Seizures, Epilepsy, and NORSE Secondary to Autoimmune Encephalitis: A Practical Guide for Clinicians
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Search Strategy and Selection Criteria
3. Autoimmune and Paraneoplastic Encephalitis: General Concepts
4. MRI
5. CSF Analysis and Antibody Testing
6. EEG Findings
7. Malignancy Screening
8. Challenging Clinical Scenarios: NORSE and FIRES
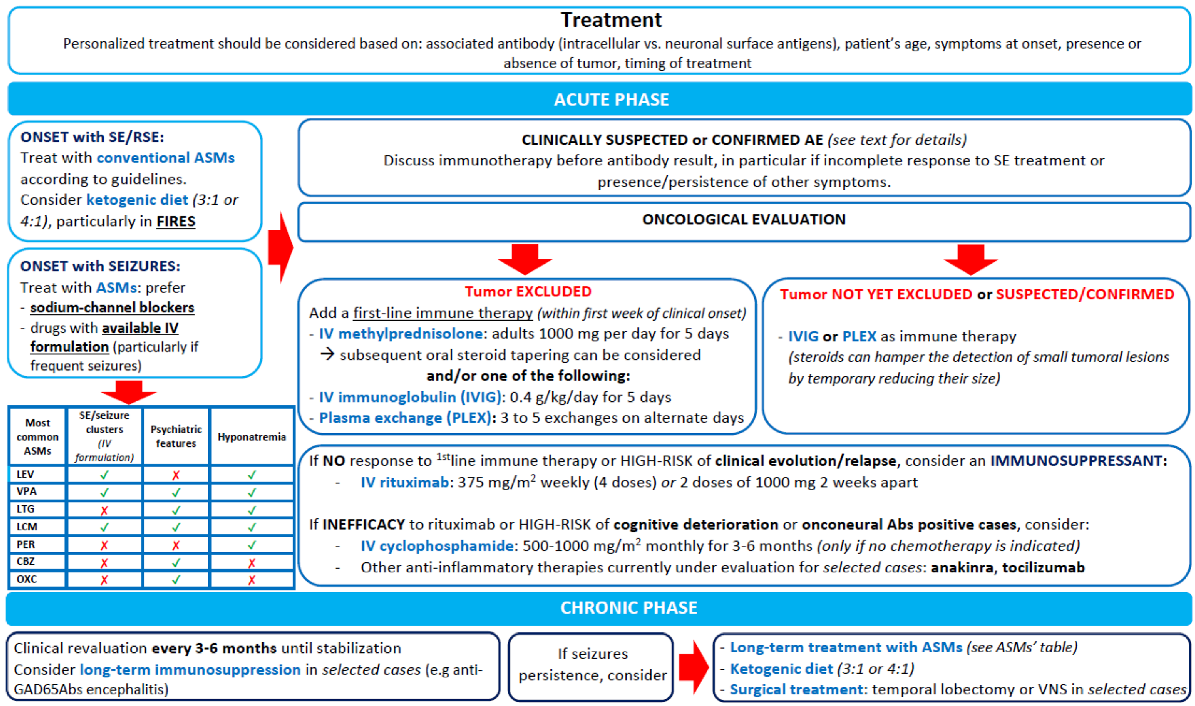
9. Treatment
Immunotherapy
10. ASMs
11. Treatment of Status Epilepticus
12. Ketogenic Diets
13. Surgical Treatment
14. Outcome
15. Concluding Remarks and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Ethical Publication Statement
References
- Fattorusso, A.; Matricardi, S.; Mencaroni, E.; Dell’Isola, G.B.; Di Cara, G.; Striano, P.; Verrotti, A. The Pharmacoresistant Epilepsy: An Overview on Existant and New Emerging Therapies. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 674483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahl-Hansen, E.; Koht, J.; Syvertsen, M. Epilepsy at different ages—Etiologies in a Norwegian population. Epilepsia Open 2018, 4, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogrig, A.; Joubert, B.; André-Obadia, N.; Gigli, G.L.; Rheims, S.; Honnorat, J. Seizure specificities in patients with antibody-mediated autoimmune encephalitis. Epilepsia 2019, 60, 1508–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matricardi, S.; Casciato, S.; Bozzetti, S.; Mariotto, S.; Stabile, A.; Freri, E.; Deleo, F.; Sartori, S.; Nosadini, M.; Pappalardo, I.; et al. Epileptic phenotypes in autoimmune encephalitis: From acute symptomatic seizures to autoimmune-associated epilepsy. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2022, 93, 1194–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheffer, I.E.; Berkovic, S.; Capovilla, G.; Connolly, M.B.; French, J.; Guilhoto, L.; Hirsch, E.; Jain, S.; Mathern, G.W.; Moshé, S.L.; et al. ILAE classification of the epilepsies: Position paper of the ILAE Commission for Classification and Terminology. Epilepsia 2017, 58, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bruijn, M.A.; van Sonderen, A.; van Coevorden-Hameete, M.H.; Bastiaansen, A.E.; Schreurs, M.W.; Rouhl, R.P.; van Donselaar, C.A.; Majoie, M.H.; Neuteboom, R.F.; Smitt, P.A.S.; et al. Evaluation of seizure treatment in anti-LGI1, anti-NMDAR, and anti-GABABR encephalitis. Neurology 2019, 92, e2185–e2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steriade, C.; Britton, J.; Dale, R.C.; Gadoth, A.; Irani, S.R.; Linnoila, J.; McKeon, A.; Shao, X.; Venegas, V.; Bien, C.G. Acute symptomatic seizures secondary to autoimmune encephalitis and autoimmune-associated epilepsy: Conceptual definitions. Epilepsia 2020, 61, 1341–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corsellis, J.A.N.; Goldberg, G.J.; Norton, A.R. “Limbic encephalitis” and its association with carcinoma. Brain 1968, 91, 481–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogrig, A.; Muñiz-Castrillo, S.; Desestret, V.; Joubert, B.; Honnorat, J. Pathophysiology of paraneoplastic and autoimmune encephalitis: Genes, infections, and checkpoint inhibitors. Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 2020, 13, 1756286420932797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trotter, J.L.; Hendin, B.A.; Osterland, C.K. Cerebellar Degeneration with Hodgkin Disease. An Immunological Study. Arch. Neurol. 1976, 33, 660–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, E.; Do, L.D.; Hannoun, S.; Muñiz-Castrillo, S.; Vogrig, A.; Wucher, V.; Pinto, A.-L.; Chounlamountri, N.; Zakaria, W.; Rogemond, V.; et al. Cerebellar Ataxia with Anti-DNER Antibodies: Outcomes and Immunologic Features. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2022, 9, e200018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graus, F.; Keime-Guibert, F.; Reñe, R.; Benyahia, B.; Ribalta, T.; Ascaso, C.; Escaramis, G.; Delattre, J.Y. Anti-Hu-associated paraneoplastic encephalomyelitis: Analysis of 200 patients. Brain 2001, 124, 1138–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honnorat, J.; Antoine, J.C.; Derrington, E.; Aguera, M.; Belin, M.F. Antibodies to a subpopulation of glial cells and a 66 kDa developmental protein in patients with paraneoplastic neurological syndromes. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1996, 61, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandel-Brehm, C.; Dubey, D.; Kryzer, T.J.; O’Donovan, B.D.; Tran, B.; Vazquez, S.E.; Sample, H.A.; Zorn, K.C.; Khan, L.M.; Bledsoe, I.O.; et al. Kelch-like Protein 11 Antibodies in Seminoma-Associated Paraneoplastic Encephalitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogrig, A.; Péricart, S.; Pinto, A.