Presynaptic Acetylcholine Receptors Modulate the Time Course of Action Potential-Evoked Acetylcholine Quanta Secretion at Neuromuscular Junctions
Abstract
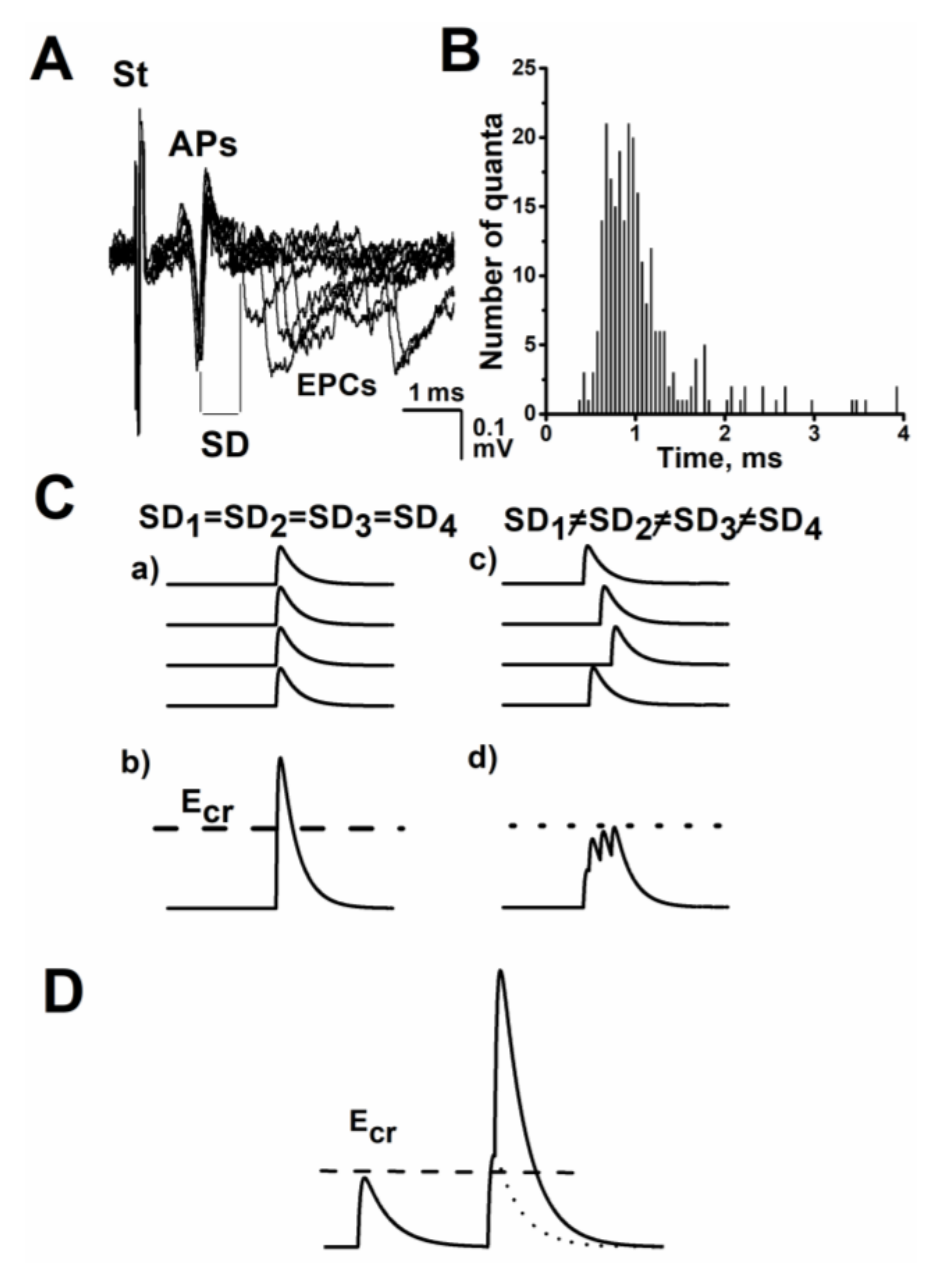
:1. The Time Course or Kinetics of the Evoked Acetylcholine Quanta Release
2. The Role of Evoked Quantal-Secretion Kinetics in the Formation of a Multiquantal Postsynaptic Response
3. Presynaptic Acetylcholine Receptors Modulate the Kinetics of Acetylcholine Quanta Release
3.1. Do Nicotinic Agonists Change the Kinetics of Evoked ACh Neurosecretion?
3.2. Muscarinic Agonists and Antagonists Modulate the Time Course of Evoked ACh Secretion
4. Possible Mechanisms for Modulation of the Kinetics of Quanta ACh Secretion by Presynaptic AChRs
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Del Castillo, J.; Katz, B. Quantal components of the end-plate potential. J. Physiol. 1954, 124, 560–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, B. The release of neural transmitter substances. In The Sherrington Lecture, No.10; Liverpool University Press: Liverpool, UK, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Katz, B.; Miledi, R. The measurement of synaptic delay and the time course of acetylcholine release at the neuromuscular junction. Proc. R. Soci. 1965, 161, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldo, G.J.; Cohen, I.S.; Van der Kloot, W. Estimating the time course of evoked quantal release at the frog neuromuscular junction using end-plate current latencies. J. Physiol. 1986, 374, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barrett, E.; Stevens, S. The kinetics of transmitter release at the frog neuromuscular junction. J. Physiol. 1972, 227, 691–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minenko, M.L.; Magazanik, L.G. Phenomena of asynchronous evoked transmitter release at the neuromuscular junction of the frog. Neurophysiology 1986, 18, 346–354. [Google Scholar]
- Bukcharaeva, E.; Kim, K.; Moravec, J.; Nikolsky, E.; Vyskocil, F. Noradrenaline synchronizes evoked quantal release at frog neuromuscular junctions. J. Physiol. 1999, 517, 879–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fesce, R. The kinetics of nerve evoked quantal secretion. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 1999, 354, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sabatini, B.; Regehr, W. Timing of synaptic transmission. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 1999, 61, 521–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, J.W.; Faber, S. Modulation of synaptic delay during synaptic plasticity. Trends Neurosci. 2002, 25, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saveliev, A.; Khuzakhmetova, V.; Samigullin, D.; Skorinkin, A.; Kovyazina, I.; Nikolsky, E.; Bukharaeva, E. Bayesian analysis of the kinetics of quantal transmitter secretion at the neuromuscular junction. J. Comput. Neurosci. 2015, 39, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goda, Y.; Stevens, C.F. Two components of transmitter release at a central synapse. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 12942–12946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van der Kloot, W. Estimating the timing of quantal release during end-plate currents at the frog neuromuscular junction. J. Physiol. 