Neuronal and Neuroaxonal Damage Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarkers in Autoimmune Encephalitis Associated or Not with the Presence of Tumor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Diagnostic Evaluation
2.3. CSF Measurements
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
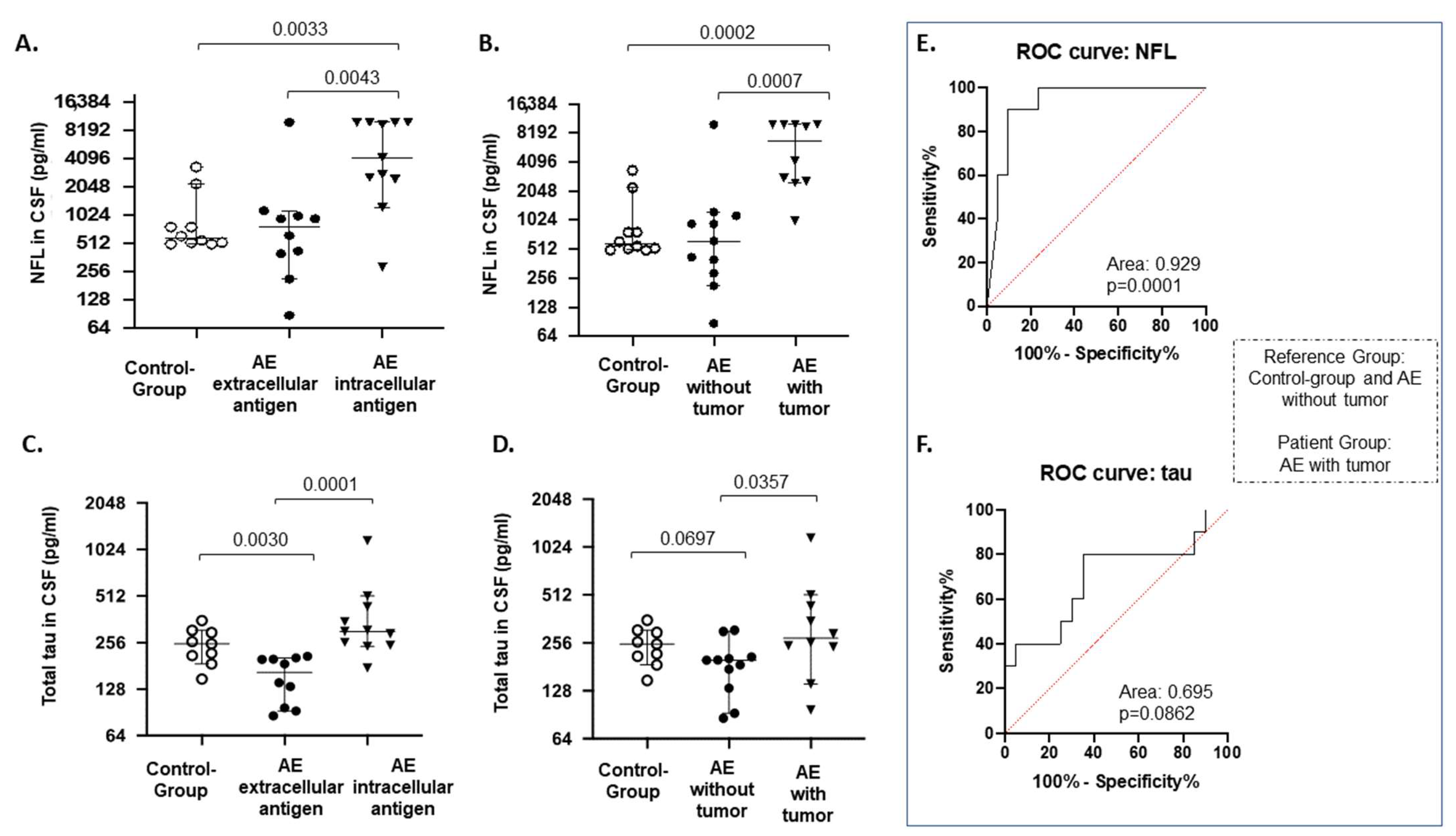
3.2. CSF Brain Damage Markers
3.3. Correlation of CSF Brain Damage Markers with Various Clinical and Radiological Parameters
3.4. Brain MRI
3.5. Presence of Tumor
3.6. ROC Curve Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Major Findings
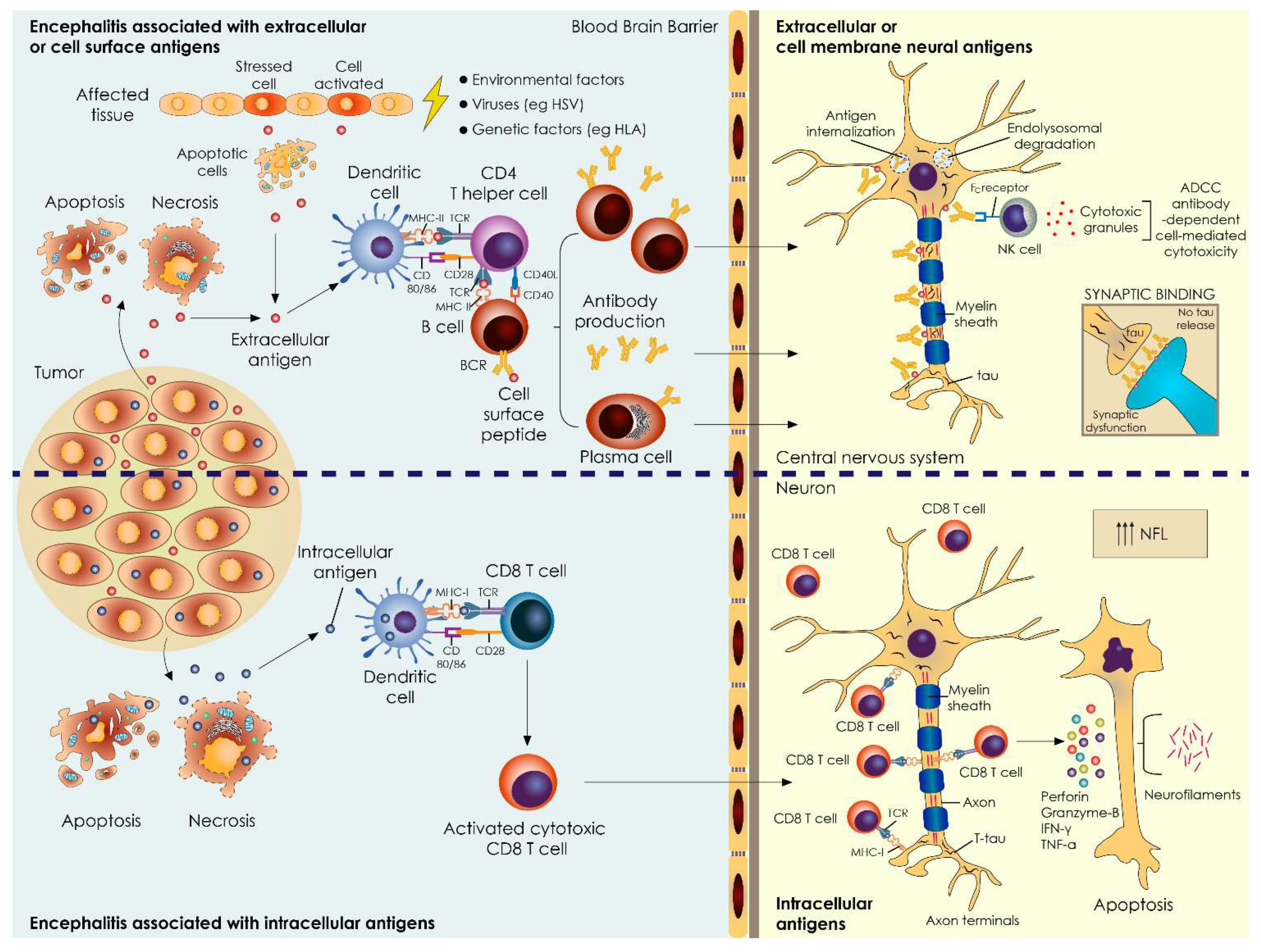
4.2. Total Tau Levels in AE Associated with Extracellular Antigens—Minor Changes
4.3. NFL Levels in AE Associated with Intracellular/Synaptic Antigens Correlate with Disease Severity and Coexistence of Tumors
4.4. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Granerod, J.; Ambrose, H.E.; Davies, N.W.; Clewley, J.P.; Walsh, A.L.; Morgan, D.; Cunningham, R.; Zuckerman, M.; Mutton, K.J.; Solomon, T.; et al. Causes of encephalitis and differences in their clinical presentations in England: A multicentre, population-based prospective study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2010, 10, 835–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dalmau, J.; Geis, C.; Graus, F. Autoantibodies to synaptic receptors and neuronal cell surface proteins in autoimmune diseases of the central nervous system. Physiol. Rev. 2017, 97, 839–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raspotnig, M.; Vedeler, C.A.; Storstein, A. Onconeural antibodies in patients with neurological symptoms: Detection and clinical significance. Acta Neurol. Scand. Suppl. 2011, 191, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rössling, R.; Prüss, H. SOP: Antibody-associated autoimmune encephalitis. Neurol. Res. Pract. 2020, 2, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Constantinescu, R.; Krýsl, D.; Andrén, K.; Asztély, F.; Bergquist, F.; Zetterberg, H.; Andreasson, U.; Axelsson, M.; Menachem, E.B.; Jons, D.; et al. Cerebrospinal fluid markers of neuronal and glial cell damage in patients with autoimmune neurologic syndromes with and without underlying malignancies. J. Neuroimmunol. 2017, 306, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Constantinescu, R.; Krýsl, D.; Bergquist, F.; Andrén, K.; Malmeström, C.; Asztély, F.; Axelsson, M.; Menachem, E.B.; Blennow, K.; Rosengren, L.; et al. Cerebrospinal fluid markers of neuronal and glial cell damage to monitor disease activity and predict long-term outcome in patients with autoimmune encephalitis. Eur. J. Neurol. 