-L.; Rogemond, V.; Muñiz-Castrillo, S.; Picard, G.; Selton, M.; Mittelbronn, M.; Lanoiselée, H.-M.; Michenet, P.; et al. Immunopathogenesis and proposed clinical score for identifying Kelch-like protein-11 encephalitis. Brain Commun. 2021, 3, fcab185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalmau, J.; Graus, F.; Villarejo, A.; Posner, J.B.; Blumenthal, D.; Thiessen, B.; Saiz, A.; Meneses, P.; Rosenfeld, M.R. Clinical analysis of anti-Ma2-associated encephalitis. Brain 2004, 127, 1831–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graus, F.; Titulaer, M.J.; Balu, R.; Benseler, S.; Bien, C.G.; Cellucci, T.; Cortese, I.; Dale, R.C.; Gelfand, J.M.; Geschwind, M.; et al. A clinical approach to diagnosis of autoimmune encephalitis. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 15, 391–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graus, F.; Vogrig, A.; Muñiz-Castrillo, S.; Antoine, J.-C.G.; Desestret, V.; Dubey, D.; Giometto, B.; Irani, S.R.; Joubert, B.; Leypoldt, F.; et al. Updated Diagnostic Criteria for Paraneoplastic Neurologic Syndromes. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 8, e1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irani, S.; Alexander, S.; Waters, P.; Kleopa, K.A.; Pettingill, P.; Zuliani, L.; Peles, E.; Buckley, C.; Lang, B.; Vincent, A. Antibodies to Kv1 potassium channel-complex proteins leucine-rich, glioma inactivated 1 protein and contactin-associated protein-2 in limbic encephalitis, Morvan’s syndrome and acquired neuromyotonia. Brain 2010, 133, 2734–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hébert, J.; Riche, B.; Vogrig, A.; Muñiz-Castrillo, S.; Joubert, B.; Picard, G.; Rogemond, V.; Psimaras, D.; Alentorn, A.; Berzero, G.; et al. Epidemiology of paraneoplastic neurologic syndromes and autoimmune encephalitides in France. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 7, e883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irani, S.; Michell, A.W.; Lang, B.; Bsc, P.P.; Waters, P.; Johnson, M.R.; Schott, J.; Armstrong, R.J.E.; Zagami, A.S.; Bleasel, A.; et al. Faciobrachial dystonic seizures precede Lgi1 antibody limbic encephalitis. Ann. Neurol. 2010, 69, 892–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalmau, J.; Tüzün, E.; Wu, H.-Y.; Masjuan, J.; Ba, J.E.R.; Voloschin, A.; Baehring, J.M.; Shimazaki, H.; Koide, R.; King, D.; et al. Paraneoplastic anti-N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor encephalitis associated with ovarian teratoma. Ann. Neurol. 2007, 61, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Titulaer, M.J.; McCracken, L.; Gabilondo, I.; Armangue, T.; Glaser, C.; Iizuka, T.; Honig, L.S.; Benseler, S.M.; Kawachi, I.; Martinez-Hernandez, E.; et al. Treatment and prognostic factors for long-term outcome in patients with anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis: An observational cohort study. Lancet Neurol. 2013, 12, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, D.; Pittock, S.J.; Kelly, C.R.; McKeon, A.; Lopez-Chiriboga, A.S.; Lennon, V.A.; Gadoth, A.; Smith, C.Y.; Bryant, S.C.; Klein, C.J.; et al. Autoimmune encephalitis epidemiology and a comparison to infectious encephalitis. Ann. Neurol. 2018, 83, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, S.; Flanagan, E.P.; Paul, P.; Smith, C.Y.; Bryant, S.C.; Devine, M.F.; Lennon, V.A.; McKeon, A.; Pittock, S.J.; Dubey, D. Population-Based Epidemiology Study of Paraneoplastic Neurologic Syndromes. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 9, e1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogrig, A.; Gigli, G.L.; Segatti, S.; Corazza, E.; Marini, A.; Bernardini, A.; Valent, F.; Fabris, M.; Curcio, F.; Brigo, F.; et al. Epidemiology of paraneoplastic neurological syndromes: A population-based study. J. Neurol. 2019, 267, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogrig, A.; Joubert, B.; Ducray, F.; Thomas, L.; Izquierdo, C.; Decaestecker, K.; Martinaud, O.; Gerardin, E.; Grand, S.; Honnorat, J. Glioblastoma as differential diagnosis of autoimmune encephalitis. J. Neurol. 2018, 265, 669–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escudero, D.; Guasp, M.; Ariño, H.; Gaig, C.; Martínez-Hernández, E.; Dalmau, J.; Graus, F. Antibody-associated CNS syndromes without signs of inflammation in the elderly. Neurology 2017, 89, 1471–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabater, L.; Gaig, C.; Gelpi, E.; Bataller, L.; Lewerenz, J.; Torres-Vega, E.; Contreras, A.; Giometto, B.; Compta, Y.; Embid, C.; et al. A novel non-rapid-eye movement and rapid-eye-movement parasomnia with sleep breathing disorder associated with antibodies to IgLON5: A case series, characterisation of the antigen, and post-mortem study. Lancet Neurol. 