1988, 402, 595–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aumann, Y.; Parnas, H. Evaluation of the time course of neurotransmitter release from the measured psc and mpsc. Bull. Math. Biol. 1991, 53, 537–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorobieva, O.N.; Hackett, J.T.; Worden, M.K.; Bykhovskaia, M. Evaluation of quantal neurosecretion from evoked and miniature postsynaptic responses by deconvolution method. J. Neurosci. Meth. 1999, 92, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gainulov, R.; Bukharaeva, E.; Nikolsky, E. A method for assessing the kinetics of evoked secretion of transmitter quanta determining the generation of multiquantum endplate currents. Neurosci. Behav. Physiol. 2002, 32, 613–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, C.F. Synaptic physiology. Proc. IEEE 1968, 56, 916–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, M.R.; Kearns, J.L. Statistics of transmitter release at nerve terminals. Progr. Neurobiol. 2000, 60, 545–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giniatullin, R.A.; Kheeroug, L.S.; Vyskocil, F. Modelling endplate current: Dependence on quantum secretion probability and postsynaptic miniature current parameters. Eur. Biophys. J. 1995, 23, 443–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Kloot, W. The kinetics of quantal release during end-plate currents at the frog neuromuscular junction. J. Physiol. 1988, 402, 605–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soucek, B. Influence of latency fluctuations and the quantal process of transmitter release on the end-plate potential`s amplitude distribution. Biophys. J. 1971, 11, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gilmanov, I.; Samigullin, D.; Vyskocil, F.; Nikolsky, E.; Bukharaeva, E. Modeling of quantal neurotransmitter release kinetics in the presence of fixed and mobile calcium buffers. J. Comput. Neurosci. 2008, 25, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowman, W.C.; Prior, C.; Marshall, I.G. Presynaptic Receptors in the Neuromuscular Junction. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1990, 604, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrov, K.A.; Nikolsky, E.E.; Masson, P.; Kovyazina, I.V.; Tsentsevitsky, A.N. Presynaptic nicotinic cholinoreceptors modulate velocity of the action potential propagation along the motor nerve endings at a high-frequency synaptic activity. Dokl. Biol. Sci. 2016, 468, 115–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balezina, O.P.; Fedorin, V.V.; Gaidukov, A.E. Effect of nicotine on neuromuscular transmission in mouse motor synapses. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2006, 142, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhilyakov, N.; Arkhipov, A.; Malomouzh, A.; Samigullin, D. Activation of Neuronal Nicotinic Receptors Inhibits Acetylcholine Release in the Neuromuscular Junction by Increasing Ca2+ Flux through Cav1 Channels. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomàs, J.; Santafé, M.M.; Garcia, N.; Lanuza, M.A.; Tomàs, M.; Besalduch, N. Presynaptic membrane receptors in acetylcholine release modulation in the neuromuscular synapse. J. Neurosci. 2014, 92, 543–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomàs, J.; Garcia, N.; Lanuza, M.A.; Santafé, M.M.; Tomàs, M.; Nadal, L.; Hurtado, E.; Simó, A.; Cilleros, V. Presynaptic Membrane Receptors Modulate ACh Release, Axonal Competition and Synapse Elimination during Neuromuscular Junction Development. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matzner, H.; Parnas, H.; Parnas, I. Presynaptic effects of d-tubocurarine on neurotransmitter release at the neuromuscular junction of the frog. J. Physiol. 1988, 398, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Slutsky, I.; Parnas, H.; Parnas, I. Presynaptic effects of muscarine on Ach release at the frog neuromuscular junction. J. Physiol. 