2016, 23, 796–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Lee, E.J.; Kim, S.; Choi, L.K.; Kim, K.; Kim, H.W.; Kim, K.K.; Lim, Y.M. Serum biomarkers in myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein antibody-associated disease. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 7, e708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kapaki, E.; Paraskevas, G.P.; Michalopoulou, M.; Kilidireas, K. Increased cerebrospinal fluid tau protein in multiple sclerosis. Eur. Neurol. 2000, 43, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momtazmanesh, S.; Shobeiri, P.; Saghazadeh, A.; Teunissen, C.E.; Burman, J.; Szalardy, L.; Klivenyi, P.; Bartos, A.; Fernandes, A.; Rezaei, N. Neuronal and glial CSF biomarkers in multiple sclerosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Rev. Neurosci. 2021, 32, 573–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graus, F.; Titulaer, M.J.; Balu, R.; Benseler, S.; Bien, C.G.; Cellucci, T.; Cortese, I.; Dale, R.C.; Gelfand, J.M.; Geschwind, M.; et al. A clinical approach to diagnosis of autoimmune encephalitis. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 15, 391–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Del Campo, M.; Mollenhauer, B.; Bertolotto, A.; Engelborghs, S.; Hampel, H.; Simonsen, A.H.; Kapaki, E.; Kruse, N.; Le Bastard, N.; Lehmann, S.; et al. Recommendations to standardize preanalytical confounding factors in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers: An update. Biomark Med. 2012, 6, 419–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalmau, J.; Graus, F. Antibody-mediated encephalitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 840–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zuliani, L.; Graus, F.; Giometto, B.; Bien, C.; Vincent, A. Central nervous system neuronal surface antibody associated syndromes: Review and guidelines for recognition. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2012, 83, 638–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fagan, A.M.; Roe, C.M.; Xiong, C.; Mintun, M.A.; Morris, J.C.; Holtzman, D.M. Cerebrospinal fluid tau/beta-amyloid(42) ratio as a prediction of cognitive decline in nondemented older adults. Arch. Neurol. 2007, 64, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatoon, S.; Grundke-Iqbal, I.; Iqbal, K. Levels of normal and abnormally phosphorylated tau in different cellular and regional compartments of Alzheimer disease and control brains. FEBS Lett. 1994, 351, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mondragón-Rodríguez, S.; Trillaud-Doppia, E.; Dudilot, A.; Bourgeois, C.; Lauzon, M.; Leclerc, N.; Boehm, J. Interaction of endogenous tau protein with synaptic proteins is regulated by N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor-dependent tau phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 32040–32053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sotiropoulos, I.; Galas, M.C.; Silva, J.M.; Skoulakis, E.; Wegmann, S.; Maina, M.B.; Blum, D.; Sayas, C.L.; Mandelkow, E.M.; Mandelkow, E.; et al. Atypical, non-standard functions of the microtubule associated Tau protein. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2017, 5, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Melzer, N.; Meuth, S.G.; Wiendl, H. Paraneoplastic and non-paraneoplastic autoimmunity to neurons in the central nervous system. J. Neurol. 2013, 260, 1215–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Day, G.S.; Yarbrough, M.Y.; Körtvelyessy, P.; Prüss, H.; Bucelli, R.C.; Fritzler, M.J.; Mason, W.; Tang-Wai, D.F.; Steriade, C.; Hébert, J.; et al. Prospective quantification of CSF biomarkers in antibody-mediated encephalitis. Neurology 2021, 96, e2546–e2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Körtvelyessy, P.; Prüss, H.; Thurner, L.; Maetzler, W.; Vittore-Welliong, D.; Schultze-Amberger, J.; Heinze, H.J.; Reinhold, D.; Leypoldt, F.; Schreiber, S.; et al. Biomarkers of neurodegeneration in autoimmune-mediated encephalitis. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saiz, A.; Blanco, Y.; Sabater, L.; González, F.; Bataller, L.; Casamitjana, R.; Ramió-Torrentà, L.; Graus, F. Spectrum of neurological syndromes associated with glutamic acid decarboxylase antibodies: Diagnostic clues for this association. Brain 2008, 131, 2553–2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosenfeld, M.R.; Titulaer, M.J.; Dalmau, J. Paraneoplastic syndromes and autoimmune encephalitis: Five new things. Neurol. Clin. Pract. 2012, 2, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khalil, M.; Teunissen, C.E.; Otto, M.; Piehl, F.; Sormani, M.P.; Gattringer, T.; Barro, C.; Kappos, L.; Comabella, M.; Fazekas, F.; et al. Neurofilaments as biomarkers in neurological disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2018, 14, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronald, T.; National Institute on Aging Working Group. Consensus report of the Working Group on: “Molecular and Biochemical Markers of Alzheimer’s Disease”. The Ronald and Nancy Reagan Research Institute of the Alzheimer’s Association and the National Institute on Aging Working Group. Neurobiol. Aging 1998, 19, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariotto, S.; Gajofatto, A.; Zuliani, L.; Zoccarato, M.; Gastaldi, M.; Franciotta, D.; Cantalupo, G.; Piardi, F.; Polo, A.; Alberti, D.; et al. Serum and CSF neurofilament light chain levels in antibody-mediated encephalitis. J. Neurol. 