2014, 13, 575–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cellucci, T.; Van Mater, H.; Graus, F.; Muscal, E.; Gallentine, W.; Klein-Gitelman, M.S.; Benseler, S.M.; Frankovich, J.; Gorman, M.P.; Van Haren, K.; et al. Clinical approach to the diagnosis of autoimmune encephalitis in the pediatric patient. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 7, e663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, E.; Treilleux, I.; Wucher, V.; Jougla, E.; Vogrig, A.; Pissaloux, D.; Paindavoine, S.; Berthet, J.; Picard, G.; Rogemond, V.; et al. Immune and Genetic Signatures of Breast Carcinomas Triggering Anti-Yo–Associated Paraneoplastic Cerebellar Degeneration. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2022, 9, e200015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villagrán-García, M.; Muñiz-Castrillo, S.; Ciano-Petersen, N.L.; Vogrig, A.; Farina, A.; Villard, M.; Psimaras, D.; Alentorn, A.; Gonçalves, D.; Fabien, N.; et al. Paraneoplastic neurological syndromes associated with renal or bladder cancer: Case series and PRISMA-IPD systematic review. J. Neurol. 2022, 270, 283–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogrig, A.; Muñiz-Castrillo, S.; Farina, A.; Honnorat, J.; Joubert, B. How to diagnose and manage neurological toxicities of immune checkpoint inhibitors: An update. J. Neurol. 2021, 269, 1701–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marini, A.; Bernardini, A.; Gigli, G.L.; Valente, M.; Muñiz-Castrillo, S.; Honnorat, J.; Vogrig, A. Neurologic Adverse Events of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Systematic Review. Neurology 2021, 96, 754–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogrig, A.; Muñiz-Castrillo, S.; Joubert, B.; Picard, G.; Rogemond, V.; Marchal, C.; Chiappa, A.M.; Chanson, E.; Skowron, F.; Leblanc, A.; et al. Central nervous system complications associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2020, 91, 772–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nersesjan, V.; McWilliam, O.; Krarup, L.-H.; Kondziella, D. Autoimmune Encephalitis Related to Cancer Treatment with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Systematic Review. Neurology 2021, 97, e191–e202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco, R.; Villagrán, M.; Jové, M.; Simó, M.; Vilariño, N.; Alemany, M.; Palmero, R.; Martínez-Villacampa, M.M.; Nadal, E.; Bruna, J. Encephalitis Induced by Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Systematic Review. JAMA Neurol. 2021, 78, 864–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeshokumar, A.K.; Coughlin, A.; Fastman, J.; Psaila, K.; Harmon, M.; Randell, T.; Schorr, E.M.; Han, H.; Hoang, H.; Soudant, C.; et al. Seizures in autoimmune encephalitis—A systematic review and quantitative synthesis. Epilepsia 2021, 62, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillinder, L.; Tjoa, L.; Mantzioris, B.; Blum, S.; Dionisio, S. Refractory chronic epilepsy associated with neuronal auto-antibodies: Could perisylvian semiology be a clue? Epileptic Disord. 2017, 19, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogrig, A.; Pauletto, G.; Lettieri, C.; Valente, M.; Gigli, G.L. Peculiar EEG signatures, ictal drinking and long-term follow-up in anti-LGI1 encephalitis. Neurol. Sci. 2019, 40, 1503–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, D.; Alqallaf, A.; Hays, R.; Freeman, M.; Chen, K.; Ding, K.; Agostini, M.; Vernino, S. Neurological Autoantibody Prevalence in Epilepsy of Unknown Etiology. JAMA Neurol. 2017, 74, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, D.; Kothapalli, N.; McKeon, A.; Flanagan, E.P.; Lennon, V.A.; Klein, C.J.; Britton, J.W.; So, E.; Boeve, B.F.; Tillema, J.-M.; et al. Predictors of neural-specific autoantibodies and immunotherapy response in patients with cognitive dysfunction. J. Neuroimmunol. 2018, 323, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Bruijn, M.A.; Bastiaansen, A.E.M.; Mojzisova, H.; Sonderen, A.; Thijs, R.D.; Majoie, M.J.; Rouhl, R.P.W.; Coevorden-Hameete, M.H.; Vries, J.M.; Lopetegi, A.M.; et al. Antibodies Contributing to Focal Epilepsy Signs and Symptoms Score. Ann. Neurol. 