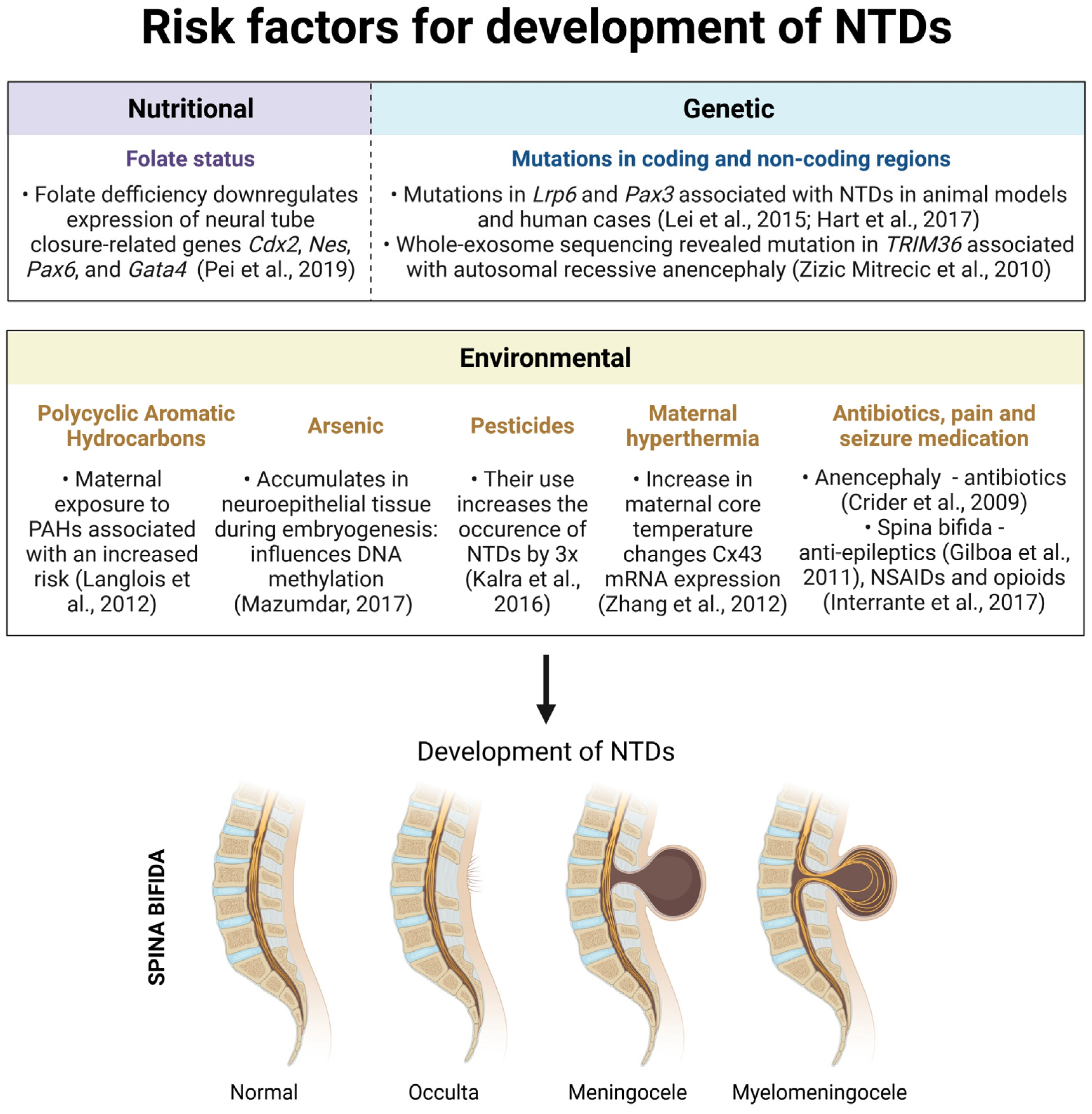
3.1. Nutritional Risk Factors
3.2. Genetic Risk Factors
3.3. Gene–Environment Interactions
3.3.1. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons
3.3.2. Arsenic
3.3.3. Pesticides
3.3.4. Maternal Hyperthermia
3.3.5. Antibiotics, Seizure and Pain Medication
4. Prevention of NTDs
4.1. Folic Acid
4.2. Inositol
5. Preventative, Management and Treatment Approaches
5.1. In Utero
5.2. Infant Care
5.3. Adult Care
6. Discussion
7. Future Perspectives
7.1. Neural Organoid Systems
7.2. Surgical Approaches
7.3. Engineered Nanomaterials and Teratogenicity
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Corsello, G.; Giuffrè, M. Congenital Malformations. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal. Med. 2012, 25 (Suppl. S1), 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abbafati, C.; Abbas, K.M.; Abbasi-Kangevari, M.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abdelalim, A.; Abdollahi, M.; Abdollahpour, I.; Abegaz, K.H.; Abolhassani, H.; Aboyans, V.; et al. Global Burden of 369 Diseases and Injuries in 204 Countries and Territories, 1990–2019: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet 2020, 396, 1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yacob, A.; Carr, C.J.; Foote, J.; Scullen, T.; Werner, C.; Mathkour, M.; Bui, C.J.; Dumont, A.S. The Global Burden of Neural Tube Defects and Disparities in Neurosurgical Care. World Neurosurg. 2021, 149, e803–e820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catala, M. Overview of Secondary Neurulation. J. Korean Neurosurg. Soc. 2021, 64, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zizic Mitrecic, M.; Mitrecic, D.; Pochet, R.; Kostovic-Knezevic, L.; Gajovic, S. The Mouse Gene Noto Is Expressed in the Tail Bud and Essential for Its Morphogenesis. Cells Tissues Organs 2010, 192, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Juriloff, D.M.; Harris, M.J. Insights into the Etiology of Mammalian Neural Tube Closure Defects from Developmental, Genetic and Evolutionary Studies. J. Dev. Biol. 2018, 6, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Avagliano, L.; Massa, V.; George, T.M.; Qureshy, S.; Bulfamante, G.P.; Finnell, R.H. Overview on Neural Tube Defects: From Development to Physical Characteristics. Birth Defects Res. 2019, 111, 1455–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnell, R.H.; Caiaffa, C.D.; Kim, S.E.; Lei, Y.; Steele, J.; Cao, X.; Tukeman, G.; Lin, Y.L.; Cabrera, R.M.; Wlodarczyk, B.J. Gene Environment Interactions in the Etiology of Neural Tube Defects. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krantz, D.A.; Hallahan, T.W.; Sherwin, J.E. Screening for Open Neural Tube Defects. Clin. Lab. Med. 2010, 30, 721–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, R.B.; Filly, R.A. Prenatal Diagnosis of Anencephaly: Spectrum of Sonographic Appearances and Distinction from the Amniotic Band Syndrome. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 1988, 151, 547–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Infant with Anencephaly. N. Engl. J. Med. 1990, 322, 669–674. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godeau, D.; Petit, A.; Richard, I.; Roquelaure, Y.; Descatha, A. Return-to-Work, Disabilities and Occupational Health in the Age of COVID-19. Scand. J. Work Environ. Health 2021, 47, 408–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sewell, M.J.; Chiu, Y.E.; Drolet, B.A. Neural Tube Dysraphism: Review of Cutaneous Markers and Imaging. Pediatr. Derm. 2015, 32, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hertzler, D.A.; DePowell, J.J.; Stevenson, C.B.; Mangano, F.T. Tethered Cord Syndrome: A Review of the Literature from Embryology to Adult Presentation. Neurosurg. Focus 2010, 29, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrzik, K.; Bailey, L.; Shane, B. Folic Acid and L-5-Methyltetrahydrofolate: Comparison of Clinical Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics. Clin. Pharm. 2010, 49, 535–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joubert, B.R.; den Dekker, H.T.; Felix, J.F.; Bohlin, J.; Ligthart, S.; Beckett, E.; Tiemeier, H.; van Meurs, J.B.; Uitterlinden, A.G.; Hofman, A.; et al. Maternal Plasma Folate Impacts Differential DNA Methylation in an Epigenome-Wide Meta-Analysis of Newborns. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Chang, S.; Wang, Z.; Wang, S.; Huo, J.; Ding, G.; Li, R.; Liu, C.; Shangguan, S.; Lu, X.; et al. Altered GNAS Imprinting Due to Folic Acid Deficiency Contributes to Poor Embryo Development and May Lead to Neural Tube Defects. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 110797–110810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pei, P.; Cheng, X.; Yu, J.; Shen, J.; Li, X.; Wu, J.; Wang, S.; Zhang, T. Folate Deficiency Induced H2A Ubiquitination to Lead to Downregulated Expression of Genes Involved in Neural Tube Defects. Epigenetics Chromatin 2019, 12, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, M.J.; Juriloff, D.M. An Update to the List of Mouse Mutants with Neural Tube Closure Defects and Advances toward a Complete Genetic Perspective of Neural Tube Closure. Birth. Defects Res. A Clin. Mol. Teratol. 2010, 88, 653–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Fathe, K.; Mccartney, D.; Zhu, H.; Yang, W.; Ross, M.E.; Shaw, G.M.; Finnell, R.H. Rare LRP6 Variants Identified in Spina Bifida Patients. Hum. Mutat 2015, 36, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hart, J.; Miriyala, K. Neural Tube Defects in Waardenburg Syndrome: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2017, 173, 2472–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, N.; Bhat, V.K.; Tiwari, A.; Kodaganur, S.G.; Tontanahal, S.J.; Sarda, A.; Malini, K.V.; Kumar, A. A Homozygous Mutation in TRIM36 Causes Autosomal Recessive Anencephaly in an Indian Family. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2017, 26, 1104–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Ren, A.; Tian, T.; Li, N.; Cao, X.; Zhang, P.; Jin, L.; Li, Z.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, B.; et al. Whole-Exome Sequencing Identifies Damaging de Novo Variants in Anencephalic Cases. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, M.; Cullup, T.; Boustred, C.; James, C.; Docker, J.; English, C.; Lench, N.; Copp, A.J.; Moore, G.E.; Greene, N.D.E.; et al. A Targeted Sequencing Panel Identifies Rare Damaging Variants in Multiple Genes in the Cranial Neural Tube Defect, Anencephaly. Clin. Genet. 2018, 93, 870–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aguiar-Pulido, V.; Wolujewicz, P.; Martinez-Fundichely, A.; Elhaik, E.; Thareja, G.; Aleem, A.A.; Chalhoub, N.; Cuykendall, T.; Al-Zamer, J.; Lei, Y.; et al. Systems Biology Analysis of Human Genomes Points to Key Pathways Conferring Spina Bifida Risk. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2106844118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Shafy, H.I.; Mansour, M.S.M. A Review on Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons: Source, Environmental Impact, Effect on Human Health and Remediation. Egypt. J. Pet. 2016, 25, 107–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, L.; Ye, R.; Pei, L.; Liu, J.; Zheng, X.; Ren, A. Indoor Air Pollution from Coal Combustion and the Risk of Neural Tube Defects in a Rural Population in Shanxi Province, China. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2011, 174, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langlois, P.H.; Hoyt, A.T.; Lupo, P.J.; Lawson, C.C.; Waters, M.A.; Desrosiers, T.A.; Shaw, G.M.; Romitti, P.A.; Lammer, E.J. Maternal Occupational Exposure to Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Risk of Neural Tube Defect-Affected Pregnancies. Birth Defects Res. A Clin. Mol. Teratol. 2012, 94, 693–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ren, A.; Qiu, X.; Jin, L.; Ma, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, H.; Finnell, R.H.; Zhu, T. Association of Selected Persistent Organic Pollutants in the Placenta with the Risk of Neural Tube Defects. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 12770–12775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, B.; Jin, L.; Ren, A.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, L.; Yi, D.; Wang, L.L.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Levels of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Maternal Serum and Risk of Neural Tube Defects in Offspring. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 588–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Lin, S.; Jin, L.; Wang, L.; Ren, A. Decreased Global DNA Hydroxymethylation in Neural Tube Defects: Association with Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons. Epigenetics 2019, 14, 1019–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.B.; Shaikh, S.; Jain, K.R.; Desai, C.; Madamwar, D. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons: Sources, Toxicity, and Remediation Approaches. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 562813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amitai, Y.; Koren, G. High Risk for Neural Tube Defects; the Role of Arsenic in Drinking Water and Rice in Asia. Med. Hypotheses 2018, 119, 88–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wlodarczyk, B.J.; Cabrera, R.M.; Hill, D.S.; Bozinov, D.; Zhu, H.; Finnell, R.H. Arsenic-Induced Gene Expression Changes in the Neural Tube of Folate Transport Defective Mouse Embryos. Neurotoxicology 2006, 27, 547–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazumdar, M. Does Arsenic Increase the Risk of Neural Tube Defects among a Highly Exposed Population? A New Case-Control Study in Bangladesh. Birth Defects Res. 2017, 109, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Z.J.; Song, G.; Cui, Y.; Xia, H.F.; Ma, X. Oxidative Stress Is Implicated in Arsenic-Induced Neural Tube Defects in Chick Embryos. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2011, 29, 673–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalat, S.L.; Walker, D.B.; Finnell, R.H. Role of Arsenic as a Reproductive Toxin with Particular Attention to Neural Tube Defects. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health 1996, 48, 253–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, F.; Guan, J.; Le, J.; Wu, L.; Zou, J.; Zhao, H.; Pei, L.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, T. Relation between Hypomethylation of Long Interspersed Nucleotide Elements and Risk of Neural Tube Defects. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 91, 1359–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kalra, S.; Dewan, P.; Batra, P.; Sharma, T.; Tyagi, V.; Banerjee, B.D. Organochlorine Pesticide Exposure in Mothers and Neural Tube Defects in Offsprings. Reprod. Toxicol. 2016, 66, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brender, J.D.; Felkner, M.; Suarez, L.; Canfield, M.A.; Henry, J.P. Maternal Pesticide Exposure and Neural Tube Defects in Mexican Americans. Ann. Epidemiol. 2010, 20, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gashaw, A.; Shine, S.; Yimer, O.; Wodaje, M. Risk Factors Associated to Neural Tube Defects among Mothers Who Gave Birth in North Shoa Zone Hospitals, Amhara Region, Ethiopia 2020: Case Control Study. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0250719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atlaw, D.; Tekalegn, Y.; Sahiledengle, B.; Seyoum, K.; Solomon, D.; Gezahegn, H.; Tariku, Z.; Tekle, Y.; Chattu, V.K. Magnitude and Determinants of Neural Tube Defect in Africa: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2021, 21, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makelarski, J.A.; Romitti, P.A.; Rocheleau, C.M.; Burns, T.L.; Stewart, P.A.; Waters, M.A.; Lawson, C.C.; Bell, E.M.; Lin, S.; Shaw, G.M.; et al. Maternal Periconceptional Occupational Pesticide Exposure and Neural Tube Defects. Birth Defects Res. A Clin. Mol. Teratol. 2014, 100, 877–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baldacci, S.; Gorini, F.; Santoro, M.; Pierini, A.; Minichilli, F.; Bianchi, F. Environmental and Individual Exposure and the Risk of Congenital Anomalies: A Review of Recent Epidemiological Evidence. Epidemiol. Prev. 2018, 42, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suarez, L.; Felkner, M.; Brender, J.D.; Canfield, M.; Zhu, H.; Hendricks, K.A. Neural Tube Defects on the Texas-Mexico Border: What We’ve Learned in the 20 Years since the Brownsville Cluster. Birth Defects Res. A Clin. Mol. Teratol. 2012, 94, 882–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sever, L.E.; Hessol, N.A.; Gilbert, E.S.; Mcintyre, J.M. The Prevalence at Birth of Congenital Malformations in Communities near the Hanford Site. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1988, 127, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, G.M.; Wasserman, C.R.; O’Malley, C.D.; Nelson, V.; Jackson, R.J. Maternal Pesticide Exposure from Multiple Sources and Selected Congenital Anomalies. Epidemiology 1999, 10, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez, L.; Hendricks, K.; Felkner, M.; Gunter, E. Maternal Serum B12 Levels and Risk for Neural Tube Defects in a Texas-Mexico Border Population. Ann. Epidemiol. 2003, 13, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balarajan, R.; Mcdowall, M. Congenital Malformations and Agricultural Workers. Lancet 1983, 1, 1112–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretti, M.E.; Bar-Oz, B.; Fried, S.; Koren, G. Maternal Hyperthermia and the Risk for Neural Tube Defects in Offspring: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Epidemiology 2005, 16, 216–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.P. Syndromes, Disorders and Maternal Risk Factors Associated with Neural Tube Defects (II). Taiwan J. Obs. Gynecol. 2008, 47, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, F.Z.; Gao, Q.; Sun, J.H.; Tian, G.P.; Gao, Y.M. Hyperthermia Induces Upregulation of Connexin43 in the Golden Hamster Neural Tube. Birth Defects Res. A Clin. Mol. Teratol. 2012, 94, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundberg, Y.W.; Wing, M.J.; Xiong, W.; Zhao, J.; Finnell, R.H. Genetic Dissection of Hyperthermia-Induced Neural Tube Defects in Mice. Birth Defects Res. A Clin. Mol. Teratol. 2003, 67, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luteijn, J.M.; Brown, M.J.; Dolk, H. Influenza and Congenital Anomalies: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Hum. Reprod. 2014, 29, 809–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Salih, M.A.; Murshid, W.R.; Seidahmed, M.Z. Epidemiology, Prenatal Management, and Prevention of Neural Tube Defects. Saudi Med. J. 2014, 35 (Suppl S1), S15–S28. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sandford, M.K.; Kissling, G.E.; Joubert, P.E. Neural Tube Defect Etiology: New Evidence Concerning Maternal Hyperthermia, Health and Diet. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 1992, 34, 661–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedgwick Harvey, M.A.; McRorie, M.M.; Smith, D.W. Suggested Limits to the Use of the Hot Tub and Sauna by Pregnant Women. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 1981, 125, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Leng, Z.; Liu, W.; Wang, X.; Yan, X.; Yu, L. Suppressed Expression of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases in Hyperthermia Induced Defective Neural Tube. Neurosci. Lett. 2015, 594, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, G.M.; Todoroff, K.; Velie, E.M.; Lammer, E.J. Maternal Illness, Including Fever and Medication Use as Risk Factors for Neural Tube Defects. Teratology 1998, 57, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milunsky, A.; Ulcickas, M.; Rothman, K.J.; Willett, W.; Jick, S.S.; Jick, H. Maternal Heat Exposure and Neural Tube Defects. JAMA 1992, 268, 882–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez, L.; Felkner, M.; Hendricks, K. The Effect of Fever, Febrile Illnesses, and Heat Exposures on the Risk of Neural Tube Defects in a Texas-Mexico Border Population. Birth Defects Res. A Clin. Mol. Teratol. 2004, 70, 815–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blakeway, H.; Prasad, S.; Kalafat, E.; Heath, P.T.; Ladhani, S.N.; le Doare, K.; Magee, L.A.; O’Brien, P.; Rezvani, A.; von Dadelszen, P.; et al. COVID-19 Vaccination during Pregnancy: Coverage and Safety. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2022, 226, 236.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimabukuro, T.T.; Kim, S.Y.; Myers, T.R.; Moro, P.L.; Oduyebo, T.; Panagiotakopoulos, L.; Marquez, P.L.; Olson, C.K.; Liu, R.; Chang, K.T.; et al. Preliminary Findings of MRNA COVID-19 Vaccine Safety in Pregnant Persons. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 2273–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trostle, M.E.; Limaye, M.A.; Avtushka, V.; Lighter, J.L.; Penfield, C.A.; Roman, A.S. COVID-19 Vaccination in Pregnancy: Early Experience from a Single Institution. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Mfm. 2021, 3, 100464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruderman, R.S.; Mormol, J.; Trawick, E.; Perry, M.F.; Allen, E.C.; Millan, D.; Miller, E.S. Association of COVID-19 Vaccination During Early Pregnancy With Risk of Congenital Fetal Anomalies. JAMA Pediatrics 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratama, N.R.; Wafa, I.A.; Budi, D.S.; Putra, M.; Wardhana, M.P.; Wungu, C.D.K. MRNA Covid-19 Vaccines in Pregnancy: A Systematic Review. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0261350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakahara, A.; Biggio, J.R.; Elmayan, A.; Williams, F.B. Safety-Related Outcomes of Novel MRNA COVID-19 Vaccines in Pregnancy. Am. J. Perinatol. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fell, D.B.; Dhinsa, T.; Alton, G.D.; Török, E.; Dimanlig-Cruz, S.; Regan, A.K.; Sprague, A.E.; Buchan, S.A.; Kwong, J.C.; Wilson, S.E.; et al. Association of COVID-19 Vaccination in Pregnancy with Adverse Peripartum Outcomes. JAMA 2022, 327, 1478–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharbanda, E.O.; Vazquez-Benitez, G. COVID-19 MRNA Vaccines During Pregnancy: New Evidence to Help Address Vaccine Hesitancy. JAMA 2022, 327, 1451–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rottenstreich, M.; Sela, H.Y.; Rotem, R.; Kadish, E.; Wiener-Well, Y.; Grisaru-Granovsky, S. COVID-19 Vaccination during the Third Trimester of Pregnancy: Rate of Vaccination and Maternal and Neonatal Outcomes, a Multicentre Retrospective Cohort Study. Int. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2022, 129, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamieson, D.J.; Rasmussen, S.A. An Update on COVID-19 and Pregnancy. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2022, 226, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joubert, E.; Kekeh, A.C.; Amin, C.N. COVID-19 and Novel MRNA Vaccines in Pregnancy: An Updated Literature Review. Int. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2022, 129, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magon, N.; Prasad, S.; Mahato, C.; Sharma, J.B. COVID-19 Vaccine and Pregnancy: A Safety Weapon against Pandemic. Taiwan J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2022, 61, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, D.G.; Wobst, H.J. A Decade of FDA-Approved Drugs (2010-2019): Trends and Future Directions. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 2312–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crider, K.S.; Cleves, M.A.; Reefhuis, J.; Berry, R.J.; Hobbs, C.A.; Hu, D.J. Antibacterial Medication Use during Pregnancy and Risk of Birth Defects: National Birth Defects Prevention Study. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 2009, 163, 978–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gilboa, S.M.; Broussard, C.S.; Devine, O.J.; Duwe, K.N.; Flak, A.L.; Boulet, S.L.; Moore, C.A.; Werler, M.M.; Honein, M.A. Influencing Clinical Practice Regarding the use of Antiepileptic Medications during Pregnancy: Modeling the Potential Impact on the Prevalences of Spina Bifida and Cleft Palate in the United States. Am. J. Med. Genet. C Semin. Med. Genet. 2011, 157C, 234–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Interrante, J.D.; Ailes, E.C.; Lind, J.N.; Anderka, M.; Feldkamp, M.L.; Werler, M.M.; Taylor, L.G.; Trinidad, J.; Gilboa, S.M.; Broussard, C.S. Risk Comparison for Prenatal Use of Analgesics and Selected Birth Defects, National Birth Defects Prevention Study 1997–2011. Ann. Epidemiol. 2017, 27, 645–653.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broussard, C.S.; Rasmussen, S.A.; Reefhuis, J.; Friedman, J.M.; Jann, M.W.; Riehle-Colarusso, T.; Honein, M.A. Maternal Treatment with Opioid Analgesics and Risk for Birth Defects. Am. J. Obs. Gynecol. 2011, 204, 314.e1–314.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdy, M.M.; Mitchell, A.A.; Tinker, S.C.; Parker, S.E.; Werler, M.M. Periconceptional Use of Opioids and the Risk of Neural Tube Defects. Obs. Gynecol. 2013, 122, 838–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wald, N.; Sneddon, J.; Densem, J.; Frost, C.; Stone, R. Prevention of Neural Tube Defects: Results of the Medical Research Council Vitamin Study. Lancet 1991, 338, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.; Mai, C.T.; Mulinare, J.; Isenburg, J.; Flood, T.J.; Ethen, M.; Frohnert, B.; Kirby, R.S.; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Updated Estimates of Neural Tube Defects Prevented by Mandatory Folic Acid Fortification—United States, 1995–2011. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2015, 64, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Chitayat, D.; Matsui, D.; Amitai, Y.; Kennedy, D.; Vohra, S.; Rieder, M.; Koren, G. Folic Acid Supplementation for Pregnant Women and Those Planning Pregnancy: 2015 Update. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2016, 56, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Wals, P.; Tairou, F.; van Allen, M.I.; Uh, S.-H.; Lowry, R.B.; Sibbald, B.; Evans, J.A.; van den Hof, M.C.; Zimmer, P.; Crowley, M.; et al. Reduction in Neural-Tube Defects after Folic Acid Fortification in Canada. N. Engl. J Med 2007, 357, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sudiwala, S.; Palmer, A.; Massa, V.; Burns, A.J.; Dunlevy, L.P.E.; de Castro, S.C.P.S.C.P.; Savery, D.; Leung, K.Y.; Copp, A.J.; Greene, N.D.E. Cellular Mechanisms Underlying Pax3- Related Neural Tube Defects and Their Prevention by Folic Acid. Dis. Model Mech. 2019, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martinez Barbera, J.P.; Rodriguez, T.A.; Greene, N.D.E.; Weninger, W.J.; Simeone, A.; Copp, A.J.; Beddington, R.S.P.; Dunwoodie, S. Folic Acid Prevents Exencephaly in Cited2 Deficient Mice. Hum. Mol. Genet 2002, 11, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fleming, A.; Copp, A.J. Embryonic Folate Metabolism and Mouse Neural Tube Defects. Science 1998, 280, 2107–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carter, M.; Chen, X.; Slowinska, B.; Minnerath, S.; Glickstein, S.; Shi, L.; Campagne, F.; Weinstein, H.; Ross, M.E. Crooked Tail (Cd) Model of Human Folate-Responsive Neural Tube Defects Is Mutated in Wnt Coreceptor Lipoprotein Receptor-Related Protein 6. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 12843–12848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Straaten, H.W.M.; Copp, A.J. Curly Tail: A 50-Year History of the Mouse Spina Bifida Model. Anat. Embryol. 2001, 203, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Castro, S.C.P.; Leung, K.Y.; Savery, D.; Burren, K.; Rozen, R.; Copp, A.J.; Greene, N.D.E. Neural Tube Defects Induced by Folate Deficiency in Mutant Curly Tail (Grhl3) Embryos Are Associated with Alteration in Folate One-Carbon Metabolism but Are Unlikely to Result from Diminished Methylation. Birth Defects Res. A Clin. Mol. Teratol. 2010, 88, 612–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burren, K.A.; Scott, J.M.; Copp, A.J.; Greene, N.D.E. The Genetic Background of the Curly Tail Strain Confers Susceptibility to Folate-Deficiency-Induced Exencephaly. Birth Defects Res. A Clin. Mol. Teratol. 2010, 88, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilson, R.D.; O’Connor, D.L. Maternal Folic Acid and Multivitamin Supplementation: International Clinical Evidence with Considerations for the Prevention of Folate-Sensitive Birth Defects. Prev. Med. Rep. 2021, 24, 101617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, M.; Stronati, M.; Lanari, M. Mediterranean Diet, Folic Acid, and Neural Tube Defects. Ital. J. Pediatrics 2017, 43, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carmichael, S.L.; Yang, W.; Feldkamp, M.L.; Munger, R.G.; Siega-Riz, A.M.; Botto, L.D.; Shaw, G. Higher Diet Quality Reduces Risks of Neural Tube Defects and Orofacial Clefts. Arch Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 2012, 166, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lecorguillé, M.; Teo, S.; Phillips, C.M. Maternal Dietary Quality and Dietary Inflammation Associations with Offspring Growth, Placental Development, and DNA Methylation. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, N.D.E.; Leung, K.Y.; Copp, A.J. Inositol, Neural Tube Closure and the Prevention of Neural Tube Defects. Birth Defects Res. 2017, 109, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cockroft, D.L.; Brook, F.A.; Copp, A.J. Inositol Deficiency Increases the Susceptibility to Neural Tube Defects of Genetically Predisposed (Curly Tail) Mouse Embryos in Vitro. Teratology 1992, 45, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.Y.; Wong, M.M.H.; Pang, S.S.H.; Lo, K.K.H. Dietary Supplementation for Gestational Diabetes Prevention and Management: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2021, 303, 1381–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celentano, C.; Matarrelli, B.; Pavone, G.; Vitacolonna, E.; Mattei, P.A.; Berghella, V.; Liberati, M. The Influence of Different Inositol Stereoisomers Supplementation in Pregnancy on Maternal Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Fetal Outcomes in High-Risk Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Matern.-Fetal Neonatal. Med. 2020, 33, 743–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitagliano, A.; Saccone, G.; Cosmi, E.; Visentin, S.; Dessole, F.; Ambrosini, G.; Berghella, V. Inositol for the Prevention of Gestational Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Arch. Gynecol. Obs. 2019, 299, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalli, P.; Tonni, G.; Grosso, E.; Poggiani, C. Effects of Inositol Supplementation in a Cohort of Mothers at Risk of Producing an NTD Pregnancy. Birth Defects Res. A Clin. Mol. Teratol. 2011, 91, 962–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noventa, M.; Vitagliano, A.; Quaranta, M.; Borgato, S.; Abdulrahim, B.; Gizzo, S. Preventive and Therapeutic Role of Dietary Inositol Supplementation in Periconceptional Period and During Pregnancy: A Summary of Evidences and Future Applications. Reprod. Sci. 2016, 23, 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dell’Edera, D.; Sarlo, F.; Allegretti, A.; Epifania, A.A.; Simone, F.; Lupo, M.G.; Benedetto, M.; D’Apice, M.R.; Capalbo, A. Prevention of Neural Tube Defects and Maternal Gestational Diabetes through the Inositol Supplementation: Preliminary Results. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 21, 3305–3311. [Google Scholar]
- Russo, M.; Forte, G.; Oliva, M.M.; Laganà, A.S.; Unfer, V. Melatonin and Myo-Inositol: Supporting Reproduction from the Oocyte to Birth. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Souza, S.W.; Copp, A.J.; Greene, N.D.E.; Glazier, J.D. Maternal Inositol Status and Neural Tube Defects: A Role for the Human Yolk Sac in Embryonic Inositol Delivery? Adv. Nutr. 2021, 12, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinicola, S.; Unfer, V.; Facchinetti, F.; Soulage, C.O.; Greene, N.D.; Bizzarri, M.; Laganà, A.S.; Chan, S.Y.; Bevilacqua, A.; Pkhaladze, L.; et al. Inositols: From Established Knowledge to Novel Approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, C.N.; Mennuti, M.T. Fetal Neural Tube Defects: Diagnosis, Management, and Treatment; The Foundation for The Global Library of Women’s Medicine: Carlisle, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Moldenhauer, J.S.; Adzick, N.S. Fetal Surgery for Myelomeningocele: After the Management of Myelomeningocele Study (MOMS). Semin. Fetal Neonatal. Med. 2017, 22, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adzick, N.S.; Thom, E.A.; Spong, C.Y.; Brock, J.W.; Burrows, P.K.; Johnson, M.P.; Howell, L.J.; Farrell, J.A.; Dabrowiak, M.E.; Sutton, L.N.; et al. A Randomized Trial of Prenatal versus Postnatal Repair of Myelomeningocele. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 993–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sim, K.B.; Cho, B.K.; Lee, Y.J.; Lee, M.S.; Wang, K.C. Chronological Changes of Re-Closure Capacity in Surgically Induced Spinal Open Neural Tube Defects of Chick Embryos. Neurosci. Lett. 2000, 292, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H.; Eun, Y.K.; Park, S.; Ji, H.P.; Kim, S.K.; Cho, B.K.; Lim, J.; Wang, K.C. Reclosure of Surgically Induced Spinal Open Neural Tube Defects by the Intraamniotic Injection of Human Embryonic Stem Cells in Chick Embryos 24 Hours after Lesion Induction. J. Neurosurg. 2006, 105, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauza, D.O.; Jennings, R.W.; Teng, Y.D.; Snyder, E.Y. Neural Stem Cell Delivery to the Spinal Cord in an Ovine Model of Fetal Surgery for Spina Bifida. Surgery 2008, 144, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volarevic, V.; Markovic, B.S.; Gazdic, M.; Volarevic, A.; Jovicic, N.; Arsenijevic, N.; Armstrong, L.; Djonov, V.; Lako, M.; Stojkovic, M. Ethical and Safety Issues of Stem Cell-Based Therapy. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 15, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gupta, D.K.; Sharma, S.; Venugopal, P.; Kumar, L.; Mohanty, S.; Dattagupta, S. Stem Cells as a Therapeutic Modality in Pediatric Malformations. Transpl. Proc. 2007, 39, 700–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhaulakhandi, D.B.; Rohilla, S.; Rattan, K.N. Neural Tube Defects: Review of Experimental Evidence on Stem Cell Therapy and Newer Treatment Options. Fetal Diagn. Ther. 2010, 28, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitrecic, D.; Nicaise, C.; Klimaschewski, L.; Gajovic, S.; Bohl, D.; Pochet, R. Genetically Modified Stem Cells for the Treatment of Neurological Diseases. Front. Biosci. (Elite Ed.) 2012, 4, 1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrečić, D. Current Advances in Intravascular Administration of Stem Cells for Neurological Diseases: A New Dose of Rejuvenation Injected. Rejuvenation. Res. 2011, 14, 553–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godzik, J.; Ravindra, V.M.; Ray, W.Z.; Eskandari, R.; Dailey, A.T. Primary Repair of Open Neural Tube Defect in Adulthood: Case Example and Review of Management Strategies. Spine J. 2015, 15, e57–e63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fofou-Caillierez, M.B.; Guéant-Rodriguez, R.M.; Alberto, J.M.; Chéry, C.; Josse, T.; Gérard, P.; Forges, T.; Foliguet, B.; Feillet, F.; Guéant, J.L. Vitamin B-12 and Liver Activity and Expression of Methionine Synthase Are Decreased in Fetuses with Neural Tube Defects. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 109, 674–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayaz, R.; Asoglu, M.R. Neural Tube Defects in Eastern Turkey; Is Low Folate Status or Vitamin B12 Deficiency or Both Associated with a High Rate of NTDs? J. Matern. Fetal. Neonatal. Med. 2020, 33, 3835–3840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senousy, S.M.; Farag, M.K.; Gouda, A.S.; el Noury, M.A.; Dabbous, O.A.; Gaber, K.R. Association between Biomarkers of Vitamin B12 Status and the Risk of Neural Tube Defects. J. Obs. Gynaecol. Res. 2018, 44, 1902–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molloy, A.M. Should Vitamin B 12 Status Be Considered in Assessing Risk of Neural Tube Defects? Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2018, 1414, 109–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murphy, M.E.; Westmark, C.J. Folic Acid Fortification and Neural Tube Defect Risk: Analysis of the Food Fortification Initiative Dataset. Nutrients 2020, 12, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kancherla, V.; Pachón, H.; Blencowe, H.; Martinez, H.; Oakley, G.P.; Berry, R.J. The Fallacy of Using Administrative Data in Assessing the Effectiveness of Food Fortification. Comment on: “Folic Acid Fortification and Neural Tube Defect Risk: Analysis of the Food Fortification Initiative Dataset. Nutrients 2020, 12, 247”. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westmark, C.J.; Murphy, M.E. Reply to “The Fallacy of Using Administrative Data in Assessing the Effectiveness of Food Fortification. Comment on: Folic Acid Fortification and Neural Tube Defect Risk: Analysis of the Food Fortification Initiative Dataset. Nutrients 2020, 12, 247”. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, H.; Walker, N. Current Levels of Coverage of Iron and Folic Acid Fortification Are Insufficient to Meet the Recommended Intake for Women of Reproductive Age in Low- and Middle-Income Countries. J. Glob. Health 2021, 11, 18002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kehoe, L.; Walton, J.; Hopkins, S.M.; McNulty, B.A.; Nugent, A.P.; Flynn, A. Modelling the Impact of Mandatory Folic Acid Fortification of Bread or Flour in Ireland on the Risk of Occurrence of NTD-Affected Pregnancies in Women of Childbearing Age and on Risk of Masking Vitamin B 12 Deficiency in Older Adults. Eur. J. Nutr. 2020, 59, 2631–2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herter-Aeberli, I.; Wehrli, N.; Bärlocher, K.; Andersson, M.; Sych, J. Inadequate Status and Low Awareness of Folate in Switzerland-A Call to Strengthen Public Health Measures to Ensure Sufficient Intakes. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caceres, A.; Blount, J.P.; Messing-Jünger, M.; Chatterjee, S.; Fieggen, G.; Salomao, J.F. The International Society for Pediatric Neurosurgery Resolution on Mandatory Folic Acid Fortification of Staple Foods for Prevention of Spina Bifida and Anencephaly and Associated Disability and Child Mortality. Child’s Nervous System 2021, 37, 1809–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kancherla, V.; Wagh, K.; Pachón, H.; Oakley, G.P. A 2019 Global Update on Folic Acid-Preventable Spina Bifida and Anencephaly. Birth Defects Res. 2021, 113, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, H.; Pachón, H.; Kancherla, V.; Oakley, G.P. Food Fortification With Folic Acid for Prevention of Spina Bifida and Anencephaly: The Need for a Paradigm Shift in Evidence Evaluation for Policy-Making. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2021, 190, 1972–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wald, N.J.; Hoffbrand, A.V. Mandatory UK Folic Acid Fortification. Lancet 2021, 398, 1961–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGowan, E.C.; Hong, X.; Selhub, J.; Paul, L.; Wood, R.A.; Matsui, E.C.; Keet, C.A.; Wang, X. Association Between Folate Metabolites and the Development of Food Allergy in Children. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pr. 2020, 8, 132–140.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pentieva, K.; Selhub, J.; Paul, L.; Molloy, A.M.; McNulty, B.; Ward, M.; Marshall, B.; Dornan, J.; Reilly, R.; Parle-McDermott, A.; et al. Evidence from a Randomized Trial That Exposure to Supplemental Folic Acid at Recommended Levels during Pregnancy Does Not Lead to Increased Unmetabolized Folic Acid Concentrations in Maternal or Cord Blood. J. Nutr. 2016, 146, 494–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paniz, C.; Bertinato, J.F.; Lucena, M.R.; de Carli, E.; da Silva Amorim, P.M.; Gomes, G.W.; Palchetti, C.Z.; Figueiredo, M.S.; Pfeiffer, C.M.; Fazili, Z.; et al. A Daily Dose of 5 Mg Folic Acid for 90 Days Is Associated with Increased Serum Unmetabolized Folic Acid and Reduced Natural Killer Cell Cytotoxicity in Healthy Brazilian Adults. J. Nutr. 2017, 147, 1677–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Best, K.P.; Green, T.J.; Sulistyoningrum, D.C.; Sullivan, T.R.; Aufreiter, S.; Prescott, S.L.; Makrides, M.; Skubisz, M.; O’connor, D.L.; Palmer, D.J. Maternal Late-Pregnancy Serum Unmetabolized Folic Acid Concentrations Are Not Associated with Infant Allergic Disease: A Prospective Cohort Study. J. Nutr. 2021, 151, 1553–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molloy, A.M.; Mills, J.L. Folic Acid and Infant Allergy: Avoiding Rash Judgments. J. Nutr. 2021, 151, 1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molloy, J.; Collier, F.; Saffery, R.; Allen, K.J.; Koplin, J.J.; Louise Ponsonby, A.; Tang, M.L.K.; Ward, A.C.; Martino, D.; Burgner, D.; et al. Folate Levels in Pregnancy and Offspring Food Allergy and Eczema. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2020, 31, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezo, Y.; Elder, K.; Clement, A.; Clement, P. Folic Acid, Folinic Acid, 5 Methyl TetraHydroFolate Supplementation for Mutations That Affect Epigenesis through the Folate and One-Carbon Cycles. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.R.; Sobczyńska-Malefora, A. The Adverse Effects of an Excessive Folic Acid Intake. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 71, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selhub, J.; Rosenberg, I.H. Excessive Folic Acid Intake and Relation to Adverse Health Outcome. Biochimie 2016, 126, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orjuela, M.A.; Cabrera-Muñoz, L.; Paul, L.; Ramirez-Ortiz, M.A.; Liu, X.; Chen, J.; Mejia-Rodriguez, F.; Medina-Sanson, A.; Diaz-Carreño, S.; Suen, I.H.; et al. Risk of Retinoblastoma Is Associated with a Maternal Polymorphism in Dihydrofolatereductase (DHFR) and Prenatal Folic Acid Intake. Cancer 2012, 118, 5912–5919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Philip, D.; Buch, A.; Moorthy, D.; Scott, T.M.; Parnell, L.D.; Lai, C.Q.; Ordovás, J.M.; Selhub, J.; Rosenberg, I.H.; Tucker, K.L.; et al. Dihydrofolate Reductase 19-Bp Deletion Polymorphism Modifies the Association of Folate Status with Memory in a Cross-Sectional Multi-Ethnic Study of Adults. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 102, 1279–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kubo, Y.; Fukuoka, H.; Kawabata, T.; Shoji, K.; Mori, C.; Sakurai, K.; Nishikawa, M.; Ohkubo, T.; Oshida, K.; Yanagisawa, N.; et al. Distribution of 5-Methyltetrahydrofolate and Folic Acid Levels in Maternal and Cord Blood Serum: Longitudinal Evaluation of Japanese Pregnant Women. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrazzi, E.; Tiso, G.; di Martino, D. Folic Acid versus 5- Methyl Tetrahydrofolate Supplementation in Pregnancy. Eur. J. Obs. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2020, 253, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, Y.; Finnell, R.H. New Techniques for the Study of Neural Tube Defects. Adv. Tech. Biol. Med. 2016, 4, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, S.E.; Georgescu, A.; Huh, D. Organoids-on-a-Chip. Science 2019, 364, 960–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rifes, P.; Isaksson, M.; Rathore, G.S.; Aldrin-Kirk, P.; Møller, O.K.; Barzaghi, G.; Lee, J.; Egerod, K.L.; Rausch, D.M.; Parmar, M.; et al. Modeling Neural Tube Development by Differentiation of Human Embryonic Stem Cells in a Microfluidic WNT Gradient. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 1265–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinhardt, A.; Eberle, D.; Tazaki, A.; Ranga, A.; Niesche, M.; Wilsch-Bräuninger, M.; Stec, A.; Schackert, G.; Lutolf, M.; Tanaka, E.M. 3D Reconstitution of the Patterned Neural Tube from Embryonic Stem Cells. Stem Cell Rep. 2014, 3, 987–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, Y.; Peng, S.; Finnell, R.H.; Zheng, Y. Organoids as a New Model System to Study Neural Tube Defects. FASEB J. 2021, 35, e21545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnard, C.; Navaratnam, N.; Ghosh, K.; Chan, P.W.; Tan, T.T.; Pomp, O.; Yu Jin Ng, A.; Tohari, S.; Changede, R.; Carling, D.; et al. A Loss-of-Function NUAK2 Mutation in Humans Causes Anencephaly Due to Impaired Hippo-YAP Signaling. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 217, e20191561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roll, L.; Lessmann, K.; Brüstle, O.; Faissner, A. Cerebral Organoids Maintain the Expression of Neural Stem Cell-Associated Glycoepitopes and Extracellular Matrix. Cells 2022, 11, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Tian, T.; Steele, J.W.; Cabrera, R.M.; Aguiar-Pulido, V.; Wadhwa, S.; Bhavani, N.; Bi, P.; Gargurevich, N.H.; Hoffman, E.N.; et al. Loss of RAD9B Impairs Early Neural Development and Contributes to the Risk for Human Spina Bifida. Hum. Mutat. 2020, 41, 786–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libby, A.R.G.; Joy, D.A.; Elder, N.H.; Bulger, E.A.; Krakora, M.Z.; Gaylord, E.A.; Mendoza-Camacho, F.; Butts, J.C.; McDevitt, T.C. Axial Elongation of Caudalized Human Organoids Mimics Aspects of Neural Tube Development. Development 2021, 148, dev198275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.-H.; Shin, H.; Shaker, M.R.; Kim, H.J.; Park, S.-H.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, N.; Kang, M.; Cho, S.; Kwak, T.H.; et al. Production of Human Spinal-Cord Organoids Recapitulating Neural-Tube Morphogenesis. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troesch, B.; Demmelmair, J.; Gimpfl, M.; Hecht, C.; Lakovic, G.; Roehle, R.; Sipka, L.; Trisic, B.; Vusurovic, M.; Schoop, R.; et al. Suitability and Safety of L-5-Methyltetrahydrofolate as a Folate Source in Infant Formula: A Randomized-Controlled Trial. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eibach, S.; Moes, G.; Hou, Y.J.; Zovickian, J.; Pang, D. New Surgical Paradigm for Open Neural Tube Defects. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2021, 37, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ema, M.; Okuda, H.; Gamo, M.; Honda, K. A Review of Reproductive and Developmental Toxicity of Silver Nanoparticles in Laboratory Animals. Reprod. Toxicol. 2017, 67, 149–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ema, M.; Hougaard, K.S.; Kishimoto, A.; Honda, K. Reproductive and Developmental Toxicity of Carbon-Based Nanomaterials: A Literature Review. Nanotoxicology 2016, 10, 391–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ema, M.; Gamo, M.; Honda, K. Developmental Toxicity of Engineered Nanomaterials in Rodents. Toxicol. Appl. Pharm. 2016, 299, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavičić, I.; Milić, M.; Pongrac, I.M.; Brkić Ahmed, L.; Matijević Glavan, T.; Ilić, K.; Zapletal, E.; Ćurlin, M.; Mitrečić, D.; Vinković Vrček, I. Neurotoxicity of Silver Nanoparticles Stabilized with Different Coating Agents: In Vitro Response of Neuronal Precursor Cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 136, 110935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, Q.Q.; Hong, Y. Global Gene Expression Signatures in Response to Citrate-Coated Silver Nanoparticles Exposure. Toxicology 2021, 461, 152898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.J.; Son, J.M.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, I.C.; Baek, H.S.; Shin, I.S.; Moon, C.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, J.C. Effects of Silver Nanoparticles on Pregnant Dams and Embryo-Fetal Development in Rats. Nanotoxicology 2014, 8 (Suppl. S1), 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Austin, C.A.; Umbreit, T.H.; Brown, K.M.; Barber, D.S.; Dair, B.J.; Francke-Carroll, S.; Feswick, A.; Saint-Louis, M.A.; Hikawa, H.; Siebein, K.N.; et al. Distribution of Silver Nanoparticles in Pregnant Mice and Developing Embryos. Nanotoxicology 2012, 6, 912–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Austin, C.A.; Hinkley, G.K.; Mishra, A.R.; Zhang, Q.; Umbreit, T.H.; Betz, M.W.; Wildt, B.E.; Casey, B.J.; Francke-Carroll, S.; Hussain, S.M.; et al. Distribution and Accumulation of 10 Nm Silver Nanoparticles in Maternal Tissues and Visceral Yolk Sac of Pregnant Mice, and a Potential Effect on Embryo Growth. Nanotoxicology 2016, 10, 654–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Isaković, J.; Šimunić, I.; Jagečić, D.; Hribljan, V.; Mitrečić, D. Overview of Neural Tube Defects: Gene–Environment Interactions, Preventative Approaches and Future Perspectives. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 965. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10050965
Isaković J, Šimunić I, Jagečić D, Hribljan V, Mitrečić D. Overview of Neural Tube Defects: Gene–Environment Interactions, Preventative Approaches and Future Perspectives. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(5):965. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10050965
Chicago/Turabian StyleIsaković, Jasmina, Iva Šimunić, Denis Jagečić, Valentina Hribljan, and Dinko Mitrečić. 2022. "Overview of Neural Tube Defects: Gene–Environment Interactions, Preventative Approaches and Future Perspectives" Biomedicines 10, no. 5: 965. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10050965
APA StyleIsaković, J., Šimunić, I., Jagečić, D., Hribljan, V., & Mitrečić, D. (2022). Overview of Neural Tube Defects: Gene–Environment Interactions, Preventative Approaches and Future Perspectives. Biomedicines, 10(5), 965. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10050965