1999, 514, 769–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minic, J.; Molgó, J.; Karlsson, E.; Krejci, E. Regulation of acetylcholine release by muscarinic receptors at the mouse neuromuscular junction depends on the activity of acetylcholinesterase. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2002, 15, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santafé, M.M.; Salon, I.; Garcia, N.; Lanuza, M.A.; Uchitel, O.D.; Tomàs, J. Modulation of ACh release by presynaptic muscarinic autoreceptors in the neuromuscular junction of the newborn and adult rat. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2003, 17, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santafé, M.M.; Lanuza, M.A.; Garcia, N.; Tomàs, J. Muscarinic autoreceptors modulate transmitter release through protein kinase C and protein kinase A in the rat motor nerve terminal. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2006, 23, 2048–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samigullin, D.; Bukharaeva, E.A.; Nikolsky, E.; Adámek, S.; Vyskocil, F. Long release latencies are increased by acetylcholine at frog endplate. Physiol. Res. 2003, 52, 475–480. [Google Scholar]
- Nikolsky, E.; Vyskocil, F.; Bukharaeva, E.; Samigullin, D.; Magazanik, L. Cholinergic regulation of the evoked quantal release at frog neuromuscular junction. J. Physiol. 2004, 560, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samigullin, D.; Khuzakhmetova, V.; Tsentsevitsky, A.; Bukharaeva, E. Presynaptic Receptors Regulating the Time Course of Neurotransmitter Release from Vertebrate Nerve Endings. Biol. Memb. 2012, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovyazina, I.; Tsentsevitsky, A.; Nikolsky, E.; Bukharaeva, E. Kinetics of acetylcholine quanta release at the neuromuscular junction during high-frequency nerve stimulation. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2010, 32, 1480–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, M.C.; Potluri, S.; Wang, X.; Dentcheva, E.; Gautam, D.; Tessler, A. Distinct muscarinic acetylcholine receptor subtypes contribute to stability and growth, but not compensatory plasticity, of neuromuscular synapses. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 14942–14955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dudel, J. The time course of transmitter release in mouse motor nerve terminals is differentially affected by activation of muscarinic M1 or M2receptors. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2007, 26, 2160–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santafé, M.M.; Salon, I.; Garcia, N.; Lanuza, M.; Uchitel, O.D.; Tomàs, J. Muscarinic autoreceptors related with calcium channels in the strong and weak inputs at polyinnervated developing rat neuromuscular junctions. Neuroscience 2004, 123, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsentsevitsky, A.; Kovyazina, I.; Nurullin, L.; Nikolsky, E. Muscarinic cholinoreceptors (M1-, M2-, M3- and M4-type) modulate the acetylcholine secretion in the frog neuromuscular junction. Neurosci. Lett. 2017, 649, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slutsky, I.; Silman, I.; Parnas, I.; Parnas, H. Presynaptic M2 muscarinic receptors are involved in controlling the kinetics of Ach release at the frog neuromuscular junction. J. Physiol. 2001, 536, 717–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slutsky, I.; Wess, J.; Gomeza, J.; Dudel, J.; Parnas, I.; Parnas, H. Use of Knockout Mice Reveals Involvement of M2-Muscarinic Receptors in Control of the Kinetics of Acetylcholine Release. J. Neurophysiol. 2002, 89, 1954–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kaeser, P.S.; Regehr, W.G. Molecular mechanisms for synchronous, asynchronous, and spontaneous neurotransmitter release. Ann. Rev. Physiol. 