2021, 89, 698–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogrig, A.; Ferrari, S.; Tinazzi, M.; Manganotti, P.; Vattemi, G.; Monaco, S. Anti-Ma-associated encephalomyeloradiculopathy in a patient with pleural mesothelioma. J. Neurol. Sci. 2015, 350, 105–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñiz-Castrillo, S.; Haesebaert, J.; Thomas, L.; Vogrig, A.; Pinto, A.-L.; Picard, G.; Blanc, C.; Do, L.-D.; Joubert, B.; Berzero, G.; et al. Clinical and Prognostic Value of Immunogenetic Characteristics in Anti-LGI1 Encephalitis. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 8, e974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Sonderen, A.; Petit-Pedrol, M.; Dalmau, J.; Titulaer, M.J. The value of LGI1, Caspr2 and voltage-gated potassium channel antibodies in encephalitis. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2017, 13, 290–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flanagan, E.P.; Kotsenas, A.L.; Britton, J.W.; McKeon, A.; Watson, R.E.; Klein, C.J.; Boeve, B.F.; Lowe, V.; Ahlskog, J.E.; Shin, C.; et al. Basal ganglia T1 hyperintensity in LGI1-autoantibody faciobrachial dystonic seizures. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2015, 2, e161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maureille, A.; Fenouil, T.; Joubert, B.; Picard, G.; Rogemond, V.; Pinto, A.-L.; Thomas, L.; Ducray, F.; Quadrio, I.; Psimaras, D.; et al. Isolated seizures are a common early feature of paraneoplastic anti-GABAB receptor encephalitis. J. Neurol. 2018, 266, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancaster, E.; Lai, M.; Peng, X.; Hughes, E.; Constantinescu, R.; Raizer, J.; Friedman, D.; Skeen, M.B.; Grisold, W.; Kimura, A.; et al. Antibodies to the GABAB receptor in limbic encephalitis with seizures: Case series and characterisation of the antigen. Lancet Neurol. 2010, 9, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höftberger, R.; Titulaer, M.; Sabater, L.; Dome, B.; Rózsás, A.; Hegedus, B.; Hoda, M.A.; Laszlo, V.; Ankersmit, H.J.; Harms, L.; et al. Encephalitis and GABAB receptor antibodies: Novel findings in a new case series of 20 patients. Neurology 2013, 81, 1500–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spatola, M.; Petit-Pedrol, M.; Simabukuro, M.M.; Armangue, T.; Castro, F.J.; Artigues, M.I.B.; Benique, M.R.J.; Benson, L.; Gorman, M.; Felipe, A.; et al. Investigations in GABAA receptor antibody-associated encephalitis. Neurology 2017, 88, 1012–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titulaer, M.J.; Höftberger, R.; Iizuka, T.; Leypoldt, F.; McCracken, L.; Cellucci, T.; Benson, L.A.; Shu, H.; Irioka, T.; Hirano, M.; et al. Overlapping demyelinating syndromes and anti-N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor encephalitis. Ann. Neurol. 2014, 75, 411–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smitt, P.S.; Grefkens, J.; de Leeuw, B.; Bent, M.V.D.; van Putten, W.; Hooijkaas, H.; Vecht, C. Survival and outcome in 73 anti-Hu positive patients with paraneoplastic encephalomyelitis/sensory neuronopathy. J. Neurol. 2002, 249, 745–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogrig, A.; Joubert, B.; Maureille, A.; Thomas, L.; Bernard, E.; Streichenberger, N.; Cotton, F.; Ducray, F.; Honnorat, J. Motor neuron involvement in anti-Ma2-associated paraneoplastic neurological syndrome. J. Neurol. 2018, 266, 398–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mongay-Ochoa, N.; Vogrig, A.; Muñiz-Castrillo, S.; Honnorat, J. Anti-Hu-associated paraneoplastic syndromes triggered by immune-checkpoint inhibitor treatment. J. Neurol. 2020, 267, 2154–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogrig, A.; Fouret, M.; Joubert, B.; Picard, G.; Rogemond, V.; Pinto, A.-L.; Muñiz-Castrillo, S.; Roger, M.; Raimbourg, J.; Dayen, C.; et al. Increased frequency of anti-Ma2 encephalitis associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 6, e604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blinder, T.; Lewerenz, J. Cerebrospinal Fluid Findings in Patients with Autoimmune Encephalitis—A Systematic Analysis. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bien, C.G.; Holtkamp, M. “Autoimmune Epilepsy”: Encephalitis with Autoantibodies for Epileptologists. Epilepsy Curr. 2017, 17, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graus, F.; Escudero, D.; Oleaga, L.; Bruna, J.; Villarejo-Galende, A.; Ballabriga, J.; Barceló, M.I.; Gilo, F.; Popkirov, S.; Stourac, P.; et al. Syndrome and outcome of antibody-negative limbic encephalitis. Eur. J. Neurol. 