2019, 266, 1643–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridel, C.; van Wieringen, W.N.; Zetterberg, H.; Tijms, B.M.; Teunissen, C.E.; Alvarez-Cermeño, J.C.; Andreasson, U.; Axelsson, M.; Bäckström, D.C.; Bartos, A.; et al. Diagnostic value of cerebrospinal fluid neurofilament light protein in Neurology: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Neurol. 2019, 76, 1035–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Demographics | |
|---|---|
| Patients, number | 21 |
| Age at disease onset, median (years) | 67 |
| Female, n (%) | 12 (57.1) |
| Antibody status, n (%) | |
| Intracellular/synaptic antigens, n = 11 | |
| Yo | 2 (9.52) |
| Ma2 | 1 (4.76) |
| CV2/CRMP5 | 1 (4.76) |
| CV2/CRMP5 and Yo | 1 (4.76) |
| CV2/CRMP5 and Hu | 2 (9.52) |
| Zic4 | 1 (4.76) |
| GAD | 2 (9.52) |
| Amphiphysin | 1 (4.76) |
| Neuronal cell surface antigens, n = 10 | |
| NMDAR | 4 (19.05) |
| Caspr2 | 2 (9.52) |
| GABAb-R | 1 (4.76) |
| Antibody detection, n (%) | |
| Serum only | 19 (90.48) |
| CSF only | 2 (9.52) |
| Both serum and CSF | 8 (38.1) |
| Clinical presentation/symptoms, n (%) | |
| Cognitive decline | 14 (66.67) |
| Memory deficits | 13 (61.9) |
| Spatial disorientation | 9 (42.86) |
| Altered level of consciousness | 2 (9.52) |
| Change in behaviour | 8 (38.1) |
| Psychiatric symptoms | 12 (57.14) |
| Dysarthria | 4 (19.05) |
| Seizures | 7 (33.33) |
| Peripheral nerve involvement (sensory and/or motor neuropathy) | 4 (19.05) |
| Selected clinical signs, n (%) | |
| Autonomic dysfunction | 6 (28.57) |
| Parkinsonism | 7 (33.33) |
| Dystonia | 4 (19.05) |
| Cerebellar ataxia | 9 (42.86) |
| Orofacial and limb dyskinesia | 2 (9.52) |
| Ocular flatter | 1 (4.76) |
| Opsoclonus | 1 (4.76) |
| Acquired hyperekplexia | 2 (9.52) |
| Tumor association | |
| Tumor type, total n = 10, n (% of total tumors) | |
| Nasopharynx cancer | 1 (10) |
| Mediastinal | 1 (10) |
| Lung cancer | 4 (40) |
| Ovarian | 2 (20) |
| Endometrium | 1 (10) |
| Prostate | 1 (10) |
| Disease outcome, n (%) | |
| Significant improvement | 5 (23.81) |
| Partial improvement | 7 (33.33) |
| Stable | 2 (9.52) |
| Worsening of symptoms | 3 (14.29) |
| Death | 4 (19.05) |
| MRI findings | |
| Brain MRI scans | |
| Abnormal findings related to encephalitis, n (%) | 5 (23.81) |
| Significant atrophic changes, disproportionate to age, n (%) | 2 (9.52) |
| Basal ganglia involvement, n (%) | 1 (4.76) |
| Hippocampal involvement, n (%) | 2 (9.52) |
| Gadolinium enhancement, n (%) | 0 |
| EEG studies | |
| Normal, n (%) | 10 (47.62) |
| Focal showing, n (%) | 7 (33.33) |
| Generalized showing, n (%) | 4 (19.05) |
| Classic epileptic from discharge, n (%) | 5 (23.81) |
| Delta brush, n (%) | 2 (9.52) |