2014, 76, 333–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Homan, A.; Laghaei, R.; Dittrich, M.; Meriney, S.D. Impact of spatiotemporal calcium dynamics within presynaptic active zones on synaptic delay at the frog neuromuscular junction. J. Neurophysiol. 2018, 119, 688–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parnas, I.; Parnas, H.; Hochner, Y. Amount and time-course of release. The calcium hypothesis and the calcium-voltage hypothesis. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1991, 635, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bukharaeva, E.A.; Samigullin, D.; Nikolsky, E.E.; Magazanik, L.G. Modulation of the kinetics of evoked quantal release at mouse neuromuscular junctions by calcium and strontium. J. Neurochem. 2007, 100, 939–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Pinter, M.J.; Rich, M.M. Ca2dependence of the binomial parameters p and n at the mouse neuromuscular junction. J. Neurophysiol. 2010, 103, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Samigullin, D.; Bukharaeva, E.; Vyskocil, F.; Nikolsky, E.E. Calcium dependence of uni-quantal release latencies and quantal content at mouse neuromuscular junction. Physiol. Res. 2005, 54, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, B.; Miledi, R. The effect of temperature on the synaptic delay at the neuromuscular junction. J. Physiol. 1965, 181, 656–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachnoff, N.; Cohen-Kutner, M.; Trus, M.; Atlas, D. Intra-membrane signaling between the voltage-gated Ca2+-channel and cysteine residues of syntaxin 1A coordinates synchronous release. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khuzakhmetova, V.; Samigullin, D.; Nurullin, L.; Vyskočil, F.; Nikolsky, E.; Bukharaeva, E. Kinetics of neurotransmitter release in neuromuscular synapses of newborn and adult rats. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khaziev, E.; Samigullin, D.; Zhilyakov, N.; Fatikhov, N.; Bukharaeva, E.; Verkhratsky, A.; Nikolsky, E. Acetylcholine-Induced Inhibition of Presynaptic Calcium Signals and Transmitter Release in the Frog Neuromuscular Junction. Front. Physiol. 2016, 7, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shen, J.-X.; Yakel, J. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor-mediated calcium signaling in the nervous system. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2009, 30, 673–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dickinson, J.; Hanrott, K.; Mok, M.N.; Kew, J.; Wonnacott, S. Differential coupling of alpha7 and non-alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors to calcium-induced calcium release and voltage-operated calcium channels in PC12 cells. J. Neurochem. 2007, 100, 1089–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khuzakhmetova, V.F.; Nurullin, L.F.; Bukharaeva, E.A.; Nikolsky, E.E. Involvement of dihydropyridine-sensitive calcium channels in high asynchrony of transmitter release in neuromuscular synapses of newborn rats. Dokl. Biol. Sci. 2016, 470, 220–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsentsevitsky, A.N.; Petrov, A.M. L-type Ca2+ Channels at Low External Calcium Differentially Regulate Neurotransmitter Release in Proximal-Distal Compartments of the Frog Neuromuscular Junction. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; McIntosh, J.M.; Rich, M.M. Muscle Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors May Mediate Trans-Synaptic Signaling at the Mouse Neuromuscular Junction. J Neurosci. 