2018, 25, 1011–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morano, A.; Fanella, M.; Irelli, E.C.; Barone, F.A.; Fisco, G.; Orlando, B.; Albini, M.; Fattouch, J.; Manfredi, M.; Casciato, S.; et al. Seizures in autoimmune encephalitis: Findings from an EEG pooled analysis. Seizure 2020, 83, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baysal-Kirac, L.; Tuzun, E.; Altindag, E.; Ekizoglu, E.; Kinay, D.; Bilgic, B.; Tekturk, P.; Baykan, B. Are There Any Specific EEG Findings in Autoimmune Epilepsies? Clin. EEG Neurosci. 2015, 47, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limotai, C.; Denlertchaikul, C.; Saraya, A.W.; Jirasakuldej, S. Predictive values and specificity of electroencephalographic findings in autoimmune encephalitis diagnosis. Epilepsy Behav. 2018, 84, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moise, A.-M.; Karakis, I.; Herlopian, A.; Dhakar, M.; Hirsch, L.J.; Cotsonis, G.; LaRoche, S.; Kang, C.M.C.; Westover, B.; Rodriguez, A. Continuous EEG Findings in Autoimmune Encephalitis. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2019, 38, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Sonderen, A.; Arends, S.; Tavy, D.L.J.; Bastiaansen, A.; De Bruijn, M.A.A.M.; Schreurs, M.W.J.; Smitt, P.A.E.S.; Titulaer, M.J. Predictive value of electroencephalography in anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2018, 89, 1101–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñiz-Castrillo, S.; Vogrig, A.; Honnorat, J. Post-acute anti-NMDAR encephalitis mirrors schizophrenia. Trends Mol. Med. 2022, 28, 895–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irani, S.; Bera, K.; Waters, P.; Zuliani, L.; Maxwell, S.; Zandi, M.; Friese, M.A.; Galea, I.; Kullmann, D.; Beeson, D.; et al. N-methyl-d-aspartate antibody encephalitis: Temporal progression of clinical and paraclinical observations in a predominantly non-paraneoplastic disorder of both sexes. Brain 2010, 133, 1655–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steriade, C.; Mirsattari, S.M.; Murray, B.; Wennberg, R. Subclinical temporal EEG seizure pattern in LGI1-antibody-mediated encephalitis. Epilepsia 2016, 57, e155–e160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benoit, J.; Muñiz-Castrillo, S.; Vogrig, A.; Farina, A.; Pinto, A.-L.; Picard, G.; Rogemond, V.; Guery, D.; Alentorn, A.; Psimaras, D.; et al. Early-Stage Contactin-Associated Protein-like 2 Limbic Encephalitis: Clues for Diagnosis. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2022, 10, e200041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wennberg, R.A. Hyperventilation-induced focal seizures in adults: Think autoimmune encephalitis. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2022, 9, 877–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogrig, A.; Pauletto, G.; Belgrado, E.; Pegolo, E.; Di Loreto, C.; Rogemond, V.; Honnorat, J.; Eleopra, R. Effect of thymectomy on refractory autoimmune status epilepticus. J. Neuroimmunol. 2018, 317, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wennberg, R.; Steriade, C.; Chen, R.; Andrade, D. Frontal infraslow activity marks the motor spasms of anti-LGI1 encephalitis. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2018, 129, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, V.; Kas, A.; Apartis, E.; Gary-Chami, L.; Rogemond, V.; Levy, P.; Psimaras, D.; Habert, M.-O.; Baulac, M.; Delattre, J.-Y.; et al. Motor cortex and hippocampus are the two main cortical targets in LGI1-antibody encephalitis. Brain 2016, 139, 1079–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, L.J.; Gaspard, N.; Van Baalen, A.; Nabbout, R.; Demeret, S.; Loddenkemper, T.; Navarro, V.; Specchio, N.; Lagae, L.; Rossetti, A.; et al. Proposed consensus definitions for new-onset refractory status epilepticus (NORSE), febrile infection-related epilepsy syndrome (FIRES), and related conditions. Epilepsia 2018, 59, 739–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspard, N.; Foreman, B.P.; Alvarez, V.; Kang, C.C.; Probasco, J.C.; Jongeling, A.C.; Meyers, E.; Espinera, A.; Haas, K.F.; Schmitt, S.E.; et al. New-onset refractory status epilepticus: Etiology, Clinical Features, and Outcome. Neurology 2015, 85, 1604–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lattanzi, S.; Leitinger, M.; Rocchi, C.; Salvemini, S.; Matricardi, S.; Brigo, F.; Meletti, S.; Trinka, E. Unraveling the enigma of new-onset refractory status epilepticus: A systematic review of aetiologies. Eur. J. Neurol. 2021, 29, 626–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Körtvelyessy, P.; Lerche, H.; Weber, Y. FIRES and NORSE are distinct entities. Epilepsia 2012, 53, 1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sculier, C.; Gaspard, N. New onset refractory status epilepticus (NORSE). Seizure 2019, 68, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, U.; Chi, C.