| Treatment modalities | |
| Steroids (intravenous administration), n (%) | 14 (66.67) |
| Plasmapheresis, n (%) | 6 (28.57) |
| IVIG, n (%) | 2 (9.52) |
| Cyclophosphamide, n (%) | 2 (9.52) |
| Anti-CD20 therapy, n (%) | 1 (4.76) |
| CSF Biomarkers in Antibody-Associated Encephalitis | ||
|---|---|---|
| NFL Mean (SD) | Total Tau Mean (SD) | |
| Controls, n = 10 | 1029 (965) | 248 (64) |
| Extracellular/synaptic antigens | ||
| Abs directed against: | ||
| NMDA-R, n = 4 | 2826 (4800) | 128 (46) |
| CASPR2, n = 2 | 1036 | 167 |
| Gly-R, n = 3 | 585 (303) | 165 (47) |
| GABAbR, n = 1 | 620 | 209 |
| Intracellular/synaptic antigens | ||
| Yo, n = 2 | 2679 | 295 |
| Ma2, n = 1 | 4187 | 511 |
| CV2/CRMP5, n = 1 | >10,000 | 242 |
| Yo, n = 2 | 2679 | 319 |
| CV2/CRMP5 and Hu, n = 2 | 9730 | 710 |
| CV2/CRMP5 and Yo, n = 1 | >10,000 | 246 |
| Zic4, n = 1 | 2477 | 435 |
| GAD, n = 2 | 5144 | 304 |
| amphiphysin, n = 1 | 1241 | 175 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vakrakou, A.G.; Tzartos, J.S.; Strataki, E.; Boufidou, F.; Dimou, E.; Pyrgelis, E.-S.; Constantinides, V.C.; Paraskevas, G.P.; Kapaki, E. Neuronal and Neuroaxonal Damage Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarkers in Autoimmune Encephalitis Associated or Not with the Presence of Tumor. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1262. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10061262
Vakrakou AG, Tzartos JS, Strataki E, Boufidou F, Dimou E, Pyrgelis E-S, Constantinides VC, Paraskevas GP, Kapaki E. Neuronal and Neuroaxonal Damage Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarkers in Autoimmune Encephalitis Associated or Not with the Presence of Tumor. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(6):1262. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10061262
Chicago/Turabian StyleVakrakou, Aigli G., John S. Tzartos, Eleni Strataki, Fotini Boufidou, Eleni Dimou, Efstratios-Stylianos Pyrgelis, Vasilios C. Constantinides, George P. Paraskevas, and Elisabeth Kapaki. 2022. "Neuronal and Neuroaxonal Damage Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarkers in Autoimmune Encephalitis Associated or Not with the Presence of Tumor" Biomedicines 10, no. 6: 1262. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10061262
APA StyleVakrakou, A. G., Tzartos, J. S., Strataki, E., Boufidou, F., Dimou, E., Pyrgelis, E.-S., Constantinides, V. C., Paraskevas, G. P., & Kapaki, E. (2022). Neuronal and Neuroaxonal Damage Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarkers in Autoimmune Encephalitis Associated or Not with the Presence of Tumor. Biomedicines, 10(6), 1262. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10061262