2018, 38, 1725–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Pinter, M.; Rich, M. Reversible Recruitment of a Homeostatic Reserve Pool of Synaptic Vesicles Underlies Rapid Homeostatic Plasticity of Quantal Content. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 828–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parnas, H.; Segel, L.; Dudel, J.; Parnas, I. Autoreceptors, membrane potential and regulation the transmitter release. Trends Neurosci. 2000, 23, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shor, O.L.; Fidzinski, P.; Behr, J. Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors and voltage-gated calcium channels contribute to bidirectional synaptic plasticity at CA1-subiculum synapses. Neurosci. Lett. 2009, 449, 220–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukharaeva, E.; Samigullin, D.; Nikolsky, E.; Vyskocil, F. Protein kinase A cascade regulates quantal release dispersion at frog muscle endplate. J. Physiol. 2002, 538, 837–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsentsevitsky, A.N.; Khaziev, E.F.; Kovyazina, I.V.; Petrov, A.M. GIRK channel as a versatile regulator of neurotransmitter release via L-type Ca2+ channel-dependent mechanism in the neuromuscular junction. Neuropharmacology 2022, 209, 109021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santafé, M.M.; Lanuza, M.A.; Garcia, N.; Tomàs, M.; Tomàs, J. Coupling of presynaptic muscarinic autoreceptors to serine kinases in low and high release conditions on the rat motor nerve terminal. Neuroscience 2007, 148, 432–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volpicelli, L.A.; Levey, A.I. Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor subtypes in cerebral cortex and hippocampus. Prog. Brain. Res. 2004, 145, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cilleros-Mañé, V.; Just-Borràs, L.; Tomàs, M.; Garcia, N.; Tomàs, J.M.; Lanuza, M.A. The M 2 muscarinic receptor, in association to M 1, regulates the neuromuscular PKA molecular dynamics. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 4934–4955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cilleros-Mañé, V.; Lust-Borràs, L.; Polishchuk, A.; Durán, M.; Tomàs, M.; Garcia, N.; Tomàs, J.M.; Lanuza, M.A. M 1 and M 2 mAChRs activate PDK1 and regulate PKC βI and ε and the exocytotic apparatus at the NMJ. FASEB J. 2021, 35, e21724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, R.; Casañas, J.J.; TorresBenito, L.; Cano, R.; Tabares, L. Altered intracellular Ca2+ homeostasis in nerve terminals of severe spinal muscular atrophy mice. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Torres Benito, L.; Ruiz, R.; Tabares, L. Synaptic defects in spinal muscular atrophy animal models. Dev. Neurobiol. 2012, 72, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsentsevitsky, A.N.; Zakyrjanova, G.F.; Petrov, A.M. Cadmium desynchronizes neurotransmitter release in the neuromuscular junction: Key role of ROS. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 155, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, T.Y.; Hwang, J.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Shin, J.H.; Gwag, B.J.; Koh, J.Y. Accumulation of labile zinc in neurons and astrocytes in the spinal cords of G93A SOD-1 transgenic mice. Neurobiol. Dis. 2009, 34, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wang, B.; Long, C.; Wu, G.; Zheng, H. Increased asynchronous release and aberrant calcium channel activation in amyloid precursor protein deficient neuromuscular synapses. Neuroscience 2007, 149, 768–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Molgo, J.; Siegel, L.; Tabti, N.; Thesleff, S. A study of synchronization of quantal transmitter release from mammalian motor ending by the use of botulinal toxins type A and D. J. Physiol. 