-S.; Lin, K.-L.; Specchio, N.; Sahin, M.; Olson, H.; Nabbout, R.; Kluger, G.; Lin, J.-J.; Van Baalen, A. Febrile infection-related epilepsy syndrome (FIRES): Pathogenesis, treatment, and outcome: A Multicenter Study on 77 Children. Epilepsia 2011, 52, 1956–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspard, N.; Hirsch, L.; Sculier, C.; Loddenkemper, T.; Van Baalen, A.; Lancrenon, J.; Emmery, M.; Specchio, N.; Farias-Moeller, R.; Wong, N.; et al. New-onset refractory status epilepticus (NORSE) and febrile infection-related epilepsy syndrome (FIRES): State of the art and perspectives. Epilepsia 2018, 59, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iizuka, T.; Kanazawa, N.; Kaneko, J.; Tominaga, N.; Nonoda, Y.; Hara, A.; Onozawa, Y.; Asari, H.; Hata, T.; Kaneko, J.; et al. Cryptogenic NORSE: Its Distinctive Clinical Features and Response to Immunotherapy. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2017, 4, e396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meletti, S.; Giovannini, G.; D’Orsi, G.; Toran, L.; Monti, G.; Guha, R.; Kiryttopoulos, A.; Pascarella, M.G.; Martino, T.; Alexopoulos, H.; et al. New-Onset Refractory Status Epilepticus with Claustrum Damage: Definition of the Clinical and Neuroimaging Features. Front. Neurol. 2017, 8, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abboud, H.; Probasco, J.C.; Irani, S.; Ances, B.; Benavides, D.R.; Bradshaw, M.; Christo, P.P.; Dale, R.C.; Fernandez-Fournier, M.; Flanagan, E.P.; et al. Autoimmune encephalitis: Proposed best practice recommendations for diagnosis and acute management. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2021, 92, 757–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, A.; Klein, C.J.; Sechi, E.; Alden, E.; Basso, M.R.; Pudumjee, S.; Pittock, S.J.; McKeon, A.; Britton, J.W.; Lopez-Chiriboga, A.S.; et al. LGI1 antibody encephalitis: Acute treatment comparisons and outcome. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2021, 93, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, D.; Britton, J.; McKeon, A.; Gadoth, A.; Zekeridou, A.; Chiriboga, S.A.L.; Devine, M.; Cerhan, J.H.; Dunlay, K.; Sagen, J.; et al. Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial of Intravenous Immunoglobulin in Autoimmune LGI1/CASPR2 Epilepsy. Ann. Neurol. 2020, 87, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciano-Petersen, N.L.; Muñiz-Castrillo, S.; Birzu, C.; Vogrig, A.; Farina, A.; Villagrán-García, M.; Joubert, B.; Psimaras, D.; Honnorat, J. Cytokine dynamics and targeted immunotherapies in autoimmune encephalitis. Brain Commun. 2022, 4, fcac196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabezudo-García, P.; Mena-Vázquez, N.; Villagrán-García, M.; Serrano-Castro, P.J. Efficacy of antiepileptic drugs in autoimmune epilepsy: A systematic review. Seizure 2018, 59, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.; Bi, M.; Murchison, A.G.; Makuch, M.; Bien, C.G.; Chu, K.; Farooque, P.; Gelfand, J.M.; Geschwind, M.D.; Hirsch, L.; et al. The importance of early immunotherapy in patients with faciobrachial dystonic seizures. Brain 2017, 141, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Podewils, F.; Suesse, M.; Geithner, J.; Gaida, B.; Wang, Z.I.; Lange, J.; Dressel, A.; Grothe, M.; Kessler, C.; Langner, S.; et al. Prevalence and outcome of late-onset seizures due to autoimmune etiology: A prospective observational population-based cohort study. Epilepsia 2017, 58, 1542–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feyissa, A.M.; Chiriboga, A.S.L.; Britton, J.W. Antiepileptic drug therapy in patients with autoimmune epilepsy. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2017, 4, e353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baulac, M.; Rosenow, F.; Toledo, M.; Terada, K.; Li, T.; De Backer, M.; Werhahn, K.J.; Brock, M. Efficacy, safety, and tolerability of lacosamide monotherapy versus controlled-release carbamazepine in patients with newly diagnosed epilepsy: A phase 3, randomised, double-blind, non-inferiority trial. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 16, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minicucci, F.; Ferlisi, M.; Brigo, F.; Mecarelli, O.; Meletti, S.; Aguglia, U.; Michelucci, R.; Mastrangelo, M.; Specchio, N.; Sartori, S.; et al. Management of status epilepticus in adults. Position paper of the Italian League against Epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav. 2020, 102, 106675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanada, T. Ionotropic Glutamate Receptors in Epilepsy: A Review Focusing on AMPA and NMDA Receptors. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Dai, S.-H.; Jiang, Z.-Q.; Luo, P.; Jiang, X.-F.; Fei, Z.; Gui, S.-B.; Qi, Y.-L. The AMPAR Antagonist Perampanel Attenuates Traumatic Brain Injury Through Anti-Oxidative and Anti-Inflammatory Activity. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 37, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, J.D.; Filippakis, A.; Chitnis, T. Ketamine use in refractory status epilepticus associated with anti-NMDA receptor antibody encephalitis. Epilepsy Behav. Rep. 2019, 12, 100326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaadi, T.; Shakra, M.; Turkawi, L.; Hamid, J. VNS terminating refractory nonconvulsive SE secondary to anti-NMDA encephalitis: A case report. Epilepsy Behav. Rep. 2015, 3, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaliwal, J.; Ganguly, R.; Mindel, J.; Krishna, V. VNS Stopping Anti-NMDA Receptor Encephalitis–Triggered Nonconvulsive Status Epilepticus. World Neurosurg. 2020, 146, 364–366.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husari, K.S.; Cervenka, M.C. The ketogenic diet all grown up—Ketogenic diet therapies for adults. Epilepsy Res. 2020, 162, 106319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youngson, N.A.; Morris, M.J.; Ballard, J.W.O. The mechanisms mediating the antiepileptic effects of the ketogenic diet, and potential opportunities for improvement with metabolism-altering drugs. Seizure 2017, 52, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello, S.D.; Valdemarin, F.; Martinuzzi, D.; Filippi, F.; Gigli, G.L.; Valente, M. Ketogenic Diet in the Treatment of Gliomas and Glioblastomas. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, K.T.; Probasco, J.C.; Hocker, S.E.; Roehl, K.; Henry, B.; Kossoff, E.H.; Kaplan, P.W.; Geocadin, R.G.; Hartman, A.L.; Venkatesan, A.; et al. Ketogenic diet for adults in super-refractory status epilepticus. Neurology 2014, 82, 665–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervenka, M.C.; Hocker, S.; Koenig, M.; Bar, B.; Henry-Barron, B.; Kossoff, E.H.; Hartman, A.; Probasco, J.C.; Benavides, D.R.; Venkatesan, A.; et al. Phase I/II multicenter ketogenic diet study for adult superrefractory status epilepticus. Neurology 2017, 88, 938–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabbout, R.; Mazzuca, M.; Hubert, P.; Peudennier, S.; Allaire, C.; Flurin, V.; Aberastury, M.; Silva, W.; Dulac, O. Efficacy of ketogenic diet in severe refractory status epilepticus initiating fever induced refractory epileptic encephalopathy in school age children (FIRES). Epilepsia 2010, 51, 2033–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youm, Y.-H.; Nguyen, K.Y.; Grant, R.W.; Goldberg, E.L.; Bodogai, M.; Kim, D.; D’Agostino, D.; Planavsky, N.; Lupfer, C.; Kanneganti, T.-D.; et al. The ketone metabolite β-hydroxybutyrate blocks NLRP3 inflammasome–mediated inflammatory disease. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husari, K.S.; Cervenka, M.C. Ketogenic Diet Therapy for the Treatment of Post-encephalitic and Autoimmune-Associated Epilepsies. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 624202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, V.; Pimentel, J.; Campos, A.R.; Bentes, C.; Maruta, C.; Morgado, C.; Martins, I.P. Surgical control of limbic encephalitis associated with LGI1 antibodies. Epileptic Disord. 2012, 14, 345–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malter, M.; Frisch, C.; Zeitler, H.; Surges, R.; Urbach, H.; Helmstaedter, C.; Elger, C.; Bien, C.G. Treatment of immune-mediated temporal lobe epilepsy with GAD antibodies. Seizure 2015, 30, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feyissa, A.M.; Mirro, E.A.; Wabulya, A.; Tatum, W.O.; Wilmer-Fierro, K.E.; Shin, H.W. Brain-responsive neurostimulation treatment in patients with GAD65 antibody–associated autoimmune mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsia Open 2020, 5, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreño, M.; Bien, C.G.; Asadi-Pooya, A.A.; Sperling, M.; Marusic, P.; Elisak, M.; Pimentel, J.; Wehner, T.; Mohanraj, R.; Uranga, J.; et al. Epilepsy surgery in drug resistant temporal lobe epilepsy associated with neuronal antibodies. Epilepsy Res. 2017, 129, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.M.; Dubey, D.; Liebo, G.B.; Flanagan, E.P.; Britton, J.W. Clinical Course and Features of Seizures Associated with LGI1-Antibody Encephalitis. Neurology 2021, 97, e1141–e1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Fang, G.; Yang, F.; Cai, M.; Zheng, Y.; Fang, W.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, M. Seizures and risk of epilepsy in anti-NMDAR, anti-LGI1, and anti-GABABR encephalitis. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2020, 7, 1392–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Autoantibody | Demographic and Oncologic Features | Clinical Specificities | Seizure Frequency | Status Epilepticus | EEG | MRI | Risk of Long-Term Epilepsy | ASMs Discontinuation Likely? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GABAbR | PNS (>50%): aged > 45 y, male predominance, smokers, associated anti-KCTD16 Abs and SCLC. Non-PNS: younger | LE | >90% | +++ | >80% abnormal, mostly over the temporal lobes | Frequent MTL HS | Low | Yes |
| GABAaR | Non-PNS (>70%). Children can also be affected. PNS: thymoma | Encephalitis | >80% | +++ | Almost invariably abnormal | Multifocal, cortical-subcortical (ADEM-like) lesions | Moderate | Unknown |
| NMDAR | PNS: ovarian teratomas in female aged between 12–45 y (50%). Elderly have less frequently tumors (<25%). Non-PNS: children | Encephalitis | >70% | ++ | 90% abnormal, with 3 stages: (i) excessive beta activity 14-20 Hz; (ii) EDB; (iii) GDA | Normal or nonspecific changes. Demyelinating lesions in a subgroup | Low | Yes |
| LGI1 | Non-PNS (>90%): elderly, male predominance. PNS: thymoma (often with concomitant anti-CASPR2 and Morvan syndrome) | LE | >75% | + | Frequent subclinical seizures, often triggered by HV, but rare IEDs. FBDS may be preceded by contralateral F slow wave | Unilateral or bilateral MTL HS (normal in 25%) | Low-Moderate | Yes |
| CASPR2 | Non-PNS (>70%): LE PNS: Morvan syndrome and concomitant LGI1 Abs | LE, Isaac syndrome, Morvan syndrome | >60% | + | Nonspecific findings | Usually normal (bilateral MTL HS in a minority of cases) | Low | Yes |
| Autoantibody | Demographic and Oncologic Features | Clinical Specificities | Seizure Frequency | Status Epilepticus | EEG | MRI | Risk of Long-Term Epilepsy | ASMs Discontinuation Likely? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hu | PNS (85%): typically, middle-aged/elderly male smokers (tumors: mostly SCLC, less commonly NSCLC or others). ICI-triggered cases are possible. Non-PNS: younger (including children), no sex predominance | SNN, EM, and LE; some patients develop EPC | 10% overall (54% in LE) | + | Nonspecific findings | Limbic involvement (10–20%) | High if the limbic system is affected | No |
| CV2/CRMP5 | PNS (>80%): typically, middle-aged/elderly with SCLC or thymoma | EM and SNN | 9–27% | − | Nonspecific findings | Limbic involvement (13–18%) | High if the limbic system is affected | No |
| Ma2 | PNS (>75%): Young men with testicular cancer; older patients with SCLC. ICI-triggered cases are possible | LE, diencephalitis, and brainstem encephalitis | 30% overall (50% in LE) | + | Unilateral or bilateral IEDs mainly involving the temporal lobes | Frequent MTL HS, hypothalamus, thalamus, brainstem HS also possible | High | No |
| GAD65 | Non-PNS (>85%): female predominance, median age is 30 y, systemic autoimmune comorbidities. PNS: older male patients with associated Abs | LE, cerebellar ataxia, and SPS | >80% | ++ | Temporal lobe ictal or IEDs | MTL HS in half of the cases | High | No |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vogrig, A.; Gigli, G.L.; Nilo, A.; Pauletto, G.; Valente, M. Seizures, Epilepsy, and NORSE Secondary to Autoimmune Encephalitis: A Practical Guide for Clinicians. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11010044
Vogrig A, Gigli GL, Nilo A, Pauletto G, Valente M. Seizures, Epilepsy, and NORSE Secondary to Autoimmune Encephalitis: A Practical Guide for Clinicians. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(1):44. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11010044
Chicago/Turabian StyleVogrig, Alberto, Gian Luigi Gigli, Annacarmen Nilo, Giada Pauletto, and Mariarosaria Valente. 2023. "Seizures, Epilepsy, and NORSE Secondary to Autoimmune Encephalitis: A Practical Guide for Clinicians" Biomedicines 11, no. 1: 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11010044
APA StyleVogrig, A., Gigli, G. L., Nilo, A., Pauletto, G., & Valente, M. (2023). Seizures, Epilepsy, and NORSE Secondary to Autoimmune Encephalitis: A Practical Guide for Clinicians. Biomedicines, 11(1), 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11010044