1989, 411, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.W.; Feng, Y.Q.; Hao, C.J.; Guo, X.L.; He, X.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Guo, N.; Huang, H.P.; Xiong, W.; Zheng, H.; et al. DTNBP1, a schizophrenia susceptibility gene, affects kinetics of transmitter release. J. Cell. Biol. 2008, 181, 791–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambrosini, A.; de Noordhout, A.M.; Schoenen, J. Neuromuscular transmission in migraine patients with prolonged aura. Acta Neurol. Belg. 2001, 101, 166–170. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lustig, C.; Parnas, H.; Segel, I. Release kinetics as a tool to describe drug effects on neurotransmitter release. J. Theor. Biol. 1991, 144, 225–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Substance | Object | Receptor’s Type Action | Effects | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACh | frog | Agonist of nAChR and mAChR | Desynchronization (increase in synaptic delay dispersion) | [34] |
| Carbacholine | frog | Agonist of nAChR and mAChR | [35] | |
| d-Tubocurarine | frog | Antagonist of nAChR | [29] | |
| Nicotine | frog | Agonist of nAChR | [35] | |
| Methoctramine | frog | antagonist of muscarinic M2/M4 mAChR | Desynchronization (slowed exponential decay on the synaptic delay histograms; slowed rise time of the multiquantal postsynaptic current) | [42] |
| Muscarine | frog | Agonist of mAChR | Synchronization (removing quanta with long synaptic delay) without preliminary treatment and after desynchronizing action of M2/M4 antagonists | [41,42] |
| Oxotremorine, Propargyl ester of arecaidine | Frog | M1 and M2 mAChR agonists | No effects | [35] |
| Pirenzepine, AF-DX 116, Methoctramine, VU 0255035, PD 102807, 4-DAMP and J 104129 | frog | Antagonists of M1, M2, M3, M4 mAChRs | [35,41] | |
| AF-DX 116 | frog | M2 mAChR antagonist | Synchronization (shortening of the time interval during which 85% quanta are released) | [41] |
| Genetic blockade of muscarinic receptors | mouse | Knockout mice lacking functional M2 mAChRs | Desynchronization (longer duration of release in comparison to the control mouse) | [43] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bukharaeva, E.A.; Skorinkin, A.I.; Samigullin, D.V.; Petrov, A.M. Presynaptic Acetylcholine Receptors Modulate the Time Course of Action Potential-Evoked Acetylcholine Quanta Secretion at Neuromuscular Junctions. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1771. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10081771
Bukharaeva EA, Skorinkin AI, Samigullin DV, Petrov AM. Presynaptic Acetylcholine Receptors Modulate the Time Course of Action Potential-Evoked Acetylcholine Quanta Secretion at Neuromuscular Junctions. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(8):1771. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10081771
Chicago/Turabian StyleBukharaeva, Ellya A., Andrey I. Skorinkin, Dmitry V. Samigullin, and Alexey M. Petrov. 2022. "Presynaptic Acetylcholine Receptors Modulate the Time Course of Action Potential-Evoked Acetylcholine Quanta Secretion at Neuromuscular Junctions" Biomedicines 10, no. 8: 1771. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10081771
APA StyleBukharaeva, E. A., Skorinkin, A. I., Samigullin, D. V., & Petrov, A. M. (2022). Presynaptic Acetylcholine Receptors Modulate the Time Course of Action Potential-Evoked Acetylcholine Quanta Secretion at Neuromuscular Junctions. Biomedicines, 10(8), 1771. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10081771





